The Potential of Hormonal Therapies for Treatment of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
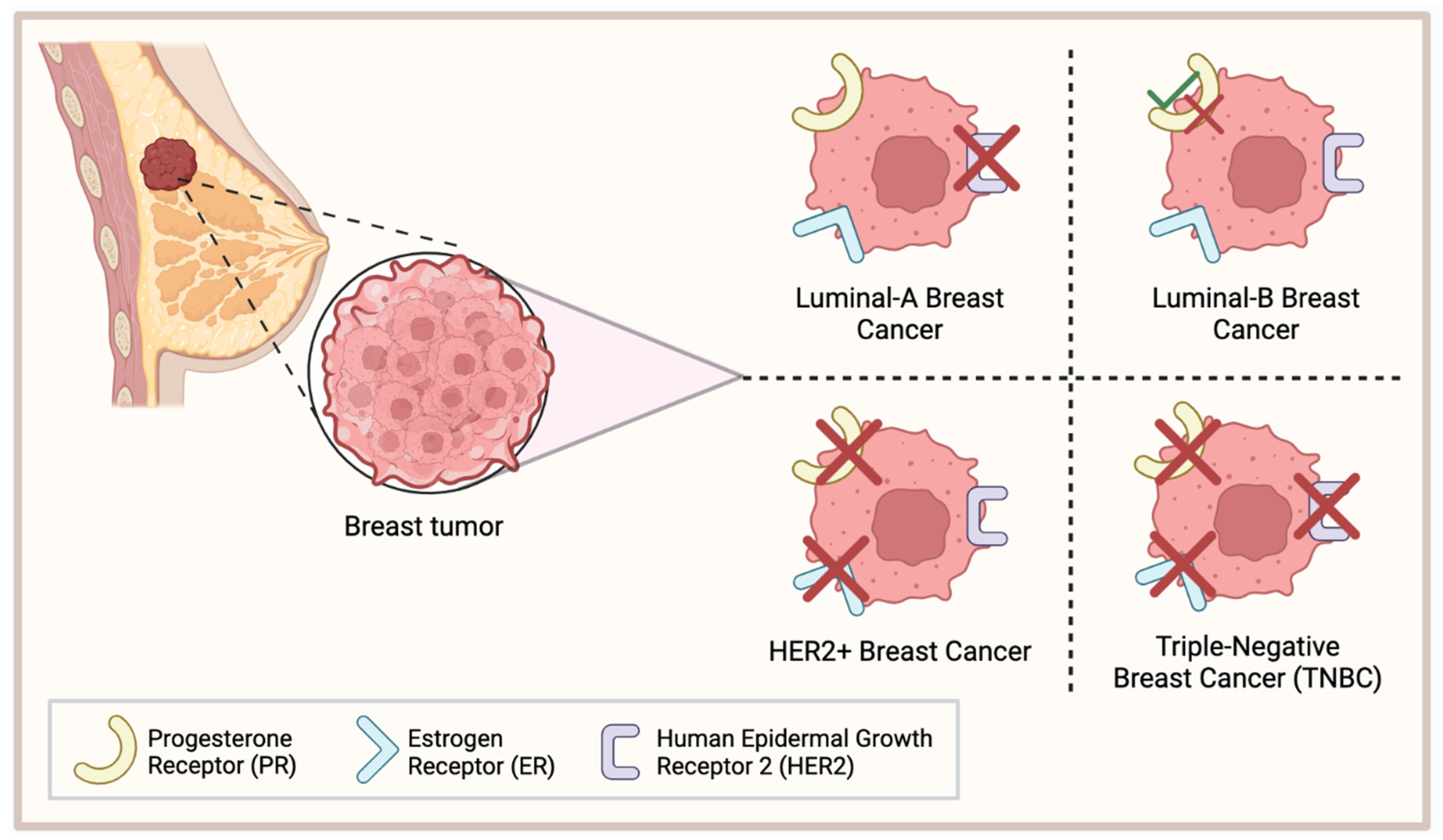
1. Introduction
2. Estrogen Receptor Beta
3. Estrogen Receptor Beta in the Progression of TNBC
4. Clinical Data regarding Estrogen Receptor Beta in TNBC
4.1. Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulators
4.2. 17β-Estradiol
5. Androgen Receptor
6. The Role of the Androgen Receptor in TNBC
7. Clinical Trials Targeting the Androgen Receptor in TNBC
7.1. Enzalutamide
7.2. Enobosarm
7.3. Bicalutamide
7.4. Seviteronel
8. Glucocorticoid Receptor
9. Glucocorticoid Receptor in TNBC
10. The Clinical Use of RU486 (Mifepristone) in GR-Positive TNBC
11. Conclusions
12. Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, J.-Y.; Chang, C.-J.; Cheng, J.-S. Survival, Treatment Regimens and Medical Costs of Women Newly Diagnosed with Metastatic Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dent, R.; Trudeau, M.; Pritchard, K.I.; Hanna, W.M.; Kahn, H.K.; Sawka, C.A.; Lickley, L.A.; Rawlinson, E.; Sun, P.; Narod, S.A. Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: Clinical Features and Patterns of Recurrence. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 4429–4434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orrantia-Borunda, E.; Anchondo-Nuñez, P.; Acuña-Aguilar, L.E.; Gómez-Valles, F.O.; Ramírez-Valdespino, C.A. Subtypes of Breast Cancer. In Breast Cancer; Mayrovitz, H.N., Ed.; Exon Publications: Brisbane, Australia, 2022; ISBN 978-0-645-33203-2. [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann, B.D.; Bauer, J.A.; Chen, X.; Sanders, M.E.; Chakravarthy, A.B.; Shyr, Y.; Pietenpol, J.A. Identification of Human Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Subtypes and Preclinical Models for Selection of Targeted Therapies. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 2750–2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, B.D.; Jovanović, B.; Chen, X.; Estrada, M.V.; Johnson, K.N.; Shyr, Y.; Moses, H.L.; Sanders, M.E.; Pietenpol, J.A. Refinement of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Molecular Subtypes: Implications for Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy Selection. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0157368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santonja, A.; Sánchez-Muñoz, A.; Lluch, A.; Chica-Parrado, M.R.; Albanell, J.; Chacón, J.I.; Antolín, S.; Jerez, J.M.; de la Haba, J.; de Luque, V.; et al. Triple Negative Breast Cancer Subtypes and Pathologic Complete Response Rate to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 26406–26416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, R.L.; Updike, K.L.; Factor, R.E.; Henry, N.L.; Boucher, K.M.; Bernard, P.S.; Varley, K.E. A Multigene Assay Determines Risk of Recurrence in Patients with Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 3466–3478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manna, S.; Holz, M.K. Tamoxifen Action in ER-Negative Breast Cancer. Sign Transduct. Insights 2016, 5, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Early Breast Cancer Trialists’ Collaborative Group. Tamoxifen for Early Breast Cancer: An Overview of the Randomised Trials. Lancet 1998, 351, 1451–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Dahlman-Wright, K.; Gustafsson, J.-Å. Estrogen Receptor β: An Overview and Update. Nucl. Recept. Signal 2008, 6, e003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Božović, A.; Mandušić, V.; Todorović, L.; Krajnović, M. Estrogen Receptor Beta: The Promising Biomarker and Potential Target in Metastases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roca, P.; Oliver, J.; Sastre-Serra, J.; Nadal-Serrano, M.; Roca, P.; Oliver, J.; Sastre-Serra, J.; Nadal-Serrano, M. The Importance of ERα/ERβ Ratio in Breast Cancer: Mitochondrial Function and Oxidative Stress. In Breast Cancer—Carcinogenesis, Cell Growth and Signalling Pathways; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2011; ISBN 978-953-307-714-7. [Google Scholar]
