Adrenal Incidentalomas and Other Endocrine-Related Adenomas: How Much Does Cortisol Secretion Matter?
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Imaging Techniques
2.3. Hormonal Data and Definitions
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics of MACS and NFAI
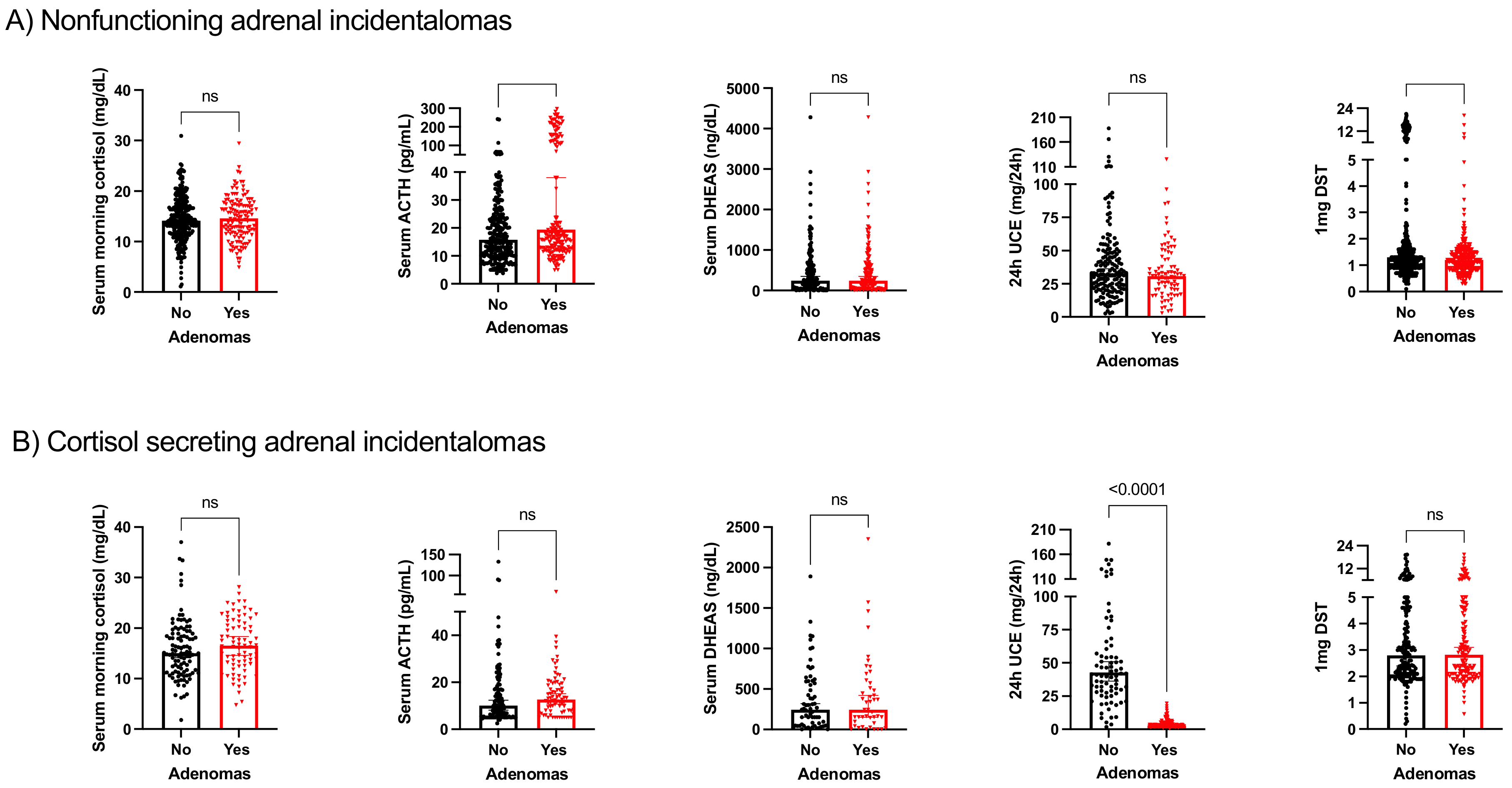
3.2. Biochemical Profile of Patients with and without Other Endocrine-Related Adenomas
3.3. Adrenal Incidentalomas and Other Endocrine-Related Adenomas
3.4. Pituitary Adenomas
3.5. Thyroid Adenomas
3.6. Parathyroid Adenomas
3.7. Adenomas in Other Locations
3.8. Metabolic Comorbidities in Patients with MACS and Adenomas
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shirodkar, M.; Jabbour, S.A. Endocrine incidentalomas. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2008, 62, 1423–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fassnacht, M.; Tsagarakis, S.; Terzolo, M.; Tabarin, A.; Sahdev, A.; Newell-Price, J.; Pelsma, I.; Marina, L.; Lorenz, K.; Bancos, I.; et al. European Society of Endocrinology clinical practice guidelines on the management of adrenal incidentalomas, in collaboration with the European Network for the Study of Adrenal Tumors. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2023, 189, G1–G42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bancos, I. Adrenal Incidentalomas: Insights Into Prevalence. Ann. Intern. Med. 2022, 175, 1481–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thakker, R.V.; Newey, P.J.; Walls, G.V.; Bilezikian, J.; Dralle, H.; Ebeling, P.R.; Melmed, S.; Sakurai, A.; Tonelli, F.; Brandi, M.L. Clinical practice guidelines for multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1 (MEN1). J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 97, 2990–3011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takenobu, M.; Moritani, S.; Kawamoto, K.; Yoshioka, K.; Kitano, H. Parathyroid carcinoma coexisting with multiple parathyroid adenomas: A case report. Endocr. J. 2020, 67, 963–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jawiarczyk-Przybyłowska, A.; Wojtczak, B.; Whitworth, J.; Sutkowski, K.; Bidlingmaier, M.; Korbonits, M.; Bolanowski, M. Acromegaly associated with GIST, non-small cell lung carcinoma, clear cell renal carcinoma, multiple myeloma, medulla oblongata tumour, adrenal adenoma, and follicular thyroid nodules. Endokrynol. Pol. 2019, 70, 213–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero Pérez, F.; Gil, A.L.; Robledo, M.; Iglesias, P.; Artero, C.V. Pituitary adenoma associated with pheochromocytoma/paraganglioma: A new form of multiple endocrine neoplasia. Endocrinol. Nutr. 2016, 63, 506–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamoun, M.; D’Herbomez, M.; Lemaire, C.; Fayard, A.; Desailloud, R.; Huglo, D.; Wemeau, J.-L. Coexistence of thyroid-stimulating hormone-secreting pituitary adenoma and graves’ hyperthyroidism. Eur. Thyroid. J. 2014, 3, 60–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Alcantara-Laguna, M.D.; Alcantara-Laguna, M.D.; Herrera-Martínez, Y.; Sánchez-Frías, M.E.; Gálvez-Moreno, M.A.; Herrera-Martínez, A.D. PTHrP-induced hypercalcemia in paragangliomas: Tumor dedifferentiation as sign of bad prognosis. Endocrinol. Diabetes Nutr. