Performance of Radiomics in Microvascular Invasion Risk Stratification and Prognostic Assessment in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Identification of Relevant Published Studies
2.3. Data Extraction
2.4. Outcome Assessment and Statistical Methods
2.4.1. Assessment of Risk of Bias
2.4.2. Data Synthesis and Analysis
2.4.3. Assessment of Publication Bias
2.4.4. Modeling
3. Results
3.1. Description of Radiomics Prediction
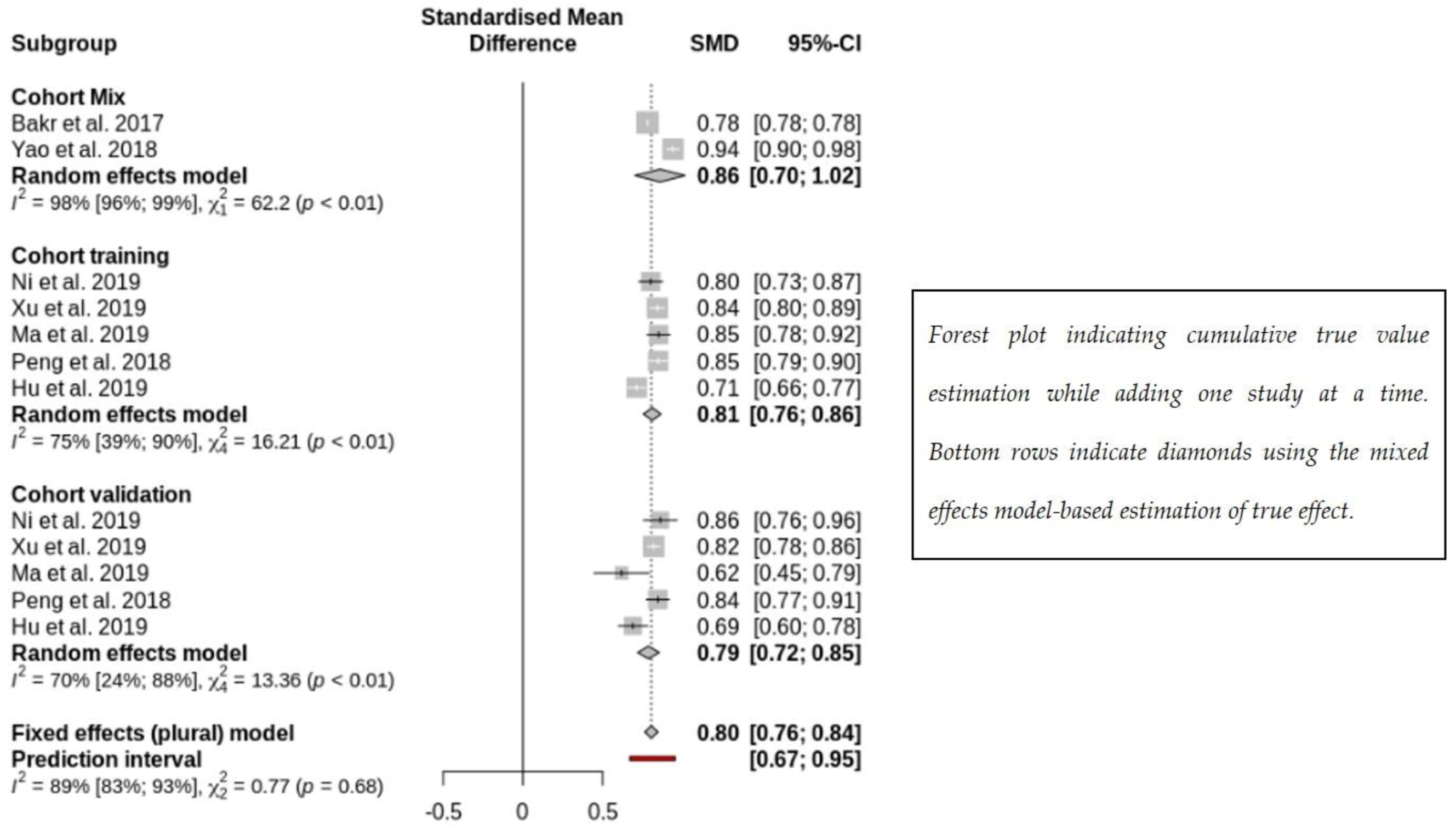
3.2. Subgroup Analysis on Radiomics Prediction of MVI
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Zheng, R.; Baade, P.D.; Zhang, S.; Zeng, H.; Bray, F.; Jemal, A.; Yu, X.Q.; He, J. Cancer Statistics in China, 2015. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2016, 66, 115–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer Statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2016, 66, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, G.; Karin, M. NF-ΚB and STAT3- Key Players in Liver Inflammation and Cancer. Cell Res. 2011, 21, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Nordic Cochrane Centre. The Cochrane Collaboration Review Manager (RevMan) [Computer Program], Version 5.3. The Nordic Cochrane Centre: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Viechtbauer, W. Conducting Meta-Analyses in R with the Metafor. J. Stat. Softw. 2010, 36, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, R.D.; Moons, K.G.M.; Snell, K.I.E.; Ensor, J.; Hooft, L.; Altman, D.G.; Hayden, J.; Collins, G.S.; Debray, T.P.A. A Guide to Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Prognostic Factor Studies. BMJ Online 2019, 364, k4597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, L.; Owen, D.; Rosen, B.; Guo, X.; Cuneo, K.; Lawrence, T.S.; Ten Haken, R.; El Naqa, I. A Deep Survival Interpretable Radiomics Model of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients. Phys. Med. 2021, 82, 295–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, Q.-y.; Hu, H.-t.; Feng, S.-t.; Peng, Z.-p.; Chen, S.-l.; Zhou, Q.; Li, X.; Xie, X.-y.; Lu, M.-d.; Wang, W.; et al. CT-Based Peritumoral Radiomics Signatures to Predict Early Recurrence in Hepatocellular Carcinoma after Curative Tumor Resection or Ablation. Cancer Imaging 2019, 19, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, C.; Wang, Z.; Gu, D.; Tian, J.; Zhao, P.; Wei, J.; Yang, X.; Hao, X.; Dong, D.; He, N.; et al. Prediction Early Recurrence of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Eligible for Curative Ablation Using a Radiomics Nomogram. Cancer Imaging 2019, 19, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.; Gu, D.; Wang, H.; Wei, J.; Wang, Z.; Hao, X.; Ji, Q.; Cao, S.; Song, Z.; Jiang, J.; et al. Radiomics Analysis Enables Recurrence Prediction for Hepatocellular Carcinoma after Liver Transplantation. Eur. J. Radiol. 2019, 117, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, P.; Gao, F.; Hai, J.; Wu, M.; Chen, J.; Zhu, S.; Wang, M.; Shi, D. Application of CT Radiomics in Prediction of Early Recurrence in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Abdom. Radiol. 2019, 45, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Zhang, H.L.; Liu, Q.P.; Sun, S.W.