The Multifaceted Functions of Prion Protein (PrPC) in Cancer
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Background
1.2. PrPC Expression and Functions
2. Aims
3. PrPC in Human Cancers
3.1. PrPC and Gastric Cancer
3.2. PrPC and Melanoma
3.3. PrPC and Breast Cancer
3.4. PrPC and Colorectal Cancer
4. The Potential Diagnostic and Therapeutic Value of PrPC in Different Types of Cancer
5. Targeting PrPC Interactions in Cancer: New Insights and Potential Strategies (Figure 4)
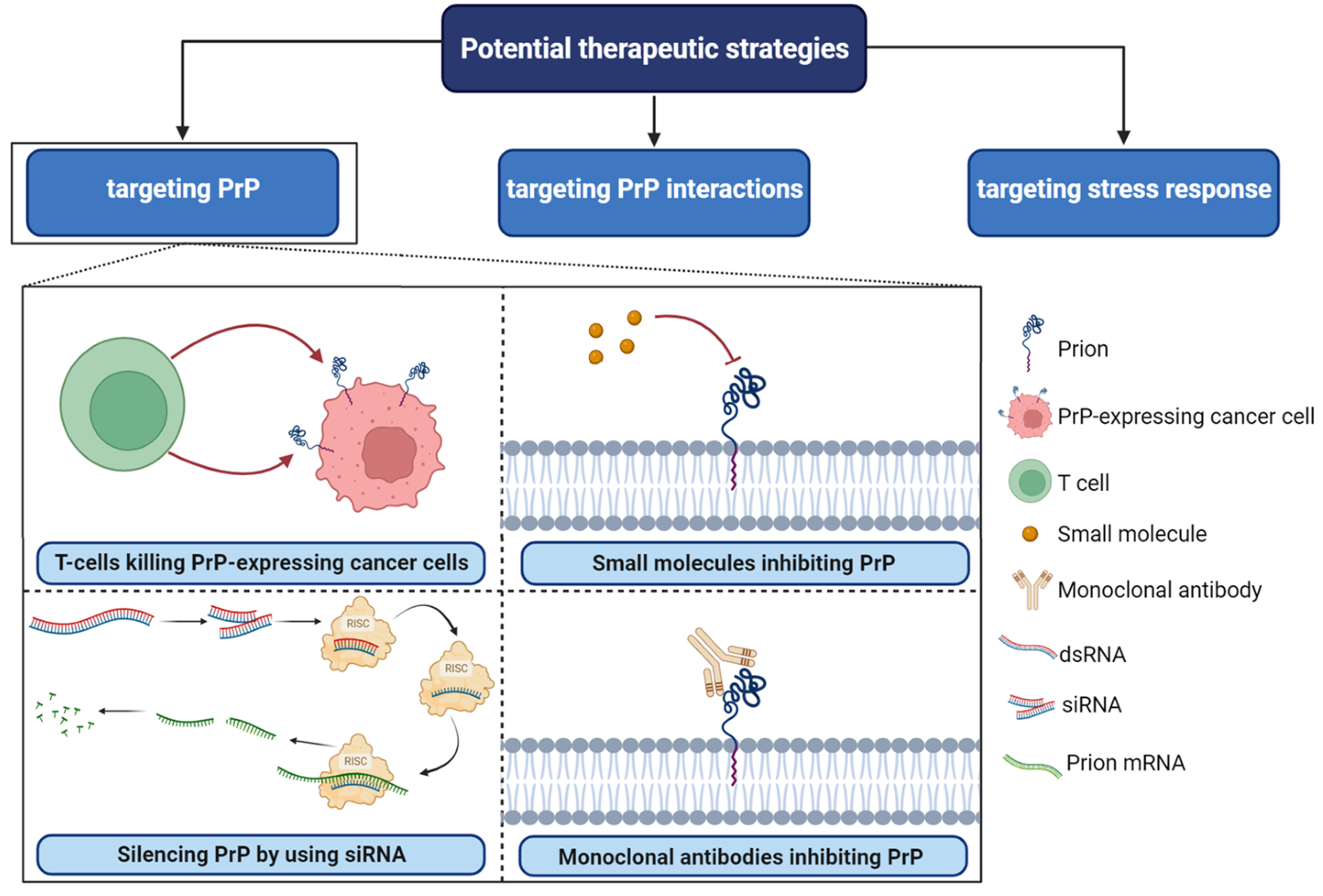
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ABC | ATP-Binding Cassette |
| Akt | Protein Kinase B |
| ATP | Adenosine Triphosphate |
| BES | Bovine encephalopathies spongiform |
| CD44 | Cluster of Differentiation 44 |
| cIAP-1 | Cellular Inhibitor of Apoptosis Protein-1 |
| CJD | Creutzfeldt-Jakob’s Disease |
| CNS | Central Nervous System |
| CRC | Colorectal Cancer |
| CSC | Cancer Stem Cells |
| Ct | C-terminal domain |
| Cu2+ | Copper ions |
| dsRNA | Double-Stranded RNA |
| ECM | Extracellular Matrix |
| ER | Endoplasmic Reticulum |
| ERK1/2 | Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinases 1 and 2 |
| FFI | Fatal Familial Insomnia |
| FLNA | Filamin A |
| Fyn | Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase Fyn |
| GA | Golgi Apparatus |
| GLUT-1 | Glucose Transporter 1 |
| GPI | Glycosylphosphatidylinositol |
| GSC | Glioma Stem Cells |
| HIF-2α | Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-2 Alpha |
| HSP27 | Heat Shock Protein 27 |
| HT29 | A colorectal carcinoma cell line |
| IAPs | Inhibitor of Apoptosis Proteins |
| LS-174T | A colorectal adenocarcinoma cell line |
| MCF7/ADR | MCF7 Adriamycin-Resistant Cells |
| MDA-MB-435 | A breast cancer cell line |
| MDR | Multidrug Resistance |
| MKN45 | A gastric cancer cell line |
| MMP | Matrix Metalloprotease |
| Nt | N-terminal domain |
| P38MAPK | p38 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase |
| PDAC | Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma |
| PGAP1/PGAP5 | Post-GPI Attachment Proteins 1 and 5 |
| P-gp | P-glycoprotein |
| PKA | Protein Kinase A |
| PKD | Protein Kinase D |
| PRNP | Prion Protein Gene |
| PrPC | Cellular Prion Protein |
| RISC | RNA-Induced Silencing Complex |
| SATB1 | Special AT-Rich Sequence-Binding Protein 1 |
| SE | spongiform encephalopathies |
| Ser82 | Serine 82 |
| SGC7901 | A gastric cancer cell line |
| siRNA | Small Interfering RNA |
| Sp1 | Specificity Protein 1 |
| TMD | Trans Membrane Domain |
| TNF-α | Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha |
| TRAIL | Tumor Necrosis Factor-Related Apoptosis Inducing Ligand |
| TSE | Transmissible spongiform encephalopathies |
| XIAP | X-Linked Inhibitor of Apoptosis |
References
- Bendheim, P.E.; Brown, H.R.; Rudelli, R.D.; Scala, L.J.; Goller, N.L.; Wen, G.Y.; Kascsak, R.J.; Cashman, N.R.; Bolton, D.C. Nearly ubiquitous tissue distribution of the scrapie agent precursor protein. Neurology 1992, 42, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnon, C.; Wendeler, M.W.; Paccaud, J.-P.; Hauri, H.-P. Selective export of human GPI-anchored proteins from the endoplasmic reticulum. J. Cell Sci. 2010, 123 Pt 10, 1705–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, S.; Maeda, Y.; Tashima, Y.; Kinoshita, T. Inositol deacylation of glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored proteins is mediated by mammalian PGAP1 and yeast Bst1p. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 14256–14263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campana, V.; Sarnataro, D.; Zurzolo, C. The highways and byways of prion protein trafficking. Trends Cell Biol. 2005, 15, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarnataro, D.; Campana, V.; Paladino, S.; Stornaiuolo, M.; Nitsch, L.; Zurzolo, C. PrP(C) association with lipid rafts in the early secretory pathway stabilizes its cellular conformation. Mol. Biol. Cell 2004, 15, 4031–4042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, C.S.; Aronoff-Spencer, E.; Dunham, C.M.; Lario, P.; Avdievich, N.I.; Antholine, W.E.; Olmstead, M.M.; Vrielink, A.; Gerfen, G.J.; Peisach, J.; et al. Molecular features of the copper binding sites in the octarepeat domain of the prion protein. Biochemistry 2002, 41, 3991–4001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, C.F.; Lawson, V.A.; Coleman, B.M.; Kim, Y.