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina-Ayala, M.; Ramírez-Rentería, C.; Manguilar-León, A.; Paúl-Gaytán, P.; Ferreira-Hermosillo, A. A Rare Presentation of Primary Hyperparathyroidism with Concurrent Aldosterone-Producing Adrenal Carcinoma. Case Rep. Endocrinol. 2015, 2015, 910984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, W.F. Management approaches to adrenal incidentalomas. A view from Rochester, Minnesota. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. N. Am. 2000, 29, 159–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fassnacht, M.; Arlt, W.; Bancos, I.; Dralle, H.; Newell-Price, J.; Sahdev, A.; Tabarin, A.; Terzolo, M.; Tsagarakis, S.; Dekkers, O.M. Management of adrenal incidentalomas: European Society of Endocrinology Clinical Practice Guideline in collaboration with the European Network for the Study of Adrenal Tumors. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2016, 175, G1–G34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araujo-Castro, M.; Ramírez, P.P.; Lázaro, C.R.; Centeno, R.G.; Gimeno, P.G.; Fernández-Ladreda, M.T.; Núñez, M.A.S.; Marazuela, M.; Escobar-Morreale, H.F.; Valderrabano, P. Accuracy of the dexamethasone suppression test for the prediction of autonomous cortisol secretion-related comorbidities in adrenal incidentalomas. Hormones 2021, 20, 735–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernabé, D.G.; Tamae, A.C.; Biasoli, R.; Oliveira, S.H. Stress hormones increase cell proliferation and regulates interleukin-6 secretion in human oral squamous cell carcinoma cells. Brain Behav. Immun. 2011, 25, 574–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, X.; Reini, S.A.; Wood, C.E.; Keller-Wood, M.; Antolic, A.; Li, M.; Richards, E.M.; Curtis, C.W.; Walejko, J.M.; Koelmel, J.P.; et al. Cortisol stimulates proliferation and apoptosis in the late gestation fetal heart: Differential effects of mineralocorticoid and glucocorticoid receptors. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2013, 305, R343–R350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Li, J.; Li, J.; Cui, L.; Meng, X.; Qu, Y.; Wang, H. The proliferative effect of cortisol on bovine endometrial epithelial cells. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 2019, 17, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobbie, J.W. Adrenocortical nodular hyperplasia: The ageing adrenal. J. Pathol. 1969, 99, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, C.S.; Kosyk, O.; Welter, E.M.; Dietrich, N.; Archer, T.K.; Zannas, A.S. Chronic stress-driven glucocorticoid receptor activation programs key cell phenotypes and functional epigenomic patterns in human fibroblasts. iScience 2022, 25, 104960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chyun, Y.S.; Kream, B.E.; Raisz, L.G. Cortisol decreases bone formation by inhibiting periosteal cell proliferation. Endocrinology 1984, 114, 477–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Kaur, R.J.; Zhang, C.D.; Ebbehoj, A.; Singh, S.; Atkinson, E.J.; Achenbach, S.J.; Rocca, W.; Khosla, S.; Bancos, I. Risk of bone fractures after the diagnosis of adrenal adenomas: A population-based cohort study. