Metabolomics of Duodenal Juice for Biliary Tract Cancer Diagnosis
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. NMR Measurements and Analysis of Metabolomics Data
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
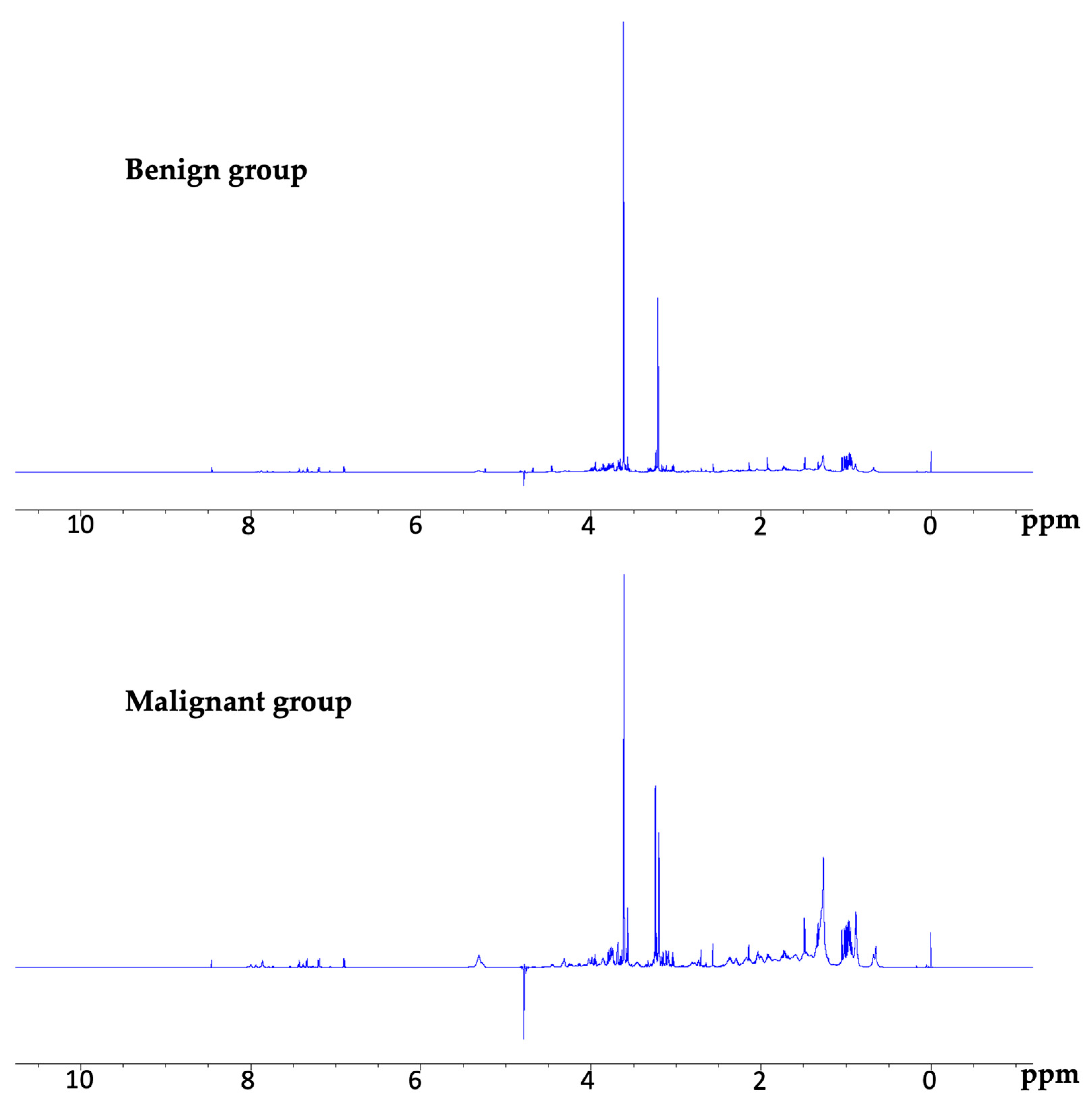
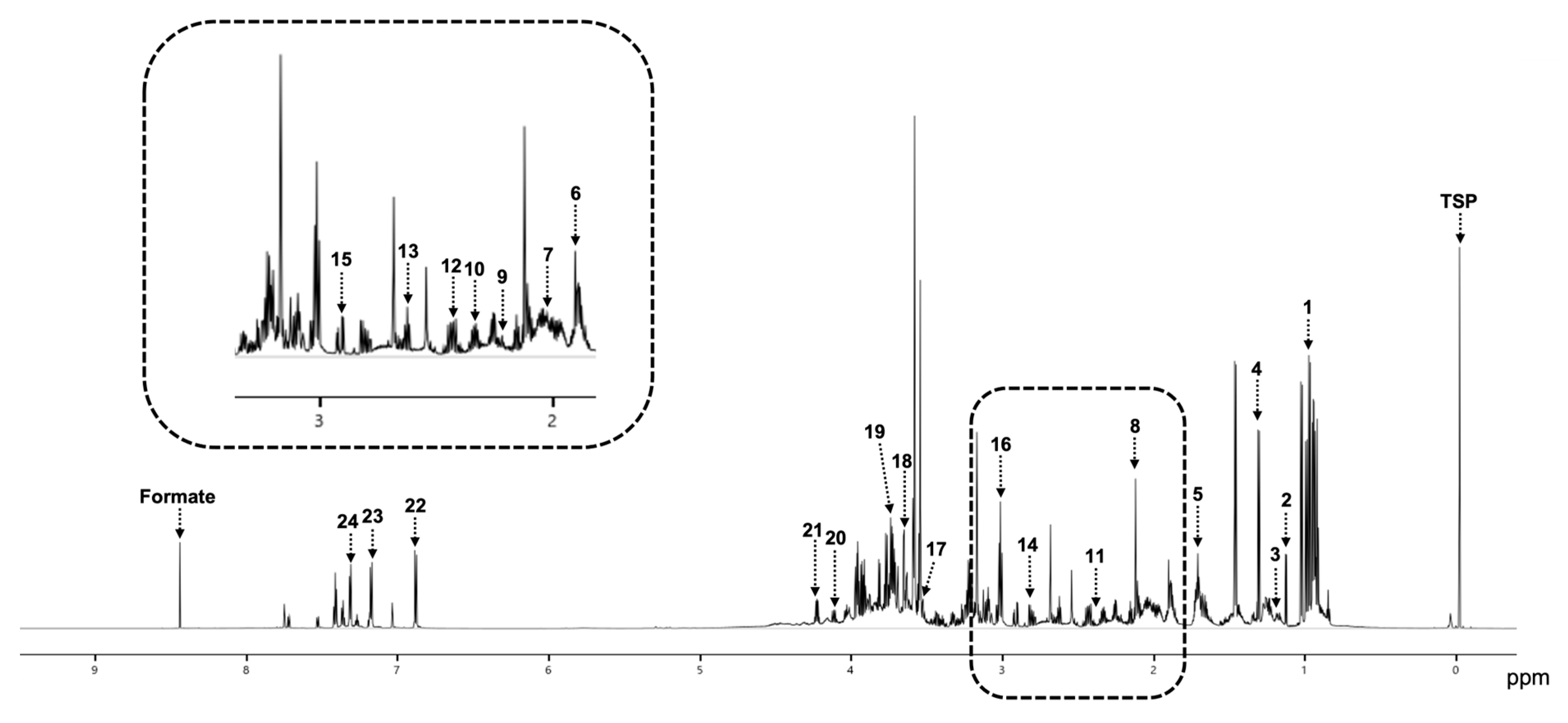
3.2. NMR Spectra
3.3. Detection of Metabolites in the Malignant and Benign Groups
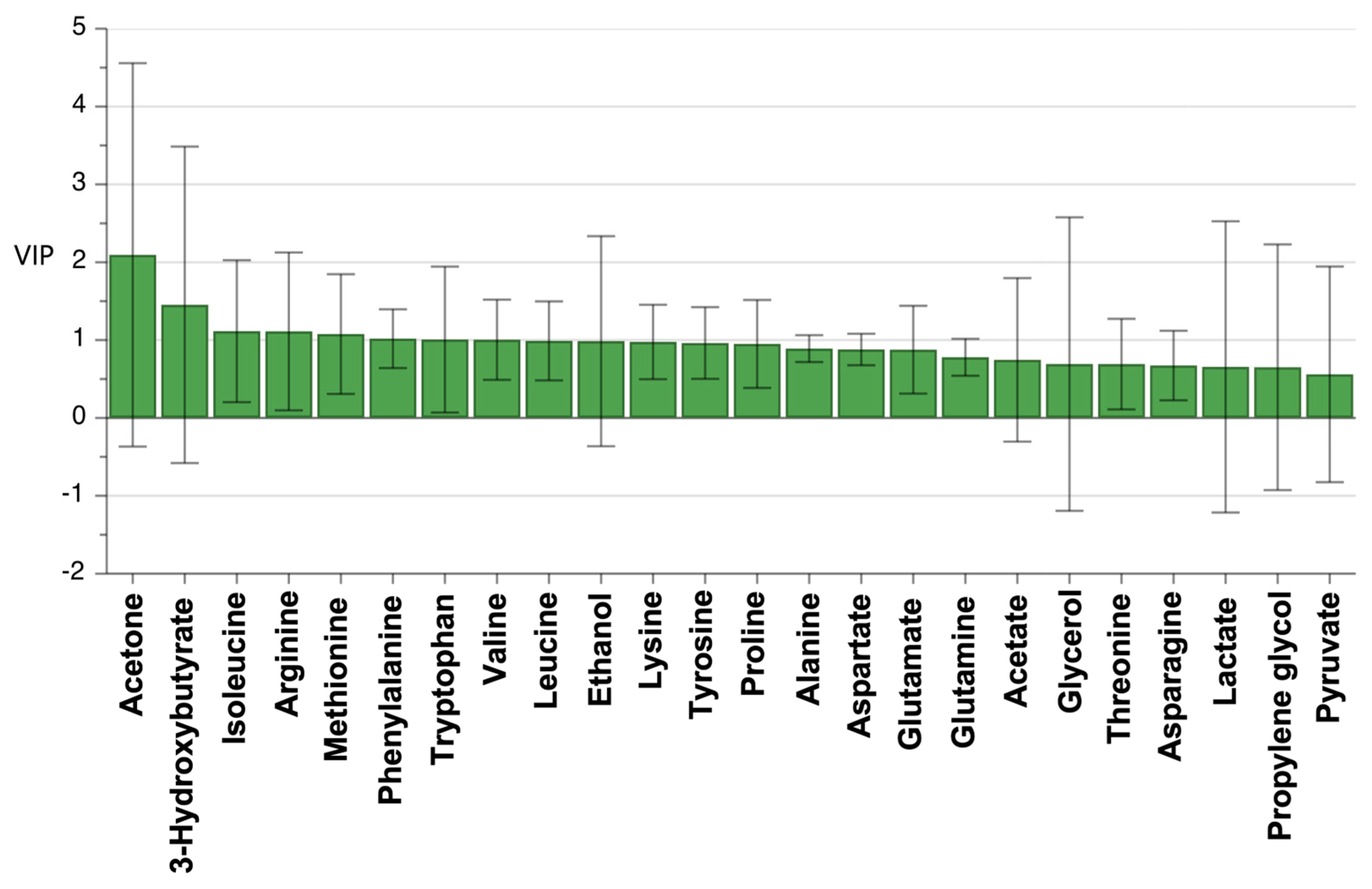
3.4. Statistical Analysis Using OPLS-DA
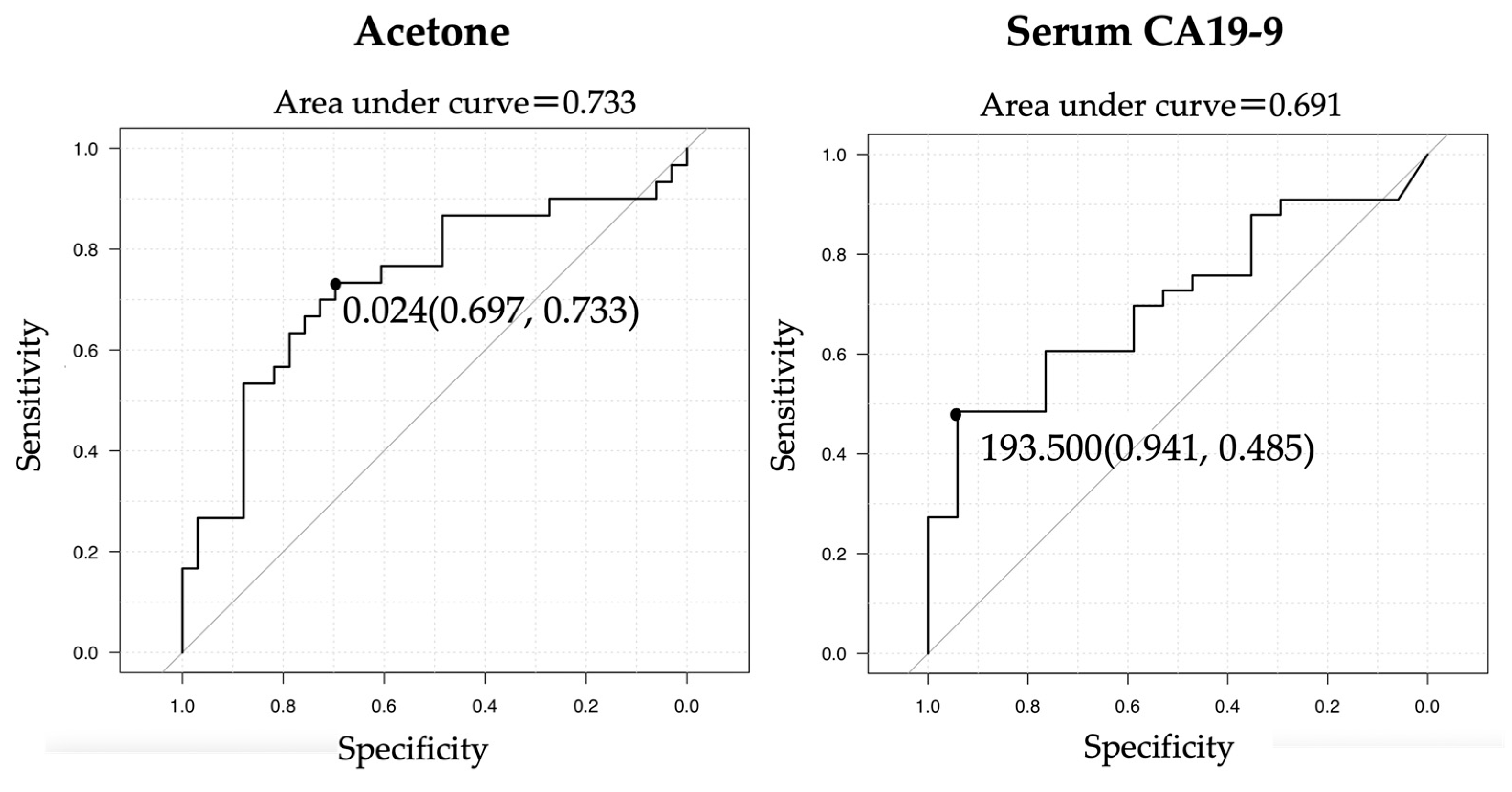
3.5. ROC Curves of CA19-9 and Acetone for a Diagnosis of Biliary Tract Cancer
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rebecca, L.S.; Kimberly, D.M.; Ahmedin, J. Cancer Statistics. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2019, 69, 7–34. [Google Scholar]
- Endo, I.; Gonen, M.; Yopp, A.C.; Dalal, K.M.; Zhou, Q.; Klimstra, D.; D’Angelica, M.; DeMatteo, R.P.; Fong, Y.; Schwartz, L.; et al. Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: Rising frequency, improved survival, and determinants of outcome after resection. Ann. Surg. 2008, 248, 84–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinberg, W. The clinical utility of the CA 19-9 tumor-associated antigen. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 1990, 85, 350–355. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Perkins, G.L.; Slater, E.D.; Sanders, G.K.; Prichard, J.G. Serum tumor markers. Am. Fam. Physician 2003, 68, 1075–1082. [Google Scholar]
- Navaneethan, U.; Njei, B.; Lourdusamy, V.; Konjeti, R.; Vargo, J.J.; Parsi, M.A. Comparative effectiveness of biliary brush cytology and intraductal biopsy for detection of malignant biliary strictures: A systematic review and meta–analysis. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2015, 81, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatfield, A.R.; Smithies, A.; Wilkins, R.; Levi, A.J. Assessment of endoscopic retrograde cholangio-pancreatography (ERCP) and pure pancreatic juice cytology in patients with pancreatic disease. Gut 1976, 17, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kameya, S.; Kuno, N.; Kasugai, T. The diagnosis of pancreatic cancer by pancreatic juice cytology. Acta Cytol. 1981, 25, 354–360. [Google Scholar]
- Siiki, A.; Tamminen, A.; Tomminen, T.; Kuusanmaki, P. ERCP procedures in a Finnish community hospital: A retrospective analysis of 1207 cases. Scand. J. Surg. 2012, 101, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapral, C.; Muhlberger, A.; Wewalka, F.; Duller, C.; Knofach, P.; Schreiber, F. Quality assessment of endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography: Results of a running nationwide Austrian benchmarking project after 5 years of implementation. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 24, 1447–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baste, T.; Esra, Y.; Gizem, G.; Kazim, Y.A.; Raghu, S. Current State of “Omics” Biomarkers in Panreatic Cancer. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 127. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, V.W.; Bathe, O.F.; Schiller, D.E.; Slupsky, C.M.; Sawyer, M.B. Metabolomics and surgical oncology: Potential role for small molecule biomarkers. J. Surg. Oncol. 2011, 103, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomase, V.S.; Changbhale, S.S.; Patil, S.A.; Kale, K.V. Metabolomics. Curr. Drug Metab. 2008, 9, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Napoli, C.; Sperandio, N.; Lawlor, R.T.; Scarpa, A.; Molinari, H.; Assfalg, M. Urine metabolic signature of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma by (1)h nuclear magnetic resonance: Identification, mapping, and evolution. J. Proteome Res. 2012, 11, 1274–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayerle, J.; Kalthoff, H.; Reszka, R.; Kamlage, B.; Peter, E.; Schniewind, B.; Maldonado, S.D.; Pilarsky, C.; Heidecke, C.