DanioCTC: Analysis of Circulating Tumor Cells from Metastatic Breast Cancer Patients in Zebrafish Xenografts
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Cell Line and Culture Conditions
2.2. Zebrafish and Housing Conditions
2.3. Standard Injection of Cell Line Cells into Zebrafish Embryos
2.4. Workflow for Injection of CTCs into Zebrafish Embryos
2.4.1. Diagnostic Leukapheresis
2.4.2. Enrichment of Viable CTCs or Spiked Cell Line Cells from DLA Samples with the Parsortix System
2.4.3. Isolation of Cell Line Cells and CTCs by Flow Cytometry and Staining for Cell Tracking
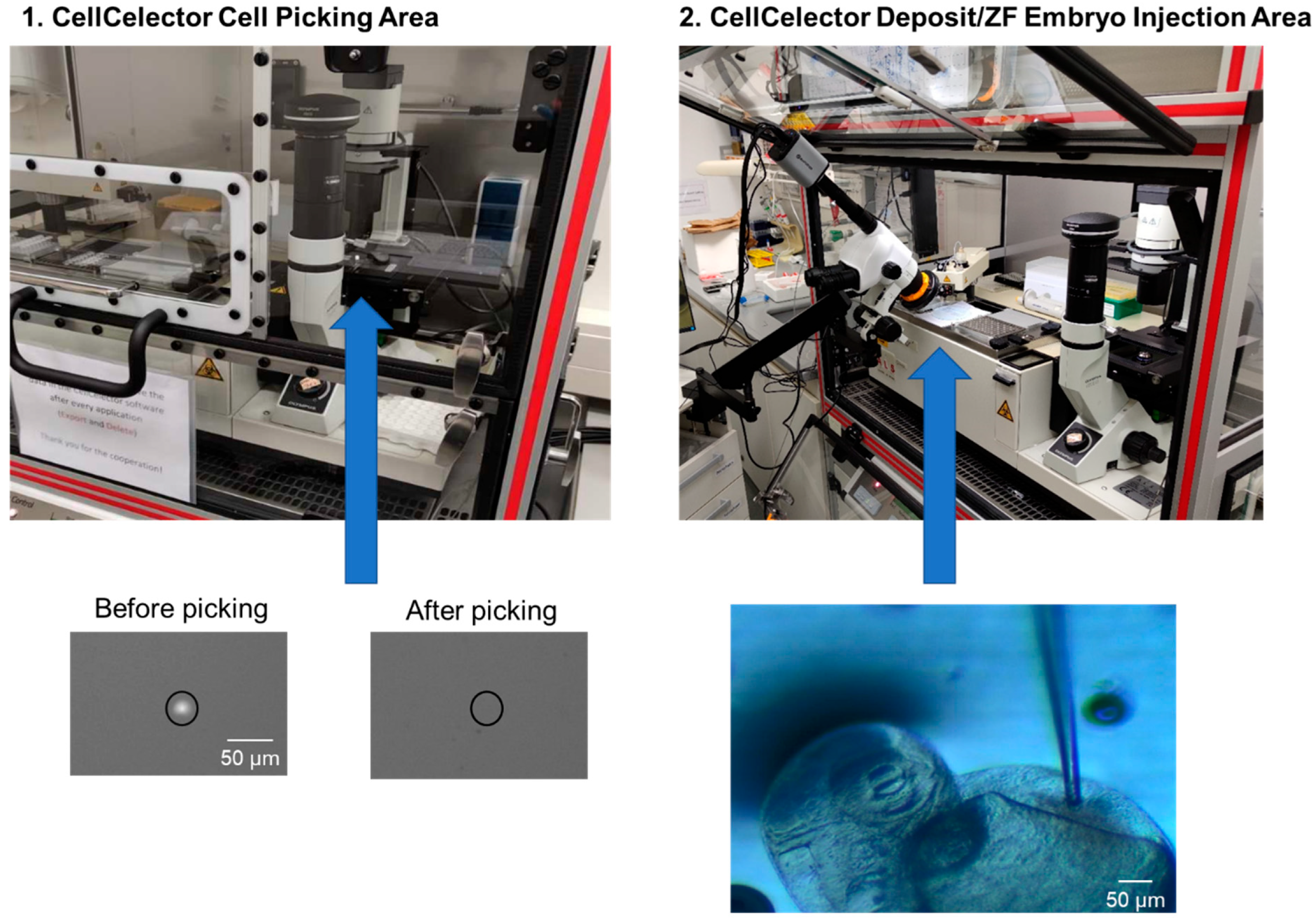
2.4.4. Detection and Picking of Single CTCs and Cell Line Cells Using the CellCelector
2.4.5. Injection of Stained CTCs and Cell Line Cells into Zebrafish Embryos by Combining the CellCelector with a Stereomicroscope
2.5. Patient Samples
2.6. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Development of a CTC Injection Workflow—Concept and Challenges
3.2. Adaptations That Were Required to Realize DanioCTC
3.2.1. Optimizing Cell Picking and Injection
3.2.2. Adaptation of the CellCelector Setup for Cell Injection
3.2.3. Installation of a Stereomicroscope at the CellCelector
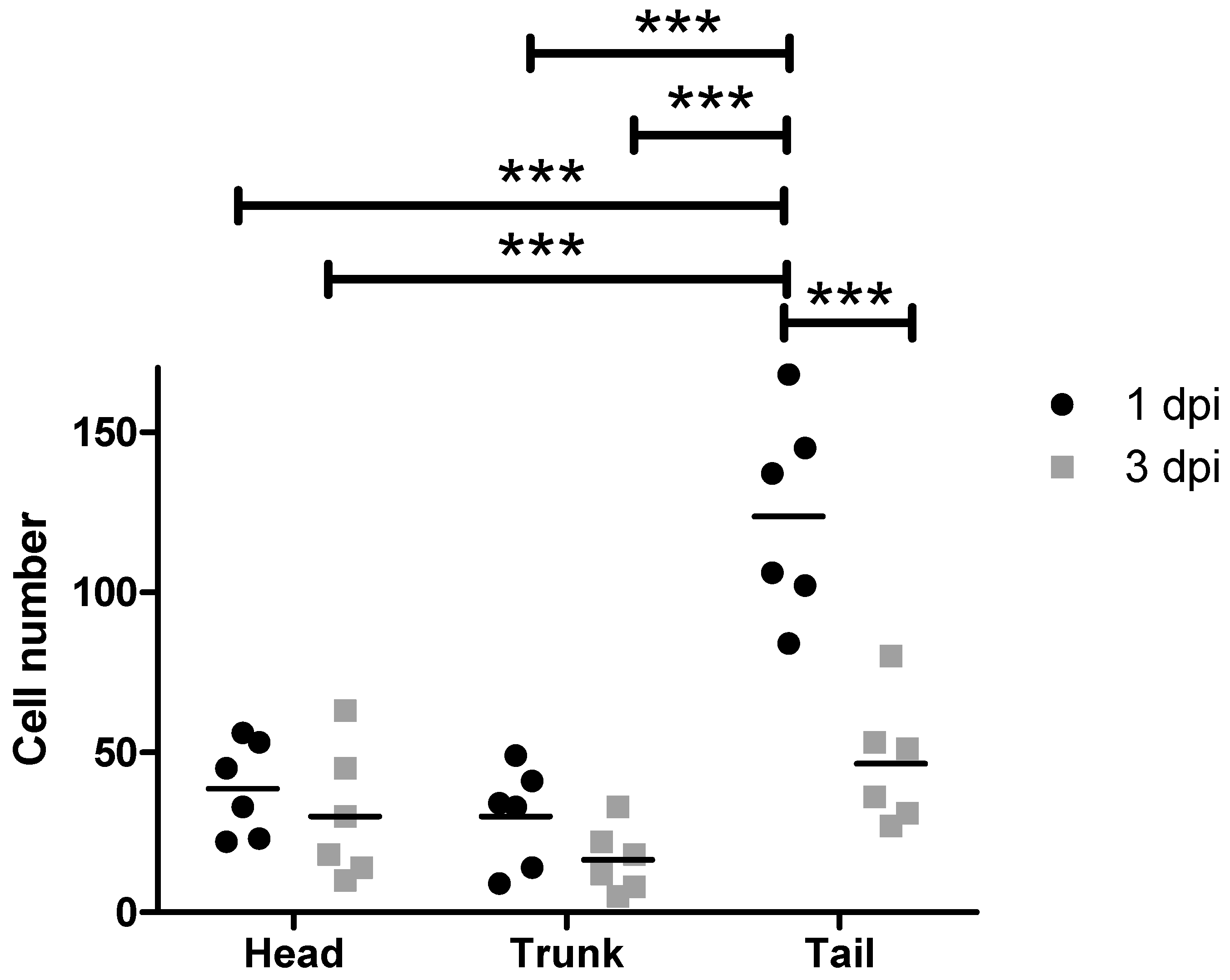
3.3. Standard Xenotransplantation Workflow Carried out with MDA-MB-231 Cells
3.4. Injection of MDA-MB-231 Cells Spiked into a DLA Aliquot with the DanioCTC Workflow
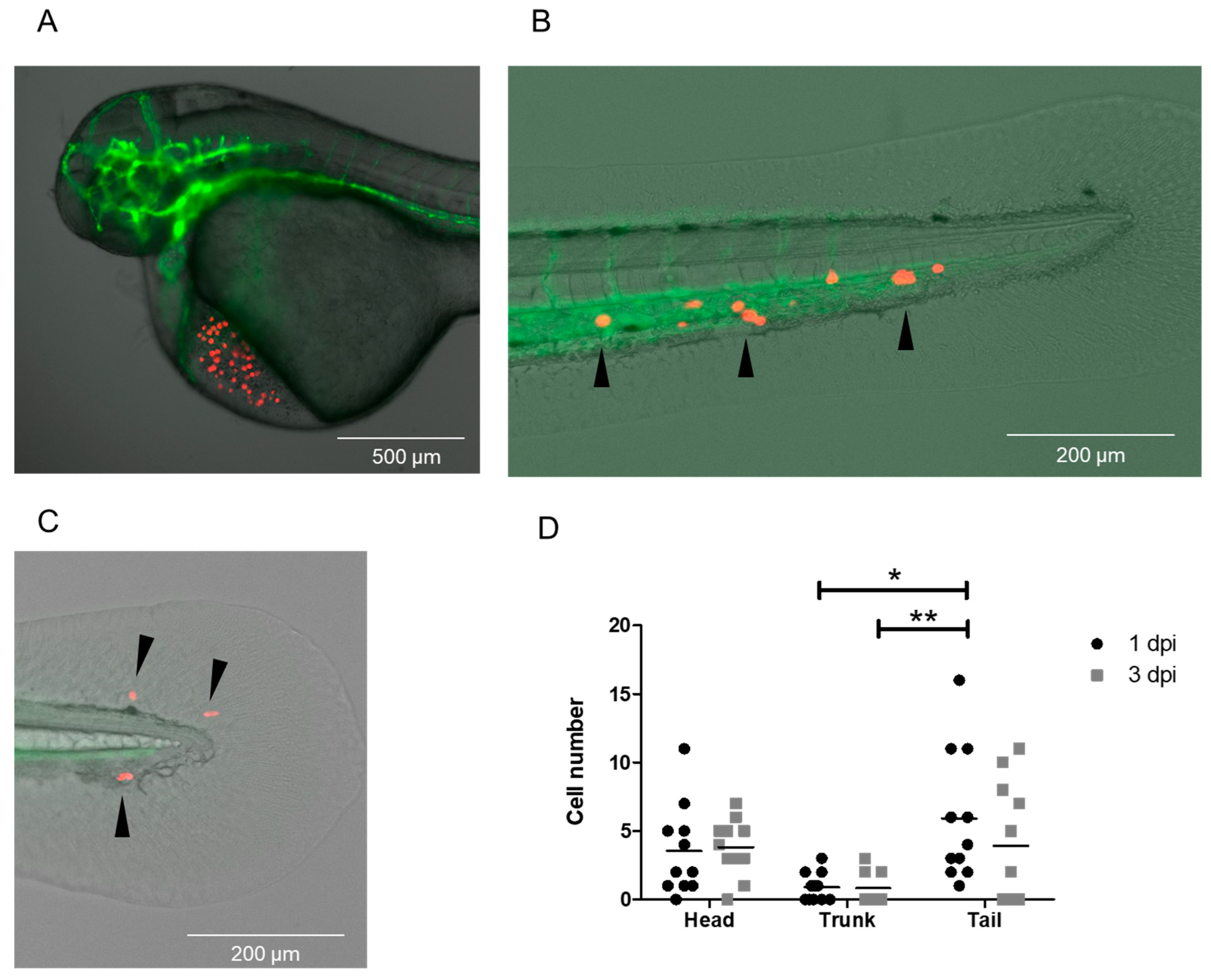
3.5. Injection of CTCs Isolated from DLA Aliquots with the DanioCTC Workflow
4. Discussion
4.1. MDA-MB-231 Cell and CTC Distribution in Zebrafish Larvae
4.2. Advantages and Limitations of DanioCTC
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Talmadge, J.E.; Fidler, I.J. AACR centennial series: The biology of cancer metastasis: Historical perspective. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 5649–5669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valastyan, S.; Weinberg, R.A. Tumor metastasis: Molecular insights and evolving paradigms. Cell 2011, 147, 275–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redig, A.J.; McAllister, S.S. Breast cancer as a systemic disease: A view of metastasis. J. Intern. Med. 2013, 274, 113–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pantel, K.; Alix-Panabières, C. Circulating tumour cells in cancer patients: Challenges and perspectives. Trends Mol. Med. 2010, 16, 398–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allard, W.J.; Matera, J.; Miller, M.C.; Repollet, M.; Connelly, M.C.; Rao, C.; Tibbe, A.G.; Uhr, J.W.; Terstappen, L.W. Tumor cells circulate in the peripheral blood of all major carcinomas but not in healthy subjects or patients with nonmalignant diseases. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 6897–6904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coumans, F.A.; Ligthart, S.T.; Uhr, J.W.; Terstappen, L.W. Challenges in the enumeration and phenotyping of CTC. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 5711–5718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoecklein, N.H.; Fischer, J.C.; Niederacher, D.; Terstappen, L.W. Challenges for CTC-based liquid biopsies: Low CTC frequency and diagnostic leukapheresis as a potential solution. Expert. Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2016, 16, 147–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bidard, F.C.; Peeters, D.J.; Fehm, T.; Nolé, F.; Gisbert-Criado, R.; Mavroudis, D.; Grisanti, S.; Generali, D.; Garcia-Saenz, J.A.; Stebbing, J.; et al. Clinical validity of circulating tumour cells in patients with metastatic breast cancer: A pooled analysis of individual patient data. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, 406–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janni, W.J.; Rack, B.; Terstappen, L.W.; Pierga, J.Y.; Taran, F.A.; Fehm, T.; Hall, C.; de Groot, M.R.; Bidard, F.C.; Friedl, T.W.; et al. Pooled Analysis of the Prognostic Relevance of Circulating Tumor Cells in Primary Breast Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 2583–2593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristofanilli, M.; Budd, G.T.; Ellis, M.J.; Stopeck, A.; Matera, J.; Miller, M.C.; Reuben, J.M.; Doyle, G.V.; Allard, W.J.; Terstappen, L.W.; et al. Circulating tumor cells, disease progression, and survival in metastatic breast cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 351, 781–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, J.C.; Niederacher, D.; Topp, S.A.; Honisch, E.; Schumacher, S.; Schmitz, N.; Zacarias Föhrding, L.; Vay, C.; Hoffmann, I.; Kasprowicz, N.S.; et al. Diagnostic leukapheresis enables reliable detection of circulating tumor cells of nonmetastatic cancer patients. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 16580–16585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andree, K.C.; Mentink, A.; Zeune, L.L.; Terstappen, L.; Stoecklein, N.H.; Neves, R.P.; Driemel, C.; Lampignano, R.; Yang, L.; Neubauer, H.; et al. Toward a real liquid biopsy in metastatic breast and prostate cancer: Diagnostic LeukApheresis increases CTC yields in a European prospective multicenter study (CTCTrap). Int. J. Cancer 2018, 143, 2584–2591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fehm, T.N.; Meier-Stiegen, F.; Driemel, C.; Jäger, B.; Reinhardt, F.; Naskou, J.; Franken, A.; Neubauer, H.; Neves, R.P.L.; van Dalum, G.; et al. Diagnostic leukapheresis for CTC analysis in breast cancer patients: CTC frequency, clinical experiences and recommendations for standardized reporting. Cytometry A 2018, 93, 1213–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franken, A.; Driemel, C.; Behrens, B.; Meier-Stiegen, F.; Endris, V.; Stenzinger, A.; Niederacher, D.; Fischer, J.C.; Stoecklein, N.H.; Ruckhaeberle, E.; et al. Label-Free Enrichment and Molecular Characterization of Viable Circulating Tumor Cells from Diagnostic Leukapheresis Products. Clin. Chem. 2019, 65, 549–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, H.K.; Schiavone, K.; Tazzyman, S.; Heymann, D.; Chico, T.J. Zebrafish xenograft models of cancer and metastasis for drug discovery. Expert. Opin. Drug Discov. 2017, 12, 379–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacRae, C.A.; Peterson, R.T. Zebrafish as tools for drug discovery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2015, 14, 721–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howe, K.; Clark, M.D.; Torroja, C.F.; Torrance, J.; Berthelot, C.; Muffato, M.; Collins, J.E.; Humphray, S.; McLaren, K.; Matthews, L.; et al. The zebrafish reference genome sequence and its relationship to the human genome. Nature 2013, 496, 498–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, R.; Rose, K.; Zon, L. Zebrafish cancer: The state of the art and the path forward. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2013, 13, 624–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konantz, M.; Balci, T.B.; Hartwig, U.F.; Dellaire, G.; André, M.C.; Berman, J.N.; Lengerke, C. Zebrafish xenografts as a tool for in vivo studies on human cancer. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2012, 1266, 124–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Pena, I.; Hurtado, P.; Carmona-Ule, N.; Abuín, C.; Dávila-Ibáñez, A.B.; Sánchez, L.; Abal, M.; Chaachou, A.; Hernández-Losa, J.; Cajal, S.R.Y.; et al. Dissecting Breast Cancer Circulating Tumor Cells Competence via Modelling Metastasis in Zebrafish. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Liu, S.; Cui, C.; Ten Dijke, P. Invasive Behavior of Human Breast Cancer Cells in Embryonic Zebrafish. J. Vis. Exp. 2017, 122, e55459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westerfield, M. The Zebrafish Book. A Guide for the Laboratory Use of Zebrafish (Danio Rerio), 5th ed.; University of Oregon Press: Eugene, OR, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Brand, M.; Granato, M.; Nuesslein-Volhard, C.D.R. Keeping and raising zebrafish. In Zebrafish: A Practical Approach; Nuesslein-Volhard, C.D.R., Ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Beis, D.; Bartman, T.; Jin, S.W.; Scott, I.C.; D’Amico, L.A.; Ober, E.A.; Verkade, H.; Frantsve, J.; Field, H.A.; Wehman, A.; et al. Genetic and cellular analyses of zebrafish atrioventricular cushion and valve development. Development 2005, 132, 4193–4204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spoorendonk, K.M.; Peterson-Maduro, J.; Renn, J.; Trowe, T.; Kranenbarg, S.; Winkler, C.; Schulte-Merker, S. Retinoic acid and Cyp26b1 are critical regulators of osteogenesis in the axial skeleton. Development 2008, 135, 3765–3774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asokan, N.; Daetwyler, S.; Bernas, S.N.; Schmied, C.; Vogler, S.; Lambert, K.; Wobus, M.; Wermke, M.; Kempermann, G.; Huisken, J.; et al. Long-term in vivo imaging reveals tumor-specific dissemination and captures host tumor interaction in zebrafish xenografts. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 13254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Mao, X.; Imrali, A.; Syed, F.; Mutsvangwa, K.; Berney, D.; Cathcart, P.; Hines, J.; Shamash, J.; Lu, Y.J. Optimization and Evaluation of a Novel Size Based Circulating Tumor Cell Isolation System. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0138032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, E.; Rugge, M.; Facchinetti, A.; Pizzi, M.; Nardo, G.; Barbieri, V.; Manicone, M.; De Faveri, S.; Chiara Scaini, M.; Basso, U.; et al. Retaining the long-survive capacity of Circulating Tumor Cells (CTCs) followed by xeno-transplantation: Not only from metastatic cancer of the breast but also of prostate cancer patients. Oncoscience 2014, 1, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baccelli, I.; Schneeweiss, A.; Riethdorf, S.; Stenzinger, A.; Schillert, A.; Vogel, V.; Klein, C.; Saini, M.; Bäuerle, T.; Wallwiener, M.; et al. Identification of a population of blood circulating tumor cells from breast cancer patients that initiates metastasis in a xenograft assay. Nat. Biotechnol. 