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2021, 184, 597–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakayama, K.; Mashima, N.; Kidani, T.; Miyazaki, T.; Yamamoto, H.; Masuno, H. Effect of cortisol on cell proliferation and the expression of lipoprotein lipase and vascular endothelial growth factor in a human osteosarcoma cell line. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2008, 61, 471–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.; De Luca, A.; Dutton, H.; Malcolm, J.C.; Doyle, M.-A. Cardiovascular Outcomes in Autonomous Cortisol Secretion and Nonfunctioning Adrenal Adenoma: A Systematic Review. J. Endocr. Soc. 2019, 3, 996–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anwar, K.; Mohammad, A.Y.; Khan, S. The sensitivity of TIRADS scoring on ultrasonography in the management of thyroid nodules. Pak. J. Med. Sci. 2023, 39, 870–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.H.; Chaudhry, F.S.; Mayo-Smith, W.W. The incidental adrenal mass on CT: Prevalence of adrenal disease in 1049 consecutive adrenal masses in patients with no known malignancy. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2008, 190, 1163–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russell, R.P.; Masi, A.T.; Richter, E.D. Adrenal cortical adenomas and hypertension. A clinical pathologic analysis of 690 cases with matched controls and a review of the literature. Medicine 1972, 51, 211–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebbehoj, A.; Li, D.; Kaur, R.J.; Zhang, C.; Singh, S.; Li, T.; Atkinson, E.; Achenbach, S.; Khosla, S.; Arlt, W.; et al. Epidemiology of adrenal tumours in Olmsted County, Minnesota, USA: A population-based cohort study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2020, 8, 894–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherlock, M.; Scarsbrook, A.; Abbas, A.; Fraser, S.; Limumpornpetch, P.; Dineen, R.; Stewart, P.M. Adrenal Incidentaloma. Endocr. Rev. 2020, 41, 775–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantero, F.; Arnaldi, G. Management approaches to adrenal incidentalomas. A view from Ancona, Italy. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. N. Am. 2000, 29, 107–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, C.; Ming, X.; Tian, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yao, M.; Ni, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, Z. Mapping global epidemiology of thyroid nodules among general population: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 1029926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Invitti, C.; Manfrini, R.; Romanini, B.M.; Cavagnini, F. High prevalence of nodular thyroid disease in patients with Cushing’s disease. Clin. Endocrinol. 1995, 43, 359–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semple, C.G.; Thomson, J.A. Cushing’s syndrome and autonomous thyroid nodules, a variant of multiple endocrine neoplasia? Acta Endocrinol. 