Lenalidomide in Multiple Myeloma: Review of Resistance Mechanisms, Current Treatment Strategies and Future Perspectives
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Characteristics of Lenalidomide
2.1. Overall Characteristic of Lenalidomide
2.2. Chemical Structure of IMiDs
3. Resistance to Lenalidomide
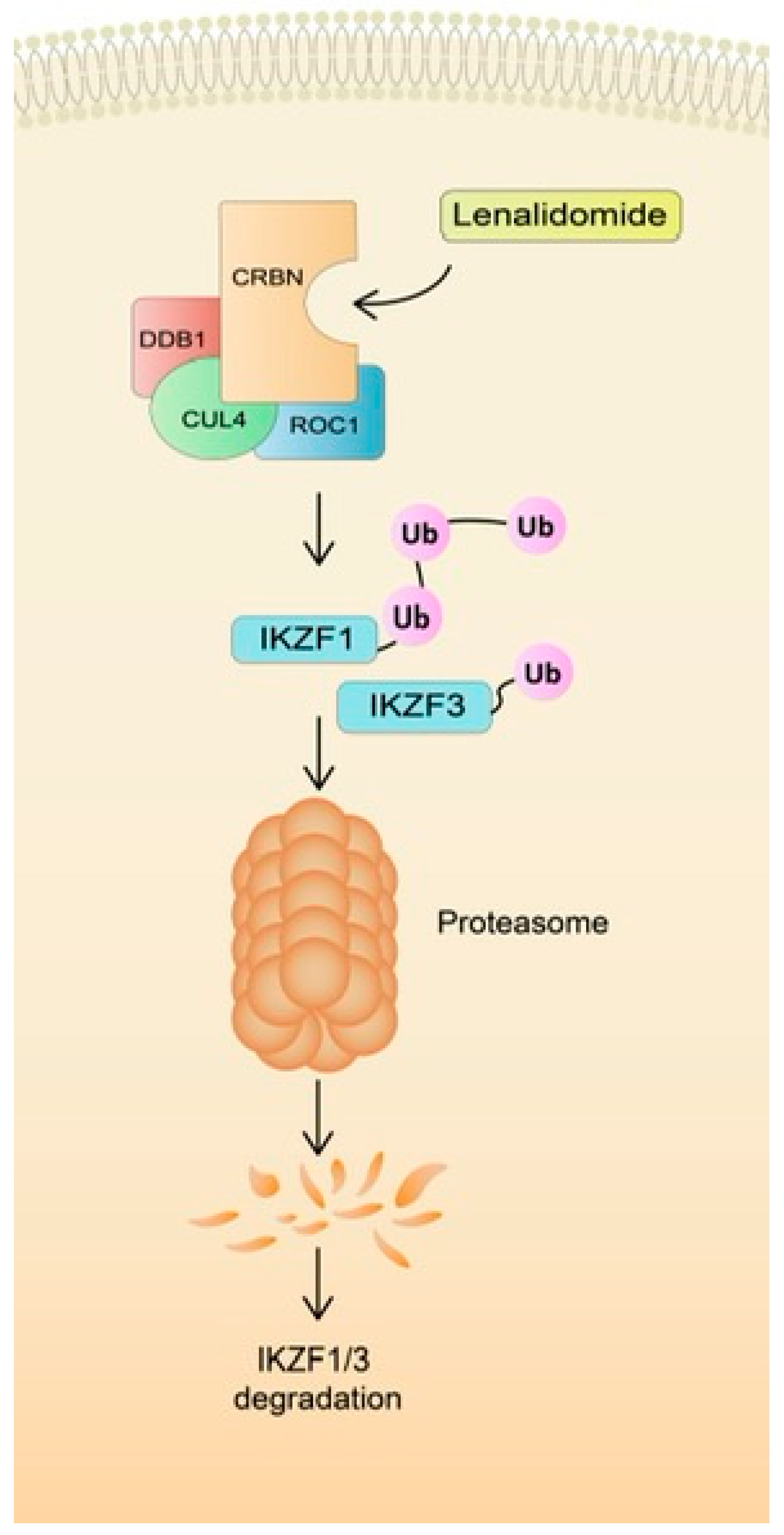
3.1. Role of CRBN Suppression in the Development of LEN Resistance
3.2. Role of Mutations in CRBN and Genes Encoding Related Downstream Proteins in LEN Resistance
3.3. Role of Epigenetics in the LEN Resistance Development
3.4. The Expression Pattern of Certain Surface Antigens Associated with Diminished LEN Sensitivity
3.5. Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway
3.6. Miscellaneous
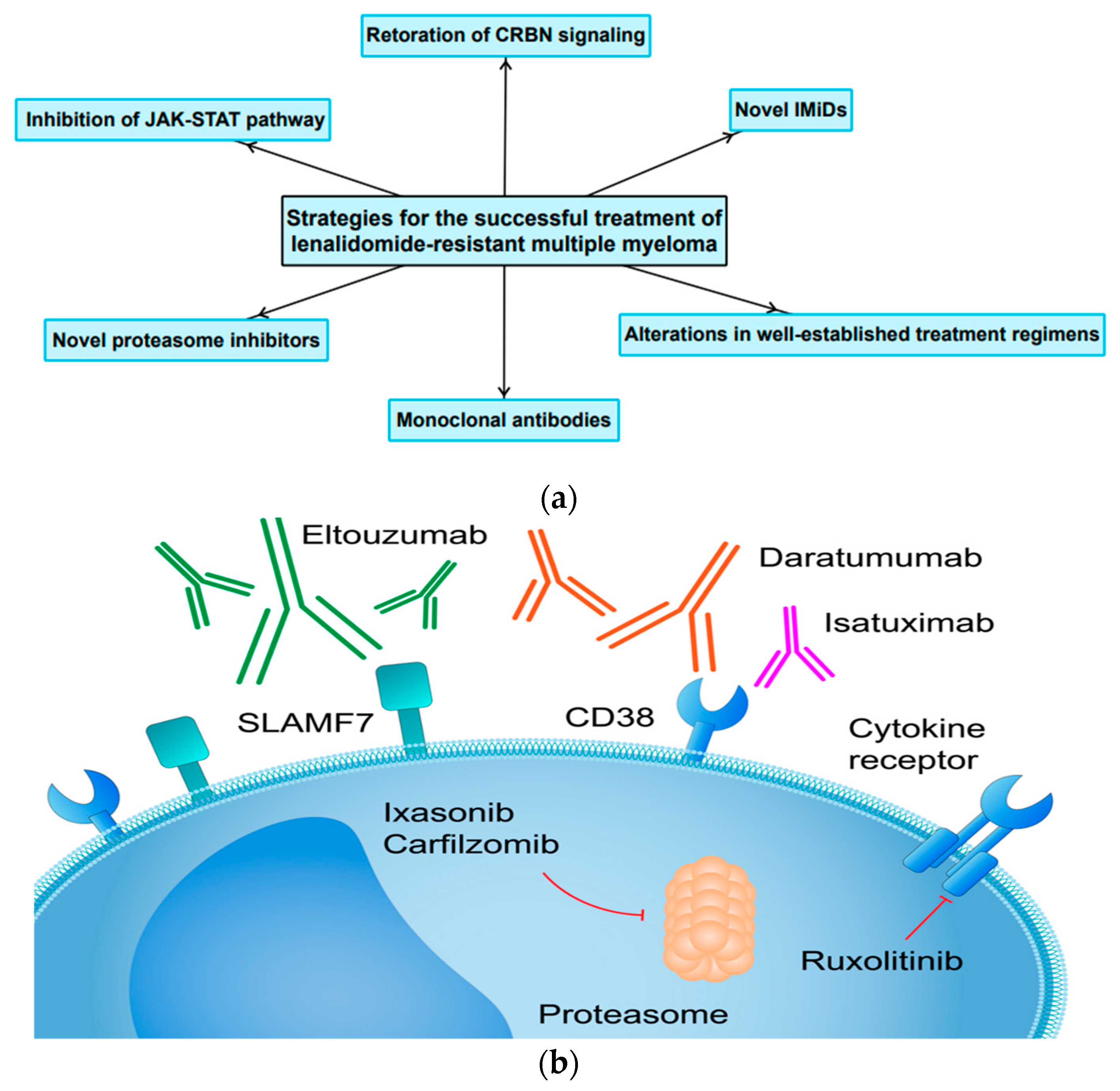
4. Current Therapeutic Strategies and Future Perspectives
4.1. Restoration or Modulation of CRBN Signaling in Resynthesis of MM Cells to IMiDs
4.2. Lack of Cross-Resistance within the Immunomodulatory Drug Class
4.3. Unconventional Changes to Already Existing Treatment Regimens for LEN-Resistant MM
4.4. The Application of Monoclonal Antibodies and Novel Proteasome Inhibitors in Patients with LEN-Resistant MM
4.5. The Role of JAK-STAT Pathway
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancerstatistics, 2016 Cancer Statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2016, 66, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazandjian, D. Multiplemyeloma Epidemiology survival: A unique malignancy. Semin. Oncol. 2016, 43, 676–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorsteinsdottir, S.; Dickman, P.W.; Landgren, O.; Blimark, C.; Hultcrantz, M.; Turesson, I.; Björkholm, M.; Kristinsson, S.Y. Dramatically improved Survival multiple myeloma patients Recent decade Results Swedish population-based study. Haematologica 2018, 103, e412–e415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Speirs, A. Thalidomide and congenital abnormalities. Lancet 1962, 279, 303–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Frezza, M.; Schmitt, S.; Kanwar, J.P.; Dou, Q. Bortezomib First Proteasome Inhibitor Anticancer Drug: Current Status Future Perspectives. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2011, 11, 239–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreau, P.; Hulin, C.; Macro, M.; Caillot, D.; Chaleteix, C.; Roussel, M.; Garderet, L.; Royer, B.; Brechignac, S.; Tiab, M.; et al. VTD is superior to VCD prior to intensive therapy in multiple myeloma: Results of the prospective IFM2013-04 trial. Blood 2016, 127, 2569–2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koeppen, S. Treatment of multiple myeloma: Thalidomide-, bortezomib-, and lenalidomide-induced peripheral neuropathy. Oncol. Res. Treat. 