- Mal, R.; Magner, A.; David, J.; Datta, J.; Vallabhaneni, M.; Kassem, M.; Manouchehri, J.; Willingham, N.; Stover, D.; Vandeusen, J.; et al. Estrogen Receptor Beta (ERβ): A Ligand Activated Tumor Suppressor. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 587386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuiper, G.G.; Shughrue, P.J.; Merchenthaler, I.; Gustafsson, J.A. The Estrogen Receptor Beta Subtype: A Novel Mediator of Estrogen Action in Neuroendocrine Systems. Front. Neuroendocrinol. 1998, 19, 253–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crandall, D.L.; Busler, D.E.; Novak, T.J.; Weber, R.V.; Kral, J.G. Identification of Estrogen Receptor Beta RNA in Human Breast and Abdominal Subcutaneous Adipose Tissue. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1998, 248, 523–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawse, J.R.; Carter, J.M.; Aspros, K.G.M.; Bruinsma, E.S.; Koepplin, J.W.; Negron, V.; Subramaniam, M.; Ingle, J.N.; Rech, K.L.; Goetz, M.P. Optimized Immunohistochemical Detection of Estrogen Receptor Beta Using Two Validated Monoclonal Antibodies Confirms Its Expression in Normal and Malignant Breast Tissues. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2020, 179, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Subramaniam, M.; Negron, V.; Cicek, M.; Reynolds, C.; Lingle, W.L.; Goetz, M.P.; Ingle, J.N.; Spelsberg, T.C.; Hawse, J.R. Development, Characterization, and Applications of a Novel Estrogen Receptor Beta Monoclonal Antibody. J. Cell Biochem. 2012, 113, 711–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, A.W.; Groen, A.J.; Miller, J.L.; Warren, A.Y.; Holmes, K.A.; Tarulli, G.A.; Tilley, W.D.; Katzenellenbogen, B.S.; Hawse, J.R.; Gnanapragasam, V.J.; et al. Comprehensive Assessment of Estrogen Receptor Beta Antibodies in Cancer Cell Line Models and Tissue Reveals Critical Limitations in Reagent Specificity. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2017, 440, 138–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, S.; Sundberg, M.; Pristovsek, N.; Ibrahim, A.; Jonsson, P.; Katona, B.; Clausson, C.-M.; Zieba, A.; Ramström, M.; Söderberg, O.; et al. Insufficient Antibody Validation Challenges Oestrogen Receptor Beta Research. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruvberger-Saal, S.K.; Bendahl, P.-O.; Saal, L.H.; Laakso, M.; Hegardt, C.; Edén, P.; Peterson, C.; Malmström, P.; Isola, J.; Borg, Å.; et al. Estrogen Receptor β Expression Is Associated with Tamoxifen Response in ERα-Negative Breast Carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 1987–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honma, N.; Horii, R.; Iwase, T.; Saji, S.; Younes, M.; Takubo, K.; Matsuura, M.; Ito, Y.; Akiyama, F.; Sakamoto, G. Clinical Importance of Estrogen Receptor-β Evaluation in Breast Cancer Patients Treated with Adjuvant Tamoxifen Therapy. JCO 2008, 26, 3727–3734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reese, J.M.; Suman, V.J.; Subramaniam, M.; Wu, X.; Negron, V.; Gingery, A.; Pitel, K.S.; Shah, S.S.; Cunliffe, H.E.; McCullough, A.E.; et al. ERβ1: Characterization, Prognosis, and Evaluation of Treatment Strategies in ERα-Positive and -Negative Breast Cancer. BMC Cancer 2014, 14, 749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, L.; Zhu, Q.; Aisimutuola, M.; Yilamu, D.; Liu, S.; Jakulin, A. Expression and Prognostic Value of Estrogen Receptor β in Patients with Triple-Negative and Triple-Positive Breast Cancer. Exp. Ther. Med. 2015, 9, 2147–2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takano, E.A.; Younes, M.M.; Meehan, K.; Spalding, L.; Yan, M.; Allan, P.; Fox, S.B.; Redfern, A.; Clouston, D.; Giles, G.G.; et