Role of Decompressive Surgery in Neurologically Intact Patients with Low to Intermediate Intraspinal Metastatic Tumor Burden
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Selection
2.2. Clinical Analysis
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
3.2. Treatment Regimes
3.3. Perioperative and Clinical Complications
3.4. Neurological Outcome
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rades, D.; Al-Salool, A.; Staackmann, C.; Cremers, F.; Cacicedo, J.; Lomidze, D.; Segedin, B.; Groselj, B.; Jankarashvili, N.; Conde-Moreno, A.J.; et al. A New Clinical Instrument for Estimating the Ambulatory Status after Irradiation for Malignant Spinal Cord Compression. Cancers 2022, 14, 3827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rades, D.; Delikanli, C.; Schild, S.E.; Kristiansen, C.; Tvilsted, S.; Janssen, S. A New Survival Score for Patients ≥65 Years Assigned to Radiotherapy of Bone Metastases. Cancers 2022, 14, 4679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, J.S.; Patchell, R.A. Metastatic epidural spinal cord compression. Lancet Neurol. 2008, 7, 459–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rades, D.; Fehlauer, F.; Schulte, R.; Veninga, T.; Stalpers, L.J.; Basic, H.; Bajrovic, A.; Hoskin, P.J.; Tribius, S.; Wildfang, I. Prognostic factors for local control and survival after radiotherapy of metastatic spinal cord compression. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 24, 3388–3393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaikova, O.; Giercksky, K.E.; Fosså, S.D.; Kvaløy, S.; Johannesen, T.B.; Skjeldal, S. A Population-based Study of Spinal Metastatic Disease in South-East Norway. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 21, 753–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loblaw, D.; Laperriere, N.; Mackillop, W. A population-based study of malignant spinal cord compression in Ontario. Clin. Oncol. 2003, 15, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patchell, R.A.; Tibbs, P.A.; Regine, W.F.; Payne, R.; Saris, S.; Kryscio, R.J.; Mohiuddin, M.; Young, B. Direct decompressive surgical resection in the treatment of spinal cord compression caused by metastatic cancer: A randomised trial. Lancet 2005, 366, 643–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bakar, D.; Tanenbaum, J.E.; Phan, K.; Alentado, V.J.; Steinmetz, M.P.; Benzel, E.C.; Mroz, T.E. Decompression surgery for spinal metastases: A systematic review. Neurosurg. Focus 2016, 41, E2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rades, D.; Küchler, J.; Graumüller, L.; Abusamha, A.; Schild, S.E.; Gliemroth, J. Radiotherapy with or without Decompressive Surgery for Metastatic Spinal Cord Compression: A Retrospective Matched-Pair Study Including Data from Prospectively Evaluated Patients. Cancers 2022, 14, 1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, H.S.; Wagner, A.; Raufer, A.; Joerger, A.-K.; Gempt, J.; Meyer, B. Surgery in Acute Metastatic Spinal Cord Compression: Timing and Functional Outcome. Cancers 2022, 14, 2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frankel, H.; Hancock, D.; Hyslop, G.; Melzak, J.; Michaelis, L.; Ungar, G.; Vernon, J.; Walsh, J. The value of postural reduction in the initial management of closed injuries of the spine with paraplegia and tetraplegia. Spinal Cord 1969, 7, 179–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ditunno, J.; Young, W.; Donovan, W.; Creasey, G. The international standards booklet for neurological and functional classification of spinal cord injury. Spinal Cord 1994, 32, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bilsky, M.H.; Laufer, I.; Fourney, D.R.; Groff, M.; Schmidt, M.H.; Varga, P.P.; Vrionis, F.D.; Yamada, Y.; Gerszten, P.C.; Kuklo, T.R. Reliability analysis of the epidural spinal cord compression scale. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2010, 13, 324–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fisher, C.G.; DiPaola, C.P.; Ryken, T.C.; Bilsky, M.H.; Shaffrey, C.I.; Berven, S.H.; Harrop, J.S.; Fehlings, M.G.; Boriani, S.; Chou, D.; et al. A Novel Classification System for Spinal Instability in Neoplastic Disease: An Evidence-Based Approach and Expert Consensus From the Spine Oncology Study Group. Spine 2010, 35, E1221–E1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lenschow, M.; Lenz, M.; von Spreckelsen, N.; Ossmann, J.; Meyer, J.; Keßling, J.; Nadjiri, L.; Telentschak, S.; Zarghooni, K.; Knöll, P.; et al. Impact of Spinal Instrumentation on Neurological Outcome in Patients with Intermediate Spinal Instability Neoplastic Score (SINS). Cancers 2022, 14, 2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fehlings, M.G.; Nater, A.; Tetreault, L.; Kopjar, B.; Arnold, P.; Dekutoski, M.; Finkelstein, J.; Fisher, C.; France, J.; Gokaslan, Z.; et al. Survival and Clinical Outcomes in Surgically Treated Patients With Metastatic Epidural Spinal Cord Compression: Results of the Prospective Multicenter AOSpine Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 268–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, G.M.; Vital, J.M.; Aurouer, N.; Obeid, I.; Palussiere, J.; Diallo, A.; Pointillart, V. Surgery improves pain, function and quality of life in patients with spinal metastases: A prospective study on 118 patients. Eur. Spine J. 2011, 20, 1970–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wise, J.J.; Fischgrund, J.S.; Herkowitz, H.N.; Montgomery, D.; Kurz, L.T. Complication, survival rates, and risk factors of surgery for metastatic disease of the spine. Spine 1999, 24, 1943–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finkelstein, J.A.; Zaveri, G.; Wai, E.; Vidmar, M.; Kreder, H.; Chow, E. A population-based study of surgery for spinal metastases. Survival rates and complications. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 2003, 85, 1045–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igoumenou, V.G.; Mavrogenis, A.F.; Angelini, A.; Baracco, R.; Benzakour, A.; Benzakour, T.; Bork, M.; Vazifehdan, F.; Nena, U.; Ruggieri, P. Complications of spine surgery for metastasis. Eur. J. Orthop. Surg. Traumatol. 2020, 30, 37–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulino Pereira, N.R.; Ogink, P.T.; Groot, O.Q.; Ferrone, M.L.; Hornicek, F.J.; van Dijk, C.N.; Bramer, J.A.M.; Schwab, J.H. Complications and reoperations after surgery for 647 patients with spine metastatic disease. Spine J. 2019, 19, 144–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sundaresan, N.; Rothman, A.; Manhart, K.; Kelliher, K. Surgery for solitary metastases of the spine: Rationale and results of treatment. Spine 2002, 27, 1802–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.J.; Konodi, M.A.; Cizik, A.M.; Weinreich, M.A.; Bransford, R.J.; Bellabarba, C.; Chapman, J. Risk factors for medical complication after cervical spine surgery: A multivariate analysis of 582 patients. Spine 2013, 38, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, N.; Zaw, A.S.; Khine, H.E.; Maharajan, K.; Wai, K.L.; Tan, B.; Mastura, S.; Goy, R. Blood Loss and Transfusion Requirements in Metastatic Spinal Tumor Surgery: Evaluation of Influencing Factors. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2016, 23, 2079–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maseda, M.; Uei, H.; Nakahashi, M.; Sawada, H.; Tokuhashi, Y. Neurological outcome of treatment for patients with impending paralysis due to epidural spinal cord compression by metastatic spinal tumor. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2019, 14, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dakson, A.; Leck, E.; Brandman, D.M.; Christie, S.D. The clinical utility of the Spinal Instability Neoplastic Score (SINS) system in spinal epidural metastases: A retrospective study. Spinal Cord 2020, 58, 892–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quraishi, N.A.; Arealis, G.; Salem, K.M.; Purushothamdas, S.; Edwards, K.L.; Boszczyk, B.M. The surgical management of metastatic spinal tumors based on an Epidural Spinal Cord Compression (ESCC) scale. Spine J. 2015, 15, 1738–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uei, H.; Tokuhashi, Y.; Maseda, M. Relationship Between Paralysis and the Epidural Spinal Cord Compression Scale in Spinal Metastasis. Orthopedics 2020, 43, e567–e573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennington, Z.; Ahmed, A.K.; Molina, C.A.; Ehresman, J.; Laufer, I.; Sciubba, D.M. Minimally invasive versus conventional spine surgery for vertebral metastases: A systematic review of the evidence. Ann. Transl. Med. 2018, 6, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berenson, J.; Pflugmacher, R.; Jarzem, P.; Zonder, J.; Schechtman, K.; Tillman, J.B.; Bastian, L.; Ashraf, T.; Vrionis, F.; Investigators, C.P.F.E. Balloon kyphoplasty versus non-surgical fracture management for treatment of painful vertebral body compression fractures in patients with cancer: A multicentre, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2011, 12, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stangenberg, M.; Viezens, L.; Eicker, S.O.; Mohme, M.; Mende, K.C.; Dreimann, M. Cervical vertebroplasty for osteolytic metastases as a minimally invasive therapeutic option in oncological surgery: Outcome in 14 cases. Neurosurg. Focus 2017, 43, E3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mohme, M.; Riethdorf, S.; Dreimann, M.; Werner, S.; Maire, C.L.; Joosse, S.A.; Bludau, F.; Mueller, V.; Neves, R.P.; Stoecklein, N.H. Circulating tumour cell release after cement augmentation of vertebral metastases. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 7196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laufer, I.; Rubin, D.G.; Lis, E.; Cox, B.W.; Stubblefield, M.D.; Yamada, Y.; Bilsky, M.H. The NOMS framework: Approach to the treatment of spinal metastatic tumors. Oncologist 2013, 18, 744–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yahanda, A.T.; Buchowski, J.M.; Wegner, A.M. Treatment, complications, and outcomes of metastatic disease of the spine: From Patchell to PROMIS. Ann. Transl. Med. 2019, 7, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ganesh, K.; Massague, J. Targeting metastatic cancer. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Decompression n = 145 | No Decompression n = 36 | Overall n = 181 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Decomp. Alone | Decomp. + Instrumentation | Surgery without Decomp | RT Alone | All Treatment Modalities p = | Decomp vs. No Decomp p = | ||
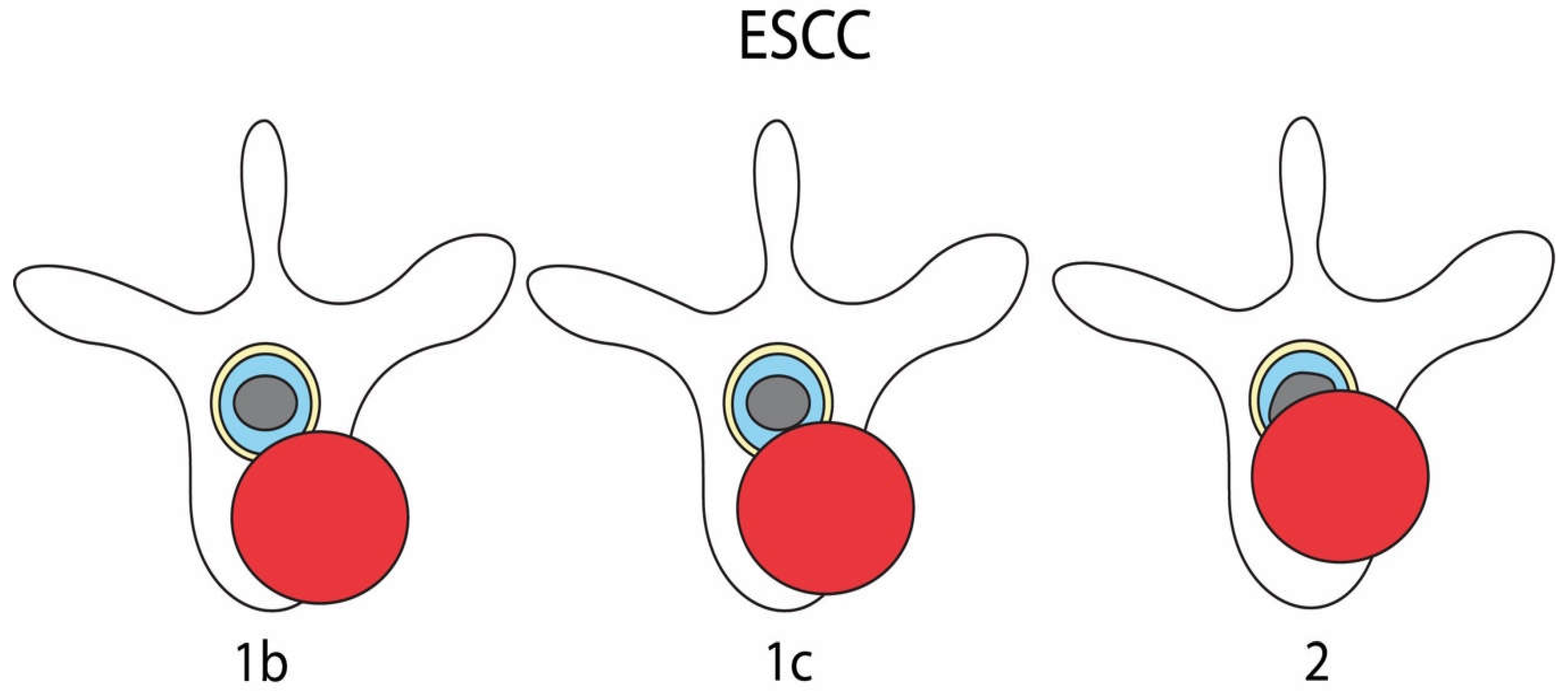
| ESCC | n = 11 | n = 134 | n = 23 | n = 13 | n = 181 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| 1b | 2 (18.2) | 12 (9%) | 11 (47.8%) | 8 (61.5%) | 33 (18.2%) | ||
