Urinary PSA and Serum PSA for Aggressive Prostate Cancer Detection
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods and Materials
2.1. Urine Samples and PSA Assay
2.2. Human Metastatic and Non-Metastatic Tissue Samples
2.3. IHC Staining for Tissue
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
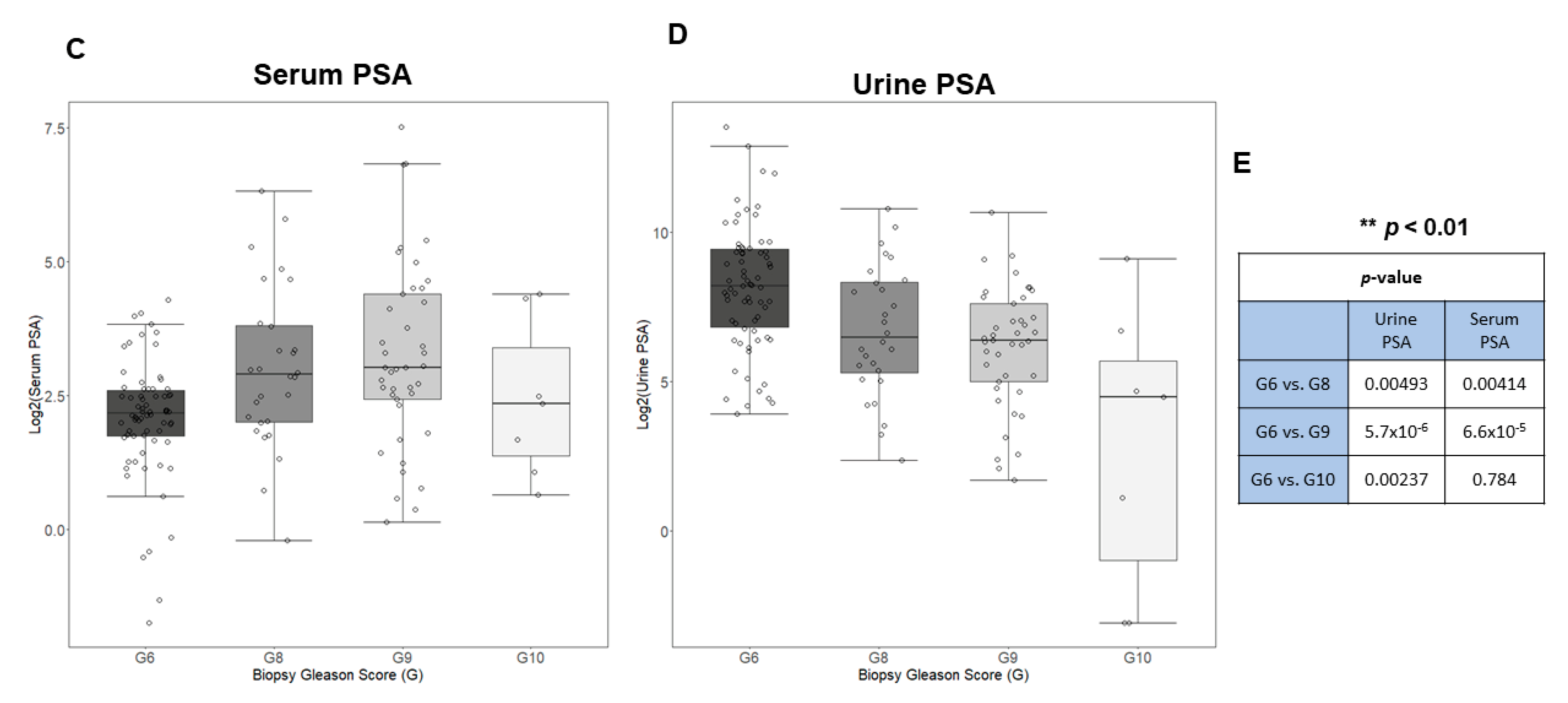
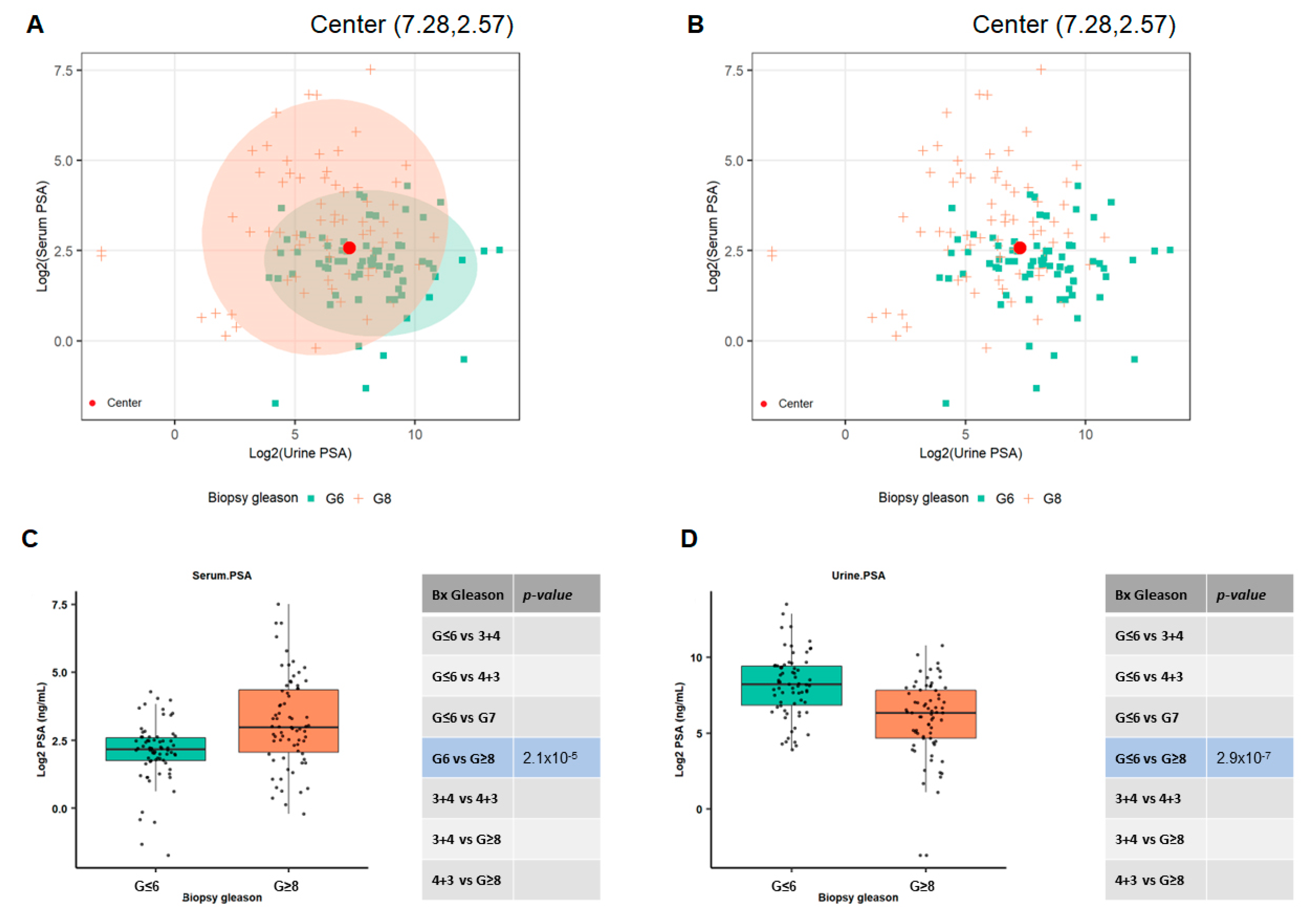
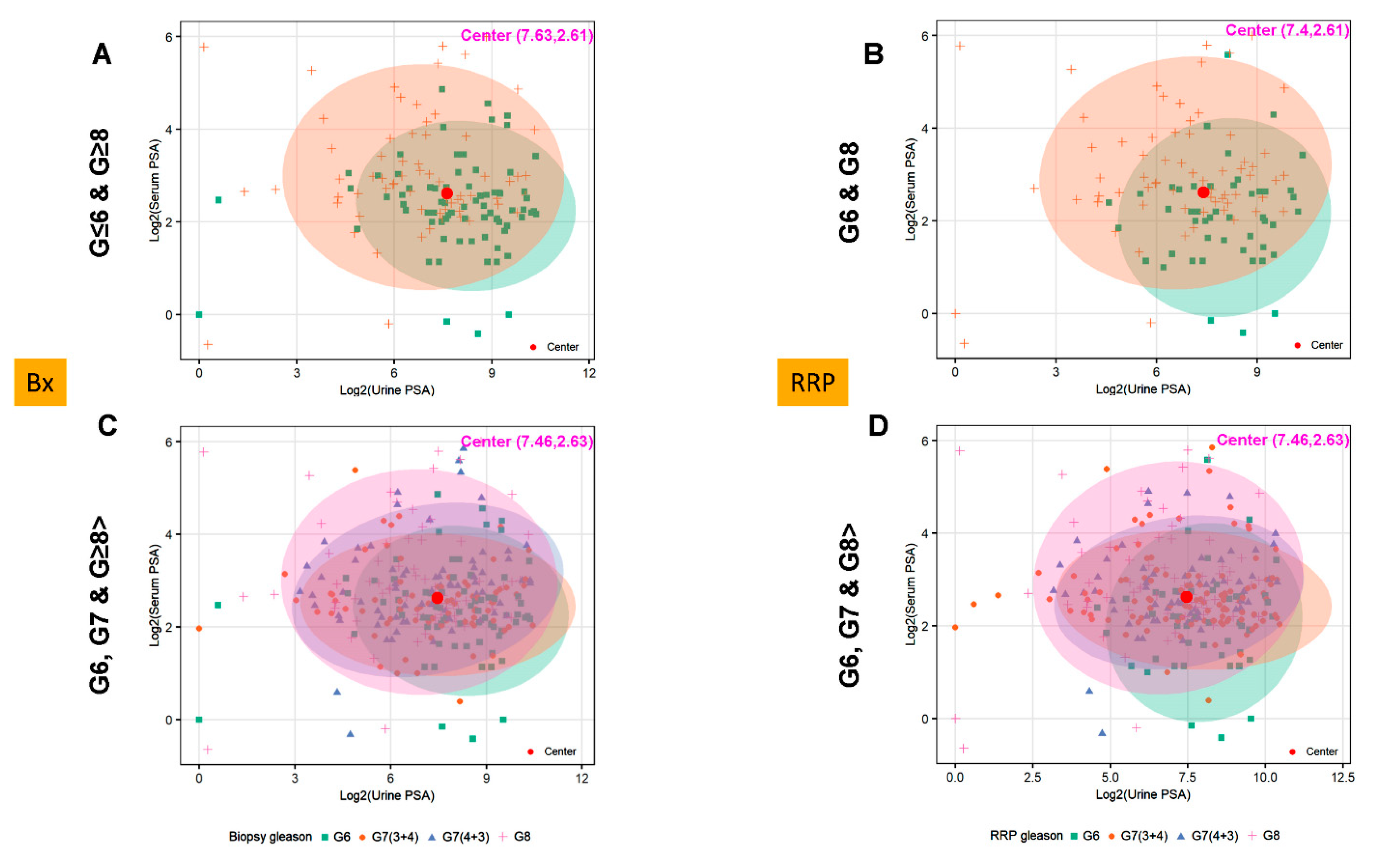
3.1. Urine and Serum PSA in Aggressive and Non-Aggressive Prostate Cancer
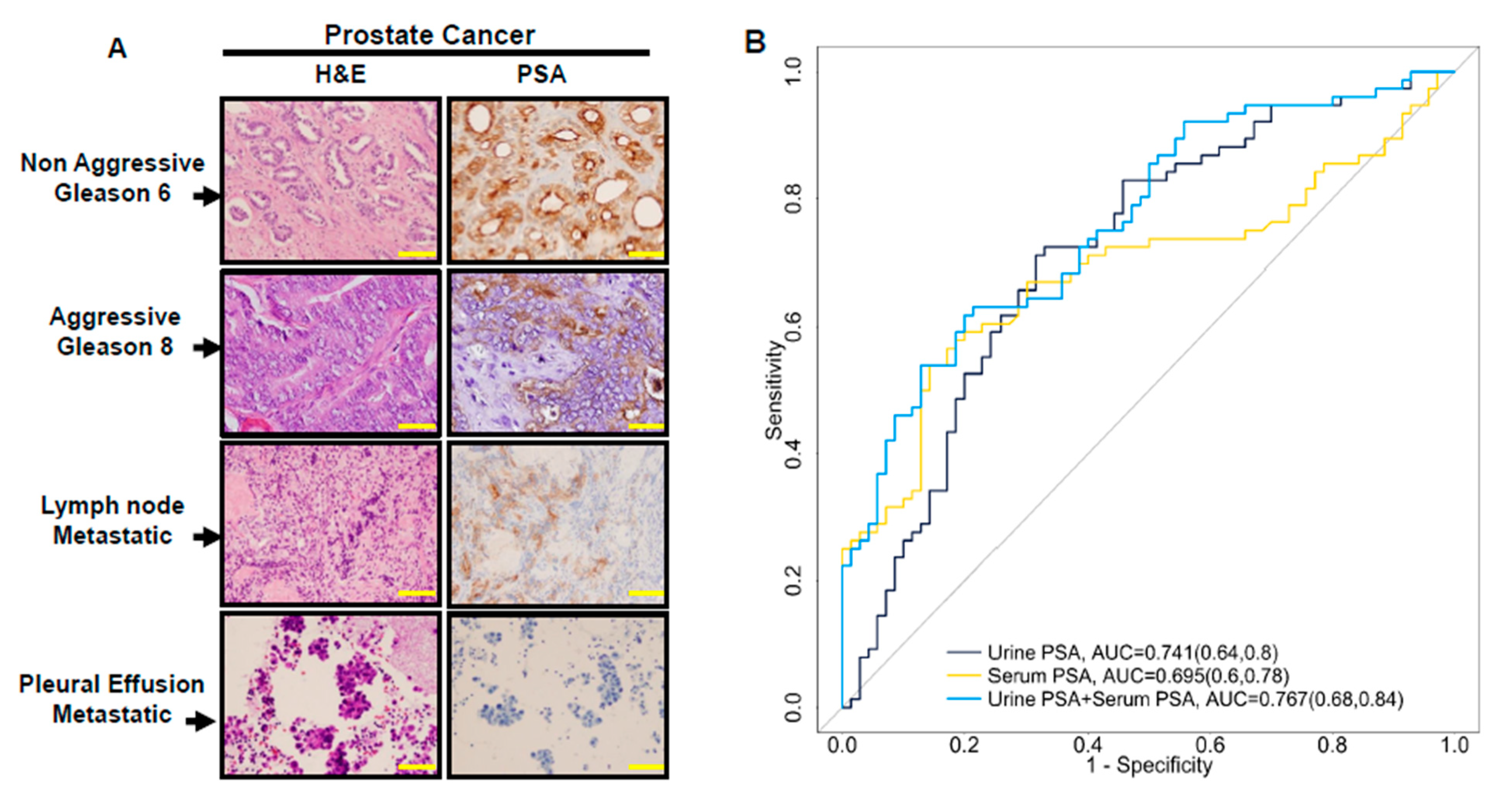
3.2. Urine PSA—A Proxy for PSA Level in Prostate Cancer Tissue
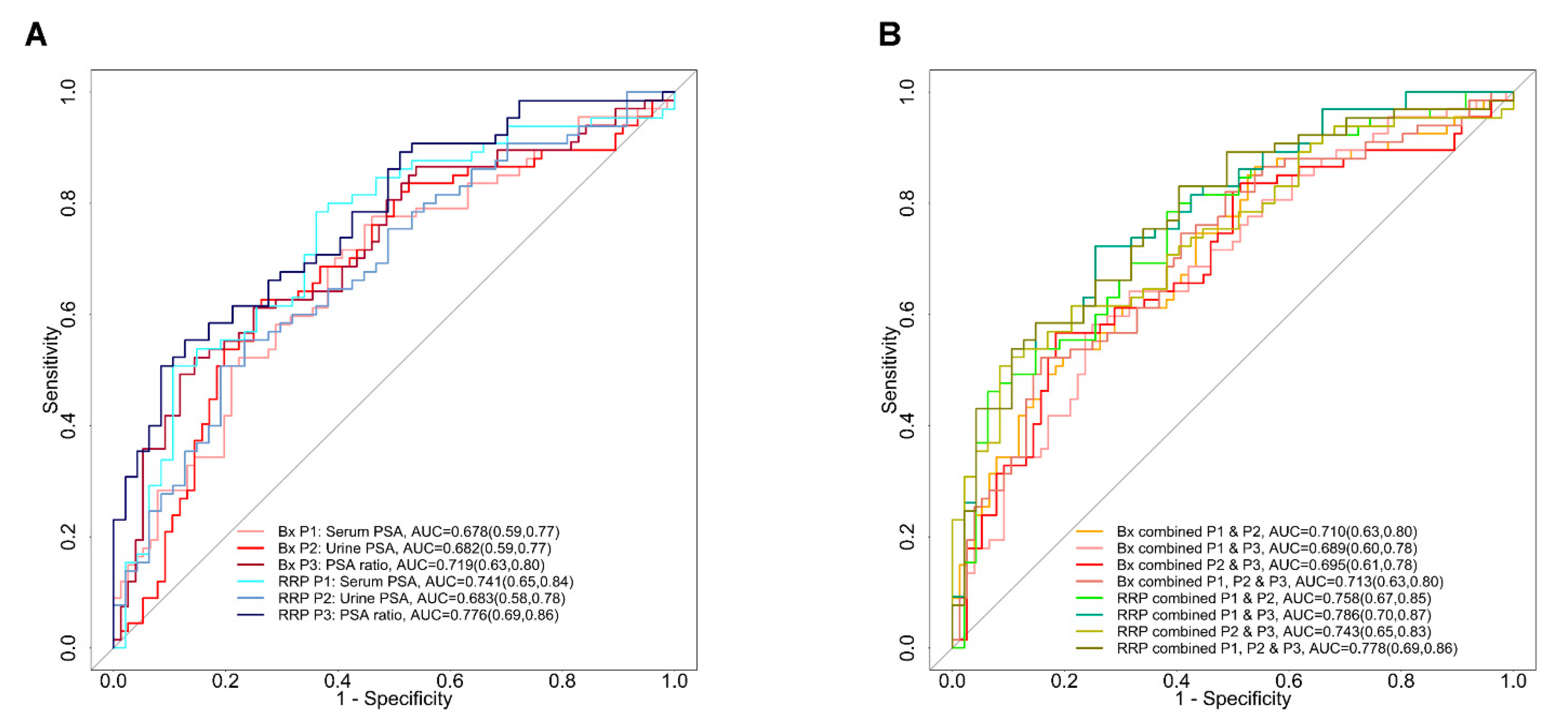
3.3. The Combination of Serum and Urine PSA in Predicating Aggressive Prostate Cancer
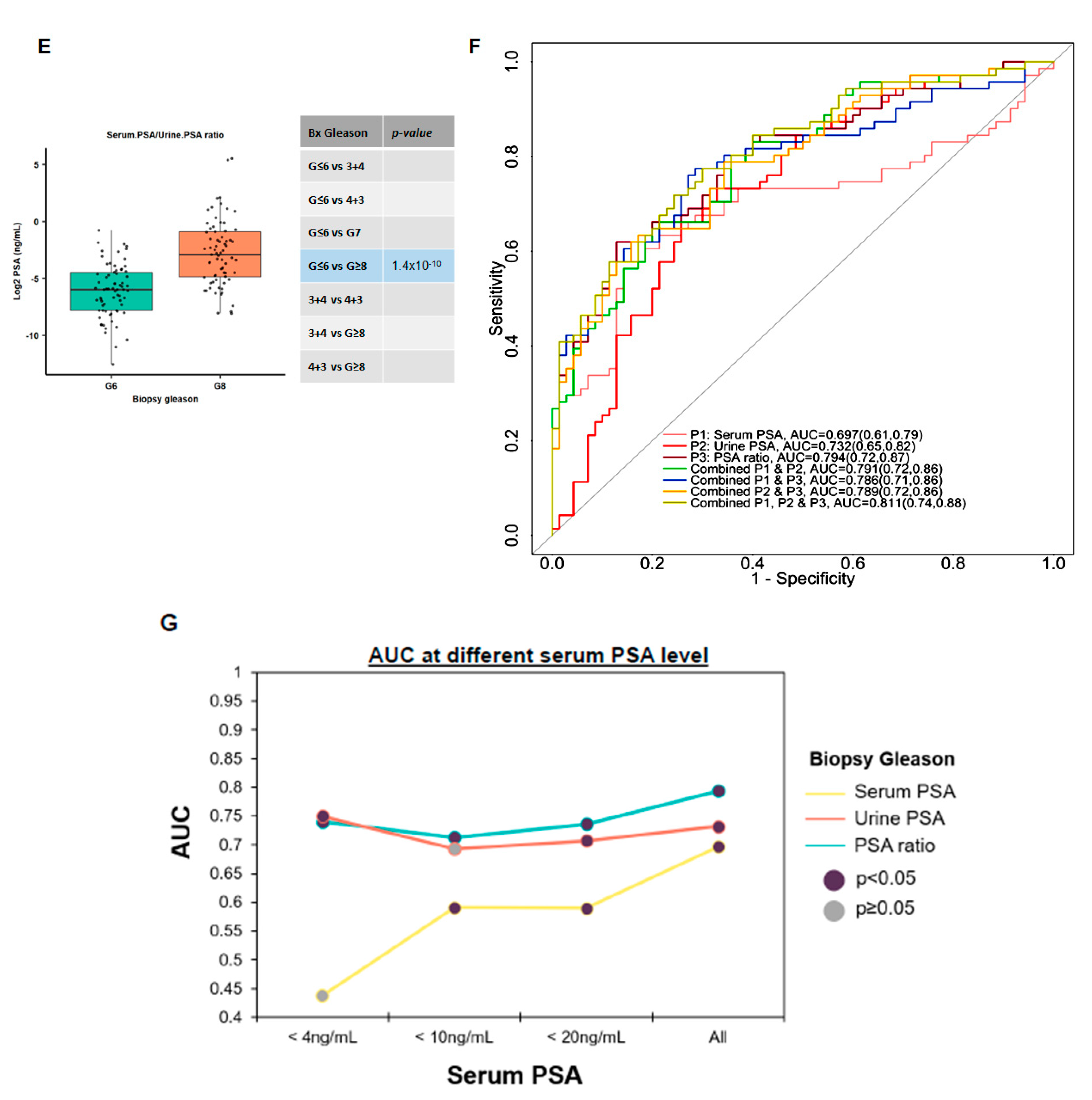
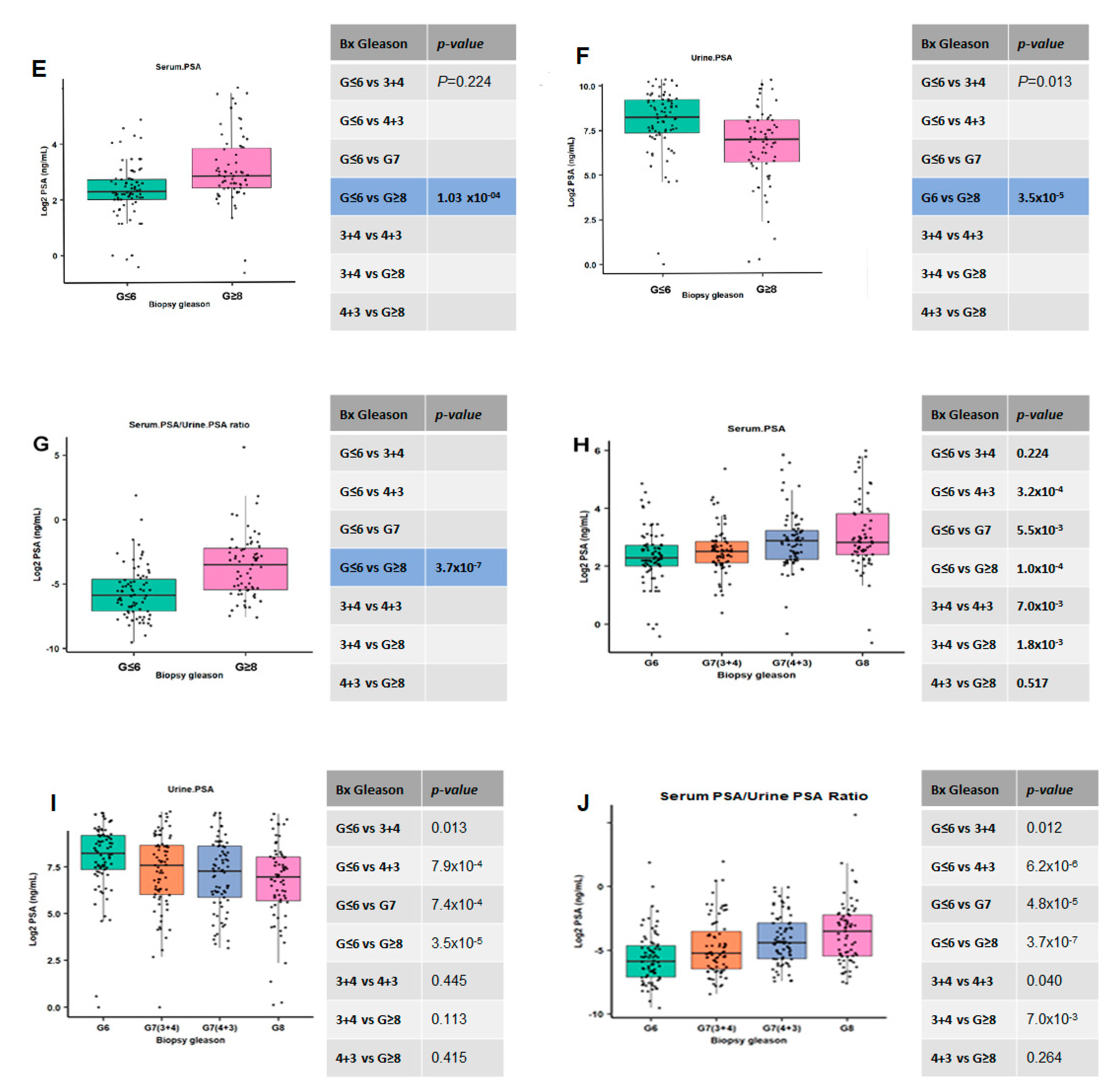
3.4. Utilizing Serum and Urinary PSA Ratio for Discriminating Aggressive (AG) from Non-Aggressive (NAG) Disease
3.5. Ratios of Serum to Urine PSA Levels in Predicting the Biopsy and Radical Prostatectomy-Based Gleason Outcomes
3.6. Evaluating the Performance of Serum to Urine Alone and Their Ratios across Different Gleason Scores
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pinsky, P.F.; Prorok, P.C.; Kramer, B.S. Prostate Cancer Screening — A Perspective on the Current State of the Evidence. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 1285–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duffy, M.J. Biomarkers for prostate cancer: Prostate-specific antigen and beyond. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2019, 58, 326–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prcic, A.; Begic, E. Hiros Usefulness of Total PSA Value in Prostate Diseases Diagnosis. Acta Inform. Medica 2016, 24, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stamey, T.A.; Yang, N.; Hay, A.R.; McNeal, J.E.; Freiha, F.S.; Redwine, E. Prostate-Specific Antigen as a Serum Marker for Adenocarcinoma of the Prostate. N. Engl. J. Med. 1987, 317, 909–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balk, S.P.; Ko, Y.-J.; Bubley, G.J. Biology of Prostate-Specific Antigen. J. Clin. Oncol. 2003, 21, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schalken, J. Molecular and cellular prostate biology: Origin of prostate-specific antigen expression and implications for benign prostatic hyperplasia. BJU Int. 2004, 93, 5–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denmeade, S.R.; Litvinov, I.; Sokoll, L.J.; Lilja, H.; Isaacs, J.T. Prostate-specific antigen (PSA) protein does not affect growth of prostate cancer cells in vitro or prostate cancer xenografts in vivo. Prostate 2003, 56, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weir, E.G.; Partin, A.W.; Epstein, J.I. Correlation of serum prostate specific antigen and quantitative immunohistochemis-try. J. Urol. 2000, 163, 1739–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Occhipinti, S.; Mengozzi, G.; Oderda, M.; Zitella, A.; Molinaro, L.; Novelli, F.; Giovarelli, M.; Gontero, P. Low Levels of Urinary PSA Better Identify Prostate Cancer Patients. Cancers 2021, 13, 3570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moyer, V.A. Screening