CBCT-Based Dose Monitoring and Adaptive Planning Triggers in Head and Neck PBS Proton Therapy
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Selection and Image Data
2.2. Treatment Planning
2.3. Image Set Overview
2.4. Ground Truth CT (gtCT) and Defining Adaptive Therapy Triggers
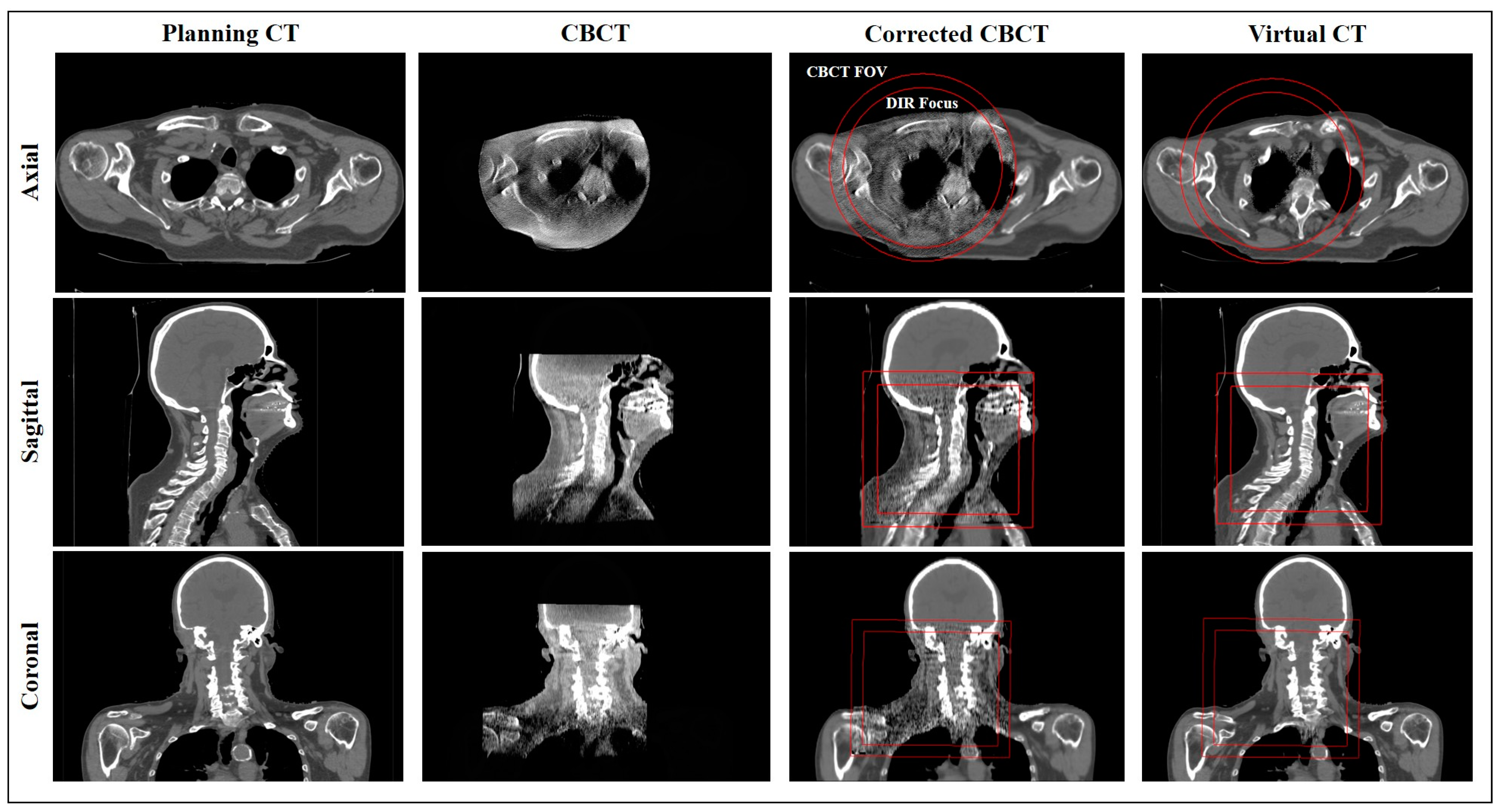
2.5. Corrected CBCT (corrCBCT)
2.6. Virtual CT (virtCT)
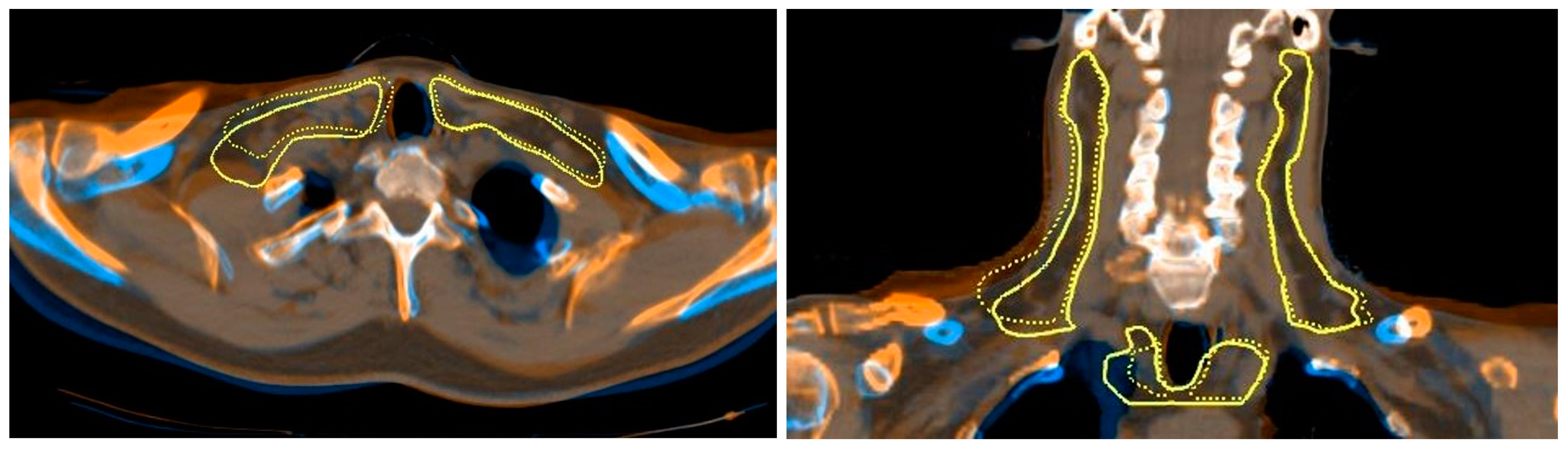
2.7. Deformable Image Registration
2.8. Dose Metrics and Statistical Testing
2.9. CBCT Reconstruction Parameter Testing
3. Results
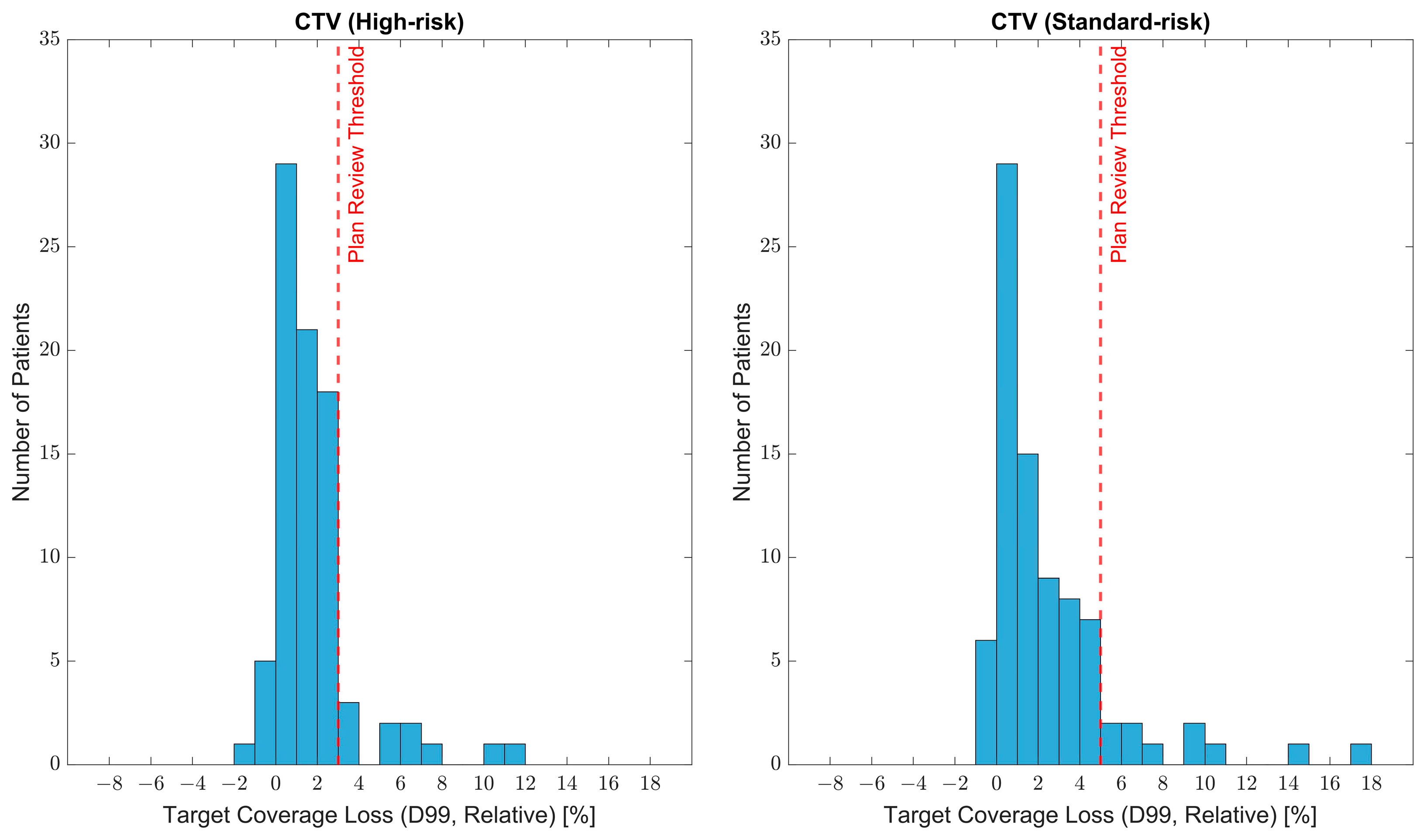
3.1. Target Coverage Loss and Adaptive Planning Trigger Criteria
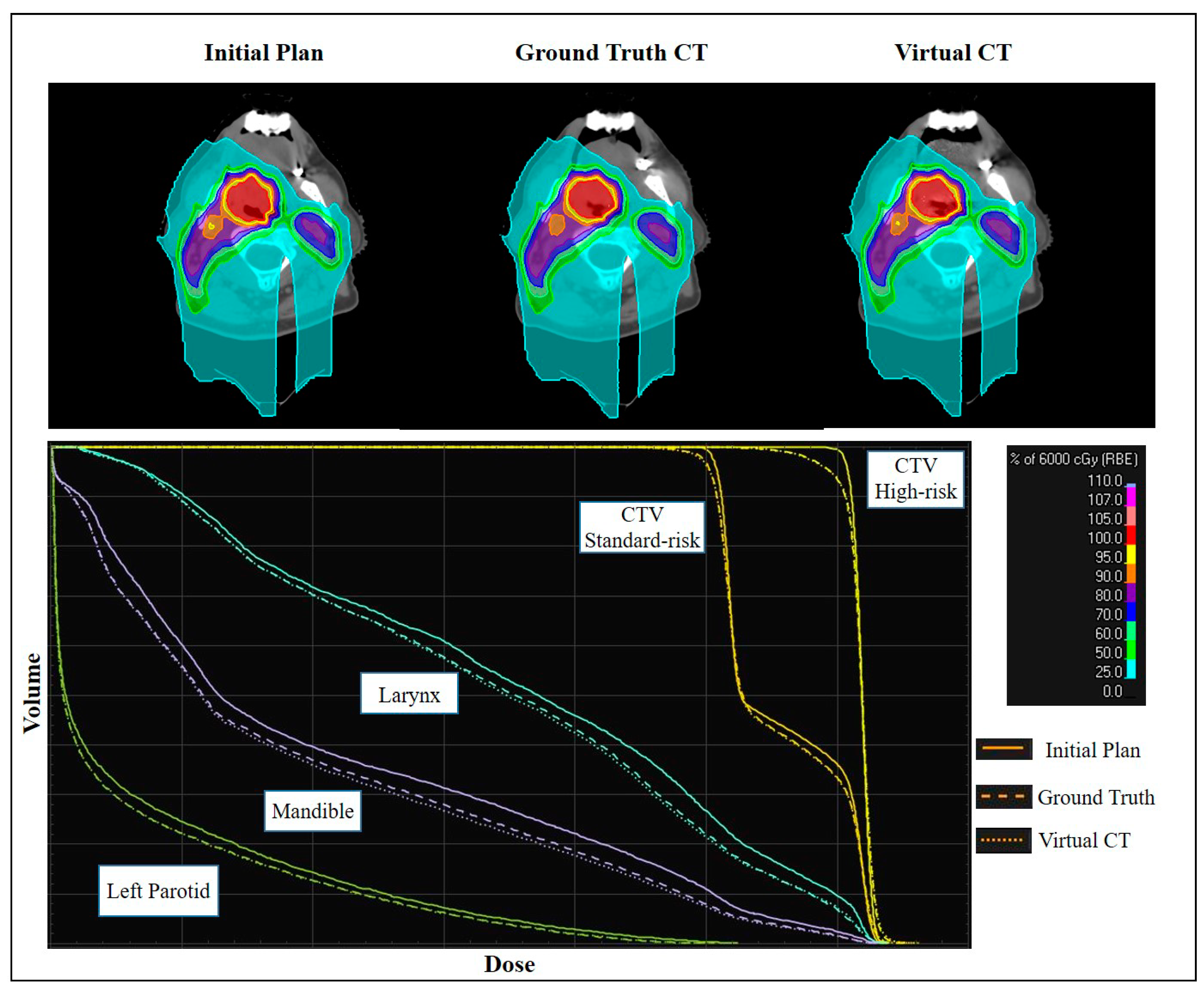
3.2. Comparing Dose Accuracy of Synthetic CTs and Verification CT
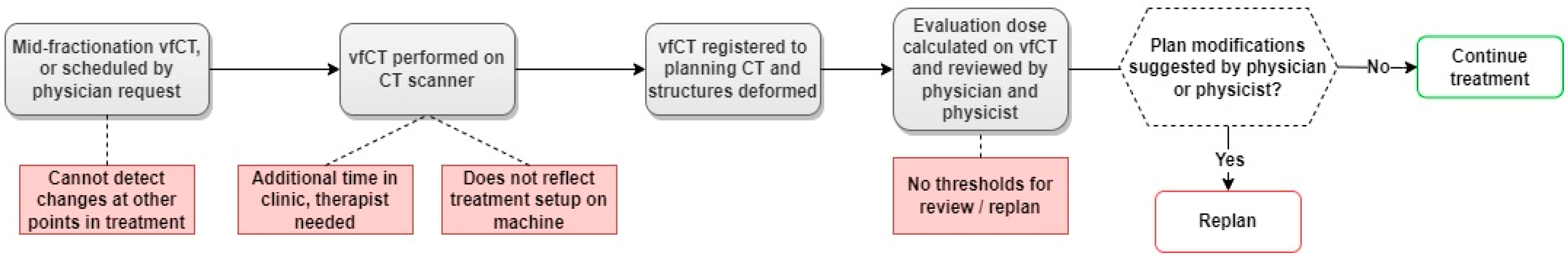
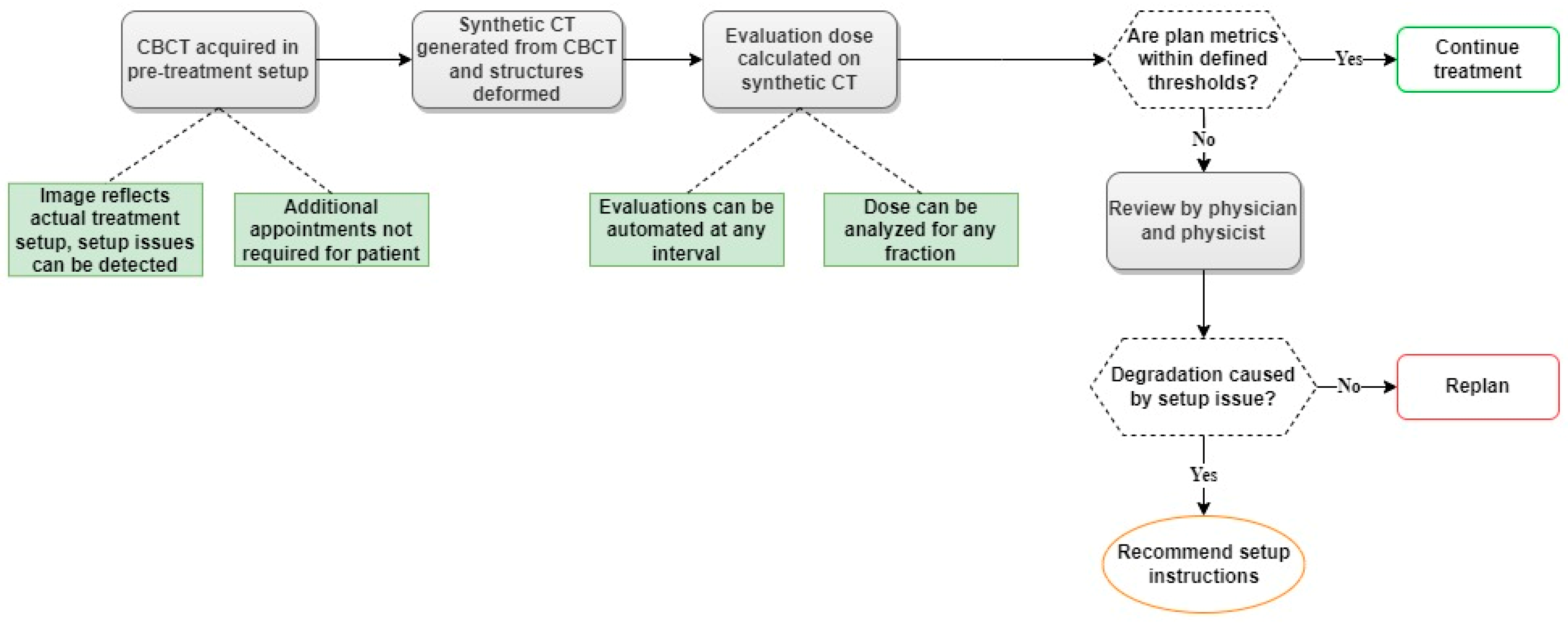
3.3. Established Workflow for Dose Monitoring on CBCT-Based Synthetic CTs
4. Discussion
4.1. Cohort Findings
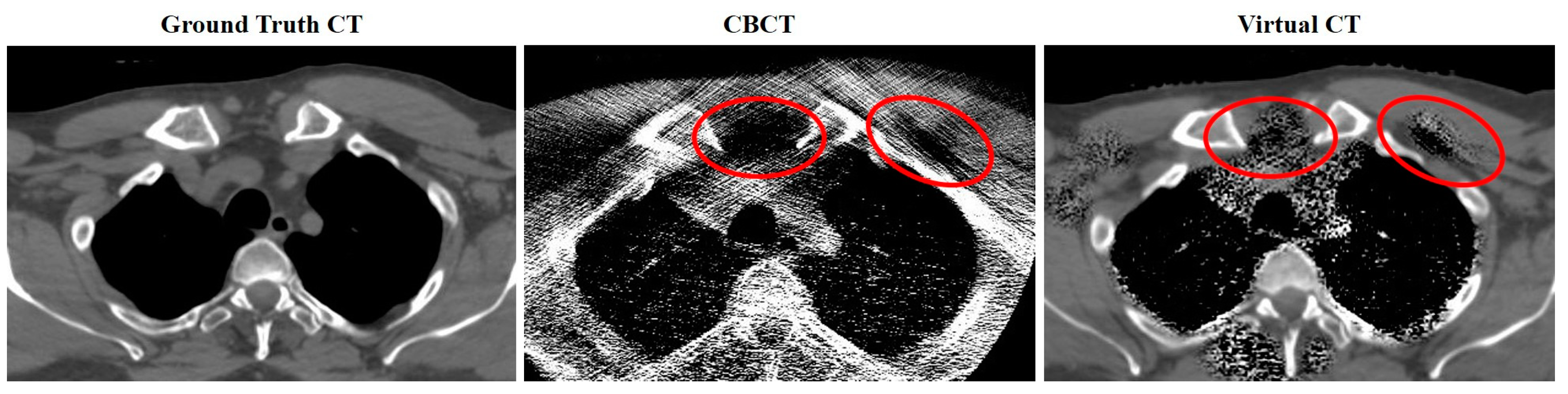
4.2. Image Accuracy
4.3. Workflow Improvement
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Morgan, H.E.; Sher, D.J. Adaptive Radiotherapy for Head and Neck Cancer. Cancers Head Neck 2020, 5, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huiskes, M.; Astreinidou, E.; Kong, W.; Breedveld, S.; Heijmen, B.; Rasch, C. Dosimetric Impact of Adaptive Proton Therapy in Head and Neck Cancer—A Review. Clin. Transl. Radiat. Oncol. 