-S.; Masters, C.L.; Cappai, R.; Barnham, K.J.; Hill, A.F. Conservation of a glycine-rich region in the prion protein is required for uptake of prion infectivity. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 20213–20223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, D.A.; Lele, P.; Snider, W.D. Localization of the mRNA for a chicken prion protein by in situ hybridization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 4309–4313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manson, J.; West, J.D.; Thomson, V.; McBride, P.; Kaufman, M.H.; Hope, J. The prion protein gene: A role in mouse embryogenesis? Development 1992, 115, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, D.R.; Schmidt, B.; Groschup, M.H.; Kretzschmar, H.A. Prion protein expression in muscle cells and toxicity of a prion protein fragment. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 1998, 75, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Liu, D.; Zanusso, G.; Liu, T.; Fayen, J.D.; Huang, J.-H.; Petersen, R.B.; Gambetti, P.; Sy, M.-S. The expression and potential function of cellular prion protein in human lymphocytes. Cell. Immunol. 2001, 207, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pammer, J.; Cross, H.S.; Frobert, Y.; Tschachler, E.; Oberhuber, G. The pattern of prion-related protein expression in the gastrointestinal tract. Virchows Arch. 2000, 436, 466–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pammer, J.; Weninger, W.; Tschachler, E. Human keratinocytes express cellular prion-related protein in vitro and during inflammatory skin diseases. Am. J. Pathol. 1998, 153, 1353–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liemann, S.; Glockshuber, R. Transmissible spongiform encephalopathies. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1998, 250, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prusiner, S.B. Novel proteinaceous infectious particles cause scrapie. Science 1982, 216, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffrey, M.; Gonzalez, L. Pathology and pathogenesis of bovine spongiform encephalopathy and scrapie. Curr. Top Microbiol. Immunol. 2004, 284, 65–97. [Google Scholar]
- Bregman, N.; Shiner, T.; Kavé, G.; Alcalay, R.; Gana-Weisz, M.; Goldstein, O.; Glinka, T.; Aizenstein, O.; Ben Bashat, D.; Alcalay, Y.; et al. Correction: The natural history study of preclinical genetic Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease (CJD): A prospective longitudinal study protocol. BMC Neurol. 2023, 23, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Wang, S.; Han, S.; Hu, N.; Shang, X. Case report: Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease: A case that initiated with the onset of obsessive-compulsive state. Front. Neurol. 2023, 14, 1227566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, Z.; Bollu, P.C. Fatal Familial Insomnia. In StatPearls; StatPearls: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Bounhar, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Goodyer, C.G.; LeBlanc, A.C. Prion protein protects human neurons against Bax-mediated apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 39145–39149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, D.R.; Qin, K.; Herms, J.W.; Madlung, A.; Manson, J.; Strome, R.; Fraser, P.E.; Kruck, T.; von Bohlen, A.; Schulz-Schaeffer, W.; et al. The cellular prion protein binds copper in vivo. Nature 1997, 390, 