for Prostate Cancer: U.S. Preventive Services Task Force Recommendation Statement. Ann. Intern. Med. 2012, 157, 120–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bibbins-Domingo, K.; Grossman, D.C.; Curry, S.J. The US Preventive Services Task Force 2017 Draft Recommendation Statement on Screening for Prostate Cancer. JAMA 2017, 317, 1949–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayan, V.M.; Konety, B.R.; Warlick, C. Novel biomarkers for prostate cancer: An evidence-based review for use in clinical practice. Int. J. Urol. 2017, 24, 352–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, C.E.; Sexton, W.; Benson, K.; Sutphen, R.; Koomen, J. Urine Collection and Processing for Protein Biomarker Discovery and Quantification. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2010, 19, 953–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harpole, M.; Davis, J.; Espina, V. Current state of the art for enhancing urine biomarker discovery. Expert Rev. Proteom. 2016, 13, 609–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selman, S.H. The McNeal Prostate: A Review. Urology 2011, 78, 1224–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, A.H. The Prostate Gland: A Review of its Anatomy, Pathology, and Treatment. JAMA 2014, 312, 562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Minno, A.; Aveta, A.; Gelzo, M.; Tripodi, L.; Pandolfo, S.D.; Crocetto, F.; Imbimbo, C.; Castaldo, G. 8-Hydroxy-2-Deoxyguanosine and 8-Iso-Prostaglandin F2α: Putative Biomarkers to assess Oxidative Stress Damage Following Robot-Assisted Radical Prostatectomy (RARP). J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 6102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höti, N.; Lih, T.