The Current Treatment Landscape of Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma and Future Directions
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Molecular Biology, Genomics and Immunology
3. Current Treatments
3.1. Chemotherapy and the Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor (VEGFR) Pathway
3.2. Immunotherapy
4. Novel Treatments for MPM
4.1. Chemoimmunotherapy
4.2. Novel Immunotherapy Approaches
4.2.1. Immune Checkpoints
4.2.2. Oncoviral Therapy
4.2.3. Cellular Therapy
CAR-T
Dendritic Cell Therapy
4.3. Targeted Agents
4.3.1. EZH2
4.3.2. ASS1
4.3.3. Molecular-Stratified Therapy
4.4. Tumor-Treating Fields
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Broeckx, G.; Pauwels, P. Malignant Peritoneal Mesothelioma: A Review. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2018, 7, 537–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wadowski, B.; De Rienzo, A.; Bueno, R. The Molecular Basis of Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma. Thorac. Surg. Clin. 2020, 30, 383–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.H.; Vaynblat, A.; Pass, H.I. Diagnosis and Prognosis-Review of Biomarkers for Mesothelioma. Ann. Transl. Med. 2017, 5, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carbone, M.; Adusumilli, P.S.; Alexander, H.R.; Baas, P.; Bardelli, F.; Bononi, A.; Bueno, R.; Felley-Bosco, E.; Galateau-Salle, F.; Jablons, D.; et al. Mesothelioma: Scientific Clues for Prevention, Diagnosis, and Therapy. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2019, 69, 402–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attanoos, R.L.; Churg, A.; Galateau-Salle, F.; Gibbs, A.R.; Roggli, V.L. Malignant Mesothelioma and Its Non-Asbestos Causes. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2018, 142, 753–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsao, A.S.; Pass, H.I.; Rimner, A.; Mansfield, A.S. New Era for Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma: Updates on Therapeutic Options. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 681–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janes, S.M.; Alrifai, D.; Fennell, D.A. Perspectives on the Treatment of Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 1207–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courtiol, P.; Maussion, C.; Moarii, M.; Pronier, E.; Pilcer, S.; Sefta, M.; Manceron, P.; Toldo, S.; Zaslavskiy, M.; Le Stang, N.; et al. Deep Learning-Based Classification of Mesothelioma Improves Prediction of Patient Outcome. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 1519–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blum, Y.; Meiller, C.; Quetel, L.; Elarouci, N.; Ayadi, M.; Tashtanbaeva, D.; Armenoult, L.; Montagne, F.; Tranchant, R.; Renier, A.; et al. Dissecting Heterogeneity in Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma through Histo-Molecular Gradients for Clinical Applications. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hmeljak, J.; Sanchez-Vega, F.; Hoadley, K.A.; Shih, J.; Stewart, C.; Heiman, D.I.; Tarpey, P.; Danilova, L.; Drill, E.; Gibb, E.A.; et al. Integrative Molecular Characterization of Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma. Cancer Discov. 2018, 8, 1549–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minnema-Luiting, J.; Vroman, H.; Aerts, J.; Cornelissen, R. Heterogeneity in Immune Cell Content in Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornelissen, R.; Lievense, L.A.; Maat, A.P.; Hendriks, R.W.; Hoogsteden, H.C.; Bogers, A.J.; Hegmans, J.P.; Aerts, J.G. Ratio of Intratumoral Macrophage Phenotypes Is a Prognostic Factor in Epithelioid Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e106742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hegmans, J.P.J.J.; Aerts, J.G.J.V. Immunomodulation in Cancer. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2014, 17, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ujiie, H.; Kadota, K.; Nitadori, J.I.; Aerts, J.G.; Woo, K.M.; Sima, C.S.; Travis, W.D.; Jones, D.R.; Krug, L.M.; Adusumilli, P.S. The Tumoral and Stromal Immune Microenvironment in Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma: A Comprehensive Analysis Reveals Prognostic Immune Markers. Oncoimmunology 2015, 4, e1009285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bograd, A.J.; Suzuki, K.; Vertes, E.; Colovos, C.; Morales, E.A.; Sadelain, M.; Adusumilli, P.S. Immune Responses and Immunotherapeutic Interventions in Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2011, 60, 1509–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shamseddin, M.; Obacz, J.; Garnett, M.J.; Rintoul, R.C.; Francies, H.E.; Marciniak, S.J. Use of Preclinical Models for Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma. Thorax 2021, 76, 1154–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, F.; Kato, K.; Yanatori, I.; Maeda, Y.; Murohara, T.; Toyokuni, S. Matrigel-Based Organoid Culture of Malignant Mesothelioma Reproduces Cisplatin Sensitivity through CTR1. BMC Cancer 2023, 23, 487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malignant Mesothelioma Early Detection, Diagnosis, and Staging. Available online: https://www.cancer.org/cancer/types/malignant-mesothelioma/detection-diagnosis-staging.html (accessed on 27 November 2023).