| 1c | 0 (0%) | 32 (23.9%) | 8 (34.8%) | 2 (15.4%) | 42 (23.2%) | ||
| 2 | 9 (81.8%) | 90 (67.2%) | 4 (17.4%) | 3 (23.1%) | 106 (58.6%) | ||
| Radiotherapy | n = 9 | n = 107 | n = 20 | n = 13 | n = 149 | 0.057 | 0.541 |
| Yes | 7 (77.8%) | 89 (83.2%) | 14 (70.0%) | 13 (100%) | 123 (82.6%) | ||
| No | 2 (22.2%) | 18 (16.8%) | 6 (30.0%) | / | 26 (17.4%) | ||
| Decompression n = 145 | No Decompression n = 35 | Overall n = 180 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Decomp. Alone n = 11 | Decomp. + Instrumentation n = 134 | Surgery without Decomp n = 23 | RT Alone n = 12 | All Treatment Modalities p | Decomp vs. No Decomp p | ||
| Overall complications | 0 (0%) | 40 (29.9%) | 7 (30.4%) | 3 (25.0%) | 50 (27.8%) | 0.227 | 0.907 |
| Wound infection | 0 (0%) | 9 (6.7%) | 1 (4.3%) | / | 10 (5.6%) | 0.458 | 0.689 |
| Misplaced implants | / | 5 (3.7%) | 2 (8.7%) | / | 7 (3.9%) | 0.478 | 0.623 |
| Thrombosis/PE | 0 (0%) | 8 (6.0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 8 (4.4%) | 0.899 | 0.358 |
| Pneumonia | 0 (0%) | 9 (6.7%) | 1 (4.3%) | 0 (0%) | 10 (5.6%) | >0.999 | 0.689 |
| Other * | 0 (0%) | 16 (11.9%) | 1 (4.3%) | 3 (25.0%) | 20 (11.1%) | 0.399 | >0.999 |
| Revision surgery | 0 (0%) | 16 (11.9%) | 4 (17.4%) | / | 20 (11.1%) | 0.408 | >0.999 |
| Delay of adj. treatment due to complication | 0 (0%) | 16 (11.9%) | 1 (2.9%) | 0 | 17 (9.4%) | 0.243 | 0.201 |
| Decompression n = 134 | No Decompression n = 31 | Overall n = 165 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Frankel Grade at last follow-up | C | 1 (0.7%) | 1 (3.2%) | 2 (1.2%) | p = 0.246 |
| D | 5 (3.7%) | 0 | 5 (3.0%) | ||
| E | 128 (95.5%) | 30 (96.8%) | 158 (95.8%) |
| ESCC 1b n = 29 | ESCC 1c n = 39 | ESCC 2 n = 97 | Overall n = 165 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Frankel Grade at last follow-up | C | 1 (3.4%) | 0 | 1 (1%) | 2 (1.2%) | p = 0.627 |
| D | 0 | 1 (2.6%) | 4 (4.1%) | 5 (3.0%) | ||
| E | 28 (96.6%) | 38 (97.4%) | 92 (94.8%) | 158 (95.8%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
von Spreckelsen, N.; Ossmann, J.; Lenz, M.; Nadjiri, L.; Lenschow, M.; Telentschak, S.; Meyer, J.; Keßling, J.; Knöll, P.; Eysel, P.; et al. Role of Decompressive Surgery in Neurologically Intact Patients with Low to Intermediate Intraspinal Metastatic Tumor Burden. Cancers 2023, 15, 385. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15020385
von Spreckelsen N, Ossmann J, Lenz M, Nadjiri L, Lenschow M, Telentschak S, Meyer J, Keßling J, Knöll P, Eysel P, et al. Role of Decompressive Surgery in Neurologically Intact Patients with Low to Intermediate Intraspinal Metastatic Tumor Burden. Cancers. 2023; 15(2):385. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15020385
Chicago/Turabian Stylevon Spreckelsen, Niklas, Julian Ossmann, Maximilian Lenz, Lukas Nadjiri, Moritz Lenschow, Sergej Telentschak, Johanna Meyer, Julia Keßling, Peter Knöll, Peer Eysel, and et al. 2023. "Role of Decompressive Surgery in Neurologically Intact Patients with Low to Intermediate Intraspinal Metastatic Tumor Burden" Cancers 15, no. 2: 385. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15020385
APA Stylevon Spreckelsen, N., Ossmann, J., Lenz, M., Nadjiri, L., Lenschow, M., Telentschak, S., Meyer, J., Keßling, J., Knöll, P., Eysel, P., Goldbrunner, R., Perrech, M., Scheyerer, M., Celik, E., Zarghooni, K., & Neuschmelting, V. (2023). Role of Decompressive Surgery in Neurologically Intact Patients with Low to Intermediate Intraspinal Metastatic Tumor Burden. Cancers, 15(2), 385. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15020385