2023, 39, 100598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alves, N.; Dias, J.M.; Rocha, H.; Ventura, T.; Mateus, J.; Capela, M.; Khouri, L.; Lopes, M. do C. Assessing the Need for Adaptive Radiotherapy in Head and Neck Cancer Patients Using an Automatic Planning Tool. Rep. Pr. Oncol. Radiother 2021, 26, 423–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surucu, M.; Shah, K.K.; Roeske, J.C.; Choi, M.; Small, W.; Emami, B. Adaptive Radiotherapy for Head and Neck Cancer. Technol Cancer Res. Treat 2017, 16, 218–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Hu, W.; Wang, W.; Chen, P.; Ding, W.; Luo, W. Replanning During Intensity Modulated Radiation Therapy Improved Quality of Life in Patients With Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2013, 85, e47–e54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Wan, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Deng, X.; Xie, C.; Wu, S. The Role of Replanning in Fractionated Intensity Modulated Radiotherapy for Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. Radiother. Oncol. 2011, 98, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, A.C.; Frank, S.J.; Garden, A.S.; Rosenthal, D.I.; Fuller, C.D.; Gunn, G.B.; Reddy, J.P.; Morrison, W.H.; Williamson, T.D.; Holliday, E.B.; et al. Intensity Modulated Proton Therapy (IMPT)—The Future of IMRT for Head and Neck Cancer. Oral Oncol. 2019, 88, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchard, P.; Gunn, G.B.; Lin, A.; Foote, R.L.; Lee, N.Y.; Frank, S.J. Proton Therapy for Head and Neck Cancers. Semin. Radiat. Oncol. 2018, 28, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.K.; Leeman, J.E.; Riaz, N.; McBride, S.; Tsai, C.J.; Lee, N.Y. Proton Therapy for Head and Neck Cancer. Curr. Treat. Options Oncol. 