DKK1 Promotes Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition and Cisplatin Resistance in Gastric Cancer via Activation of the PI3K/AKT Pathway
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Drugs and Reagents
2.2. Cell lines and Cell Culture
2.3. Western Blot
2.4. Vector Construction and Transfection
2.5. Colony Formation Assay
2.6. CCK-8 Assay
2.7. Flow Cytometry
2.8. Wound Scratch and Transwell Assays
2.9. Xenograft Tumors in Nude Mice
2.10. Immunohistochemistry
2.11. Bioinformatical Analysis
2.12. Immunofluorescence (IF)
2.13. Short Hairpin RNA (shRNA) Transfection
- shRNA1: 5′-CCTGTCCTGAAAGAAGGTCAA-3′
- shRNA2: 5′-CCAGAAGAACCACCTTGTCTT-3′
- shRNA3: 5′-CCTGTCCTGAAAGAAGGTCAA-3′
- shRNA-NC: 5′-TTCTCCGAACGTGTCACGTAA-3′
2.14. RNA-Sequencing
2.15. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. DKK1 Is Highly Expressed in GC Tissues and Associated with Poor Prognosis in GC Patients
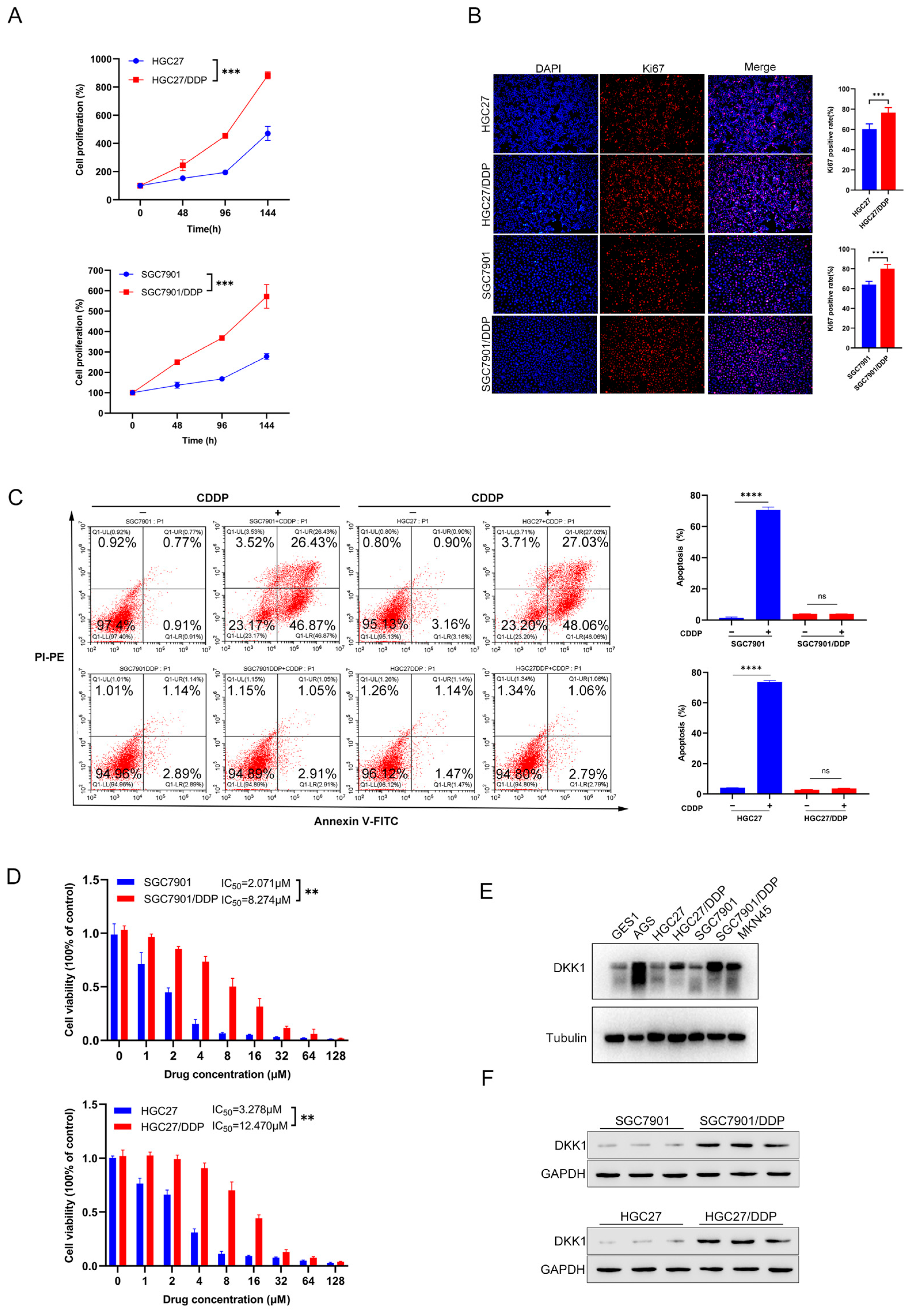
3.2. Characterization of Cisplatin Resistant Gastric Cancer Cell Lines
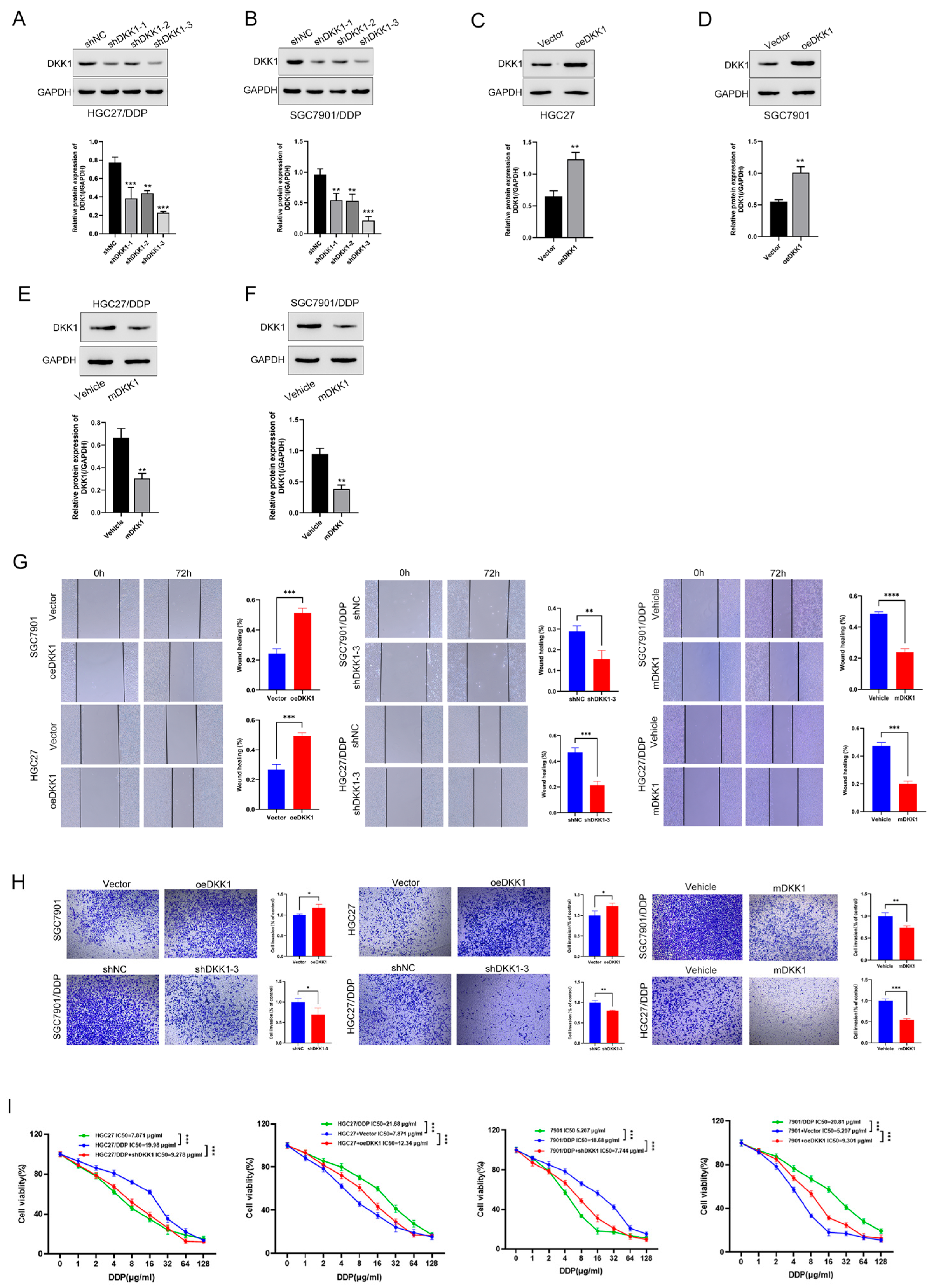
3.3. High DKK1 Expression Promotes Migration, Invasion and Proliferation in GC Cells
3.4. DKK1 Promotes Metastasis in GC Cell Lines and Is Associated with the EMT Phenotype
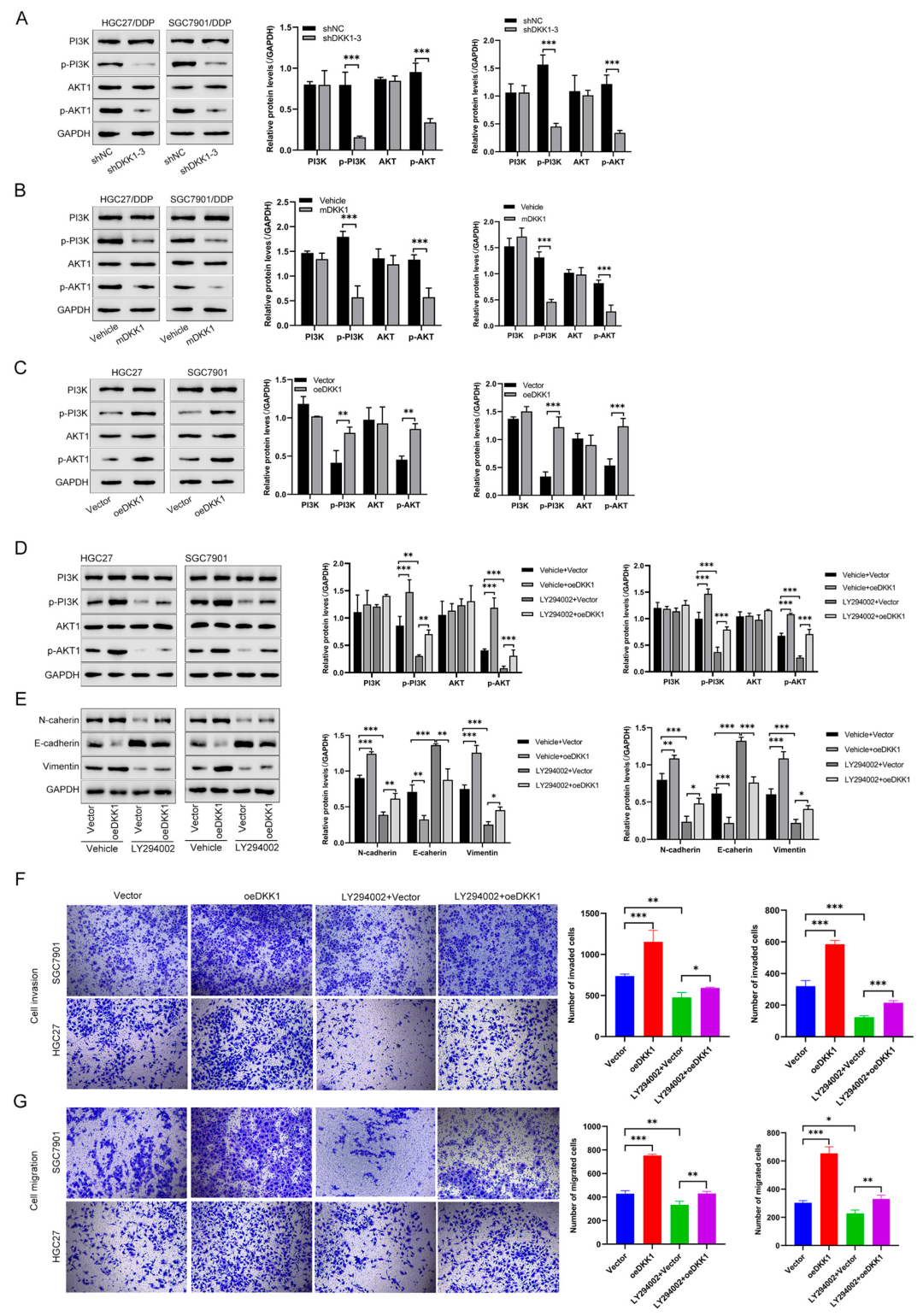
3.5. DKK1 Promotes EMT and Proliferation by Activating the PI3K/AKT Pathway in GC Cells
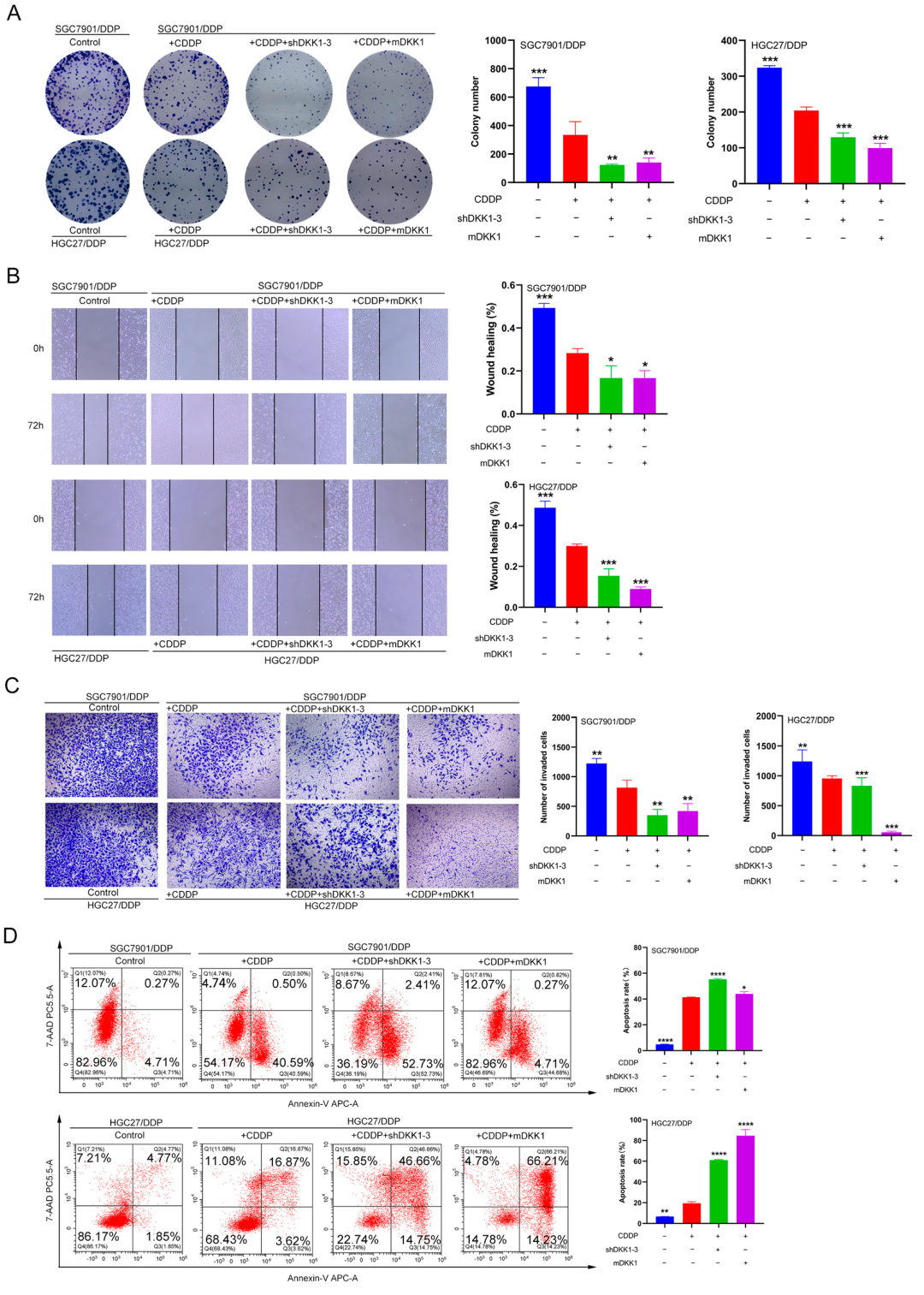
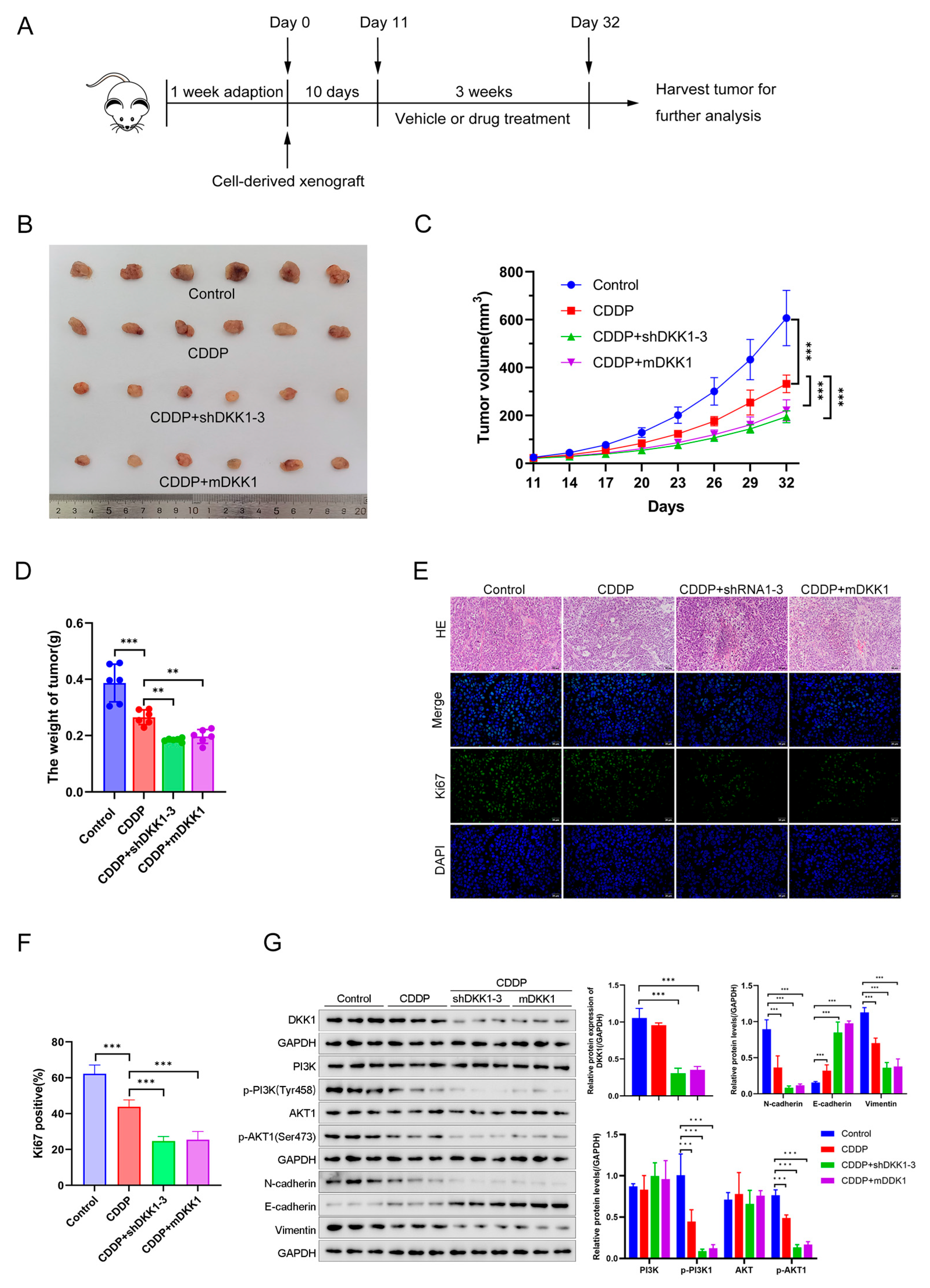
3.6. DKK1 Inhibition Overcomes Cisplatin Resistance In Vitro and In Vivo
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sexton, R.E.; Al Hallak, M.N.; Diab, M.; Azmi, A.S. Gastric cancer: A comprehensive review of current and future treatment strategies. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2020, 39, 1179–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.H.; Zhang, X.T.; Li, Y.F.; Tang, L.; Qu, X.J.; Ying, J.E.; Zhang, J.; Sun, L.Y.; Lin, R.B.; Qiu, H.; et al. The Chinese Society of Clinical Oncology (CSCO): Clinical guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of gastric cancer, 2021. Cancer Commun. 