2014, 37, 506–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ao, L.; Wu, Y.; Kim, D.; Jang, E.R.; Kim, K.; Lee, D.; Kim, K.B.; Lee, W. Development Peptide-Based Reversing Agents PG lycoprotein Mediated Resistance Carfilzomib. Mol. Pharm. 2012, 9, 2197–2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, J.; Salama, N.N.; Azab, A.K. Therole P-glycoprotein Drug resistance multiple myeloma. Leuk. Lymphoma 2015, 56, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukowski, K.; Kciuk, M.; Kontek, R. Mechanisms Multidrug ResistanceCancerChemotherapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, T.; Pandey, V.; Banjare, N.; Gupta, P.N.; Soni, V. Drugresistance cancer: Mechanisms Tackling strategies. Pharmacol. Rep. 2020, 72, 1125–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longley, D.; Johnston, P. Molecularmechanisms drug resistance. J. Pathol. 2005, 205, 275–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holohan, C.; Van Schaeybroeck, S.; Longley, D.B.; Johnston, P.G. Cancerdrug Resistance evolving paradigm. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2013, 13, 714–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hideshima, T.; Chauhan, D.; Shima, Y.; Raje, N.; Davies, F.E.; Tai, Y.T.; Treon, S.P.; Lin, B.; Schlossman, R.L.; Richardson, P.; et al. Thalidomide its analogs overcome drug resistance Human multiple Myeloma cells conventional therapy. Blood 2000, 96, 2943–2950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, P.G.; Schlossman, R.L.; Weller, E.; Hideshima, T.; Mitsiades, C.; Davies, F.; LeBlanc, R.; Catley, L.P.; Doss, D.; Kelly, K.; et al. Immunomodulatory drug CC5013 Overcomes drug Resistance is well tolerated Patients relapsed multiple myeloma. Blood 2002, 100, 3063–3067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajkumar, S.V.; Hayman, S.R.; Lacy, M.Q.; Dispenzieri, A.; Geyer, S.M.; Kabat, B.; Zeldenrust, S.R.; Kumar, S.; Greipp, P.R.; Fonseca, R.; et al. Combination therapy lenalidomide Dexamethasone (Rev/Dex) newly diagnosed myeloma. Blood 2005, 106, 4050–4053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, M.; Lewis, D.J. Implementation Pregnancy Prevention Programme (PPP) Controlled Distribution System (CDS) Generic Teratogenic Phthalimides Thalidomide, Lenalidomide Pomalidomide. Ther. Innov. Regul. Sci. 2021, 55, 1155–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, C.L.; Schumock, G.T.; Desai, A.A.; Kwaan, H.C.; Raisch, D.W.; Newlin, R.; Stadler, W. Thalidomide-associated deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism. Am. J. Med. 2002, 113, 603–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsh, J. Risk Thrombosis With Lenalidomide Its Prevention With Aspirin. Chest 2007, 131, 275–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, P.G.; Blood, E.; Mitsiades, C.S.; Jagannath, S.; Zeldenrust, S.R.; Alsina, M.; Schlossman, R.L.; Rajkumar, S.V.; Desikan, K.R.; Hideshima, T.; et