Endoscopic Resection of Residual or Recurrent Lesions after Circumferential Radiofrequency Ablation for Flat Superficial Esophageal Squamous Cell Neoplasias
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
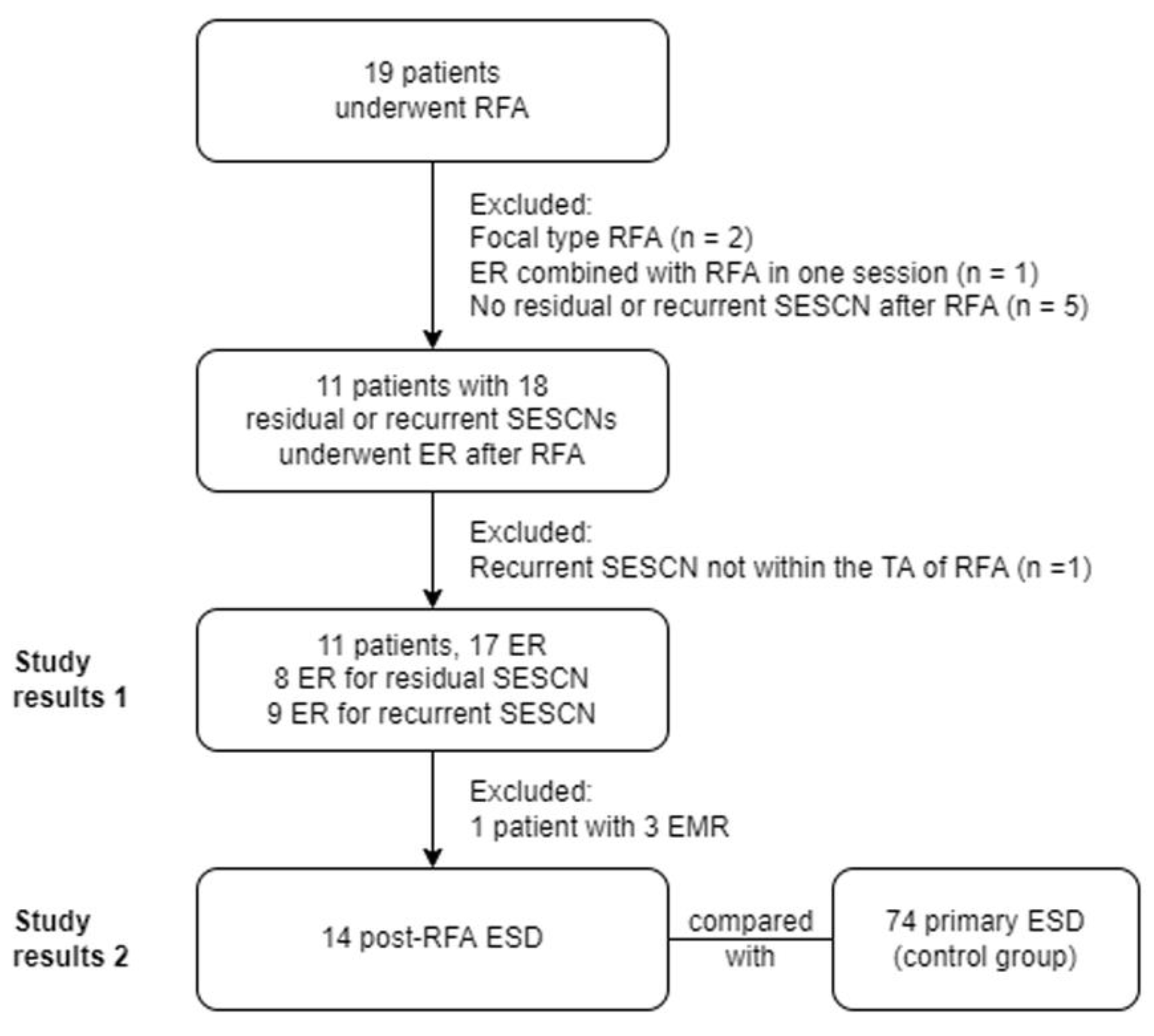
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Selection
2.2. Radiofrequency Ablation
2.3. Endoscopic Resection
2.4. Control Group
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Index Radiofrequency Ablation
3.2. Endoscopic Resection
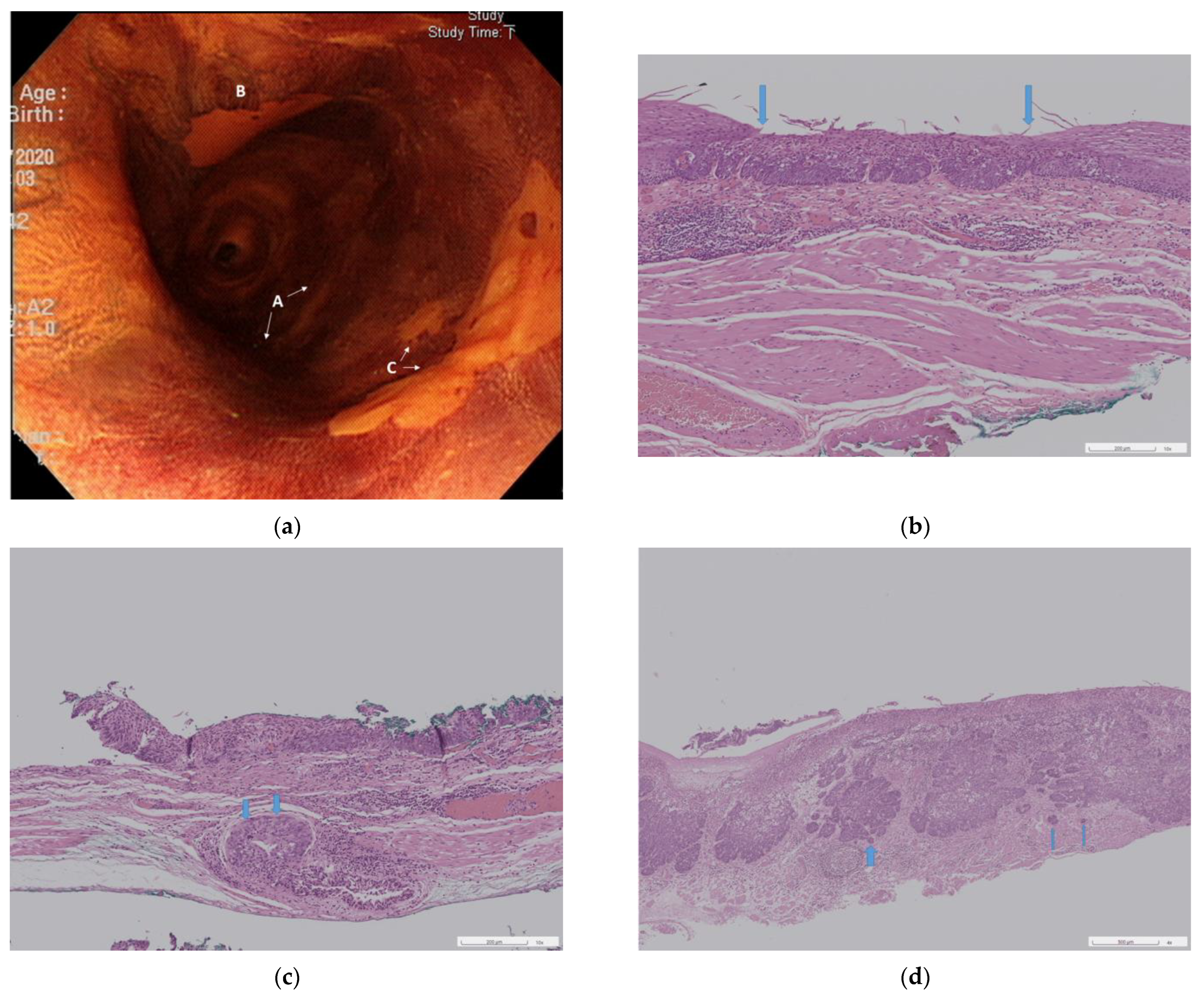
3.3. Pathological Results of the Resected Specimens
3.3.1. Neoplasia Extension to Ducts and Submucosal Glands
3.3.2. Three Pathological Groups
3.4. Results of Post-RFA ESD Versus Primary ESD
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Paiji, C.; Sedarat, A. Endoscopic Management of Esophageal Cancer. Cancers 2022, 14, 3583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, S.; Fujishiro, M.; Niimi, K.; Goto, O.; Kodashima, S.; Yamamichi, N.; Omata, M. Long-term outcomes of endoscopic submucosal dissection for superficial esophageal squamous cell neoplasms. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2009, 70, 860–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aadam, A.A.; Abe, S. Endoscopic submucosal dissection for superficial esophageal cancer. Dis. Esophagus 2018, 31, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimentel-Nunes, P.; Libânio, D.; Bastiaansen, B.A.J.; Bhandari, P.; Bisschops, R.; Bourke, M.J.; Esposito, G.; Lemmers, A.; Maselli, R.; Messmann, H.; et al. Endoscopic submucosal dissection for superficial gastrointestinal lesions: European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) Guideline—Update 2022. Endoscopy 2022, 54, 591–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, M.; Nagata, K.; Yamaguchi, H.; Kita, H. Squamous intraepithelial neoplasia of the esophagus: Past, present, and future. J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 44, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawsey, S.M.; Fleischer, D.E.; Wang, G.Q.; Zhou, B.; Kidwell, J.A.; Lu, N.; Lewin, K.J.; Roth, M.J.; Tio, T.L.; Taylor, P.R. Mucosal iodine staining improves endoscopic visualization of squamous dysplasia and squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus in Linxian, China. Cancer 1998, 83, 220–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Codipilly, D.C.; Qin, Y.; Dawsey, S.M.; Kisiel, J.; Topazian, M.; Ahlquist, D.; Iyer, P.G. Screening for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: Recent advances. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2018, 88, 413–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muto, M.; Hironaka, S.; Nakane, M.; Boku, N.; Ohtsu, A.; Yoshida, S. Association of multiple Lugol-voiding lesions with synchronous and metachronous esophageal squamous cell carcinoma in patients with head and neck cancer. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2002, 56, 517–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishihara, R.; Arima, M.; Iizuka, T.; Oyama, T.; Katada, C.; Kato, M.; Goda, K.; Goto, O.; Tanaka, K.; Yano, T.; et al. Endoscopic submucosal dissection/endoscopic mucosal resection guidelines for esophageal cancer. Dig. Endosc. 2020, 32, 452–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.L.; Chang, I.W.; Chen, C.C.; Chang, C.Y.; Mo, L.R.; Lin, J.T.; Wang, H.P.; Lee, C.T. Radiofrequency Ablation Versus Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection in Treating Large Early Esophageal Squamous Cell Neoplasia. Medicine 2015, 94, e2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.L.; Chang, I.W.; Chen, C.C.; Chang, C.Y.; Mo, L.R.; Lin, J.T.; Wang, H.P.; Lee, C.T. A case series on the use of circumferential radiofrequency ablation for early esophageal squamous neoplasias in patients with esophageal varices. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2017, 85, 322–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, S.; Mulmi Shrestha, S.; Shi, R. Radiofrequency Ablation for Early Superficial Flat Esophageal Squamous Cell Neoplasia: A Comprehensive Review. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2020, 2020, 4152453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergman, J.J.; Zhang, Y.M.; He, S.; Weusten, B.; Xue, L.; Fleischer, D.E.; Lu, N.; Dawsey, S.M.; Wang, G.Q. Outcomes from a prospective trial of endoscopic radiofrequency ablation of early squamous cell neoplasia of the esophagus. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2011, 74, 1181–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; van Munster, S.N.; Zhang, Y.; Xue, L.; Fleischer, D.E.; Weusten, B.; Lu, N.; Dawsey, S.S.M.; Bergman, J.; Wang, G. Durability of radiofrequency ablation for treatment of esophageal squamous cell neoplasia: 5-year follow-up of a treated cohort in China. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2019, 89, 736–748.e732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haidry, R.J.; Butt, M.A.; Dunn, J.; Banks, M.; Gupta, A.; Smart, H.; Bhandari, P.; Smith, L.A.; Willert, R.; Fullarton, G.; et al. Radiofrequency ablation for early oesophageal squamous neoplasia: Outcomes form United Kingdom registry. World J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 19, 6011–6019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Bergman, J.; Zhang, Y.; Weusten, B.; Xue, L.; Qin, X.; Dou, L.; Liu, Y.; Fleischer, D.; Lu, N.; et al. Endoscopic radiofrequency ablation for early esophageal squamous cell neoplasia: Report of safety and effectiveness from a large prospective trial. Endoscopy 2015, 47, 398–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.L.; Chang, I.W.; Chen, C.C.; Chang, C.Y.; Tseng, C.H.; Tai, C.M.; Lin, J.T.; Wang, H.P.; Lee, C.T. Lessons from pathological analysis of recurrent early esophageal squamous cell neoplasia after complete endoscopic radiofrequency ablation. Endoscopy 2018, 50, 743–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makuuchi, H. Endoscopic Mucosal Resection for Early Esophageal Cancer. Dig. Endosc. 1996, 8, 175–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsou, Y.K.; Chuang, W.Y.; Liu, C.Y.; Ohata, K.; Lin, C.H.; Lee, M.S.; Cheng, H.T.; Chiu, C.T. Learning curve for endoscopic submucosal dissection of esophageal neoplasms. Dis. Esophagus 2016, 29, 544–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunkin, B.J.; Martinez, J.; Bejarano, P.A.; Smith, C.D.; Chang, K.; Livingstone, A.S.; Melvin, W.S. Thin-layer ablation of human esophageal epithelium using a bipolar radiofrequency balloon device. Surg. Endosc. 2006, 20, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overwater, A.; van Munster, S.N.; Offerhaus, G.J.A.; Seldenrijk, C.A.; Raicu, G.M.; Koch, A.D.; Bergman, J.; Pouw, R.E.; Brosens, L.A.A.; Jansen, M.; et al. Extension of early esophageal squamous cell neoplasia into ducts and submucosal glands and the role of endoscopic ablation therapy. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2021, 94, 832–842.e832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tajima, Y.; Nakanishi, Y.; Tachimori, Y.; Kato, H.; Watanabe, H.; Yamaguchi, H.; Yoshimura, K.; Kusano, M.; Shimoda, T. Significance of involvement by squamous cell carcinoma of the ducts of esophageal submucosal glands. Analysis of 201 surgically resected superficial squamous cell carcinomas. Cancer 2000, 89, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oyama, T.; Inoue, H.; Arima, M.; Momma, K.; Omori, T.; Ishihara, R.; Hirasawa, D.; Takeuchi, M.; Tomori, A.; Goda, K. Prediction of the invasion depth of superficial squamous cell carcinoma based on microvessel morphology: Magnifying endoscopic classification of the Japan Esophageal Society. Esophagus 2017, 14, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawamoto, T.; Shikama, N.; Mine, S.; Kosugi, Y.; Yamaguchi, N.; Oshima, M.; Muramoto, Y.; Sasai, K. Clinical outcomes of definitive radiotherapy for patients with cT1aN0M0 esophageal cancer unsuitable for endoscopic resection and surgery. J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2022, 13, 454–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Patient Characteristics (n = 11) | Number (%), or Median (Range) |
|---|---|
| Age, years | 55 (40–69) |
| Sex, male | 11 (100%) |
| Underlying disease | |
| Hypertension | 1 (9.1%) |
| Liver cirrhosis | 5 (45.5%) |
| Hepatocellular carcinoma | 3 (27.3%) |
| Synchronous head and neck cancer | 3 (27.3%) |
| Chronic pancreatitis | 1 (9.1%) |
| Any ER before RFA | 4 (36.4%) |
| Length of tumor area †, mm | 160 (60–180) |
| Length of index RFA, mm | 180 (70–240) |
| Esophageal stricture after index RFA | 2 ‡ (18.2%) |
| Additional RFA required after index RFA | 2 (18.2%) |
| Tumor Characteristics (n = 17) | Number (%), or Median (Range) |
|---|---|
| Residual SESCN after index RFA | 8 (47.1%) |
| Recurrent SESCN after index RFA | 9 (52.9%) |
| Time between index RFA and ER, months | |
| For residual SESCN (n = 8) | 4.3 (2.8–5.6) |
| For recurrent SESCN (n = 9) | 13.0 (11.8–28.5) |
| Tumor length, mm | 25 (10–66) |
| Of residual SESCN (n = 8) | 35 (10–66) |
| Of recurrent SESCN (n = 9) | 23 (18–46) |
| ER method | |
| ESD | 14 † (82.4%) |
| EMR | 3 ‡ (17.6%) |
| Pathologic results after ER (n = 16) * | |
| Duct/SMG involvement | 8 (50%) |
| Of HGIN (n = 10) | 4 (40%) |
| Of SCC (n = 6) | 4 (66.7%) |
| Of residual SESCN (n = 7) * | 5 (71.4%) |
| Of recurrent SESCN (n = 9) | 3 (33.3%) |
| HGIN without duct/SMG involvement | 6 (37.5%) |