- Pemetrexed for the Treatment of Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma. Available online: www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ta135 (accessed on 1 August 2023).
- Lim, E.; Darlison, L.; Edwards, J.; Elliott, D.; Fennell, D.A.; Popat, S.; Rintoul, R.C.; Waller, D.; Ali, C.; Bille, A.; et al. Mesothelioma and Radical Surgery 2 (MARS 2): Protocol for a Multicentre Randomised Trial Comparing (Extended) Pleurectomy Decortication versus No (Extended) Pleurectomy Decortication for Patients with Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma. BMJ Open 2020, 10, e038892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadal, E.; Bosch-Barrera, J.; Cedrés, S.; Coves, J.; García-Campelo, R.; Guirado, M.; López-Castro, R.; Ortega, A.L.; Vicente, D.; de Castro-Carpeño, J. SEOM Clinical Guidelines for the Treatment of Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma (2020). Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2021, 23, 980–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brims, F.; Gunatilake, S.; Lawrie, I.; Marshall, L.; Fogg, C.; Qi, C.; Creech, L.; Holtom, N.; Killick, S.; Yung, B.; et al. Early Specialist Palliative Care on Quality of Life for Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma: A Randomised Controlled Trial. Thorax 2019, 74, 354–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogelzang, N.J.; Rusthoven, J.J.; Symanowski, J.; Denham, C.; Kaukel, E.; Ruffie, P.; Gatzemeier, U.; Boyer, M.; Emri, S.; Manegold, C.; et al. Phase III Study of Pemetrexed in Combination with Cisplatin versus Cisplatin Alone in Patients with Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2003, 21, 2636–2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zalcman, G.; Mazieres, J.; Margery, J.; Greillier, L.; Audigier-Valette, C.; Moro-Sibilot, D.; Molinier, O.; Corre, R.; Monnet, I.; Gounant, V.; et al. Bevacizumab for Newly Diagnosed Pleural Mesothelioma in the Mesothelioma Avastin Cisplatin Pemetrexed Study (MAPS): A Randomised, Controlled, Open-Label, Phase 3 Trial. Lancet 2016, 387, 1405–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steele, J.P.C.; Shamash, J.; Evans, M.T.; Gower, N.H.; Tischkowitz, M.D.; Rudd, R.M. Phase II Study of Vinorelbine in Patients With Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2000, 18, 3912–3917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giaccone, G.; O’brien, M.E.R.; Byrne, M.J.; Bard, M.; Kaukel, E.; Smit, B. Phase II Trial of ZD0473 as Second-Line Therapy in Mesothelioma. Eur. J. Cancer 2002, 38, S19–S24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zucali, P.A.; Ceresoli, G.L.; Garassino, I.; De Vincenzo, F.; Cavina, R.; Campagnoli, E.; Cappuzzo, F.; Salamina, S.; Soto Parra, H.J.; Santoro, A. Gemcitabine and Vinorelbine in Pemetrexed-Pretreated Patients with Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma. Cancer 2008, 112, 1555–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinto, C.; Zucali, P.A.; Pagano, M.; Grosso, F.; Pasello, G.; Garassino, M.C.; Tiseo, M.; Soto Parra, H.; Grossi, F.; Cappuzzo, F.; et al. Gemcitabine with or without Ramucirumab as Second-Line Treatment for Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma (RAMES): A Randomised, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Phase 2 Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2021, 22, 1438–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fennell, D.A.; Ewings, S.; Ottensmeier, C.; Califano, R.; Hanna, G.G.; Hill, K.; Danson, S.; Steele, N.; Nye, M.; Johnson, L.; et al. Nivolumab versus Placebo in Patients with Relapsed Malignant Mesothelioma (CONFIRM): A Multicentre, Double-Blind, Randomised, Phase 3 Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2021, 22, 1530–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scherpereel, A.; Mazieres, J.; Greillier, L.; Lantuejoul, S.; Dô, P.; Bylicki, O.; Monnet, I.; Corre, R.; Audigier-Valette, C.; Locatelli-Sanchez, M.; et al. Nivolumab or Nivolumab plus Ipilimumab in Patients with Relapsed Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma (IFCT-1501 MAPS2): A Multicentre, Open-Label, Randomised, Non-Comparative, Phase 2 Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 239–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, S.; Scherpereel, A.; Cornelissen, R.; Oulkhouir, Y.; Greillier, L.; Kaplan, M.A.; Talbot, T.; Monnet, I.; Hiret, S.; Baas, P.; et al. First-Line Nivolumab plus Ipilimumab versus Chemotherapy in Patients with Unresectable Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma: 3-Year Outcomes from CheckMate 743. Ann. Oncol. 2022, 33, 488–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zalcman, G.; Oulkhouir, Y.; Cornelissen, R.; Greillier, L.; Cid, J.R.R.; Mazieres, J.; Briggs, P.; Nowak, A.K.; Tsao, A.; Fujimoto, N.; et al. LBA71 First-Line Nivolumab (NIVO) plus Ipilimumab (IPI) vs Chemotherapy (Chemo) in Patients (Pts) with Unresectable Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma (UMPM): 4-Year Update from CheckMate 743. Ann. Oncol. 2022, 33, S1438–S1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alley, E.W.; Lopez, J.; Santoro, A.; Morosky, A.; Saraf, S.; Piperdi, B.; van Brummelen, E. Clinical Safety and Activity of Pembrolizumab in Patients with Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma (KEYNOTE-028): Preliminary Results from a Non-Randomised, Open-Label, Phase 1b Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 623–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popat, S.; Curioni-Fontecedro, A.; Dafni, U.; Shah, R.; O’Brien, M.; Pope, A.; Fisher, P.; Spicer, J.; Roy, A.; Gilligan, D.; et al. A Multicentre Randomised Phase III Trial Comparing Pembrolizumab versus Single-Agent Chemotherapy for Advanced Pre-Treated Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma: The European Thoracic Oncology Platform (ETOP 9-15) PROMISE-Meso Trial. Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, 1734–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowak, A.K.; Lesterhuis, W.J.; Kok, P.-S.; Brown, C.; Hughes, B.G.; Karikios, D.J.; John, T.; Kao, S.C.-H.; Leslie, C.; Cook, A.M.; et al. Durvalumab with First-Line Chemotherapy in Previously Untreated Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma (DREAM): A Multicentre, Single-Arm, Phase 2 Trial with a Safety Run-In. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, 1213–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deiana, C.; Fabbri, F.; Tavolari, S.; Palloni, A.; Brandi, G. Improvements in Systemic Therapies for Advanced Malignant Mesothelioma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piccirillo, M.C.; Chu, Q.; Bradbury, P.; Tu, W.; Coschi, C.H.; Grosso, F.; Florescu, M.; Mencoboni, M.; Goffin, J.R.; Pagano, M.; et al. Brief Report: Canadian Cancer Trials Group IND.227: A Phase 2 Randomized Study of Pembrolizumab in Patients With Advanced Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma (NCT02784171). J. Thorac. Oncol. 2023, 18, 813–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Study Details|BEAT-Meso: Bevacizumab and Atezolizumab in Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma|ClinicalTrials.Gov. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT03762018 (accessed on 27 November 2023).