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, F.P.; Yang, G.; Yan, X.; Zhang, Y.D.; Liu, X.S. Radiomic Analysis of Contrast-Enhanced CT Predicts Microvascular Invasion and Outcome in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2019, 70, 1133–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, W.; He, B.; Hu, M.; Zhang, W.; Xiao, D.; Yu, H.; Song, Q.; Xiang, N.; Yang, J.; He, S.; et al. A Radiomics-Based Nomogram for the Preoperative Prediction of Posthepatectomy Liver Failure in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Surg. Oncol. 2019, 28, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akai, H.; Yasaka, K.; Kunimatsu, A.; Nojima, M.; Kokudo, T.; Kokudo, N.; Hasegawa, K.; Abe, O.; Ohtomo, K.; Kiryu, S. Predicting Prognosis of Resected Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Radiomics Analysis with Random Survival Forest. Diagn. Interv. Imaging 2018, 99, 643–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, B.-H.; Liu, L.-Z.; Zhang, Z.-Z.; Shi, J.-Y.; Dong, L.-Q.; Tian, L.-Y.; Ding, Z.-b.; Ji, Y.; Rao, S.-X.; Zhou, J.; et al. Radiomics Score: A Potential Prognostic Imaging Feature for Postoperative Survival of Solitary HCC Patients. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Choi, S.J.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, H.Y.; Park, H. Predicting Survival Using Pretreatment CT for Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma Treated with Transarterial Chemoembolization: Comparison of Models Using Radiomics. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2018, 211, 1026–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; He, L.; Huang, Y.; Chen, S.; Wu, P.; Ye, W.; Liu, Z.; Liang, C. CT-Based Radiomics Signature: A Potential Biomarker for Preoperative Prediction of Early Recurrence in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Abdom. Radiol. 2017, 42, 1695–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, C.; Ma, X. Deep Learning Radiomics Based on Contrast Enhanced Computed Tomography Predicts Microvascular Invasion and Survival Outcome in Early Stage Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2022, 48, 1068–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.-C.; Lai, J.; Huang, J.-Y.; Cho, C.-F.; Lee, P.H.; Lu, M.-H.; Yeh, C.-C.; Yu, J.; Lin, W.-C. Predicting Microvascular Invasion in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Deep Learning Model Validated across Hospitals. Cancer Imaging 2021, 21, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, T.; Ren, L.; Liao, M.; Zhao, B.; Wei, R.; Zhou, Z.; He, Y.; Zhang, H.; Chen, D.; Chen, H.; et al. Preoperative Radiomics Analysis of Contrast-Enhanced CT for Microvascular Invasion and Prognosis Stratification in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Hepatocell. Carcinoma 2022, 9, 189–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Tan, X.-Z.; Zhang, T.; Gu, Q.-B.; Mao, X.-H.; Li, Y.-C.; He, Y.-Q. Prediction of Microvascular Invasion in Solitary Hepatocellular Carcinoma ≤ 5 Cm Based on Computed Tomography Radiomics. World J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 27, 2015–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Feng, Z.; Li, H.; Yao, S.; Zheng, W.; Rong, P. Influence of Different Region of Interest Sizes on CT-Based Radiomics Model for Microvascular Invasion Prediction in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Cent. South University. Med. Sci. 2022, 47, 1049–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cozzi, L.; Dinapoli, N.; Fogliata, A.; Hsu, W.C.; Reggiori, G.; Lobefalo, F.; Kirienko, M.; Sollini, M.; Franceschini, D.; Comito, T.; et al. Radiomics Based Analysis to Predict Local Control and Survival in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients Treated with Volumetric Modulated Arc Therapy. BMC Cancer 2017, 17, 829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.