-D.; Schatz, P.; et al. Metabolic biomarker signature to differentiate pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma from chronic pancreatitis. Gut 2018, 67, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markar, S.R.; Brodie, B.; Chin, S.T.; Romano, A.; Spalding, D.; Hanna, G.B. Profile of exhaled-breath volatile organic compounds to diagnose pancreatic cancer. Br. J. Surg. 2018, 105, 1493–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenka, M.; Stepan, H.; Jan, S.; Lucie, H.; Vladimir, S.; Bohus, B. Early Detection of Pancreatic Cancer in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients Based on 1H NMR Metabolomics. J. Proteome Res. 2021, 20, 1744–1753. [Google Scholar]
- Jesus, M.U.; Jose, M.H.; Iker, U.; Maria, R.; Daniel, O.; Belen, G.; Ignacio, F.; Juan, C.; Federico, B.; Lucia, Z.; et al. Pilot Multi-Omics Analysis of Human Bile from Benign and Malignant Biliary Strictures: A Machine-Learning Approach. Cancers 2020, 12, 1644. [Google Scholar]
- Nina, C.; Giovanni, C.; Marialuisa, B.; Alessandra, R.; Panteleimon, G.T.; Giovanni, F.C.; Debora, V.; Giulia, M.; Francesca, G.; Cristine, R.; et al. Metabolome of Pancreatic juice Delineates Distinct Clinical Profiles of Pancreatic Cancer and Reveals a Link between Glucose Metabolism and PD-1+ Cells. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2020, 8, 493–505. [Google Scholar]
- Akashi, R.; Kiyozumi, T.; Tanaka, T.; Sakurai, K.; Oda, Y.; Sagawa, K. Mechanism of pancreatitis caused by ERCP. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2002, 55, 50–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kisiel, J.B.; Raimondo, M.; Taylor, W.R.; Yab, T.C.; Mahoney, D.W.; Sun, Z.; Middha, S.; Baheti, S.; Zou, H.; Smyrk, T.C.; et al. New DNA methylation markers for pancreatic cancer: Discovery, tissue validation, and pilot testing in pancreatic juice. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 4473–4481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsunaga, T.; Ohtsuka, T.; Asano, K.; Kimura, H.; Ohuchida, K.; Kitada, H.; Ideno, N.; Mori, Y.; Tokunaga, S.; Oda, Y.; et al. S100P in duodenal fluid is a useful diagnostic marker for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Pancreas 2017, 46, 1288–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumas, M.E.; Maibaum, E.C.; Teague, C.; Ueshima, H.; Zhou, B.F.; Lindon, J.C.; Nicholson, J.K.; Stamler, J.; Elliott, P.; Chan, Q.; et al. Assesment of analytical reproducibility of 1H NMR spectroscopy based metabonomics for large-scale epidemiological research: The Intermap Study. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 2199–2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanda, Y. Investigation of the freely available easy-to-use software ‘EZR’ for medical statistics. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2013, 48, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jesus, M.B.; Mercedes, I.; Ander, A.; Piotr, M.; Jordi, M.; Luis, M.B.; Adelaida, L.C.; Luis, M.G.; Enara, A.; Cristina, A.; et al. Serum Metabolites as Diagnostic Biomarkers for Cholangiocarcinoma, Hepatocellular Carcinoma, and Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis. Hepatology 2019, 70, 547–562. [Google Scholar]
- He, W.; Sung, S.Y.; Jinho, K.; Hee, G.K.; Jin, S.P.; Seok, J.; Jung, L.; Hyuk, N.K.; Sunmi, K.; Don, H.L.; et al. A new NMR-based metabolomics approach for the diagnosis of biliary tract cancer. J. Hepatol. 2010, 52, 228–233. [Google Scholar]
