Single-Step IGHV Next-Generation Sequencing Detects Clonality and Somatic Hypermutation in Lymphoid Malignancies: A Phase III Diagnostic Accuracy Study
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Case Selection
2.2. DNA Extraction
2.3. IGH Clonal Analysis by PCR/Capillary Electrophoresis
2.4. IGH Hypermutation Analysis by Sanger Sequencing
2.5. Library Preparation and Sequencing on MiSeq Platform
2.6. IGH Clonality and Hypermutation Analysis by NGS
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
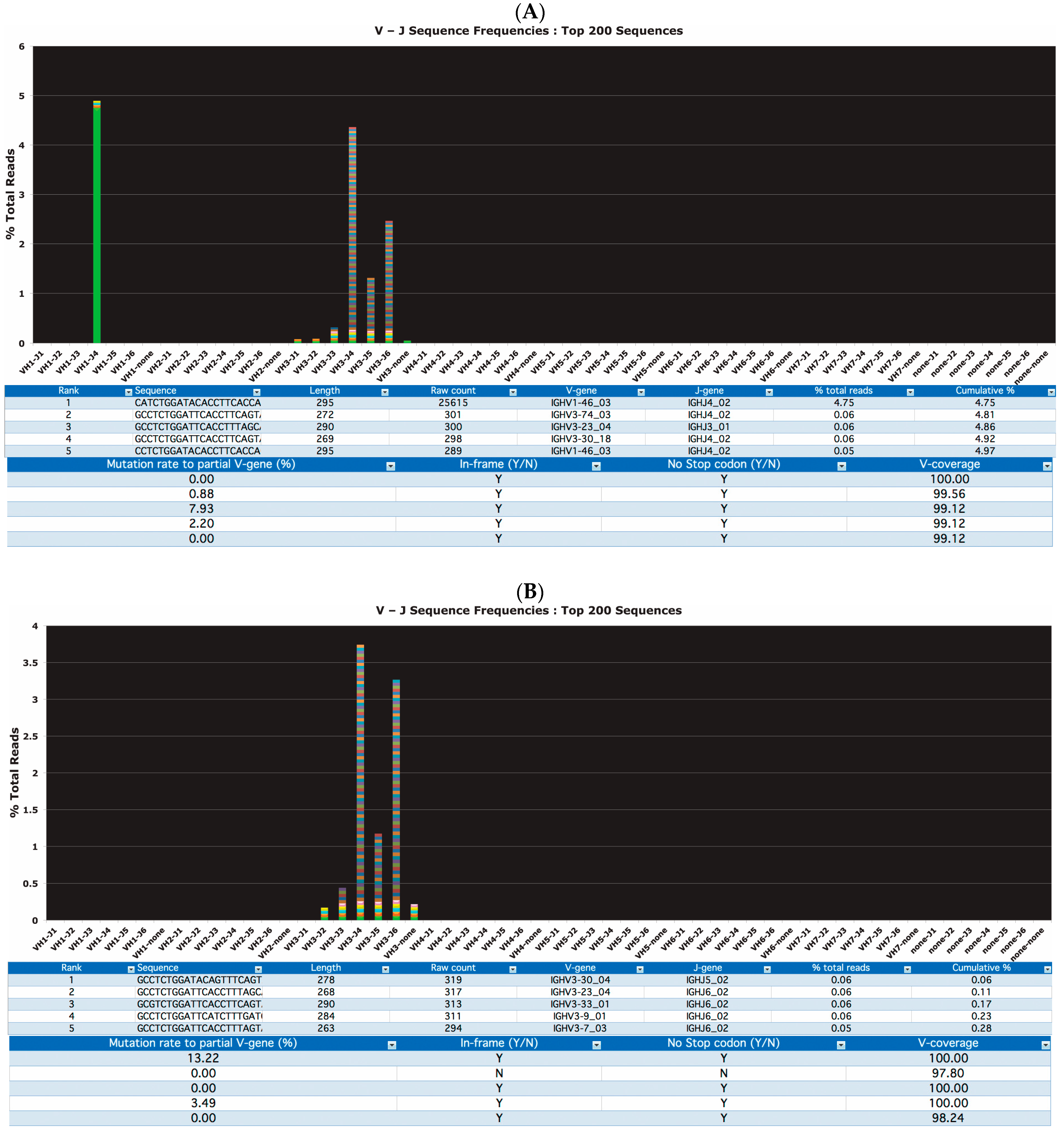
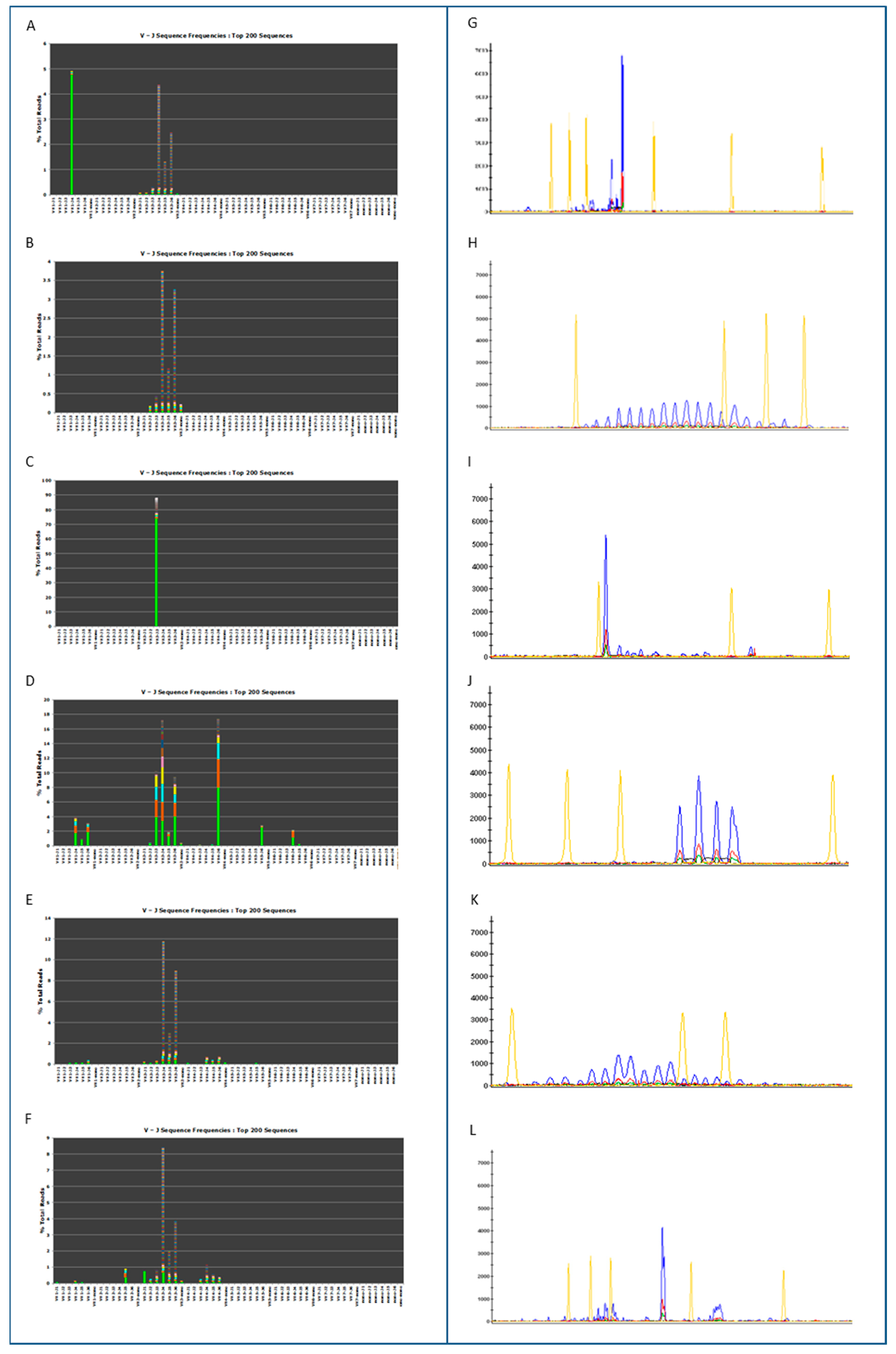
3.1. Clonality Assessment by Classical and NGS Analysis
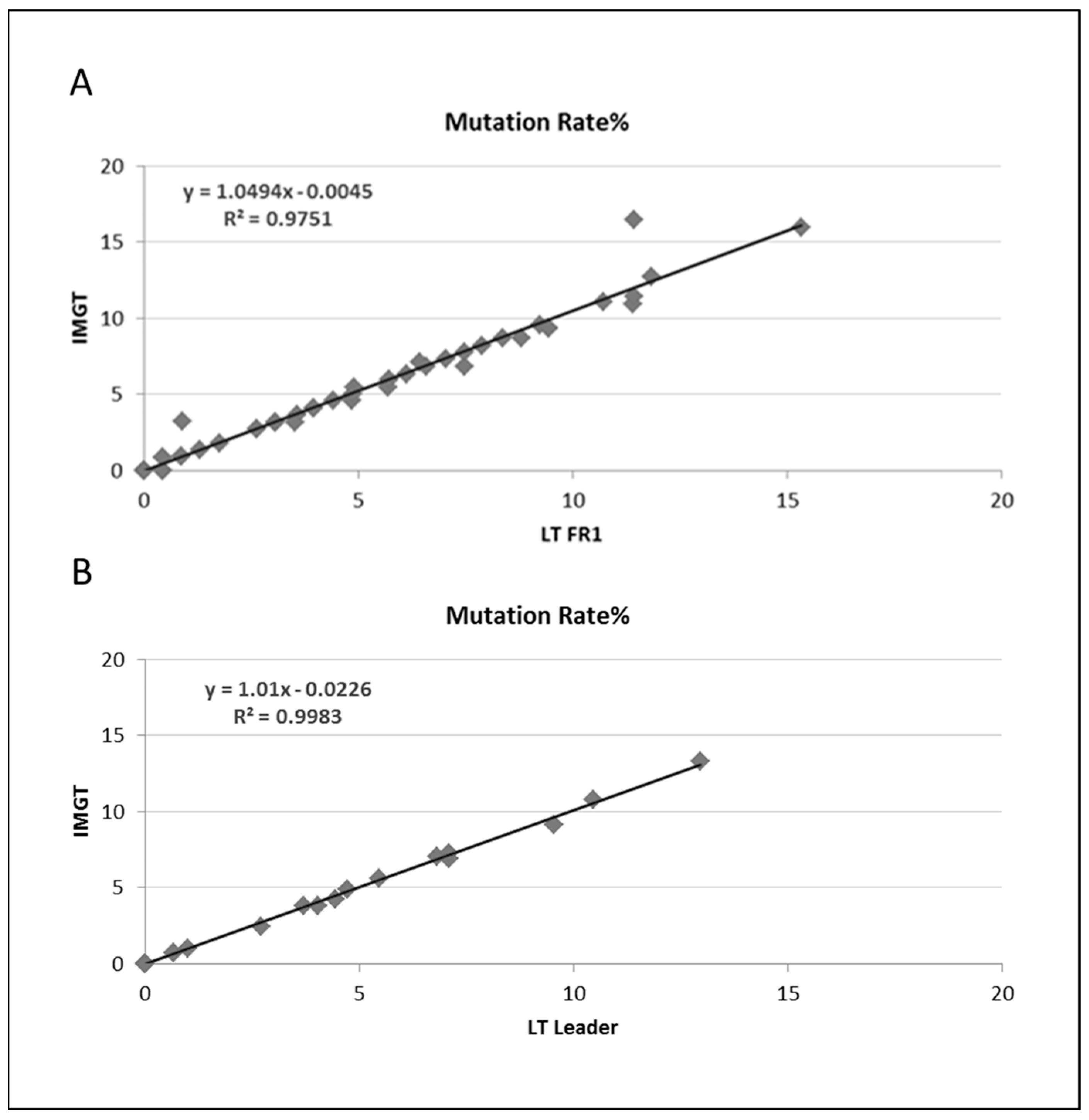
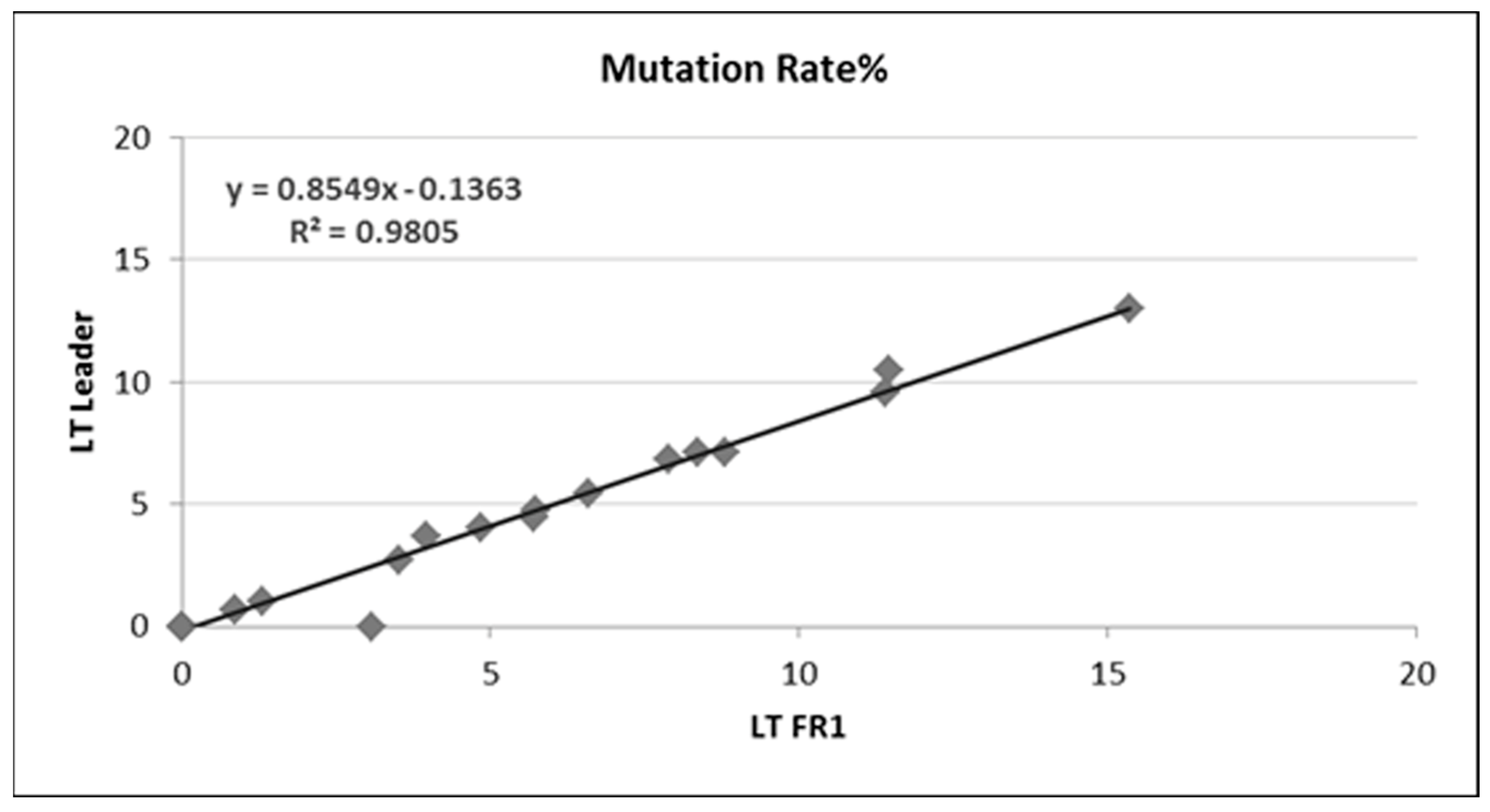
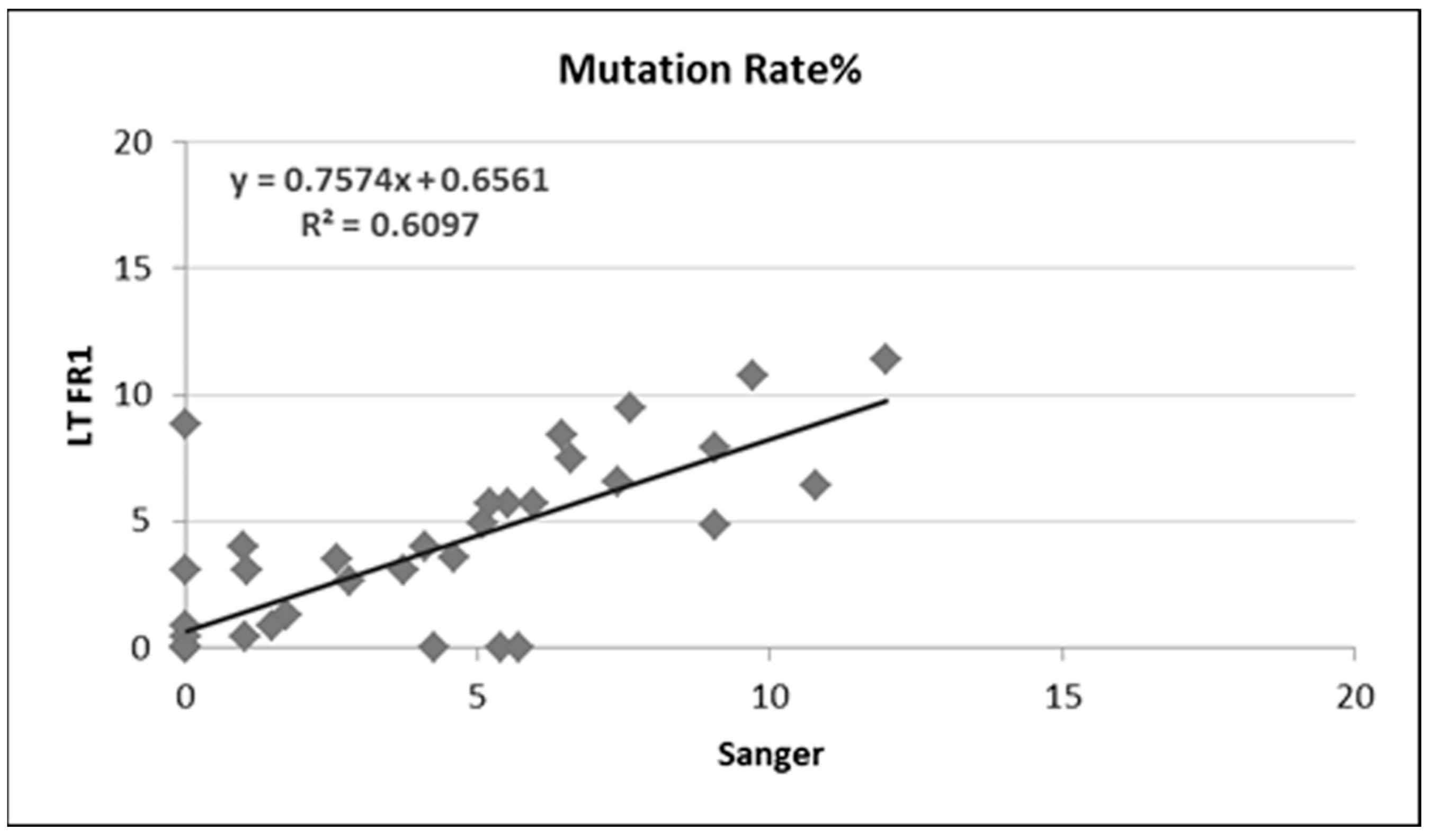
3.2. Somatic Hypermutation Detection by Classical and NGS Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Langerak, A.W.; Szczepański, T.; van der Burg, M.; Wolvers-Tettero, I.; van Dongen, J. Heteroduplex PCR analysis of rearranged T cell receptor genes for clonality assessment in suspect T cell proliferations. Leukemia 1997, 11, 2192–2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Dongen, J.J.M.; Langerak, A.W.; Brüggemann, M.; Evans, P.A.S.; Hummel, M.; Lavender, F.L.; Delabesse, E.; Davi, F.; Schuuring, E.; García-Sanz, R.; et al. Design and standardization of PCR primers and protocols for detection of clonal immunoglobulin and T-cell receptor gene recombinations in suspect lymphoproliferations: Report of the BIOMED-2 Concerted Action BMH4-CT98-3936. Leukemia 2003, 17, 2257–2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mannu, C.; Gazzola, A.; Bacci, F.; Sabattini, E.; Sagramoso, C.; Roncolato, F.; Rossi, M.; Laginestra, M.A.; Sapienza, M.R.; Agostinelli, C.; et al. Use of IGK gene rearrangement analysis for clonality assessment of lymphoid malignancies: A single center experience. Am. J. Blood Res. 2011, 1, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rezuke, W.N.; Abernathy, E.C.; Tsongalis, G.J. Molecular diagnosis of B- and T-cell lymphomas: Fundamental principles and clinical applications. Clin. Chem. 1997, 43, 1814–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swerdlow, S.C.E.; Harris, N.L.; Jaffe, E.S.; Pileri, S.A.; Stein, H.; Thiele, J. WHO Classification of Tumors of Hematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues, 4th ed.; IARC: Lyon, France, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Gazzola, A.; Mannu, C.; Rossi, M.; Laginestra, M.A.; Sapienza, M.R.; Fuligni, F.; Etebari, M.; Melle, F.; Sabattini, E.; Agostinelli, C.; et al. The evolution of clonality testing in the diagnosis and monitoring of hematological malignancies. Ther. Adv. Hematol. 