-Q.; Cao, S.-E.; Cao, S.; Chen, J.-N.; Wang, G.-Y.; Shi, W.-Q.; Deng, Y.-N.; Cheng, N.; Ma, K.; Zeng, K.-N.; et al. Preoperative Identification of Microvascular Invasion in Hepatocellular Carcinoma by XGBoost and Deep Learning. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 147, 821–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Jiang, H.; Chen, J.; Wei, Y.; Cao, L.; Ye, Z.; Li, X.; Ma, L.; Song, B. Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Radiomics Nomogram on Gadoxetic Acid-Enhanced MR Imaging for Early Postoperative Recurrence Prediction. Cancer Imaging 2019, 19, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-D.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, Z.-P.; Lin, B.; Jiang, Z.-J.; Tang, C.; Dang, Y.-W.; Xia, Y.-W.; Song, B.; Long, L.-L. Radiomics and Nomogram of Magnetic Resonance Imaging for Preoperative Prediction of Microvascular Invasion in Small Hepatocellular Carcinoma. World J. Gastroenterol. 2022, 28, 4399–4416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Xia, Y.; Tolat, P.P.; Long, L.; Jiang, Z.; Huang, Z.; Tang, Q. Comparison of Conventional Gadoxetate Disodium-Enhanced MRI Features and Radiomics Signatures With Machine Learning for Diagnosing Microvascular Invasion. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2021, 216, 1510–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Shin, J.; Kim, D.Y.; Choi, G.H.; Kim, M.J.; Choi, J.Y. Radiomics on Gadoxetic Acid-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging for Prediction of Postoperative Early and Late Recurrence of Single Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 3847–3855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hui, T.C.H.; Chuah, T.K.; Low, H.M.; Tan, C.H. Predicting Early Recurrence of Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Texture Analysis of Preoperative MRI: A Radiomics Study. Clin. Radiol. 2018, 73, 1056.e11–1056.e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chong, H.-H.; Yang, L.; Sheng, R.-F.; Yu, Y.-L.; Wu, D.-J.; Rao, S.-X.; Yang, C.; Zeng, M.-S. Multi-Scale and Multi-Parametric Radiomics of Gadoxetate Disodium-Enhanced MRI Predicts Microvascular Invasion and Outcome in Patients with Solitary Hepatocellular Carcinoma ≤ 5 Cm. Eur. Radiol. 2021, 31, 4824–4838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, H.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, J.; Liao, M.; Xu, L.; Wu, Z.; Yuan, K.; Song, B.; Zeng, Y. Preoperative Radiomic Approach to Evaluate Tumor-Infiltrating CD8+ T Cells in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients Using Contrast-Enhanced Computed Tomography. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2019, 26, 4537–4547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, M.; Zhou, X.; Lv, Q.; Li, Z.; Gao, Y.; Tan, Y.; Liu, J.; Liu, F.; Yu, H.; Jiao, L.; et al. Radiomics Models for Diagnosing Microvascular Invasion in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Which Model Is the Best Model? Cancer Imaging 2019, 19, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokrane, F.Z.; Lu, L.; Vavasseur, A.; Otal, P.; Peron, J.M.; Luk, L.; Yang, H.; Ammari, S.; Saenger, Y.; Rousseau, H.; et al. Radiomics Machine-Learning Signature for Diagnosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Cirrhotic Patients with Indeterminate Liver Nodules. Eur. Radiol. 