Tissue Classification of Breast Cancer by Hyperspectral Unmixing
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Hyperspectral Imaging
2.3. Pipeline to Assign Ground-Truth Labels
2.3.1. Reference Image
2.3.2. Pathology Processing
2.3.3. Assigning Ground-Truth Labels with Hyperspectral Unmixing
| Algorithm 1 Label assignment based on hyperspectral unmixing |
Input: Training samples with labels at locations P Output: Certain Labeled representative spectra Ł
|
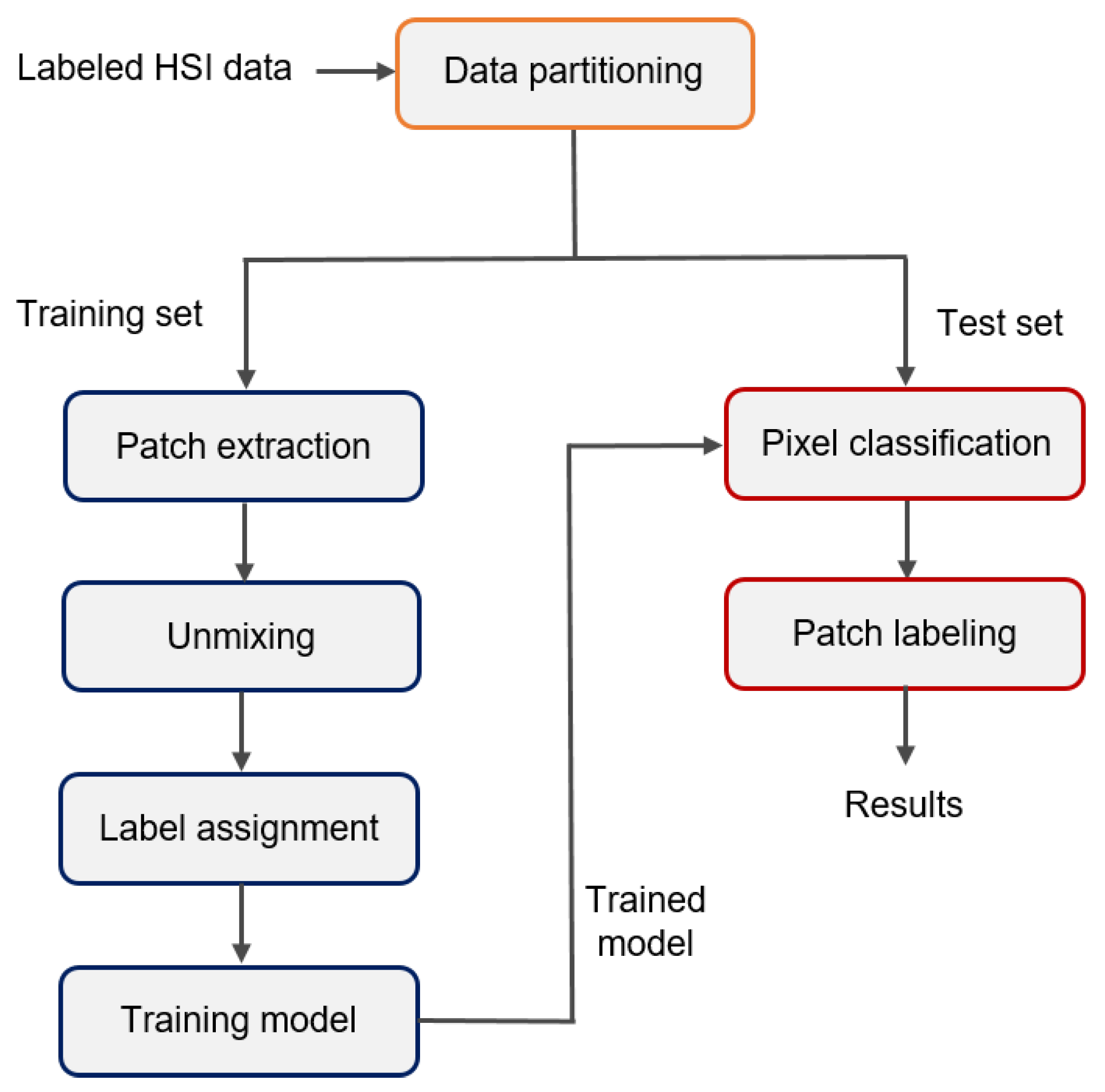
2.4. Tissue Classification
Performance Testing
3. Results
3.1. Dataset Description
3.2. Assigning Ground-Truth Labels with Hyperspectral Unmixing
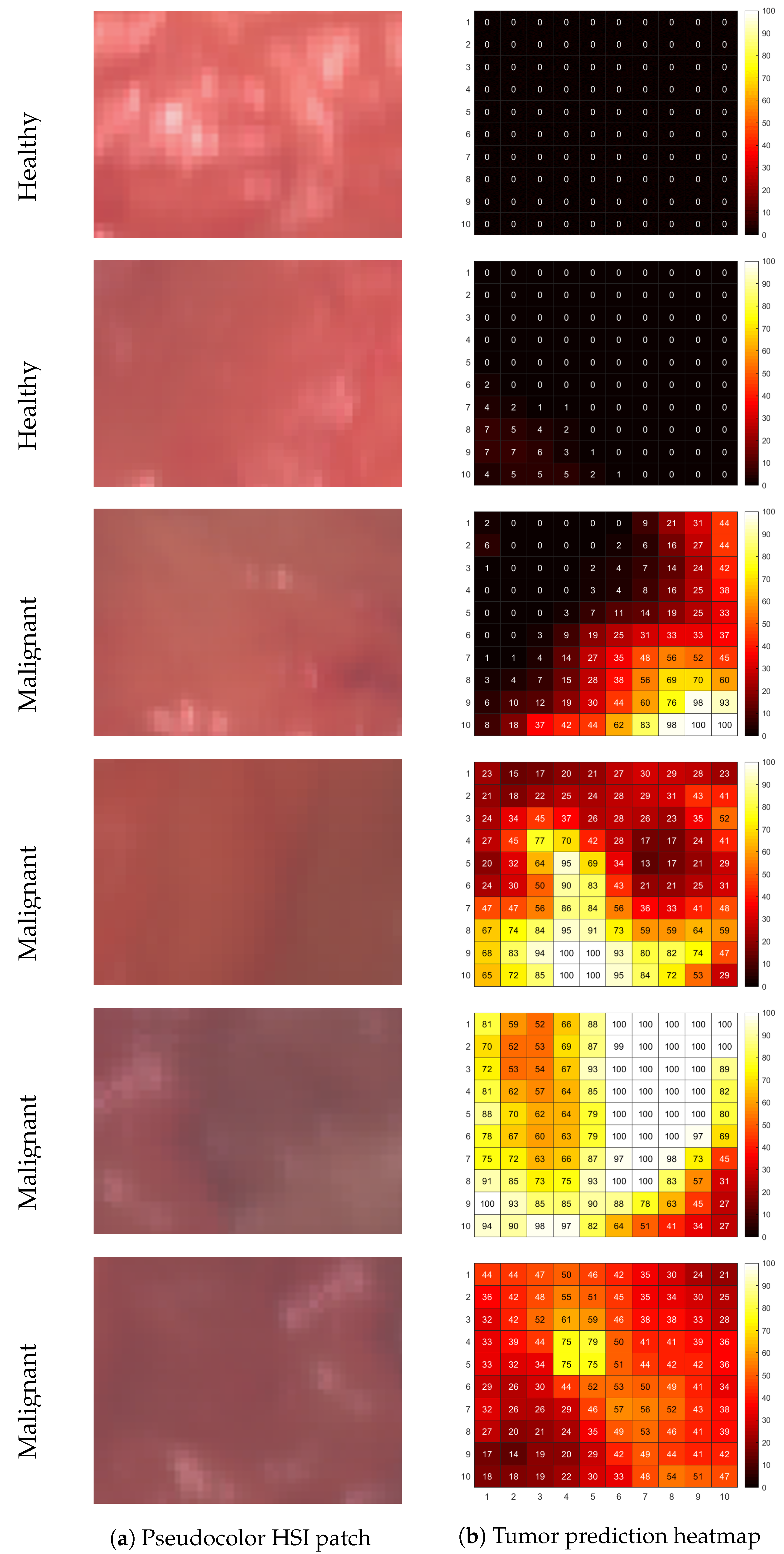
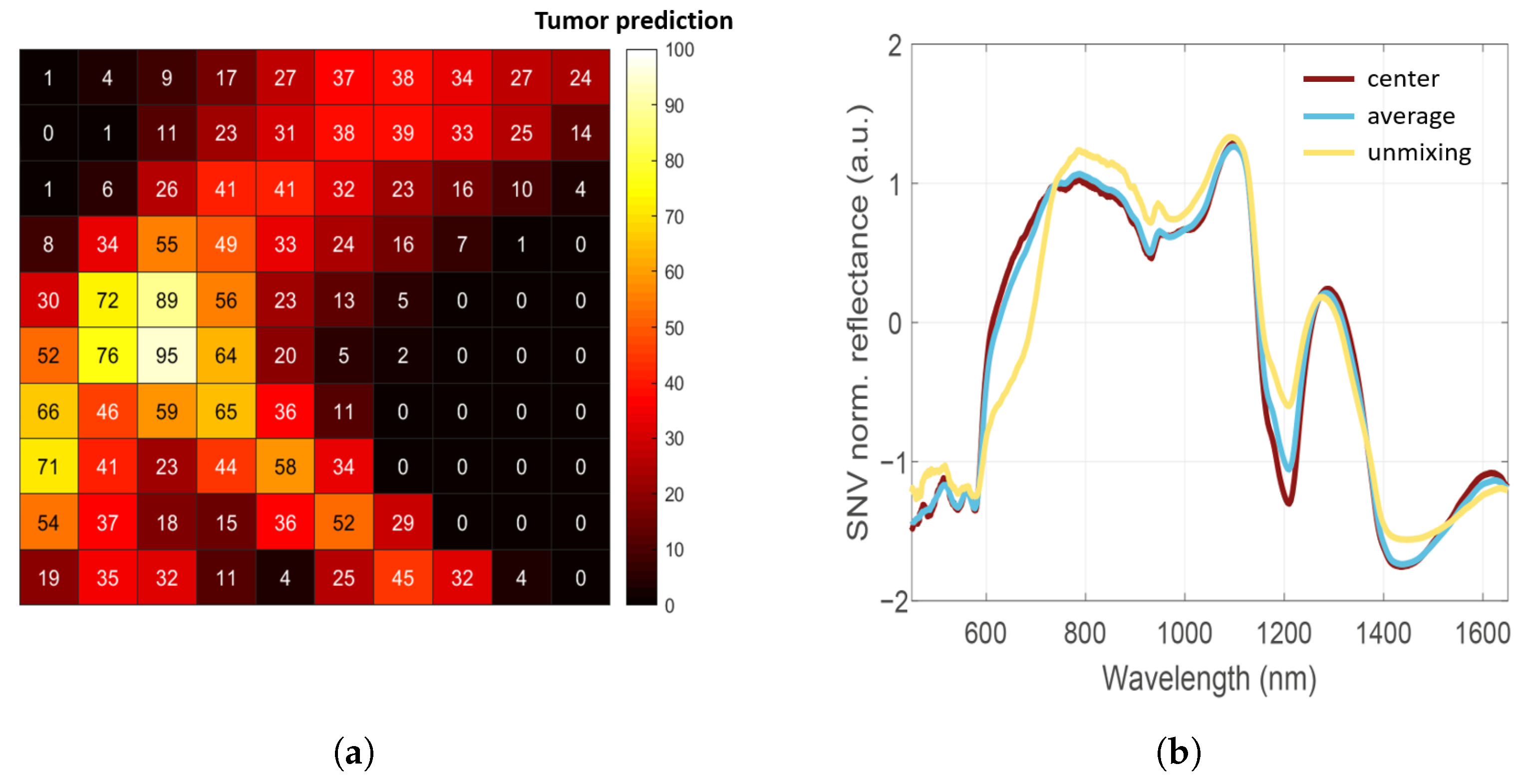
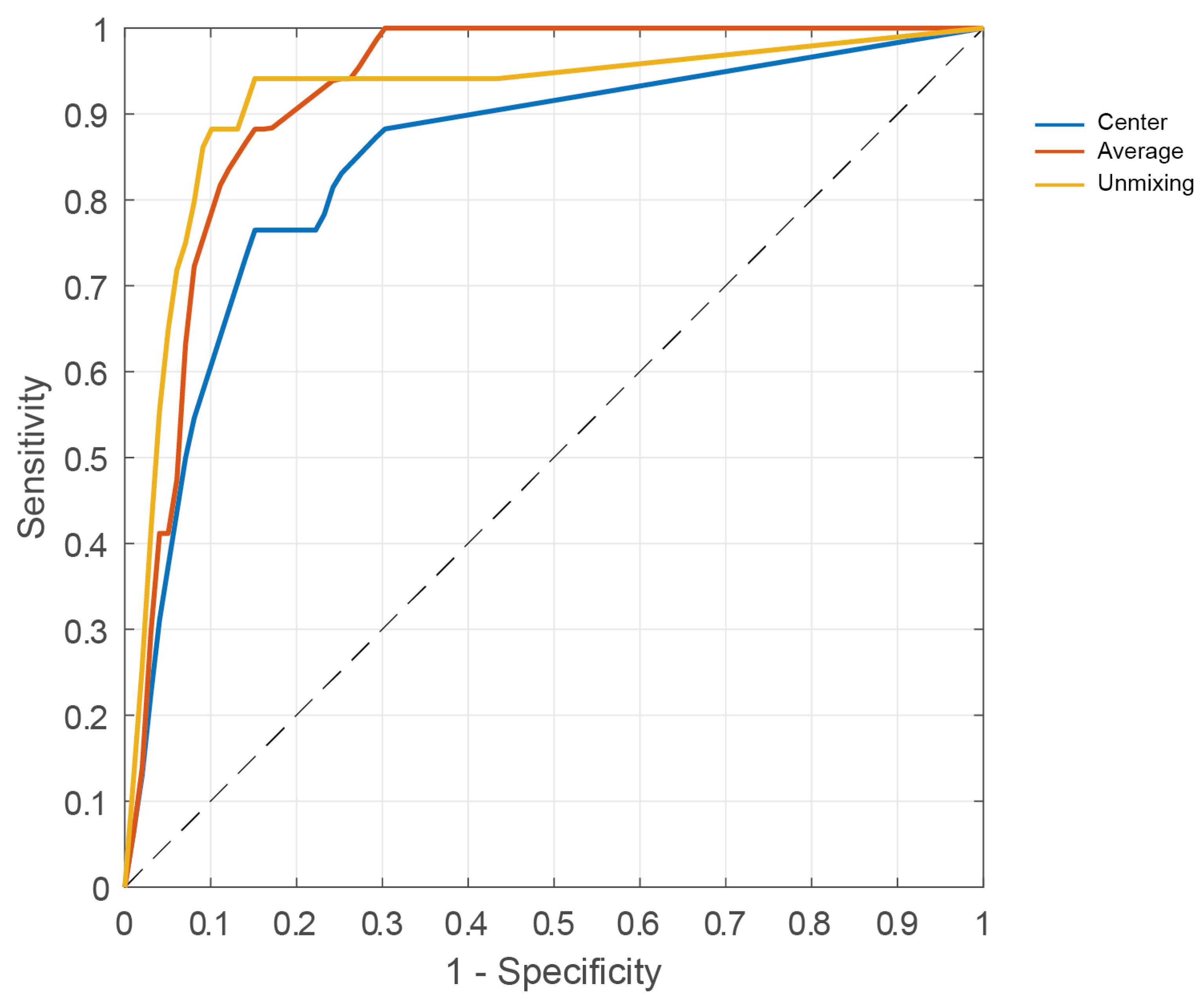
3.3. Tissue Classification
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Etienne, C.A.; Tomatis, M.; Heil, J.; Friedrichs, K.; Kreienberg, R.; Denk, A.; Kiechle, M.; Lorenz-Salehi, F.; Kimmig, R.; Emons, G.; et al. Mastectomy trends for early-stage breast cancer: A report from the EUSOMA multi-institutional European database. Eur. J. Cancer 2012, 48, 1947–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeevan, R.; Cromwell, D.; Trivella, M.; Lawrence, G.; Kearins, O.; Pereira, J.; Sheppard, C.; Caddy, C.; Van Der Meulen, J. Reoperation rates after breast conserving surgery for breast cancer among women in England: Retrospective study of hospital episode statistics. BMJ 2012, 345, e4505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Koning, S.G.B.; Peeters, M.J.T.V.; Jóźwiak, K.; Bhairosing, P.A.; Ruers, T.J. Tumor resection margin definitions