684–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuwahara, C.; Takeuchi, A.M.; Nishimura, T.; Haraguchi, K.; Kubosaki, A.; Matsumoto, Y.; Saeki, K.; Matsumoto, Y.; Yokoyama, T.; Itohara, S.; et al. Prions prevent neuronal cell-line death. Nature 1999, 400, 225–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouillet-Richard, S.; Ermonval, M.; Chebassier, C.; Laplanche, J.L.; Lehmann, S.; Launay, J.M.; Kellermann, O. Signal transduction through prion protein. Science 2000, 289, 1925–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paitel, E.; Fahraeus, R.; Checler, F. Cellular prion protein sensitizes neurons to apoptotic stimuli through Mdm2-regulated and p53-dependent caspase 3-like activation. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 10061–10066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stella, R.; Massimino, M.L.; Sandri, M.; Sorgato, M.C.; Bertoli, A. Cellular prion protein promotes regeneration of adult muscle tissue. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2010, 30, 4864–4876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stürmer, C.; Langhorst, M.F.; Wiechers, M.F.; Legler, D.F.; von Hanwehr, S.H.; Guse, A.H.; Plattner, H. PrPc capping in T cells promotes its association with the lipid raft proteins reggie-1 and reggie-2 and leads to signal transduction. FASEB J. 2004, 18, 1731–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimaldi, I.; Leser, F.S.; Janeiro, J.M.; da Rosa, B.G.; Campanelli, A.C.; Romão, L.; Lima, F.R.S. The multiple functions of PrP(C) in physiological, cancer, and neurodegenerative contexts. J. Mol. Med. 2022, 100, 1405–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Büeler, H.; Fischer, M.; Lang, Y.; Bluethmann, H.; Lipp, H.-P.; DeArmond, S.J.; Prusiner, S.B.; Aguet, M.; Weissmann, C. Normal development and behaviour of mice lacking the neuronal cell-surface PrP protein. Nature 1992, 356, 577–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makarava, N.; Katorcha, E.; Chang, J.C.-Y.; Lau, J.T.Y.; Baskakov, I.V. Deficiency in ST6GAL1, one of the two alpha2,6-sialyltransferases, has only a minor effect on the pathogenesis of prion disease. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2022, 9, 1058602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavallaro, U.; Christofori, G. Cell adhesion and signalling by cadherins and Ig-CAMs in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2004, 4, 118–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Pan, Y.; Shi, Y.; Guo, C.; Jin, X.; Sun, L.; Liu, N.; Qiao, T.; Fan, D. Overexpression and significance of prion protein in gastric cancer and multidrug-resistant gastric carcinoma cell line SGC7901/ADR. Int. J. Cancer 2005, 113, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graner, E.; Mercadante, A.F.; Zanata, S.M.; Forlenza, O.V.; Cabral, A.L.; Veiga, S.S.; Juliano, M.A.; Roesler, R.; Walz, R.; Minetti, A.; et al. Cellular prion protein binds laminin and mediates neuritogenesis. Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 2000, 76, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, T.; Wong, B.-S.; Liu, T.; Li, R.; Petersen, R.B.; Sy, M.-S. Cell-surface prion protein interacts with glycosaminoglycans. Biochem. J. 2002, 368 Pt 1, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Zhao, L.; Liang, J.; Liu, J.; Shi, Y.; Liu, N.; Zhang, G.; Jin, H.; Gao, J.; Xie, H.; et al. Cellular prion protein promotes invasion and metastasis of gastric cancer. FASEB J. 2006, 20, 1886–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rieger, R.; Edenhofer, F.; Lasmézas, C.I.; Weiss, S. The human 37-kDa laminin receptor precursor interacts with the prion protein in eukaryotic cells. Nat. Med. 1997, 3, 1383–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satoh, J.-I.; Kuroda, Y.; Katamine, S. Gene expression profile in prion protein-deficient fibroblasts in culture. Am. J. Pathol. 