2018, 19, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steneker, M.; Lomax, A.; Schneider, U. Intensity Modulated Photon and Proton Therapy for the Treatment of Head and Neck Tumors. Radiother. Oncol. 2006, 80, 263–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van de Water, T.A.; Lomax, A.J.; Bijl, H.P.; de Jong, M.E.; Schilstra, C.; Hug, E.B.; Langendijk, J.A. Potential Benefits of Scanned Intensity-Modulated Proton Therapy Versus Advanced Photon Therapy With Regard to Sparing of the Salivary Glands in Oropharyngeal Cancer. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2011, 79, 1216–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minatogawa, H.; Yasuda, K.; Dekura, Y.; Takao, S.; Matsuura, T.; Yoshimura, T.; Suzuki, R.; Yokota, I.; Fujima, N.; Onimaru, R.; et al. Potential Benefits of Adaptive Intensity-Modulated Proton Therapy in Nasopharyngeal Carcinomas. J. Appl. Clin. Med. Phys. 2021, 22, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lester-Coll, N.H.; Margalit, D.N. Modeling the Potential Benefits of Proton Therapy for Patients With Oropharyngeal Head and Neck Cancer. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2019, 104, 563–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stützer, K.; Jakobi, A.; Bandurska-Luque, A.; Barczyk, S.; Arnsmeyer, C.; Löck, S.; Richter, C. Potential Proton and Photon Dose Degradation in Advanced Head and Neck Cancer Patients by Intratherapy Changes. J. Appl. Clin. Med. Phys. 2017, 18, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thummerer, A.; Zaffino, P.; Meijers, A.; Marmitt, G.G.; Seco, J.; Steenbakkers, R.J.H.M.; Langendijk, J.A.; Both, S.; Spadea, M.F.; Knopf, A.C. Comparison of CBCT Based Synthetic CT Methods Suitable for Proton Dose Calculations in Adaptive Proton Therapy. Phys. Med. Biol. 2020, 65, 095002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Liang, J.; Zhou, D.; Krauss, D.J.; Chen, P.Y.; Yan, D. Dosimetric Evaluation of Incorporating Patient Geometric Variations Into Adaptive Plan Optimization Through Probabilistic Treatment Planning in Head and Neck Cancers. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2018, 101, 985–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhide, S.A.; Davies, M.; Burke, K.; McNair, H.A.; Hansen, V.; Barbachano, Y.; El-Hariry, I.A.; Newbold, K.; Harrington, K.J.; Nutting, C.M. Weekly Volume and Dosimetric Changes During Chemoradiotherapy With Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy for Head and Neck Cancer: A Prospective Observational Study. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2010, 76, 1360–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mnejja, W.; Daoud, H.; Fourati, N.; Sahnoun, T.; Siala, W.; Farhat, L.; Daoud, J. Dosimetric Impact on Changes in Target Volumes during Intensity-Modulated Radiotherapy for Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. Rep Pr. Oncol Radiother 2020, 25, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, P.H.; Chen, C.-C.; Ahn, A.I.; Hong, L.; Scripes, P.G.; Shen, J.; Lee, C.