GNL3 and PA2G4 as Prognostic Biomarkers in Prostate Cancer
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Identification of Prognostic Biomarker(s) in Prostate Cancer
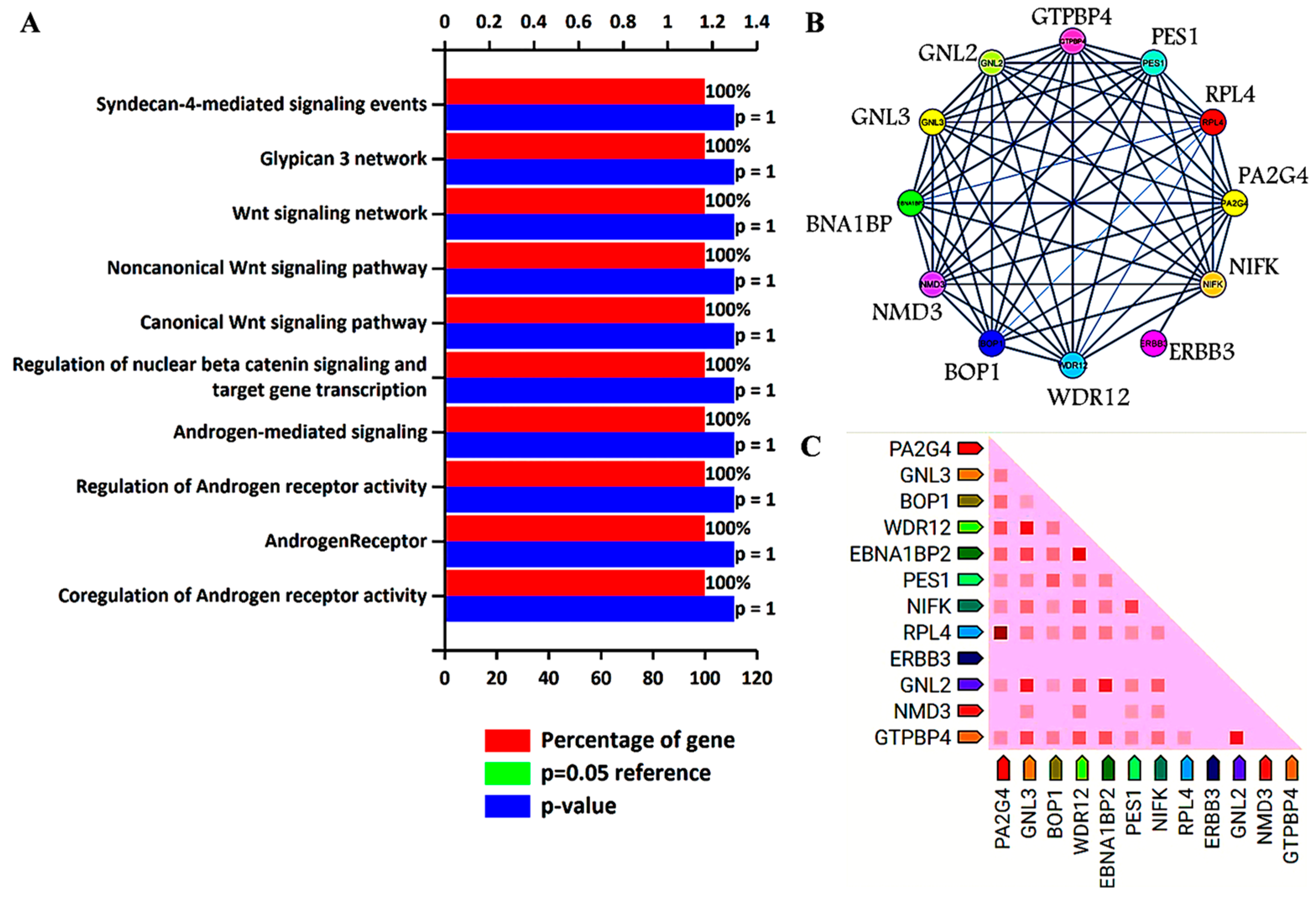
3. Biological Pathways and Protein–Protein Interaction Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rawla, P. Epidemiology of Prostate Cancer. World J. Oncol. 2019, 10, 63–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catalona, W.J. Prostate Cancer Screening. Med. Clin. N. Am. 2018, 102, 199–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alberts, A.R.; Schoots, I.G.; Roobol, M.J. Prostate-Specific Antigen-Based Prostate Cancer Screening: Past and Future: Past and Future. Int. J. Urol. 2015, 22, 524–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, C.; Castro, E.; Fizazi, K.; Heidenreich, A.; Ost, P.; Procopio, G.; Tombal, B.; Gillessen, S. Prostate Cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diagnosis, Treatment and Follow-Up. Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, 1119–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parry, M.G.; Cowling, T.E.; Sujenthiran, A.; Nossiter, J.; Berry, B.; Cathcart, P.; Aggarwal, A.; Payne, H.; van der Meulen, J.; Clarke, N.W.; et al. Risk stratification for prostate cancer management: Value of the Cambridge Prognostic Group classification for assessing treatment allocation. BMC Med. 2020, 18, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Troyer, D.A.; Mubiru, J.; Leach, R.J.; Naylor, S.L. Promise and Challenge: Markers of Prostate Cancer Detection, Diagnosis and Prognosis. Dis. Markers 2004, 20, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crocetto, F.; Russo, G.; Di Zazzo, E.; Pisapia, P.; Mirto, B.F.; Palmieri, A.; Pepe, F.; Bellevicine, C.; Russo, A.; La Civita, E.; et al. Liquid biopsy in prostate cancer management—Current challenges and future perspectives. Cancers 2022, 14, 3272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durand, X.; Moutereau, S.; Xylinas, E.; De La Taille, A. ProgensaTM PCA3 Test for Prostate Cancer. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2011, 11, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khatami, F.; Aghamir, S.M.K.; Salmaninejad, A.; Shivarani, S.; Khorrami, M.H. Biomarkers for prostate cancer diagnosis from genetic perspectives. Transl. Res. Urol. 2020, 2, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strimbu, K.; Tavel, J.A. What are biomarkers? Curr. Opin. HIV AIDS 2010, 5, 463–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Karsh, L.I.; Nissenblatt, M.J.; Canfield, S.E. Androgen Receptor Splice Variant, AR-V7, as a Biomarker of Resistance to Androgen Axis-Targeted Therapies in Advanced Prostate Cancer. Clin. Genitourin. Cancer 2020, 18, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCabe, N.; Kennedy, R.D.; Prise, K.M. The role of PTEN as a cancer biomarker. Oncoscience 2016, 3, 54–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, W.; Dean, D.C.; Hornicek, F.J.; Spentzos, D.; Hoffman, R.M.; Shi, H.; Duan, Z. Myc is a prognostic biomarker and potential therapeutic target in osteosarcoma. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2020, 12, 1758835920922055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushwaha, P.P.; Verma, S.; Gupta, S. Aquaporins as Prognostic Biomarker in Prostate Cancer. Cancers 2023, 15, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanguedolce, F.; Cormio, A.; Brunelli, M.; D’Amuri, A.; Carrieri, G.; Bufo, P.; Cormio, L. Urine TMPRSS2: ERG Fusion Transcript as a Biomarker for Prostate Cancer: Literature Review. Clin. Genitourin. Cancer 2016, 14, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eggener, S.E.; Badani, K.; Barocas, D.A.; Barrisford, G.W.; Cheng, J.S.; Chin, A.I.; Corcoran, A.; Epstein, J.I.; George, A.K.; Gupta, G.N.; et al. Gleason 6 prostate cancer: Translating biology into population health. J. Urol. 2015, 194, 626–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klatte, T.; Waldert, M.; De Martino, M.; Schatzl, G.; Mannhalter, C.; Remzi, M. Age-Specific PCA3 Score Reference Values for Diagnosis of Prostate Cancer. World J. Urol. 2012, 30, 405–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crocetto, F.; Barone, B.; Caputo, V.F.; Fontana, M.; de Cobelli, O.; Ferro, M. BRCA Germline Mutations in Prostate Cancer: The Future Is Tailored. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewing, C.M.; Ray, A.M.; Lange, E.M.; Zuhlke, K.A.; Robbins, C.M.; Tembe, W.D.; Wiley, K.E.; Isaacs, S.D.; Johng, D.; Wang, Y.; et al. Germline mutations in HOXB13 and prostate-cancer risk. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allemailem, K.S.; Almatroudi, A.; Alrumaihi, F.; Makki Almansour, N.; Aldakheel, F.M.; Rather, R.A.; Afroze, D.; Rah, B. Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in prostate cancer: Its implications in diagnostics and therapeutics. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2021, 13, 3868–3889. [Google Scholar]
- Ferro, M.; De Cobelli, O.; Lucarelli, G.; Porreca, A.; Busetto, G.M.; Cantiello, F.; Damiano, R.; Autorino, R.; Musi, G.; Vartolomei, M.D.; et al. Beyond PSA: The Role of Prostate Health Index (Phi). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayan, V.M.; Konety, B.R.; Warlick, C. Novel Biomarkers for Prostate Cancer: An Evidence-Based Review for Use in Clinical Practice. Int. J. Urol. 2017, 24, 352–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maccini, M.A.; Westfall, N.J.; Van Bokhoven, A.; Lucia, M.S.; Poage, W.; Maroni, P.D.; Wilson, S.S.; Glodé, L.M.; Arangua, P.; Newmark, J.; et al. The Effect of Digital Rectal Exam on the 4Kscore for Aggressive Prostate Cancer. Prostate 2018, 78, 506–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlsson, S.V.; Roobol, M.J. Improving the Evaluation and Diagnosis of Clinically Significant Prostate Cancer in 2017. Curr. Opin. Urol. 2017, 27, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olleik, G.; Kassouf, W.; Aprikian, A.; Hu, J.; Vanhuyse, M.; Cury, F.; Peacock, S.; Bonnevier, E.; Palenius, E.; Dragomir, A. Evaluation of New Tests and Interventions for Prostate Cancer Management: A Systematic Review. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2018, 16, 1340–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kish, E.K.; Choudhry, M.; Gamallat, Y.; Buharideen, S.M.; Bismar, T.A. The expression of proto-oncogene ETS-related gene (ERG) plays a central role in the oncogenic mechanism involved in the development and progression of prostate cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, L.; Johnson, M.T. How precisely can prostate cancer be managed? Int. Neurourol. J. 2016, 20 (Suppl. S2), S120–S130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koo, K.M.; Wee, E.J.H.; Mainwaring, P.N.; Trau, M. A Simple, Rapid, Low-Cost Technique for Naked-Eye Detection of Urine-Isolated TMPRSS2:ERG Gene Fusion RNA. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haese, A.; Trooskens, G.; Steyaert, S.; Hessels, D.; Brawer, M.; Vlaeminck-Guillem, V.; Ruffion, A.; Tilki, D.; Schalken, J.; Groskopf, J.; et al. Multicenter Optimization and Validation of a 2-Gene MRNA Urine Test for Detection of Clinically Significant Prostate Cancer before Initial Prostate Biopsy. J. Urol. 2019, 202, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legisi, L.; DeSa, E.; Qureshi, M.N. Use of the prostate core mitomic test in repeated biopsy decision-making: Real-world assessment of clinical utility in a multicenter patient population. Am. Health Drug Benefits 2016, 9, 497–502. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ross, A.E.; D’Amico, A.V.; Freedland, S.J. Which, when and why? Rational use of tissue-based molecular testing in localized prostate cancer. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2016, 19, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toribio-Vázquez, C.; Rivas, J.G.; Yebes, Á.; Carrión, D.M.; Barrado, M.Y.; Álvarez-Maestro, M.; Martinez-Piñeiro, L. New strategies for decision making in prostate cancer. The role of oncotypedx. Actas Urol. Esp. 2022, 46, 385–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falzarano, S.M.; Ferro, M.; Bollito, E.; Klein, E.A.; Carrieri, G.; Magi-Galluzzi, C. Novel biomarkers and genomic tests in prostate cancer: A critical analysis. Ital. J. Urol. Nephrol. 2015, 67, 211–231. [Google Scholar]
- Bhargava, H.K.; Leo, P.; Elliott, R.; Janowczyk, A.; Whitney, J.; Gupta, S.; Fu, P.; Yamoah, K.; Khani, F.; Robinson, B.D.; et al. Computationally Derived Image Signature of Stromal Morphology Is Prognostic of Prostate Cancer Recurrence Following Prostatectomy in African American Patients. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 1915–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, S.; Prajapati, K.S.; Kushwaha, P.P.; Shuaib, M.; Kumar Singh, A.; Kumar, S.; Gupta, S. Resistance to second generation antiandrogens in prostate cancer: Pathways and mechanisms. Cancer Drug Resist. 2020, 3, 742–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Culig, Z.; Santer, F.R. Androgen receptor signaling in prostate cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2014, 33, 413–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Cheng, L.; Li, J.; Farah, E.; Atallah, N.M.; Pascuzzi, P.E.; Gupta, S.; Liu, X. Inhibition of the Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway Overcomes Resistance to Enzalutamide in Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 3147–3162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shankar, E.; Franco, D.; Iqbal, O.; El-Hayek, V.; Gupta, S. Novel approach to therapeutic targeting of castration-resistant prostate cancer. Med. Hypotheses 2020, 140, 109639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, R.; Xing, Q.S. Roles of Wnt Signaling Pathway and ROR2 Receptor in Embryonic Development: An Update Review Article. Epigenetics Insights 2022, 15, 25168657211064232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bland, T.; Wang, J.; Yin, L.; Pu, T.; Li, J.; Gao, J.; Lin, T.P.; Gao, A.C.; Wu, B.J. WLS-Wnt signaling promotes neuroendocrine prostate cancer. iScience 2021, 24, 101970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Chen, Q.; Xu, H. Wnt/β-catenin signal transduction pathway in prostate cancer and associated drug resistance. Discover. Oncology 2021, 12, 40. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, J.; Wang, D.; Wan, X.; Xu, Y.; Lu, Y.; Kong, Z.; Li, D.; Gu, W.; Wang, C.; Li, Y.; et al. Crosstalk Between AR and Wnt Signaling Promotes Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer Growth. OncoTargets Ther. 2020, 13, 9257–9267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bestwick, M.; Jeong, M.Y.; Khalimonchuk, O.; Kim, H.; Winge, D.R. Analysis of Leigh Syndrome Mutations in the Yeast Surf1 Homolog Reveals a New Member of the Cytochrome Oxidase Assembly Factor Family. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2010, 30, 4480–4491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longen, S.; Bien, M.; Bihlmaier, K.; Kloeppel, C.; Kauff, F.; Hammermeister, M.; Westermann, B.; Herrmann, J.M.; Riemer, J. Systematic Analysis of the Twin Cx9C Protein Family. J. Mol. Biol. 2009, 393, 356–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bode, M.; Longen, S.; Morgan, B.; Peleh, V.; Dick, T.P.; Bihlmaier, K.; Herrmann, J.M. Inaccurately Assembled Cytochrome c Oxidase Can Lead to Oxidative Stress-Induced Growth Arrest. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2013, 18, 1597–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srinivasan, S.; Guha, M.; Dong, D.W.; Whelan, K.A.; Ruthel, G.; Uchikado, Y.; Natsugoe, S.; Nakagawa, H.; Avadhani, N.G. Disruption of Cytochrome c Oxidase Function Induces the Warburg Effect and Metabolic Reprogramming. Oncogene 2016, 35, 1585–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krobthong, S.; Yingchutrakul, Y.; Sittisaree, W.; Tulyananda, T.; Samutrtai, P.; Choowongkomon, K.; Lao-On, U. Evaluation of Potential Anti-Metastatic and Antioxidative Abilities of Natural Peptides Derived from Tecoma stans (L.) Juss. Ex Kunth in A549 Cells. PeerJ 2022, 10, e13693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Meng, L.; Hsu, J.K.; Lin, T.; Teishima, J.; Tsai, R.Y. GNL3L stabilizes the TRF1 complex and promotes mitotic transition. J. Cell Biol. 2009, 185, 827–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, R.Y.L.; McKay, R.D.G. A Nucleolar Mechanism Controlling Cell Proliferation in Stem Cells and Cancer Cells. Genes Dev. 2002, 16, 2991–3003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, X.; Zha, L.; Li, H.; Liao, G.; Huang, Z.; Peng, X.; Wang, Z. Upregulation of GNL3 Expression Promotes Colon Cancer Cell Proliferation, Migration, Invasion and Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition via the Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 38, 2023–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.L.; Zhang, Z.H.; Zhao, W.M.; Wang, M.; Qi, S.Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, S.Z.; Xu, Y. Expression of nucleostemin in prostate cancer and its effect on the proliferation of PC-3 cells. Chin. Med. J. 2008, 121, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhao, H.