| HGIN with duct/SMG involvement | 4 (25.0%) |
| SCC | 6 (37.5%) |
| Post-RFA ESD (n = 14) | Primary ESD (n = 74) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 53 (41–69) | 59 (40–82) | 0.064 |
| Tumor length (mm) | 29 (18–66) | 35 (18–67) | 0.222 |
| Procedure time, min | 53 (25–340) | 110 (26–315) | 0.09 |
| Dissection speed, mm2/min | 7.0 (4.4–20.6) | 8.6 (2.1–54.8) | 0.644 |
| En bloc resection, n (%) | 14 (100%) | 74 (100%) | - |
| Completeness of resection | 1 | ||
| R0, n (%) | 12 (85.7%) | 65 (87.8%) | |
| R1, n (%) | 2 † (14.3%) | 9 ‡ (12.2%) | |
| Complications | |||
| Significant bleeding, n (%) | 1 (7.1%) | 0 | 0.159 |
| Perforation, n (%) | 0 | 0 | - |
| Esophageal stricture after ESD, n (%) | 1 (7.1%) | 22 (29.7%) | 0.102 |
| Tumor invasion depth | 0.435 | ||
| HIGN, n (%) | 8 (57.1%) | 28 (37.8%) | 0.178 |
| T1a-m2, n (%) | 0 | 10 (13.5%) | 0.353 |
| T1a-m3, n (%) | 3 (21.4%) | 12 (16.2%) | 0.700 |
| T1b-sm1, n (%) | 1 (7.1%) | 5 (6.8%) | 1 |
| T1b-sm2, n (%) | 2 (14.3%) | 19 (25.7%) | 0.504 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tsou, Y.-K.; Yeh, C.-J.; Le, P.-H.; Chen, B.-H.; Lin, C.-H. Endoscopic Resection of Residual or Recurrent Lesions after Circumferential Radiofrequency Ablation for Flat Superficial Esophageal Squamous Cell Neoplasias. Cancers 2023, 15, 3558. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15143558
Tsou Y-K, Yeh C-J, Le P-H, Chen B-H, Lin C-H. Endoscopic Resection of Residual or Recurrent Lesions after Circumferential Radiofrequency Ablation for Flat Superficial Esophageal Squamous Cell Neoplasias. Cancers. 2023; 15(14):3558. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15143558
Chicago/Turabian StyleTsou, Yung-Kuan, Chi-Ju Yeh, Puo-Hsien Le, Bo-Huan Chen, and Cheng-Hui Lin. 2023. "Endoscopic Resection of Residual or Recurrent Lesions after Circumferential Radiofrequency Ablation for Flat Superficial Esophageal Squamous Cell Neoplasias" Cancers 15, no. 14: 3558. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15143558
APA StyleTsou, Y.-K., Yeh, C.-J., Le, P.-H., Chen, B.-H., & Lin, C.-H. (2023). Endoscopic Resection of Residual or Recurrent Lesions after Circumferential Radiofrequency Ablation for Flat Superficial Esophageal Squamous Cell Neoplasias. Cancers, 15(14), 3558. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15143558