2014, 5, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Dongen, J.J.; Wolvers-Tettero, I.L. Analysis of immunoglobulin and T cell receptor genes. Part I: Basic and technical aspects. Clin. Chim. Acta 1991, 198, 1–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunn–Walters, D.; Thiede, C.; Alpen, B.; Spencer, J. Somatic hypermutation and B—cell lymphoma. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2001, 356, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamblin, T.J.; Davis, Z.; Gardiner, A.; Oscier, D.G.; Stevenson, F.K. Unmutated Ig V(H) genes are associated with a more aggressive form of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 1999, 94, 1848–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Algara, P.; Mateo, M.S.; Sanchez-Beato, M.; Mollejo, M.; Navas, I.C.; Romero, L.; Solé, F.; Salido, M.; Florensa, L.; Martınez, P.; et al. Analysis of the IgV(H) somatic mutations in splenic marginal zone lymphoma defines a group of unmutated cases with frequent 7q deletion and adverse clinical course. Blood 2002, 99, 1299–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertoni, F.; Conconi, A.; Cogliatti, S.B.; Schmitz, S.-F.H.; Ghielmini, M.; Cerny, T.; Fey, M.; Pichert, G.; Bertolini, F.; Ponzoni, M.; et al. Immunoglobulin heavy chain genes somatic hypermutations and chromosome 11q22-23 deletion in classic mantle cell lymphoma: A study of the Swiss Group for Clinical Cancer Research. Br. J. Haematol. 2004, 124, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cogliatti, S.B.; Bertoni, F.; Zimmermann, D.R.; Henz, S.; Diss, T.C.; Ghielmini, M.; Schmid, U. IgV H mutations in blastoid mantle cell lymphoma characterize a subgroup with a tendency to more favourable clinical outcome. J. Pathol. 2005, 206, 320–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camacho, F.I.; Algara, P.; Rodríguez, A.; Ruíz-Ballesteros, E.; Mollejo, M.; Martínez, N.; Martínez-Climent, J.A.; González, M.; Mateo, M.; Caleo, A.; et al. Molecular heterogeneity in MCL defined by the use of specific VH genes and the frequency of somatic mutations. Blood 2003, 101, 4042–4046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, R.; Lefresne, S.V.; Franko, B.; Hui, D.; Mirza, I.; Mansoor, A.; Amin, H.M.; Ma, Y. Immunoglobulin VH somatic hypermutation in mantle cell lymphoma: Mutated genotype correlates with better clinical outcome. Mod. Pathol. 2006, 19, 1498–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langerak, A.W.; Davi, F.; Ghia, P.; Hadzidimitriou, A.; Murray, F.; Potter, K.N.; Rosenquist, R.; Stamatopoulos, K.; Belessi, C.; on behalf of the European Research Initiative on CLL (ERIC). Immunoglobulin sequence analysis and prognostication in CLL: Guidelines from the ERIC review board for reliable interpretation of problematic cases. Leukemia 2011, 25, 979–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groenen, P.J.T.A.; van Raaij, A.; van Altena, M.C.; Rombout, P.M.; van Krieken, J.M.H. A practical approach to diagnostic Ig/TCR clonality evaluation in clinical pathology. J. Hematop. 