- Kok, P.S.; Forde, P.M.; Hughes, B.; Sun, Z.; Brown, C.; Ramalingam, S.; Cook, A.; Lesterhuis, W.J.; Yip, S.; O’Byrne, K.; et al. Protocol of DREAM3R: DuRvalumab with ChEmotherapy as First-Line TreAtment in Advanced Pleural Mesothelioma-a Phase 3 Randomised Trial. BMJ Open 2022, 12, e057663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcq, E.; De Waele, J.; Van Audenaerde, J.; Lion, E.; Santermans, E.; Hens, N.; Pauwels, P.; Van Meerbeeck, J.P.; Smits, E.L.J. Abundant Expression of TIM-3, LAG-3, PD-1 and PD-L1 as Immunotherapy Checkpoint Targets in Effusions of Mesothelioma Patients. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 89722–89735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, S.G. Emerging Avenues in Immunotherapy for the Management of Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma. BMC Pulm. Med. 2021, 21, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcq, E.; Van Audenaerde, J.R.M.; De Waele, J.; Merlin, C.; Pauwels, P.; Van Meerbeeck, J.P.; Fisher, S.A.; Smits, E.L.J. The Search for an Interesting Partner to Combine with PD-L1 Blockade in Mesothelioma: Focus on TIM-3 and LAG-3. Cancers 2021, 13, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luke, J.J.; Patel, M.R.; Hamilton, E.P.; Chmielowski, B.; Ulahannan, S.V.; Kindler, H.L.; Bahadur, S.W.; Clingan, P.R.; Mallesara, G.; Weickhardt, A.J.; et al. A Phase I, First-in-Human, Open-Label, Dose-Escalation Study of MGD013, a Bispecific DART Molecule Binding PD-1 and LAG-3, in Patients with Unresectable or Metastatic Neoplasms. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 3004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lines, J.L.; Sempere, L.F.; Broughton, T.; Wang, L.; Noelle, R. VISTA Is a Novel Broad-Spectrum Negative Checkpoint Regulator for Cancer Immunotherapy. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2014, 2, 510–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ladanyi, M.; Robinson, B.W.; Campbell, P.J. The TCGA Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma (MPM) Project: VISTA Expression and Delineation of a Novel Clinical-Molecular Subtype of MPM. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 8516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterman, D.H.; Alley, E.; Stevenson, J.P.; Friedberg, J.; Metzger, S.; Recio, A.; Moon, E.K.; Haas, A.R.; Vachani, A.; Katz, S.I.; et al. Pilot and Feasibility Trial Evaluating Immuno-Gene Therapy of Malignant Mesothelioma Using Intrapleural Delivery of Adenovirus-IFNα Combined with Chemotherapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 3791–3800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Study Details|A Phase 3, Open-Label, Randomized, Parallel Group Study to Evaluate the Efficacy and Safety of Intrapleural Administration of Adenovirus-Delivered Interferon Alpha-2b (RAd-IFN) in Combination with Celecoxib and Gemcitabine in Patients with Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma|ClinicalTrials.Gov. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT03710876 (accessed on 27 November 2023).
- Castelletti, L.; Yeo, D.; van Zandwijk, N.; Rasko, J.E.J. Anti-Mesothelin CAR T Cell Therapy for Malignant Mesothelioma. Biomark. Res. 2021, 9, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiesgen, S.; Chicaybam, L.; Chintala, N.K.; Adusumilli, P.S. Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR) T-Cell Therapy for Thoracic Malignancies. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2018, 13, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- June, C.H.; Sadelain, M. Chimeric Antigen Receptor Therapy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adusumilli, P.S.; Zauderer, M.G.; Rivière, I.; Solomon, S.B.; Rusch, V.W.; O’Cearbhaill, R.E.; Zhu, A.; Cheema, W.; Chintala, N.K.; Halton, E.; et al. A Phase I Trial of Regional Mesothelin-Targeted CAR T-Cell Therapy in Patients with Malignant Pleural Disease, in Combination with the Anti–PD-1 Agent Pembrolizumab. Cancer Discov. 2021, 11, 2748–2763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Study Details|A Phase 1 Study of SynKIR-110, Autologous T Cells Transduced with Mesothelin KIR-CAR, in Subjects with Mesothelin-Expressing Advanced Ovarian Cancer, Cholangiocarcinoma, or Mesothelioma|ClinicalTrials.Gov. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT05568680 (accessed on 5 September 2023).
- Study Details|A Single-Arm, Open-Label, Phase I Trial to Assess the Safety of Genetically Engineered Autologous T Cells Targeting the Cell Surface Antigen Mesothelin with Cell-Intrinsic Checkpoint Inhibition in Patients with Mesothelioma|ClinicalTrials.Gov. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT04577326 (accessed on 5 September 2023).