2019, 30, 558–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakr, S.; Echegaray, S.; Shah, R.; Kamaya, A.; Louie, J. Noninvasive Radiomics Signature Based on Quantitative Analysis of Computed Tomography Images as a Surrogate for Microvascular Invasion in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Pilot Study. J. Med. Imaging 2017, 4, 041303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.; Wei, J.; Gu, D.; Zhu, Y.; Feng, B.; Liang, M.; Wang, S.; Zhao, X.; Tian, J. Preoperative Radiomics Nomogram for Microvascular Invasion Prediction in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Using Contrast-Enhanced CT. Eur. Radiol. 2019, 29, 3595–3605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Liu, L. A Radiomics Nomogram for Preoperative Prediction of Microvascular Invasion Risk in Hepatitis b Virus-Related Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Diagn. Interv. Radiol. 2018, 24, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Yan, B.; Zeng, L.; Wu, M.; Tan, H.; Hai, J.; Ning, P.; Shi, D. [Quantitative Analysis of Hepatocellular Carcinomas Pathological Grading in Non-Contrast Magnetic Resonance Images]. Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi J. Biomed. Eng. Shengwu Yixue Gongchengxue Zazhi 2019, 36, 581–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Liu, A.; Cui, J.; Chen, A.; Song, Q.; Xie, L. Radiomics-Based Classification of Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Hepatic Haemangioma on Precontrast Magnetic Resonance Images. BMC Med. Imaging 2019, 19, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Feng, S.; Wei, J.; Liu, F.; Li, B.; Li, X.; Hou, Y.; Gu, D.; Tang, M.; Xiao, H.; et al. Pretreatment Prediction of Immunoscore in Hepatocellular Cancer: A Radiomics-Based Clinical Model Based on Gd-EOB-DTPA-Enhanced MRI Imaging. Eur. Radiol. 2019, 29, 4177–4187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Tan, H.; Gao, F.; Hai, J.; Ning, P.; Chen, J.; Zhu, S.; Wang, M.; Dou, S.; Shi, D. Predicting the Grade of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Based on Non-Contrast-Enhanced MRI Radiomics Signature. Eur. Radiol. 2019, 29, 2802–2811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.-t.; Wang, Z.; Huang, X.-w.; Chen, S.-l.; Zheng, X.; Ruan, S.-m.; Xie, X.-y.; Lu, M.-d.; Yu, J.; Tian, J.; et al. Ultrasound-Based Radiomics Score: A Potential Biomarker for the Prediction of Microvascular Invasion in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Eur. Radiol. 2019, 29, 2890–2901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Z.; Dong, Y.; Wu, G.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, D.; Yu, J.H.; Wang, W.P. Preoperative Diagnosis and Prediction of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Radiomics Analysis Based on Multi-Modal Ultrasound Images. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erstad, D.J.; Tanabe, K.K. Prognostic and Therapeutic Implications of Microvascular Invasion in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2019, 26, 1474–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, K.; Cao, X.; Du, P.; Fu, J.-Y.; Geng, D.-Y.; Zhang, J. Radiomics for the Detection of Microvascular Invasion in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. World J. Gastroenterol. 