2013, 31, 539–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, M.H.; Schneck, H.; Decker, Y.; Schömer, S.; Franken, A.; Endris, V.; Pfarr, N.; Weichert, W.; Niederacher, D.; Fehm, T.; et al. Isolation and characterization of circulating tumor cells using a novel workflow combining the CellSearch® system and the CellCelector™. Biotechnol. Prog. 2016, 33, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berens, E.B.; Sharif, G.M.; Wellstein, A.; Glasgow, E. Testing the Vascular Invasive Ability of Cancer Cells in Zebrafish (Danio Rerio). J. Vis. Exp. 2016, 117, e55007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoneda, T.; Williams, P.J.; Hiraga, T.; Niewolna, M.; Nishimura, R. A bone-seeking clone exhibits different biological properties from the MDA-MB-231 parental human breast cancer cells and a brain-seeking clone in vivo and in vitro. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2001, 16, 1486–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rejniak, K.A. Circulating Tumor Cells: When a Solid Tumor Meets a Fluid Microenvironment. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2016, 936, 93–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Follain, G.; Osmani, N.; Azevedo, A.S.; Allio, G.; Mercier, L.; Karreman, M.A.; Solecki, G.; Garcia Leòn, M.J.; Lefebvre, O.; Fekonja, N.; et al. Hemodynamic Forces Tune the Arrest, Adhesion, and Extravasation of Circulating Tumor Cells. Dev. Cell 2018, 45, 33–52.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadamkulam Syriac, A.; Nandu, N.S.; Leone, J.P. Central Nervous System Metastases from Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: Current Treatments and Future Prospective. Breast Cancer 2022, 14, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franken, A.; Honisch, E.; Reinhardt, F.; Meier-Stiegen, F.; Yang, L.; Jaschinski, S.; Esposito, I.; Alberter, B.; Polzer, B.; Huebner, H.; et al. Detection of ESR1 Mutations in Single Circulating Tumor Cells on Estrogen Deprivation Therapy but Not in Primary Tumors from Metastatic Luminal Breast Cancer Patients. J. Mol. Diagn. 