A Comparison of Total Thoracoscopic and Robotic Surgery for Lung Cancer Lymphadenectomy
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Study Variables
2.3. Surgical Technique and Lymph Node Dissection Procedures
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Analysis of Dissected Lymph Nodes
3.2. Lymph Node Upstaging
4. Discussion
5. Limitation of the Study
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- D’Amico, T.; Niland, J.; Mamet, R.; Zornosa, C.; Dexter, E.; Onaitis, M. Efficacy of mediastinal lymph node dissection during lobectomy for lung cancer by thoracoscopy and thoracotomy. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2011, 92, 226–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, S.; Altorki, N.K.; Sheng, S.; Lee, P.C.; Harpole, D.H.; Onaitis, M.W.; Stiles, B.M.; Port, J.L.; D’Amico, T.A. Thoracoscopic lobectomy is associated with lower morbidity than open lobectomy: A propensity-matched analysis from the STS database. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2010, 139, 366–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Izbicki, J.R.; Passlick, B.; Pantel, K.; Pichlmeier, U.; Hosch, S.B.; Karg, O.; Thetter, O. Effectiveness of radical systematic mediastinal lymphadenectomy in patients with resectable non-small cell lung cancer: Results of a prospective randomized trial. Ann. Surg. 1998, 227, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, N.; Yan, S.; Lv, C.; Feng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Yang, Y. Comparison of systematic mediastinal lymph node dissection versus systematic sampling for lung cancer staging and completeness of surgery. J. Surg. Res. 2011, 171, e169–e173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugi, K.; Nawata, K.; Fujita, N.; Ueda, K.; Tanaka, T.; Matsuoka, T.; Kaneda, Y.; Esato, K. Systematic lymph node dissection for clinically diagnosed peripheral non-small-cell lung cancer less than 2 cm in diameter. World J. Surg. 1998, 22, 290–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, D.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Lv, W.; Hu, J. Lymphadenectomy for clinical early-stage non-small-cell lung cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2016, 50, 597–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Korasidis, S.; Menna, C.; Andreetti, C.; Maurizi, G.; D’Andrilli, A.; Ciccone, A.; Cassiano, F.; Rendina, E.; Ibrahim, M. Lymph node dissection after pulmonary resection for lung cancer: A mini review. Ann. Transl. Med. 2016, 4, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Darling, G.E.; Allen, M.S.; Decker, P.A.; Ballman, K.; Malthaner, R.A.; Inculet, R.I.; Jones, D.R.; McKenna, R.J.; Landreneau, R.J.; Rusch, V.W.; et al. Randomized trial of mediastinal lymph node sampling versus complete lymphadenectomy during pulmonary resection in the patient with N0 or N1 (less than hilar) non-small cell carcinoma: Results of the American College of Surgery Oncology Group Z0030 Trial. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2011, 141, 662–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Palade, E.; Passlick, B.; Osei-Agyemang, T.; Günter, J.; Wiesemann, S. Video-assisted vs open mediastinal lymphadenectomy for Stage I non-small-cell lung cancer: Results of a prospective randomized trial. Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2013, 44, 244–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, W.; Wei, Y.; Jiang, H.; Xu, J.; Yu, D. Video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery versus thoracotomy lymph node dissection in clinical stage I lung cancer: A meta-analysis and system review. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2016, 101, 2417–2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hennon, M.W.; De Graaff, L.H.; Groman, A.; Demmy, T.L.; Yendamuri, S. The association of nodal upstaging with surgical approach and its impact on long-term survival after resection of non-small-cell lung cancer. Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2020, 57, 888–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toker, A.; Ozyurtkan, M.O.; Demirhan, O.; Ayalp, K.; Kaba, E.; Uyumaz, E. Lymph node dissection in surgery for lung cancer: Comparison of open vs. video-assisted vs. robotic-assisted approaches. Ann. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2016, 22, 284–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Toosi, K.; Velez-Cubian, F.O.; Glover, J.; Ng, E.P.; Moodie, C.C.; Garrett, J.R.; Fontaine, J.P.; Toloza, E.M. Upstaging and survival after robotic-assisted thoracoscopic lobectomy for non-small cell lung cancer. Surgery 2016, 160, 1211–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velez-Cubian, F.O.; Rodriguez, K.L.; Thau, M.R.; Moodie, C.C.; Garrett, J.R.; Fontaine, J.P.; Toloza, E.M. Efficacy of lymph node dissection during robotic-assisted lobectomy for non-small cell lung cancer: Retrospective review of 159 consecutive cases. J. Thorac. Dis. 2016, 8, 2454–2463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kneuertz, P.J.; Cheufou, D.H.; D’Souza, D.M.; Mardanzai, K.; Abdel-Rasoul, M.; Theegarten, D.; Moffatt-Bruce, S.D.; Aigner, C.; Merritt, R.E. Propensity-score adjusted comparison of pathologic nodal upstaging by robotic, video-assisted thoracoscopic, and open lobectomy for non-small cell lung cancer. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2019, 158, 1457–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gossot, D. Technical tricks to facilitate totally endoscopic major pulmonary resections. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2008, 86, 323–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leong, T.L.; Loveland, P.M.; Gorelik, A.; Irving, L.; Steinfort, D.P. Preoperative Staging by EBUS in cN0/N1 Lung Cancer: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Bronchol. Interv. Pulmonol. 2019, 26, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Katayama, H.; Kurokawa, Y.; Nakamura, K.; Ito, H.; Kanemitsu, Y.; Masuda, N.; Tsubosa, Y.; Satoh, T.; Yokomizo, A.; Fukuda, H.; et al. Extended Clavien-Dindo classification of surgical complications: Japan Clinical Oncology Group postoperative complications criteria. Surg. Today 2016, 46, 668–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Petersen, R.; Pham, D.; Burfeind, W.; Hanish, S.; Toloza, E.; Harpole, D.; D’Amico, T. Thoracoscopic Lobectomy Facilitates the Delivery of Chemotherapy after Resection for Lung Cancer. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2007, 83, 1245–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denlinger, C.; Fernandez, F.; Meyers, B.; Pratt, W.; Zoole, J.; Patterson, G.; Krupnick, A.; Kreisel, D.; Crabtree, T. Lymph Node Evaluation in Video-Assisted Thoracoscopic Lobectomy Versus Lobectomy by Thoracotomy. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2010, 89, 1730–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagawa, M.; Sato, M.; Sakurada, A.; Matsumura, Y.; Chiaki, C.; Handa, M.; Kondo, T. A prospective trial systematic nodal dissection for lung cancer by video-assisted thoracic surgery: Can it be perfect? Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2002, 73, 900–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shigemura, N.; Akashi, A.; Funaki, S.; Nakagiri, T.; Inoue, M.; Sawabata, N.; Shiono, H.; Minami, M.; Takeuchi, Y.; Okumura, M.; et al. Long-term outcomes after a variety of video-assisted thoracoscopic lobectomy approaches for clinical stage 1A lung cancer: A multi-institunional study. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2006, 132, 507–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ramos, R.; Girard, P.; Masuet, C.; Validire, P.; Gossot, D. Mediastinal lymph node dissection in early-stage non-small cell lung cancer: Totally thoracoscopic vs. thoracotomy. Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2012, 41, 1342–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cugat, P.; Aranda, F.P. Robotic hepato-pancreato-biliary surgery: A real opportunity with great prospects for the future. Cirgugía Española 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samayoa, A.X.; Pezzi, T.A.; Pezzi, C.M.; Greer Gay, E.; Asai, M.; Kulkarni, N.; Carp, N.; Chun, S.G.; Putnam, J.B. Rationale for a minimum number of lymph nodes removed with nonsmall cell lung cancer resection: Correlating the number of nodes removed with survival in 98,970 patients. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2016, 23, 1005–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, W.; He, J.; Shen, Y.; Shen, J.; He, Q.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, G.; Wang, Q.; Liu, L.; Gao, S.; et al. Impact of examined lymph node count on precise staging and long-term survival of resected non-small-cell lung cancer: A population study of the US SEER database and a Chinese Multi-Institutional Registry. JCO 2017, 35, 1162–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catarino, P.A.; Goldstraw, P. The future in diagnosis and staging of lung cancer: Surgical techniques. Respir. Int. Rev. Thorac. Dis. 2006, 73, 717–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izbicki, J.R.; Passlick, B.; Karg, O.; Bloechle, C.; Pantel, K.; Knoefel, W.T.; Thetter, O. Impact of radical systematic mediastinal lymphadenectomy on tumor staging in lung cancer. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 1995, 59, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.L.; Huang, Z.F.; Wang, S.Y.; Yang, X.N.; Ou, W. A randomized trial of systematic nodal dissection in resectable non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2002, 36, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lardinois, D.; Suter, H.; Hakki, H.; Rousson, V.; Betticher, D.; Ris, H.B. Morbidity, survival, and site of recurrence after mediastinal lymph-node dissection versus systematic sampling after complete resection for non-small cell lung cancer. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2005, 80, 268–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doddoli, C.; Aragon, A.; Barlesi, F.; Chetaille, B.; Robitail, S.; Giudicelli, R.; Fuentes, P.; Thomas, P. Does the extent of lymph node dissection influence outcome in patients with stage I non-small-cell lung cancer? Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2005, 27, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hirata, T.; Koizumi, K.; Tanaka, S. Changes in hemodynamics in patients who underwent extended mediastinal lymphadenectomy through median sternotomy for primary lung cancer. Jpn. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2003, 51, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kużdżał, J.; Warmus, J.; Grochowski, Z. Optimal mediastinal staging in non-small cell lung cancer: What is the role of TEMLA and VAMLA? Lung Cancer 2014, 86, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzdzał, J.; Zieliński, M.; Papla, B.; Szlubowski, A.; Hauer, Ł.; Nabiałek, T.; Sośnicki, W.; Pankowski, J. Transcervical extended mediastinal lymphadenectomy—The new operative technique and early results in lung cancer staging. Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2005, 27, 384–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kuzdzał, J.; Zieliński, M.; Papla, B.; Urbanik, A.; Wojciechowski, W.; Narski, M.; Szlubowski, A.; Hauer, L. The transcervical extended mediastinal lymphadenectomy versus cervical mediastinoscopy in non-small cell lung cancer staging. Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2007, 31, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kużdżał, J.; Szlubowski, A.; Grochowski, Z.; Czajkowski, W. Current evidence on transcervical mediastinal lymph nodes dissection. Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2011, 40, 1470–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leyn, P.; Lardinois, D.; Van Schil, P.E.; Rami-Porta, R.; Passlick, B.; Zielinski, M.; Waller, D.A.; Lerut, T.; Weder, W. ESTS guidelines for preoperative lymph node staging for non-small cell lung cancer. Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2007, 32, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leyn, P.; Dooms, C.; Kuzdzal, J.; Lardinois, D.; Passlick, B.; Rami-Porta, R.; Turna, A.; Van Schil, P.; Venuta, F.; Waller, D.; et al. Revised ESTS guidelines for preoperative mediastinal lymph node staging for non-small-cell lung cancer. Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2014, 45, 787–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zirafa, C.; Aprile, V.; Ricciardi, S.; Romano, G.; Davini, F.; Cavaliere, I.; Alì, G.; Fontanini, G.; Melfi, F. Nodal upstaging evaluation in NSCLC patients treated by robotic lobectomy. Surg. Endosc. 2019, 33, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.E.; Shapiro, M.; Rutledge, J.R.; Korst, R.J. Nodal upstaging in robotic and video assisted thoracic surgery lobectomy for clinical n0 lung cancer. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2015, 100, 229–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, A.; Raja, S.; Bribriesco, A.; Raymond, D.; Sudarshan, M.; Murthy, S.C.; Ahmad, U. Robotic approach offers similar nodal upstaging to open lobectomy for clinical stage I NSCLC. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2020, 110, 424–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rami-Porta, R.; Wittekind, C.; Goldstraw, P. Complete resection in lung cancer surgery: Proposed definition. Lung Cancer 2005, 49, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haruki, T.; Takagi, Y.; Kubouchi, Y.; Kidokoro, Y.; Nakanishi, A.; Nozaka, Y.; Oshima, Y.; Matsui, S.; Nakamura, H. Comparison between robot-assisted thoracoscopic surgery and video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery for mediastinal and hilar lymph node dissection in lung cancer surgery. Interact. Cardiovasc. Thorac. Surg. 2021, 33, 409–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
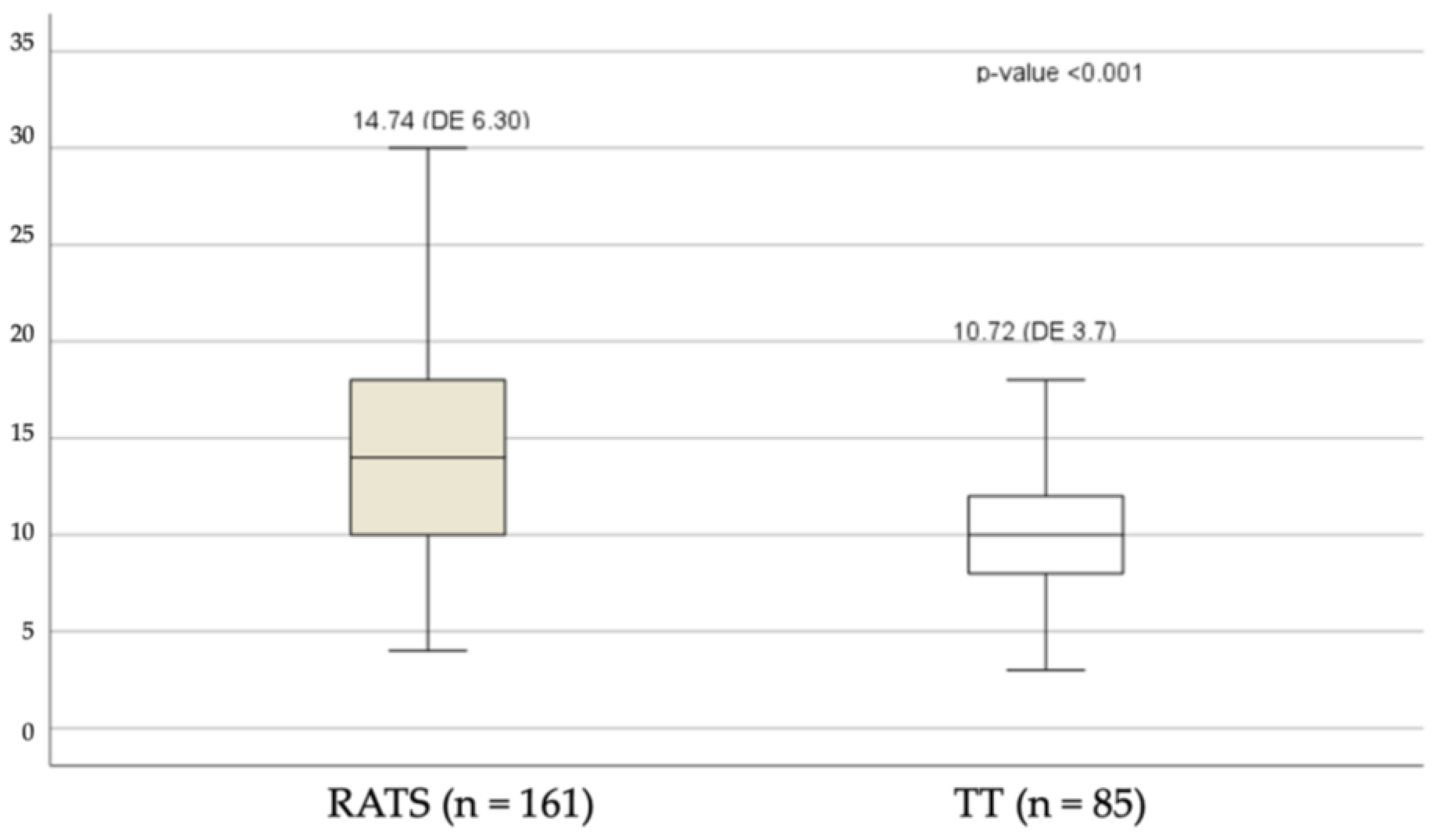

| RATS (n = 161) | TT (n = 85) | Total (n = 146) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | % | n | % | n | % | p-Value | ||
| Age (years) | 67.2 | 9.40 | 65.47 | 8.04 | 66.66 | 8.98 | 0.066 | |
| Sex | F | 62 | 38.5% | 31 | 36.5% | 93 | 37.8% | 0.754 |
| M | 99 | 61.5% | 54 | 63.5% | 153 | 62.2% | ||
| HTN | 75 | 46.6% | 37 | 43.5% | 112 | 45.5% | 0.647 | |
| DM | 20 | 12.4% | 17 | 20.0% | 37 | 15.0% | 0.114 | |
| COPD | 29 | 18.0% | 27 | 31.8% | 56 | 22.8% | 0.014 | |
| CKD | 9 | 5.6% | 2 | 2.4% | 11 | 4.5% | 0.339 | |
| PVD | 22 | 13.7% | 8 | 9.4% | 30 | 12.2% | 0.332 | |
| IHD | 9 | 5.6% | 3 | 3.5% | 12 | 4.9% | 0.552 | |
| AF | 2 | 1.2% | 4 | 4.7% | 6 | 2.4% | 0.186 | |
| Non-smoker | 36 | 22.4% | 18 | 21.2% | 54 | 22.0% | 0.831 | |
| Ex-smoker | 79 | 49.1% | 29 | 34.1% | 108 | 43.9% | 0.025 | |
| Current smoker | 46 | 28.6% | 38 | 44.7% | 84 | 34.1% | 0.011 | |
| Previous cancer | 44 | 27.3% | 18 | 21.2% | 62 | 25.2% | 0.291 | |
| RATS (n = 161) | TT (n = 85) | Total | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | % | n | % | n | % | p-Value | ||
| Type of resection | Wedge | 3 | 1.9% | 0 | 0.0% | 3 | 1.2% | 0.127 |
| Segmentectomy | 11 | 6.8% | 2 | 2.4% | 13 | 5.3% | −0.412 | |
| Lobectomy | 137 | 85.1% | 83 | 97.6% | 220 | 89.4% | ||
| Bilobectomy | 2 | 1.2% | 0 | 0.0% | 2 | 0.8% | ||
| Pneumonectomy | 3 | 1.9% | 0 | 0.0% | 3 | 1.2% | ||
| Bronchial sleeve + lobectomy | 4 | 2.5% | 0 | 0.0% | 4 | 1.6% | ||
| Bronchial sleeve | 1 | 0.6% | 0 | 0.0% | 1 | 0.4% | ||
| Clinical stage | IA1 | 5 | 3.1% | 3 | 3.5% | 8 | 3.3% | 0.656 |
| IA2 | 64 | 39.8% | 39 | 45.9% | 103 | 41.9% | −0.093 | |
| IA3 | 46 | 28.6% | 26 | 30.6% | 72 | 29.3% | ||
