Time-Dependent ROC Curve Analysis for Assessing the Capability of Radiation-Induced CD8 T-Lymphocyte Apoptosis to Predict Late Toxicities after Adjuvant Radiotherapy of Breast Cancer Patients
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. The Clinical Trial Data
2.2. The Time-Dependent ROC Curve Approach
2.3. Statistical Analysis
2.3.1. Prediction
2.3.2. Endpoints
2.4. Methodology of Analysis
2.5. Software
3. Results
3.1. Baseline RILA Alone
3.2. Composite Marker
3.3. Baseline RILA Alone and Composite Marker Comparison
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Darby, S.C.; Ewertz, M.; McGale, P.; Bennet, A.M.; Blom-Goldman, U.; Brønnum, D.; Correa, C.; Cutter, D.; Gagliardi, G.; Gigante, B.; et al. Risk of ischemic heart disease in women after radiotherapy for breast cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 987–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferini, G.; Molino, L.; Tripoli, A.; Valenti, V.; Illari, S.I.; Marchese, V.A.; Cravagno, I.R.; Borzi, G.R. Anatomical Predictors of Dosimetric Advantages for Deep-inspiration-breath-hold 3D-conformal Radiotherapy Among Women with Left Breast Cancer. Anticancer. Res. 2021, 41, 1529–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferini, G.; Valenti, V.; Viola, A.; Umana, G.E.; Martorana, E. A Critical Overview of Predictors of Heart Sparing by Deep-Inspiration-Breath-Hold Irradiation in Left-Sided Breast Cancer Patients. Cancers 2022, 14, 3477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Straub, J.M.; New, J.; Hamilton, C.D.; Lominska, C.; Shnayder, Y.; Thomas, S.M. Radiation-induced fibrosis: Mechanisms and implications for therapy. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 141, 1985–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fhoghlú, M.N.; Barrett, S. A Review of Radiation-Induced Lymphocyte Apoptosis as a Predictor of Late Toxicity after Breast Radiotherapy. J. Med. Imaging Radiat. Sci. 2019, 50, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azria, D.; Betz, M.; Bourgier, C.; Sozzi, W.J.; Ozsahin, M. Identifying patients at risk for late radiation-induced toxicity. Crit. Rev. Oncol. 2012, 84, e35–e41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordón, E.; Henríquez-Hernández, L.A.; Lara, P.C.; Ruíz, A.; Pinar, B.; Rodríguez-Gallego, C.; Lloret, M. Prediction of clinical toxicity in locally advanced head and neck cancer patients by radio-induced apoptosis in peripheral blood lymphocytes (PBLs). Radiat. Oncol. 2010, 5, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foro, P.; Algara, M.; Lozano, J.; Rodriguez, N.; Sanz, X.; Torres, E.; Carles, J.; Reig, A.; Membrive, I.; Quera, J.; et al. Relationship between radiation-induced apoptosis of T lymphocytes and chronic toxicity in patients with prostate cancer treated by radiation therapy: A prospective study. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2014, 88, 1057–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnarr, K.; Boreham, D.; Sathya, J.; Julian, J.; Dayes, I.S. Radiation-induced lymphocyte apoptosis to predict radiation therapy late toxicity in prostate cancer patients. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2009, 74, 1424–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozsahin, M.; Crompton, N.E.; Gourgou, S.; Kramar, A.; Li, L.; Shi, Y.; Sozzi, W.J.; Zouhair, A.; Mirimanoff, R.O.; Azria, D. CD4 and CD8 T-Lymphocyte Apoptosis Can Predict Radiation-Induced Late Toxicity: A Prospective Study in 399 Patients. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 7426–7433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azria, D.; Riou, O.; Castan, F.; Nguyen, T.D.; Peignaux, K.; Lemanski, C.; Lagrange, J.