Mechanisms of PARP-Inhibitor-Resistance in BRCA-Mutated Breast Cancer and New Therapeutic Approaches
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Mutations in BRCA 1/2 Genes
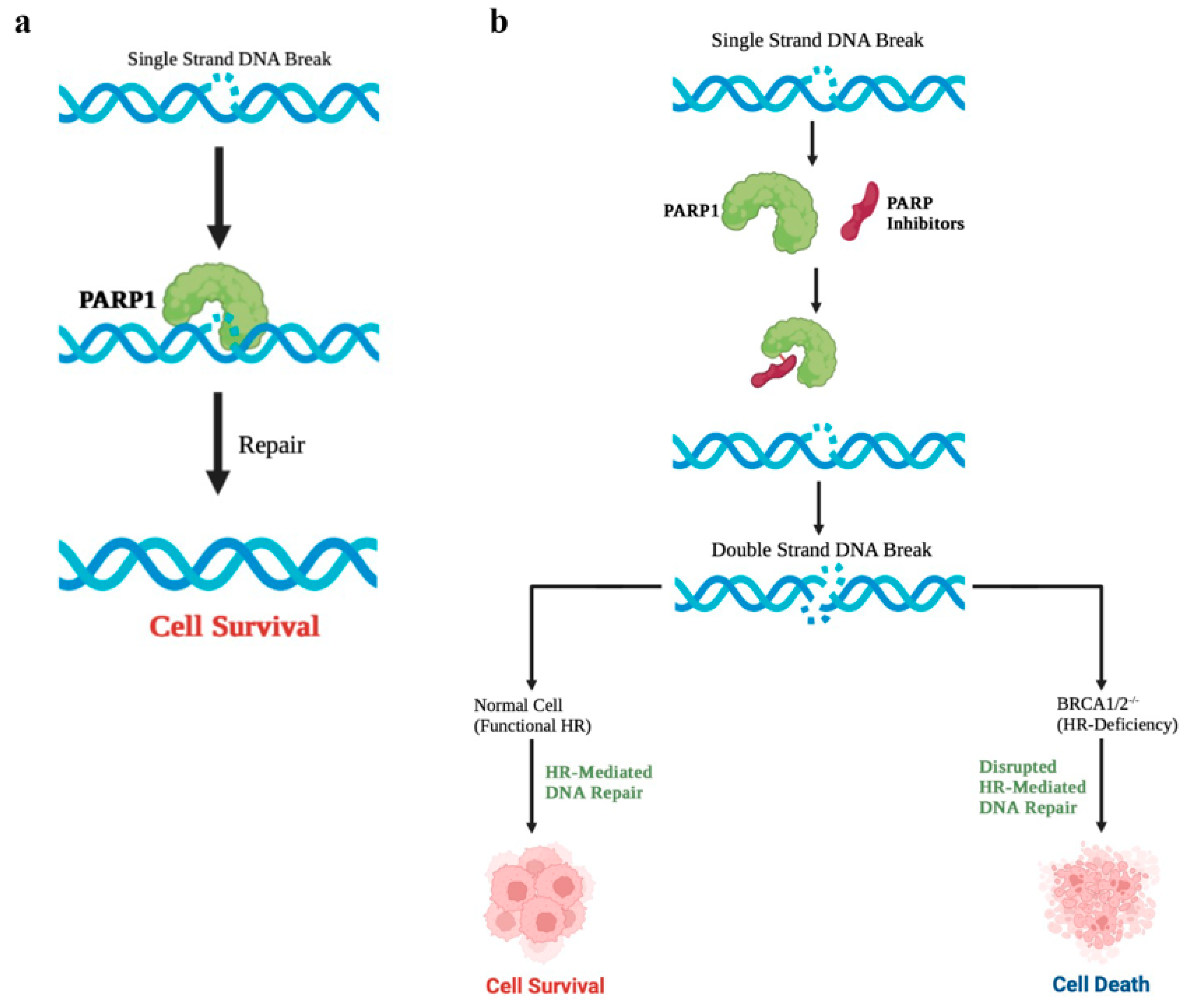
3. Poly (ADP-Ribose) Polymerase 1 (PARP1) Is Critical for the Survival of BRCA-Mutated Cells
4. PARPi Induces Synthetic Lethality in BRCA-Mutated Cells
5. Resistance to PARPi
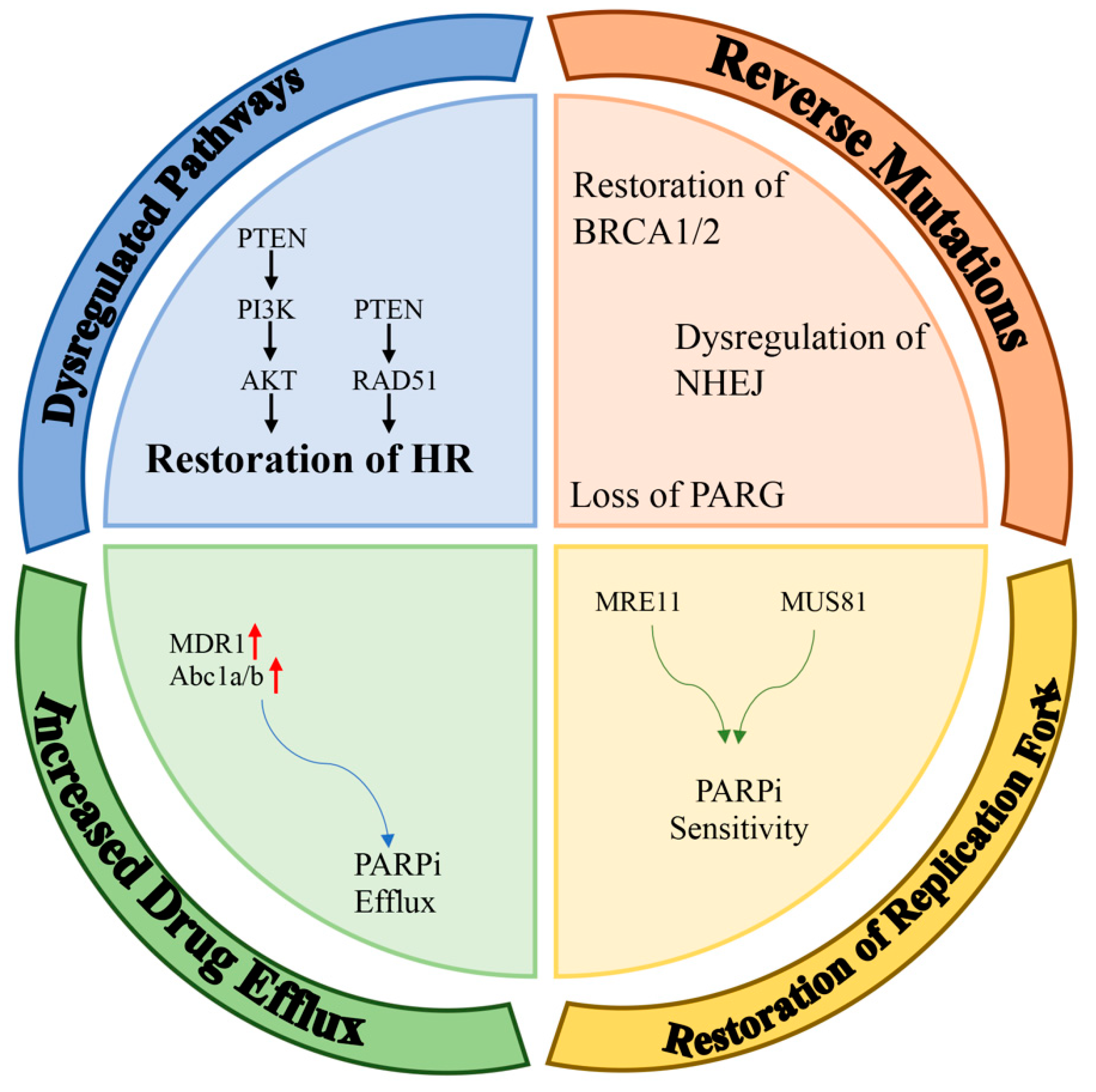
6. Molecular Mechanisms for Resistance to PARPi
6.1. Dysregulated Molecular Signaling
6.2. Reverse Mutations
6.3. Restoration of Replication Fork Stability
6.4. Effect of the Increased Drug Efflux
7. Approaches to Enhance the Effects of the PARPi Treatment
7.1. PARPi and Chemotherapy
7.2. PARPi and Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors
7.3. PARPi and ATR/Chk1/Wee1-Inhibitor Therapy
7.4. PARPi and BRD4/BET Inhibitor Therapy
7.5. PARPi and CDK12 Inhibitor Therapy
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Romagnolo, A.P.; Romagnolo, D.F.; Selmin, O.I. BRCA1 as target for breast cancer prevention and therapy. Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 2015, 15, 4–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, K.; Miki, Y. Role of BRCA1 and BRCA2 as regulators of DNA repair, transcription, and cell cycle in response to DNA damage. Cancer Sci. 2004, 95, 866–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wooster, R.; Bignell, G.; Lancaster, J.; Swift, S.; Seal, S.; Mangion, J.; Collins, N.; Gregory, S.; Gumbs, C.; Micklem, G. Identification of the breast cancer susceptibility gene BRCA2. Nature 1995, 378, 789–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wooster, R.; Neuhausen, S.L.; Mangion, J.; Quirk, Y.; Ford, D.; Collins, N.; Nguyen, K.; Seal, S.; Tran, T.; Averill, D.; et al. Localization of a breast cancer susceptibility gene, BRCA2, to chromosome 13q12-13. Science 1994, 265, 2088–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharan, S.K.; Morimatsu, M.; Albrecht, U.; Lim, D.S.; Regel, E.; Dinh, C.; Sands, A.; Eichele, G.; Hasty, P.; Bradley, A. Embryonic lethality and radiation hypersensitivity mediated by Rad51 in mice lacking Brca2. Nature 1997, 386, 804–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bertwistle, D.; Swift, S.; Marston, N.J.; Jackson, L.E.; Crossland, S.; Crompton, M.R.; Marshall, C.J.; Ashworth, A. Nuclear location and cell cycle regulation of the BRCA2 protein. Cancer Res. 1997, 57, 5485–5488. [Google Scholar]
- Blackford, A.N.; Jackson, S.P. ATM, ATR, and DNA-PK: The Trinity at the Heart of the DNA Damage Response. Mol. Cell 2017, 66, 801–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lisby, M.; Rothstein, R. Cell biology of mitotic recombination. Cold Spring Harb Perspect. Biol. 2015, 7, a016535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Siu, A.L.; U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. Screening for Breast Cancer: U.S. Preventive Services Task Force Recommendation Statement. Ann. Intern. Med. 2016, 164, 279–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rahman, N.; Stratton, M.R. The genetics of breast cancer susceptibility. Annu. Rev. Genet. 1998, 32, 95–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Futreal, P.A.; Liu, Q.; Shattuck-Eidens, D.; Cochran, C.; Harshman, K.; Tavtigian, S.; Bennett, L.M.; Haugen-Strano, A.; Swensen, J.; Miki, Y.; et al. BRCA1 mutations in primary breast and ovarian carcinomas. Science 1994, 266, 120–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lancaster, J.M.; Wooster, R.; Mangion, J.; Phelan, C.M.; Cochran, C.; Gumbs, C.; Seal, S.; Barfoot, R.; Collins, N.; Bignell, G.; et al. BRCA2 mutations in primary breast and ovarian cancers. Nat. Genet. 