Comparison of the Effectiveness of Radiotherapy with 3D-CRT, IMRT, VMAT and PT for Newly Diagnosed Glioblastoma: A Bayesian Network Meta-Analysis
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Background
2. Method
2.1. Literature Search
2.2. Study Selection
2.3. Data Extraction and Risk of Bias Assessment
2.4. Data Synthesis and Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Overall Characteristics of Selected Studies and Quality of Evidence
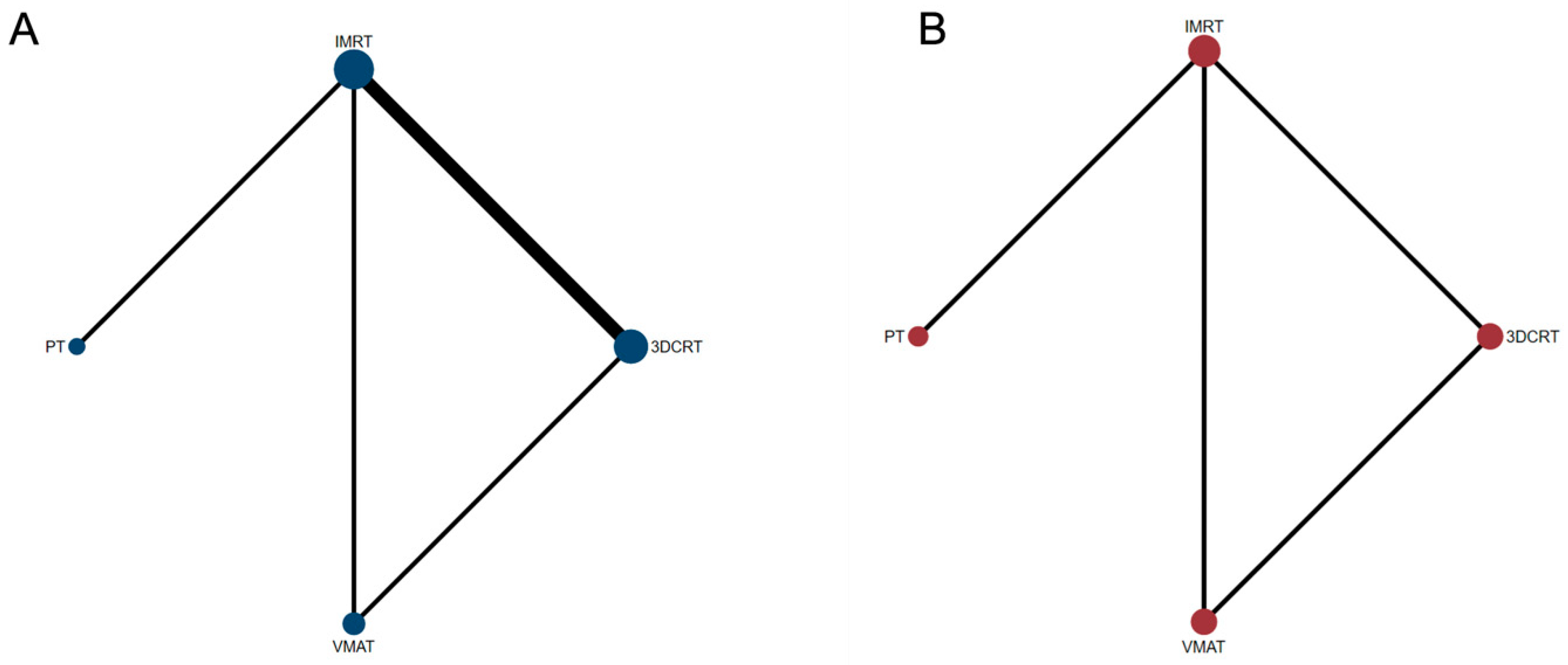
3.2. Overall Survival
3.3. Progression-Free Survival
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brown, P.D.; Chung, C.; Liu, D.D.; McAvoy, S.; Grosshans, D.; Al Feghali, K.; Mahajan, A.; Li, J.; McGovern, S.L.; McAleer, M.-F. A prospective phase II randomized trial of proton radiotherapy vs intensity-modulated radiotherapy for patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma. Neuro-Oncology 2021, 23, 1337–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanif, F.; Muzaffar, K.; Perveen, K.; Malhi, S.M.; Simjee, S.U. Glioblastoma multiforme: A review of its epidemiology and pathogenesis through clinical presentation and treatment. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. APJCP 2017, 18, 3. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Davis, M.E. Glioblastoma: Overview of disease and treatment. Clin. J. Oncol. Nurs. 2016, 20, S2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrlinger, U.; Tzaridis, T.; Mack, F.; Steinbach, J.P.; Schlegel, U.; Sabel, M.; Hau, P.; Kortmann, R.-D.; Krex, D.; Grauer, O.; et al. Lomustine-temozolomide combination therapy versus standard temozolomide therapy in patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma with methylated MGMT promoter (CeTeG/NOA-09): A randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2019, 393, 678–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizumoto, M.; Yamamoto, T.; Takano, S.; Ishikawa, E.; Matsumura, A.; Ishikawa, H.; Okumura, T.; Sakurai, H.; Miyatake, S.-I.; Tsuboi, K. Long-term survival after treatment of glioblastoma multiforme with hyperfractionated concomitant boost proton beam therapy. Pract. Radiat. Oncol. 2015, 5, e9–e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Chakravarti, A. Novel radiation-enhancing agents in malignant gliomas. In Seminars in Radiation Oncology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2006; pp. 29–37. [Google Scholar]