-C.; Miller, E.; Kalnicki, S.; Garg, M.K. Adaptive Planning in Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy for Head and Neck Cancers: Single-Institution Experience and Clinical Implications. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2011, 80, 677–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikh, K.; Liu, D.; Li, H.; Acharya, S.; Ladra, M.M.; Hrinivich, W.T. Dosimetric Evaluation of Cone-Beam CT-Based Synthetic CTs in Pediatric Patients Undergoing Intensity-Modulated Proton Therapy. J. Appl. Clin. Med. Phys. 2022, 23, e13604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanforth, A.; Lin, L.; Beitler, J.J.; Janopaul-Naylor, J.R.; Chang, C.-W.; Press, R.H.; Patel, S.A.; Zhao, J.; Eaton, B.; Schreibmann, E.E.; et al. Onboard Cone-Beam CT-Based Replan Evaluation for Head and Neck Proton Therapy. J. Appl. Clin. Med. Phys. 2022, 23, e13550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veiga, C.; Alshaikhi, J.; Amos, R.; Lourenço, A.M.; Modat, M.; Ourselin, S.; Royle, G.; McClelland, J.R. Cone-Beam Computed Tomography and Deformable Registration-Based “Dose of the Day” Calculations for Adaptive Proton Therapy. Int. J. Part. Ther. 2015, 2, 404–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veiga, C.; Janssens, G.; Teng, C.-L.; Baudier, T.; Hotoiu, L.; McClelland, J.R.; Royle, G.; Lin, L.; Yin, L.; Metz, J.; et al. First Clinical Investigation of Cone Beam Computed Tomography and Deformable Registration for Adaptive Proton Therapy for Lung Cancer. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2016, 95, 549–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veiga, C.; Janssens, G.; Baudier, T.; Hotoiu, L.; Brousmiche, S.; McClelland, J.; Teng, C.