2022, 28, 2176–2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Wu, C.; Huang, Y.; Chen, J.; Ye, D.; Su, Z. Radiomics for the Preoperative Evaluation of Microvascular Invasion in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Meta-Analysis. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 831996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, X.; Long, H.; Su, L.; Zheng, R.; Wang, W.; Duan, Y.; Hu, H.; Lin, M.; Xie, X. Radiomics Models for Preoperative Prediction of Microvascular Invasion in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Abdom. Radiol. 2022, 47, 2071–2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segal, E.; Sirlin, C.B.; Ooi, C.; Adler, A.S.; Gollub, J.; Chen, X.; Chan, B.K.; Matcuk, G.R.; Barry, C.T.; Chang, H.Y.; et al. Decoding Global Gene Expression Programs in Liver Cancer by Noninvasive Imaging. Nat. Biotechnol. 2007, 25, 675–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taouli, B.; Hoshida, Y.; Kakite, S.; Chen, X.; Tan, P.S.; Sun, X.; Kihira, S.; Kojima, K.; Toffanin, S.; Fiel, M.I.; et al. Imaging-Based Surrogate Markers of Transcriptome Subclasses and Signatures in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Preliminary Results. Eur. Radiol. 2017, 27, 4472–4481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinter, M.; Peck-Radosavljevic, M. Review Article: Systemic Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 48, 598–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finn, R.S.; Ducreux, M.; Qin, S.; Galle, P.R.; Zhu, A.X.; Ikeda, M.; Kim, T.-Y.; Xu, D.-Z.; Verret, W.; Liu, J.; et al. IMbrave150: A Randomized Phase III Study of 1L Atezolizumab plus Bevacizumab vs Sorafenib in Locally Advanced or Metastatic Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, TPS4141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, A.-L.; Qin, S.; Ikeda, M.; Galle, P.; Ducreux, M.; Zhu, A.; Kim, T.-Y.; Kudo, M.; Breder, V.; Merle, P.; et al. IMbrave150: Efficacy and Safety Results from a Ph III Study Evaluating Atezolizumab (Atezo) + Bevacizumab (Bev) vs Sorafenib (Sor) as First Treatment (Tx) for Patients (Pts) with Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC). Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30 (Suppl. S9), ix186–ix187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
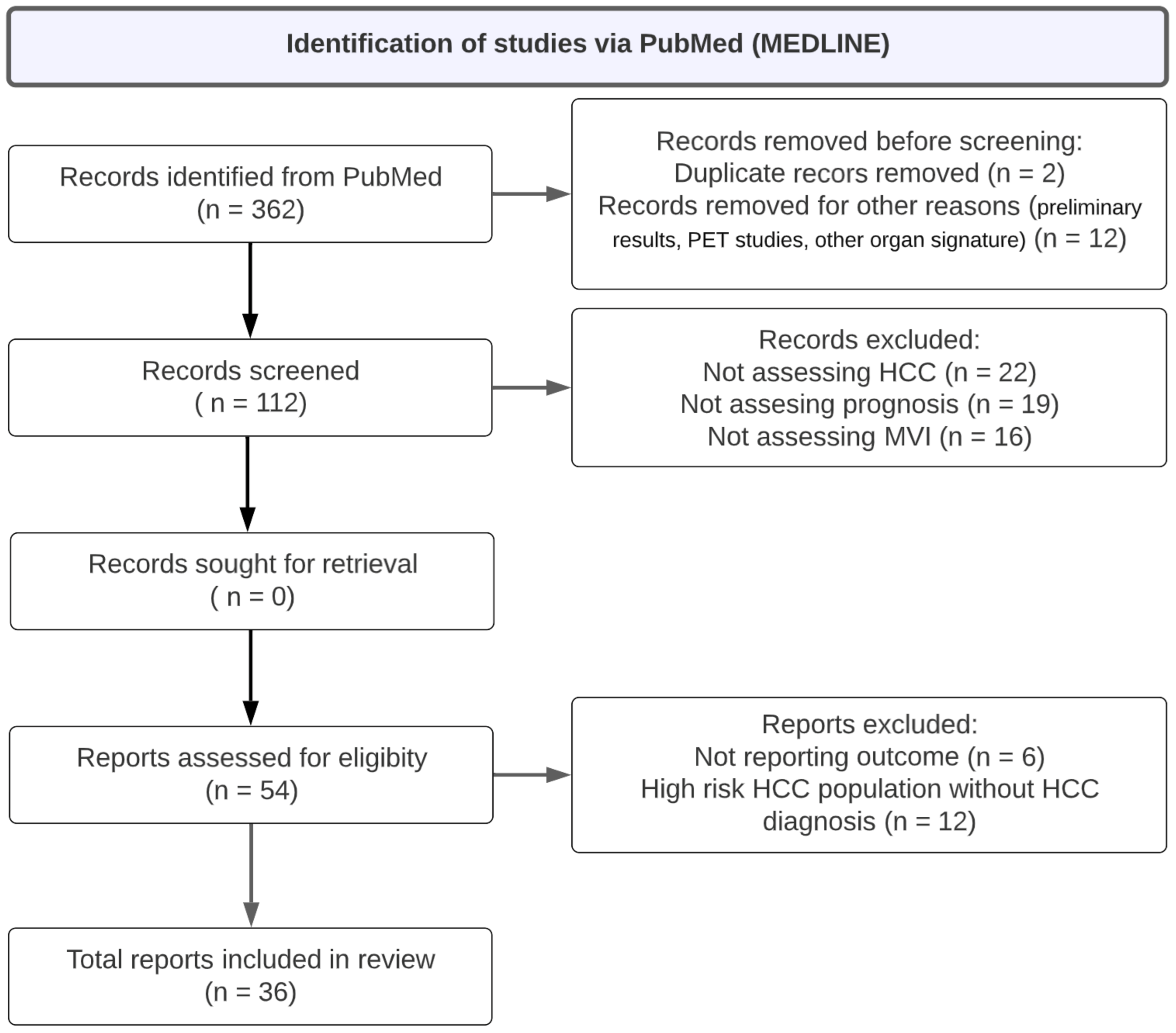



| Search keywords | (imaging data extraction OR radiomics AND hepatocellular carcinoma AND microvascular invasion) NOT ([animals]/lim NOT [humans]/lim) NOT ([Conference Abstract]/lim OR [Letter]/lim OR [Note]/lim OR [Editorial]/lim) |
| Period | To January 2023 |
| Author/Year | Study Objectives | Training Set Sample Size | Validation Set Sample Size | Performance (Training Set) | Performance (Validation Set) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [95%CI] | [95%CI] | |||||
| Wei et al. 2021 [8] | To identify a new radiomics signature using imaging phenotypes and clinical variables for risk prediction of OS after stereotactic body radiation therapy. | 167 data were split into training (75% of 4-folds), validation (25% of 4-folds) and testing fold (1-fold) | c-indices nested cross-validation scheme: | |||
| - radiomics: 0.579 (95%CI: 0.544–0.621) | ||||||
| - clinical: 0.629 (95%CI: 0.601–0.643) | ||||||
| - image input: 0.581 (95%CI: 0.553–0.613) | ||||||
| - combined models: 0.650 (95%CI: 0.635–0.683) | ||||||
| Shan et al. 2019 [9] | To predict early recurrence after surgical or ablation. | 109 | 47 | PT-RO: AUC 0.80 [0.72, 0.89] | PT-RO: AUC 0.79 [0.66, 0.92] | |