- Chambrelant, I.; Eber, J.; Antoni, D.; Burckel, H.; Noël, G.; Auvergne, R. Proton therapy and gliomas: A systematic review. Radiation 2021, 1, 218–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzek, M.M.; Thornton, A.F.; Rabinov, J.D.; Lev, M.H.; Pardo, F.S.; Munzenrider, J.E.; Okunieff, P.; Bussière, M.; Braun, I.; Hochberg, F.H. Accelerated fractionated proton/photon irradiation to 90 cobalt gray equivalent for glioblastoma multiforme: Results of a phase II prospective trial. J. Neurosurg. 1999, 91, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsien, C.; Moughan, J.; Michalski, J.M.; Gilbert, M.R.; Purdy, J.; Simpson, J.; Kresel, J.J.; Curran, W.J.; Diaz, A.; Mehta, M.P. Phase I three-dimensional conformal radiation dose escalation study in newly diagnosed glioblastoma: Radiation Therapy Oncology Group Trial 98-03. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2009, 73, 699–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeberg, S.; Harrabi, S.; Bougatf, N.; Bernhardt, D.; Rieber, J.; Koerber, S.; Syed, M.; Sprave, T.; Mohr, A.; Abdollahi, A. Intensity-modulated proton therapy, volumetric-modulated arc therapy, and 3D conformal radiotherapy in anaplastic astrocytoma and glioblastoma. Strahlenther. Und Onkol. 2016, 192, 770–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesueur, P.; Calugaru, V.; Nauraye, C.; Stefan, D.; Cao, K.; Emery, E.; Reznik, Y.; Habrand, J.L.; Tessonnier, T.; Chaikh, A. Proton therapy for treatment of intracranial benign tumors in adults: A systematic review. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2019, 72, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. Version 5.1. 0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration. Available online: www.cochrane-handbook.org (accessed on 14 November 2011).
