A Radiomics-Clinical Model Predicts Overall Survival of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients Treated with Immunotherapy: A Multicenter Study
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials & Methods
2.1. Description of Cohorts
2.2. PD-L1 Assessment
2.3. Overall Survival Assessment
2.4. CT Scan Annotation
2.5. Extraction of Radiomics Features and Pre-Processing
2.6. Feature Selection and Machine Learning Methods
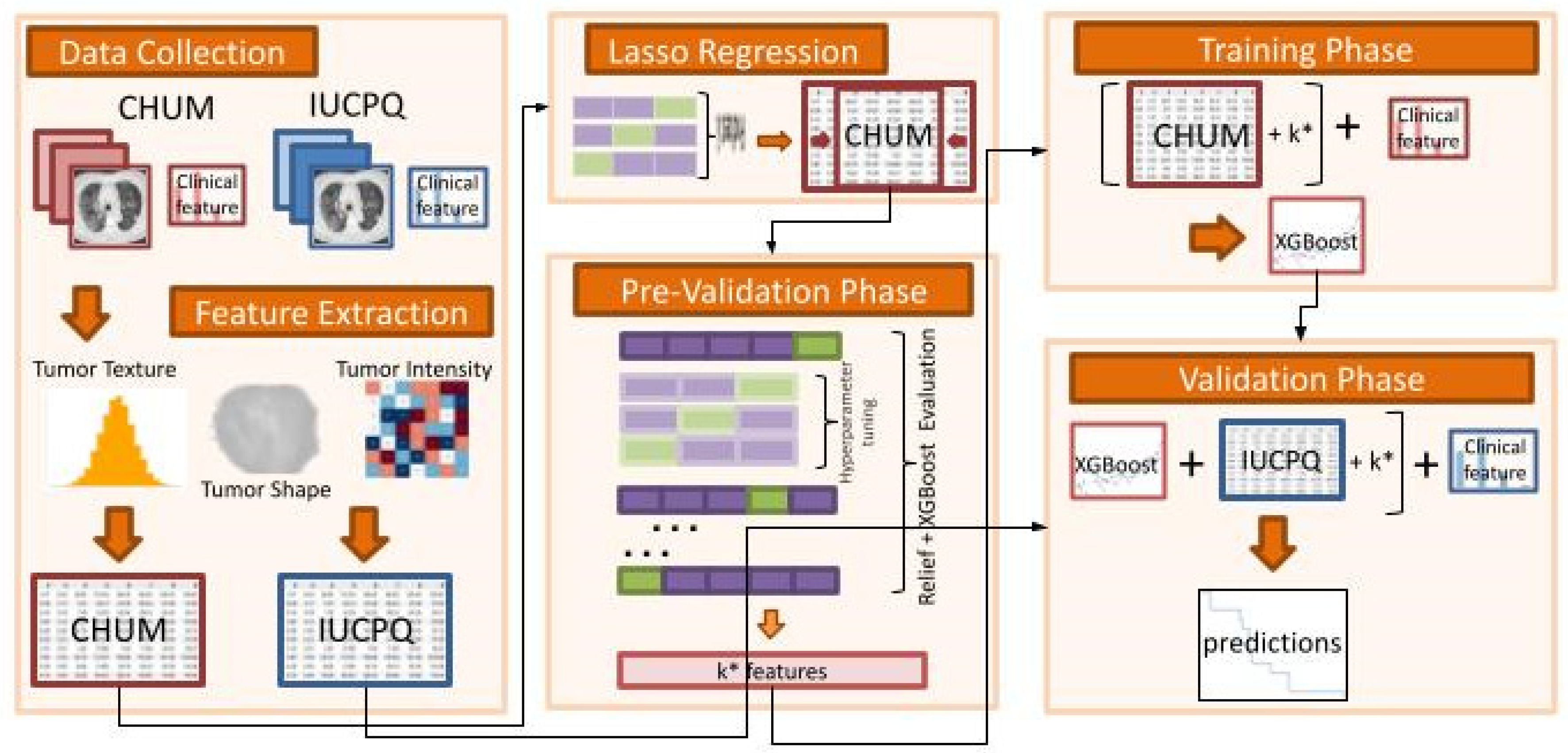
2.7. Analysis Framework and Model Overview
- Data Collection:
- ○
- The IUCPQ and CHUM centers served as the study’s two academic reference centers for thoracic oncology, and the study included a retrospective cohort of samples obtained from those institutions.