al. Arandomized Phase2 Study lenalidomide therapy Patients relapsed Relapsed refractory multiple myeloma. Blood 2006, 108, 3458–3464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fonseca, R.; Rajkumar, S.V. Consolidation Therapy with Bortezomib/Lenalidomide/Dexamethasone Versus Bortezomib/Dexamethasone After a Dexamethasone-Based Induction Regimen in Patients with Multiple Myeloma: A Randomized Phase III Trial. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma 2008, 8, 315–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimopoulos, M.A.; Oriol, A.; Nahi, H.; San-Miguel, J.; Bahlis, N.J.; Usmani, S.Z.; Rabin, N.; Orlowski, R.Z.; Komarnicki, M.; Suzuki, K.; et al. Daratumumab, Lenalidomide, Dexamethasone Multiple Myeloma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 1319–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hazarika, M.; Rock, E.; Williams, G.; Dagher, R.; Sridhara, R.; Booth, B.; Farrell, A.; Justice, R.; Pazdur, R. Lenalidomide combination Dexamethasone treatment Multiple myeloma one prior therapy. Oncologist 2008, 13, 1120–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, N.; Zhou, S.; Palmisano, M. Clinical Pharmacokinetics Pharmacodynamics Lenalidomide. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2017, 56, 139–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kortüm, K.M.; Zhu, Y.X.; Shi, C.X.; Jedlowski, P.; Stewart, A.K. Cereblon binding molecules in multiple myeloma. Blood Rev. 2015, 29, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krönke, J.; Udeshi, N.D.; Narla, A.; Grauman, P.; Hurst, S.N.; McConkey, M.; Svinkina, T.; Heckl, D.; Comer, E.; Li, X.; et al. Lenalidomide Causes Selective Degradation IKZF1IKZF3 Multiple Myeloma Cells. Science 2014, 343, 301–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martiniani, R.; Di Loreto, V.; Di Sano, C.; Lombardo, A.; Liberati, A.M. Biological Activity Lenalidomide Its Underlying Therapeutic Effects Multiple Myeloma. Adv. Hematol. 2012, 2012, 842945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, D.; Corral, L.G.; Fleming, Y.W.; Stein, B. Immunomodulatory drugs Revlimid® (lenalidomide) CC-4047 induce apoptosis Both hematological solid tumor cells NK cell Activation. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2008, 57, 1849–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhi, A.K.; Kang, J.; Havens, C.G.; Conklin, T.; Ning, Y.; Wu, L.; Ito, T.; Ando, H.; Waldman, M.F.; Thakurta, A.; et al. Immunomodulatory agents lenalidomide and pomalidomide co-stimulate T cells by inducing degradation of T cell repressors Ikaros and Aiolos via modulation of the E3 ubiquitin ligase complex CRL4CRBN. Br. J. Haematol. 2014, 164, 811–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dredge, K.; Marriott, J.B.; Macdonald, C.D.; Man, H.