in breast-conserving surgery: Systematic review and meta-analysis of the current literature. Clin. Breast Cancer 2018, 18, e595–e600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghian, A.; Mohiuddin, M.; Jagsi, R.; Goldberg, S.; Ceilley, E.; Powell, S. Current perceptions regarding surgical margin status after breast-conserving therapy: Results of a survey. Ann. Surg. 2005, 241, 629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smitt, M.C.; Nowels, K.; Carlson, R.W.; Jeffrey, S.S. Predictors of reexcision findings and recurrence after breast conservation. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2003, 57, 979–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakedis, J.M.; Tang, A.; Savitz, A.; Lyon, L.L.; Palacios, P.E.; Vuong, B.; Kavanagh, M.A.; Kuehner, G.E.; Chang, S.B. Economic Impact of Reducing Reexcision Rates after Breast-Conserving Surgery in a Large, Integrated Health System. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2022, 29, 6288–6296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grant, Y.; Al-Khudairi, R.; St. John, E.; Barschkett, M.; Cunningham, D.; Al-Mufti, R.; Hogben, K.; Thiruchelvam, P.; Hadjiminas, D.; Darzi, A.; et al. Patient-level costs in margin re-excision for breast-conserving surgery. J. Br. Surg. 2019, 106, 384–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kho, E.; de Boer, L.L.; Van de Vijver, K.K.; van Duijnhoven, F.; Vrancken Peeters, M.J.T.; Sterenborg, H.J.; Ruers, T.J. Hyperspectral Imaging for Resection Margin Assessment during Cancer Surgery Hyperspectral Imaging for Resection Margin Assessment. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 3572–3580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kho, E.; Dashtbozorg, B.; De Boer, L.L.; Van de Vijver, K.K.; Sterenborg, H.J.; Ruers, T.J. Broadband hyperspectral imaging for breast tumor detection using spectral and spatial information. Biomed. Opt. Express 2019, 10, 4496–4515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jong, L.J.S.; de Kruif, N.; Geldof, F.; Veluponnar, D.; Sanders, J.; Peeters, M.J.T.V.; van Duijnhoven, F.; Sterenborg, H.J.; Dashtbozorg, B.; Ruers, T.J. Discriminating healthy from tumor tissue in breast lumpectomy specimens using deep learning-based hyperspectral imaging. Biomed. Opt. Express 2022, 13, 2581–2604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panasyuk, S.V.; Yang, S.; Faller, D.V.; Ngo, D.; Lew, R.A.; Freeman, J.E.; Rogers, A.E. Medical hyperspectral imaging to facilitate residual tumor identification during surgery. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2007, 6, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pourreza-Shahri, R.; Saki, F.; Kehtarnavaz, N.; Leboulluec, P.; Liu, H. Classification of ex-vivo breast cancer positive margins measured by hyperspectral imaging. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Image Processing, Melbourne, Australia, 15–18 September 2013; pp. 1408–1412. [Google Scholar]
- Aboughaleb, I.H.; Aref, M.H.; El-Sharkawy, Y.H. Hyperspectral imaging for diagnosis and detection of ex-vivo breast cancer. Photodiagnosis Photodyn. Ther. 2020, 31, 101922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baltussen, E.J.; Kok, E.N.; de Koning, S.G.B.; Sanders, J.; Aalbers, A.G.; Kok, N.F.; Beets, G.L.; Flohil, C.C.; Bruin, S.C.; Kuhlmann, K.F.; et