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y. GNL3 Regulates SIRT1 Transcription and Promotes Hepatocellular Carcinoma Stem Cell-Like Features and Metastasis. J. Oncol. 2022, 2022, 1555670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Li, L.; Wu, X.; Tian, K.; Wang, Y. The oncogenic role of GNL3 in the progression and metastasis of osteosarcoma. Cancer Manag. Res. 2019, 11, 2179–2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, R.; Wu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Shi, J. G protein nucleolar 3 promotes non-Hodgkin lymphoma progression by activating the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Exp. Cell Res. 2021, 409, 112911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawford, M.; Liu, X.; Cheng, Y.L.; Tsai, R.Y. Nucleostemin upregulation and STAT3 activation as early events in oral epithelial dysplasia progression to squamous cell carcinoma. Neoplasia 2021, 23, 1289–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sami, M.M.; Hachim, M.Y.; Hachim, I.Y.; Elbarkouky, A.H.; López-Ozuna, V.M. Nucleostemin expression in breast cancer is a marker of more aggressive phenotype and unfavorable patients’ outcome: A STROBE-compliant article. Medicine 2019, 98, e14744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, T.; Lin, T.C.; McGrail, D.J.; Bhupal, P.K.; Ku, Y.H.; Zhang, W.; Meng, L. Nucleostemin reveals a dichotomous nature of genome maintenance in mammary tumor progression. Oncogene 2019, 38, 3919–3931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.L.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, Z.H.; Wang, M.; Sun, J.T.; Zhang, Y.; Li, S.Z. Gene profiling after knocking-down the expression of NS gene in prostate cancer PC-3 cells. Chin. J. Oncol. 2009, 31, 561–565. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, R.L.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, Z.H.; Wang, M.; Sun, J.T.; Qi, S.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, S.Z. Expression of nucleostemin in prostate cancer tissues and its clinical significance. Natl. J. Androl. 2008, 14, 418–422. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, R.L.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, Z.H.; Wang, M.; Sun, J.T.; Zhang, Y.; Li, S.Z. Silencing nucleostemin expression reduces the proliferation of PC-3 cells. Natl. J. Androl. 2009, 15, 593–598. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, R.L.; Wang, W.Y.; Zhang, Z.H.; Xu, Y. Silencing effect of cell-specific RNA interference plasmid pPSMAe/p-shNS-ploy(A) loaded by transgenic vector Tf-PEG-PEI targeting nucleostemin on prostate cancer cells in vitro. Chin. J. Oncol. 2012, 34, 725–729. [Google Scholar]
- Yoo, J.-Y.; Wang, X.W.; Rishi, A.K.; Lessor, T.; Xia, X.-M.; Gustafson, T.A.; Hamburger, A.W. Interaction of the PA2G4 (EBP1) Protein with ErbB-3 and Regulation of This Binding by Heregulin. Br. J. Cancer 2000, 82, 683–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Lessor, T.J.; Zhang, Y.; Woodford, N.; Hamburger, A.W. Analysis of the expression pattern of Ebp1, an ErbB-3-binding protein. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2001, 289, 240–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gannon, P.O.; Koumakpayi, I.H.; Le Page, C.; Karakiewicz, P.I.; Mes-Masson, A.