-W.; Chen, R.; Muller, G.W.; Stirling, D.; Dalgleish, A.G. Novel thalidomide analogues display anti-angiogenic activity independently of immunomodulatory effects. Br. J. Cancer 2002, 87, 1166–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vacca, A.; Ria, R.; Reale, A.; Ribatti, D. Angiogenesis Multiple Myeloma. In Chemical Immunology and Allergy; Marone, G., Granata, F., Eds.; S. Karger AG: Basel, Switzerland, 2014; Volume 99, pp. 180–196. ISBN1 978-3-318-02480-7. ISBN2 978-3-318-02481-4. [Google Scholar]
- Sebastian, S.; Zhu, Y.X.; Braggio, E.; Shi, C.-X.; Panchabhai, S.C.; Van Wier, S.A.; Ahmann, G.J.; Chesi, M.; Bergsagel, P.L.; Stewart, A.K.; et al. Multiplemyeloma Cells’ capacity decompose H2O2 determines lenalidomide sensitivity. Blood 2017, 129, 991–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, D.; Zhang, K.; Zhu, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Zou, L.; Hu, J.; Cui, Y.; Zhou, W.; Chen, F.; He, Y. Chidamide Induced Accumulation Reactive Oxygen Species Increases Lenalidomide Sensitivity Against Multiple Myeloma Cells. OncoTargets Ther. 2021, 14, 4061–4075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotla, V.; Goel, S.; Nischal, S.; Heuck, C.; Vivek, K.; Das, B.; Verma, A. Mechanism action Lenalidomide hematological malignancies. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2009, 2, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.X.; Kortuem, K.M.; Stewart, A.K. Molecular mechanism action Immunemodulatory Drugsthalidomide, Lenalidomide pomalidomide Multiplemyeloma. Leuk. Lymphoma 2013, 54, 683–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quach, H.; Ritchie, D.; Stewart, A.K.; Neeson, P.; Harrison, S.; Smyth, M.J.; Prince, H.M. Mechanism actionImmunomodulatorydrugs(IMiDS) multiple myeloma. Leukemia 2010, 24, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, F.; Baz, R. Lenalidomidemode action: Linking bench Clinical findings. Blood Rev. 2010, 24, S13–S19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Girona, A.; Mendy, D.; Ito, T.; Miller, K.; Gandhi, A.K.; Kang, J.; Karasawa, S.; Carmel, G.; Jackson, P.; Abbasian, M.; et al. Cereblonis direct protein target Immunomodulatory antiproliferative activities Lenalidomide pomalidomide. Leukemia 2012, 26, 2326–2335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.X.; Braggio, E.; Shi, C.-X.; Bruins, L.A.; Schmidt, J.E.; Van Wier, S.; Chang, X.-B.; Bjorklund, C.C.; Fonseca, R.; Bergsagel, P.L.; et al. Cereblon expression Isrequired antimyeloma activity Lenalidomide pomalidomide. Blood 2011, 118, 4771–4779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franssen, L.E.; Nijhof, I.S.; Couto, S.; Levin, M.