| T-RO: AUC 0.82 [0.74, 0.90] | T-RO: AUC 0.62 [0.46, 0.79] | |||||
| PT-E: AUC 0.64 [0.56, 0.72] | PT-E: AUC 0.61 [0.47, 0.74] | |||||
| Yuan et al. 2019 [10] | To predict early recurrence after curative ablation. | 129 | 55 | Portal venous phase model + clinicopathological factors. | Portal venous phase model + clinicopathological factors. | |
| C-index: 0.792 [0.727–0.857] | C-index: 0.755 [0.651–0.860] | |||||
| Guo et al. 2019 [11] | To predict recurrence of HCC after liver transplantation. | 93 | 40 | C-index of 0.785 [0.674–0.895] | C-index of 0.789 [0.620–0.957] | |
| Ning et al. 2019 [12] | To predict early recurrence (at least 1-year FU). | 225 | 100 | AUC: 0.818 [0.760–0.865] | AUC: 0.719 [0.621–0.805] | |
| Xu et al. 2019 [13] | To predict PFS and OS. | 495 | - | OR: 2.34 | ||
| Median PFS: 49.5 vs. 12.9 months; median OS: 76.3 vs. 47.3 months | ||||||
| Cai et al. 2019 [14] | To predict post-hepatectomy liver failure. | 80 | 32 | AUC: 0.822 [0.726–0.917] | AUC: 0.762 [0.576–0.948] | |
| Akai et al. 2018 [15] | To predict random survival forest. | 127 | - | Predicted individual risk (P = 1.1 × 10−4 for DFS, 4.8 × 10−7 for OS). | ||
| The only unfavorable prognostic factors were high predicted risk (HR = 1.06 per 1% increase, P = 8.4 × 10−8) and vascular invasion (HR = 1.74, P = 0.039). | ||||||
| Zheng et al. 2018 [16] | To predict postoperative recurrence and survival. | 212 | 107 | HR: 2.387 [1.321–4.310] | HR: 3.236 [1.416–7.407] | |
| Kim et al. 2018 [17] | To predict survival with TACE (pretreatment CT). | 88 | - | The combined model was a better predictor of survival (HR 19.88; p < 0.0001). | ||
| Zhou et al. 2017 [18] | To predict the early recurrence (≤1 year) of HCC. | 215 | No | AUC of 0.82 [0.76–0.87], sensitivity of 0.79, and specificity of 0.70. | NA | |
| The AUC of the combined model was 0.84 [0.78–0.88], with the sensitivity being 0.82 and specificity 0.71. | ||||||
| Yang et al. 2022 [19] | To predict MVI status. | 198 | 85 | AUC of 0.909, accuracy of 96.47%, sensitivity of 90.91%, specificity of 97.30%, positive predictive value of 83.33%, and negative predictive value of 98.63% in the testing cohort. | ||
| Liu et al. 2021 [20] | To estimate MVI preoperatively. | 216 | 93 | AUC: 0.98, Accuracy: 0.95, Sensitivity 0.91, Specificity: 0.97 | AUC: 0.82, Accuracy: 0.68, Sensitivity 0.96, Specificity: 0.56 | |
| Xu et al. 2022 [21] | To develop a novel nomogram to predict MVI and patients' prognosis based on radiomic features of contrast-enhanced CT. | 295 | 126 | AUC of 0.793 (0.714–0.874) | AUC of 0.750 (0.666–0.834) | |
| Liu et al. 2021 [22] | To investigate the predictive value of computed tomography radiomics for MVI in solitary HCC ≤5 cm. | 124 | 61 | The radiomics model exhibited a better correction and identification ability in the training and validation groups [area under the curve: 0.72 (95% confidence interval: 0.58–0.86) and 0.74 (95% confidence interval: 0.66–0.83), respectively]. | ||