1996, 13, 238–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortez, D.; Wang, Y.; Qin, J.; Elledge, S.J. Requirement of ATM-dependent phosphorylation of brca1 in the DNA damage response to double-strand breaks. Science 1999, 286, 1162–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gatei, M.; Zhou, B.B.; Hobson, K.; Scott, S.; Young, D.; Khanna, K.K. Ataxia telangiectasia mutated (ATM) kinase and ATM and Rad3 related kinase mediate phosphorylation of Brca1 at distinct and overlapping sites. In vivo assessment using phospho-specific antibodies. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 17276–17280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chaturvedi, P.; Eng, W.K.; Zhu, Y.; Mattern, M.R.; Mishra, R.; Hurle, M.R.; Zhang, X.; Annan, R.S.; Lu, Q.; Faucette, L.F.; et al. Mammalian Chk2 is a downstream effector of the ATM-dependent DNA damage checkpoint pathway. Oncogene 1999, 18, 4047–4054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatei, M.; Scott, S.P.; Filippovitch, I.; Soronika, N.; Lavin, M.F.; Weber, B.; Khanna, K.K. Role for ATM in DNA damage-induced phosphorylation of BRCA1. Cancer Res. 2000, 60, 3299–3304. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Silver, D.P.; Walpita, D.; Cantor, S.B.; Gazdar, A.F.; Tomlinson, G.; Couch, F.J.; Weber, B.L.; Ashley, T.; Livingston, D.M.; et al. Stable interaction between the products of the BRCA1 and BRCA2 tumor suppressor genes in mitotic and meiotic cells. Mol. Cell 1998, 2, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scully, R.; Chen, J.; Plug, A.; Xiao, Y.; Weaver, D.; Feunteun, J.; Ashley, T.; Livingston, D.M. Association of BRCA1 with Rad51 in mitotic and meiotic cells. Cell 1997, 88, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moynahan, M.E.; Pierce, A.J.; Jasin, M. BRCA2 is required for homology-directed repair of chromosomal breaks. Mol. Cell 2001, 7, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, V.P.; Koehler, M.; Steinlein, C.; Schmid, M.; Hanakahi, L.A.; van Gool, A.J.; West, S.C.; Venkitaraman, A.R. Gross chromosomal rearrangements and genetic exchange between nonhomologous chromosomes following BRCA2 inactivation. Genes Dev. 2000, 14, 1400–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Sekine, E.; Fujimori, A.; Ochiya, T.; Okayasu, R. Down regulation of BRCA2 causes radio-sensitization of human tumor cells in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Sci. 2008, 99, 810–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.C.; Feng, W.; Lim, P.X.; Kass, E.M.; Jasin, M. Homology-Directed Repair and the Role of BRCA1, BRCA2, and Related Proteins in Genome Integrity and Cancer. Annu. Rev. Cancer Biol. 2018, 2, 313–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dias, M.P.; Moser, S.C.; Ganesan, S.; Jonkers, J. Understanding and overcoming resistance to PARP inhibitors in cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 18, 773–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scully, R.; Panday, A.; Elango, R.; Willis, N.A. DNA double-strand break repair-pathway choice in somatic mammalian cells. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2019, 20, 698–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bryant, H.E.; Schultz, N.; Thomas, H.D.; Parker, K.M.; Flower, D.; Lopez, E.; Kyle, S.; Meuth, M.; Curtin, N.J.; Helleday, T. Specific killing of BRCA2-deficient tumours with inhibitors of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase. Nature 2005, 434, 913–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farmer, H.; McCabe, N.; Lord, C.J.; Tutt, A.N.; Johnson, D.A.; Richardson, T.B.; Santarosa, M.; Dillon, K.J.; Hickson, I.; Knights, C.; et al. Targeting the DNA repair defect in BRCA mutant cells as a therapeutic strategy. Nature 2005, 434, 917–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray Chaudhuri, A.; Nussenzweig, A. The multifaceted roles of PARP1 in DNA repair and chromatin remodelling. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2017, 18, 610–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashworth, A.; Lord, C.J. Synthetic lethal therapies for cancer: What’s next after PARP inhibitors? Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 15, 564–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Bono, J.; Mateo, J.; Fizazi, K.; Saad, F.; Shore, N.; Sandhu, S.; Chi, K.N.; Sartor, O.; Agarwal, N.; Olmos, D.; et al. Olaparib for Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 2091–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golan, T.; Hammel, P.; Reni, M.; Van Cutsem, E.; Macarulla, T.; Hall, M.J.; Park, J.O.; Hochhauser, D.; Arnold, D.; Oh, D.Y.; et al. Maintenance Olaparib for Germline BRCA-Mutated Metastatic Pancreatic Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 317–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateo, J.; Carreira, S.; Sandhu, S.; Miranda, S.; Mossop, H.; Perez-Lopez, R.; Nava Rodrigues, D.; Robinson, D.; Omlin, A.; Tunariu, N.; et al. DNA-Repair Defects and Olaparib in Metastatic Prostate Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 1697–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robson, M.; Im, S.A.; Senkus, E.; Xu, B.; Domchek, S.M.; Masuda, N.; Delaloge, S.; Li, W.; Tung, N.; Armstrong, A.; et al. Olaparib for Metastatic Breast Cancer in Patients with a Germline BRCA Mutation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 523–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondrashova, O.; Topp, M.; Nesic, K.; Lieschke, E.; Ho, G.Y.; Harrell, M.I.; Zapparoli, G.V.; Hadley, A.; Holian, R.; Boehm, E.; et al. Methylation of all BRCA1 copies predicts response to the PARP inhibitor rucaparib in ovarian carcinoma. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lheureux, S.; Lai, Z.; Dougherty, B.A.; Runswick, S.; Hodgson, D.R.; Timms, K.M.; Lanchbury, J.S.; Kaye, S.; Gourley, C.; Bowtell, D.; et al. Long-Term Responders on Olaparib Maintenance in High-Grade Serous Ovarian Cancer: Clinical and Molecular Characterization. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 4086–4094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Takaya, H.; Nakai, H.; Takamatsu, S.; Mandai, M.; Matsumura, N. Homologous recombination deficiency status-based classification of high-grade serous ovarian carcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 2757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Telli, M.L.; Timms, K.M.; Reid, J.; Hennessy, B.; Mills, G.B.; Jensen, K.C.; Szallasi, Z.; Barry, W.T.; Winer, E.P.; Tung, N.M.; et al. Homologous Recombination Deficiency (HRD) Score Predicts Response to Platinum-Containing Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Patients with Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 3764–3773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Giudice, E.; Gentile, M.; Salutari, V.; Ricci, C.; Musacchio, L.; Carbone, M.V.; Ghizzoni, V.; Camarda, F.; Tronconi, F.; Nero, C.; et al. PARP Inhibitors Resistance: Mechanisms and Perspectives. Cancers 2022, 14, 1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watkins, J.A.; Irshad, S.; Grigoriadis, A.; Tutt, A.N. Genomic scars as biomarkers of homologous recombination deficiency and drug response in breast and ovarian cancers. Breast Cancer Res. 2014, 16, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neil, N.J.; Bailey, M.L.; Hieter, P. Synthetic lethality and cancer. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2017, 18, 613–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menear, K.A.; Adcock, C.; Boulter, R.; Cockcroft, X.L.; Copsey, L.; Cranston, A.; Dillon, K.J.; Drzewiecki, J.; Garman, S.; Gomez, S.; et al. 4-[3-(4-cyclopropanecarbonylpiperazine-1-carbonyl)-4-fluorobenzyl]-2H-phthalazin-1-one: A novel bioavailable inhibitor of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 51, 6581–6591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandhu, D.; Antolin, A.A.; Cox, A.R.; Jones, A.M. Identification of different side effects between PARP inhibitors and their polypharmacological multi-target rationale. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2022, 88, 742–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Mason, K.A.; Ang, K.K.; Buchholz, T.; Valdecanas, D.; Mathur, A.; Buser-Doepner, C.; Toniatti, C.; Milas, L. MK-4827, a PARP-1/-2 inhibitor, strongly enhances response of human lung and breast cancer xenografts to radiation. Investig. New Drugs 2012, 30, 2113–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Rehman, F.L.; Feng, Y.; Boshuizen, J.; Bajrami, I.; Elliott, R.; Wang, B.; Lord, C.J.; Post, L.E.; Ashworth, A. BMN 673, a novel and highly potent PARP1/2 inhibitor for the treatment of human cancers with DNA repair deficiency. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 5003–5015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gonzalez-Martin, A.; Pothuri, B.; Vergote, I.; DePont Christensen, R.; Graybill, W.; Mirza, M.R.; McCormick, C.; Lorusso, D.; Hoskins, P.; Freyer, G.; et al. Niraparib in Patients with Newly Diagnosed Advanced Ovarian Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 2391–2402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Litton, J.K.; Rugo, H.S.; Ettl, J.; Hurvitz, S.A.; Goncalves, A.; Lee, K.H.; Fehrenbacher, L.; Yerushalmi, R.; Mina, L.A.; Martin, M.; et al. Talazoparib in Patients with Advanced Breast Cancer and a Germline BRCA Mutation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 753–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, K.; Colombo, N.; Scambia, G.; Kim, B.G.; Oaknin, A.; Friedlander, M.; Lisyanskaya, A.; Floquet, A.; Leary, A.; Sonke, G.S.; et al. Maintenance Olaparib in Patients with Newly Diagnosed Advanced Ovarian Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 2495–2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgini, M.; Wipf, P. Synthesis of Veliparib Prodrugs and Determination of Drug-Release-Dependent PARP-1 Inhibition. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2023, 14, 652–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, Y.; Guo, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, H.; Gong, W.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Gao, Y.; Yu, F.; Su, D.; et al. Pamiparib is a potent and selective PARP inhibitor with unique potential for the treatment of brain tumor. Neoplasia 2020, 22, 431–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, R.L.; Fleming, G.F.; Brady, M.F.; Swisher, E.M.; Steffensen, K.D.; Friedlander, M.; Okamoto, A.; Moore, K.N.; Efrat Ben-Baruch, N.; Werner, T.L.; et al. Veliparib with First-Line Chemotherapy and as Maintenance Therapy in Ovarian Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 2403–2415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lord, C.J.; Ashworth, A. PARP inhibitors: Synthetic lethality in the clinic. Science 2017, 355, 1152–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, T.A.; Plummer, R.; Azad, N.S.; Helleday, T. The DNA Damaging Revolution: PARP Inhibitors and Beyond. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. Educ. Book 2019, 39, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carnero, A.; Blanco-Aparicio, C.; Renner, O.; Link, W.; Leal, J.F. The PTEN/PI3K/AKT signalling pathway in cancer, therapeutic implications. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2008, 8, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, T.; Ohashi, A.; Huang, Y.; Pandita, T.K.; Ludwig, T.; Powell, S.N.; Yang, Q. Negative Regulation of AKT Activation by BRCA1. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 10040–10044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Saal, L.H.; Gruvberger-Saal, S.K.; Persson, C.; Lovgren, K.; Jumppanen, M.; Staaf, J.; Jonsson, G.; Pires, M.M.; Maurer, M.; Holm, K.; et al. Recurrent gross mutations of the PTEN tumor suppressor gene in breast cancers with deficient DSB repair. Nat. Genet. 2008, 40, 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes-Pereira, A.M.; Martin, S.A.; Brough, R.; McCarthy, A.; Taylor, J.R.; Kim, J.S.; Waldman, T.; Lord, C.J.; Ashworth, A. Synthetic lethal targeting of PTEN mutant cells with PARP inhibitors. EMBO Mol. Med. 2009, 1, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dedes, K.J.; Wetterskog, D.; Mendes-Pereira, A.M.; Natrajan, R.; Lambros, M.B.; Geyer, F.C.; Vatcheva, R.; Savage, K.; Mackay, A.; Lord, C.J.; et al. PTEN deficiency in endometrioid endometrial adenocarcinomas predicts sensitivity to PARP inhibitors. Sci. Transl. Med. 2010, 2, 53ra75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piombino, C.; Cortesi, L. Insights into the Possible Molecular Mechanisms of Resistance to PARP Inhibitors. Cancers 2022, 14, 2804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murai, J.; Huang, S.Y.; Das, B.B.; Renaud, A.; Zhang, Y.; Doroshow, J.H.; Ji, J.; Takeda, S.; Pommier, Y. Trapping of PARP1 and PARP2 by Clinical PARP Inhibitors. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 5588–5599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Noordermeer, S.M.; van Attikum, H. PARP Inhibitor Resistance: A Tug-of-War in BRCA-Mutated Cells. Trends Cell Biol. 2019, 29, 820–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, K.K.; Harrell, M.I.; Oza, A.M.; Oaknin, A.; Ray-Coquard, I.; Tinker, A.V.; Helman, E.; Radke, M.R.; Say, C.; Vo, L.T.; et al. BRCA Reversion Mutations in Circulating Tumor DNA Predict Primary and Acquired Resistance to the PARP Inhibitor Rucaparib in High-Grade Ovarian Carcinoma. Cancer Discov. 2019, 9, 210–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Patel, A.G.; Sarkaria, J.N.; Kaufmann, S.H. Nonhomologous end joining drives poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) inhibitor lethality in homologous recombination-deficient cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 3406–3411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gogola, E.; Duarte, A.A.; de Ruiter, J.R.; Wiegant, W.W.; Schmid, J.A.; de Bruijn, R.; James, D.I.; Guerrero Llobet, S.; Vis, D.J.; Annunziato, S.; et al. Selective Loss of PARG Restores PARylation and Counteracts PARP Inhibitor-Mediated Synthetic Lethality. Cancer Cell 2018, 33, 1078–1093.