2021, 41, 747–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddik, Z.H. Cisplatin: Mode of cytotoxic action and molecular basis of resistance. Oncogene 2003, 22, 7265–7279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galanski, M.S. Recent Developments in the Field of Anticancer Platinum Complexes. Recent Pat. Anti-Cancer Drug Discov. 2006, 1, 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amable, L. Cisplatin resistance and opportunities for precision medicine. Pharmacol. Res. 2016, 106, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Savage, S.R.; Calinawan, A.P.; Lin, C.; Zhang, B.; Wang, P.; Starr, T.K.; Birrer, M.J.; Paulovich, A.G. A highly annotated database of genes associated with platinum resistance in cancer. Oncogene 2021, 40, 6395–6405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, Y.; Chu, H.Y.; Yu, S.; Yao, S.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, B.T. Drug Discovery of DKK1 Inhibitors. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 847387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Gong, W.; Li, X.; Wan, R.; Mo, F.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, P.; Hu, Z.; Lai, Z.; Lu, X.; et al. Recent Progress of Wnt Pathway Inhibitor Dickkopf-1 in Liver Cancer. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2018, 18, 5192–5206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, L.; Zhang, D.; Zhao, X.; Sun, B.; Liu, Y.; Gu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Che, N.; Zheng, Y.; et al. Dickkopf-1-promoted vasculogenic mimicry in non-small cell lung cancer is associated with EMT and development of a cancer stem-like cell phenotype. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2016, 20, 1673–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.H.; Liu, Z.B.; Yang, C.; Qin, W.; Shao, Z.M. Expression of dickkopf-1 and beta-catenin related to the prognosis of breast cancer patients with triple negative phenotype. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e37624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Huang, L.; Zhang, S. DKK-1 in serum as a clinical and prognostic factor in patients with cervical cancer. Int. J. Biol. Markers 2013, 28, 221–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rachner, T.D.; Thiele, S.; Gobel, A.; Browne, A.; Fuessel, S.; Erdmann, K.; Wirth, M.P.; Frohner, M.; Todenhofer, T.; Muders, M.H.; et al. High serum levels of Dickkopf-1 are associated with a poor prognosis in prostate cancer patients. BMC Cancer 2014, 14, 649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Sun, B.; Qi, L.; Li, Y.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, Y. Dickkopf-1 expression is down-regulated during the colorectal adenoma-carcinoma sequence and correlates with reduced microvessel density and VEGF expression. Histopathology 2015, 67, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikheev, A.M.; Mikheeva, S.A.; Rostomily, R.; Zarbl, H. Dickkopf-1 activates cell death in MDA-MB435 melanoma cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007, 352, 675–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Wu, J.; Chen, B.; Li, M.; Tian, Y.; He, M.; Xue, J.; Wang, J.; Bai, S.; Sharma, A.; et al. Serum Dickkopf-1 (DKK1) is significantly lower in patients with lung cancer but is rapidly normalized after treatment. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2014, 6, 850–856. [Google Scholar]
- Salim, H.; Zong, D.; Haag, P.; Novak, M.; Mork, B.; Lewensohn, R.; Lundholm, L.; Viktorsson, K. DKK1 is a potential novel mediator of cisplatin-refractoriness in non-small cell lung cancer cell lines. BMC Cancer 2015, 15, 628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaffer, C.L.; Weinberg, R.A. A perspective on cancer cell metastasis. Science 2011, 331, 1559–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loh, C.Y.; Chai, J.Y.; Tang, T.F.; Wong, W.F.; Sethi, G.; Shanmugam, M.K.; Chong, P.P.; Looi, C.Y. The E-Cadherin and N-Cadherin Switch in Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition: Signaling, Therapeutic Implications, and Challenges. Cells 2019, 8, 1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satelli, A.; Li, S. Vimentin in cancer and its potential as a molecular target for cancer therapy. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. CMLS 2011, 68, 3033–3046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.K.; Lee, H.; Kwon, O.S.; Song, N.Y.; Lee, H.J.; Kang, S.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, M.; Kim, W.; Cha, H.J. Large-scale pharmacogenomics based drug discovery for ITGB3 dependent chemoresistance in mesenchymal lung cancer. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Debaugnies, M.; Rodriguez-Acebes, S.; Blondeau, J.; Parent, M.A.; Zocco, M.; Song, Y.; de Maertelaer, V.; Moers, V.; Latil, M.; Dubois, C.; et al. RHOJ controls EMT-associated resistance to chemotherapy. Nature 2023, 616, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brabletz, T.; Kalluri, R.; Nieto, M.A.; Weinberg, R.A. EMT in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2018, 18, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibue, T.; Weinberg, R.A. EMT, CSCs, and drug resistance: The mechanistic link and clinical implications. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 14, 611–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, H.Y.; Chen, Z.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Z.K.; Tan, X.; Liu, S.; Zhang, B.T.; Lu, A.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, G. Dickkopf-1: A Promising Target for Cancer Immunotherapy. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 658097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Song, J.; Chen, W.; Yuan, D.; Wang, W.; Chen, X.; Liu, H.; Su, H.; Zhu, J. Expression and Role of Dickkopf-1 (Dkk1) in Tumors: From the Cells to the Patients. Cancer Manag. Res. 2021, 13, 659–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fezza, M.; Moussa, M.; Aoun, R.; Haber, R.; Hilal, G. DKK1 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma inflammation, migration and invasion: Implication of TGF-beta1. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0223252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doucet, D.; Brubaker, C.; Turner, D.; Gregory, C.A. Factors affecting the role of canonical Wnt inhibitor Dickkopf-1 in cancer progression. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1114822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, G.F.; Tan, Y.; Zeng, J.T.; Zhang, J.W.; Tang, J.; Zeng, S.P.; Qin, X. Expression of serum Dickkopf-1 in gastric cancer patients. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2015, 8, 870–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.S.; Lee, H.E.; Park, D.J.; Kim, H.H.; Kim, W.H.; Park, K.U. Clinical significance of serum and tissue Dickkopf-1 levels in patients with gastric cancer. Clin. Chim. Acta Int. J. Clin. Chem. 2012, 413, 1753–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, T.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Song, X.; Wang, H.; Zhou, X.; Liang, K.; Luo, Y.; Che, K.; Wang, X.; et al. DKK1 Promotes Tumor Immune Evasion and Impedes Anti-PD-1 Treatment by Inducing Immunosuppressive Macrophages in Gastric Cancer. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2022, 10, 1506–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Gong, W.; Wu, H.; Wang, J.; Jin, Q.; Lin, C.; Xu, S.; Bao, W.; Wang, Y.; Wu, J.; et al. DKK1 suppresses WWP2 to enhance bortezomib resistance in multiple myeloma via regulating GLI2 ubiquitination. Carcinogenesis 2021, 42, 1223–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marin, J.J.; Al-Abdulla, R.; Lozano, E.; Briz, O.; Bujanda, L.; Banales, J.M.; Macias, R.I. Mechanisms of Resistance to Chemotherapy in Gastric Cancer. Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 2016, 16, 318–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navaei, Z.N.; Khalili-Tanha, G.; Zangouei, A.S.; Abbaszadegan, M.R.; Moghbeli, M. PI3K/AKT signaling pathway as a critical regulator of Cisplatin response in tumor cells. Oncol. Res. 2021, 29, 235–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Miller, Z.; Musich, P.R.; Thomas, A.E.; Yao, Z.Q.; Xie, Q.; Howe, P.H.; Jiang, Y. DSTYK Promotes Metastasis and Chemoresistance via EMT in Colorectal Cancer. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, L.; Li, D.S.; Chen, F.; Feng, J.D.; Li, B.; Wang, T.J. TAZ overexpression is associated with epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cisplatin-resistant gastric cancer cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2017, 51, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, X.; Luo, M.; Li, J.; Shen, Z.; Xie, K. Overcoming therapeutic resistance to platinum-based drugs by targeting Epithelial-Mesenchymal transition. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 1008027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carnero, A.; Blanco-Aparicio, C.; Renner, O.; Link, W.; Leal, J.F. The PTEN/PI3K/AKT signalling pathway in cancer, therapeutic implications. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2008, 8, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brozovic, A.; Osmak, M. Activation of mitogen-activated protein kinases by cisplatin and their role in cisplatin-resistance. Cancer Lett. 2007, 251, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corradetti, M.N.; Guan, K.L. Upstream of the mammalian target of rapamycin: Do all roads pass through mTOR? Oncogene 2006, 25, 6347–6360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.Z.; Zhou, X.D.; Qian, G.; Shi, X.; Fang, J.; Jiang, B.H. AKT1 amplification regulates cisplatin resistance in human lung cancer cells through the mammalian target of rapamycin/p70S6K1 pathway. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 6325–6332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Y.; Tan, X.; Liu, J.; Shen, Y.; Wu, D.; Ren, M.; Huang, P.; Yu, D. Inhibition of PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway enhances the sensitivity of the SKOV3/DDP ovarian cancer cell line to cisplatin in vitro. Chin. J. Cancer Res. Chung-Kuo Yen Cheng Yen Chiu 2014, 26, 564–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gohr, K.; Hamacher, A.; Engelke, L.H.; Kassack, M.U. Inhibition of PI3K/Akt/mTOR overcomes cisplatin resistance in the triple negative breast cancer cell line HCC38. BMC Cancer 2017, 17, 711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suchitha, G.P.; Balaya, R.D.A.; Raju, R.; Prasad, T.S.K.; Dagamajalu, S. A network map of cytoskeleton-associated protein 4 (CKAP4) mediated signaling pathway in cancer. J. Cell Commun. Signal. 