Role of Glucose Metabolic Reprogramming in Breast Cancer Progression and Drug Resistance
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
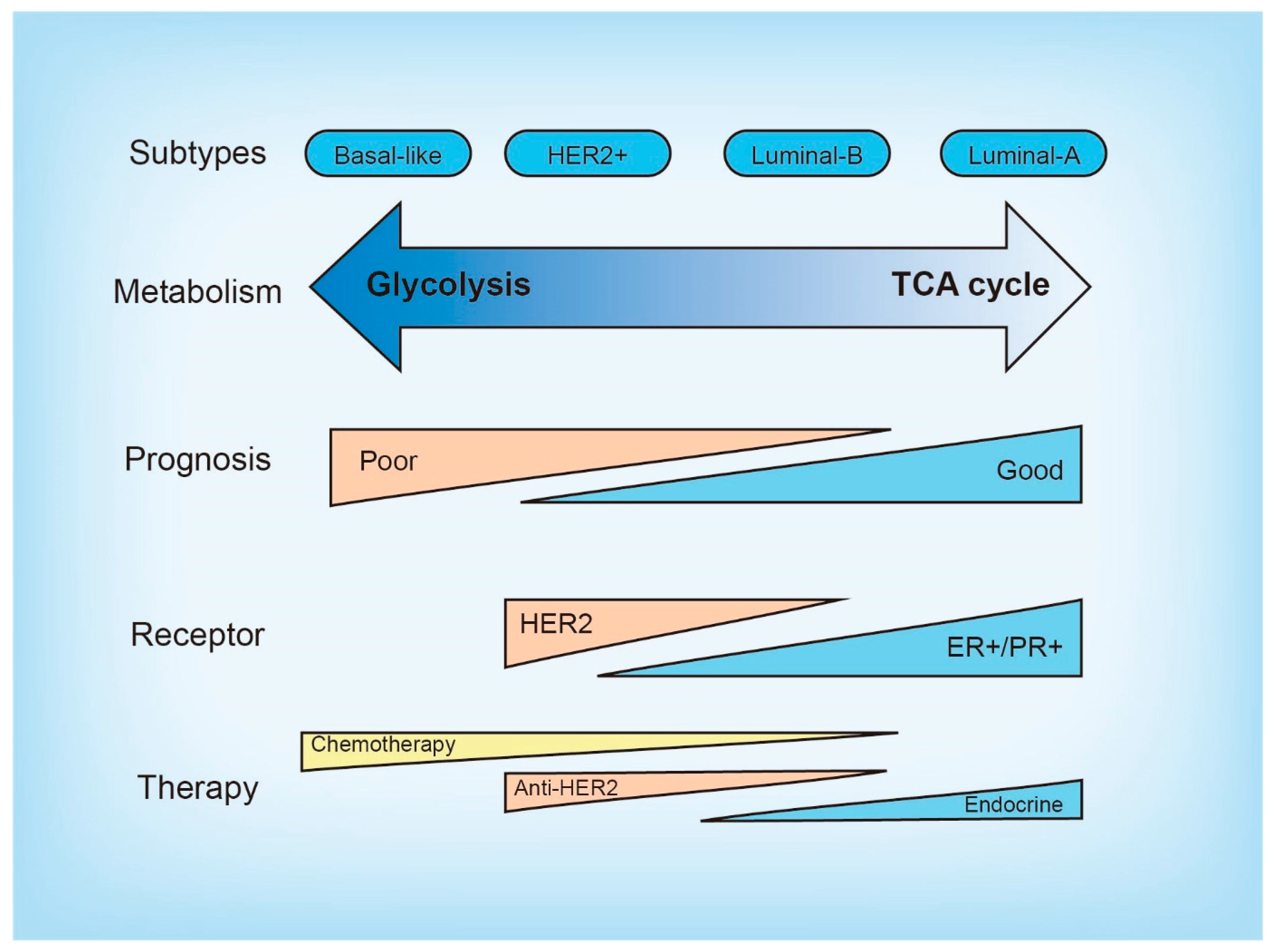
2. Molecular and Metabolic Heterogeneity in Breast Cancer
3. Reprogramming of Glucose Metabolism in Breast Cancer Progression and Therapy Response
3.1. Hexokinase (HK)
3.2. Phosphofructokinase (PFK)
3.3. Pyruvate Kinase (PK)
3.4. Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Kinase (PDK)
3.5. 3-phosphoglycerate Dehydrogenase (PHGDH)
3.6. Lactate Dehydrogenase (LDH)
4. Glucose Metabolism Reprogramming in the Breast Tumor Microenvironment (TME)
4.1. Tumor-Associated Macrophages (TAMs)
4.2. Tumor-Infiltrating T Cells (TILs)
4.3. Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts (CAFs)
4.4. Other Immune Cells in the TME
5. Targeting Glucose Metabolism to Improve Cancer Therapy
| Druggable Target | Drug | Stage of Development | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| GLUTs | STF-31 | Preclinical | [127] |
| WZB117, WZB27, WZB115 | Preclinical | [126,130] | |
| BAY-876 | Preclinical | [128] | |
| HK2 | Silybin | Phase I (NCT00487721) | [141] |
| 2-DG | Phase I (NCT00096707) | [142] | |
| lonidamine | Phase I–III | [115] | |
| GAPDH | 3-BrPA | Preclinical | [143] |
| Koningic acid | Preclinical | [144] | |
| PDK | Dichloroacetate | Phase I (NCT01111097) | [145] |
| MCTs | AZD3965 | Phase I (NCT01791595) | [146] |
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waks, A.G.; Winer, E.P. Breast Cancer Treatment: A Review. JAMA 2019, 321, 288–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perou, C.M.; Sørlie, T.; Eisen, M.B.; van de Rijn, M.; Jeffrey, S.S.; Rees, C.A.; Pollack, J.R.; Ross, D.T.; Johnsen, H.; Akslen, L.A.; et al. Molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature 2000, 406, 747–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loibl, S.; Poortmans, P.; Morrow, M.; Denkert, C.; Curigliano, G. Breast cancer. Lancet 2021, 397, 1750–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perou, C.M. Molecular stratification of triple-negative breast cancers. Oncologist 2010, 15 (Suppl. 5), 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallejos, C.S.; Gómez, H.L.; Cruz, W.R.; Pinto, J.A.; Dyer, R.R.; Velarde, R.; Suazo, J.F.; Neciosup, S.P.; León, M.; de la Cruz, M.A.; et al. Breast cancer classification according to immunohistochemistry markers: Subtypes and association with clinicopathologic variables in a peruvian hospital database. Clin. Breast Cancer 2010, 10, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheang, M.C.; Chia, S.K.; Voduc, D.; Gao, D.; Leung, S.; Snider, J.; Watson, M.; Davies, S.; Bernard, P.S.; Parker, J.S.; et al. Ki67 index, HER2 status, and prognosis of patients with luminal B breast cancer. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2009, 101, 736–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanker, A.B.; Sudhan, D.R.; Arteaga, C.L. Overcoming Endocrine Resistance in Breast Cancer. Cancer Cell 2020, 37, 496–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggelis, V.; Johnston, S.R.D. Advances in Endocrine-Based Therapies for Estrogen Receptor-Positive Metastatic Breast Cancer. Drugs 2019, 79, 1849–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, N.C.; Neven, P.; Loibl, S.; Andre, F. Advances in the treatment of advanced oestrogen-receptor-positive breast cancer. Lancet 2017, 389, 2403–2414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warburg, O. The Metabolism of Carcinoma Cells. Journal. Cancer Res. 1925, 9, 148–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlides, S.; Whitaker-Menezes, D.; Castello-Cros, R.; Flomenberg, N.; Witkiewicz, A.K.; Frank, P.G.; Casimiro, M.C.; Wang, C.; Fortina, P.; Addya, S.; et al. The reverse Warburg effect: Aerobic glycolysis in cancer associated fibroblasts and the tumor stroma. Cell Cycle 2009, 8, 3984–4001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hay, N. Reprogramming glucose metabolism in cancer: Can it be exploited for cancer therapy? Nat. Rev. Cancer 2016, 16, 635–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharya, B.; Mohd Omar, M.F.; Soong, R. The Warburg effect and drug resistance. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 173, 970–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stine, Z.E.; Schug, Z.T.; Salvino, J.M.; Dang, C.V. Targeting cancer metabolism in the era of precision oncology. Nat. Rev. Drug. Discov. 2022, 21, 141–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanotelli, M.R.; Zhang, J.; Reinhart-King, C.A. Mechanoresponsive metabolism in cancer cell migration and metastasis. Cell Metab. 2021, 33, 1307–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Kim, D.H.; Jung, W.H.; Koo, J.S. Metabolic interaction between cancer cells and stromal cells according to breast cancer molecular subtype. Breast Cancer Res. 2013, 15, R78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comprehensive molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature 2012, 490, 61–70. [CrossRef]