2000, 157, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt-Ulms, G.; Legname, G.; Baldwin, M.A.; Ball, H.L.; Bradon, N.; Bosque, P.J.; Crossin, K.L.; Edelman, G.M.; DeArmond, S.J.; Cohen, F.E.; et al. Binding of neural cell adhesion molecules (N-CAMs) to the cellular prion protein. J. Mol. Biol. 2001, 314, 1209–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Q.; Zheng, H.; Li, M.; Wang, H.; Guo, X.; Zheng, Z.; Chen, C.; Liu, J.; Zhan, T.; Li, Z.; et al. LGR4 cooperates with PrPc to endow the stemness of colorectal cancer stem cells contributing to tumorigenesis and liver metastasis. Cancer Lett. 2022, 540, 215725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.-J.; Cho, Y.-A.; Kim, E.; Choe, J.-Y.; Park, J.-W.; Lee, J.; Lee, J.-W.; Moon, S.-H.; Kim, Y.-S.; Kim, S.-E.; et al. Cellular Prion Protein Is Closely Associated with Early Recurrence and Poor Survival in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, M.; Chen, Y.; Lang, Y.; Cui, L. The Role of Cellular Prion Protein in Cancer Biology: A Potential Therapeutic Target. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 742949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousaf, S.; Ahmad, M.; Wu, S.; Zia, M.A.; Ahmed, I.; Iqbal, H.M.; Liu, Q.; Rehman, S.U. Cellular Prion Protein Role in Cancer Biology: Is It A Potential Therapeutic Target? Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blasi, F.; Carmeliet, P. uPAR: A versatile signalling orchestrator. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2002, 3, 932–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.S.; Linden, R.; Brentani, R.R.; Martins, V.R.; Prado, M.A.M. Towards cellular receptors for prions. Rev. Med. Virol. 2003, 13, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khasigov, P.Z.; Podobed, O.V.; Gracheva, T.S.; Salbiev, K.D.; Grachev, S.V.; Berezov, T.T. Role of matrix metalloproteinases and their inhibitors in tumor invasion and metastasis. Biochemistry 2003, 68, 711–717. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Y.; Walsh, C.A. The many faces of filamin: A versatile molecular scaffold for cell motility and signalling. Nat. Cell Biol. 2004, 6, 1034–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, J.; Wu, G.; Zhang, J.; Li, H.; Gao, S.; Shao, M.; Gao, Z.; Sy, M.-S.; Cao, Y.; Yang, X.; et al. Melanoma migration is promoted by prion protein via Akt-hsp27 signaling axis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 523, 375–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Yu, S.; Nakamura, F.; Pentikäinen, O.T.; Singh, N.; Yin, S.; Xin, W.; Sy, M.S. Pro-prion binds filamin A, facilitating its interaction with integrin beta1, and contributes to melanomagenesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 30328–30339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stossel, T.P.; Condeelis, J.; Cooley, L.; Hartwig, J.H.; Noegel, A.; Schleicher, M.; Shapiro, S.S. Filamins as integrators of cell mechanics and signalling. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2001, 2, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandasamy, K.; Srinivasula, S.M.; Alnemri, E.S.; Thompson, C.B.; Korsmeyer, S.J.; Bryant, J.L.; Srivastava, R.K. Involvement of proapoptotic molecules Bax and Bak in tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL)-induced mitochondrial disruption and apoptosis: Differential regulation of cytochrome c and Smac/DIABLO release. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 1712–1721. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, T.H.; Noh, K.H.; Kim, J.H.; Bae, H.C.; Lin, K.Y.; Monie, A.; Pai, S.I.; Hung, C.-F.; Wu, T.-C.; Kim, T.W. Ectopic expression of X-linked lymphocyte-regulated protein pM1 renders tumor cells resistant to antitumor immunity. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 3062–3070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keane, M.M.; Ettenberg, S.A.; Nau, M.M.; Russell, E.K.; Lipkowitz, S. Chemotherapy augments TRAIL-induced apoptosis in breast cell lines. Cancer Res. 1999, 59, 734–741. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, E.J.; Suliman, A.; Lam, A.; Srivastava, R.K. Failure of Bcl-2 to block mitochondrial dysfunction during TRAIL-induced apoptosis. Tumor necrosis-related apoptosis-inducing ligand. Int. J. Oncol. 2001, 18, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simstein, R.; Burow, M.; Parker, A.; Weldon, C.; Beckman, B. Apoptosis, chemoresistance, and breast cancer: Insights from the MCF-7 cell model system. Exp. Biol. Med. 2003, 228, 995–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprick, M.R.; Rieser, E.; Stahl, H.; Grosse-Wilde, A.; Weigand, M.A.; Walczak, H. Caspase-10 is recruited to and activated at the native TRAIL and CD95 death-inducing signalling complexes in a FADD-dependent manner but can not functionally substitute caspase-8. EMBO J. 2002, 21, 4520–4530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, R.K. Intracellular mechanisms of TRAIL and its role in cancer therapy. Mol. Cell Biol. Res. Commun. 2000, 4, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chieng, C.K.-L.; Say, Y.-H. Cellular prion protein contributes to LS 174T colon cancer cell carcinogenesis by increasing invasiveness and resistance against doxorubicin-induced apoptosis. Tumour. Biol. 2015, 36, 8107–8120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, M.; Kim, Y.K.; Kim, K.-E.; Kim, W.; Park, C.-S.; Lee, K.J. Cellular prion protein regulates invasion and migration of breast cancer cells through MMP-9 activity. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 470, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.-Q.; Cao, X.-X.; Xu, J.-D.; Chen, Q.; Wang, W.-J.; Tang, F.; Chen, Z.-Q.; Liu, X.-P.; Xu, Z.-D. The role of P-glycoprotein/cellular prion protein interaction in multidrug-resistant breast cancer cells treated with paclitaxel. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2009, 66, 504–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fantin, V.R.; St-Pierre, J.; Leder, P. Attenuation of LDH-A expression uncovers a link between glycolysis, mitochondrial physiology, and tumor maintenance. Cancer Cell 2006, 9, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.-Q.; Sun, Y.-P.; Ruan, C.-P.; Xu, X.-Y.; Ge, J.-H.; He, J.; Xu, Z.-D.; Wang, Q.; Gao, W.-C. Cellular prion protein promotes glucose uptake through the Fyn-HIF-2α-Glut1 pathway to support colorectal cancer cell survival. Cancer Sci. 2011, 102, 400–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warburg, O. On the origin of cancer cells. Science 1956, 123, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Rao, G.; Wang, H.; Li, B.; Tian, W.; Cui, J.; He, L.; Laffin, B.; Tian, X.; Hao, C.; et al. CD44-positive cancer stem cells expressing cellular prion protein contribute to metastatic capacity in colorectal cancer. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 2682–2694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Qian, J.; Wang, F.; Ma, Z. Cellular prion protein accelerates colorectal cancer metastasis via the Fyn-SP1-SATB1 axis. Oncol. Rep. 2012, 28, 2029–2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Bearss, D.J.; Browne, L.W.; Calaluce, R.; Nagle, R.B.; Von Hoff, D.D. Identification of differentially expressed genes in pancreatic cancer cells using cDNA microarray. Cancer Res. 2002, 62, 2890–2896. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.H.; Yun, C.W.; Lee, S.H. Cellular Prion Protein Enhances Drug Resistance of Colorectal Cancer Cells via Regulation of a Survival Signal Pathway. Biomol. Ther. 2018, 26, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Yu, S.; Nakamura, F.; Yin, S.; Xu, J.; Petrolla, A.A.; Singh, N.; Tartakoff, A.; Abbott, D.W.; Xin, W.; et al. Binding of pro-prion to filamin A disrupts cytoskeleton and correlates with poor prognosis in pancreatic cancer. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 119, 2725–2736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sy, M.