- Feature Extraction:
- ○
- To extract handcrafted radiomics features from the region of interest of CT scan data for CHUM and IUCPQ, we utilized the PyRadiomics Python package. There were 851 radiomics features.
- ○
- We performed the data standardization, i.e., all variables were required to have a mean of zero, and a standard deviation of one was done for both cohorts.
- Lasso Regression:
- ○
- As a first step feature selection method, we used Lasso regression for the OS-R task and Lasso Logistic regression with penalty ‘l1′ for the OS short-term and long-term survival binary task. The Lasso and Lasso Logistic regressions were implemented on the whole training cohort, with the main feature selection Relief and the XGBoost machine learning method applied separately in the next step. However, to find the best alpha for Lasso regression and C for Logistic regression, we applied grid-search with 5-fold cross validation. Then, we removed all features with coefficients equal to zero after training Lasso on the whole CHUM cohort.
- Pre-Validation Phase:
- ○
- Using the resulting features (with those that were retained after the LASSO), we incrementally selected features by employing the ReliefF feature selection method and XGBoost machine learning approach. This was performed in the pre-validation phase on the discovery dataset, which consisted of a 5-fold cross-validation with 10-times repetitions. At this stage, ReliefF feature selection method was employed for each fold.
- ○
- The highest C-index for OS-R and AUC for OS short-term and long-term survival was used to determine the best number of features.
- ○
- The hyperparameter tuning of XGBoost was also performed through a cross-validation using the GridSearchCV class of sklearn. The ReliefF feature selection was implemented using the Rebate [32] open-source library, and the XGBoost regressor and classifier were implemented using the XGBoost [33] library in Python (scikit-learn version 1.0.2, Python version 3.9.13, XGBoost version 1.6.2 and Skrebate version 0.62) [34].
- Training Phase (without clinical data):
- ○
- The XGBoost model with the best hyperparameter was trained on the discovery cohort (CHUM) with the best features based on the pre-validation phase.
- Validation Phase (without clinical data):
- ○
- The final model was validated on the independent cohort with best features (IUCPQ).
2.8. Radiomics-Clinical Model
2.9. Model Performance
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
3.2. Univariate Analysis of Clinical Variables
3.3. Radiomics Features
3.4. Univariate Analysis of Radiomics Features
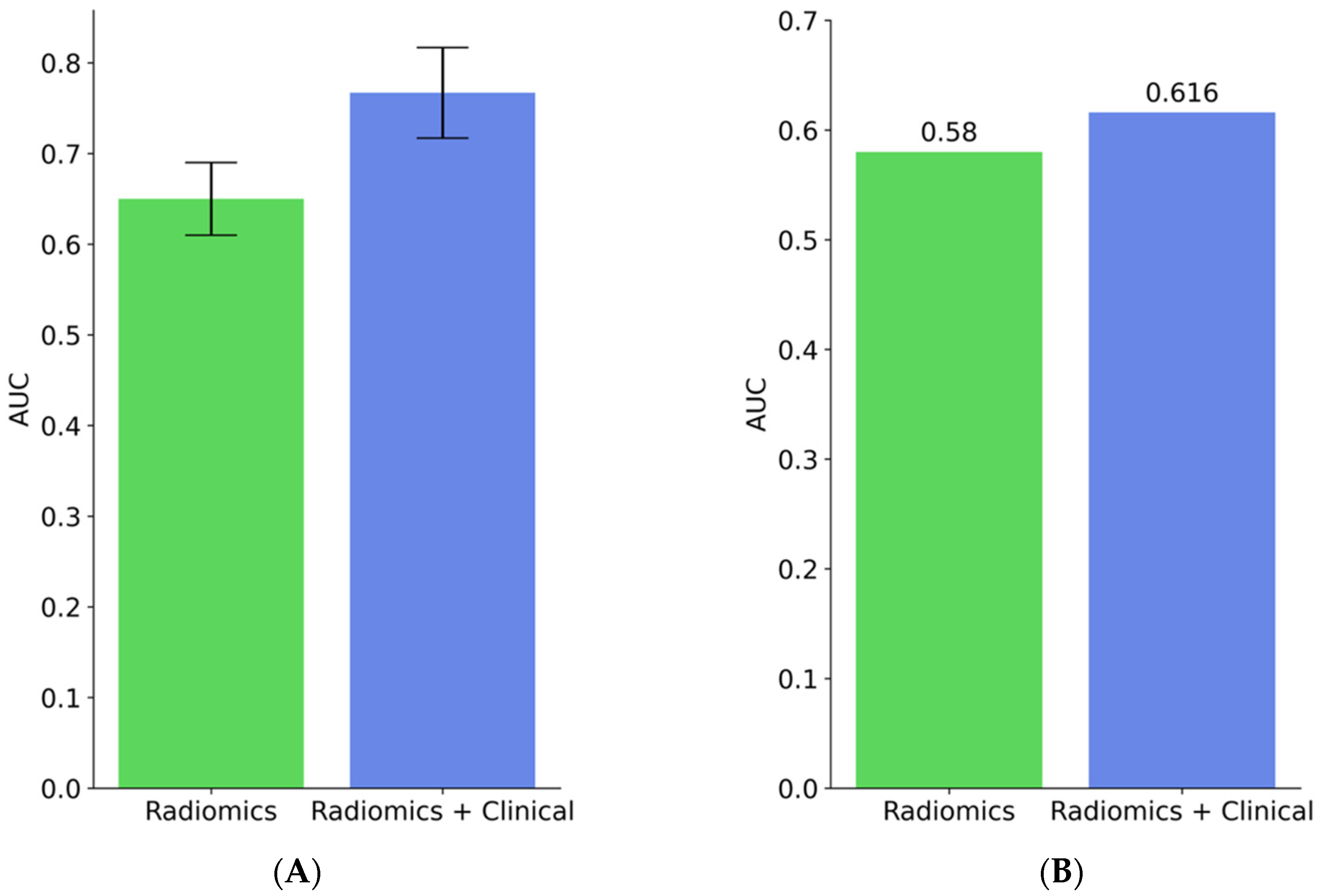
3.5. Model Evaluation
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zappa, C.; Mousa, S.A. Non-small cell lung cancer: Current treatment and future advances. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2016, 5, 288–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chan, B.A.; Hughes, B.G.M. Targeted therapy for non-small cell lung cancer: Current standards and the promise of the future. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2015, 4, 36–54. [Google Scholar]