- Gomes, A.S.; Ramos, H.; Soares, J.; Saraiva, L. p53 and glucose metabolism: An orchestra to be directed in cancer therapy. Pharmacol. Res. 2018, 131, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matoba, S.; Kang, J.G.; Patino, W.D.; Wragg, A.; Boehm, M.; Gavrilova, O.; Hurley, P.J.; Bunz, F.; Hwang, P.M. p53 regulates mitochondrial respiration. Science 2006, 312, 1650–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bensaad, K.; Tsuruta, A.; Selak, M.A.; Vidal, M.N.; Nakano, K.; Bartrons, R.; Gottlieb, E.; Vousden, K.H. TIGAR, a p53-inducible regulator of glycolysis and apoptosis. Cell 2006, 126, 107–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fallah, Y.; Brundage, J.; Allegakoen, P.; Shajahan-Haq, A.N. MYC-Driven Pathways in Breast Cancer Subtypes. Biomolecules 2017, 7, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, S.O.; Li, C.W.; Xia, W.; Lee, H.H.; Chang, S.S.; Shen, J.; Hsu, J.L.; Raftery, D.; Djukovic, D.; Gu, H.; et al. EGFR Signaling Enhances Aerobic Glycolysis in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells to Promote Tumor Growth and Immune Escape. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 1284–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ros, S.; Wright, A.J.; D’Santos, P.; Hu, D.E.; Hesketh, R.L.; Lubling, Y.; Georgopoulou, D.; Lerda, G.; Couturier, D.L.; Razavi, P.; et al. Metabolic Imaging Detects Resistance to PI3Kα Inhibition Mediated by Persistent FOXM1 Expression in ER(+) Breast Cancer. Cancer Cell 2020, 38, 516–533.e519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, J.E. Isozymes of mammalian hexokinase: Structure, subcellular localization and metabolic function. J. Exp. Biol. 2003, 206, 2049–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Criss, W.E. A Review of Isozymes in Cancer. Cancer Res. 1971, 31, 1523–1542. [Google Scholar]
- Wyatt, E.; Wu, R.; Rabeh, W.; Park, H.W.; Ghanefar, M.; Ardehali, H. Regulation and cytoprotective role of hexokinase III. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e13823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Zhang, L.F.; Zhang, H.W.; Hu, S.; Lu, M.H.; Liang, S.; Li, B.; Li, Y.; Li, D.; Wang, E.D.; et al. A novel miR-155/miR-143 cascade controls glycolysis by regulating hexokinase 2 in breast cancer cells. EMBO J. 2012, 31, 1985–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Wang, M.; Dong, Y.; Xu, B.; Chen, J.; Ding, Y.; Qiu, S.; Li, L.; Karamfilova Zaharieva, E.; Zhou, X.; et al. Circular RNA circRNF20 promotes breast cancer tumorigenesis and Warburg effect through miR-487a/HIF-1alpha/HK2. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Li, C.F.; Ruan, D.; He, J.; Montal, E.D.; Lorenz, S.; Girnun, G.D.; Chan, C.H. Non-proteolytic ubiquitination of Hexokinase 2 by HectH9 controls tumor metabolism and cancer stem cell expansion. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Ren, C.; Qiao, P.; Han, X.; Wang, L.; Lv, S.; Sun, Y.; Liu, Z.; Du, Y.; Yu, Z. PIM2-mediated phosphorylation of hexokinase 2 is critical for tumor growth and paclitaxel resistance in breast cancer. Oncogene 2018, 37, 5997–6009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patra, K.C.; Wang, Q.; Bhaskar, P.T.; Miller, L.; Wang, Z.; Wheaton, W.; Chandel, N.; Laakso, M.; Muller, W.J.; Allen, E.L.; et al. Hexokinase 2 is required for tumor initiation and maintenance and its systemic deletion is therapeutic in mouse models of cancer. Cancer Cell 2013, 24, 213–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishfaq, M.; Bashir, N.; Riaz, S.K.; Manzoor, S.; Khan, J.S.; Bibi, Y.; Sami, R.; Aljahani, A.H.; Alharthy, S.A.; Shahid, R. Expression of HK2, PKM2, and PFKM Is Associated with Metastasis and Late Disease Onset in Breast Cancer Patients. Genes 2022, 13, 549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blaha, C.S.; Ramakrishnan, G.; Jeon, S.M.; Nogueira, V.; Rho, H.; Kang, S.; Bhaskar, P.; Terry, A.R.; Aissa, A.F.; Frolov, M.V.; et al. A non-catalytic scaffolding activity of hexokinase 2 contributes to EMT and metastasis. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Miao, W.; Huang, M.; Li, L.; Dai, X.; Wang, Y. Elevated Hexokinase II Expression Confers Acquired Resistance to 4-Hydroxytamoxifen in Breast Cancer Cells. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2019, 18, 2273–2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, C.P.; Sodergren, K.; Andersson, T. Reduced production and uptake of lactate are essential for the ability of WNT5A signaling to inhibit breast cancer cell migration and invasion. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 71471–71488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umar, S.M.; Kashyap, A.; Kahol, S.; Mathur, S.R.; Gogia, A.; Deo, S.V.S.; Prasad, C.P. Prognostic and therapeutic relevance of phosphofructokinase platelet-type (PFKP) in breast cancer. Exp. Cell Res. 2020, 396, 112282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeerken, D.; Hong, R.; Wang, Y.; Gong, Y.; Liu, R.; Yang, D.; Li, J.; Fan, J.; Chen, J.; Zhang, W.; et al. PFKP is transcriptionally repressed by BRCA1/ZBRK1 and predicts prognosis in breast cancer. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0233750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inaishi, T.; Shibata, M.; Ichikawa, T.; Kanda, M.; Hayashi, M.; Soeda, I.; Takeuchi, D.; Takano, Y.; Tsunoda, N.; Kodera, Y.; et al. Platelet isoform of phosphofructokinase accelerates malignant features in breast cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2022, 47, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okar, D.A.; Manzano, A.; Navarro-Sabate, A.; Riera, L.; Bartrons, R.; Lange, A.J. PFK-2/FBPase-2: Maker and breaker of the essential biofactor fructose-2,6-bisphosphate. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2001, 26, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, B.C.; Pohlmann, P.R.; Clarke, R.; Sengupta, S. Treatment against glucose-dependent cancers through metabolic PFKFB3 targeting of glycolytic flux. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Belle Flynn, A.; Calhoun, B.C.; Sharma, A.; Chang, J.C.; Almasan, A.; Schiemann, W.P. Autophagy inhibition elicits emergence from metastatic dormancy by inducing and stabilizing Pfkfb3 expression. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, J.S.; Kim, H.E.; Koh, E.; Park, S.H.; Jin, W.J.; Park, B.W.; Park, S.W.; Kim, K.S. Kruppel-like factor 4 (KLF4) activates the transcription of the gene for the platelet isoform of phosphofructokinase (PFKP) in breast cancer. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 23808–23816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, M.; Yang, D.; Hou, Y.; Liu, S.; Zhao, M.; Qin, Y.; Chen, R.; Teng, Y.; Liu, M. Intracellular citrate accumulation by oxidized ATM-mediated metabolism reprogramming via PFKP and CS enhances hypoxic breast cancer cell invasion and metastasis. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasgupta, S.; Rajapakshe, K.; Zhu, B.; Nikolai, B.C.; Yi, P.; Putluri, N.; Choi, J.M.; Jung, S.Y.; Coarfa, C.; Westbrook, T.F.; et al. Metabolic enzyme PFKFB4 activates transcriptional coactivator SRC-3 to drive breast cancer. Nature 2018, 556, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domenech, E.; Maestre, C.; Esteban-Martinez, L.; Partida, D.; Pascual, R.; Fernandez-Miranda, G.; Seco, E.; Campos-Olivas, R.; Perez, M.; Megias, D.; et al. AMPK and PFKFB3 mediate glycolysis and survival in response to mitophagy during mitotic arrest. Nat. Cell. Biol. 2015, 17, 1304–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, C.; Qiao, P.; Sun, Y.; Ren, C.; Yu, Z. Positive regulation of PFKFB3 by PIM2 promotes glycolysis and paclitaxel resistance in breast cancer. Clin. Transl. Med. 2021, 11, e400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Shu, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Mao, W.; Pang, L.; Redwood, A.; Jeter-Jones, S.L.; Jennings, N.B.; Ornelas, A.; Zhou, J.; et al. 6-Phosphofructo-2-Kinase/Fructose-2,6-Biphosphatase-2 Regulates TP53-Dependent Paclitaxel Sensitivity in Ovarian and Breast Cancers. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 5702–5716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truong, T.H.; Benner, E.A.; Hagen, K.M.; Temiz, N.A.; Kerkvliet, C.P.; Wang, Y.; Cortes-Sanchez, E.; Yang, C.H.; Trousdell, M.C.; Pengo, T.; et al. PELP1/SRC-3-dependent regulation of metabolic PFKFB kinases drives therapy resistant ER(+) breast cancer. Oncogene 2021, 40, 4384–4397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christofk, H.R.; Vander Heiden, M.G.; Harris, M.H.; Ramanathan, A.; Gerszten, R.E.; Wei, R.; Fleming, M.D.; Schreiber, S.L.; Cantley, L.C. The M2 splice isoform of pyruvate kinase is important for cancer metabolism and tumour growth. Nature 2008, 452, 230–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Luo, H.; Zhu, X.; Hu, X.; Zheng, L.; Zhu, X. Pyruvate kinase M2 (PKM2) expression correlates with prognosis in solid cancers: A meta-analysis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 1628–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.; Lv, F.; Liu, F.; Guo, X.; Fan, Y.; Gu, F.; Gu, J.; Fu, L. High Expression of Pyruvate Kinase M2 is Associated with Chemosensitivity to Epirubicin and 5-Fluorouracil in Breast Cancer. J. Cancer 2015, 6, 1130–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.; Li, A.X.; Chen, X.S.; Tian, M.; Wang, H.Y.; Wang, X.L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, K.S.; Cheng, Y. PKM2-c-Myc-Survivin Cascade Regulates the Cell Proliferation, Migration, and Tamoxifen Resistance in Breast Cancer. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 550469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, H.; Zhao, P.; Wang, X. Targeting PKM2 promotes chemosensitivity of breast cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Biomark. 2021, 32, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Israelsen, W.J.; Dayton, T.L.; Davidson, S.M.; Fiske, B.P.; Hosios, A.M.; Bellinger, G.; Li, J.; Yu, Y.; Sasaki, M.; Horner, J.W.; et al. PKM2 isoform-specific deletion reveals a differential requirement for pyruvate kinase in tumor cells. Cell 2013, 155, 397–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clower, C.V.; Chatterjee, D.; Wang, Z.; Cantley, L.C.; Vander Heiden, M.G.; Krainer, A.R. The alternative splicing repressors hnRNP A1/A2 and PTB influence pyruvate kinase isoform expression and cell metabolism. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 1894–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Israelsen, W.J.; Vander Heiden, M.G. Pyruvate kinase: Function, regulation and role in cancer. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2015, 43, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vander Heiden, M.G.; Locasale, J.W.; Swanson, K.D.; Sharfi, H.; Heffron, G.J.; Amador-Noguez, D.; Christofk, H.R.; Wagner, G.; Rabinowitz, J.D.; Asara, J.M.; et al. Evidence for an alternative glycolytic pathway in rapidly proliferating cells. Science 2010, 329, 1492–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Li, M.