-S.; Pan, J.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, G.; Deng, A.; Chen, L.; Dong, M.; Yang, R.-B.; Tu, C.-F.; et al. A Comprehensive Analysis of FUT8 Overexpressing Prostate Cancer Cells Reveals the Role of EGFR in Castration Resistance. Cancers 2020, 12, 468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Höti, N.; Shah, P.; Hu, Y.; Yang, S.; Zhang, H. Proteomics analyses of prostate cancer cells reveal cellular pathways associated with androgen resistance. Proteomics 2017, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höti, N.; Yang, S.; Aiyetan, P.; Kumar, B.; Hu, Y.; Clark, D.; Eroglu, A.U.; Shah, P.; Johnson, T.; Chowdery, W.H.; et al. Overexpression of Exportin-5 Overrides the Inhibitory Effect of miRNAs Regulation Control and Stabilize Proteins via Posttranslation Modifications in Prostate Cancer. Neoplasia 2017, 19, 817–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Partin, A.W.; Hanks, G.E.; Klein, E.A.; Moul, J.W.; Nelson, W.G.; Scher, H.I. Prostate-specific antigen as a marker of disease activity in prostate cancer. Oncology (Williston Park) 2002, 16, 1024–1038, 1042; discussion 1042, 1047–1028, 1051. [Google Scholar]
- Oldenburg, J.; Bjerner, J.L.; Lilja, H.; Aas, K.; Fossa, S.D.; Mueller, C.; Mueller, S.; Thomas, O.; Stensvold, A.; Walz, J.; et al. Long-term predictive value of serum PSA values obtained in clinical practice: Results from the Norwegian Prostate