-D.; Bos, G.M.J.; Broijl, A.; Klein, S.K.; Ren, Y.; Wang, M.; Koene, H.R.; et al. Cereblonloss-regulation Mycare Associated lenalidomide resistance Multiplemyeloma Patients. Haematologica 2018, 103, e368–e371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gooding, S.; Ansari-Pour, N.; Kazeroun, M.; Karagoz, K.; Polonskaia, A.; Salazar, M.; Fitzsimons, E.; Sirinukunwattana, K.; Chavda, S.; Ortiz Estevez, M.; et al. Loss COP9 signalosome genes 2q37 is Associated IMiD resistance Multiplemyeloma. Blood 2022, 140, 1816–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Song, T.; Zhou, W.; Xing, L.; Wang, S.; Ho, M.; Peng, Z.; Tai, Y.-T.; Hideshima, T.; Anderson, K.C.; et al. AgenomeScaleCRISPRCas9screening myeloma cells identifies regulators Immunomodulatory drug Sensitivity. Leukemia 2019, 33, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimopoulos, K.; Fibiger Munch-Petersen, H.; Winther Eskelund, C.; Dissing Sjö, L.; Ralfkiaer, E.; Gimsing, P.; Grønbaek, K. Expression of CRBN, IKZF1, and IKZF3 does not predict lenalidomide sensitivity and mutations in the cereblon pathway are infrequent in multiple myeloma. Leuk. Lymphoma 2019, 60, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gandhi, A.K.; Mendy, D.; Waldman, M.; Chen, G.; Rychak, E.; Miller, K.; Gaidarova, S.; Ren, Y.; Wang, M.; Breider, M.; et al. Measuring cereblon as a biomarker of response or resistance to lenalidomide and pomalidomide requires use of standardized reagents and understanding of gene complexity. Br. J. Haematol. 2014, 164, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heintel, D.; Rocci, A.; Ludwig, H.; Bolomsky, A.; Caltagirone, S.; Schreder, M.; Pfeifer, S.; Gisslinger, H.; Zojer, N.; Jäger, U.; et al. High expression of cereblon (CRBN) is associated with improved clinical response in patients with multiple myeloma treated with lenalidomide and dexamethasone. Br. J. Haematol. 2013, 161, 695–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, J.; Jones, R.J.; Wang, H.; Kuiatse, I.; Shirazi, F.; Manasanch, E.E.; Lee, H.C.; Sullivan, R.; Fung, L.; Richard, N.; et al. The novel protein homeostatic modulator BTX306 is active in myeloma and overcomes bortezomib and lenalidomide resistance. J. Mol. Med. 2020, 98, 1161–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kortüm, K.M.; Mai, E.K.; Hanafiah, N.H.; Shi, C.-X.; Zhu, Y.-X.; Bruins, L.; Barrio, S.; Jedlowski, P.; Merz, M.; Xu, J.; et al. Targeted sequencing of refractory myeloma reveals a high incidence of mutations in CRBN and Ras pathway genes. Blood 2016, 128, 1226–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gooding, S.; Ansari-Pour, N.; Towfic, F.; Ortiz Estévez, M.; Chamberlain, P.P.; Tsai, K.-T.; Flynt, E.; Hirst, M.; Rozelle, D.; Dhiman, P.; et al. Multiple cereblon genetic changes are associated with acquired resistance to lenalidomide or pomalidomide in multiple myeloma. Blood 2021, 137, 232–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrio, S.; Munawar, U.; Zhu, Y.X.; Giesen, N.; Shi, C.