Atypical Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia—The Current Status
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
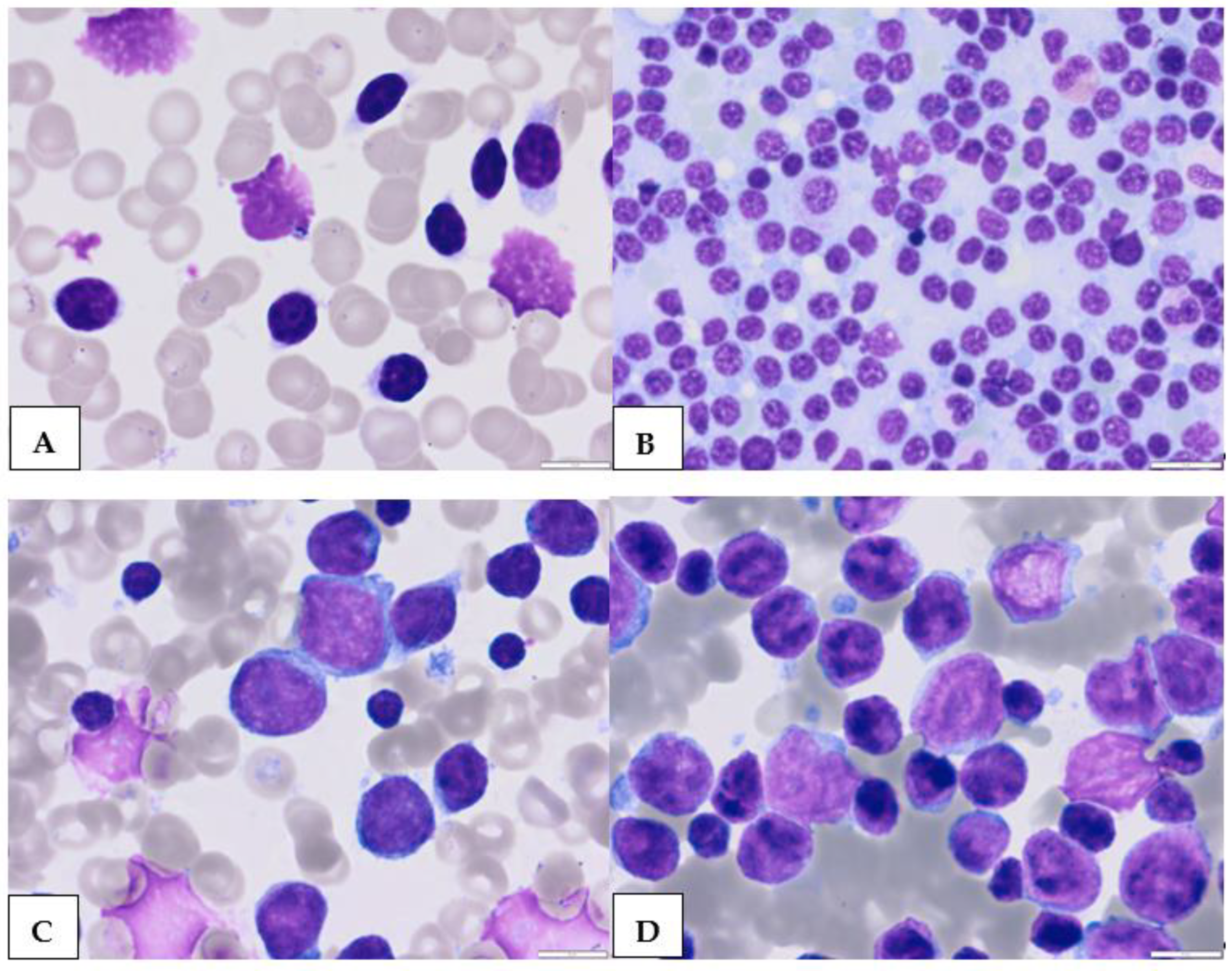
2. Atypical Morphological Feature
3. Atypical Immunophenotype
3.1. CD5-Negative CLL
3.2. CD23-Negative CLL
4. Atypical Genotype
5. Scoring Systems for CLL Diagnosis
6. Differential Diagnosis of Atypical CLL with Other Lymphoproliferative Disorders
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hallek, M.; Cheson, B.D.; Catovsky, D.; Caligaris-Cappio, F.; Dighiero, G.; Dohner, H.; Hillmen, P.; Keating, M.; Montserrat, E.; Chiorazzi, N.; et al. iwCLL guidelines for diagnosis, indications for treatment, response assessment, and supportive management of CLL. Blood 2018, 131, 2745–2760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eichhorst, B.; Robak, T.; Montserrat, E.; Ghia, P.; Niemann, C.U.; Kater, A.P.; Gregor, M.; Cymbalista, F.; Buske, C.; Hillmen, P.; et al. ESMO Guidelines Committee. Chronic lymphocytic leukaemia: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2021, 32, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scarfò, L.; Ferreri, A.J.M.; Ghia, P. Chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2016, 104, 169–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teras, L.R.; DeSantis, C.E.; Cerhan, J.R.; Morton, L.M.; Jemal, A.; Flowers, C.R. 2016 US lymphoid malignancy statistics by World Health Organization subtypes. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2016, 66, 443–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Wagle, N.S.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2023, 73, 17–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) Program of the National Cancer Institute. Cancer Stat Facts: Leukemia—Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL). 2021. Available online: https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/clyl.html (accessed on 1 April 2023).
- Campo, E.; Jaffe, E.S.; Cook, J.R.; Quintanilla-Martinez, L.; Swerdlow, S.H.; Anderson, K.C.; Brousset, P.; Cerroni, L.; de Leval, L.; Dirnhofer, S.; et al. The International Consensus Classification of Mature Lymphoid Neoplasms: A report from the Clinical Advisory Committee. Blood 2022, 140, 1229–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaggio, R.; Amador, C.; Anagnostopoulos, I.; Attygalle, A.D.; Araujo, I.B.O.; Berti, E.; Bhagat, G.; Borges, A.B.; Boyer, D.; Calaminici, M.; et al. The 5th edition of the World Health Organization Classification of Haematolymphoid Tumours: Lymphoid Neoplasms. Leukemia 2022, 36, 1720–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawstron, A.C.; Kreuzer, K.A.; Soosapilla, A.; Spacek, M.; Stehlikova, O.; Gambell, P.; McIver-Brown, N.; Villamor, N.; Psarra, K.; Arroz, M.; et al. Reproducible diagnosis of chronic lymphocytic leukemia by flow cytometry: An European Research Initiative on CLL (ERIC) & European Society for Clinical Cell Analysis (ESCCA) Harmonisation project. Cytom. B Clin. Cytom. 2018, 94, 121–128. [Google Scholar]