-L.; Yin, L.; Royle, G.; Teo, B.-K.K. A Comprehensive Evaluation of the Accuracy of CBCT and Deformable Registration Based Dose Calculation in Lung Proton Therapy. Biomed. Phys. Eng. Express 2017, 3, 015003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurz, C.; Dedes, G.; Resch, A.; Reiner, M.; Ganswindt, U.; Nijhuis, R.; Thieke, C.; Belka, C.; Parodi, K.; Landry, G. Comparing Cone-Beam CT Intensity Correction Methods for Dose Recalculation in Adaptive Intensity-Modulated Photon and Proton Therapy for Head and Neck Cancer. Acta Oncol. 2015, 54, 1651–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurz, C.; Kamp, F.; Park, Y.-K.; Zöllner, C.; Rit, S.; Hansen, D.; Podesta, M.; Sharp, G.C.; Li, M.; Reiner, M.; et al. Investigating Deformable Image Registration and Scatter Correction for CBCT-Based Dose Calculation in Adaptive IMPT. Med. Phys. 2016, 43, 5635–5646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landry, G.; Hansen, D.; Kamp, F.; Li, M.; Hoyle, B.; Weller, J.; Parodi, K.; Belka, C.; Kurz, C. Comparing Unet Training with Three Different Datasets to Correct CBCT Images for Prostate Radiotherapy Dose Calculations. Phys. Med. Biol. 2019, 64, 035011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, A.G.; Park, Y.-K.; Elstrøm, U.V.; Petersen, J.B.B.; Sharp, G.C.; Winey, B.; Dong, L.; Muren, L.P. Evaluation of an a Priori Scatter Correction Algorithm for Cone-Beam Computed Tomography Based Range and Dose Calculations in Proton Therapy. Phys. Imaging Radiat. Oncol. 