al. Estrogen Receptor Beta Expression in Triple Negative Breast Cancers Is Not Associated with Recurrence or Survival. BMC Cancer 2023, 23, 459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novelli, F.; Milella, M.; Melucci, E.; Di Benedetto, A.; Sperduti, I.; Perrone-Donnorso, R.; Perracchio, L.; Venturo, I.; Nisticò, C.; Fabi, A.; et al. A Divergent Role for Estrogen Receptor-Beta in Node-Positive and Node-Negative Breast Cancer Classified According to Molecular Subtypes: An Observational Prospective Study. Breast Cancer Res. 2008, 10, R74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanle, E.K.; Zhao, Z.; Hawse, J.; Wisinski, K.; Keles, S.; Yuan, M.; Xu, W. Research Resource: Global Identification of Estrogen Receptor β Target Genes in Triple Negative Breast Cancer Cells. Mol. Endocrinol. 2013, 27, 1762–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schüler-Toprak, S.; Häring, J.; Inwald, E.C.; Moehle, C.; Ortmann, O.; Treeck, O. Agonists and Knockdown of Estrogen Receptor β Differentially Affect Invasion of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells in Vitro. BMC Cancer 2016, 16, 951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austin, D.; Hamilton, N.; Elshimali, Y.; Pietras, R.; Wu, Y.; Vadgama, J. Estrogen Receptor-Beta Is a Potential Target for Triple Negative Breast Cancer Treatment. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 33912–33930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Dey, P.; Ziegler, Y.; Jiao, X.; Kim, S.H.; Katzenellenbogen, J.A.; Katzenellenbogen, B.S. Contrasting Activities of Estrogen Receptor Beta Isoforms in Triple Negative Breast Cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2021, 185, 281–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koboldt, D.C.; Fulton, R.S.; McLellan, M.D.; Schmidt, H.; Kalicki-Veizer, J.; McMichael, J.F.; Fulton, L.L.; Dooling, D.J.; Ding, L.; Mardis, E.R.; et al. Comprehensive Molecular Portraits of Human Breast Tumours. Nature 2012, 490, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noll, J.E.; Jeffery, J.; Al-Ejeh, F.; Kumar, R.; Khanna, K.K.; Callen, D.F.; Neilsen, P.M. Mutant P53 Drives Multinucleation and Invasion through a Process That Is Suppressed by ANKRD11. Oncogene 2012, 31, 2836–2848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adorno, M.; Cordenonsi, M.; Montagner, M.; Dupont, S.; Wong, C.; Hann, B.; Solari, A.; Bobisse, S.; Rondina, M.B.; Guzzardo, V.; et al. A Mutant-P53/Smad Complex Opposes P63 to Empower TGFbeta-Induced Metastasis. Cell 2009, 137, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bado, I.; Nikolos, F.; Rajapaksa, G.; Gustafsson, J.-Å.; Thomas, C. ERβ Decreases the Invasiveness of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells by Regulating Mutant P53 Oncogenic Function. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 13599–13611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukhopadhyay, U.K.; Oturkar, C.C.; Adams, C.; Wickramasekera, N.; Bansal, S.; Medisetty, R.; Miller, A.; Swetzig, W.M.; Silwal-Pandit, L.; Børresen-Dale, A.-L.; et al. TP53 Status as a Determinant of Pro- vs Anti-Tumorigenic Effects of Estrogen Receptor-Beta in Breast Cancer. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2019, 111, 1202–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarpetti, L.; Oturkar, C.C.; Juric, D.; Shellock, M.; Malvarosa, G.; Post, K.; Isakoff, S.; Wang, N.; Nahed, B.; Oh, K.; et al. Therapeutic Role of Tamoxifen for Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: Leveraging the Interaction Between ERβ and Mutant P53. Oncologist 2023, 28, 358–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evaluation of Tamoxifen’s Efficacy for ER/PR Negative, ER-Beta Positive Operable Breast Cancer Patients. Available online: https://www.smartpatients.com/trials/NCT02062489 (accessed on 10 September 2023).