-L.; Kirova, Y.; Lartigau, E.; Belkacemi, Y.; et al. Radiation-induced CD8 T-lymphocyte Apoptosis as a Predictor of Breast Fibrosis After Radiotherapy: Results of the Prospective Multicenter French Trial. EBioMedicine 2015, 2, 1965–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fawcett, T. An introduction to ROC analysis. Pattern Recogn. Lett. 2006, 27, 861–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swets, J.A. Measuring the accuracy of diagnostic systems. Science 1988, 240, 1285–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, K.H.; O’Malley, A.J.; Mauri, L. Receiver-Operating Characteristic Analysis for Evaluating Diagnostic Tests and Predictive Models. Circulation 2007, 115, 654–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamarudin, A.N.; Cox, T.; Kolamunnage-Dona, R. Time-dependent ROC curve analysis in medical research: Current methods and applications. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2017, 17, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heagerty, P.J.; Lumley, T.; Pepe, M.S. Time-Dependent ROC Curves for Censored Survival Data and a Diagnostic Marker. Biometrics 2000, 56, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trotti, A.; Colevas, A.D.; Setser, A.; Rusch, V.; Jaques, D.; Budach, V.; Langer, C.; Murphy, B.; Cumberlin, R.; Coleman, C.N.; et al. CTCAE v3.0: Development of a comprehensive grading system for the adverse effects of cancer treatment. Semin. Radiat. Oncol. 2003, 13, 176–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, D.R. Regression Models and Life-Tables. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B Stat. Methodol. 1972, 34, 187–202. Available online: https://rss.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/epdf/10.1111/j.2517-6161.1972.tb00899.x (accessed on 27 June 2023). [CrossRef]
- Hanley, J.A. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) methodology: The state of the art. Crit. Rev. Comput. Tomogr. 1989, 29, 307–335. [Google Scholar]
- Begg, C.B. Advances in statistical methodology for diagnostic medicine in the 1980’s. Stat. Med. 1991, 10, 1887–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepe, M.; Leisenring, W.; Rutter, C. Evaluating diagnostic tests in public health. In Handbook of Statistics; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2000; pp. 397–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zweig, M.H.; Campbell, G. Receiver-operating characteristic (ROC) plots: A fundamental evaluation tool in clinical medicine. Clin. Chem. 1993, 39, 561–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepe, M.S. The Statistical Evaluation of Medical Tests for Classification and Prediction; Oxford University Press: Oxford, NY, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Bamber, D. The area above the ordinal dominance graph and the area below the receiver operating characteristic graph. J. Math. Psychol. 1975, 12, 387–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanley, J.A.; McNeil, B.J. The meaning and use of the area under a receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve. Radiology 1982, 143, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youden, W.J. Index for rating diagnostic tests. Cancer 1950, 3, 32–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altman, D.G.; Bland, J.M. Statistics Notes: Diagnostic tests 2: Predictive values. BMJ 1994, 309, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Refaeilzadeh, P.; Tang, L.; Liu, H. Cross-Validation. In Encyclopedia of Database Systems; Liu, L., Özsu, M.T., Eds.; Springer US: Boston, MA, USA, 2009; pp. 532–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, G.; Witten, D.M.; Hastie, T.; Tibshirani, R. An Introduction to Statistical Learning; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Core Team: Vienna, Austria, 2017; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 27 June 2022).
- Therneau, T.M. A Package for Survival Analysis in R, R Package Version 3.5-5. 2023. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=survival (accessed on 27 June 2022).
- Patrick, J. Heagerty and Packaging by Paramita Saha-Chaudhuri, survivalROC: Time-Dependent ROC Curve Estimation from Censored Survival Data, R Package Version 1.0.3.1. 2022. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=survivalROC (accessed on 27 June 2022).