- Guyot, P.; Ades, A.; Ouwens, M.J.; Welton, N.J. Enhanced secondary analysis of survival data: Reconstructing the data from published Kaplan-Meier survival curves. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2012, 12, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins Julian, P.; Altman, A.; Sterne, J. Assessing risk of bias in included studies. In Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions: Cochrane Book Series; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Hutton, B.; Salanti, G.; Caldwell, D.M.; Chaimani, A.; Schmid, C.H.; Cameron, C.; Ioannidis, J.P.; Straus, S.; Thorlund, K.; Jansen, J.P. The PRISMA extension statement for reporting of systematic reviews incorporating network meta-analyses of health care interventions: Checklist and explanations. Ann. Intern. Med. 2015, 162, 777–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devji, T.; Levine, O.; Neupane, B.; Beyene, J.; Xie, F. Systemic therapy for previously untreated advanced BRAF-mutated melanoma: A systematic review and network meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. JAMA Oncol. 2017, 3, 366–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.; Sak, A.; Erol, Y.B. Network Meta-analysis of First-Line Systemic Treatment for Patients With Metastatic Colorectal Cancer. Cancer Control 2021, 28, 10732748211033497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, J. Identifying and Addressing Inconsistency in Network Meta-Analysis. Cochrane Comparing Multiple Interventions Methods Group Oxford Training Event 2013. 2013. Available online: https://methods.cochrane.org/cmi/sites/methods.cochrane.org.cmi/files/uploads/S9-L%20Identifying%20and%20addressing%20inconsistency%20in%20network%20meta-analysis.pdf (accessed on 21 September 2016).
- Higgins, J.P.; Thompson, S.G. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat. Med. 2002, 21, 1539–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.-D.; Feng, J.; Fang, T.; Yang, M.; Qiu, X.-g.; Jiang, T. Effect of intensity-modulated radiotherapy versus three-dimensional conformal radiotherapy on clinical outcomes in patients with glioblastoma multiforme. Chin. Med. J. 2013, 126, 2320–2324. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Navarria, P.; Pessina, F.; Cozzi, L.; Ascolese, A.M.; Lobefalo, F.; Stravato, A.; D’Agostino, G.; Franzese, C.; Caroli, M.; Bello, L. Can advanced new radiation therapy technologies improve outcome of high grade glioma (HGG) patients? Analysis of 3D-conformal radiotherapy (3DCRT) versus volumetric-modulated arc therapy (VMAT) in patients treated with surgery, concomitant and adjuvant chemo-radiotherapy. BMC Cancer 2016, 16, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Thibouw, D.; Truc, G.; Bertaut, A.; Chevalier, C.; Aubignac, L.; Mirjolet, C. Clinical and dosimetric study of radiotherapy for glioblastoma: Three-dimensional conformal radiotherapy versus intensity-modulated radiotherapy. J. Neuro-Oncol. 2018, 137, 429–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haneefa, A.; Dusane, R.R.; Saluja, V.; Sridhar, C. Retrospective analysis of patients of Glioblastoma multiforme treated with stem cell sparing intensity-modulated radiation therapy and nonstem cell sparing three-dimensional conformal radiation therapy: A single-institution experience. J. Radiat. Cancer Res. 2018, 9, 114. [Google Scholar]