2020, 22, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendelaar, P.A.J.; Kraan, J.; Van, M.; Zeune, L.L.; Terstappen, L.W.M.M.; Oomen-de Hoop, E.; Martens, J.W.M.; Sleijfer, S. Defining the dimensions of circulating tumor cells in a large series of breast, prostate, colon, and bladder cancer patients. Mol. Oncol. 2021, 15, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powell, A.A.; Talasaz, A.H.; Zhang, H.; Coram, M.A.; Reddy, A.; Deng, G.; Telli, M.L.; Advani, R.H.; Carlson, R.W.; Mollick, J.A.; et al. Single cell profiling of circulating tumor cells: Transcriptional heterogeneity and diversity from breast cancer cell lines. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e33788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinhardt, F.; Franken, A.; Meier-Stiegen, F.; Driemel, C.; Stoecklein, N.H.; Fischer, J.C.; Niederacher, D.; Ruckhaeberle, E.; Fehm, T.; Neubauer, H. Diagnostic Leukapheresis Enables Reliable Transcriptomic Profiling of Single Circulating Tumor Cells to Characterize Inter-Cellular Heterogeneity in Terms of Endocrine Resistance. Cancers 2019, 11, 903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Reinhardt, F.; Coen, L.; Rivandi, M.; Franken, A.; Setyono, E.S.A.; Lindenberg, T.; Eberhardt, J.; Fehm, T.; Niederacher, D.; Knopf, F.; et al. DanioCTC: Analysis of Circulating Tumor Cells from Metastatic Breast Cancer Patients in Zebrafish Xenografts. Cancers 2023, 15, 5411. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15225411
Reinhardt F, Coen L, Rivandi M, Franken A, Setyono ESA, Lindenberg T, Eberhardt J, Fehm T, Niederacher D, Knopf F, et al. DanioCTC: Analysis of Circulating Tumor Cells from Metastatic Breast Cancer Patients in Zebrafish Xenografts. Cancers. 2023; 15(22):5411. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15225411
Chicago/Turabian StyleReinhardt, Florian, Luisa Coen, Mahdi Rivandi, André Franken, Eunike Sawitning Ayu Setyono, Tobias Lindenberg, Jens Eberhardt, Tanja Fehm, Dieter Niederacher, Franziska Knopf, and et al. 2023. "DanioCTC: Analysis of Circulating Tumor Cells from Metastatic Breast Cancer Patients in Zebrafish Xenografts" Cancers 15, no. 22: 5411. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15225411
APA StyleReinhardt, F., Coen, L., Rivandi, M., Franken, A., Setyono, E. S. A., Lindenberg, T., Eberhardt, J., Fehm, T., Niederacher, D., Knopf, F., & Neubauer, H. (2023). DanioCTC: Analysis of Circulating Tumor Cells from Metastatic Breast Cancer Patients in Zebrafish Xenografts. Cancers, 15(22), 5411. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15225411