-S.; Altekruse, S.F.; Li, C.; Lynch, C.F.; Goodman, M.T.; Hernandez, B.Y.; Zhou, L.; Saber, M.S.; Hewitt, S.M.; Xin, W. Association of prion protein expression with pancreatic adenocarcinoma survival in the SEER residual tissue repository. Cancer Biomark 2011, 10, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauer, H.; Dagdanova, A.; Hescheler, J.; Wartenberg, M. Redox-regulation of intrinsic prion expression in multicellular prostate tumor spheroids. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 1999, 27, 1276–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sollazzo, V.; Galasso, M.; Volinia, S.; Carinci, F. Prion proteins (PRNP and PRND) are over-expressed in osteosarcoma. J. Orthop. Res. 2012, 30, 1004–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thellung, S.; Corsaro, A.; Bosio, A.; Zambito, M.; Barbieri, F.; Mazzanti, M.; Florio, T. Emerging Role of Cellular Prion Protein in the Maintenance and Expansion of Glioma Stem Cells. Cells 2019, 8, 1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Jiang, L.; Xu, Y.; Guo, H.; Liu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, H.; Yuan, C.; Ma, J. Silencing prion protein in MDA-MB-435 breast cancer cells leads to pleiotropic cellular responses to cytotoxic stimuli. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e48146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouadri, A.; El Khatib, M.; Cormenier, J.; Chauvet, S.; Zeinyeh, W.; El Khoury, M.; Macari, L.; Richaud, P.R.; Coraux, C.; Michaud-Soret, I.; et al. Involvement of the Prion Protein in the Protection of the Human Bronchial Epithelial Barrier Against Oxidative Stress. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2019, 31, 59–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.-C.; Lin, C.-H.; Shih, N.-C.; Liu, H.-L.; Wang, W.-C.; Lin, K.-Y.; Liu, Z.-Y.; Tseng, Y.-J.; Chang, H.-K.; Lin, Y.-C.; et al. Cellular prion protein transcriptionally regulated by NFIL3 enhances lung cancer cell lamellipodium formation and migration through JNK signaling. Oncogene 2020, 39, 385–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryskalin, L.; Biagioni, F.; Busceti, C.L.; Giambelluca, M.A.; Morelli, L.; Frati, A.; Fornai, F. The Role of Cellular Prion Protein in Promoting Stemness and Differentiation in Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrier, V.; Solassol, J.; Crozet, C.; Frobert, Y.; Mourton-Gilles, C.; Grassi, J.; Lehmann, S. Anti-PrP antibodies block PrPSc replication in prion-infected cell cultures by accelerating PrPC degradation. J. Neurochem. 2004, 89, 454–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limone, A.; Maggisano, V.; Sarnataro, D.; Bulotta, S. Emerging roles of the cellular prion protein (PrP(C)) and 37/67 kDa laminin receptor (RPSA) interaction in cancer biology. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2023, 80, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassallo, N.; Herms, J. Cellular prion protein function in copper homeostasis and redox signalling at the synapse. J. Neurochem. 2003, 86, 538–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavoie, J.; Gingras-Breton, G.; Tanguay, R.; Landry, J. Induction of Chinese hamster HSP27 gene expression in mouse cells confers resistance to heat shock. HSP27 stabilization of the microfilament organization. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 3420–3429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomura, N.; Nomura, M.; Sugiyama, K.; Hamada, J.-I. Phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA)-induced migration of glioblastoma cells is mediated via p38MAPK/Hsp27 pathway. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2007, 74, 690–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clerk, A.; Michael, A.; Sugden, P.H. Stimulation of multiple mitogen-activated protein kinase sub-families by oxidative stress and phosphorylation of the small heat shock protein, HSP25/27, in neonatal ventricular myocytes. Biochem. J. 1998, 333 Pt 3, 581–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLaughlin, M.M.; Kumar, S.; McDonnell, P.C.; Van Horn, S.; Lee, J.C.; Livi, G.P.; Young, P.R. Identification of mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase-activated protein kinase-3, a novel substrate of CSBP p38 MAP kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 8488–8492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- New, L.; Jiang, Y.; Zhao, M.; Liu, K.; Zhu, W.; Flood, L.J.; Kato, Y.; Parry, G.C.; Han, J. PRAK, a novel protein kinase regulated by the p38 MAP kinase. EMBO J. 1998, 17, 3372–3384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouse, J.; Cohen, P.; Trigon, S.; Morange, M.; Alonso-Llamazares, A.; Zamanillo, D.; Hunt, T.; Nebreda, A.R. A novel kinase cascade triggered by stress and heat shock that stimulates MAPKAP kinase-2 and phosphorylation of the small heat shock proteins. Cell 1994, 78, 1027–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santell, L.; Bartfeld, N.S.; Levin, E.G. Identification of a protein transiently phosphorylated by activators of endothelial cell function as the heat-shock protein HSP27. A possible role for protein kinase C. Biochem. J. 1992, 284 Pt 3, 705–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morelli, J.G.; Yohn, J.J.; Zekman, T.; Norris, D.A. Melanocyte movement in vitro: Role of matrix proteins and integrin receptors. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1993, 101, 605–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baxter, E.; Windloch, K.; Gannon, F.; Lee, J.S. Epigenetic regulation in cancer progression. Cell Biosci. 2014, 4, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Malerva, L.; Park, J.; Zou, L.; Hu, Y.; Moradpour, Z.; Pearlberg, J.; Sawyer, J.; Stevens, H.; Harlow, E.; LaBaer, J. High-throughput ectopic expression screen for tamoxifen resistance identifies an atypical kinase that blocks autophagy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 2058–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meijer, D.; van Agthoven, T.; Bosma, P.T.; Nooter, K.; Dorssers, L.C. Functional screen for genes responsible for tamoxifen resistance in human breast cancer cells. Mol. Cancer Res. 2006, 4, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meslin, F.; Hamai, A.; Gao, P.; Jalil, A.; Cahuzac, N.; Chouaib, S.; Mehrpour, M. Silencing of prion protein sensitizes breast adriamycin-resistant carcinoma cells to TRAIL-mediated cell death. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 10910–10919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Wit, M.; Jimenez, C.R.; Carvalho, B.; Belien, J.A.; Delis-van Diemen, P.M.; Mongera, S.; Piersma, S.R.; Vikas, M.; Navani, S.; Pontén, F.; et al. Cell surface proteomics identifies glucose transporter type 1 and prion protein as candidate biomarkers for colorectal adenoma-to-carcinoma progression. Gut 2012, 61, 855–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.H.; Go, G.; Lee, S.H. PrPC Regulates the Cancer Stem Cell Properties via Interaction With c-Met in Colorectal Cancer Cells. Anticancer Res. 2021, 41, 3459–3470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.C.; Chuang, F.C.; Chang, C.L.; Huang, C.R.; Chen, H.H.; Yip, H.K.; Chen, Y.T. Melatonin-Assisted Cisplatin Suppresses Urinary Bladder Cancer Cell Proliferation and Growth through Inhibiting PrP(C)-Regulated Cell Stress and Cell Proliferation Signaling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameyar-Zazoua, M.; Larochette, N.; Dorothée, G.; Daugas, E.; Haddada, H.; Gouloumet, V.; Métivier, D.; Stancou, R.; Mami-Chouaib, F.; Kroemer, G.; et al. Wild-type p53 induced sensitization of mutant p53 TNF-resistant cells: Role of caspase-8 and mitochondria. Cancer Gene Ther. 2002, 9, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenzi, P.; Busceti, C.L.; Lazzeri, G.; Ferese, R.; Biagioni, F.; Salvetti, A.; Pompili, E.; De