| Zhao et al. 2022 [23] | To investigate the influence of different region of interest (ROI) sizes on CT-based radiomics model for MVI prediction in HCC | In the training set, the sensitivity, specificity, and area under the curve (AUC) of OROI were 0.759, 0.806, and 0.855, respectively. The AUC values of Plus2 (0.979) and Plus3 (0.954) were higher than that of OROI. The AUC values of Plus1 (0.802), Plus4 (0.792), and Plus5 (0.774) were not significantly different from those of OROI. In the validation set, the sensitivity, specificity, and AUC value of OROI were 0.640, 0.630, and 0.664, respectively. The AUC value of Plus3 was 0.903, which was higher than that of OROI. The AUC values of Plus1 (0.679), Plus2 (0.536), Plus4 (0.708), and Plus5 (0.757) were not significantly different from that of OROI (P > 0.05). | ||||
| Cozzi et al. 2016 [24] | To predict local response and OS treated with VMRT | 138 | No | Model 1 energy p < 0.05, AUC 0.66 [0.56–0.77] | NA | |
| Model-2 GLNU p < 0.05, AUC 0.64 [0.53–0.75] | ||||||
| After elastic net regularization, with only compacity significant to Cox model fitting, AUC = 0.80 | ||||||
| Yi-Quan et al. 2021 [25] | To predict MVI preoperatively | 110 | 110 | 0.980 (CI 0.959–0.993) | 0.906 (CI 0.821–0.960) | |
| Author/Year | Study Objectives | Training Set Sample Size | Validation Set Sample Size | Performance (Training Set) [95%CI] | Performance (Validation Set) [95%CI] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zhang et al. 2019 [26] | To predict early recurrence Gadoxetic acid-enhanced MR (1-year follow-up). | 108 | 47 | AUC: 0.844 [0.769–0.919] | ||
| Chen et al. 2022 [27] | To develop and validate radiomics scores and a nomogram of gadolinium ethoxybenzyl-diethylenetriamine pentaacetic acid enhanced MRI for preoperative prediction of MVI in sHCC. | 94 | 100 | The AUC of HBP was 0.979, 0.970, and 0.803, respectively, and the AUC of DWI was 0.971, 0.816, and 0.801 (p < 0.05), respectively. Good calibration and discrimination of the radiomics and clinical combined nomogram model were exhibited in the testing and two external validation cohorts (C-index of HBP and DWI were 0.971, 0.912, 0.808, and 0.970, 0.843, 0.869, respectively). | ||
| Chen et al. 2021 [28] | To determine the best model for predicting MVI of HCC using conventional gadolinium-ethoxybenzyl-diethylenetriamine pentaacetic acid (gadoxetate disodium)-enhanced MRI features and radiomics signatures with machine learning. | 188 | 81 | ADC value, non-smooth tumor margin, and 20-minute T1 relaxation time showed diagnostic accuracy with AUC values of 0.850, 0.847, and 0.846, respectively (p < 0.05 for all). | ||
| Kim et al. 2019 [29] | To predict the early and late recurrence of single HCC gadoextic acid-enhanced MR (<2 years vs. >2 years). | 128 | 39 | Combined clinicopathologic-radiomic model with 3-mm border extension showed highest c-index: 0.716 [0.627–0.799]; clinicopathologic model: 0.696 [0.557–0.799]. | ||
| Hui et al. 2018 [30] | To predict early recurrence (730 days). | 50 | - | 84% accuracy | ||
| Chong et al. 2021 [31] | To predict preoperative MVI and RFS. | 230 | 99 | C-indices of 0.700 (0.638–0.763)/C-indices of 0.673 (0.570–0.776) AUCs: 0.920 (0.861–0.979) | ||
| Author/Year | Study Objectives | Training Set Sample Size | Validation Set Sample Size | Performance (Training Set) [95%CI] | Performance (Validation Set) [95%CI] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Liao et al. 2019 [32] | To associate with CD8+ T cells | 100 | 42 | AUC 0.751 [0.656–0.846] | AUC 0.705 [0.547–0.863] | |
| Ni et al. 2019 [33] | To diagnose MVI. | 148 | 58 | The AUCs of the 21 methods ranged from 0.63 to 0.88. | ||
| Mokrane et al. 2019 [34] | To diagnose HCC in cirrhotic patients with indeterminate liver nodules. | 142 | 36 | AUC: 0.70 [0.61–0.80] | AUC: 0.66 [0.64–0.84] | |