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schlacher, K.; Christ, N.; Siaud, N.; Egashira, A.; Wu, H.; Jasin, M. Double-strand break repair-independent role for BRCA2 in blocking stalled replication fork degradation by MRE11. Cell 2011, 145, 529–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rondinelli, B.; Gogola, E.; Yucel, H.; Duarte, A.A.; van de Ven, M.; van der Sluijs, R.; Konstantinopoulos, P.A.; Jonkers, J.; Ceccaldi, R.; Rottenberg, S.; et al. EZH2 promotes degradation of stalled replication forks by recruiting MUS81 through histone H3 trimethylation. Nat. Cell Biol. 2017, 19, 1371–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dungrawala, H.; Bhat, K.P.; Le Meur, R.; Chazin, W.J.; Ding, X.; Sharan, S.K.; Wessel, S.R.; Sathe, A.A.; Zhao, R.; Cortez, D. RADX Promotes Genome Stability and Modulates Chemosensitivity by Regulating RAD51 at Replication Forks. Mol. Cell 2017, 67, 374–386.e375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taglialatela, A.; Alvarez, S.; Leuzzi, G.; Sannino, V.; Ranjha, L.; Huang, J.W.; Madubata, C.; Anand, R.; Levy, B.; Rabadan, R.; et al. Restoration of Replication Fork Stability in BRCA1- and BRCA2-Deficient Cells by Inactivation of SNF2-Family Fork Remodelers. Mol. Cell 2017, 68, 414–430.e418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Murai, J.; Tang, S.W.; Leo, E.; Baechler, S.A.; Redon, C.E.; Zhang, H.; Al Abo, M.; Rajapakse, V.N.; Nakamura, E.; Jenkins, L.M.M.; et al. SLFN11 Blocks Stressed Replication Forks Independently of ATR. Mol. Cell 2018, 69, 371–384.e376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choi, Y.H.; Yu, A.M. ABC transporters in multidrug resistance and pharmacokinetics, and strategies for drug development. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2014, 20, 793–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rottenberg, S.; Jaspers, J.E.; Kersbergen, A.; van der Burg, E.; Nygren, A.O.; Zander, S.A.; Derksen, P.W.; de Bruin, M.; Zevenhoven, J.; Lau, A.; et al. High sensitivity of BRCA1-deficient mammary tumors to the PARP inhibitor AZD2281 alone and in combination with platinum drugs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 17079–17084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christie, E.L.; Pattnaik, S.; Beach, J.; Copeland, A.; Rashoo, N.; Fereday, S.; Hendley, J.; Alsop, K.; Brady, S.L.; Lamb, G.; et al. Multiple ABCB1 transcriptional fusions in drug resistant high-grade serous ovarian and breast cancer. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leitner, I.; Nemeth, J.; Feurstein, T.; Abrahim, A.; Matzneller, P.; Lagler, H.; Erker, T.; Langer, O.; Zeitlinger, M. The third-generation P-glycoprotein inhibitor tariquidar may overcome bacterial multidrug resistance by increasing intracellular drug concentration. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2011, 66, 834–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Han, Y.; Yu, X.; Li, S.; Tian, Y.; Liu, C. New Perspectives for Resistance to PARP Inhibitors in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 578095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dent, R.A.; Lindeman, G.J.; Clemons, M.; Wildiers, H.; Chan, A.; McCarthy, N.J.; Singer, C.F.; Lowe, E.S.; Watkins, C.L.; Carmichael, J. Phase I trial of the oral PARP inhibitor olaparib in combination with paclitaxel for first- or second-line treatment of patients with metastatic triple-negative breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2013, 15, R88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sulai, N.H.; Tan, A.R. Development of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitors in the treatment of BRCA-mutated breast cancer. Clin. Adv. Hematol. Oncol. 2018, 16, 491–501. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Keenan, T.E.; Overmoyer, B.; Tung, N.M.; Gelman, R.S.; Habin, K.; Garber, J.E.; Ellisen, L.W.; Winer, E.P.; Goss, P.E.; et al. Phase II trial of veliparib and temozolomide in metastatic breast cancer patients with and without BRCA1/2 mutations. Breast Cancer Res. Treat 2021, 189, 641–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazareth, D.; Jones, M.J.; Gabrielli, B. Everything in Moderation: Lessons Learned by Exploiting Moderate Replication Stress in Cancer. Cancers 2019, 11, 1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parkes, E.E.; Walker, S.M.; Taggart, L.E.; McCabe, N.; Knight, L.A.; Wilkinson, R.; McCloskey, K.D.; Buckley, N.E.; Savage, K.I.; Salto-Tellez, M.; et al. Activation of STING-Dependent Innate Immune Signaling By S-Phase-Specific DNA Damage in Breast Cancer. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2017, 109, djw199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, Y.; Li, C.W.; Hsu, J.M.; Hsu, J.L.; Chan, L.C.; Tan, X.; He, G.J. Metformin reverses PARP inhibitors-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition and PD-L1 upregulation in triple-negative breast cancer. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2019, 9, 800–815. [Google Scholar]
- Jiao, S.; Xia, W.; Yamaguchi, H.; Wei, Y.; Chen, M.K.; Hsu, J.M.; Hsu, J.L.; Yu, W.H.; Du, Y.; Lee, H.H.; et al. PARP Inhibitor Upregulates PD-L1 Expression and Enhances Cancer-Associated Immunosuppression. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 3711–3720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Domchek, S.M.; Postel-Vinay, S.; Im, S.A.; Park, Y.H.; Delord, J.P.; Italiano, A.; Alexandre, J.; You, B.; Bastian, S.; Krebs, M.G.; et al. Olaparib and durvalumab in patients with germline BRCA-mutated metastatic breast cancer (MEDIOLA): An open-label, multicentre, phase 1/2, basket study. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, 1155–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazinski, S.A.; Comaills, V.; Buisson, R.; Genois, M.M.; Nguyen, H.D.; Ho, C.K.; Todorova Kwan, T.; Morris, R.; Lauffer, S.; Nussenzweig, A.; et al. ATR inhibition disrupts rewired homologous recombination and fork protection pathways in PARP inhibitor-resistant BRCA-deficient cancer cells. Genes Dev. 2017, 31, 318–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wengner, A.M.; Siemeister, G.; Lucking, U.; Lefranc, J.; Wortmann, L.; Lienau, P.; Bader, B.; Bomer, U.; Moosmayer, D.; Eberspacher, U.; et al. The Novel ATR Inhibitor BAY 1895344 Is Efficacious as Monotherapy and Combined with DNA Damage-Inducing or Repair-Compromising Therapies in Preclinical Cancer Models. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2020, 19, 26–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Do, K.T.; Kochupurakkal, B.; Kelland, S.; de Jonge, A.; Hedglin, J.; Powers, A.; Quinn, N.; Gannon, C.; Vuong, L.; Parmar, K.; et al. Phase 1 Combination Study of the CHK1 Inhibitor Prexasertib and the PARP Inhibitor Olaparib in High-grade Serous Ovarian Cancer and Other Solid Tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 27, 4710–4716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parsels, L.A.; Karnak, D.; Parsels, J.D.; Zhang, Q.; Velez-Padilla, J.; Reichert, Z.R.; Wahl, D.R.; Maybaum, J.; O’Connor, M.J.; Lawrence, T.S.; et al. PARP1 Trapping and DNA Replication Stress Enhance Radiosensitization with Combined WEE1 and PARP Inhibitors. Mol. Cancer Res. 2018, 16, 222–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fang, Y.; McGrail, D.J.; Sun, C.; Labrie, M.; Chen, X.; Zhang, D.; Ju, Z.; Vellano, C.P.; Lu, Y.; Li, Y.; et al. Sequential Therapy with PARP and WEE1 Inhibitors Minimizes Toxicity while Maintaining Efficacy. Cancer Cell 2019, 35, 851–867.e857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karnak, D.; Engelke, C.G.; Parsels, L.A.; Kausar, T.; Wei, D.; Robertson, J.R.; Marsh, K.B.; Davis, M.A.; Zhao, L.; Maybaum, J.; et al. Combined inhibition of Wee1 and PARP1/2 for radiosensitization in pancreatic cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 5085–5096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, N.; Wu, R.; Tang, D.; Kang, R. The BET family in immunity and disease. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Yin, J.; Fang, Y.; Chen, J.; Jeong, K.J.; Chen, X.; Vellano, C.P.; Ju, Z.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, D.; et al. BRD4 Inhibition Is Synthetic Lethal with PARP Inhibitors through the Induction of Homologous Recombination Deficiency. Cancer Cell 2018, 33, 401–416.e408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wilson, A.J.; Stubbs, M.; Liu, P.; Ruggeri, B.; Khabele, D. The BET inhibitor INCB054329 reduces homologous recombination efficiency and augments PARP inhibitor activity in ovarian cancer. Gynecol. Oncol. 2018, 149, 575–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Shan, W.; Hu, Z.; Yuan, J.; Pi, J.; Wang, Y.; Fan, L.; Tang, Z.; Li, C.; et al. Repression of BET activity sensitizes homologous recombination-proficient cancers to PARP inhibition. Sci. Transl. Med. 2017, 9, eaal1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chirackal Manavalan, A.P.; Pilarova, K.; Kluge, M.; Bartholomeeusen, K.; Rajecky, M.; Oppelt, J.; Khirsariya, P.; Paruch, K.; Krejci, L.; Friedel, C.C.; et al. CDK12 controls G1/S progression by regulating RNAPII processivity at core DNA replication genes. EMBO Rep. 2019, 20, e47592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krajewska, M.; Dries, R.; Grassetti, A.V.; Dust, S.; Gao, Y.; Huang, H.; Sharma, B.; Day, D.S.; Kwiatkowski, N.; Pomaville, M.; et al. CDK12 loss in cancer cells affects DNA damage response genes through premature cleavage and polyadenylation. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Joshi, P.M.; Sutor, S.L.; Huntoon, C.J.; Karnitz, L.M. Ovarian cancer-associated mutations disable catalytic activity of CDK12, a kinase that promotes homologous recombination repair and resistance to cisplatin and poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitors. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 9247–9253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Quereda, V.; Bayle, S.; Vena, F.; Frydman, S.M.; Monastyrskyi, A.; Roush, W.R.; Duckett, D.R. Therapeutic Targeting of CDK12/CDK13 in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Cancer Cell 2019, 36, 545–558.e547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajrami, I.; Frankum, J.R.; Konde, A.; Miller, R.E.; Rehman, F.L.; Brough, R.; Campbell, J.; Sims, D.; Rafiq, R.; Hooper, S.; et al. Genome-wide profiling of genetic synthetic lethality identifies CDK12 as a novel determinant of PARP1/2 inhibitor sensitivity. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 287–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dilmac, S.; Ozpolat, B. Mechanisms of PARP-Inhibitor-Resistance in BRCA-Mutated Breast Cancer and New Therapeutic Approaches. Cancers 2023, 15, 3642. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15143642
Dilmac S, Ozpolat B. Mechanisms of PARP-Inhibitor-Resistance in BRCA-Mutated Breast Cancer and New Therapeutic Approaches. Cancers. 2023; 15(14):3642. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15143642
Chicago/Turabian StyleDilmac, Sayra, and Bulent Ozpolat. 2023. "Mechanisms of PARP-Inhibitor-Resistance in BRCA-Mutated Breast Cancer and New Therapeutic Approaches" Cancers 15, no. 14: 3642. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15143642
APA StyleDilmac, S., & Ozpolat, B. (2023). Mechanisms of PARP-Inhibitor-Resistance in BRCA-Mutated Breast Cancer and New Therapeutic Approaches. Cancers, 15(14), 3642. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15143642