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, H.; Şahin, Ö.; Chen, J.; Zhao, J.J.; Songyang, Z.; Yu, D. Oncogenic Kinase-Induced PKM2 Tyrosine 105 Phosphorylation Converts Nononcogenic PKM2 to a Tumor Promoter and Induces Cancer Stem-like Cells. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 2248–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.H.; Ozden, O.; Liu, G.; Song, H.Y.; Zhu, Y.; Yan, Y.; Zou, X.; Kang, H.J.; Jiang, H.; Principe, D.R.; et al. SIRT2-Mediated Deacetylation and Tetramerization of Pyruvate Kinase Directs Glycolysis and Tumor Growth. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 3802–3812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Ma, F.; Wang, Y.; Hao, L.; Zeng, H.; Jia, C.; Wang, Y.; Liu, P.; Ong, I.M.; Li, B.; et al. PKM2 methylation by CARM1 activates aerobic glycolysis to promote tumorigenesis. Nat. Cell Biol. 2017, 19, 1358–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fong, M.Y.; Zhou, W.; Liu, L.; Alontaga, A.Y.; Chandra, M.; Ashby, J.; Chow, A.; O’Connor, S.T.; Li, S.; Chin, A.R.; et al. Breast-cancer-secreted miR-122 reprograms glucose metabolism in premetastatic niche to promote metastasis. Nat. Cell Biol. 2015, 17, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stacpoole, P.W. Therapeutic Targeting of the Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Complex/Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Kinase (PDC/PDK) Axis in Cancer. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2017, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolbright, B.L.; Rajendran, G.; Harris, R.A.; Taylor, J.A., 3rd. Metabolic Flexibility in Cancer: Targeting the Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Kinase:Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Axis. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2019, 18, 1673–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, F.; Wang, J.H.; Fan, W.J.; Meng, Y.T.; Li, M.M.; Li, T.T.; Cui, B.; Wang, H.F.; Zhao, Y.; An, F.; et al. Glycolysis gatekeeper PDK1 reprograms breast cancer stem cells under hypoxia. Oncogene 2018, 37, 1062–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dupuy, F.; Tabaries, S.; Andrzejewski, S.; Dong, Z.; Blagih, J.; Annis, M.G.; Omeroglu, A.; Gao, D.; Leung, S.; Amir, E.; et al. PDK1-Dependent Metabolic Reprogramming Dictates Metastatic Potential in Breast Cancer. Cell Metab. 2015, 22, 577–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jansen, V.M.; Bhola, N.E.; Bauer, J.A.; Formisano, L.; Lee, K.M.; Hutchinson, K.E.; Witkiewicz, A.K.; Moore, P.D.; Estrada, M.V.; Sánchez, V.; et al. Kinome-Wide RNA Interference Screen Reveals a Role for PDK1 in Acquired Resistance to CDK4/6 Inhibition in ER-Positive Breast Cancer. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 2488–2499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J. Cancer’s sweet tooth for serine. Breast Cancer Res. 2011, 13, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrika, M.; Chua, P.J.; Muniasamy, U.; Huang, R.Y.J.; Thike, A.A.; Ng, C.T.; Tan, P.H.; Yip, G.W.; Bay, B.H. Prognostic significance of phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2021, 186, 655–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Possemato, R.; Marks, K.M.; Shaul, Y.D.; Pacold, M.E.; Kim, D.; Birsoy, K.; Sethumadhavan, S.; Woo, H.K.; Jang, H.G.; Jha, A.K.; et al. Functional genomics reveal that the serine synthesis pathway is essential in breast cancer. Nature 2011, 476, 346–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, C.; Wu, H.; Sun, X.X.; Li, Y.; Huang, S.; Yue, X.; Lu, S.E.; Shen, Z.; Su, X.; et al. Parkin ubiquitinates phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase to suppress serine synthesis and tumor progression. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 3253–3269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Chung, F.; Yang, G.; Pu, M.; Gao, H.; Jiang, W.; Yin, H.; Capka, V.; Kasibhatla, S.; Laffitte, B.; et al. Phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase is dispensable for breast tumor maintenance and growth. Oncotarget 2013, 4, 2502–2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samanta, D.; Park, Y.; Andrabi, S.A.; Shelton, L.M.; Gilkes, D.M.; Semenza, G.L. PHGDH Expression Is Required for Mitochondrial Redox Homeostasis, Breast Cancer Stem Cell Maintenance, and Lung Metastasis. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 4430–4442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngo, B.; Kim, E.; Osorio-Vasquez, V.; Doll, S.; Bustraan, S.; Liang, R.J.; Luengo, A.; Davidson, S.M.; Ali, A.; Ferraro, G.B.; et al. Limited Environmental Serine and Glycine Confer Brain Metastasis Sensitivity to PHGDH Inhibition. Cancer Discov. 