- Giné, E.; Martinez, A.; Villamor, N.; López-Guillermo, A.; Camos, M.; Martinez, D.; Esteve, J.; Calvo, X.; Muntañola, A.; Abrisqueta, P.; et al. Expanded and highly active proliferation centers identify a histological subtype of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (“accelerated” chronic lymphocytic leukemia) with aggressive clinical behavior. Haematologica 2010, 95, 1526–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, J.M.; Catovsky, D.; Daniel, M.T.; Flandrin, G.; Galton, D.A.; Gralnick, H.R.; Sultan, C. Proposals for the classification of chronic (mature) B and T lymphoid leukaemias. French-American-British (FAB) Cooperative Group. J. Clin. Pathol. 1989, 42, 567–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Criel, A.; Michaux, L.; De Wolf-Peeters, C. The concept of typical and atypical chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Leuk. Lymphoma 1999, 33, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landau, D.A.; Tausch, E.; Taylor-Weiner, A.N.; Stewart, C.; Reiter, J.G.; Bahlo, J.; Kluth, S.; Bozic, I.; Lawrence, M.; Böttcher, S.; et al. Mutations driving CLL and their evolution in progression and relapse. Nature 2015, 526, 525–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaffe, E.S.; Harris, N.L.; Stein, H.; Vardiman, J.W. (Eds.) Pathology and Genetics of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues; WHO Press: Lyon, France, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Swerdlow, S.H.; Campo, E.; Harris, N.L.; Jaffe, E.S.; Pileri, S.A.; Stein, H.; Thiele, J. (Eds.) WHO Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues; WHO Press: Lyon, France, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Navarro, A.; Clot, G.; Martínez-Trillos, A.; Pinyol, M.; Jares, P.; González-Farré, B.; Martínez, D.; Trim, N.; Fernández, V.; Villamor, N.; et al. Improved classification of leukemic B-cell lymphoproliferative disorders using a transcriptional and genetic classifier. Haematologica 2017, 102, e360–e363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorigue, M.; Junca, J. Atypical chronic lymphocytic leukemia: Brief historical overview and current usage of an equivocal concept. Int. J. Lab. Hematol. 2019, 41, e17–e19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frater, J.L.; McCarron, K.F.; Hammel, J.P.; Shapiro, J.L.; Miller, M.L.; Tubbs, R.R.; Pettay, J.; Hsi, E.D. Typical and atypical chronic lymphocytic leukemia differ clinically and immunophenotypically. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2001, 116, 655–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, S.J.; Su’ut, L.; Morgan, G.J.; Jack, A.S. The relationship between typical and atypical B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. A comparative genomic hybridization-based study. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2000, 114, 448–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marionneaux, S.; Maslak, P.; Keohane, E.M. Morphologic identification of atypical chronic lymphocytic leukemia by digital microscopy. Int. J. Lab. Hematol. 2014, 36, 459–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matutes, E.; Attygalle, A.; Wotherspoon, A.; Catovsky, D. Diagnostic issues in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (CLL). Best Pract. Res. Clin. Haematol. 2010, 23, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallek, M.; Al-Sawaf, O. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia: 2022 update on diagnostic and therapeutic procedures. Am. J. Hematol. 2021, 96, 1679–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oscier, D.G.; Matutes, E.; Copplestone, A.; Pickering, R.M.; Chapman, R.; Gillingham, R.; Catovsky, D.; Hamblin, T.J. Atypical lymphocyte morphology: An adverse prognostic factor for disease progression in stage A CLL independent of trisomy 12. Br. J. Haematol. 1997, 98, 934–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo, J.V.; Catovsky, D.; Galton, D.A. The relationship between chronic lymphocytic leukaemia and prolymphocytic leukaemia. I. Clinical and laboratory features of 300 patients and characterization of an intermediate group. Br. J. Haematol. 