| IB | 29 | 18.0% | 13 | 15.3% | 42 | 17.1% | ||
| IIA | 6 | 3.7% | 2 | 2.4% | 8 | 3.3% | ||
| IIB | 11 | 6.8% | 2 | 2.4% | 13 | 5.3% | ||
| Histology | Adenocarcinoma | 104 | 64.6% | 60 | 70.6% | 164 | 66.7% | 0.129 |
| Squamous | 31 | 19.3% | 19 | 22.4% | 50 | 20.3% | ||
| Other | 26 | 16.1% | 6 | 7.1% | 32 | 13.0% | ||
|
Pathological Stage TNM 8th | 0 | 3 | 1.9% | 1 | 1.2% | 4 | 1.6% | 0.099 |
| IA1 | 9 | 5.6% | 7 | 8.2% | 16 | 6.5% | −0.835 | |
| IA2 | 47 | 29.2% | 18 | 21.2% | 65 | 26.4% | ||
| IA3 | 32 | 19.9% | 17 | 20.0% | 49 | 19.9% | ||
| IB | 20 | 12.4% | 23 | 27.1% | 43 | 17.5% | ||
| IIA | 9 | 5.6% | 2 | 2.4% | 11 | 4.5% | ||
| IIB | 22 | 13.7% | 7 | 8.2% | 29 | 11.8% | ||
| IIIA | 16 | 9.9% | 10 | 11.8% | 26 | 10.6% | ||
| IIIB | 3 | 1.9% | 0 | 0.0% | 3 | 1.2% | ||
| RATS (n = 161) | TT (n = 85) | Total | p-Value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Complications (Yes) | n | % | n | % | n | % | |
| Air leak | 57 | 35.4% | 23 | 27.1% | 80 | 32.5% | 0.184 |
| Pneumonia | 8 | 5.0% | 2 | 2.4% | 10 | 4.1% | 0.501 |
| Wound infection | 0 | 0% | 0 | 0% | 0 | 0% | ---- |
| Pneumothorax | 0 | 0.0% | 3 | 3.5% | 3 | 3.5% | ---- |
| Atrial fibrillation | 7 | 4.3% | 1 | 1.2% | 8 | 3.3% | 0.269 |
| Haemothorax | 2 | 1.2% | 0 | 0.0% | 2 | 0.8% | 0.546 |
| Chylothorax | 1 | 0.6% | 1 | 1.2% | 2 | 0.8% | 1 |
| Reoperation | 1 | 0.6% | 0 | 0.0% | 1 | 0.4% | 1 |
| Readmission | 8 | 5.0% | 4 | 4.7% | 12 | 4.9% | 1 |
| Death | 2 | 1.2% | 0 | 0.0% | 2 | 0.8% | 0.546 |
| RATS (n = 161) | TT (n = 85) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nodal upstages | 32 | 14 | 0.515 |
| cN0 to pN1 | 15 | 6 | 0.547 |
| cN0 to pN2 | 17 | 8 | 0.777 |
| cN1 to pN2 | - | - | NA |
| Nodal downstages | - | - | NA |
| No changes | 129 | 71 | 0.515 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ureña, A.; Moreno, C.; Macia, I.; Rivas, F.; Déniz, C.; Muñoz, A.; Serratosa, I.; García, M.; Masuet-Aumatell, C.; Escobar, I.; et al. A Comparison of Total Thoracoscopic and Robotic Surgery for Lung Cancer Lymphadenectomy. Cancers 2023, 15, 3442. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15133442
Ureña A, Moreno C, Macia I, Rivas F, Déniz C, Muñoz A, Serratosa I, García M, Masuet-Aumatell C, Escobar I, et al. A Comparison of Total Thoracoscopic and Robotic Surgery for Lung Cancer Lymphadenectomy. Cancers. 2023; 15(13):3442. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15133442
Chicago/Turabian StyleUreña, Anna, Camilo Moreno, Ivan Macia, Francisco Rivas, Carlos Déniz, Anna Muñoz, Ines Serratosa, Marta García, Cristina Masuet-Aumatell, Ignacio Escobar, and et al. 2023. "A Comparison of Total Thoracoscopic and Robotic Surgery for Lung Cancer Lymphadenectomy" Cancers 15, no. 13: 3442. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15133442
APA StyleUreña, A., Moreno, C., Macia, I., Rivas, F., Déniz, C., Muñoz, A., Serratosa, I., García, M., Masuet-Aumatell, C., Escobar, I., & Ramos, R. (2023). A Comparison of Total Thoracoscopic and Robotic Surgery for Lung Cancer Lymphadenectomy. Cancers, 15(13), 3442. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15133442