2020, 10, 1352–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, M.; Altea-Manzano, P.; Demicco, M.; Doglioni, G.; Bornes, L.; Fukano, M.; Vandekeere, A.; Cuadros, A.M.; Fernández-García, J.; Riera-Domingo, C.; et al. PHGDH heterogeneity potentiates cancer cell dissemination and metastasis. Nature 2022, 605, 747–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.; Xiong, Y.; Qiao, T.; Li, X.; Jia, L.; Han, Y. Lactate dehydrogenase A: A key player in carcinogenesis and potential target in cancer therapy. Cancer Med. 2018, 7, 6124–6136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fantin, V.R.; St-Pierre, J.; Leder, P. Attenuation of LDH-A expression uncovers a link between glycolysis, mitochondrial physiology, and tumor maintenance. Cancer Cell 2006, 9, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.H.; Zhou, M.; Liu, H.; Ding, Y.; Khong, H.T.; Yu, D.; Fodstad, O.; Tan, M. Upregulation of lactate dehydrogenase A by ErbB2 through heat shock factor 1 promotes breast cancer cell glycolysis and growth. Oncogene 2009, 28, 3689–3701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, C.K.; Parekh, A.; Parida, P.K.; Bhutia, S.K.; Mandal, M. Lactate dehydrogenase A regulates autophagy and tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2019, 1866, 1004–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, B.; Luo, Y.; Tian, P.; Peng, F.; Lu, J.; Yang, Y.; Su, Q.; Liu, B.; Yu, J.; Luo, X.; et al. Stress-induced epinephrine enhances lactate dehydrogenase A and promotes breast cancer stem-like cells. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 129, 1030–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munir, M.T.; Kay, M.K.; Kang, M.H.; Rahman, M.M.; Al-Harrasi, A.; Choudhury, M.; Moustaid-Moussa, N.; Hussain, F.; Rahman, S.M. Tumor-Associated Macrophages as Multifaceted Regulators of Breast Tumor Growth. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bader, J.E.; Voss, K.; Rathmell, J.C. Targeting Metabolism to Improve the Tumor Microenvironment for Cancer Immunotherapy. Mol. Cell. 2020, 78, 1019–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, S.; Wang, X. The Metabolic Mechanisms of Breast Cancer Metastasis. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 602416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, X.; Wang, J.; Lu, D.; Xu, X. Targeting tumor-associated macrophages to synergize tumor immunotherapy. Signal. Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeNardo, D.G.; Ruffell, B. Macrophages as regulators of tumour immunity and immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2019, 19, 369–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henze, A.T.; Mazzone, M. The impact of hypoxia on tumor-associated macrophages. J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 126, 3672–3679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenes, M.; Shang, M.; Di Matteo, M.; Goveia, J.; Martín-Pérez, R.; Serneels, J.; Prenen, H.; Ghesquière, B.; Carmeliet, P.; Mazzone, M. Macrophage Metabolism Controls Tumor Blood Vessel Morphogenesis and Metastasis. Cell Metab. 2016, 24, 701–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Q.; Shen, Q.; Liu, Y.; Shi, Y.; Huang, W.; Wang, X.; Li, Z.; Chai, Y.; Wang, H.; Hu, X.; et al. Increased glucose metabolism in TAMs fuels O-GlcNAcylation of lysosomal Cathepsin B to promote cancer metastasis and chemoresistance. Cancer Cell 2022, 40, 1207–1222.e1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colegio, O.R.; Chu, N.Q.; Szabo, A.L.; Chu, T.; Rhebergen, A.M.; Jairam, V.; Cyrus, N.; Brokowski, C.E.; Eisenbarth, S.C.; Phillips, G.M.; et al. Functional polarization of tumour-associated macrophages by tumour-derived lactic acid. Nature 2014, 513, 559–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmona-Fontaine, C.; Bucci, V.; Akkari, L.; Deforet, M.; Joyce, J.A.; Xavier, J.B. Emergence of spatial structure in the tumor microenvironment due to the Warburg effect. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 19402–19407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Zuo, H.; Xiong, H.; Kolar, M.J.; Chu, Q.; Saghatelian, A.; Siegwart, D.J.; Wan, Y. Gpr132 sensing of lactate mediates tumor-macrophage interplay to promote breast cancer metastasis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 580–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DePeaux, K.; Delgoffe, G.M. Metabolic barriers to cancer immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2021, 21, 785–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.H.; Curtis, J.D.; Maggi, L.B., Jr.; Faubert, B.; Villarino, A.V.; O’Sullivan, D.; Huang, S.C.; van der Windt, G.J.; Blagih, J.; Qiu, J.; et al. Posttranscriptional control of T cell effector function by aerobic glycolysis. Cell 2013, 153, 1239–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerriets, V.A.; Kishton, R.J.; Nichols, A.G.; Macintyre, A.N.; Inoue, M.; Ilkayeva, O.; Winter, P.S.; Liu, X.; Priyadharshini, B.; Slawinska, M.E.; et al. Metabolic programming and PDHK1 control CD4+ T cell subsets and inflammation. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 125, 194–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, K.; Hoffmann, P.; Voelkl, S.; Meidenbauer, N.; Ammer, J.; Edinger, M.; Gottfried, E.; Schwarz, S.; Rothe, G.; Hoves, S.; et al. Inhibitory effect of tumor cell-derived lactic acid on human T cells. Blood 2007, 109, 3812–3819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quinn, W.J., 3rd; Jiao, J.; TeSlaa, T.; Stadanlick, J.; Wang, Z.; Wang, L.; Akimova, T.; Angelin, A.; Schäfer, P.M.; Cully, M.D.; et al. Lactate Limits T Cell Proliferation via the NAD(H) Redox State. Cell Rep. 2020, 33, 108500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelin, A.; Gil-de-Gómez, L.; Dahiya, S.; Jiao, J.; Guo, L.; Levine, M.H.; Wang, Z.; Quinn, W.J., 3rd; Kopinski, P.K.; Wang, L.; et al. Foxp3 Reprograms T Cell Metabolism to Function in Low-Glucose, High-Lactate Environments. Cell Metab. 