| Xu et al. 2019 [13] | To associate with MVI. | 495 | - | AUC: 0.909 in training/validation. | AUC: 0.889 (test setting). | |
| Bakr et al. 2017 [35] | To associate with MVI. | 28 | - | Slight to moderate agreement (Cohen's kappa range: 0.03 to 0.59) | ||
| Ma et al. 2019 [36] | To associate with MVI. | 110 | 47 | C-indices: 0.827 | C-indices: 0.820 | |
| Peng et al. 2018 [37] | To associate with MVI | 184 | 120 | C-index 0.846 [0.787–0.905] | C-index 0.844 [0.77–0.915] | |
| Author/Year | Study Objectives | Training Set Sample Size | Validation Set Sample Size | Performance (Training Set) [95%CI] | Performance (Validation set) [95%CI] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gao et al. 2019 [38] | To associate with pathological grading (non-contrast MR). | 125 | 45 | AUC: 0.909 | AUC: 0.800 |
| Wu et al. 2019 [39] | To differentiate HCC and hepatic hemangioma (non-contrast MR). | 295 | 74 | AUC: 0.86 | AUC: 0.89 |
| Chen et al. 2019 [40] | To associate with immuno-score in HCC (with Gd-EOB-DTPA MR). | 150 | 57 | The combined radiomics-based clinical model AUC: 0.926 [0.884–0.967] The combined radiomics model AUC: 0.904 [0·855–0·953]. | Confirmed |
| Wu et al. 2019 [41] | To associate the grade of HCC with non-contrast-enhanced MR. | 125 | 45 | Clinical factor AUC: 0.600 Radiomics signatures AUC: 0.742 the combined clinical and radiomics signature AUC: 0.800 | |
| Author/Year | Study Objectives | Training Set Sample Size | Validation Set Sample Size | Performance (Training Set) [95%CI] | Performance (Validation set) [95%CI] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hu et al. 2019 [42] | To associate with MVI in HCC (contrast-enhanced ultrasound). | 341 | 141 | AUC: 0.731 [0.647, 0.815] | |
| Yao et al. 2018 [43] | To diagnose HCC and predict PD-1, Ki67, and MVI. | 177 | AUC: 0.94 [0.88-0.98] for benign and malignant classification, AUC: 0.97 [0.93–0.99] for malignant subtyping, AUC: 0.97 [0.89–0.98] for PD-1 prediction, AUC: 0.94 [0.87–0.97] for Ki-67 prediction, and AUC: 0.98 [0.93–0.99] for MVI prediction. | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bodard, S.; Liu, Y.; Guinebert, S.; Kherabi, Y.; Asselah, T. Performance of Radiomics in Microvascular Invasion Risk Stratification and Prognostic Assessment in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Meta-Analysis. Cancers 2023, 15, 743. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15030743
Bodard S, Liu Y, Guinebert S, Kherabi Y, Asselah T. Performance of Radiomics in Microvascular Invasion Risk Stratification and Prognostic Assessment in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Meta-Analysis. Cancers. 2023; 15(3):743. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15030743
Chicago/Turabian StyleBodard, Sylvain, Yan Liu, Sylvain Guinebert, Yousra Kherabi, and Tarik Asselah. 2023. "Performance of Radiomics in Microvascular Invasion Risk Stratification and Prognostic Assessment in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Meta-Analysis" Cancers 15, no. 3: 743. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15030743
APA StyleBodard, S., Liu, Y., Guinebert, S., Kherabi, Y., & Asselah, T. (2023). Performance of Radiomics in Microvascular Invasion Risk Stratification and Prognostic Assessment in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Meta-Analysis. Cancers, 15(3), 743. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15030743