2020, 16, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.-K.; Sharp, G.C.; Phillips, J.; Winey, B.A. Proton Dose Calculation on Scatter-Corrected CBCT Image: Feasibility Study for Adaptive Proton Therapy. Med. Phys. 2015, 42, 4449–4459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szmul, A.; Taylor, S.; Lim, P.; Cantwell, J.; Moreira, I.; Zhang, Y.; D’Souza, D.; Moinuddin, S.; Gaze, M.; Gains, J.; et al. Deep Learning Based Synthetic CT from Cone Beam CT Generation for Abdominal Paediatric Radiotherapy. Phys. Med. Biol. 2023, 68, 105006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, D.C.; Landry, G.; Kamp, F.; Li, M.; Belka, C.; Parodi, K.; Kurz, C. ScatterNet: A Convolutional Neural Network for Cone-Beam CT Intensity Correction. Med. Phys. 2018, 45, 4916–4926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harms, J.; Lei, Y.; Wang, T.; McDonald, M.; Ghavidel, B.; Stokes, W.; Curran, W.J.; Zhou, J.; Liu, T.; Yang, X. Cone-Beam CT-Derived Relative Stopping Power Map Generation via Deep Learning for Proton Radiotherapy. Med. Phys. 2020, 47, 4416–4427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arai, K.; Kadoya, N.; Kato, T.; Endo, H.; Komori, S.; Abe, Y.; Nakamura, T.; Wada, H.; Kikuchi, Y.; Takai, Y.; et al. Feasibility of CBCT-Based Proton Dose Calculation Using a Histogram-Matching Algorithm in Proton Beam Therapy. Phys. Med. 2017, 33, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- 4.8. Image Conversion. In RayStation 12A Reference Manual; RaySearch Laboratories AB: Stockholm, Sweden, 2022.