2017, 25, 1282–1293.e1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Ji, P.; Yang, Y.S.; Xie, S.; Yu, T.J.; Xiao, Y.; Jin, M.L.; Ma, D.; Guo, L.W.; Pei, Y.C.; et al. Metabolic-Pathway-Based Subtyping of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Reveals Potential Therapeutic Targets. Cell Metab. 2021, 33, 51–64.e59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zappasodi, R.; Serganova, I.; Cohen, I.J.; Maeda, M.; Shindo, M.; Senbabaoglu, Y.; Watson, M.J.; Leftin, A.; Maniyar, R.; Verma, S.; et al. CTLA-4 blockade drives loss of T(reg) stability in glycolysis-low tumours. Nature 2021, 591, 652–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, M.J.; Vignali, P.D.A.; Mullett, S.J.; Overacre-Delgoffe, A.E.; Peralta, R.M.; Grebinoski, S.; Menk, A.V.; Rittenhouse, N.L.; DePeaux, K.; Whetstone, R.D.; et al. Metabolic support of tumour-infiltrating regulatory T cells by lactic acid. Nature 2021, 591, 645–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renner, K.; Bruss, C.; Schnell, A.; Koehl, G.; Becker, H.M.; Fante, M.; Menevse, A.N.; Kauer, N.; Blazquez, R.; Hacker, L.; et al. Restricting Glycolysis Preserves T Cell Effector Functions and Augments Checkpoint Therapy. Cell Rep. 2019, 29, 135–150.e139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rundqvist, H.; Veliça, P.; Barbieri, L.; Gameiro, P.A.; Bargiela, D.; Gojkovic, M.; Mijwel, S.; Reitzner, S.M.; Wulliman, D.; Ahlstedt, E.; et al. Cytotoxic T-cells mediate exercise-induced reductions in tumor growth. Elife 2020, 9, e59996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, L.M.; O’Connell, J.T.; Vo, A.P.; Cain, M.P.; Tampe, D.; Bizarro, L.; Sugimoto, H.; McGow, A.K.; Asara, J.M.; Lovisa, S.; et al. Epigenetic Reprogramming of Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts Deregulates Glucose Metabolism and Facilitates Progression of Breast Cancer. Cell Rep. 2020, 31, 107701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, T.; Yang, G.; Hou, Y.; Tang, X.; Wu, C.; Wu, X.A.; Guo, L.; Zhu, Q.; Luo, H.; Du, Y.E.; et al. Cytoplasmic GPER translocation in cancer-associated fibroblasts mediates cAMP/PKA/CREB/glycolytic axis to confer tumor cells with multidrug resistance. Oncogene 2017, 36, 2131–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, A.; Kieffer, Y.; Scholer-Dahirel, A.; Pelon, F.; Bourachot, B.; Cardon, M.; Sirven, P.; Magagna, I.; Fuhrmann, L.; Bernard, C.; et al. Fibroblast Heterogeneity and Immunosuppressive Environment in Human Breast Cancer. Cancer Cell 2018, 33, 463–479.e410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlides, S.; Vera, I.; Gandara, R.; Sneddon, S.; Pestell, R.G.; Mercier, I.; Martinez-Outschoorn, U.E.; Whitaker-Menezes, D.; Howell, A.; Sotgia, F.; et al. Warburg meets autophagy: Cancer-associated fibroblasts accelerate tumor growth and metastasis via oxidative stress, mitophagy, and aerobic glycolysis. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2012, 16, 1264–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, S.; Chen, J.; Yao, H.; Liu, J.; Yu, S.; Lao, L.; Wang, M.; Luo, M.; Xing, Y.; Chen, F.; et al. CD10(+)GPR77(+) Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts Promote Cancer Formation and Chemoresistance by Sustaining Cancer Stemness. Cell 2018, 172, 841–856.e816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.X.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Shen, J.; Sun, X.; Liu, Y.; Liu, H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J. Nanoenabled Modulation of Acidic Tumor Microenvironment Reverses Anergy of Infiltrating T Cells and Potentiates Anti-PD-1 Therapy. Nano Lett. 2019, 19, 2774–2783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raychaudhuri, D.; Bhattacharya, R.; Sinha, B.P.; Liu, C.S.C.; Ghosh, A.R.; Rahaman, O.; Bandopadhyay, P.; Sarif, J.; D’Rozario, R.; Paul, S.; et al. Lactate Induces Pro-tumor Reprogramming in Intratumoral Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cells. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Wahab, A.F.; Mahmoud, W.; Al-Harizy, R.M. Targeting glucose metabolism to suppress cancer progression: Prospective of anti-glycolytic cancer therapy. Pharmacol. Res. 2019, 150, 104511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Sun, G.; Sun, X.; Li, F.; Zhao, L.; Zhong, R.; Peng, Y. The Potential of Lonidamine in Combination with Chemotherapy and Physical Therapy in Cancer Treatment. Cancers 2020, 12, 3332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, M.; Kim, S.S.; Lee, J. Cancer cell metabolism: Implications for therapeutic targets. Exp. Mol. Med. 2013, 45, e45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansi, J.L.; de Graeff, A.; Newell, D.R.; Glaholm, J.; Button, D.; Leach, M.O.; Payne, G.; Smith, I.E. A phase II clinical and pharmacokinetic study of Lonidamine in patients with advanced breast cancer. Br. J. Cancer 1991, 64, 593–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogliotti, L.; Berruti, A.; Buniva, T.; Zola, P.; Baù, M.G.; Farris, A.; Sarobba, M.G.; Bottini, A.; Alquati, P.; Deltetto, F.; et al. Lonidamine significantly increases the activity of epirubicin in patients with advanced breast cancer: Results from a multicenter prospective randomized trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 1996, 14, 1165–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berruti, A.; Bitossi, R.; Gorzegno, G.; Bottini, A.; Alquati, P.; De Matteis, A.; Nuzzo, F.; Giardina, G.; Danese, S.; De Lena, M.; et al. Time to progression in metastatic breast cancer patients treated with epirubicin is not improved by the addition of either cisplatin or lonidamine: Final results of a phase III study with a factorial design. J. Clin. Oncol. 