al. Hyperspectral imaging for tissue classification, a way toward smart laparoscopic colorectal surgery. J. Biomed. Opt. 2019, 24, 016002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen-Winkeln, B.; Barberio, M.; Chalopin, C.; Schierle, K.; Diana, M.; Köhler, H.; Gockel, I.; Maktabi, M. Feedforward artificial neural network-based colorectal cancer detection using hyperspectral imaging: A step towards automatic optical biopsy. Cancers 2021, 13, 967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Vliet-Pérez, S.M.; van de Berg, N.J.; Manni, F.; Lai, M.; Rijstenberg, L.; Hendriks, B.H.; Dankelman, J.; Ewing-Graham, P.C.; Nieuwenhuyzen-de Boer, G.M.; Van Beekhuizen, H.J. Hyperspectral Imaging for Tissue Classification after Advanced Stage Ovarian Cancer Surgery—A Pilot Study. Cancers 2022, 14, 1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halicek, M.; Dormer, J.D.; Little, J.V.; Chen, A.Y.; Fei, B. Tumor detection of the thyroid and salivary glands using hyperspectral imaging and deep learning. Biomed. Opt. Express 2020, 11, 1383–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, G.; Little, J.V.; Wang, X.; Zhang, H.; Patel, M.R.; Griffith, C.C.; El-Deiry, M.W.; Chen, A.Y.; Fei, B. Detection of Head and Neck Cancer in Surgical Specimens Using Quantitative Hyperspectral ImagingHyperspectral Imaging for Head and Neck Cancer Detection. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 5426–5436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindholm, V.; Raita-Hakola, A.M.; Annala, L.; Salmivuori, M.; Jeskanen, L.; Saari, H.; Koskenmies, S.; Pitkänen, S.; Pölönen, I.; Isoherranen, K.; et al. Differentiating Malignant from Benign Pigmented or Non-Pigmented Skin Tumours—A Pilot Study on 3D Hyperspectral Imaging of Complex Skin Surfaces and Convolutional Neural Networks. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmivuori, M.; Neittaanmäki, N.; Pölönen, I.; Jeskanen, L.; Snellman, E.; Grönroos, M. Hyperspectral imaging system in the delineation of Ill-defined basal cell carcinomas: A pilot study. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2019, 33, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kho, E.; Dashtbozorg, B.; Sanders, J.; Vrancken Peeters, M.J.T.; van Duijnhoven, F.; Sterenborg, H.J.; Ruers, T.J. Feasibility of ex vivo margin assessment with hyperspectral imaging during breast-conserving surgery: From imaging tissue slices to imaging lumpectomy specimen. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 8881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, R.; Dhanoa, M.S.; Lister, S.J. Standard normal variate transformation and de-trending of near-infrared diffuse reflectance spectra. Appl. Spectrosc. 1989, 43, 772–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bioucas-Dias, J.M.; Plaza, A.; Dobigeon, N.; Parente, M.; Du, Q.; Gader, P.; Chanussot, J. Hyperspectral unmixing overview: Geometrical, statistical, and sparse regression-based approaches. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2012, 5, 354–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palsson, B.; Sveinsson, J.R.; Ulfarsson, M.O. Blind hyperspectral unmixing using autoencoders: A critical comparison. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2022, 15, 1340–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, D.; Gao, L.; Yao, J.; Yokoya, N.; Chanussot, J.; Heiden, U.; Zhang, B. Endmember-guided unmixing network (EGU-Net): A general deep learning framework for self-supervised hyperspectral unmixing. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2021, 33, 6518–6531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heylen, R.; Parente, M.; Gader, P. A review of nonlinear hyperspectral unmixing methods. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2014, 7, 1844–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinz, D.C.; Chein-I-Chang. Fully constrained least squares linear spectral mixture analysis method for material quantification in hyperspectral imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2001, 39, 529–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boardman, J.W. Geometric mixture analysis of imaging spectrometry data. In Proceedings of the IGARSS’94-1994 International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Pasadena, CA, USA, 8–12 August 1994; pp. 2369–2371. [Google Scholar]
- Mehrotra, S. On the implementation of a primal-dual interior point method. SIAM J. Optim. 1992, 2, 575–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altman, A.; Gondzio, J. Regularized symmetric indefinite systems in interior point methods for linear and quadratic optimization. Optim. Methods Softw. 1999, 11, 275–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KNL. Richtlijn Mammacarcinoom. 2012. Available online: https://richtlijnen.nhg.org/multidisciplinaire-richtlijnen/mammacarcinoom (accessed on 19 April 2023).