- Shukla, S.K.; Gebregiworgis, T.; Purohit, V.; Chaika, N.V.; Gunda, V.; Radhakrishnan, P.; Mehla, K.; Pipinos, I.I.; Powers, R.; Yu, F.; et al. Metabolic reprogramming induced by ketone bodies diminishes pancreatic cancer cachexia. Cancer Metab. 2014, 2, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poff, A.M.; Ari, C.; Arnold, P.; Seyfried, T.N.; D’Agostino, D.P. Ketone supplementation decreases tumor cell viability and prolongs survival of mice with metastatic cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2014, 135, 1711–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Jin, H.; Guo, X.; Yang, Z.; Zhao, L.; Tang, S.; Mo, P.; Wu, K.; Nie, Y.; Pan, Y.; et al. Distinguishing pancreatic cancer from chronic pancreatitis and healthy individuals by H nuclear magnetic resonance-based metabonomic profile. Clonical. Viochemistry 2012, 45, 1064–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, F.B.; Rustem, S.; Karen, K.; Aalim, M.W.; Andrew, M.; Francis, R.S.; Elijah, D.; Nicole, D.; Dina, S.; Hans, J.V. Feasibility of identifying Pancreatic Cancer Based on serum Metabolomics. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2011, 20, 140–147. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Xia, B.; Zheng, H.; Ning, J.; Zhu, Y.; Shao, X.; Liu, B.; Dong, B.; Gao, H. Identification of characteristic merabolic panels for different stages of prostate cancer by 1H NMR-based metabolomics analysis. J. Transl. Med. 2022, 20, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michihito, T.; Kenichi, H.; Aya, K.; Masashi, M.; Yoshika, S. Study on human skin gases emanating from pancreatic cancer patients. Jpn. J. Clin. Ecol. 2021, 30, 7–16. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, H.T.; Olson, L.K.; Schwartz, K.A. Ketolytic and glycolytic enzymatic expression profiles in malignant gliomas: Implication for ketogenic diet therapy. Nutr. Metab. 