- Arbour, K.C.; Riely, G.J. Systemic Therapy for Locally Advanced and Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Review. JAMA 2019, 322, 764–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shields, M.D.; Marin-Acevedo, J.A.; Pellini, B. Immunotherapy for Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Decade of Progress. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. Educ. Book 2021, 41, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ernani, V.; Ganti, A.K. Immunotherapy in treatment naïve advanced non-small cell lung cancer. J. Thorac. Dis. 2018, 10, S412–S421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ito, F.; Ernstoff, M. Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Cancer; Elsevier Health Sciences: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Borghaei, H.; Paz-Ares, L.; Horn, L.; Spigel, D.R.; Steins, M.; Ready, N.E.; Chow, L.Q.; Vokes, E.E.; Felip, E.; Holgado, E.; et al. Nivolumab versus Docetaxel in Advanced Nonsquamous Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 1627–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horn, L.; Spigel, D.R.; Vokes, E.E.; Holgado, E.; Ready, N.; Steins, M.; Poddubskaya, E.; Borghaei, H.; Felip, E.; Paz-Ares, L.; et al. Nivolumab versus Docetaxel in Previously Treated Patients with Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Two-Year Outcomes From Two Randomized, Open-Label, Phase III Trials (CheckMate 017 and CheckMate 057). J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 3924–3933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbst, R.S.; Baas, P.; Kim, D.-W.; Felip, E.; Pérez-Gracia, J.L.; Han, J.-Y.; Molina, J.; Kim, J.-H.; Arvis, C.D.; Ahn, M.-J.; et al. Pembrolizumab versus docetaxel for previously treated, PD-L1-positive, advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (KEYNOTE-010): A randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2016, 387, 1540–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batouty, N.M.; Saleh, G.A.; Sharafeldeen, A.; Kandil, H.; Mahmoud, A.; Shalaby, A.; Yaghi, M.; Khelifi, A.; Ghazal, M.; El-Baz, A. State of the art: Lung cancer staging using updated imaging modalities. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Jochems, A.; Refaee, T.; Ibrahim, A.; Yan, C.; Sanduleanu, S.; Woodruff, H.C.; Lambin, P. Structural and functional radiomics for lung cancer. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2021, 48, 3961–3974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yolchuyeva, S.; Giacomazzi, E.; Tonneau, M.; Lamaze, F.; Orain, M.; Coulombe, F.; Malo, J.; Belkaid, W.; Routy, B.; Joubert, P.; et al. Radiomics approaches to predict PD-L1 and PFS in advanced non-small cell lung patients treated with immunotherapy: A multi-institutional study. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 11065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aerts, H.J.W.L.; Velazquez, E.R.; Leijenaar, R.T.H.; Parmar, C.; Grossmann, P.; Carvalho, S.; Bussink, J.; Monshouwer, R.; Haibe-Kains, B.; Rietveld, D.; et al. Decoding tumour phenotype by noninvasive imaging using a quantitative radiomics approach. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zerunian, M.; Caruso, D.; Zucchelli, A.; Polici, M.; Capalbo, C.; Filetti, M.; Mazzuca, F.; Marchetti, P.; Laghi, A. CT based radiomic approach on first line pembrolizumab in lung cancer. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 6633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braghetto, A.; Marturano, F.; Paiusco, M.; Baiesi, M.; Bettinelli, A. Radiomics and deep learning methods for the prediction of 2-year overall survival in LUNG1 dataset. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 14132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Liu, D.; Li, L. PD-1/PD-L1 pathway: Current researches in cancer. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2020, 10, 727–742. [Google Scholar]