- Sheu, T.; Briere, T.M.; Olanrewaju, A.M.; McAleer, M.F. Intensity Modulated Radiation Therapy Versus Volumetric Arc Radiation Therapy in the Treatment of Glioblastoma—Does Clinical Benefit Follow Dosimetric Advantage? Adv. Radiat. Oncol. 2019, 4, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Tang, Y.Y.; Yu, Y.X.; Yun, Q.; Yang, J.P.; Zhang, H.; Peng, Q.; Sun, X.; Yang, L.L.; Fu, S. Novel composite drug delivery system as a novel radio sensitizer for the local treatment of cervical carcinoma. Drug Deliv. 2017, 24, 1139–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Sak, A.; Niedermaier, B.; Erol, Y.B.; Groneberg, M.; Mladenov, E.; Kang, M.; Iliakis, G.; Stuschke, M. Selective vulnerability of ARID1A deficient colon cancer cells to combined radiation and ATR-inhibitor therapy. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 999626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelefsky, M.J.; Marion, C.; Fuks, Z.; Leibel, S.A. Improved biochemical disease-free survival of men younger than 60 years with prostate cancer treated with high dose conformal external beam radiotherapy. J. Urol. 2003, 170, 1828–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, A.; Santanam, L.; Solanki, A.A.; Padilla, L.; Vlashi, E.; Guerrieri, P.; Dominello, M.M.; Burmeister, J.; Joiner, M.C. Three discipline collaborative radiation therapy (3DCRT) special debate: Peer review in radiation oncology is more effective today than 20 years ago. J. Appl. Clin. Med. Phys. 2020, 21, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afrin, K.T.; Ahmad, S. 3D conformal, IMRT and VMAT for the treatment of head and neck cancer: A brief literature review. J. Radiother. Pract. 2022, 21, 259–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begnozzi, L.; Benassi, M.; Bertanelli, M.; Bonini, A.; Cionini, L.; Conte, L.; Fiorino, C.; Gabriele, P.; Gardani, G.; Giani, A. Quality assurance of 3D-CRT: Indications and difficulties in their applications. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2009, 70, 24–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benali, I.; Kaanouch, O.; Naim, A.; El Gouach, H.; Dahbi, Z.; Kouhen, F. Dosimetric Comparison: Volumetric Modulated Arc Therapy (VMAT) and 3D Conformal Radiotherapy (3D-CRT) in High Grade Glioma Cancer—Experience of Casablanca Cancer Center at the Cheikh Khalifa International University Hospital. Int. J. Med. Phys. Clin. Eng. Radiat. Oncol. 2021, 10, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortfeld, T. IMRT: A review and preview. Phys. Med. Biol. 2006, 51, R363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, M.F.; Schupak, K.; Burman, C.; Chui, C.-S.; Ling, C.C. Comparison of intensity-modulated radiotherapy with three-dimensional conformal radiation therapy planning for glioblastoma multiforme. Med. Dosim. 2003, 28, 261–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, D.; Christiansen, H.; Wolff, H.; Vorwerk, H. Radiotherapy of malignant gliomas: Comparison of volumetric single arc technique (RapidArc), dynamic intensity-modulated technique and 3D conformal technique. Radiother. Oncol. 2009, 93, 593–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thilmann, C.; Zabel, A.; Grosser, K.H.; Hoess, A.; Wannenmacher, M.; Debus, J. Intensity-modulated radiotherapy with an integrated boost to the macroscopic tumor volume in the treatment of high-grade gliomas. Int. J. Cancer 2001, 96, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDonald, S.M.; Ahmad, S.; Kachris, S.; Vogds, B.J.; DeRouen, M.; Gitttleman, A.E.; DeWyngaert, K.; Vlachaki, M.T. Intensity modulated radiation therapy versus three-dimensional conformal radiation therapy for the treatment of high grade glioma: A dosimetric comparison. J. Appl. Clin. Med. Phys. 2007, 8, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panet-Raymond, V.; Souhami, L.; Roberge, D.; Kavan, P.; Shakibnia, L.; Muanza, T.; Lambert, C.; Leblanc, R.; Del Maestro, R.; Guiot, M.-C. Accelerated hypofractionated intensity-modulated radiotherapy with concurrent and adjuvant temozolomide for patients with glioblastoma multiforme: A safety and efficacy analysis. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2009, 73, 473–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morganti, A.G.; Balducci, M.; Salvati, M.; Esposito, V.; Romanelli, P.; Ferro, M.; Calista, F.; Digesù, C.; Macchia, G.; Ianiri, M. A phase I dose-escalation study (ISIDE-BT-1) of accelerated IMRT with temozolomide in patients with glioblastoma. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2010, 77, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otto, K. Volumetric modulated arc therapy: IMRT in a single gantry arc. Med. Phys. 2008, 35, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, M.; Yang, W.; Chen, F.; Sheng, K.; Ye, J.; Mehta, V.; Shepard, D.; Cao, D. Comparison of Elekta VMAT with helical tomotherapy and fixed field IMRT: Plan quality, delivery efficiency and accuracy. Med. Phys. 2010, 37, 1350–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teoh, M.; Clark, C.; Wood, K.; Whitaker, S.; Nisbet, A. Volumetric modulated arc therapy: A review of current literature and clinical use in practice. Br. J. Radiol. 2011, 84, 967–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briere, T.M.; McAleer, M.F.; Levy, L.B.; Yang, J.N. Sparing of normal tissues with volumetric arc radiation therapy for glioblastoma: Single institution clinical experience. Radiat. Oncol. 2017, 12, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaffer, R.; Nichol, A.M.; Vollans, E.; Fong, M.; Nakano, S.; Moiseenko, V.; Schmuland, M.; Ma, R.; McKenzie, M.; Otto, K. A comparison of volumetric modulated arc therapy and conventional intensity-modulated radiotherapy for frontal and temporal high-grade gliomas. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2010, 76, 1177–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Feng, C.; Cai, B.-N.; Yang, J.; Liu, H.-X.; Ma, L. Comparison of three-dimensional conformal radiation therapy, intensity-modulated radiation therapy, and volumetric-modulated arc therapy in the treatment of cervical esophageal carcinoma. Dis. Esophagus 2017, 30, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhou, Z.; Bi, N.; Wang, J.; Wang, L.; Deng, L.; Feng, Q.; Liang, J.; Xiao, Z.; Chen, D. VMAT for Unresectable locally advanced NSCLC does not increase the risk of radiation pneumonitis compared with IMRT. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2019, 105, E543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, W.; Kooy, H.; Loeffler, J.S.; Delaney, T.F. Proton beam therapy. Br. J. Cancer 2005, 93, 849–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jhaveri, J.; Cheng, E.; Tian, S.; Buchwald, Z.; Chowdhary, M.; Liu, Y.; Gillespie, T.W.; Olson, J.J.; Diaz, A.Z.; Voloschin, A. Proton vs. photon radiation therapy for primary gliomas: An analysis of the national cancer data base. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusthoven, K.E.; Olsen, C.; Franklin, W.; Kleinschmidt-DeMasters, B.; Kavanagh, B.D.; Gaspar, L.E.; Lillehei, K.; Waziri, A.; Damek, D.M.; Chen, C. Favorable prognosis in patients with high-grade glioma with radiation necrosis: The University of Colorado reoperation series. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2011, 81, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palm, R.F.; Oliver, D.E.; Yang, G.Q.; Abuodeh, Y.; Naghavi, A.O.; Johnstone, P.A. The role of dose escalation and proton therapy in perioperative or definitive treatment of chondrosarcoma and chordoma: An analysis of the National Cancer Data Base. Cancer 2019, 125, 642–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuss, M.; Hug, E.B.; Schaefer, R.A.; Nevinny-Stickel, M.; Miller, D.W.; Slater, J.M.; Slater, J.D. Proton radiation therapy (PRT) for pediatric optic pathway gliomas: Comparison with 3D planned conventional photons and a standard photon technique. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 1999, 45, 1117–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darzy, K.H.; Shalet, S.M. Hypopituitarism following radiotherapy. Pituitary 2009, 12, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taphoorn, M.; Heimans, J.; Van der Veen, E.; Karim, A. Endocrine functions in long-term survivors of low-grade supratentorial glioma treated with radiation therapy. J. Neuro-Oncol. 