2013, 10, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maurer, G.D.; Brucker, D.P.; Bahr, O.; Harter, P.N.; Hattingen, E.; Walenta, S.; Mueller-Klieser, W.; Steinbach, J.P.; Rieger, J. Differential utilization of ketone bodies by neurons and glioma cell lines: A rationale for ketogenic diet as experimental glioma therapy. BMC Cancer 2011, 11, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moller, N.; Body, K. 3-Hydroxybutyrate: Minor Metabolite-Major Medical Manifestations. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metabolosm 2020, 105, 2884–2892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Etsuko, H.; Terumi, T.; Satoshi, B.; Masato, M. Investigation of unexpected serum CA19-9 elevation in Lewis-Negative cancer patients. Ann. Clin. Biochem. 2012, 49, 266–272. [Google Scholar]
- Nagana, G.G.A. NMR spectroscopy for discovery and quantitation of biomarkers of disease in human bile. Bioanalysis 2011, 3, 1877–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayers, J.R.; Torrence, M.E.; Danai, L.V.; Papagiannakopulos, T.; Davidson, S.M.; Bauer, M.R.; Lau, A.N.; Ji, B.W.; Dixit, P.D.; Hosios, A.M.; et al. Tissue of origin dictated branched-chain amino acid metabolism in mutant Kras-driven cancers. Science 2016, 353, 1161–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.S.; Dennis, C.; Naqvi, I.; Dailey, L.; Lorzadeh, A.; Ye, G.; Zaytouni, T.; Adler, A.; Hitchcock, D.S.; Lin, L.; et al. Ornithin aminotransferase supports polyamine synthesis in pancreatic cancer. Nature 2023, 616, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanders, D.; Hobson, K.; Ji, X. Methionine Restriction and Cancer Biology. Nutrients 2020, 12, 684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Xu, L.; Shen, J.; Cao, B.; Cheng, T. Metabolic signatures of esophageal cancer: NMR-based metabolomics and UHPLC-based focused metabolomics of blood serum. Biochim. Biophys Acta 2013, 1832, 