1986, 113, 463–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sington, J.D.; Syn, W.-K.; Suvarna, S.K.; Rassl, D.M.; Jenkins, R.C.; Weetman, A.P.; Ross, R.J.M. Lack of association between thyroid and adrenal nodules: A histological study. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 1999, 22, 262–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanety, H.; Feinstein, R.; Papa, M.Z.; Hemi, R.; Karasik, A. Tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced phosphorylation of insulin receptor substrate-1 (IRS-1). Possible mechanism for suppression of insulin-stimulated tyrosine phosphorylation of IRS-1. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 23780–23784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terzolo, M.; Bovio, S.; Reimondo, G.; Pia, A.; Osella, G.; Borretta, G.; Angeli, A. Subclinical Cushing’s syndrome in adrenal incidentalomas. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. N. Am. 2005, 34, 423–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reincke, M.; Fassnacht, M.; Väth, S.; Mora, P.; Allolio, B. Adrenal incidentalomas: A manifestation of the metabolic syndrome? Endocr. Res. 1996, 22, 757–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Real, J.M.; Ricart Engel, W.; Simó, R.; Salinas, I.; Webb, S.M.; Study Group of Incidental Adrenal Adenoma. Study of glucose tolerance in consecutive patients harbouring incidental adrenal tumours. Clin. Endocrinol. 1998, 49, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrera-Martinez, A.D.; Herrero-Aguayo, V.; Pérez-Gómez, J.M.; Gahete, M.D.; Luque, R.M. Inflammasomes: Cause or consequence of obesity-associated comorbidities in humans. Obesity 2022, 30, 2351–2362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitworth, J.A.; Mangos, G.J.; Kelly, J.J. Cushing, cortisol, and cardiovascular disease. Hypertension 2000, 36, 912–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amasi-Hartoonian, N.; Sforzini, L.; Cattaneo, A.; Pariante, C.M. Cause or consequence? Understanding the role of cortisol in the increased inflammation observed in depression. Curr. Opin. Endocr. Metab. Res. 2022, 24, 100356. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, S.; Janicki-Deverts, D.; Doyle, W.J.; Miller, G.E.; Frank, E.; Rabin, B.S.; Turner, R.B. Chronic stress, glucocorticoid receptor resistance, inflammation, and disease risk. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 5995–5999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhou, T.; Feng, S.; Wang, W.; Liu, H.; Wang, P.; Sha, Z.; Yu, X. The chronic effect of cortisol on orchestrating cerebral blood flow and brain functional connectivity: Evidence from Cushing’s disease. Metabolism 2021, 115, 154432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giordano, R.; Marinazzo, E.; Berardelli, R.; Picu, A.; Maccario, M.; Ghigo, E.; Arvat, E. Long-term morphological, hormonal, and clinical follow-up in a single unit on 118 patients with adrenal incidentalomas. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2010, 162, 779–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ezzat, S.; Asa, S.L.; Couldwell, W.T.; Barr, C.E.; Dodge, W.E.; Vance, M.L.; McCutcheon, I.E. The prevalence of pituitary adenomas: A systematic review. Cancer 2004, 101, 613–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrisoulidou, A.; Alexandraki, K.I.; Kita, M.; Tsolakidou, K.; Papanastasiou, L.; Samara, C.; Anastasiou, A.; Piaditis, G.; Kaltsas, G. Incidence of pituitary incidentalomas in patients with adrenal adenomas. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 2014, 122, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edafe, O.; Collins, E.; Ubhi, C.; Balasubramanian, S. Current predictive models do not accurately differentiate between single and multi gland disease in primary hyperparathyroidism: A retrospective cohort study of two endocrine surgery units. Ann. R. Coll. Surg. Engl. 2018, 100, 140–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, M.W.; Ituarte, P.H.G.; Zhou, H.C.; Nishimoto, S.; Liu, I.-L.A.; Harari, A.; Haigh, P.I.; Adams, A.L. Incidence and prevalence of primary hyperparathyroidism in a racially mixed population. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 98, 1122–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassiliadi, D.A.; Tsagarakis, S. Endocrine incidentalomas—Challenges imposed by incidentally discovered lesions. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2011, 7, 668–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, S.J.; Ruppe, M.D.; Tabatabai, L.S. The Parathyroid Gland and Heart Disease. Methodist. Debakey Cardiovasc. J. 2017, 13, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristic | All Patients (n = 923) | Nonfunctioning AI (n = 647) | MACS (n = 276) | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age at diagnosis (years) | 62.4 ± 11.12 | 62.15 ± 11.04 | 64.12 ± 10.32 | 0.02 |
| Sex (%male/%female) | 53.6/46.4 | 52.9/47.1 | 55.3/44.7 | 0.28 |
| Adenoma size | 22.3 ± 3.5 | 20.3 ± 3.8 | 23.1 ± 2.0 | 0.57 |
| Tobacco exposure | ||||
| Active smoker (% and n) | 27.4 (52/190) | 24.6 (34/138) | 34.6 (18/52) | 0.28 |
| Former smoker (% and n) | 39.9 (215/552) | 40.1 (150/374) | 36.5 (65/178) | 0.11 |
| Complications | ||||
| Hypertension (% and n) | 54.7 (502/918) | 51.4 (331/644) | 62.4(171/274) | 0.001 |
| Diabetes (% and n) | 24.5 (224/913) | 23.3 (149/639) | 27.4 (75/274) | 0.11 |
| Dyslipidemia (% and n) | 48.2 (440/913) | 47.3 (303/640) | 50.2 (137/273) | 0.23 |
| Cardiovascular complications (% and n) | 2 (18/914) | 1.9 (12/640) | 2.2 (6/274) | 0.46 |
| Cerebrovascular complications (% and n) | 10.9 (99/910) | 10.2 (65/640) | 12.6 (34/270) | 0.16 |
| Obesity (% and n) | 40.5 (293/723) | 41.9 (209/499) | 37.5 (84/224) | 0.15 |
| Adenomas in other locations | 36 (298/827) | 32 (207/647) | 33 (91/276) | 0.41 |
| Location | ||||
| Pituitary (% and n) | 4.1 (38/935) | 1.1 (7/647) | 1.4 (4/276) | 0.42 |
| Thyroid (% and n) | 24.4 (229/935) | 25.2 (163/647) | 23.9 (66/276) | 0.38 |
| Parathyroid (% and n) | 4.3 (40/935) | 2.5 (16/647) | 2.5 (7/276) | 0.54 |
| Others (% and n) | 33.4 (297/889) | 31.8 (206/647) | 33 (91/276) | 0.38 |
| Mortality (% and n) | 2.2 (20/923) | 1.2 (8/647) | 4.3 (12/276) | 0.005 |