- Dang, T.O.; Ogunniyi, A.; Barbee, M.S.; Drilon, A. Pembrolizumab for the treatment of PD-L1 positive advanced or metastatic non-small cell lung cancer. Expert Rev. Anticancer Ther. 2016, 16, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brody, R.; Zhang, Y.; Ballas, M.; Siddiqui, M.K.; Gupta, P.; Barker, C.; Midha, A.; Walker, J. PD-L1 expression in advanced NSCLC: Insights into risk stratification and treatment selection from a systematic literature review. Lung Cancer 2017, 112, 200–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Pham, P. Breast Cancer: From Biology to Medicine; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Osman, A.F.I. A Multi-parametric MRI-Based Radiomics Signature and a Practical ML Model for Stratifying Glioblastoma Patients Based on Survival Toward Precision Oncology. Front. Comput. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van Griethuysen, J.J.M.; Fedorov, A.; Parmar, C.; Hosny, A.; Aucoin, N.; Narayan, V.; Beets-Tan, R.G.H.; Fillion-Robin, J.-C.; Pieper, S.; Aerts, H.J.W.L. Computational Radiomics System to Decode the Radiographic Phenotype. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, e104–e107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kononenko, I. Estimating Attributes: Analysis and Extensions of RELIEF. In Machine Learning: ECML-94; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1994; pp. 171–182. [Google Scholar]
- Urbanowicz, R.J.; Olson, R.S.; Schmitt, P.; Meeker, M.; Moore, J.H. Benchmarking relief-based feature selection methods for bioinformatics data mining. J. Biomed. Inform. 2018, 85, 168–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naheed, N.; Shaheen, M.; Khan, S.A.; Alawairdhi, M.; Khan, M.A. Importance of Features Selection, Attributes Selection, Challenges and Future Directions for Medical Imaging Data: A Review. Comput. Model. Eng. Sci. 2020, 125, 314–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, P.; Deng, S.; Li, H. Improved Relief Weight Feature Selection Algorithm Based on Relief and Mutual Information. Information 2021, 12, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Guestrin, C. XGBoost: A Scalable Tree Boosting System. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, Association for Computing Machinery, New York, NY, USA, 6–11 August 2016; pp. 785–794. [Google Scholar]
- González-Recio, O.; Jiménez-Montero, J.A.; Alenda, R. The gradient boosting algorithm and random boosting for genome-assisted evaluation in large data sets. J. Dairy Sci. 2013, 96, 614–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mayr, A.; Binder, H.; Gefeller, O.; Schmid, M. The Evolution of Boosting Algorithms. Methods Inf. Med. 2014, 53, 419–427. [Google Scholar]
- Ogunleye, A.; Wang, Q.-G. XGBoost Model for Chronic Kidney Disease Diagnosis. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinform. 2020, 17, 2131–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, B.; Zhang, L.; Ning, P.; Ding, F.; Wu, F.; Lu, G.; Geng, Y.; Ma, J. Preoperative prediction for pathological grade of hepatocellular carcinoma via machine learning-based radiomics. Eur. Radiol. 2020, 30, 6924–6932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, R.S.; Urbanowicz, R.J. Installation—Scikit-Rebate. Available online: https://epistasislab.github.io/scikit-rebate/installing/ (accessed on 1 March 2023).