2012, 5, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langerak, A.W.; Groenen, P.J.T.A.; Brüggemann, M.; Beldjord, K.; Bellan, C.; Bonello, L.; Boone, E.; Carter, G.I.; Catherwood, M.; Davi, F.; et al. EuroClonality/BIOMED-2 guidelines for interpretation and reporting of Ig/TCR clonality testing in suspected lymphoproliferations. Leukemia 2012, 26, 2159–2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.; Wu, J.; Jiao, Y.; Wagner-Johnston, N.; Ambinder, R.F.; Diaz, L.A., Jr.; Kinzler, K.W.; Vogelstein, B.; Papadopoulos, N. IgH gene rearrangements as plasma biomarkers in Non- Hodgkin’s lymphoma patients. Oncotarget 2011, 2, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, S.D.; Gaëta, B.A.; Jackson, K.J.; Fire, A.Z.; Marshall, E.L.; Merker, J.D.; Maniar, J.M.; Zhang, L.N.; Sahaf, B.; Jones, C.D.; et al. Individual Variation in the Germline Ig Gene Repertoire Inferred from Variable Region Gene Rearrangements. J. Immunol. 2010, 184, 6986–6992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, S.D.; Marshall, E.L.; Merker, J.D.; Maniar, J.M.; Zhang, L.N.; Sahaf, B.; Jones, C.D.; Simen, B.B.; Hanczaruk, B.; Nguyen, K.D.; et al. Measurement and Clinical Monitoring of Human Lymphocyte Clonality by Massively Parallel V-D-J Pyrosequencing. Sci. Transl. Med. 2009, 1, 12ra23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohlmann, A.; Grossmann, V.; Haferlach, T. Integration of Next-Generation Sequencing Into Clinical Practice: Are We There Yet? Semin. Oncology. 2012, 39, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robins, H. Detecting and monitoring lymphoma with high-throughput sequencing. Oncotarget 2011, 2, 287–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oki, Y.; Neelapu, S.S.; Fanale, M.; Kwak, L.W.; Fayad, L.; Rodriguez, M.A.; Wallace, M.; Klinger, M.; Carlton, V.; Kong, K.; et al. Detection of classical Hodgkin lymphoma specific sequence in peripheral blood using a next-generation sequencing approach. Br. J. Haematol. 2015, 169, 689–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Šimundić, A.-M. Measures of Diagnostic Accuracy: Basic Definitions. EJIFCC 2009, 19, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Syed, M.H.; Ho, C.; Petrova-Drus, K.; Yao, J.; Yu, W.; Zehir, A.; Nafa, K.; Arcila, M.E. Clinical utility of clonality testing by next generation sequencing in the monitoring of B-cell and T-cell malignancies. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcila, M.E.; Yu, W.; Syed, M.; Kim, H.; Maciag, L.; Yao, J.; Caleb, H.; Petrova, K.; Moung, C.; Salazar, P.; et al. Establishment of Ig Heavy Chain Clonality Testing by Next-Generation Sequencing for Routine Characterization of B-Cell and Plasma Cell Neoplasms. J. Mol. Diagn. 2018, 21, 330–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wren, D.; Walker, B.A.; Brüggemann, M.; Catherwood, M.A.; Pott, C.; Stamatopoulos, K.; Langerak, A.W.; Gonzalez, D. Comprehensive translocation and clonality detection in lymphoproliferative disorders by next-generation sequencing. Haematologica 2016, 102, e57–e60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheijen, B.; Meijers, R.W.J.; Rijntjes, J.; van der Klift, M.Y.; Möbs, M.; Steinhilber, J.; Reigl, T.; van den Brand, M.; Kotrová, M.; Ritter, J.-M.; et al. Next-generation sequencing of immunoglobulin gene rearrangements for clonality assessment: A technical feasibility study by EuroClonality-NGS. Leukemia 2019, 33, 2227–2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lay, L.; Stroup, B.; Payton, J.E. Validation and interpretation of IGH and TCR clonality testing by Ion Torrent S5 NGS for diagnosis and disease monitoring in B and T cell cancers. Practical. Lab. Med. 2020, 22, e00191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulsen, K.; Marincevic, M.; Cavelier, L.; Hollander, P.; Amini, R.-M. LymphoTrack Is Equally Sensitive as PCR GeneScan and Sanger Sequencing for Detection of Clonal Rearrangements in ALL Patients. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, J.; Lee, H.; Shin, S.; Cho, H.; Chung, H.; Jang, J.E.; Kim, S.-J.; Cheong, J.-W.; Lee, S.-T.; Kim, J.S.; et al. Ig Gene Clonality Analysis Using Next-Generation Sequencing for Improved Minimal Residual Disease Detection with Significant Prognostic Value in Multiple Myeloma Patients. J. Mol. Diagn. 2021, 24, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina, A.; Jiménez, C.; Puig, N.; Sarasquete, M.E.; Flores-Montero, J.; García-Álvarez, M.; Prieto-Conde, I.; Chillón, C.; Alcoceba, M.; González-Calle, V.; et al. Interlaboratory Analytical Validation of a Next-Generation Sequencing Strategy for Clonotypic Assessment and Minimal Residual Disease Monitoring in Multiple Myeloma. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2021, 146, 862–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Krieken, J.H.J.M.; Langerak, A.W.; Macintyre, E.A.; Kneba, M.; Hodges, E.; Sanz, R.G.; Morgan, G.J.; Parreira, A.; Molina, T.J.; Cabeçadas, J.; et al. Improved reliability of lymphoma diagnostics via PCR-based clonality testing:—Report of the BIOMED-2 Concerted Action BHM4-CT98-3936. Leukemia 2006, 21, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brüggemann, M.; White, H.; Gaulard, P.; Garcia-Sanz, R.; Gameiro, P.; Oeschger, S.; Jasani, B.; Ott, M.; Delsol, G.; Orfao, A.; et al. Powerful strategy for polymerase chain reaction-based clonality assessment in T-cell malignancies Report of the BIOMED-2 Concerted Action BHM4 CT98-3936. Leukemia 2006, 21, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Short, N.J.; Kantarjian, H.M.; Ravandi, F.; Konopleva, M.Y.; Jain, N.; Kanagal-Shamanna, R.; Patel, K.P.; Macaron, W.; Kadia, T.M.; Wang, S.A.; et al. High-sensitivity next-generation sequencing MRD assessment in ALL identifies patients at very low risk of relapse. Blood Adv. 2022, 6, 4006–4014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Frequency of Clonal Population | Margin of Error | Power * | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 95% | 99% | ||
| 1.0% | 0.1% (0.9–1.1%) | 134,379 | 191,545 |
| 1.0% | 1.0% (0–2%) | 1809 | 2712 |
| 2.5% | 0.5% (2–3%) | 11,009 | 19,760 |
| 2.5% | 1% (1.5–3.5%) | 2933 | 5381 |
| 5.0% | 0.5% (4.5–5.5%) | 25,739 | 36,675 |
| 5.0% | 1.0% (4–6%) | 6688 | 9597 |
| N | Sample | Diagnostic | NGS | Capillary Electrophoresis |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | PBL | CLL | Clonal | Clonal |
| 2 | PBL | CLL | Clonal | Clonal |
| 3 | PBL | CLL | Clonal | Clonal |
| 4 | PBL | CLL | Clonal | Clonal |
| 5 | PBL | CLL | Clonal | Clonal |
| 6 | PBL | CLL | Clonal | Clonal |
| 7 | PBL | CLL | Clonal | Clonal |
| 8 | PBL | CLL | Clonal | Clonal |
| 9 | PBL | CLL | Clonal | Clonal |
| 10 | PBL | CLL | Clonal | Clonal |
| 11 | PBL | CLL | Clonal | Clonal |
| 12 | PBL | CLL | Clonal | Clonal |
| 13 | PBL | CLL | Clonal | Clonal |
| 14 | PBL | CLL | Clonal | Clonal |
| 15 | PBL | CLL | Clonal | Clonal |
| 16 | PBL | CLL | Clonal | Clonal |
| 17 | PBL | CLL | Clonal | Clonal |
| 18 | PBL | CLL | Clonal | Clonal |
| 19 | PBL | CLL | Clonal | Clonal |
| 20 | PBL | CLL | Clonal | Clonal |
| 21 | PBL | CLL | Clonal | Clonal |
| 22 | PBL | CLL | Clonal | Clonal |
| 23 | PBL | CLL | Clonal | Clonal |
| 24 | PBL | CLL | Clonal | Clonal |
| 25 | PBL | CLL | Clonal | Clonal |
| 26 | PBL | CLL | Clonal | Clonal |
| 27 | PBL | CLL | Clonal | Clonal |
| 28 | PBL | CLL | Clonal | Clonal |
| 29 | PBL | CLL | Clonal | Clonal |
| 30 | PBL | CLL | Clonal | Clonal |
| 31 | PBL | CLL | Clonal | Clonal |
| 32 | PBL | CLL | Clonal | Clonal |
| 33 | PBL | CLL | Clonal | Clonal |
| 34 | PBL | CLL | Clonal | Clonal |
| 35 | PBL | CLL | Clonal | Clonal |
| 36 | PBL | CLL | Clonal | Clonal |
| 37 | PBL | CLL | Clonal | Clonal |
| 38 | PBL | CLL | Clonal | Clonal |
| 39 | PBL | CLL | Clonal | Clonal |
| 40 | PBL | CLL | Clonal | Clonal |