Cancer Consortium (NPCC). J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 5021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albertsen, P.C. Is screening for prostate cancer with prostate specific antigen an appropriate public health measure? Acta Oncol. 2005, 44, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.P.; E Staggers, F.; Roach, M. Benefits and pitfalls of prostate cancer screening: "no proof of benefit" does not equal "proof of no benefit". Oncology 2011, 25, 466, 468. [Google Scholar]
- Croswell, J.M.; Kramer, B.S.; Crawford, E.D. Screening for prostate cancer with PSA testing: Current status and future direc-tions. Oncology (Williston Park) 2011, 25, 452–460, 463. [Google Scholar]
- Noguez, J.H.; Fantz, C.R. Pathology Consultation on Prostate-Specific Antigen Testing. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2014, 142, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Björk, T.; Piironen, T.; Pettersson, K.; Lövgren, T.; Stenman, U.-H.; Oesterling, J.E.; Abrahamsson, P.-A.; Lilja, H. Comparison of analysis of the different prostate-specific antigen forms in serum for detection of clinically localized prostate cancer. Urology 1996, 48, 882–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadler, R.B.; Humphrey, P.A.; Smith, D.S.; Catalona, W.J.; Ratliff, T.L. Effect of Inflammation and Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia on Elevated Serum Prostate Specific Antigen Levels. J. Urol. 1995, 154, 407–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christensson, A.; Björk, T.; Nilsson, O.; Dahlén, U.; Matikainen, M.