-M.; Saad, F. Ebp1 Expression in Benign and Malignant Prostate. Cancer Cell Int. 2008, 8, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevenson, B.W.; Gorman, M.A.; Koach, J.; Cheung, B.B.; Marshall, G.M.; Parker, M.W.; Holien, J.K. A Structural View of PA2G4 Isoforms with Opposing Functions in Cancer. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 16100–16112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, M.; Wen, J.; Xue, L.; Han, S.; Liang, J.; Wang, Y.; Wei, Y.; Yu, J.; et al. PA2G4 Promotes the Metastasis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Stabilizing FYN MRNA in a YTHDF2-Dependent Manner. Cell Biosci. 2022, 12, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Cai, H.; Tu, W.; Ding, L.; Luo, R. Increased PA2G4 Expression Is an Unfavorable Factor in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. Appl. Immunohistochem. Mol. Morphol. 2021, 29, 513–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Li, X.D.; Chen, H.Y.; Cui, J.S.; Xu, D.Y. Significance of Ebp1 and P53 Protein Expression in Cervical Cancer. Genet. Mol. Res. 2015, 14, 11860–11866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Tang, W. Pseudogene PA2G4P4 Promotes Oncogene PA2G4 Expression and Nuclear Translocation to Affect Glioblastoma Cell Viability and Apoptosis. Life Sci. 2021, 265, 118793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellinghoff, I.K.; Tran, C.; Sawyers, C.L. Growth inhibitory effects of the dual ErbB1/ErbB2 tyrosine kinase inhibitor PKI-166 on human prostate cancer xenografts. Cancer Res. 2002, 62, 5254–5259. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Agus, D.B.; Akita, R.W.; Fox, W.D.; Lewis, G.D.; Higgins, B.; Pisacane, P.I.; Lofgren, J.A.; Tindell, C.; Evans, D.P.; Maiese, K.; et al. Targeting Ligand-Activated ErbB2 Signaling Inhibits Breast and Prostate Tumor Growth. Cancer Cell 2002, 2, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza, N.; Phillips, G.L.; Silva, J.; Schwall, R.; Wickramasinghe, D. Inhibition of ligand-mediated HER2 activation in androgen-independent prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2002, 62, 5485–5488. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Fondell, J.D.; Wang, Q.; Xia, X.; Cheng, A.; Lu, M.L.; Hamburger, A.W. Repression of Androgen Receptor Mediated Transcription by the ErbB-3 Binding Protein, Ebp1. Oncogene 2002, 21, 5609–5618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awasthi, S.; Ezelle, H.; Hassel, B.A.; Hamburger, A.W. The ErbB3-Binding Protein EBP1 Modulates Lapatinib Sensitivity in Prostate Cancer Cells. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2015, 405, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Lin, J.; Ye, K. Structural and Functional Analysis of the U3 SnoRNA Binding Protein Rrp9. RNA 2013, 19, 701–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clerget, G.; Bourguignon-Igel, V.; Marmier-Gourrier, N.; Rolland, N.; Wacheul, L.; Manival, X.; Charron, C.; Kufel, J.; Méreau, A.; Senty-Ségault, V.; et al. Synergistic Defects in Pre-RRNA Processing from Mutations in the U3-Specific Protein Rrp9 and U3 SnoRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, 3848–3868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, M.; Liu, F.; Chang, Y.; Tong, S.; Liu, W.; Chen, Y.; Xie, P. Correction: Neddylation Modification of the U3 SnoRNA-Binding Protein RRP9 by Smurf1 Promotes Tumorigenesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2022, 298, 102567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Yu, H.; Yao, W.; Zhu, N.; Miao, R.; Liu, Z.; Song, X.; Xue, C.; Cai, C.; Cheng, M.; et al. RRP9 Promotes Gemcitabine Resistance in Pancreatic Cancer via Activating AKT Signaling Pathway. Cell Commun. Signal. 