| 41 | PBL | CLL | Clonal | Clonal |
| 42 | PBL | CLL | Clonal | Clonal |
| 43 | PBL | CLL | Clonal | Clonal |
| 44 | PBL | CLL | Clonal | Clonal |
| 45 | PBL | CLL | Clonal | Clonal |
| 46 | PBL | CLL | Clonal | Clonal |
| 47 | PBL | CLL | Clonal | Clonal |
| 48 | PBL | CLL | Clonal | Clonal |
| 49 | PBL | CLL | Clonal | Clonal |
| 50 | PBL | CLL | Clonal | Clonal |
| 51 | PBL | CLL | Clonal | Clonal |
| 52 | FFPE | FL | Clonal | Clonal |
| 53 | FFPE | MCL | Clonal | Clonal |
| 54 | FFPE | MCL | Polyclonal | Clonal |
| 55 | FFPE | FL | Polyclonal | Clonal |
| 56 | FFPE | FL | Clonal | Clonal |
| 57 | FFPE | FL | Oligoclonal | Oligoclonal |
| 58 | FFPE | MCL | * Not evaluable | Oligoclonal |
| 59 | FFPE | FL | * Not evaluable | Oligoclonal |
| 60 | FFPE | RLH | Polyclonal | Clonal |
| 61 | FFPE | FL | Polyclonal | Polyclonal |
| 62 | FFPE | FL | Polyclonal | Polyclonal |
| 63 | FFPE | FL | Polyclonal | Polyclonal |
| 64 | FFPE | RLH | Polyclonal | Polyclonal |
| 65 | FFPE | RLH | Polyclonal | Polyclonal |
| 66 | FFPE | RLH | Polyclonal | Polyclonal |
| 67 | FFPE | RLH | Polyclonal | Polyclonal |
| 68 | FFPE | RLH | Polyclonal | Polyclonal |
| Capillary Electrophoresis | |||||
| Clonal | Non-Monoclonal | ||||
| NGS | Clonal | 54 | 0 | ||
| Non-monoclonal | 3 | 9 | |||
| Parameter | Value | 95% CI | |||
| ST | 95% | 89–100 | |||
| SP | 100% | 100–100 | |||
| Pre-test probability | 86% | 78–95 | |||
| PPV | 100% | 100–100 | |||
| NPV | 75% | 51–100 | |||
| LR+ | Not evaluable | Not evaluable | |||
| LR− | 0.05 | 0.02–0.16 | |||
| N | Sanger | NGS-FR1 | NGS-Leader | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| V | J | %Mut Rate | V | J | %Mut Rate | V | J | %Mut Rate | |
| 1 | V1-69_13 | J6_02 | 0 | V1-69_13 | J6_02 | 0.00 | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| 2 | V3-74_03 | J4_02 | 0 | V3-74_01 | J4_02 | 0.00 | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| 3 | V1-18_01 | J6_02 | 1.03 | V1-18_01 | J6_02 | 0.44 | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| 4 | V3-33_03 | J3_02 | 5.53 | V3-33_01 | J3_02 | 5.73 | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| 5 | V3-15_07 | J6_02 | 9.7 | V3-15_02 | J6_02 | 10.73 | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| 6 | IV3-21_01 | J4_02 | 0 | V3-21_02 | J4_02 | 0.00 | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| 7 | V1-18_01 | J6_02 | 0 | V1-18_01 | J6_02 | 0.00 | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| 8 | NV | NV | NV | V4-34_02 | J4_02 | 0.00 | V4-34_01 | J4_02 | 0 |
| 9 | V5-a_04 | J4_02 | 5.1 | V5-a_03 | J4_02 | 4.91 | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| 10 | V3 | J4_02 | 4.1 | V3-30_02 | J4_02 | 3.96 | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| 11 | V1-69_13 | J6_02 | 5.4 | V1-69_13 | J6_02 | 0.00 | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| 12 | NV | NV | NV | V4-39_01 | J5_02 | 0.00 | V4-39_01 | J5_02 | 0 |