- Clopper, C.J.; Pearson, E.S. The use of confidence or fiducial limits illustrated in the case of the binomial. Biometrika 1934, 26, 404–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boughorbel, S.; Jarray, F.; El-Anbari, M. Optimal classifier for imbalanced data using Matthews Correlation Coefficient metric. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0177678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esbona, K.; Li, Z.; Wilke, L.G. Intraoperative imprint cytology and frozen section pathology for margin assessment in breast conservation surgery: A systematic review. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2012, 19, 3236–3245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keating, J.J.; Fisher, C.; Batiste, R.; Singhal, S. Advances in intraoperative margin assessment for breast cancer. Curr. Surg. Rep. 2016, 4, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrow, M.; Van Zee, K.J.; Solin, L.J.; Houssami, N.; Chavez-MacGregor, M.; Harris, J.R.; Horton, J.; Hwang, S.; Johnson, P.L.; Marinovich, M.L.; et al. Society of Surgical Oncology—American Society for Radiation Oncology–American Society of Clinical Oncology consensus guideline on margins for breast-conserving surgery with whole-breast irradiation in ductal carcinoma in situ. Pract. Radiat. Oncol. 2016, 6, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, R.A.; Homer, M.J.; Katz, J.; Rothschild, J.; Safaii, H.; Supran, S. The pancake phenomenon contributes to the inaccuracy of margin assessment in patients with breast cancer. Am. J. Surg. 2002, 184, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Characteristic | No. of Patients (%) | Mean ± STD |
|---|---|---|
| Age, years | 57 ± 11 | |
| <50 | 48 (25) | |
| 50–59 | 69 (37) | |
| 60–69 | 43 (23) | |
| ≥70 | 29 (15) | |
| Menopausal stage | ||
| Pre | 41 (22) | |
| Peri | 16 (8) | |
| Post | 109 (58) | |
| Unknown | 23 (12) | |
| Breast side | ||
| Left | 92 (49) | |
| Right | 97 (51) | |
| Breast density, ACR score | ||
| 1 | 15 (8) | |
| 2 | 75 (40) | |
| 3 | 75 (40) | |
| 4 | 20 (11) | |
| Unknown | 4 (2) | |
| Neoadjuvant therapy | ||
| Chemotherapy | 19 (10) | |
| Hormone therapy | 13 (7) | |
| Immunotherapy | 2 (1) | |
| None | 155 (82) | |
| Size lumpectomy, cm | 57 ± 56 |
| Tissue Class | Training Set | Test Set |
|---|---|---|
| #Patients (#Locations) | Labeled | Labeled |
| Healthy | 129 (221) | 35 (53) |
| Malignant | 59 (81) | 12 (17) |
| Total | 151 (302) | 38 (70) |
| Sensitivity Mean [95% CI] | Specificity Mean [95% CI] | Accuracy Mean [95% CI] | MCC | AUC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patch center | 0.76 [0.50, 0.93] | 0.85 [0.72, 0.93] | 0.83 [0.72, 0.91] | 0.57 | 0.85 |
| Patch average | 0.88 [0.64, 0.99] | 0.85 [0.72, 0.93] | 0.86 [0.75, 0.93] | 0.67 | 0.93 |
| Patch unmixing | 0.94 [0.71, 1.00] | 0.85 [0.72, 0.93] | 0.87 [0.77, 0.94] | 0.71 | 0.92 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jong, L.-J.S.; Post, A.L.; Veluponnar, D.; Geldof, F.; Sterenborg, H.J.C.M.; Ruers, T.J.M.; Dashtbozorg, B. Tissue Classification of Breast Cancer by Hyperspectral Unmixing. Cancers 2023, 15, 2679. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15102679
Jong L-JS, Post AL, Veluponnar D, Geldof F, Sterenborg HJCM, Ruers TJM, Dashtbozorg B. Tissue Classification of Breast Cancer by Hyperspectral Unmixing. Cancers. 2023; 15(10):2679. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15102679
Chicago/Turabian StyleJong, Lynn-Jade S., Anouk L. Post, Dinusha Veluponnar, Freija Geldof, Henricus J. C. M. Sterenborg, Theo J. M. Ruers, and Behdad Dashtbozorg. 2023. "Tissue Classification of Breast Cancer by Hyperspectral Unmixing" Cancers 15, no. 10: 2679. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15102679
APA StyleJong, L.-J. S., Post, A. L., Veluponnar, D., Geldof, F., Sterenborg, H. J. C. M., Ruers, T. J. M., & Dashtbozorg, B. (2023). Tissue Classification of Breast Cancer by Hyperspectral Unmixing. Cancers, 15(10), 2679. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15102679