1995, 25, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazda, T.; Jancalek, R.; Pospisil, P.; Sevela, O.; Prochazka, T.; Vrzal, M.; Burkon, P.; Slavik, M.; Hynkova, L.; Slampa, P. Why and how to spare the hippocampus during brain radiotherapy: The developing role of hippocampal avoidance in cranial radiotherapy. Radiat. Oncol. 2014, 9, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kut, C.; Redmond, K.J. New considerations in radiation treatment planning for brain tumors: Neural progenitor cell–containing niches. In Seminars in Radiation Oncology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 265–272. [Google Scholar]
- Goings, G.E.; Sahni, V.; Szele, F.G. Migration patterns of subventricular zone cells in adult mice change after cerebral cortex injury. Brain Res. 2004, 996, 213–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arvidsson, A.; Collin, T.; Kirik, D.; Kokaia, Z.; Lindvall, O. Neuronal replacement from endogenous precursors in the adult brain after stroke. Nat. Med. 2002, 8, 963–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehling, N.S.; Grosshans, D.R.; Bluett, J.B.; Palmer, M.T.; Song, X.; Amos, R.A.; Sahoo, N.; Meyer, J.J.; Mahajan, A.; Woo, S.Y. Dosimetric comparison of three-dimensional conformal proton radiotherapy, intensity-modulated proton therapy, and intensity-modulated radiotherapy for treatment of pediatric craniopharyngiomas. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2012, 82, 643–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karunamuni, R.; Bartsch, H.; White, N.S.; Moiseenko, V.; Carmona, R.; Marshall, D.C.; Seibert, T.M.; McDonald, C.R.; Farid, N.; Krishnan, A. Dose-dependent cortical thinning after partial brain irradiation in high-grade glioma. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2016, 94, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laack, N.N.; Brown, P.D.; Ivnik, R.J.; Furth, A.F.; Ballman, K.V.; Hammack, J.E.; Arusell, R.M.; Shaw, E.G.; Buckner, J.C. Cognitive function after radiotherapy for supratentorial low-grade glioma: A North Central Cancer Treatment Group prospective study. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2005, 63, 1175–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, J.; Rewcastle, N.; Brasher, P.; Fulton, D.; Hagen, N.; MacKinnon, J.; Sutherland, G.; Cairncross, J.; Forsyth, P. Long-term glioblastoma multiforme survivors: A population-based study. Can. J. Neurol. Sci. 1998, 25, 197–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merchant, T.E.; Hua, C.h.; Shukla, H.; Ying, X.; Nill, S.; Oelfke, U. Proton versus photon radiotherapy for common pediatric brain tumors: Comparison of models of dose characteristics and their relationship to cognitive function. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2008, 51, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, G.T. Long-term survivors of childhood central nervous system malignancies: The experience of the Childhood Cancer Survivor Study. Eur. J. Paediatr. Neurol. 2010, 14, 298–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalali, R.; Mallick, I.; Dutta, D.; Goswami, S.; Gupta, T.; Munshi, A.; Deshpande, D.; Sarin, R. Factors influencing neurocognitive outcomes in young patients with benign and low-grade brain tumors treated with stereotactic conformal radiotherapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2010, 77, 974–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, X.; Björk-Eriksson, T.; Nill, S.; Oelfke, U.; Johansson, K.-A.; Gagliardi, G.; Johansson, L.; Karlsson, M.; Zackrisson, D.B. Does electron and proton therapy reduce the risk of radiation induced cancer after spinal irradiation for childhood medulloblastoma? A comparative treatment planning study. Acta Oncol. 2005, 44, 554–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miralbell, R.; Lomax, A.; Cella, L.; Schneider, U. Potential reduction of the incidence of radiation-induced second cancers by using proton beams in the treatment of pediatric tumors. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2002, 54, 824–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Yang, X.; Wu, J.; Yang, H.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Liu, Q.; Wu, C.; Xing, H.; Liu, P.; et al. Tumor-treating fields in glioblastomas: Past, present, and future. Cancers 2022, 14, 3669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, G.; Rao, M.; Zhu, P.; Liang, B.; El-Nazer, R.T.; Fonkem, E.; Bhattacharjee, M.B.; Zhu, J.-J. Triple-drug therapy with bevacizumab, irinotecan, and temozolomide plus tumor treating fields for recurrent glioblastoma: A retrospective study. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Author/ Year | Design | Treatment Planning | Patients (n) | Median Age (y) | Extent of Resection n (%) | Radiation Treatment Planning | Median Follow-Up | OS (Median) | PFS (Median) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brown 2021 [1] | P | PT | 26 | 55.2 | GTR: 19 (73.1%) STR: 5 (19.2%) Biopsy: 2 (7.7%) | GTV:T1 CTV:GTV+2 cm PTV:CTV+3-5 mm | 48.7 months | 24.5 months | 8.9 months |
| IMRT | 41 | 52 | GTR: 20 (48.8%) STR: 17 (41.5%) Biopsy: 4 (9.8%) | 21.2 months | 6.6 months | ||||
| Chen 2013 [20] | R | 3D-CRT | 33 | 47 | GTR/STR: 23 (69.7) Partial/biopsy: 10 (30.3) | GTV1: FLAIR or T2 CTV:GTV1+2 cm PTV:CTV+0.5 cm | 13 months | NR1 | NR1 |
| IMRT | 21 | 47 | GTR/STR: 11 (52.3) Partial/biopsy: 10 (47.7) | NR1 | NR1 | ||||
| Navarria 2016 [21] | R | 3D-CRT | 167 | 53 | GTR: 47 (28%) STR: 15 (9%) Partial: 58 (35%) Biopsy:47 (28%) | GTV: FLAIR or T1 CTV: GTV+10 mm PTV:CTV+3 mm | 1.3 years | 14.52 months | 11.88 months |
| VMAT | 174 | 54 | GTR: 68 (39%) STR: 26 (15%) Partial: 58 (33%) Biopsy: 22 (13%) | 18.72 months | 15.48 months | ||||
| Thibouw 2018 [22] | R | 3D-CRT | 142 | 61 | GTR: 21 (14.8%) STR: 30 (21.1%) Partial: 32 (22.5%) Biopsy: 59 (41.5%) | GTV:T1 CTV:GTV+15 mm PTV:CTV+3-5 mm | 12.9 months | 16.0 months | NR |
| IMRT | 78 | 62.5 | GTR: 10 (12.8%) STR: 18 (23.1%) Partial: 26 (33.3%) Biopsy: 24 (30.8%) | 13.4 months | NR | ||||
| Huilgol 2018 [23] | R | IMRT | 28 | 58.5 | GTR: 7 (25%) STR: 17 (60.7%) Biopsy: 4 (14.3%) | NR | 22.27 months | 19.22 months | NR |
| 3D-CRT | 18 | 54.11 | GTR: 4 (22.2%) STR: 10 (55.6%) Biopsy: 4 (22.2%) | 19.22 months | NR | ||||
| Sheu 2019 [24] | R | VMAT | 43 | 56 | GTR: 53% | GTV:T1 CTV:GTV+2 cm PTV:CTV+3-5 mm | 27.4 months | 22.0 months | 8.0 months |
| IMRT | 45 | 53 | GTR: 60% | 18.4 months | 8.8 months |
| A. SUCRA rankings for overall survival | |
| PT | 72.6 |
| VMAT | 66.5 |
| IMRT | 44.9 |
| 3DCRT | 26.3 |
| B. SUCRA rankings for progression-free survival | |
| PT | 78.25 |
| VMAT | 42 |
| IMRT | 57 |
| 3DCRT | 21.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, S.; Frakulli, R.; Lin, Y. Comparison of the Effectiveness of Radiotherapy with 3D-CRT, IMRT, VMAT and PT for Newly Diagnosed Glioblastoma: A Bayesian Network Meta-Analysis. Cancers 2023, 15, 5698. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15235698
Xu S, Frakulli R, Lin Y. Comparison of the Effectiveness of Radiotherapy with 3D-CRT, IMRT, VMAT and PT for Newly Diagnosed Glioblastoma: A Bayesian Network Meta-Analysis. Cancers. 2023; 15(23):5698. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15235698
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Shan, Rezarta Frakulli, and Yilan Lin. 2023. "Comparison of the Effectiveness of Radiotherapy with 3D-CRT, IMRT, VMAT and PT for Newly Diagnosed Glioblastoma: A Bayesian Network Meta-Analysis" Cancers 15, no. 23: 5698. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15235698
APA StyleXu, S., Frakulli, R., & Lin, Y. (2023). Comparison of the Effectiveness of Radiotherapy with 3D-CRT, IMRT, VMAT and PT for Newly Diagnosed Glioblastoma: A Bayesian Network Meta-Analysis. Cancers, 15(23), 5698. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15235698