| 13 | V1-69 | J3_02 | 0 | V1-69_06 | J3_02 | 0.00 | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| 14 | V3 | J5_02 | 6.6 | V3-11_05 | J5_02 | 7.49 | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| 15 | V1-18_01 | J4_02 | 0 | V1-18_01 | J4_02 | 0.44 | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| 16 | NV | NV | NV | V3-21_02 | J4_02 | 9.25 | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| 17 | V3-72_02 | J6_02 | 10.8 | V3-72_01 | J6_02 | 6.44 | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| 18 | V4-34_13 | J4_02 | 2.81 | V4-34_02 | J4_02 | 2.63 | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| 19 | V1-2_03 | J4_02 | 4.6 | V1-2_04 | J4_02 | 3.57 | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| 20 | V3-21_02 | J6_02 | 1.05 | V3-21_02 | J6_02 | 3.08 | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| 21 | V3-21_02 | J6_02 | 0 | V1-2_04 | J6_02 | 0.00 | V1-2_04 | J6_02 | 0 |
| 22 | V3-9_02 | J4_02 | 3.75 | V3-9_01 | J4_02 | 3.06 | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| 23 | V3-72_02 | J3_02 | 7.6 | V3-72_01 | J3_02 | 9.44 | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| 24 | NV | NV | NV | V3-49_05 | J5_02 | 0.00 | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| 25 | NV | NV | NV | V3-21_02 | none | 7.49 | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| 26 | V5-a_04 | J6_02 | 0 | V5-a_03 | J6_02 | 0.00 | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| 27 | V4-34_02 | J6_02 | 7.4 | V4-34_02 | J6_02 | 6.58 | V4-34_01 | J6_02 | 5.46 |
| 28 | V3-21_02 | J5_02 | 1.74 | V3-21_02 | J5_02 | 1.32 | V3-21_01 | J5_02 | 1.01 |
| 29 | V3-21_02 | J5_02 | 0 | V3-7_01 | J1_01 | 8.81 | V3-7_01 | J1_01 | 7.09 |
| 30 | V4-34_02 | J5_02 | 5.94 | V4-34_02 | J5_02 | 5.70 | V4-34_01 | J5_02 | 4.44 |
| 31 | V3-30_04 | J4_02 | 0 | V3-30_04 | J4_02 | 0.00 | V3-30_04 | J4_02 | 0.00 |
| 32 | V4-34_01 | J4_02 | 0 | V3-48_02 | J3_02 | 3.08 | V4-34_01 | J4_02 | 0.00 |
| 33 | V4-4_02 | J6_02 | 0 | V4-4_02 | J6_02 | 0.00 | V4-4_02 | J6_02 | 0.00 |
| 34 | V4-59_01 | J6_02 | 0 | V4-59_01 | J6_02 | 0.00 | V4-59_01 | J6_02 | 0.00 |
| 35 | V3-74_03 | J4_02 | 2.6 | V3-74_03 | J4_02 | 3.52 | V3-74_03 | J4_02 | 2.70 |
| 36 | V1-69_01 | J6_04 | 0 | V1-69_13 | J6_04 | 0.00 | V1-69_01 | J6_04 | 0.00 |
| 37 | V3-21_01 | J6_02 | 0 | V3-21_02 | J6_02 | 0.00 | V3-21_01 | J6_02 | 0.00 |
| 38 | V1-69_13 | J6_02 | 0 | V1-69_13 | J6_02 | 0.00 | V1-69_01 | J6_02 | 0.00 |
| 39 | V4-34_03 | J4_02 | 12 | V4-34_02 | J5_02 | 11.40 | V4-34_01 | J5_02 | 9.56 |