2022, 20, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Panel | Specimen | AUC for Prostate Cancer Detection | Limitations | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PCA3 | Urine | 0.65 | Recommended only for the precise population of prostate cancer patients who have a first negative biopsy report. PCA3 score rises with age, independent of PC occurrence. | [17,18] |
| PHI | Serum | 0.70 | Used to detect the probability of finding any prostate cancer on repeat biopsy, irrespective of the GS. It does not have de facto common use because of pre-analytical stability of [2] proPSA and high cost. | [22,23] |
| 4Kscore® | Serum | 0.71 | 4Kscore® test has been restricted to those prostate cancer patients who have not had DRE in the previous 96 h. | [24] |
| ConfirmMDx® | Prostate biopsy tissues | 0.74 | Recommended for those prostate cancer patients who had negative prostate biopsy. There is no recommendation for the routine clinical application. | [25] |
| ExoDX Prostate IntelliScore | Urine | 0.70 | Lack of evidence in respect of clinical utility | [26] |
| Prostate Core Mitomic Test | Serum | - | False negative results in malice of high sensitivity. | [27,28] |
| MiPS Mi(chigan) Prostate Scor | Urine | 0.69 | Lack of evidence in respect of clinical utility | [26] |
| TMPRSS2-ERG gene fusion | Urine | - | Not widely used due to long processing time, very high cost, and the necessity of dedicated equipment. | [28] |
| SelectMDX | Urine | 0.71–0.81 | Diagnostic as well as prognostic correctness in ethnically diverse study population is unidentified till date. SelectMDx shows declined sensitivity, specificity, and NPV. | [29,30] |
| Prolaris | Tissue | 0.78 | There is no evidence to describe the effect of the prolaris cell cycle progression test on patient-important clinical outcome results. | [30,31] |
| OncotypeDx | Tissue | 0.73 | This test is not intended to take ethnic discrimination into account. | [32,33] |
| ProMark | Tissue | 0.72 | Test is imperfect and skips the high-risk nearby zone of prostate tumor. | [26,33] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kumar, S.; Shuaib, M.; AlAsmari, A.F.; Alqahtani, F.; Gupta, S. GNL3 and PA2G4 as Prognostic Biomarkers in Prostate Cancer. Cancers 2023, 15, 2723. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15102723
Kumar S, Shuaib M, AlAsmari AF, Alqahtani F, Gupta S. GNL3 and PA2G4 as Prognostic Biomarkers in Prostate Cancer. Cancers. 2023; 15(10):2723. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15102723
Chicago/Turabian StyleKumar, Shashank, Mohd Shuaib, Abdullah F. AlAsmari, Faleh Alqahtani, and Sanjay Gupta. 2023. "GNL3 and PA2G4 as Prognostic Biomarkers in Prostate Cancer" Cancers 15, no. 10: 2723. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15102723
APA StyleKumar, S., Shuaib, M., AlAsmari, A. F., Alqahtani, F., & Gupta, S. (2023). GNL3 and PA2G4 as Prognostic Biomarkers in Prostate Cancer. Cancers, 15(10), 2723. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15102723