2023, 17, 1097–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikuchi, A.; Fumoto, K.; Kimura, H. The Dickkopf1-cytoskeleton-associated protein 4 axis creates a novel signalling pathway and may represent a molecular target for cancer therapy. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 174, 4651–4665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, H.; Fumoto, K.; Shojima, K.; Nojima, S.; Osugi, Y.; Tomihara, H.; Eguchi, H.; Shintani, Y.; Endo, H.; Inoue, M.; et al. CKAP4 is a Dickkopf1 receptor and is involved in tumor progression. J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 126, 2689–2705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinno, N.; Kimura, H.; Sada, R.; Takiguchi, S.; Mori, M.; Fumoto, K.; Doki, Y.; Kikuchi, A. Activation of the Dickkopf1-CKAP4 pathway is associated with poor prognosis of esophageal cancer and anti-CKAP4 antibody may be a new therapeutic drug. Oncogene 2018, 37, 3471–3484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iguchi, K.; Sada, R.; Matsumoto, S.; Kimura, H.; Zen, Y.H.; Akita, M.; Gon, H.; Fukumoto, T.; Kikuchi, A. DKK1-CKAP4 signal axis promotes hepatocellular carcinoma aggressiveness. Cancer Sci. 2023, 114, 2063–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Chen, Y.J.; Xie, Y.; Wang, Q.R.; Xiang, Y.N.; Long, N.Y.; Yang, W.X.; Zhao, Y.; Zhou, J.J. Dickkopf-related protein 1/cytoskeleton-associated protein 4 signaling activation by Helicobacter pylori-induced activator protein-1 promotes gastric tumorigenesis via the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. World J. Gastroenterol. 2022, 28, 6769–6787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Clinical Parameters | Cases | DKK1 Expression | χ2 | p Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low | High | |||||
| Sex | Male | 45 | 30 | 15 | 0.615 | 0.433 |
| Female | 21 | 16 | 5 | |||
| Age | ≤60 | 40 | 27 | 13 | 0.232 | 0.630 |
| >60 | 26 | 19 | 7 | |||
| Tumor size | ≤3 cm | 27 | 15 | 12 | 4.326 | 0.038 |
| >3 cm | 39 | 31 | 8 | |||
| Pathologic_T | T1–2 | 19 | 16 | 3 | 2.661 | 0.103 |
| T3–4 | 47 | 30 | 17 | |||
| Pathologic_N | N0 | 21 | 18 | 3 | 3.741 | 0.053 |
| N1–3 | 45 | 28 | 17 | |||
| Pathologic_M | M0 | 62 | 43 | 19 | 0.000 | 1.000 |