- Duchaud, E.; Ridet, A.; Delic, Y.; Cundari, E.; Moustacchi, E.; Rosselli, F. Changes in the radiation-induced apoptotic response in homozygotes and heterozygotes for the ataxia-telangiectasia gene. C. R. Acad. Sci. III 1994, 317, 983–989. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/7882143/ (accessed on 15 September 2023).
- Mirjolet, C.; Merlin, J.; Truc, G.; Noël, G.; Thariat, J.; Domont, J.; Sargos, P.; Renard-Oldrini, S.; Ray-Coquard, I.; Liem, X.; et al. RILA blood biomarker as a predictor of radiation-induced sarcoma in a matched cohort study. EBioMedicine 2019, 41, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourgier, C.; Kerns, S.; Gourgou, S.; Lemanski, C.; Gutowski, M.; Fenoglietto, P.; Romieu, G.; Crompton, N.; Lacombe, J.; Pèlegrin, A.; et al. Concurrent or sequential letrozole with adjuvant breast radiotherapy: Final results of the CO-HO-RT phase II randomized trial. Ann. Oncol. 2016, 27, 474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henríquez-Hernández, L.A.; Carmona-Vigo, R.; Pinar, B.; Bordón, E.; Lloret, M.; Núñez, M.I.; Rodríguez-Gallego, C.; Lara, P.C. Combined low initial DNA damage and high radiation-induced apoptosis confers clinical resistance to long-term toxicity in breast cancer patients treated with high-dose radiotherapy. Radiat. Oncol. 2011, 6, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azria, D.; Ozsahin, M.; Kramar, A.; Peters, S.; Atencio, D.P.; Crompton, N.E.; Mornex, F.; Pèlegrin, A.; Dubois, J.-B.; Mirimanoff, R.-O.; et al. Single nucleotide polymorphisms, apoptosis, and the development of severe late adverse effects after radiotherapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 6284–6288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crompton, N.E.; Shi, Y.-Q.; Emery, G.C.; Wisser, L.; Blattmann, H.; Maier, A.; Li, L.; Schindler, D.; Ozsahin, H.; Ozsahin, M. Sources of variation in patient response to radiation treatment. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2001, 49, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuentes-Raspall, M.J.; Caragol, I.; Alonso, C.; Cajal, T.R.Y.; Fisas, D.; Seoane, A.; Carvajal, N.; Bonache, S.; Díez, O.; Gutiérrez-Enríquez, S. Apoptosis for prediction of radiotherapy late toxicity: Lymphocyte subset sensitivity and potential effect of TP53 Arg72Pro polymorphism. Apoptosis Int. J. Program. Cell Death. Apoptosis 2015, 20, 371–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaitelman, S.F.; Howell, R.M.; Smith, B.D. The Effects of Smoking on Late toxicity from breast radiation. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 1633–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourgier, C.; Castan, F.; Riou, O.; Nguyen, T.-D.; Peignaux, K.; Lemanski, C.; Lagrange, J.-L.; Kirova, Y.; Lartigau, E.; Belkacemi, Y.; et al. Impact of adjuvant hormonotherapy on radiation-induced breast fibrosis according to the individual radiosensitivity: Results of a multicenter prospective French trial. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 15757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasquier, D.; Bataille, B.; Le Tinier, F.; Bennadji, R.; Langin, H.; Escande, A.; Tresch, E.; Darloy, F.; Carlier, D.; Crop, F.; et al. Lartigau, Correlation between toxicity and dosimetric parameters for adjuvant intensity modulated radiation therapy of breast cancer: A prospective study. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 3626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayer, E.L. Early and Late Long-Term Effects of Adjuvant Chemotherapy. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. Educ. Book 2013, 33, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Santis, M.; Bonfantini, F.; Di Salvo, F.; Dispinzieri, M.; Mantero, E.; Soncini, F.; Baili, P.; Sant, M.; Bianchi, G.; Maggi, C.; et al. Factors influencing acute and late toxicity in the era of adjuvant hypofractionated breast radiotherapy. Breast 2016, 29, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moons, K.G.M.; Altman, D.G.; Reitsma, J.B.; Ioannidis, J.P.A.; Macaskill, P.; Steyerberg, E.W.; Vickers, A.J.; Ransohoff, D.F.; Collins, G.S. Transparent Reporting of a multivariable prediction model for Individual Prognosis or Diagnosis (TRIPOD): Explanation and Elaboration. Ann. Intern. Med. 2015, 162, W1–W73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanche, P.; Dartigues, J.