- Peking Union Medical College Hospital. Evaluation of Adjuvant Endocrine Therapy for Operable ER-Beta Positive, ER-Alpha/PR Negative, Her-2 Negative Breast Cancer Patients; 2016. Available online: clinicaltrials.gov (accessed on 17 September 2023).
- Wisinski, K.B.; Xu, W.; Tevaarwerk, A.J.; Saha, S.; Kim, K.; Traynor, A.; Dietrich, L.; Hegeman, R.; Patel, D.; Blank, J.; et al. Targeting Estrogen Receptor Beta in a Phase 2 Study of High-Dose Estradiol in Metastatic Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: A Wisconsin Oncology Network Study. Clin. Breast Cancer 2016, 16, 256–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayo Clinic. Therapeutic Targeting of ER Beta in Triple Negative Breast Cancer; 2023. Available online: clinicaltrials.gov (accessed on 7 September 2023).
- Hong, J.; Huang, J.; Shen, L.; Zhu, S.; Gao, W.; Wu, J.; Huang, O.; He, J.; Zhu, L.; Chen, W.; et al. A Prospective, Randomized Study of Toremifene vs. Tamoxifen for the Treatment of Premenopausal Breast Cancer: Safety and Genital Symptom Analysis. BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gucalp, A.; Traina, T.A. Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: Role of the Androgen Receptor. Cancer J. 2010, 16, 62–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattarai, S.; Klimov, S.; Mittal, K.; Krishnamurti, U.; Li, X.B.; Oprea-Ilies, G.; Wetherilt, C.S.; Riaz, A.; Aleskandarany, M.A.; Green, A.R.; et al. Prognostic Role of Androgen Receptor in Triple Negative Breast Cancer: A Multi-Institutional Study. Cancers 2019, 11, 995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.H.E.; Li, J.; Xu, H.E.; Melcher, K.; Yong, E. Androgen Receptor: Structure, Role in Prostate Cancer and Drug Discovery. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2015, 36, 3–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elgehama, A.; Sun, L.; Yu, B.; Guo, W.; Xu, Q. Selective Targeting of the Androgen Receptor-DNA Binding Domain by the Novel Antiandrogen SBF-1 and Inhibition of the Growth of Prostate Cancer Cells. Invest. New Drugs 2021, 39, 442–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.-L.; Kyprianou, N. Androgen Receptor and Growth Factor Signaling Cross-Talk in Prostate Cancer Cells. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2008, 15, 841–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bryan, R.M.; Mercer, R.J.; Bennett, R.C.; Rennie, G.C.; Lie, T.H.; Morgan, F.J. Androgen Receptors in Breast Cancer. Cancer 1984, 54, 2436–2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Persijn, J.P.; Korsten, C.B.; Engelsman, E. Oestrogen and Androgen Receptors in Breast Cancer and Response to Endocrine Therapy. Br. Med. J. 1975, 4, 503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, K.; Davey, R.A.; Zajac, J.D. Human Androgen Deficiency: Insights Gained from Androgen Receptor Knockout Mouse Models. Asian J. Androl. 2014, 16, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burstein, M.D.; Tsimelzon, A.; Poage, G.M.; Covington, K.R.; Contreras, A.; Fuqua, S.A.W.; Savage, M.I.; Osborne, C.K.; Hilsenbeck, S.G.; Chang, J.C.; et al. Comprehensive Genomic Analysis Identifies Novel Subtypes and Targets of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 1688–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masuda, H.; Baggerly, K.A.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Gonzalez-Angulo, A.M.; Meric-Bernstam, F.; Valero, V.; Lehmann, B.D.; Pietenpol, J.A.; Hortobagyi, G.N.; et al. Differential Response to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy among 7 Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Molecular Subtypes. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 5533–5540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christenson, J.L.; O’Neill, K.I.; Williams, M.M.; Spoelstra, N.S.; Jones, K.L.; Trahan, G.D.; Reese, J.; Van Patten, E.T.; Elias, A.; Eisner, J.R.; et al. Activity of Combined Androgen Receptor Antagonism and Cell Cycle Inhibition in Androgen Receptor Positive Triple Negative Breast Cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2021, 20, 1062–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cimino-Mathews, A.; Hicks, J.L.; Illei, P.B.; Halushka, M.K.; Fetting, J.H.; De Marzo, A.M.; Park, B.H.; Argani, P. Androgen Receptor Expression Is Usually Maintained in Initial Surgically-Resected Breast Cancer Metastases, But Often Lost in End-Stage Metastases Found at Autopsy. Hum. Pathol. 2012, 43, 1003–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barton, V.N.; Christenson, J.L.; Gordon, M.A.; Greene, L.I.; Rogers, T.J.; Butterfield, K.; Babbs, B.; Spoelstra, N.S.; D’Amato, N.C.; Elias, A.; et al. Androgen Receptor Supports an Anchorage-Independent, Cancer Stem Cell-like Population in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 3455–3466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giovannelli, P.; Di Donato, M.; Auricchio, F.; Castoria, G.; Migliaccio, A. Androgens Induce Invasiveness of Triple Negative Breast Cancer Cells Through AR/Src/PI3-K Complex Assembly. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asano, Y.; Kashiwagi, S.; Goto, W.; Tanaka, S.; Morisaki, T.; Takashima, T.; Noda, S.; Onoda, N.; Ohsawa, M.; Hirakawa, K.; et al. Expression and Clinical Significance of Androgen Receptor in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Cancers 2017, 9, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyalkin, S.A.; Verevkina, N.O.; Alekseyenko, O.O.; Syvak, L.A. Prognostic Role of Androgen Receptor Expression in Patients with Metastatic Triple Negative Breast Cancer. Exp. Oncol. 2020, 42, 140–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Pan, B.; Zhu, H.; Zhou, Y.; Mao, F.; Lin, Y.; Xu, Q.; Sun, Q. Prognostic Value of Androgen Receptor in Triple Negative Breast Cancer: A Meta-Analysis. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 46482–46491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, R.; Dawood, S.; Holmes, M.D.; Collins, L.C.; Schnitt, S.J.; Cole, K.; Marotti, J.D.; Hankinson, S.E.; Colditz, G.A.; Tamimi, R.M. Androgen Receptor Expression and Breast Cancer Survival in Postmenopausal Women. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 1867–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGhan, L.J.; McCullough, A.E.; Protheroe, C.A.; Dueck, A.C.; Lee, J.J.; Nunez-Nateras, R.; Castle, E.P.; Gray, R.J.; Wasif, N.; Goetz, M.P.; et al. Androgen Receptor-Positive Triple Negative Breast Cancer: A Unique Breast Cancer Subtype. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2014, 21, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sridhar, N.; Glisch, C.; Jawa, Z.; Chaudhary, L.N.; Kamaraju, S.; Burfeind, J.; Charlson, J.; Chitambar, C.R.; Jorns, J.M.; Cheng, Y.C. Androgen Receptor Expression in Patients with Triple Negative Breast Cancer Treated with Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy: A Single Institution Study. J. Cancer 2022, 13, 2472–2476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mrklić, I.; Pogorelić, Z.; Capkun, V.; Tomić, S. Expression of Androgen Receptors in Triple Negative Breast Carcinomas. Acta Histochem. 2013, 115, 344–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubrava, A.L.; Kyaw, P.S.P.; Newman, J.; Pringle, J.; Westhuyzen, J.; La Hera Fuentes, G.; Shakespeare, T.P.; Sakalkale, R.; Aherne, N.J. Androgen Receptor Status in Triple Negative Breast Cancer: Does It Correlate with Clinicopathological Characteristics? Breast Cancer Targets Ther. 2023, 15, 359–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traina, T.A.; Miller, K.; Yardley, D.A.; Eakle, J.; Schwartzberg, L.S.; O’Shaughnessy, J.; Gradishar, W.; Schmid, P.; Winer, E.; Kelly, C.; et al. Enzalutamide for the Treatment of Androgen Receptor-Expressing Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 884–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, E.M.; Gucalp, A.; Patil, S.; Edelweiss, M.; Ross, D.S.; Razavi, P.; Modi, S.; Iyengar, N.M.; Sanford, R.; Troso-Sandoval, T.; et al. Adjuvant Enzalutamide for the Treatment of Early-Stage Androgen-Receptor Positive, Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: A Feasibility Study. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2022, 195, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Lee, J.S.; Yost, S.E.; Frankel, P.H.; Ruel, C.; Egelston, C.A.; Guo, W.; Gillece, J.D.; Folkerts, M.; Reining, L.; et al. A Phase II Clinical Trial of Pembrolizumab and Enobosarm in Patients with Androgen Receptor-Positive Metastatic Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Oncologist 2021, 26, 99-e217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gucalp, A.; Tolaney, S.; Isakoff, S.J.; Ingle, J.N.; Liu, M.C.; Carey, L.A.; Blackwell, K.; Rugo, H.; Nabell, L.; Forero, A.; et al. Phase II Trial of Bicalutamide in Patients with Androgen Receptor–Positive, Estrogen Receptor–Negative Metastatic Breast Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 5505–5512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gucalp, A.; Boyle, L.A.; Alano, T.; Arumov, A.; Gounder, M.M.; Patil, S.; Feigin, K.; Edelweiss, M.; D’Andrea, G.; Bromberg, J.; et al. Phase II Trial of Bicalutamide in Combination with Palbociclib for the Treatment of Androgen Receptor (+) Metastatic Breast Cancer. JCO 2020, 38, 1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifi, M.; Wisinski, K.; Burkard, M.; Tevaarwerk, A.; Tamkus, D.; Chan, N.; Truica, C.; Danciu, O.; Hoskins, K.; O’Regan, R. Abstract OT1-02-01: Phase I Trial of Bicalutamide and Ribociclib in Androgen Receptor-Positive Triple Negative Breast Cancer. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, OT1-02–01. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardia, A.; Gucalp, A.; DaCosta, N.; Gabrail, N.; Danso, M.; Ali, H.; Blackwell, K.L.; Carey, L.A.; Eisner, J.R.; Baskin-Bey, E.S.; et al. Phase 1 Study of Seviteronel, a Selective CYP17 Lyase and Androgen Receptor Inhibitor, in Women with Estrogen Receptor-Positive or Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2018, 171, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menon, M.P.; Higano, C.S. Enzalutamide, a Second Generation Androgen Receptor Antagonist: Development and Clinical Applications in Prostate Cancer. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2013, 15, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narayanan, R.; Ahn, S.; Cheney, M.D.; Yepuru, M.; Miller, D.D.; Steiner, M.S.; Dalton, J.T. Selective Androgen Receptor Modulators (SARMs) Negatively Regulate Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Growth and Epithelial:Mesenchymal Stem Cell Signaling. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e103202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, M.A.; Malhotra, S.V.; Stoyanova, T. Second-Generation Antiandrogens: From Discovery to Standard of Care in Castration Resistant Prostate Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Gao, J.; Wang, M.; Li, M. Potential Prospect of CDK4/6 Inhibitors in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Cancer Manag. Res. 2021, 13, 5223–5237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michmerhuizen, A.R.; Chandler, B.; Olsen, E.; Wilder-Romans, K.; Moubadder, L.; Liu, M.; Pesch, A.M.; Zhang, A.; Ritter, C.; Ward, S.T.; et al. Seviteronel, a Novel CYP17 Lyase Inhibitor and Androgen Receptor Antagonist, Radiosensitizes AR-Positive Triple Negative Breast Cancer Cells. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchi, D.; van Eeden, F.J.M. Homeostatic Regulation of Glucocorticoid Receptor Activity by Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1: From Physiology to Clinic. Cells 2021, 10, 3441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Postel, S.; Wissler, L.; Johansson, C.A.; Gunnarsson, A.; Gordon, E.; Collins, B.; Castaldo, M.; Köhler, C.; Öling, D.; Johansson, P.; et al. Quaternary Glucocorticoid Receptor Structure Highlights Allosteric Interdomain Communication. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2023, 30, 286–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dwyer, A.R.; Perez Kerkvliet, C.; Truong, T.H.; Hagen, K.M.; Krutilina, R.I.; Parke, D.N.; Oakley, R.H.; Liddle, C.; Cidlowski, J.A.; Seagroves, T.N.; et al. Glucocorticoid Receptors Drive Breast Cancer Cell Migration and Metabolic Reprogramming via PDK4. Endocrinology 2023, 164, bqad083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noureddine, L.M.; Trédan, O.; Hussein, N.; Badran, B.; Le Romancer, M.; Poulard, C. Glucocorticoid Receptor: A Multifaceted Actor in Breast Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abduljabbar, R.; Negm, O.H.; Lai, C.-F.; Jerjees, D.A.; Al-Kaabi, M.; Hamed, M.R.; Tighe, P.J.; Buluwela, L.; Mukherjee, A.; Green, A.R.; et al. Clinical and Biological Significance of Glucocorticoid Receptor (GR) Expression in Breast Cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2015, 150, 335–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, G.M.; Murphy, T.; Block, T.; Nguyen, D.; Lynch, F.J. Development and Validation of an Immunohistochemistry Assay to Assess Glucocorticoid Receptor Expression for Clinical Trials of Mifepristone in Breast Cancer. CMAR 2015, 7, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buxant, F.; Engohan-Aloghe, C.; Noël, J.-C. Estrogen Receptor, Progesterone Receptor, and Glucocorticoid Receptor Expression in Normal Breast Tissue, Breast In Situ Carcinoma, and Invasive Breast Cancer. Appl. Immunohistochem. Mol. Morphol. 2010, 18, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, D.; Kocherginsky, M.; Conzen, S.D. Activation of the Glucocorticoid Receptor Is Associated with Poor Prognosis in Estrogen Receptor-Negative Breast Cancer. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 6360–6370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Chaudhuri, S.; Brickley, D.R.; Pang, D.; Karrison, T.; Conzen, S.D. Microarray Analysis Reveals Glucocorticoid-Regulated Survival Genes That Are Associated with Inhibition of Apoptosis in Breast Epithelial Cells. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 1757–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conway, M.E.; McDaniel, J.M.; Graham, J.M.; Guillen, K.P.; Oliver, P.G.; Parker, S.L.; Yue, P.; Turkson, J.; Buchsbaum, D.J.; Welm, B.E.; et al. STAT3 and GR Cooperate to Drive Gene Expression and Growth of Basal-Like Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Cancer Res. 2020, 80, 4355–4370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez Kerkvliet, C.; Dwyer, A.R.; Diep, C.H.; Oakley, R.H.; Liddle, C.; Cidlowski, J.A.; Lange, C.A. Glucocorticoid Receptors Are Required Effectors of TGFβ1-Induced P38 MAPK Signaling to Advanced Cancer Phenotypes in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2020, 22, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elkashif, A.; Bingham, V.; Haddock, P.; Humphries, M.P.; McQuaid, S.; Mullan, P.B.; McCarthy, H.O.; Buckley, N.E. Glucocorticoid Receptor Expression Predicts Good Outcome in Response to Taxane-Free, Anthracycline-Based Therapy in Triple Negative Breast Cancer. J. Oncol. 