- Study Details|Phase I Study of Human Chimeric Antigen Receptor Modified T Cells in Patients with Mesothelin Expressing Cancers|ClinicalTrials.Gov. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT03054298 (accessed on 5 September 2023).
- Tumeh, P.C.; Harview, C.L.; Yearley, J.H.; Shintaku, I.P.; Taylor, E.J.M.; Robert, L.; Chmielowski, B.; Spasic, M.; Henry, G.; Ciobanu, V.; et al. PD-1 Blockade Induces Responses by Inhibiting Adaptive Immune Resistance. Nature 2014, 515, 568–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aerts, J.G.; Hegmans, J.P. Tumor-Specific Cytotoxic T Cells Are Crucial for Efficacy of Immunomodulatory Antibodies in Patients with Lung Cancer. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 2381–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belderbos, R.A.; Baas, P.; Berardi, R.; Cornelissen, R.; Fennell, D.A.; van Meerbeeck, J.P.; Scherpereel, A.; Vroman, H.; Aerts, J.G.J.V. A Multicenter, Randomized, Phase II/III Study of Dendritic Cells Loaded with Allogeneic Tumor Cell Lysate (MesoPher) in Subjects with Mesothelioma as Maintenance Therapy after Chemotherapy: DENdritic Cell Immunotherapy for Mesothelioma (DENIM) Trial. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2019, 8, 280–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buonaguro, L.; Petrizzo, A.; Tornesello, M.L.; Buonaguro, F.M. Translating Tumor Antigens into Cancer Vaccines. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2011, 18, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aerts, J.G.J.V.; de Goeje, P.L.; Cornelissen, R.; Kaijen-Lambers, M.E.H.; Bezemer, K.; van der Leest, C.H.; Mahaweni, N.M.; Kunert, A.; Eskens, F.A.L.M.; Waasdorp, C.; et al. Autologous Dendritic Cells Pulsed with Allogeneic Tumor Cell Lysate in Mesothelioma: From Mouse to Human. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 766–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LaFave, L.M.; Béguelin, W.; Koche, R.; Teater, M.; Spitzer, B.; Chramiec, A.; Papalexi, E.; Keller, M.D.; Hricik, T.; Konstantinoff, K.; et al. Loss of BAP1 Function Leads to EZH2-Dependent Transformation. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 1344–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zauderer, M.G.; Szlosarek, P.W.; Le Moulec, S.; Popat, S.; Taylor, P.; Planchard, D.; Scherpereel, A.; Koczywas, M.; Forster, M.; Cameron, R.B.; et al. EZH2 Inhibitor Tazemetostat in Patients with Relapsed or Refractory, BAP1-Inactivated Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma: A Multicentre, Open-Label, Phase 2 Study. Lancet Oncol. 2022, 23, 758–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beddowes, E.; Spicer, J.; Chan, P.Y.; Khadeir, R.; Corbacho, J.G.; Repana, D.; Steele, J.P.; Schmid, P.; Szyszko, T.; Cook, G.; et al. Phase 1 Dose-Escalation Study of Pegylated Arginine Deiminase, Cisplatin, and Pemetrexed in Patients With Argininosuccinate Synthetase 1–Deficient Thoracic Cancers. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 1778–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Study Details|Randomized, Double-Blind, Phase 2/3 Study in Subjects with Malignant Pleural Mesotheliomato Assess ADI-PEG 20 with Pemetrexed and Cisplatin (ATOMIC-Meso Phase 2/3 Study)|ClinicalTrials.Gov. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT02709512 (accessed on 23 July 2023).