| Variable | OR | CI | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adenoma location | All types of adenomas | 1.02 | 0.75–1.38 | 0.89 |
| Pituitary | 1.34 | 0.38–4.46 | 0.64 | |
| Thyroid | 0.91 | 0.65–1.28 | 0.76 | |
| Parathyroid | 0.99 | 0.40–2.45 | 0.98 | |
| Other | 1.03 | 0.76–1.40 | 0.82 | |
| Mortality | 3.30 | 1.32–8.23 | 0.01 |
| Characteristic | All Patients (n = 11) | Nonfunctioning AI (n = 7) | MACS (n = 4) | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex (male/female) | 54.5/45.5 | 71.4/28.6 | 25/75 | 0.19 |
| Age at diagnosis of AI | 64.5 ± 9.20 | 65.6 ± 3.69 | 62.5 ± 4.56 | 0.78 |
| Tobacco exposure | ||||
| Active smoker | 0 | 0 | 0 | - |
| Former smoker | 22.2 (4/9) | 20 (1/5) | 25 (3/4) | 0.72 |
| Complications | ||||
| Hypertension | 63.6 (7/11) | 57.1 (4/7) | 75 (3/4) | 0.53 |
| Diabetes | 36.4 (4/11) | 14.3 (1/7) | 75 (3/4) | 0.08 |
| Dyslipidemia | 27.3 (3/11) | 28.6 (2/7) | 25 (1/4) | 0.72 |
| Cardiovascular complications | 0 | 0 | 0 | - |
| Cerebrovascular complications | 9.1 (1/11) | 0 | 25 (1/4) | 0.36 |
| Obesity | 71.4 (7/7) | 50 (2/4) | 100 (3/3) | 0.28 |
| Mortality | 0 | 0 | 0 | - |
| Characteristic | All Patients (n = 229) | Nonfunctioning AI (n = 163) | MACS (n = 66) | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex (male/female) | 55/45 | 55.2/44.8 | 54.5/44.5 | 0.52 |
| Age at diagnosis of AI | 63.5 ± 10.80 | 63.1 ± 10.70 | 64.57 ± 10.90 | 0.39 |
| Tobacco exposure | ||||
| Active smoker | 9.1 (1/11) | 0 | 33.3 (1/3) | 0.27 |
| Former smoker | 40.6 (52/128) | 43.7 (38/87) | 34.1 (14/41) | 0.20 |
| Complications | ||||
| Hypertension | 53.9 (123/228) | 49.1 (80/163) | 66.2 (43/65) | 0.01 |
| Diabetes | 22.4 (51/228) | 19.0 (31/163) | 31.01 (20/65) | 0.04 |
| Dyslipidemia | 50 (114/228) | 46.6 (75/163) | 58.5 (38/65) | 0.07 |
| Cardiovascular complications | 0.9 (2/228) | 0.6 (1/163) | 1.5/1/65) | 0.49 |
| Cerebrovascular complications | 11.8 (27/228) | 9.2/15/63) | 18.5 (12/65) | 0.04 |
| Obesity | 43 (74/172) | 47 (55/117) | 34.5 (19/55) | 0.08 |
| Mortality | 1.7 (4/229) | 0 | 6.2 (4/66) | 0.006 |
| Characteristic | All Patients (n = 23) | Nonfunctioning AI (n = 16) | MACS (n = 7) | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex (male/female) | 69.6/30.4 | 68.8/31.3 | 71.4/28.6 | 0.64 |
| Age at diagnosis of AI | 66 ± 11.28 | 67.9 ± 10.23 | 61.6 ± 12.12 | 0.24 |
| Tobacco exposure | ||||
| Active smoker | 0 | 0 | 0 | - |
| Former smoker | 28.6 (4/14) | 33.3 (4/12) | 0 | 0.49 |
| Complications | ||||
| Hypertension | 60.9 (14/23) | 56.3 (9/16) | 71.4 (5/7) | 0.42 |
| Diabetes | 26.1 (6/23) | 25 (4/16) | 2.6 (2/7) | 0.61 |
| Dyslipidemia | 52.2 (12/23) | 56.3 (9/16) | 42.9 (3/7) | 0.44 |
| Cardiovascular complications | 0 | 0 | 0 | - |
| Cerebrovascular complications | 4.3 (1/23) | 0 | 14.3 (1/7) | 0.30 |
| Obesity | 42.1 (8/19) | 50 (7/14) | 20 (1/5) | 0.27 |
| Mortality | 0 | 0 | 0 | - |
| Characteristic | All Patients (n = 297) | Nonfunctioning AI (n = 206) | MACS (n = 91) | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex (male/female) | 69.6/30.4 | 55.8/44.2 | 57.1/42.9 | 0.46 |