1986, 63, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghani, A.M.; Krause, J.R. Investigation of cell size and nuclear clefts as prognostic parameters in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Cancer 1986, 58, 2233–2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molica, S.; Alberti, A. Investigation of nuclear clefts as a prognostic parameter in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Eur. J. Haematol. 1988, 41, 62–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallespí, T.; Montserrat, E.; Sanz, M.A. Chronic lymphocytic leukaemia: Prognostic value of lymphocyte morphological subtypes. A multivariate survival analysis in 146 patients. Br. J. Haematol. 1991, 77, 478–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, A.; Kim, M.S.; Park, C.J.; Seo, E.J.; Jang, S.; Cho, Y.U.; Ji, M.; Choi, Y.M.; Lee, K.H.; Lee, J.; et al. Atypical chronic lymphocytic leukemia has a worse prognosis than CLL and shows different clinical and laboratory features from B-cell prolymphocytic leukemia. HemaSphere 2019, 3, 864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Arena, G.; Dell’Olio, M.; Musto, P.; Cascavilla, N.; Perla, G.; Savino, L.; Greco, M.M. Morphologically typical and atypical B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemias display a different pattern of surface antigenic density. Leuk. Lymphoma 2001, 42, 649–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cro, L.; Ferrario, A.; Lionetti, M.; Bertoni, F.; Zucal, N.N.; Nobili, L.; Fabris, S.; Todoerti, K.; Cortelezzi, A.; Guffanti, A.; et al. The clinical and biological features of a series of immunophenotypic variant of B-CLL. Eur. J. Haematol. 2010, 85, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Criel, A.; Verhoef, G.; Vlietinck, R.; Mecucci, C.; Billiet, J.; Michaux, L.; Meeus, P.; Louwagie, A.; Van Orshoven, A.; Van Hoof, A.; et al. Further characterization of morphologically defined typical and atypical CLL: A clinical, immunophenotypic, cytogenetic, and prognostic study on 390 cases. Br. J. Haematol. 1997, 97, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finn, W.G.; Thangavelu, M.; Yelavarthi, K.K.; Goolsby, C.L.; Tallman, M.S.; Traynor, A.; Peterson, L.C. Karyotype correlates with peripheral blood morphology and immunophenotype in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 1996, 105, 458–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, L.C.; Bloomfield, C.D.; Brunning, R.D. Relationship of clinical staging and lymphocyte morphology to survival in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Br. J. Haematol. 1980, 45, 563–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ralfkiaer, E.; Geisler, C.; Hansen, M.M.; Hou-Jensen, K. Nuclear clefts in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: A light microscopic and ultrastructural study of a new prognostic parameter. Scand. J. Haematol. 1983, 30, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ting, Y.S.; Smith, S.A.B.C.; Brown, D.A.; Dodds, A.J.; Fay, K.C.; Ma, D.D.F.; Milliken, S.; Moore, J.J.; Sewell, W.A. CD200 is a useful diagnostic marker for identifying atypical chronic lymphocytic leukemia by flow cytometry. Int. J. Lab. Hematol. 2018, 40, 533–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urbaniak, M.; Iskierka-Jażdżewska, E.; Majchrzak, A.; Robak, T. Atypical immunophenotype of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Acta Haematol. Pol. 2022, 53, 48–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandes, A.F.; de Lourdes Chauffaille, M.; Oliveira, C.R.; Maekawa, Y.; Tamashiro, N.; Takao, T.T.; Ritter, E.C.; Rizzatti, E.G. CD200 has an important role in the differential diagnosis of mature B-cell neoplasms by multiparameter flow cytometry. Cytom. B Clin. Cytom. 