2020, 2020, e3712825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.-H.; Chuang, P.-Y.; You, S.-L.; Chiang, C.-J.; Huang, C.-S.; Wang, M.-Y.; Chao, M.; Lu, Y.-S.; Cheng, A.-L.; Tang, C.-H. Effect of Glucocorticoid Use on Survival in Patients with Stage I–III Breast Cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2018, 171, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cadepond, F.; Ulmann, A.; Baulieu, E.-E. RU486 (MIFEPRISTONE): Mechanisms of Action and Clinical Uses. Annu. Rev. Med. 1997, 48, 129–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musgrove, E.A.; Sutherland, R.L. Effects of the Progestin Antagonist RU 486 on T-47D Breast Cancer Cell Cycle Kinetics and Cell Cycle Regulatory Genes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1993, 195, 1184–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardon, S.; Vignon, F.; Chalbos, D.; Rochefort, H. RU486, a Progestin and Glucocorticoid Antagonist, Inhibits the Growth of Breast Cancer Cells via the Progesterone Receptor. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1985, 60, 692–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Yan, C.; Wu, W.; He, S.; Liu, M.; Liu, J.; Yang, X.; Ma, J.; Lu, Y.; Jia, L. RU486 Metabolite Inhibits CCN1/Cyr61 Secretion by MDA-MB-231-Endothelial Adhesion. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.H.; Woo, S.M.; Um, H.J.; Park, E.J.; Min, K.-J.; Lee, T.-J.; Kim, S.H.; Choi, Y.H.; Kwon, T.K. RU486, a Glucocorticoid Receptor Antagonist, Induces Apoptosis in U937 Human Lymphoma Cells through Reduction in Mitochondrial Membrane Potential and Activation of P38 MAPK. Oncol. Rep. 2013, 30, 506–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanda, R.; Stringer-Reasor, E.M.; Saha, P.; Kocherginsky, M.; Gibson, J.; Libao, B.; Hoffman, P.C.; Obeid, E.; Merkel, D.E.; Khramtsova, G.; et al. A Randomized Phase I Trial of Nanoparticle Albumin-Bound Paclitaxel with or without Mifepristone for Advanced Breast Cancer. SpringerPlus 2016, 5, 947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Saha, P.; Rampurwala, M.M.; Kamaraju, S.; Hahn, O.M.; Howard, F.M.; Fleming, G.F.; Matossian, M.; Freeman, J.Q.; Karrison, T.; et al. A Randomized Phase II Trial of Nab-Paclitaxel with or without Mifepristone for Advanced Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. JCO 2023, 41, e13103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Wilks, S.; Paplomata, E.; Modiano, M.; Becerra, C.; Braiteh, F.; Spira, A.; Pluard, T.; Richards, D.; Conzen, S.; et al. Abstract P6-12-15: Efficacy Results of a Phase 1/2 Study of Glucocorticoid Receptor (GR) Antagonist Mifepristone (MIFE) in Combination with Eribulin in GR-Positive Triple-Negative Breast Cancer (TNBC). Cancer Res. 2017, 77, P6-12–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosette, C.; Agan, F.J.; Rosette, N.; Mazzetti, A.; Moro, L.; Gerloni, M. The Dual Androgen Receptor and Glucocorticoid Receptor Antagonist CB-03-10 as Potential Treatment for Tumors That Have Acquired GR-Mediated Resistance to AR Blockade. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2020, 19, 2256–2266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanai, A.; McNamara, K.M.; Iwabuchi, E.; Miki, Y.; Onodera, Y.; Guestini, F.; Khalid, F.; Sagara, Y.; Ohi, Y.; Rai, Y.; et al. Significance of Glucocorticoid Signaling in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Patients: A Newly Revealed Interaction with Androgen Signaling. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2020, 180, 97–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anestis, A.; Sarantis, P.; Theocharis, S.; Zoi, I.; Tryfonopoulos, D.; Korogiannos, A.; Koumarianou, A.; Xingi, E.; Thomaidou, D.; Kontos, M.; et al. Estrogen Receptor Beta Increases Sensitivity to Enzalutamide in Androgen Receptor-Positive Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 145, 1221–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Tang, L.; Xu, Y.; Sun, Q.; Yang, F.; Guan, X. ERβ1 Inhibits Metastasis of Androgen Receptor-Positive Triple-Negative Breast Cancer by Suppressing ZEB1. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 36, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Trial (National Clinical Trial Identifier) | Phase | Condition | Interventions | Key Results | References | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tamoxifen | ERβ+/p53-mutant TNBC patient with brain metastases | Tamoxifen | Reduction in tumor volume in the brain metastases; currently, no signs of disease progression. | [36] | ||
| Tamoxifen (NCT02062489) | III | (1) (2) | ERα/PR-negative ERβ+ operable breast cancer patients | Adjuvant Tamoxifen | No preliminary data available. Study to be completed by May 2026. | [37] |