| M1 | 4 | 3 | 1 | |||
| TNM stage | I–II | 29 | 24 | 5 | 4.179 | 0.041 |
| III–IV | 37 | 22 | 15 | |||
| Differentiation | I–II/II | 16 | 12 | 4 | 0.167 | 0.683 |
| II–III/III | 36 | 25 | 11 | |||
| Variable | Univariate Analysis | |
|---|---|---|
| p-Value | HR(95% CI) | |
| Sex (male vs. female) | 0.421 | 1.345 (0.653–2.771) |
| Age (≤60 vs. >60) | 0.300 | 1.403 (0.739–2.661) |
| Pathologic_T (T1/T2 vs. T3/T4) | 0.005 | 3.864 (1.501–9.943) |
| Pathologic_N (N0 vs. N1–3) | 0.002 | 4.618 (1.795–11.884) |
| Pathologic_M (M0 vs. M1) | 0.069 | 2.704 (0.926–7.892) |
| TNM (I/II vs. III/IV) | 0.003 | 3.061 (1.478–6.341) |
| Tumor_size (≤3 cm vs. 3 cm) | 0.050 | 2.017 (0.999–4.074) |
| Differentiation (I–II/II vs. II–II/III) | 0.793 | 0.899 (0.406–1.989) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Ye, F.; Qian, P.; Qin, Z.; Li, D.; Ye, L.; Feng, L. DKK1 Promotes Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition and Cisplatin Resistance in Gastric Cancer via Activation of the PI3K/AKT Pathway. Cancers 2023, 15, 4756. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15194756
Li J, Zhang Y, Ye F, Qian P, Qin Z, Li D, Ye L, Feng L. DKK1 Promotes Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition and Cisplatin Resistance in Gastric Cancer via Activation of the PI3K/AKT Pathway. Cancers. 2023; 15(19):4756. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15194756
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Jian, Yaqiong Zhang, Fangzhou Ye, Peiyu Qian, Zhe Qin, Deming Li, Li Ye, and Li Feng. 2023. "DKK1 Promotes Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition and Cisplatin Resistance in Gastric Cancer via Activation of the PI3K/AKT Pathway" Cancers 15, no. 19: 4756. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15194756
APA StyleLi, J., Zhang, Y., Ye, F., Qian, P., Qin, Z., Li, D., Ye, L., & Feng, L. (2023). DKK1 Promotes Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition and Cisplatin Resistance in Gastric Cancer via Activation of the PI3K/AKT Pathway. Cancers, 15(19), 4756. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15194756