| 40 | V3-9_02 | J6-02 | 5.72 | V1-69_13 | J6_04 | 0.00 | V1-69_01 | J6_04 | 0.00 |
| 41 | V3-21 | J4_02 | 1 | V3-48_03 | J4_02 | 3.96 | V3-48_03 | J4_02 | 3.72 |
| 42 | V4-34_02 | J6_03 | 1.5 | V4-34_02 | J6_03 | 0.88 | V4-34_01 | J6_03 | 0.68 |
| 43 | V3-74_03 | J5_02 | 6.45 | V3-74_03 | J5_02 | 8.37 | V3-74_03 | J5_02 | 7.09 |
| 44 | V1-69_13 | J6_02 | 0 | V1-69_13 | J6_02 | 0.00 | V1-69_01 | J6_02 | 0.00 |
| 45 | V3-33_01 | J6_02 | 5.2 | V3-33_01 | J6_02 | 5.73 | V3-33_01 | J6_02 | 4.73 |
| 46 | NV | NV | NV | V4-59_08 | J5_02 | 15.35 | V4-59_08 | J5_02 | 12.97 |
| 47 | V3-21_02 | J4_02 | 0 | V3-21_02 | J4_02 | 0.88 | V3-21_01 | J4_02 | 0.68 |
| 48 | V4-34_02 | J6_02 | 9.05 | V3-23_04 | J4_02 | 4.85 | V3-23_01 | J4_02 | 4.05 |
| 49 | V1-58_01 | J6_03 | 4.27 | V1-58_01 | J6_03 | 0.00 | V1-58_01 | J6_03 | 0.00 |
| 50 | NV | NV | NV | V3-23_04 | J4_02 | 11.45 | V3-23_01 | J4_02 | 10.47 |
| 51 | V4-34_02 | J6_02 | 9.05 | V4-34_02 | J6_02 | 7.89 | V4-34_01 | J6_02 | 6.83 |
| Characteristic | VHL/J | FR1/J |
|---|---|---|
| Amplicon size (bp) | 500–570 | 290–360 |
| PCR cycle | 32 | 29 |
| MiSeq Reagent kit | 600–cycle | 500–cycle |
| MiSeq run time (hr) | 55 | 39 |
| Pros | Whole VH region | Higher PCR efficiency Lower cost Faster results |
| Cons | Lower PCR efficiency Higher cost More time-consuming | Partial FR1 region |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gazzola, A.; Navari, M.; Mannu, C.; Donelli, R.; Etebari, M.; Piccaluga, P.P. Single-Step IGHV Next-Generation Sequencing Detects Clonality and Somatic Hypermutation in Lymphoid Malignancies: A Phase III Diagnostic Accuracy Study. Cancers 2023, 15, 4624. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15184624
Gazzola A, Navari M, Mannu C, Donelli R, Etebari M, Piccaluga PP. Single-Step IGHV Next-Generation Sequencing Detects Clonality and Somatic Hypermutation in Lymphoid Malignancies: A Phase III Diagnostic Accuracy Study. Cancers. 2023; 15(18):4624. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15184624
Chicago/Turabian StyleGazzola, Anna, Mohsen Navari, Claudia Mannu, Riccardo Donelli, Maryam Etebari, and Pier Paolo Piccaluga. 2023. "Single-Step IGHV Next-Generation Sequencing Detects Clonality and Somatic Hypermutation in Lymphoid Malignancies: A Phase III Diagnostic Accuracy Study" Cancers 15, no. 18: 4624. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15184624
APA StyleGazzola, A., Navari, M., Mannu, C., Donelli, R., Etebari, M., & Piccaluga, P. P. (2023). Single-Step IGHV Next-Generation Sequencing Detects Clonality and Somatic Hypermutation in Lymphoid Malignancies: A Phase III Diagnostic Accuracy Study. Cancers, 15(18), 4624. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15184624