-X.; Viá, M.D.; Sanchez, R.; Bruins, L.; Demler, T.; Müller, N.; et al. IKZF1/3 and CRL4CRBN E3 ubiquitin ligase mutations and resistance to immunomodulatory drugs in multiple myeloma. Haematologica 2020, 105, e237–e241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.X.; Braggio, E.; Shi, C.-X.; Kortuem, K.M.; Bruins, L.A.; Schmidt, J.E.; Chang, X.-B.; Langlais, P.; Luo, M.; Jedlowski, P.; et al. Identification of cereblon-binding proteins and relationship with response and survival after IMiDs in multiple myeloma. Blood 2014, 124, 536–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, G.; Weng, S.; Matyskiela, M.; Zheng, X.; Fang, W.; Wood, S.; Surka, C.; Mizukoshi, R.; Lu, C.-C.; Mendy, D.; et al. UBE2G1 governs the destruction of cereblon neomorphic substrates. eLife 2018, 7, e40958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varshavsky, A. The Ubiquitin System, Immense Realm. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2012, 81, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.V. USP15 antagonizes CRL4CRBN-mediated ubiquitylation of glutamine synthetase and neosubstrates. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2111391118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimopoulos, K.; Søgaard Helbo, A.; Fibiger Munch-Petersen, H.; Sjö, L.; Christensen, J.; Sommer Kristensen, L.; Asmar, F.; Hermansen, N.E.U.; O’Connel, C.; Gimsing, P.; et al. Dual inhibition of DNMTs and EZH2 can overcome both intrinsic and acquired resistance of myeloma cells to IMiDs in a cereblon-independent manner. Mol. Oncol. 2018, 12, 180–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haertle, L.; Barrio, S.; Munawar, U.; Han, S.; Zhou, X.; Vogt, C.; Fernández, R.A.; Bittrich, M.; Ruiz-Heredia, Y.; Da Viá, M.; et al. Cereblon enhancer methylation and IMiD resistance in multiple myeloma. Blood 2021, 138, 1721–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakobsen, T.; Dahl, M.; Dimopoulos, K.; Grønbæk, K.; Kjems, J.; Kristensen, L.S. Genome-Wide Circular RNA Expression Patterns Reflect Resistance to Immunomodulatory Drugs in Multiple Myeloma Cells. Cancers 2021, 13, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caracciolo, D.; Riillo, C.; Juli, G.; Scionti, F.; Todoerti, K.; Polerà, N.; Grillone, K.; Fiorillo, L.; Arbitrio, M.; Di Martino, M.T.; et al. miR-22 Modulates Lenalidomide Activity by Counteracting MYC Addiction in Multiple Myeloma. Cancers 2021, 13, 4365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawano, Y.; Fujiwara, S.; Wada, N.; Izaki, M.; Yuki, H.; Okuno, Y.; Iyama, K.; Yamasaki, H.; Sakai, A.; Mitsuya, H.; et al. Multiple myeloma cells expressing low levels of CD138 have an immature phenotype and reduced sensitivity to lenalidomide. Int. J. Oncol. 