1207–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opitz, C.A.; Litzenburger, U.M.; Sahm, F.; Ott, M.; Tritschler, I.; Trump, S.; Schumacher, T.; Jestaedt, L.; Schrenk, D.; Weller, M.; et al. An endogenous tumour-promoting ligand of the human aryl hydrocarbon receptor. Nature 2011, 478, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.J.; Yoon, S.; Ji, S.C.; Yang, J.; Kim, Y.K.; Lee, S.H.; Yu, K.S.; Jang, I.J.; Chung, J.Y.; Cho, J.Y. Ursodeoxycholic acid improves liver function via phenylalanine/tyrosine pathway and microbiome remodelling in patients with liver dysfunction. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 11874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Wang, D.; Li, Y.; Wang, H.; Hu, Q.; Wang, Y. Metabolomics in viral hepatitis: Advances and review. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1189417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepe, M.S.; Feng, Z.; Janes, H.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Potter, J.D. Pivotal Evaluation of the Accuracy of a Biomarker Used for Classification or Prediction: Standards for Study Design. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2008, 100, 1432–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Malignant Group (N = 33) | Benign Group (N = 34) | |
|---|---|---|
| Age, median (range), y | 73 (35–96) | 64.5 (27–86) |
| Sex, n (%) | ||
| Male | 21 (63.6) | 13 (38.2) |
| Female | 12 (36.4) | 21 (61.8) |
| Details of disease, n (%) | ||
| Cholangiocarcinoma | 26 (78.7) | |
| Gallbladder cancer | 5 (15.2) | — |
| Ampullary carcinoma | 2 (6.1) | |
| Bile duct stone/gallbladder stone | 16 (47.2) | |
| Gallbladder polyp | 7 (20.6) | |
| No abnormality in workup imaging | — | 6 (17.6) |
| Adenomyomatosis of gallbladder | 3 (8.8) | |
| IgG4-related disease | 1 (2.9) | |
| Chronic cholecystitis | 1 (2.9) | |