-T.; Cockett, A.T.; Abrahamsson, P.-A.; Lilja, H. Serum Prostate Specific Antigen Complexed to α1-Antichymotrypsin as an Indicator of Prostate Cancer. J. Urol. 1993, 150, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herschman, J.D.; Smith, D.S.; Catalona, W.J. Effect of ejaculation on serum total and free prostate-specific antigen concentrations. Urology 1997, 50, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tchetgen, M.-B.; Song, J.T.; Strawderman, M.; Jacobsen, S.J.; Oesterling, J.E. Ejaculation increases the serum prostate-specific antigen concentration. Urology 1996, 47, 511–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchetgen, M.-B.N.; Oesterling, J.E. The Effect of Prostatitis, Urinary Retention, Ejaculation, and Ambulation on the Serum Prostate-Specific Antigen Concentration. Urol. Clin. N. Am. 1997, 24, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desai, M.R.; Manohar, T.; Bapat, S.; Ganpule, A.P. Age-specific prostate specific antigen and prostate specific antigen density values in a community-based Indian population. Indian J. Urol. 2007, 23, 122–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loizzo, D.; Pandolfo, S.D.; Rogers, D.; Cerrato, C.; di Meo, N.A.; Autorino, R.; Mirone, V.; Ferro, M.; Porta, C.; Stella, A.; et al. Novel Insights into Autophagy and Prostate Cancer: A Comprehensive Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.G.; Liu, X.M.; Kreis, W.; Budman, D.R. Down-regulation of prostate-specific antigen expression by finasteride through inhibition of complex formation between androgen receptor and steroid receptor-binding consensus in the pro-moter of the PSA gene in LNCaP cells. Cancer Res. 1997, 57, 714–719. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dong, M.; Lih, T.M.; Chen, S.-Y.; Cho, K.-C.; Eguez, R.V.; Höti, N.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, W.; Mangold, L.; Chan, D.W.; et al. Urinary glycoproteins associated with aggressive prostate cancer. Theranostics 2020, 10, 11892–11907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, M.; Lih, T.-S.M.; Höti, N.; Chen, S.-Y.; Ponce, S.; Partin, A.; Zhang, H. Development of Parallel Reaction Monitoring Assays for the Detection of Aggressive Prostate Cancer Using Urinary Glycoproteins. J. Proteome Res. 2021, 20, 3590–3599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Höti, N.; Lih, T.-S.M.; Sokoll, L.J.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Chan, D.W. Development of a glycoproteomic strategy to detect more aggressive prostate cancer using lectin-immunoassays for serum fucosylated PSA. Clin. Proteom. 2019, 16, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höti, N.; Li, Y.; Chen, C.-L.; Chowdhury, W.; Johns, D.C.; Xia, Q.; Kabul, A.; Hsieh, J.-T.; Berg, M.; Ketner, G.; et al. Androgen Receptor Attenuation of Ad5 Replication: Implications for the Development of Conditionally Replication Competent Adenoviruses. Mol. Ther. 2007, 15, 1495–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanda, M.G.; Feng, Z.; Howard, D.H.; Tomlins, S.A.; Sokoll, L.J.; Chan, D.W.; Regan, M.M.; Groskopf, J.; Chipman, J.; Patil, D.H.; et al. Association Between Combined TMPRSS2:ERG and PCA3 RNA Urinary Testing and Detection of Aggressive Prostate Cancer. JAMA Oncol. 