- Fennell, D.; Hudka, M.; Darlison, L.; Lord, K.; Bzura, A.; Dzialo, J.; Pritchard, C.; Harber, J.; Takata, T.; Popat, S.; et al. P2.06-02 Mesothelioma Stratified Therapy (MiST): A Phase IIA Umbrella Trial for Accelerating the Development of Precision Medicines. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2019, 14, S755–S756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fennell, D.A.; King, A.; Mohammed, S.; Branson, A.; Brookes, C.; Darlison, L.; Dawson, A.G.; Gaba, A.; Hutka, M.; Morgan, B.; et al. Rucaparib in Patients with BAP1-Deficient or BRCA1-Deficient Mesothelioma (MiST1): An Open-Label, Single-Arm, Phase 2a Clinical Trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 2021, 9, 593–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fennell, D.A.; King, A.; Mohammed, S.; Greystoke, A.; Anthony, S.; Poile, C.; Nusrat, N.; Scotland, M.; Bhundia, V.; Branson, A.; et al. Abemaciclib in Patients with P16ink4A-Deficient Mesothelioma (MiST2): A Single-Arm, Open-Label, Phase 2 Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2022, 23, 374–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krebs, M.; Carter, L.; Villa, S.; King, A.; Massey, C.; Lorens, J.; Darlington, E.; Fennell, D. P2.06-09 MiST3: A Phase II Study of Oral Selective AXL Inhibitor Bemcentinib (BGB324) in Combination with Pembrolizumab in Pts with Malignant Mesothelioma. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2018, 13, S745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolini, F.; Bocchini, M.; Bronte, G.; Delmonte, A.; Guidoboni, M.; Crinò, L.; Mazza, M. Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma: State-of-the-Art on Current Therapies and Promises for the Future. Front. Oncol. 2020, 9, 1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceresoli, G.L.; Aerts, J.G.; Dziadziuszko, R.; Ramlau, R.; Cedres, S.; van Meerbeeck, J.P.; Mencoboni, M.; Planchard, D.; Chella, A.; Crinò, L.; et al. Tumour Treating Fields in Combination with Pemetrexed and Cisplatin or Carboplatin as First-Line Treatment for Unresectable Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma (STELLAR): A Multicentre, Single-Arm Phase 2 Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 1702–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
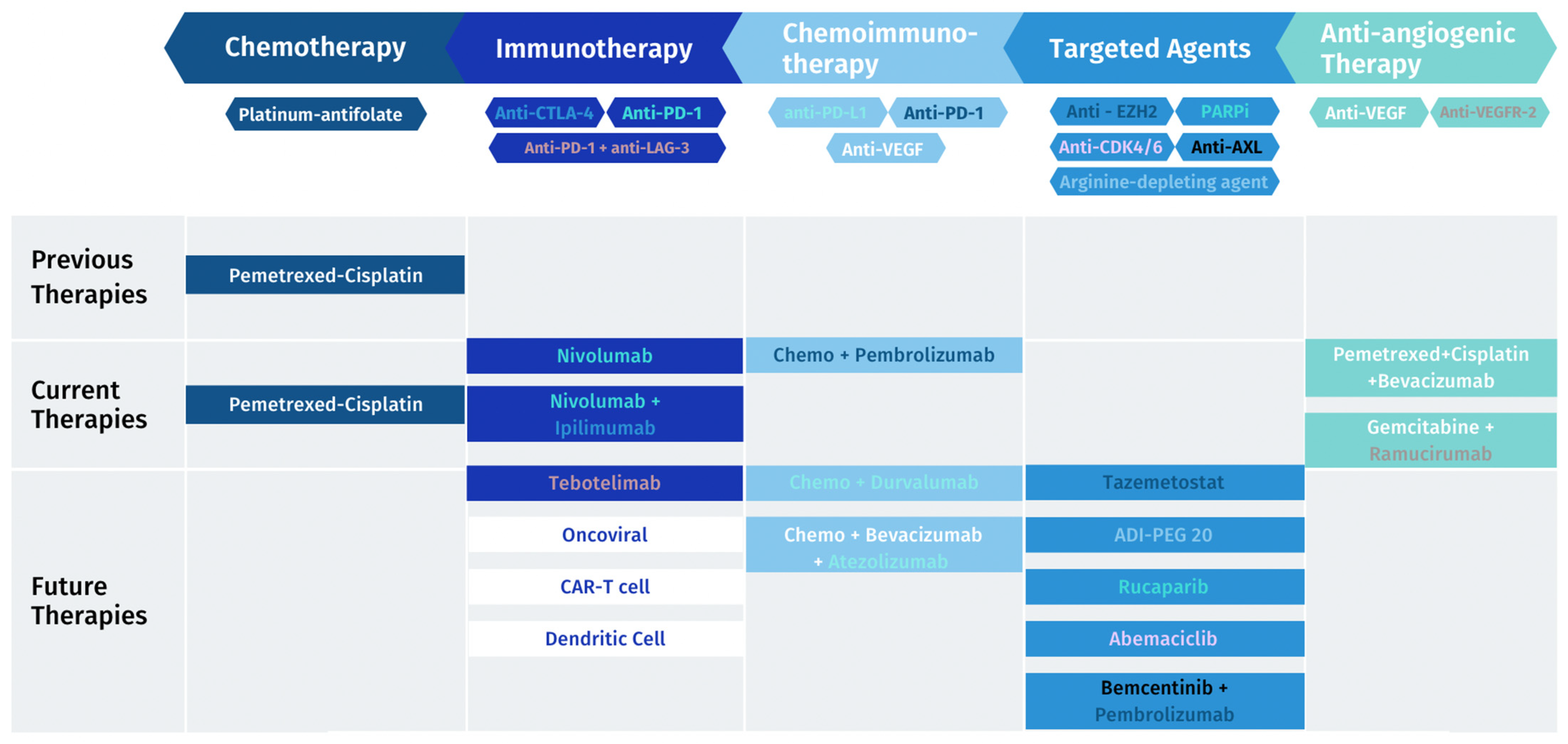
| Study Name | Description | Treatment | Study Completion | ClinicalTrials.gov Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MARS2 | Multicenter open parallel group randomized controlled trial comparing the effectiveness of surgery—(extended) pleurectomy decortication—versus no surgery for the treatment of pleural mesothelioma | Surgery + chemotherapy vs. chemotherapy | 2022 | NCT02040272 |
| EMPHACIS | Phase III trial determining whether treatment with pemetrexed and cisplatin results in a survival time superior to that achieved with cisplatin alone | Pemetrexed + cisplatin vs. cisplatin alone | 2003 | - |
| MAPS | Randomized, controlled, open-label, phase III trial assessing the effect on survival of bevacizumab when added to the present standard of care, cisplatin plus pemetrexed, as a first-line treatment of advanced MPM | Bevacizumab + pemetrexed + cisplatin vs. pemetrexed + cisplatin alone | 2016 | NCT00651456 |