2014, 86, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheikh, S.S.; Kallakury, B.V.; Al-Kuraya, K.A.; Meck, J.; Hartmann, D.P.; Bagg, A. CD5-negative, CD10-negative small B-cell leukemia: Variant of chronic lymphocytic leukemia or a distinct entity? Am. J. Hematol. 2002, 71, 306–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.C.; Finn, W.G.; Goolsby, C.L.; Variakojis, D.; Peterson, L.C. CD5-small B-cell leukemias are rarely classifiable as chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 1999, 111, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delia, D.; Bonati, A.; Giardini, R.; Villa, S.; De Braud, F.; Cattoretti, G.; Rilke, F. Expression of the T1 (CD5, p67) surface antigen in B-CLL and B-NHL and its correlation with other B-cell differentiation markers. Hematol. Oncol. 1986, 4, 237–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cartron, G.; Linassier, C.; Bremond, J.L.; Desablens, B.; Georget, M.T.; Fimbel, B.; Luthier, F.; Dutel, J.L.; Lamagnere, J.P.; Colombat, P. CD5 negative B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia: Clinical and biological features of 42 cases. Leukl. Lymphoma 1998, 31, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efstathiou, S.; Tsioulos, D.; Zacharos, I.; Tsiakou, A.; Mastorantonakis, S.; Salgami, E.; Katirtzoglou, N.; Psarra, A.; Roussou, P. The prognostic role of CD5 negativity in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukaemia: A case-control study. Haematologia 2002, 32, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demir, C.; Kara, E.; Ekinci, Ö.; Ebinç, S. Clinical and laboratory features of CD5-negative chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Med. Sci. Monit. 2017, 23, 2137–2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, D.R.; Guadalupe, E.; Volkheimer, A.; Moore, J.O.; Weinberg, J.B. Clinical outcomes in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia associated with expression of CD5, a negative regulator of B-cell receptor signalling. Br. J. Haematol. 2018, 183, 747–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurec, A.S.; Threatte, G.A.; Gottlieb, A.J.; Smith, J.R.; Anderson, J.; Davey, F.R. Immunophenotypic subclassification of chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (CLL). Br. J. Haematol. 1992, 81, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, C.; Sellitto, A.; Chiurazzi, F.; Simeone, L.; De Fanis, U.; Raia, M.; Del Vecchio, L.; Lucivero, G. Clinical and phenotypic features of CD5-negative B cell chronic lymphoproliferative disease resembling chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Int. J. Hematol. 2015, 101, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jurisic, V.; Colovic, N.; Kraguljac, N.; Atkinson, H.D.; Colovic, M. Analysis of CD23 antigen expression in B-chronic lymphocytic leukaemia and its correlation with clinical parameters. Med. Oncol. 2008, 25, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fournier, S.; Yang, L.P.; Delespesse, G.; Rubio, M.; Biron, G.; Sarfati, M. The two CD23 isoforms display differential regulation in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Br. J. Haematol. 1995, 89, 373–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kilo, M.N.; Dorfman, D.M. The utility of flow cytometric immunophenotypic analysis in the distinction of small lymphocytic lymphoma/chronic lymphocytic leukemia from mantle cell lymphoma. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 1996, 105, 451–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, J.Z.; Lagoo, A.S.; Peters, D.; Horvatinovich, J.; Benz, P.; Buckley, P.J. Value of CD23 determination by flow cytometry in differentiating mantle cell lymphoma from chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2001, 116, 893–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barna, G.; Reiniger, L.; Tátrai, P.; Kopper, L.; Matolcsy, A. The cut-off levels of CD23 expression in the differential diagnosis of MCL and CLL. Hematol. Oncol. 2008, 26, 167–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hjalmar, V.; Kimby, E.; Matutes, E.; Sundström, C.; Wallvik, J.; Hast, R. Atypical lymphocytes in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia and trisomy 12 studied by conventional staining combined with fluorescence in situ hybridization. Leuk. Lymphoma 2000, 37, 571–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matutes, E.; Oscier, D.; Garcia-Marco, J.; Ellis, J.; Copplestone, A.; Gillingham, R.; Hamblin, T.; Lens, D.; Swansbury, G.J.; Catovsky, D. Trisomy 12 defines a group of CLL with atypical morphology: Correlation between cytogenetic, clinical and laboratory features in 544 patients. Br. J. Haematol. 1996, 92, 382–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puente, X.S.; Pinyol, M.; Quesada, V.; Conde, L.; Ordóñez, G.R.; Villamor, N.; Escaramis, G.; Jares, P.; Beà, S.; González-Díaz, M.; et al. Whole-genome sequencing identifies recurrent mutations in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Nature 2011, 475, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puente, X.S.; Beà, S.; Valdés-Mas, R.; Villamor, N.; Gutiérrez-Abril, J.; Martín-Subero, J.I.; Munar, M.; Rubio-Pérez, C.; Jares, P.; Aymerich, M.; et al. Non-coding recurrent mutations in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Nature 2015, 526, 519–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huret, J. t(11;14)(q13;q32). Atlas. Genet. Cytogenet. Oncol. Haematol. 1998, 2, 129–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muddasani, R.; Talwar, N.; Suarez-Londono, J.A.; Braunstein, M. Management of atypical chronic lymphocytic leukemia presenting with extreme leukocytosis. Clin. Case Rep. 2020, 8, 877–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuneo, A.; Balboni, M.; Piva, N.; Rigolin, G.M.; Roberti, M.G.; Mejak, C.; Moretti, S.; Bigoni, R.; Balsamo, R.; Cavazzini, P.; et al. Atypical chronic lymphocytic leukaemia with t(11;14)(q13;q32): Karyotype evolution and prolymphocytic transformation. Br. J. Haematol. 1995, 90, 409–416. [Google Scholar]
- Gómez Pescie, M.; Denninghoff, V.; García, A.; Rescia, C.; Avagnina, A.; Elsner, B. Linfoma del manto vs. leucemia linfatica crónica atipica. Utilización de inmunohistoquímica, citometría de flujo y biología molecular para su correcta tipificación [Mantle cell lymphoma vs. atypical chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Use of immunohistochemistry, flow cytometry and molecular biology for their adequate typing]. Medicina 2005, 65, 419–424. [Google Scholar]
- Braekeleer, M.; Tous, C.; Guéganic, N.; LE Bris, M.-J.; Basinko, A.; Morel, F.; Douet-Guilbert, N. Immunoglobulin gene translocations in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: A report of 35 patients and review of the literature. Mol. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 4, 682–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matutes, E.; Owusu-Ankomah, K.; Morilla, R.; Marco, J.G.; Houlihan, A.; Que, T.H.; Catovsky, D. The immunological profile of B-cell disorders and proposal of a scoring system for the diagnosis of CLL. Leukemia 1994, 8, 1640–1645. [Google Scholar]