2002, 20, 4150–4159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amadori, D.; Frassineti, G.L.; De Matteis, A.; Mustacchi, G.; Santoro, A.; Cariello, S.; Ferrari, M.; Nascimben, O.; Nanni, O.; Lombardi, A.; et al. Modulating effect of lonidamine on response to doxorubicin in metastatic breast cancer patients: Results from a multicenter prospective randomized trial. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 1998, 49, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konstantakou, E.G.; Voutsinas, G.E.; Velentzas, A.D.; Basogianni, A.S.; Paronis, E.; Balafas, E.; Kostomitsopoulos, N.; Syrigos, K.N.; Anastasiadou, E.; Stravopodis, D.J. 3-BrPA eliminates human bladder cancer cells with highly oncogenic signatures via engagement of specific death programs and perturbation of multiple signaling and metabolic determinants. Mol. Cancer 2015, 14, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, T.; Sun, G.; Sun, X.; Zhao, L.; Zhong, R.; Peng, Y. Tumor Energy Metabolism and Potential of 3-Bromopyruvate as an Inhibitor of Aerobic Glycolysis: Implications in Tumor Treatment. Cancers 2019, 11, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ihrlund, L.S.; Hernlund, E.; Khan, O.; Shoshan, M.C. 3-Bromopyruvate as inhibitor of tumour cell energy metabolism and chemopotentiator of platinum drugs. Mol. Oncol. 2008, 2, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakano, A.; Tsuji, D.; Miki, H.; Cui, Q.; El Sayed, S.M.; Ikegame, A.; Oda, A.; Amou, H.; Nakamura, S.; Harada, T.; et al. Glycolysis inhibition inactivates ABC transporters to restore drug sensitivity in malignant cells. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e27222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Sayed, S.M. Enhancing anticancer effects, decreasing risks and solving practical problems facing 3-bromopyruvate in clinical oncology: 10 years of research experience. Int. J. Nanomedicine 2018, 13, 4699–4709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medina, R.A.; Owen, G.I. Glucose transporters: Expression, regulation and cancer. Biol. Res. 2002, 35, 9–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macheda, M.L.; Rogers, S.; Best, J.D. Molecular and cellular regulation of glucose transporter (GLUT) proteins in cancer. J. Cell. Physiol. 2005, 202, 654–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szablewski, L. Expression of glucose transporters in cancers. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1835, 164–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grover-McKay, M.; Walsh, S.A.; Seftor, E.A.; Thomas, P.A.; Hendrix, M.J. Role for glucose transporter 1 protein in human breast cancer. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 1998, 4, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Cao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Bergmeier, S.; Chen, X. Small compound inhibitors of basal glucose transport inhibit cell proliferation and induce apoptosis in cancer cells via glucose-deprivation-like mechanisms. Cancer Lett. 2010, 298, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, D.A.; Sutphin, P.D.; Nguyen, P.; Turcotte, S.; Lai, E.W.; Banh, A.; Reynolds, G.E.; Chi, J.T.; Wu, J.; Solow-Cordero, D.E.; et al. Targeting GLUT1 and the Warburg effect in renal cell carcinoma by chemical synthetic lethality. Sci. Transl. Med. 2011, 3, 94ra70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siebeneicher, H.; Cleve, A.; Rehwinkel, H.; Neuhaus, R.; Heisler, I.; Müller, T.; Bauser, M.; Buchmann, B. Identification and Optimization of the First Highly Selective GLUT1 Inhibitor BAY-876. ChemMedChem 2016, 11, 2261–2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Ming, J.; Zhou, Y.; Fan, L. Inhibition of Glut1 by WZB117 sensitizes radioresistant breast cancer cells to irradiation. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2016, 77, 963–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, W.; Bergmeier, S.; Qian, Y.; Akbar, H.; Colvin, R.; Ding, J.; Tong, L.; Wu, S.; et al. A small-molecule inhibitor of glucose transporter 1 downregulates glycolysis, induces cell-cycle arrest, and inhibits cancer cell growth in vitro and in vivo. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2012, 11, 1672–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Meng, Y.Q.; Xu, X.F.; Gu, J. Blockade of GLUT1 by WZB117 resensitizes breast cancer cells to adriamycin. Anticancer. Drugs 2017, 28, 880–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, A.M.; Martel, F. Targeting Glucose Transporters for Breast Cancer Therapy: The Effect of Natural and Synthetic Compounds. Cancers 2020, 12, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahl, R.L.; Cody, R.L.; Hutchins, G.D.; Mudgett, E.E. Primary and metastatic breast carcinoma: Initial clinical evaluation with PET with the radiolabeled glucose analogue 2-[F-18]-fluoro-2-deoxy-D-glucose. Radiology 1991, 179, 765–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adler, L.P.; Crowe, J.P.; al-Kaisi, N.K.; Sunshine, J.L. Evaluation of breast masses and axillary lymph nodes with [F-18] 2-deoxy-2-fluoro-D-glucose PET. Radiology 1993, 187, 743–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avril, N.; Dose, J.; Janicke, F.; Bense, S.; Ziegler, S.; Laubenbacher, C.; Romer, W.; Pache, H.; Herz, M.; Allgayer, B.; et al. Metabolic characterization of breast tumors with positron emission tomography using F-18 fluorodeoxyglucose. J. Clin. Oncol. 