| RAMES | Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase II trial assessing the efficacy and safety of the anti-VEGFR-2 antibody ramucirumab combined with gemcitabine in patients with pretreated MPM | Gemcitabine + ramucirumab vs. gemcitabine + placebo | 2020 | NCT03560973 |
| CONFIRM | Multicenter, placebo-controlled, double-blind, parallel group, randomized, phase III trial assessing the efficacy and safety of nivolumab, an anti-PD-1 antibody, in patients with pleural or peritoneal malignant mesothelioma who have progressed following platinum-based chemotherapy | Nivolumab vs. placebo | 2023 | NCT03063450 |
| MAPS2 | Multicenter randomized, non-comparative, open-label, phase II trial prospectively assessing the anti-PD-1 monoclonal antibody alone or in combination with the anti-cytotoxic T-lymphocyte protein 4 (CTLA-4) antibody in patients with MPM | Nivolumab + ipilimumab vs. nivolumab alone | 2019 | NCT0271627 |
| CHECKMATE 743 | Open-label, randomized, phase III study testing the effectiveness and tolerability of the combination of nivolumab and ipilimumab compared to pemetrexed and cisplatin or carboplatin in patients with unresectable pleural mesothelioma | Nivolumab + ipilimumab vs. pemetrexed + cisplatin/carboplatin | 2023 | NCT0289929 |
| Study Name | Description | Treatment | Study Completion | ClinicalTrials.gov Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chemoimmunotherapy | ||||
| DREAM | Multicenter, single-arm, open-label, phase 2 trial evaluating the activity of durvalumab, an anti-PD-L1 antibody, given during and after first-line chemotherapy with cisplatin and pemetrexed in patients with advanced MPM | Durvalumab + pemetrexed + cisplatin | 2019 | ACTRN12616001170415 * |
| IND227 | Phase 2 trial comparing the progression-free survival of standard platinum and pemetrexed (CP) versus CP + pembrolizumab | Platinum + pemetrexed vs. platinum + pemetrexed + pembrolizumab | 2023 | NCT02784171 |
| BEAT-meso | Multicenter randomized phase III trial comparing atezolizumab plus bevacizumab and standard chemotherapy versus bevacizumab and standard chemotherapy as first-line treatments for advanced MPM | Bevacizumab + pemetrexed + carboplatin vs. bevacizumab + pemetrexed + carboplatin + atezolizumab | 2024 | NCT03762018 |
| DREAM3R | Phase III randomized trial aiming to determine the effectiveness of including durvalumab with first-line platinum-pemetrexed chemotherapy in advanced MPM | Durvalumab + pemetrexed + cisplatin/ carboplatin vs. pemetrexed + cisplatin/ carboplatin alone | 2025 | NCT04334759 |
| Novel Immunotherapies | ||||
| INFINITE | A Phase 3, open-label, randomized, parallel group study evaluating the efficacy and safety of the intrapleural administration of adenovirus-delivered interferon Alpha-2b (rAd-IFN) in combination with celecoxib and gemcitabine in patients with MPM | rAd-IFN + celecoxib + gemcitabine vs. celecoxib + gemcitabine alone | 2024 | NCT03710876 |
| A Phase I/II Clinical Trial of MPD Treated With Autologous T Cells Genetically Engineered to Target the Cancer-Cell Surface Antigen Mesothelin | Open-label, dose-escalating, non-randomized, single-center, phase I/II study of mesothelin-targeted T cells administered intrapleurally as an infusion in patients with a diagnosis of MPD from mesothelioma, lung cancer or breast cancer | CAR T-cell + pembrolizumab | 2024 | NCT04577326 |