- Thing, R.S.; Nilsson, R.; Andersson, S.; Berg, M.; Lund, M.D. Evaluation of CBCT Based Dose Calculation in the Thorax and Pelvis Using Two Generic Algorithms. Phys. Med. 2022, 103, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchant, T.E.; Moore, C.J.; Rowbottom, C.G.; MacKay, R.I.; Williams, P.C. Shading Correction Algorithm for Improvement of Cone-Beam CT Images in Radiotherapy. Phys. Med. Biol. 2008, 53, 5719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weistrand, O.; Svensson, S. The ANACONDA Algorithm for Deformable Image Registration in Radiotherapy. Med. Phys. 2015, 42, 40–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, A.D.; Nill, S.; Huber, P.E.; Bendl, R.; Debus, J.; Münter, M.W. A Clinical Concept for Interfractional Adaptive Radiation Therapy in the Treatment of Head and Neck Cancer. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2012, 82, 590–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deiter, N.; Chu, F.; Lenards, N.; Hunzeker, A.; Lang, K.; Mundy, D. Evaluation of Replanning in Intensity-Modulated Proton Therapy for Oropharyngeal Cancer: Factors Influencing Plan Robustness. Med. Dosim. 2020, 45, 384–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scandurra, D.; Meijer, T.W.H.; Free, J.; van den Hoek, J.G.M.; Kelder, L.; Oldehinkel, E.; Steenbakkers, R.J.H.M.; Both, S.; Langendijk, J.A. Evaluation of Robustly Optimised Intensity Modulated Proton Therapy for Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. Radiother. Oncol. 2022, 168, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Su, J.; Wei, R.; Yang, H.; Hong, J.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, G.; Li, L. Different Setup Errors Assessed by Weekly Cone-Beam Computed Tomography on Different Registration in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Treated with Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy. OTT 2015, 8, 2545–2553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hamming, V.C.; Andersson, S.; Maduro, J.H.; Langendijk, J.A.; Both, S.; Sijtsema, N.M. Daily Dose Evaluation Based on Corrected CBCTs for Breast Cancer Patients: Accuracy of Dose and Complication Risk Assessment. Radiat. Oncol. 2022, 17, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taasti, V.T.; Hattu, D.; Peeters, S.; van der Salm, A.; van Loon, J.; de Ruysscher, D.; Nilsson, R.; Andersson, S.; Engwall, E.; Unipan, M.; et al. Clinical Evaluation of Synthetic Computed Tomography Methods in Adaptive Proton Therapy of Lung Cancer Patients. Phys. Imaging Radiat. Oncol. 2023, 27, 100459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Hara, C.J.; Bird, D.; Al-Qaisieh, B.; Speight, R. Assessment of CBCT–Based Synthetic CT Generation Accuracy for Adaptive Radiotherapy Planning. J. Appl. Clin. Med. Phys. 2022, 23, e13737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Image Dimensions (X, Y, Z) | Voxel Size (mm) (X, Y, Z) | Field-of-View (cm) | kVp | mAs | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CBCT | 512, 512, 110 | 0.54, 0.54, 2.50 | 26 | 100 | 110 |
| Planning CT | 512, 512, 387 | 1.17, 1.17, 1.00 | 60 | 140 | Auto mAs |
| Verification CT | 512, 512, 387 | 1.17, 1.17, 1.00 | 60 | 140 | Auto mAs |
| High-Risk CTV (N = 84) | Standard-Risk CTV (N = 84) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average discrepancy from ground truth (%) |ΔD99| | p-value | Average discrepancy from ground truth (%) |ΔD99| | p-value | |
| Verification CT | 1.1 ± 1.4 | 1.8 ± 2.6 | ||
| Corrected CBCT | 0.7 ± 0.7 | 0.04 | 0.5 ± 0.7 | <0.0001 |
| Virtual CT | 0.4 ± 0.5 | <0.0001 | 0.5 ± 0.6 | <0.0001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Reiners, K.; Dagan, R.; Holtzman, A.; Bryant, C.; Andersson, S.; Nilsson, R.; Hong, L.; Johnson, P.; Zhang, Y. CBCT-Based Dose Monitoring and Adaptive Planning Triggers in Head and Neck PBS Proton Therapy. Cancers 2023, 15, 3881. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15153881
Reiners K, Dagan R, Holtzman A, Bryant C, Andersson S, Nilsson R, Hong L, Johnson P, Zhang Y. CBCT-Based Dose Monitoring and Adaptive Planning Triggers in Head and Neck PBS Proton Therapy. Cancers. 2023; 15(15):3881. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15153881
Chicago/Turabian StyleReiners, Keaton, Roi Dagan, Adam Holtzman, Curtis Bryant, Sebastian Andersson, Rasmus Nilsson, Liu Hong, Perry Johnson, and Yawei Zhang. 2023. "CBCT-Based Dose Monitoring and Adaptive Planning Triggers in Head and Neck PBS Proton Therapy" Cancers 15, no. 15: 3881. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15153881
APA StyleReiners, K., Dagan, R., Holtzman, A., Bryant, C., Andersson, S., Nilsson, R., Hong, L., Johnson, P., & Zhang, Y. (2023). CBCT-Based Dose Monitoring and Adaptive Planning Triggers in Head and Neck PBS Proton Therapy. Cancers, 15(15), 3881. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15153881