1996, 14, 1848–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avril, N.; Rose, C.A.; Schelling, M.; Dose, J.; Kuhn, W.; Bense, S.; Weber, W.; Ziegler, S.; Graeff, H.; Schwaiger, M. Breast imaging with positron emission tomography and fluorine-18 fluorodeoxyglucose: Use and limitations. J. Clin. Oncol. 2000, 18, 3495–3502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avril, N.; Schelling, M.; Dose, J.; Weber, W.A.; Schwaiger, M. Utility of PET in Breast Cancer. Clin. Positron Imaging 1999, 2, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avril, N.; Menzel, M.; Dose, J.; Schelling, M.; Weber, W.; Janicke, F.; Nathrath, W.; Schwaiger, M. Glucose metabolism of breast cancer assessed by 18F-FDG PET: Histologic and immunohistochemical tissue analysis. J. Nucl. Med. 2001, 42, 9–16. [Google Scholar]
- Meyer, H.J.; Wienke, A.; Surov, A. Associations between GLUT expression and SUV values derived from FDG-PET in different tumors-A systematic review and meta analysis. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0217781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, E.; Koo, J.S. Glucose Metabolism and Glucose Transporters in Breast Cancer. Front. Cell. Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 728759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flaig, T.W.; Gustafson, D.L.; Su, L.J.; Zirrolli, J.A.; Crighton, F.; Harrison, G.S.; Pierson, A.S.; Agarwal, R.; Glodé, L.M. A phase I and pharmacokinetic study of silybin-phytosome in prostate cancer patients. Investig. New. Drugs 2007, 25, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raez, L.E.; Papadopoulos, K.; Ricart, A.D.; Chiorean, E.G.; Dipaola, R.S.; Stein, M.N.; Rocha Lima, C.M.; Schlesselman, J.J.; Tolba, K.; Langmuir, V.K.; et al. A phase I dose-escalation trial of 2-deoxy-D-glucose alone or combined with docetaxel in patients with advanced solid tumors. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2013, 71, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liapi, E.; Geschwind, J.F.; Vali, M.; Khwaja, A.A.; Prieto-Ventura, V.; Buijs, M.; Vossen, J.A.; Ganapathy-Kanniappan, S.; Wahl, R.L. Assessment of tumoricidal efficacy and response to treatment with 18F-FDG PET/CT after intraarterial infusion with the antiglycolytic agent 3-bromopyruvate in the VX2 model of liver tumor. J. Nucl. Med. 2011, 52, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumagai, S.; Narasaki, R.; Hasumi, K. Glucose-dependent active ATP depletion by koningic acid kills high-glycolytic cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 365, 362–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunbar, E.M.; Coats, B.S.; Shroads, A.L.; Langaee, T.; Lew, A.; Forder, J.R.; Shuster, J.J.; Wagner, D.A.; Stacpoole, P.W. Phase 1 trial of dichloroacetate (DCA) in adults with recurrent malignant brain tumors. Investig. New. Drugs 2014, 32, 452–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noble, R.A.; Bell, N.; Blair, H.; Sikka, A.; Thomas, H.; Phillips, N.; Nakjang, S.; Miwa, S.; Crossland, R.; Rand, V.; et al. Inhibition of monocarboxyate transporter 1 by AZD3965 as a novel therapeutic approach for diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and Burkitt lymphoma. Haematologica 2017, 102, 1247–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Altered Enzyme | Drug Resistance | Type of Cancer |
|---|---|---|
| HK | Tamoxifen | Breast cancer |
| Paclitaxel | Breast cancer | |
| Letrozole | Breast cancer | |
| Trastuzumab | Lung cancer | |
| PFK | Paclitaxel | Breast cancer |
| Cisplatin | Endometrial cancer | |
| PK | Tamoxifen | Breast cancer |
| PDK | Tamoxifen | Breast cancer |
| PHGDH | Tamoxifen | Breast cancer |
| Doxorubicin | Breast cancer | |
| LDH | Tamoxifen | Breast cancer |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lei, P.; Wang, W.; Sheldon, M.; Sun, Y.; Yao, F.; Ma, L. Role of Glucose Metabolic Reprogramming in Breast Cancer Progression and Drug Resistance. Cancers 2023, 15, 3390. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15133390
Lei P, Wang W, Sheldon M, Sun Y, Yao F, Ma L. Role of Glucose Metabolic Reprogramming in Breast Cancer Progression and Drug Resistance. Cancers. 2023; 15(13):3390. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15133390
Chicago/Turabian StyleLei, Pan, Wenzhou Wang, Marisela Sheldon, Yutong Sun, Fan Yao, and Li Ma. 2023. "Role of Glucose Metabolic Reprogramming in Breast Cancer Progression and Drug Resistance" Cancers 15, no. 13: 3390. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15133390
APA StyleLei, P., Wang, W., Sheldon, M., Sun, Y., Yao, F., & Ma, L. (2023). Role of Glucose Metabolic Reprogramming in Breast Cancer Progression and Drug Resistance. Cancers, 15(13), 3390. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15133390