| DENIM | Open-label, multicenter, randomized phase II/III trial patients will be randomized to receive either dendritic cell therapy plus best supportive care (BSC) or BSC alone according to the discretion of the local investigator after first-line chemotherapy treatment. | Dendritic cell therapy + BSC vs. BSC alone | 2023 | NCT03610360 |
| Targeted Agents | ||||
| A Multicenter Study of the EZH2 Inhibitor Tazemetostat in Adult Subjects With Relapsed or Refractory Malignant Mesothelioma With BAP1 Loss of Function | Phase 2, multicenter, open-label, two-part, single-arm, two-stage study aiming to evaluate the anti-tumor activity and safety of tazemetostat in patients with measurable relapsed or refractory MPM | Tazemetostat | 2019 | NCT02860286 |
| ATOMIC-Meso | Randomized, double-blind, phase II/III study in subjects with MPM assessing the efficacy of ADI-PEG 20 combined with pemetrexed and cisplatin | ADI-PEG20 + pemetrexed + cisplatin vs. placebo + pemetrexed + cisplatin | 2022 | NCT02709512 |
| Mesothelioma Stratified Therapy (MiST) | Stratified multi-arm phase IIa clinical trial enabling the accelerated evaluation of targeted therapies for relapsed malignant mesothelioma. Stage 1: molecular pre-screening for the identification of patients, biomarker testing and analysis. Stage 2: the treatment protocol will be specific to the patient based on the results of their biomarker testing in stage 1 **. Stage 3: molecular profiling to understand the genomic basis of the drug response in the MiST trial | Rucaparib ademaciclib pebrolizumab + bemcentinib Atezolizumab + bevacizumab dostarlimab + niraparib | 2023 | NCT03654833 |
| Tumor-treating Fields | ||||
| STELLAR | Prospective, single-arm, non-randomized, open-label phase II trial designed to study the safety and efficacy of a medical device, the NovoTTF-100L, concomitant with pemetrexed and cisplatin or carboplatin in MPM patients | TTFields at a frequency of 150 kHz to the thorax + pemetrexed + platinum/ carboplatin | 2018 | NCT02397928 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bertin, B.; Zugman, M.; Schvartsman, G. The Current Treatment Landscape of Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma and Future Directions. Cancers 2023, 15, 5808. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15245808
Bertin B, Zugman M, Schvartsman G. The Current Treatment Landscape of Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma and Future Directions. Cancers. 2023; 15(24):5808. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15245808
Chicago/Turabian StyleBertin, Beatriz, Miguel Zugman, and Gustavo Schvartsman. 2023. "The Current Treatment Landscape of Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma and Future Directions" Cancers 15, no. 24: 5808. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15245808
APA StyleBertin, B., Zugman, M., & Schvartsman, G. (2023). The Current Treatment Landscape of Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma and Future Directions. Cancers, 15(24), 5808. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15245808