2017, 3, 1085–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomlins, S.A.; Day, J.R.; Lonigro, R.J.; Hovelson, D.H.; Siddiqui, J.; Kunju, L.P.; Dunn, R.L.; Meyer, S.; Hodge, P.; Groskopf, J.; et al. Urine TMPRSS2:ERG Plus PCA3 for Individualized Prostate Cancer Risk Assessment. Eur. Urol. 2015, 70, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Höti, N.; Lih, T.-S.; Dong, M.; Zhang, Z.; Mangold, L.; Partin, A.W.; Sokoll, L.J.; Kay Li, Q.; Zhang, H. Urinary PSA and Serum PSA for Aggressive Prostate Cancer Detection. Cancers 2023, 15, 960. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15030960
Höti N, Lih T-S, Dong M, Zhang Z, Mangold L, Partin AW, Sokoll LJ, Kay Li Q, Zhang H. Urinary PSA and Serum PSA for Aggressive Prostate Cancer Detection. Cancers. 2023; 15(3):960. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15030960
Chicago/Turabian StyleHöti, Naseruddin, Tung-Shing Lih, Mingming Dong, Zhen Zhang, Leslie Mangold, Alan W. Partin, Lori J. Sokoll, Qing Kay Li, and Hui Zhang. 2023. "Urinary PSA and Serum PSA for Aggressive Prostate Cancer Detection" Cancers 15, no. 3: 960. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15030960
APA StyleHöti, N., Lih, T.-S., Dong, M., Zhang, Z., Mangold, L., Partin, A. W., Sokoll, L. J., Kay Li, Q., & Zhang, H. (2023). Urinary PSA and Serum PSA for Aggressive Prostate Cancer Detection. Cancers, 15(3), 960. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15030960