- Moreau, E.J.; Matutes, E.; A’hern, R.P.; Morilla, A.M.; Morilla, R.M.; Owusu-Ankomah, K.A.; Seon, B.K.; Catovsky, D. Improvement of the chronic lymphocytic leukemia scoring system with the monoclonal antibody SN8 (CD79b). Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 1997, 108, 378–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Tong, X.; Huang, L.; Li, L.; Wang, C.; He, C.; Liu, S.; Wang, Z.; Xiao, M.; Mao, X.; et al. A new score including CD43 and CD180: Increased diagnostic value for atypical chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Cancer Med. 2021, 10, 4387–4396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshino, T.; Tanaka, T.; Sato, Y. Differential diagnosis of chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma and other indolent lymphomas, including mantle cell lymphoma. J. Clin. Exp. Hematop. 2020, 60, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, A.K.; Hill, S.; Preobrazhensky, S.N.; Miller, M.E.; Chen, Z.; Bahler, D.W. Small B-cell neoplasms with typical mantle cell lymphoma immunophenotypes often include chronic lymphocytic leukemias. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2009, 131, 27–32. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, L.; Xu, J.; Tang, G.; Wang, S.A.; Lin, P.; Ok, C.Y.; Garces, S.; Yin, C.C.; Khanlari, M.; Vega, F.; et al. Mantle cell lymphoma with chronic lymphocytic leukemia-like features: A diagnostic mimic and pitfall. Hum. Pathol. 2022, 119, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sallam, M.T.; El-Sewefy, D.; Khattab, D.; Elsalakawy, W.A. Flow cytometric evaluation of CD200 as a tool for differentiation between chronic lymphocytic leukemia and mantle cell lymphoma. Egypt J. Haematol. 2014, 39, 42–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palumbo, G.A.; Parrinello, N.; Fargione, G.; Cardillo, K.; Chiarenza, A.; Berretta, S.; Conticello, C.; Villari, L.; Di Raimondo, F. CD200 expression may help in differential diagnosis between mantle cell lymphoma and B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leuk. Res. 2009, 33, 1212–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Köhnke, T.; Wittmann, V.K.; Bücklein, V.L.; Lichtenegger, F.; Pasalic, Z.; Hiddemann, W.; Spiekermann, K.; Subklewe, M. Diagnosis of CLL revisited: Increased specificity by a modified five-marker scoring system including CD200. Br. J. Haematol. 2017, 179, 480–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehrpouri, M.; Hosseini, M.S.; Jafari, L.; Mosleh, M.; Satlsar, E.S. A Flow Cytometry Panel for Differential Diagnosis of Mantle Cell Lymphoma from Atypical B-Chronic Lymphocytic Leukaemia. Iran Biomed. J. 2023, 27, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maljaei, S.; Asvadi-E-Kermani, I.; Eivazi-E-Ziaei, J.; Nikanfar, A.; Vaez, J. Usefulness of CD45 density in the diagnosis of B-cell chronic lymphoproliferative disorders. Indian J. Med. Sci. 2005, 59, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalingam, T.R.; Mohanraj, S.; Muthu, A.; Prabhakar, V.; Ramakrishnan, B.; Vaidhyanathan, L.; Easow, J.; Raja, T. Independent diagnostic utility of CD20, CD200, CD43 and CD45 in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Leuk. Lymphoma 2022, 63, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, J.; Rother, M.; Kaiser, U.; Thrun, M.C.; Wilhelm, C.; Gruen, A.; Niebergall, U.; Meissauer, U.; Neubauer, A.; Brendel, C. Determination of CD43 and CD200 surface expression improves accuracy of B-cell lymphoma immunophenotyping. Cytom. B Clin. Cytom. 2020, 98, 476–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorigue, M.; Juncà, J.; Sarrate, E.; Grau, J. Expression of CD43 in chronic lymphoproliferative leukemias. Cytom. B Clin. Cytom. 2018, 94, 136–142. [Google Scholar]