| Age at diagnosis of AI | 63.6 ± 10.11 | 63.5 ± 10.20 | 63.9 ± 11.01 | 0.92 |
| Tobacco exposure | ||||
| Active smoker | 6.3 (1/16) | 0 | 16.7 (1/16) | 0.37 |
| Former smoker | 38.7 (67/173) | 41.6 (47/113) | 33.3 (20/60) | 0.42 |
| Complications | ||||
| Hypertension | 55.4 (164/296) | 51 (105/206) | 65.6 (59/90) | 0.01 |
| Diabetes | 23 (68/296) | 19.4 (40/26) | 31.1 (28/90) | 0.02 |
| Dyslipidemia | 52 (154/296) | 50.5 (104/206) | 55.6 (50/90) | 0.24 |
| Cardiovascular complications | 0.7 (2/296) | 0.5 (1/206) | 1.1 (1/90) | 0.51 |
| Cerebrovascular complications | 12.2 (36/296) | 9.2 (19/206) | 18.9 (17/90) | 0.01 |
| Obesity | 42.3 (96/227) | 45.4 (69/152) | 36 (27/75) | 0.11 |
| Mortality | 1.7 (5/297) | 0.5 (1/206) | 4.4 (4/91) | 0.03 |
| Characteristic | No Adenoma (n = 185) | Adenoma (n = 91) | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex (male/female) | 54.3/45.7 | 57.1/42.9 | 0.37 |
| Age at diagnosis of AI | 64.2 ± 11.41 | 63.9 ± 11.01 | 0.92 |
| Tobacco exposure | |||
| Active smoker | 37 (17/46) | 16.1 (1/6) | 0.31 |
| Former smoker | 38.1 (45/118) | 33.3 (20/60) | 0.32 |
| Complications | |||
| Hypertension | 60.9 (112/184) | 65.6 (59/90) | 0.27 |
| Diabetes | 25.5 (47/184) | 31.1 (28/90) | 0.20 |
| Dyslipidemia | 47.5 (87/183) | 55.6 (50/90) | 0.13 |
| Cardiovascular complications | 2.7 (5/184) | 1.1 (1/90) | 0.35 |
| Cerebrovascular complications | 9.4 (17/180) | 18.9 (17/90) | 0.02 |
| Obesity | 38.3 (57/149) | 36 (27/75) | 0.43 |
| Mortality | 4.3 (8/185) | 4.4 (4/91) | 0.60 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Herrera-Martínez, A.D.; Rebollo Román, Á.; Pascual Corrales, E.; Idrobo, C.; Parra Ramírez, P.; Martín Rojas-Marcos, P.; Robles Lázaro, C.; Marginean, D.L.; Araujo-Castro, M. Adrenal Incidentalomas and Other Endocrine-Related Adenomas: How Much Does Cortisol Secretion Matter? Cancers 2023, 15, 4735. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15194735
Herrera-Martínez AD, Rebollo Román Á, Pascual Corrales E, Idrobo C, Parra Ramírez P, Martín Rojas-Marcos P, Robles Lázaro C, Marginean DL, Araujo-Castro M. Adrenal Incidentalomas and Other Endocrine-Related Adenomas: How Much Does Cortisol Secretion Matter? Cancers. 2023; 15(19):4735. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15194735
Chicago/Turabian StyleHerrera-Martínez, Aura D., Ángel Rebollo Román, Eider Pascual Corrales, Cindy Idrobo, Paola Parra Ramírez, Patricia Martín Rojas-Marcos, Cristina Robles Lázaro, Delia Lavinia Marginean, and Marta Araujo-Castro. 2023. "Adrenal Incidentalomas and Other Endocrine-Related Adenomas: How Much Does Cortisol Secretion Matter?" Cancers 15, no. 19: 4735. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15194735
APA StyleHerrera-Martínez, A. D., Rebollo Román, Á., Pascual Corrales, E., Idrobo, C., Parra Ramírez, P., Martín Rojas-Marcos, P., Robles Lázaro, C., Marginean, D. L., & Araujo-Castro, M. (2023). Adrenal Incidentalomas and Other Endocrine-Related Adenomas: How Much Does Cortisol Secretion Matter? Cancers, 15(19), 4735. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15194735