Franchis, V.; Puglisi-Allegra, S.; Frati, A.; et al. Autophagy Activation Associates with Suppression of Prion Protein and Improved Mitochondrial Status in Glioblastoma Cells. Cells 2023, 12, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouillet-Richard, S.; Martin-Lannerée, S.; Le Corre, D.; Hirsch, T.Z.; Ghazi, A.; Sroussi, M.; Pilati, C.; de Reyniès, A.; Djouadi, F.; Vodovar, N.; et al. A proof of concept for targeting the PrP(C)—Amyloid beta peptide interaction in basal prostate cancer and mesenchymal colon cancer. Oncogene 2022, 41, 4397–4404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linden, R.; Martins, V.R.; Prado, M.A.M.; Cammarota, M.; Izquierdo, I.; Brentani, R.R. Physiology of the prion protein. Physiol. Rev. 2008, 88, 673–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, T.G.; Lopes, M.H.; Martins, V.R. Targeting prion protein interactions in cancer. Prion 2015, 9, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Déry, M.-A.; Jodoin, J.; Ursini-Siegel, J.; Aleynikova, O.; Ferrario, C.; Hassan, S.; Basik, M.; LeBlanc, A.C. Endoplasmic reticulum stress induces PRNP prion protein gene expression in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2013, 15, R22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Ma, J. Immunotherapy against Prion Disease. Pathogens 2020, 9, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rovis, T.L.; Legname, G. Prion protein-specific antibodies-development, modes of action and therapeutics application. Viruses 2014, 6, 3719–3737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
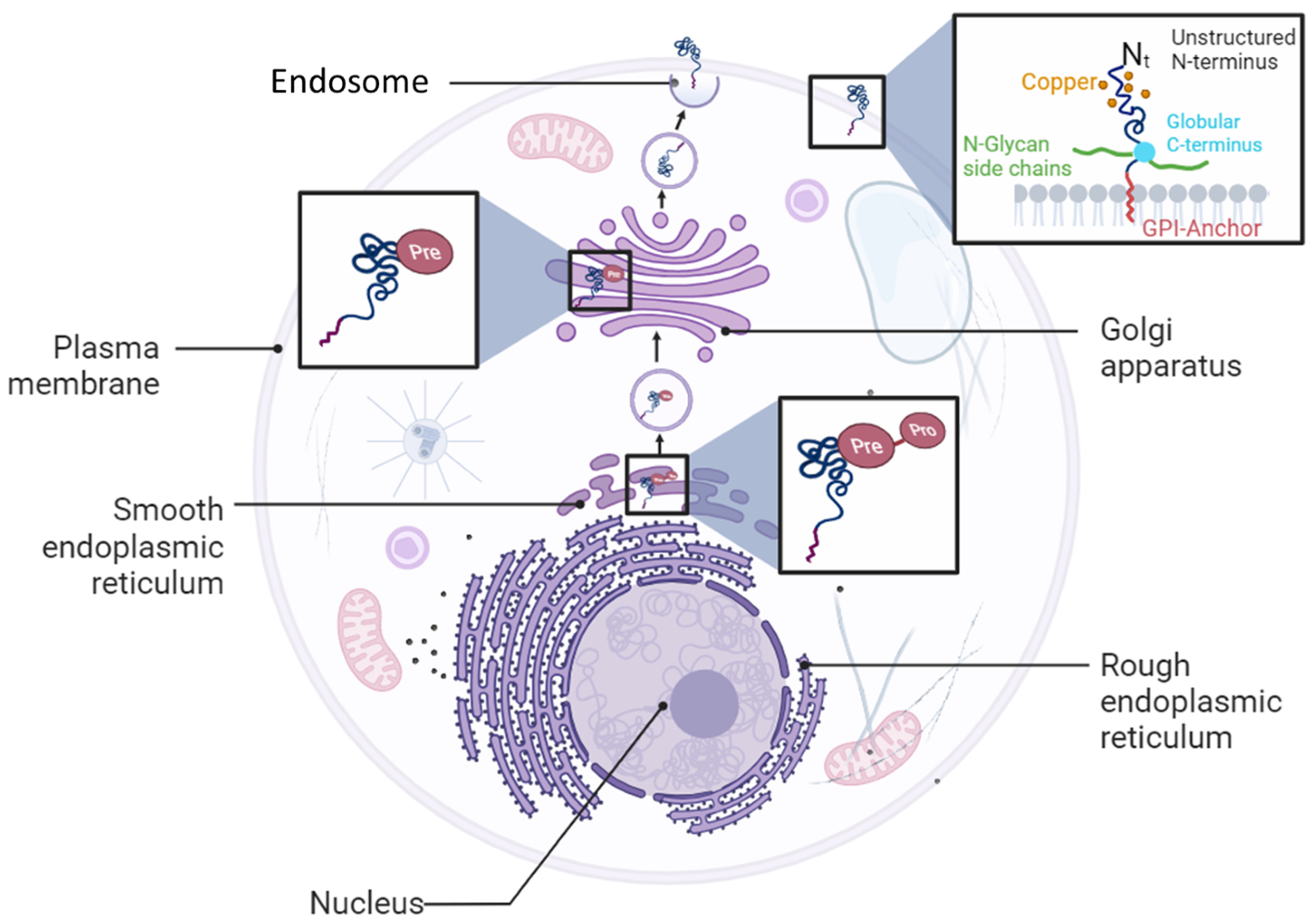
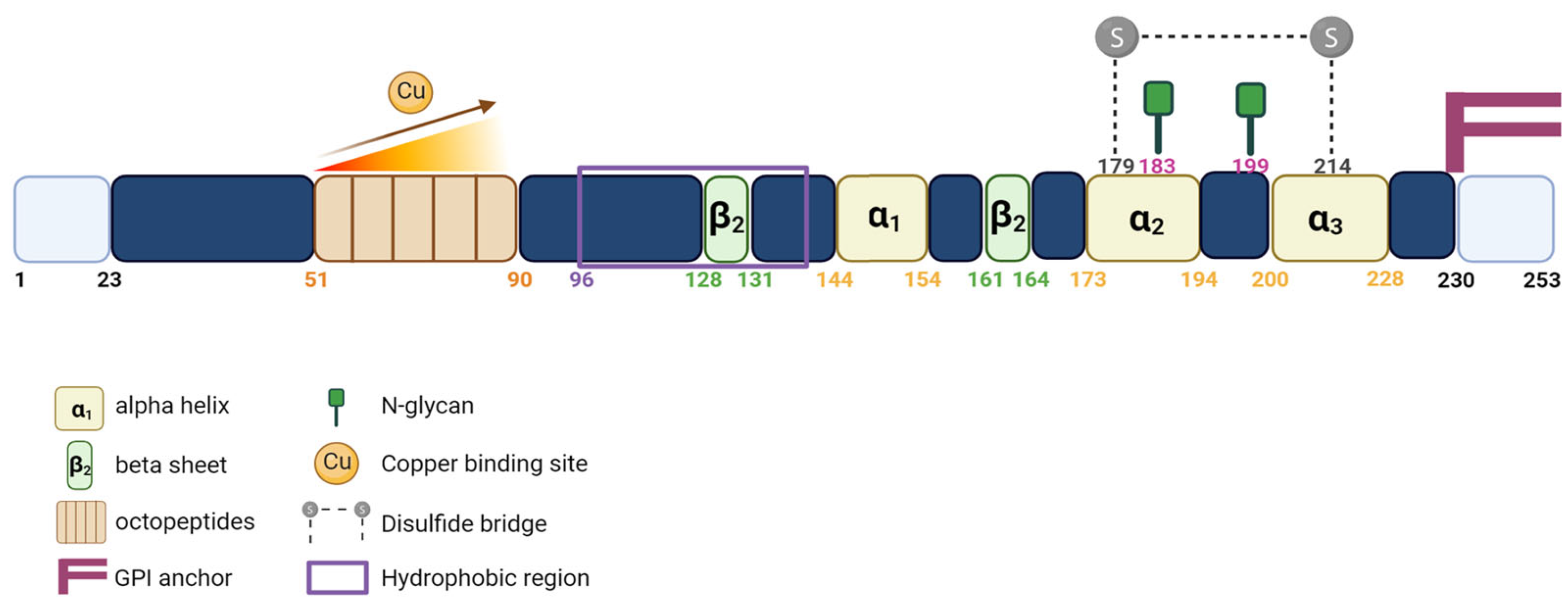
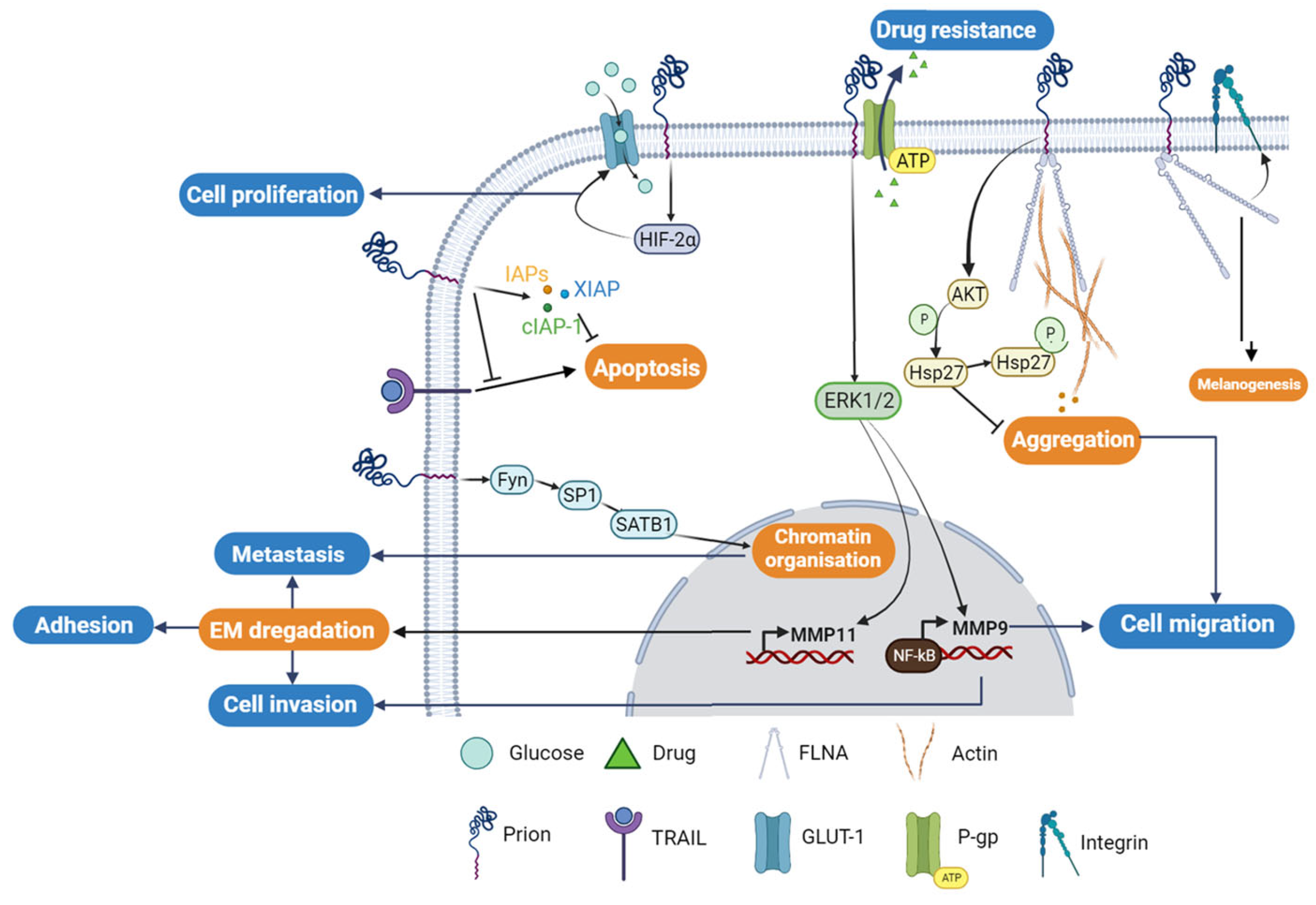
| Cancer Type | Role of PrPC | References |
|---|---|---|
| Gastric Cancer | Promotion of multidrug resistance | [31] |
| Enhancement of adhesive and invasive abilities | [33,34,36,44] | |
| Melanoma | Promotion of cancer migration | [21,45,46,47,48] |
| Disruption of Filamin A | [21,45,46,47,48] | |
| Breast Cancer | Resistance to apoptosis and drug treatment | [30,49,50,51,52,53,54,55] |
| Promotion of invasion and migration | [56,57,58] | |
| Colorectal Cancer | Promotion of tumor growth via Warburg effect | [59,60,61] |
| Enhancement of metastasis | [62,63] | |
| Confer resistance to anti-cancer drugs | [64,65,66,67] | |
| Prostate Cancer | Potential involvement in tumor development | [68] |
| Osteosarcoma | Association with tumor development | [69] |
| Glioblastoma | Enhancement of glioma stem cell proliferation | [70,71] |
| Lung Cancer | Possible involvement in tumorigenesis | [72,73] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abi Nahed, R.; Safwan-Zaiter, H.; Gemy, K.; Lyko, C.; Boudaud, M.; Desseux, M.; Marquette, C.; Barjat, T.; Alfaidy, N.; Benharouga, M. The Multifaceted Functions of Prion Protein (PrPC) in Cancer. Cancers 2023, 15, 4982. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15204982
Abi Nahed R, Safwan-Zaiter H, Gemy K, Lyko C, Boudaud M, Desseux M, Marquette C, Barjat T, Alfaidy N, Benharouga M. The Multifaceted Functions of Prion Protein (PrPC) in Cancer. Cancers. 2023; 15(20):4982. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15204982
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbi Nahed, Roland, Hasan Safwan-Zaiter, Kevin Gemy, Camille Lyko, Mélanie Boudaud, Morgane Desseux, Christel Marquette, Tiphaine Barjat, Nadia Alfaidy, and Mohamed Benharouga. 2023. "The Multifaceted Functions of Prion Protein (PrPC) in Cancer" Cancers 15, no. 20: 4982. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15204982
APA StyleAbi Nahed, R., Safwan-Zaiter, H., Gemy, K., Lyko, C., Boudaud, M., Desseux, M., Marquette, C., Barjat, T., Alfaidy, N., & Benharouga, M. (2023). The Multifaceted Functions of Prion Protein (PrPC) in Cancer. Cancers, 15(20), 4982. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15204982