| Toremifene (NCT02089854) | IV | (1) | Patients with operable ERβ+ TNBC tumors | Toremifene + Anastrozole | No preliminary data available. | [38] |
| 17β-Estradiol (E2) | II | (1) | Metastatic TNBC | E2 | Partial response: 1/13 patients (Erβ expressing); little effect on OS and PFS; grade 3–4 AE in 4/17 patients; 2 cases of grade 3 dyspnea; 1 case of grade 3 vomiting; 1 case of grade 4 thromboembolism. | [39] |
| 17β-Estradiol (E2) (NCT03941730) | II | (1) | Metastatic TNBC patients overexpressing Erβ | E2 | No preliminary data available. Study to be completed by April 2024. | [40] |
| Trial (National Clinical Trial Identifier) | Phase | Condition | Interventions | Key Results | References | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Enzalutamide (NCT01889238) | II | (1) (2) | Locally advanced or metastatic AR+ TNBC Intent-to-treat (ITT)—all patients AR expression ≥10% | Enzalutamide | PFS: (1) 2.9 months, (2) 3.3 months; OS: (1) 12.7 months, (2) 17.6 months; Fatigue (≥2%). Study to be completed by December 2023. | [64] |
| Enzalutamide (NCT02750358) | II | (1) | Stage I–III AR+ TNBC | Adjuvant Enzalutamide | DFS: 1-year: 94%; 2-year: 92%; 3-year: 80%; Grade 3 or higher AEs related to treatment: fatigue (6%), hypertension (2%). Study to be completed by May 2024. | [65] |
| Enobosarm (NCT02971761) | II | (1) | AR+ metastatic TNBC patients | Enobosarm + Pembrolizumab | Complete response: 1/16; Partial response: 1/16; Stable disease: 2/16; Response rate to combination treatment: 13%; CBR: 25% after 16 weeks; Grade 3 related AEs—pain (6%), dry skin (6%), diarrhea (6%). | [66] |
| Bicalutamide (NCT00468715) | II | (1) | ER–/PR– metastatic breast cancer patients highly expressing AR | Bicalutamide | AR+ expression (≥10%): 12%; 6-month CBR: 19%; PFS: 12-week median; Grade 3 AEs related elevated liver enzyme levels in one patient with liver metastases; Grade 3 nausea in 1/28 patients. | [67] |
| Bicalutamide (NCT02605486) | II | (1) | AR+ metastatic TNBC | Bicalutamide + Palbociclib | At 6-month mark: 35% progression-free; 32% stable disease. Study to be completed by November 2024. | [68] |
| Bicalutamide (NCT03090165) | I/II | (1) | Advanced AR+ TNBC patients | Bicalutamide + Ribociclib | No preliminary data available. Study to be completed by September 2024. | [69] |
| Seviteronel | I | (1) (2) | Women with ER+ breast cancer or TNBC 14/19: ER+ 5/19: TNBC | Seviteronel | AEs reported in only 4 patients; 7 women given 450 mg dose of seviteronel, 4/7 patients reached 16-week CBR, 2 of these patients diagnosed with TNBC. Phase II trial will expand cohort to include men and women with either ER+ or TNBC. | [70] |
| Trial (National Clinical Trial Identifier) | Phase | Condition | Interventions | Key Results | References | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mifepristone RU486 + Nab-paclitaxel (NCT01493310) | I | (1) | Advanced GR+ breast cancer patients TNBC + patients | RU486 + nab-paclitaxel | Complete response: 2/6; Partial response: 2/6; Stable disease: 1/6; Progressive disease: 1/6; Some patients experienced neutropenia. | [94] |
| Mifepristone RU486 + Nab-paclitaxel vs. Placebo (NCT02788981) | II | (1) (2) | Advanced GR+ TNBC 13/29: Nab-paclitaxel + placebo 16/29: Nab-paclitaxel + RU486 | Nab-paclitaxel + Placebo Nab-paclitaxel + RU486 | OS (2): 9 months; OS (1): 6 months; PFS: not significantly improved by addition of RU486; Grade 3 AE: Neutropenia. Study to be completed by August 2024. | [95] |
| Mifepristone RU486 + Eribulin (NCT02014337) | I/II | (1) | Patients with operable GR+ TNBC | RU486 + Eribulin | Phase I: 16 patients with meta-static breast cancer; Phase II: 21 patients with TNBC; Phase II dose combinational treatment partial response: 3/23; Stable disease: 8/23; Progressive disease: 11/23; Inconclusive: 1/23; Median PFS: 9 weeks; Grade 3/4 AEs: neutropenia, neuropathy, fatigue, hypokalemia, nausea. | [96] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kirkby, M.; Popatia, A.M.; Lavoie, J.R.; Wang, L. The Potential of Hormonal Therapies for Treatment of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Cancers 2023, 15, 4702. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15194702
Kirkby M, Popatia AM, Lavoie JR, Wang L. The Potential of Hormonal Therapies for Treatment of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Cancers. 2023; 15(19):4702. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15194702
Chicago/Turabian StyleKirkby, Melanie, Alyanna M. Popatia, Jessie R. Lavoie, and Lisheng Wang. 2023. "The Potential of Hormonal Therapies for Treatment of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer" Cancers 15, no. 19: 4702. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15194702
APA StyleKirkby, M., Popatia, A. M., Lavoie, J. R., & Wang, L. (2023). The Potential of Hormonal Therapies for Treatment of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Cancers, 15(19), 4702. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15194702