- Falay, M.; Serdar, M.A.; Dalgali, H.; Uçar, M.A.; Dagdaş, S.; Özet, G. Which markers should the used for diagnostic chronic lymphocytic leukemia immunophenotyping scoring system by flow cytometry? Clin. Lab. 2019, 65, 2049–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falay, M.; Özet, G. Immunophenotyping of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Clin. Lab. 2017, 63, 1621–1626. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ozdemir, Z.N.; Falay, M.; Parmaksiz, A.; Genc, E.; Beyler, O.; Gunes, A.K.; Ceran, F.; Dagdas, S.; Ozet, G. A novel differential diagnosis algorithm for chronic lymphocytic leukemia using immunophenotyping with flow cytometry. Hematol. Transfus Cell Ther. 2023, 45, 176–181. [Google Scholar]
- Soliman, D.S.; Al-Kuwari, E.; Siveen, K.S.; Al-Abdulla, R.; Chandra, P.; Yassin, M.; Nashwan, A.; Hilmi, F.A.; Taha, R.Y.; Nawaz, Z.; et al. Downregulation of Lymphoid enhancer-binding factor 1 (LEF-1) expression (by immunohistochemistry and/ flow cytometry) in chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia with atypical immunophenotypic and cytologic features. Int. J. Lab. Hematol. 2021, 43, 515–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Malley, D.P.; Lee, J.P.; Bellizzi, A.M. Expression of LEF1 in mantle cell lymphoma. Ann. Diagn. Pathol. 2017, 26, 57–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, K.; Lydyard, P.M.; Kulikova, N.; Tsertsvadze, T.; Volpi, E.V.; Chiorazzi, N.; Porakishvili, N. The role of CD180 in hematological malignancies and inflammatory disorders. Mol. Med. 2023, 29, 97. [Google Scholar]
- Mayeur-Rousse, C.; Guy, J.; Miguet, L.; Bouyer, S.; Genevieve, F.; Robillard, N.; Solly, F.; Maar, A.; Bene, M.C.; Mauvieux, L. CD180 expression in B-cell lymphomas: Amulticenter GEIL study. Cytom. B Clin. Cytom. 2016, 90, 462–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miguet, L.; Fornecker, L.; Wyrwas, M.; Cianferani, S.; Herbrecht, R.; Leseve, J.-F.; Latger-Cannard, V.; Mayeur-Rousse, C.; Mauvieux, L. Multicentric analyses of the CD148, CD180, and CD200 combination for the diagnosis of mature B-cell neoplasm using flow cytometry. Blood 2015, 126, 2662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meggendorfer, M.; Kern, W.; Haferlach, C.; Haferlach, T.; Schnittger, S. SOX11 overexpression is a specific marker for mantle cell lymphoma and correlates with t(11;14) translocation, CCND1 expression and an adverse prognosis. Leukemia 2013, 27, 2388–2391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozos, A.; Royo, C.; Hartmann, E.; De Jong, D.; Baró, C.; Valera, A.; Fu, K.; Weisenburger, D.D.; Delabie, J.; Chuang, S.S.; et al. SOX11 expression is highly specific for mantle cell lymphoma and identifies the cyclin D1-negative subtype. Haematologica 2009, 94, 1555–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wasik, A.M.; Priebe, V.; Lord, M.; Jeppsson-Ahlberg, Å.; Christensson, B.; Sander, B. Flow cytometric analysis of SOX11: A new diagnostic method for distinguishing B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma from mantle cell lymphoma. Leuk. Lymphoma 2015, 56, 1425–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Authors/Reference | No of pts CD5− vs. CD5+ | Median Age: CD5− vs. CD5+ | Definition of CD5− CLL | PB CD5− vs. CD5+ | Treatment CD5− vs. CD5+ | Survival CD5− vs. CD5+ | Commentary |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cartron et al., 1998 [41] | 42 vs. 79 | 68/64.8 | <5% of mononuclear cells | Hb: 126/137 G/L (p = ns) PLT: 216/200 × 109/L (p = ns) Lymphocytes: 27.3/32.7 × 109/L × 109/L (p = ns) | No initially treated:64.3% vs. 29.1% | 52% at 120 m vs. 6% at 90 m (p = 0.97) | CD5− CLL expressed a higher level of surface of immunoglobulin and had more frequently isolated splenomegaly. |
| Efstathiou et al., 2002 [42] | 29 vs. 29 | 68.8/68.4 | <5% of mononuclear cells | Hb: 131/10.5 G/L (p = ns) (p < 0.05) PLT: 211/198 × 109/L (p = ns) Lymphocytes:38.2/39.6 × 109/L (p = ns) | No initially treated:72.4% vs. 24.1% | Median:97.2 m vs. 84.0 m (p = 0.0025) | Splenomegaly, lymph node involvement, and hemolytic anemia less common in CD5− CLL. CD5− CLL patients had a more favorable prognosis compared with CD5+ patients |
| Demir et al., 2017 [43] | 19 vs. 105 | 65.8/66.5 | <20% of mononuclear cells | HB: 133/127 g/L (p = 0.180) PLT: 144/160 × 6 × 109/L (p = 0.044) Neutrophils: 3.5/3.36 × 109/L (p = 0.169) Lymphocytes: 43.2/36.7 × 109/L (p = 0.001). | NR | 84.2% vs. 90.5% at 5 yr (p = 0.393) | Lymphadenopathy less frequent in CD5− (p = 0.029). Splenomegaly more frequent in CD5− (p = 0.029). No difference in clinical stage, autoimmune phenomena, hemo globin and neutrophil count, and survival |
| Kurec et al., 1992 [45] | 12 vs. 27 | 66/67 | <20% of lymphoid cells | Hb: 11.2/13.7 g/L PLT: 172/175 × 109/L WBC: 88 × 109/L/60 × 109/L | NR | 55% vs. 90% at 5 yr | Lack of CD5 antigen was with more advanced stage of disease and poor patient survival. |
| Disease | Markers | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CD19 CD20 CD22 | CD5 | CD23 | FMC7 | CD200 | CD45 | CD43 | CD180 | Cyclin D1 | CD79b | LEF1 | SOX11 | |
| Typical CLL | + (dim) | + | + (strong) | − | + (strong) | −/+ | + | +/− (week) | − | +/− (week) | + | − |
| Atypical CLL | + | − | − | − | + | + | + | + | − | NR | +/− | NR |
| MCL | + (strong) | − | − | +/− | − | + | −/+ | + (week) | + | +/− | − | + |
| References | 7,8 36–40, 69 | 18,29, 36–40 | 18,29, 36–40 | 64,73 | 18,29, 36–40, 68–72 | 74,75 | 64,67, 76–79 | 64,76, 84–86 | 52,68 | 64,68 | 68,73, 81,82 | 68, 87–89 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Robak, T.; Krawczyńska, A.; Cebula-Obrzut, B.; Urbaniak, M.; Iskierka-Jażdżewska, E.; Robak, P. Atypical Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia—The Current Status. Cancers 2023, 15, 4427. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15184427
Robak T, Krawczyńska A, Cebula-Obrzut B, Urbaniak M, Iskierka-Jażdżewska E, Robak P. Atypical Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia—The Current Status. Cancers. 2023; 15(18):4427. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15184427
Chicago/Turabian StyleRobak, Tadeusz, Anna Krawczyńska, Barbara Cebula-Obrzut, Marta Urbaniak, Elżbieta Iskierka-Jażdżewska, and Paweł Robak. 2023. "Atypical Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia—The Current Status" Cancers 15, no. 18: 4427. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15184427
APA StyleRobak, T., Krawczyńska, A., Cebula-Obrzut, B., Urbaniak, M., Iskierka-Jażdżewska, E., & Robak, P. (2023). Atypical Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia—The Current Status. Cancers, 15(18), 4427. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15184427