- XGBoost Library. Available online: https://xgboost.readthedocs.io/en/stable/index.html (accessed on 14 March 2023).
- Garreta, R.; Moncecchi, G. Learning Scikit-Learn: Machine Learning in Python; Packt Publishing Ltd.: Birmingham, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Manem, V.S.K. Development and validation of genomic predictors of radiation sensitivity using preclinical data. BMC Cancer 2021, 21, 937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oken, M.M.; Creech, R.H.; Tormey, D.C.; Horton, J.; Davis, T.E.; McFadden, E.T.; Carbone, P. Toxicity and response criteria of the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 1982, 5, 649–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ammari, S.; Sallé de Chou, R.; Assi, T.; Touat, M.; Chouzenoux, E.; Quillent, A.; Limkin, E.; Dercle, L.; Hadchiti, J.; Elhaik, M.; et al. Machine-Learning-Based Radiomics MRI Model for Survival Prediction of Recurrent Glioblastomas Treated with Bevacizumab. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Horng, H.; Roshkovan, L.; Weeks, J.K.; Hershman, M.; Noël, P.; Luna, J.M.; Cohen, E.A.; Pantalone, L.; Shinohara, R.T.; et al. Development of a robust radiomic biomarker of progression-free survival in advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients treated with first-line immunotherapy. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 9993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Feature | p-Value (OS-R) | p-Value (OS Short- and Long-Term Survivors) |
|---|---|---|
| Age | 0.74255 | 0.93852 |
| Gender | 0.11605 | 0.13019 |
| ECOG | <10−6 | 0.0039 |
| Smoking status | 0.89194 | 0.93142 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yolchuyeva, S.; Giacomazzi, E.; Tonneau, M.; Ebrahimpour, L.; Lamaze, F.C.; Orain, M.; Coulombe, F.; Malo, J.; Belkaid, W.; Routy, B.; et al. A Radiomics-Clinical Model Predicts Overall Survival of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients Treated with Immunotherapy: A Multicenter Study. Cancers 2023, 15, 3829. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15153829
Yolchuyeva S, Giacomazzi E, Tonneau M, Ebrahimpour L, Lamaze FC, Orain M, Coulombe F, Malo J, Belkaid W, Routy B, et al. A Radiomics-Clinical Model Predicts Overall Survival of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients Treated with Immunotherapy: A Multicenter Study. Cancers. 2023; 15(15):3829. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15153829
Chicago/Turabian StyleYolchuyeva, Sevinj, Elena Giacomazzi, Marion Tonneau, Leyla Ebrahimpour, Fabien C. Lamaze, Michele Orain, François Coulombe, Julie Malo, Wiam Belkaid, Bertrand Routy, and et al. 2023. "A Radiomics-Clinical Model Predicts Overall Survival of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients Treated with Immunotherapy: A Multicenter Study" Cancers 15, no. 15: 3829. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15153829
APA StyleYolchuyeva, S., Giacomazzi, E., Tonneau, M., Ebrahimpour, L., Lamaze, F. C., Orain, M., Coulombe, F., Malo, J., Belkaid, W., Routy, B., Joubert, P., & Manem, V. S. K. (2023). A Radiomics-Clinical Model Predicts Overall Survival of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients Treated with Immunotherapy: A Multicenter Study. Cancers, 15(15), 3829. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15153829