| UICC stage (n = 33), n (%) | ||
| I | 3 (9.2) | |
| II | 9 (27.2) | — |
| Ⅲ | 12 (36.4) | — |
| Ⅳ | 9 (27.2) | |
| CA19-9, median (range), U/mL | 101.3 (2.1–167,959.3) | 17.5 (2.1–759.8) |
| No | Metabolite | Average Concentration (mM) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Leucine | 1.33 |
| 2 | Alanine | 1.11 |
| 3 | Valine | 1.09 |
| 4 | Isoleucine | 0.92 |
| 5 | Glycerol | 0.87 |
| 6 | Lysine | 0.85 |
| 7 | Phenylalanine | 0.73 |
| 8 | Ethanol | 0.68 |
| 9 | Tyrosine | 0.66 |
| 10 | Arginine | 0.63 |
| 11 | Proline | 0.57 |
| 12 | Threonine | 0.53 |
| 13 | Glutamine | 0.52 |
| 14 | Glutamate | 0.42 |
| 15 | Asparagine | 0.33 |
| 16 | Methionine | 0.26 |
| 17 | Tryptophan | 0.25 |
| 18 | Propylene glycol | 0.20 |
| 19 | Aspartate | 0.20 |
| 20 | Lactate | 0.19 |
| 21 | Acetate | 0.19 |
| 22 | 3-Hydroxubutyrate | 0.05 |
| 23 | Pyruvate | 0.03 |
| 24 | Acetone | 0.03 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kishi, K.; Kuwatani, M.; Ohnishi, Y.; Kumaki, Y.; Kumeta, H.; Hirata, H.; Takishin, Y.; Furukawa, R.; Nagai, K.; Yonemura, H.; et al. Metabolomics of Duodenal Juice for Biliary Tract Cancer Diagnosis. Cancers 2023, 15, 4370. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15174370
Kishi K, Kuwatani M, Ohnishi Y, Kumaki Y, Kumeta H, Hirata H, Takishin Y, Furukawa R, Nagai K, Yonemura H, et al. Metabolomics of Duodenal Juice for Biliary Tract Cancer Diagnosis. Cancers. 2023; 15(17):4370. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15174370
Chicago/Turabian StyleKishi, Kazuma, Masaki Kuwatani, Yuki Ohnishi, Yasuhiro Kumaki, Hiroyuki Kumeta, Hajime Hirata, Yunosuke Takishin, Ryutaro Furukawa, Kosuke Nagai, Hiroki Yonemura, and et al. 2023. "Metabolomics of Duodenal Juice for Biliary Tract Cancer Diagnosis" Cancers 15, no. 17: 4370. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15174370