-F.; Jacqmin-Gadda, H. Review and comparison of ROC curve estimators for a time-dependent outcome with marker-dependent censoring. Biom. J. 2013, 55, 687–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trevethan, R. Sensitivity, Specificity, and Predictive Values: Foundations, Pliabilities, and Pitfalls in Research and Practice. Front. Public Health 2017, 5, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

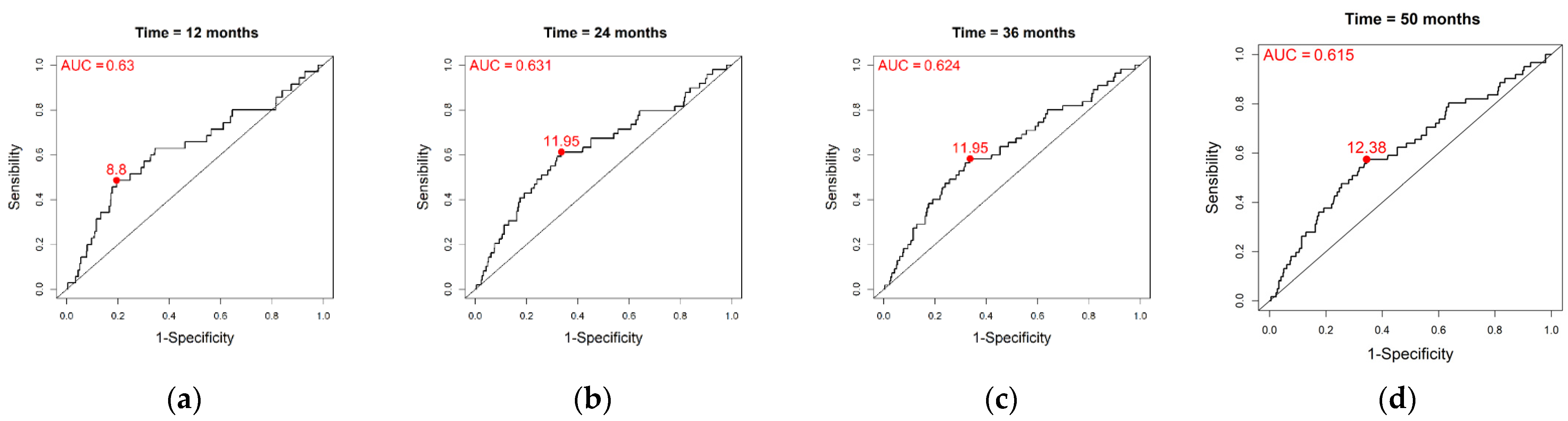

| Time | Threshold | AUC | Se | Sp | PPV | NPV | Cost | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overall population | t = 12 | 8.8 | 0.630 | 0.486 | 0.805 | 0.172 | 0.950 | −0.485 |
| t = 24 | 11.95 | 0.631 | 0.612 | 0.663 | 0.180 | 0.934 | −0.208 | |
| t = 36 | 11.95 | 0.624 | 0.582 | 0.663 | 0.192 | 0.920 | −0.186 | |
| t = 50 | 12.38 | 0.615 | 0.574 | 0.656 | 0.205 | 0.909 | −0.156 | |
| Monte Carlo simulations | t = 12 | 10.08 | 0.630 | 0.478 | 0.734 | 0.134 | 0.945 | −0.353 |
| t = 24 | 11.08 | 0.632 | 0.515 | 0.695 | 0.168 | 0.924 | −0.243 | |
| t = 36 | 10.91 | 0.624 | 0.478 | 0.702 | 0.181 | 0.908 | −0.230 | |
| t = 50 | 11.51 | 0.617 | 0.482 | 0.678 | 0.191 | 0.895 | −0.170 |
| Variable | Coefficient | HR [95% CI] | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline RILA * | 0.04 | 1.04 [1.01–1.08] | 0.012 |
| Tobacco smoking status (active/former vs. no) | 0.44 | 1.56 [0.93–2.60] | 0.091 |
| Adjuvant HT status (yes vs. no) | 1.15 | 3.17 [1.36–7.40] | 0.008 |
| Time | Threshold | AUC | Se | Sp | PPV | NPV | Cost | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overall population | t = 12 | 0.99 | 0.684 | 0.853 | 0.480 | 0.261 | 0.975 | 0.060 |
| t = 24 | 1.43 | 0.717 | 0.646 | 0.709 | 0.215 | 0.942 | −0.294 | |
| t = 36 | 1.43 | 0.704 | 0.630 | 0.712 | 0.236 | 0.932 | −0.280 | |
| t = 50 | 1.35 | 0.681 | 0.633 | 0.689 | 0.245 | 0.922 | −0.225 | |
| Monte Carlo simulations | t = 12 | 1.33 | 0.664 | 0.614 | 0.616 | 0.121 | 0.951 | −0.153 |
| t = 24 | 1.39 | 0.694 | 0.626 | 0.660 | 0.190 | 0.936 | −0.203 | |
| t = 36 | 1.34 | 0.683 | 0.627 | 0.642 | 0.201 | 0.926 | −0.156 | |
| t = 50 | 1.46 | 0.663 | 0.600 | 0.662 | 0.223 | 0.913 | −0.169 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Touraine, C.; Winter, A.; Castan, F.; Azria, D.; Gourgou, S. Time-Dependent ROC Curve Analysis for Assessing the Capability of Radiation-Induced CD8 T-Lymphocyte Apoptosis to Predict Late Toxicities after Adjuvant Radiotherapy of Breast Cancer Patients. Cancers 2023, 15, 4676. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15194676
Touraine C, Winter A, Castan F, Azria D, Gourgou S. Time-Dependent ROC Curve Analysis for Assessing the Capability of Radiation-Induced CD8 T-Lymphocyte Apoptosis to Predict Late Toxicities after Adjuvant Radiotherapy of Breast Cancer Patients. Cancers. 2023; 15(19):4676. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15194676
Chicago/Turabian StyleTouraine, Célia, Audrey Winter, Florence Castan, David Azria, and Sophie Gourgou. 2023. "Time-Dependent ROC Curve Analysis for Assessing the Capability of Radiation-Induced CD8 T-Lymphocyte Apoptosis to Predict Late Toxicities after Adjuvant Radiotherapy of Breast Cancer Patients" Cancers 15, no. 19: 4676. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15194676
APA StyleTouraine, C., Winter, A., Castan, F., Azria, D., & Gourgou, S. (2023). Time-Dependent ROC Curve Analysis for Assessing the Capability of Radiation-Induced CD8 T-Lymphocyte Apoptosis to Predict Late Toxicities after Adjuvant Radiotherapy of Breast Cancer Patients. Cancers, 15(19), 4676. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15194676