2012, 41, 876–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjorklund, C.C.; Baladandayuthapani, V.; Lin, H.Y.; Jones, R.J.; Kuiatse, I.; Wang, H.; Yang, J.; Shah, J.J.; Thomas, S.K.; Wang, M.; et al. Evidence of a role for CD44 and cell adhesion in mediating resistance to lenalidomide in multiple myeloma: Therapeutic implications. Leukemia 2014, 28, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasche, L.; Menoret, E.; Dubljevic, V.; Menu, E.; Vanderkerken, K.; Lapa, C.; Steinbrunn, T.; Chatterjee, M.; Knop, S.; Düll, J.; et al. A GRP78-Directed Monoclonal Antibody Recaptures Response in Refractory Multiple Myeloma with Extramedullary Involvement. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 4341–4349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, I.D.; Patiño-Escobar, B.; Tuomivaara, S.T.; Lin, Y.-H.T.; Nix, M.A.; Leung, K.K.; Kasap, C.; Ramos, E.; Nieves Vasquez, W.; Talbot, A.; et al. The surfaceome of multiple myeloma cells suggests potential immunotherapeutic strategies and protein markers of drug resistance. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 4121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Xiao, Q.; Xiao, J.; Niu, C.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, Z.; Shu, G.; Yin, G. Wnt/β-catenin signalling: Function, biological mechanisms, and therapeutic opportunities. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, C.; Nayak, A.; Neitzel, L.R.; Adams, A.A.; Silver-Isenstadt, M.; Sawyer, L.M.; Benchabane, H.; Wang, H.; Bunnag, N.; Li, B.; et al. The E3 ubiquitin ligase component, Cereblon, is an evolutionarily conserved regulator of Wnt signaling. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 5263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjorklund, C.C.; Ma, W.; Wang, Z.-Q.; Davis, R.E.; Kuhn, D.J.; Kornblau, S.M.; Wang, M.; Shah, J.J.; Orlowski, R.Z. Evidence of a Role for Activation of Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling in the Resistance of Plasma Cells to Lenalidomide. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 11009–11020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, Y.L.D.; Ramberger, E.; Bohl, S.R.; Dolnik, A.; Steinebach, C.; Conrad, T.; Müller, S.; Popp, O.; Kull, M.; Haji, M.; et al. Proteomic profiling reveals CDK6 upregulation as a targetable resistance mechanism for lenalidomide in multiple myeloma. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, T.; Verma, R.; Nakamoto-Matsubara, R.; Siu, K.T.; Panaroni, C.; Fulzele, K.S.; Mukaihara, K.; Onyewadume, C.; Maebius, A.; Kato, H.; et al. Low NCOR2 levels in multiple myeloma patients drive multidrug resistance via MYC upregulation. Blood Cancer J. 2021, 11, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, L.; Liu, W.; Pichiorri, F.; Rosen, S.T. SUMOylation inhibition enhances multiple myeloma sensitivity to lenalidomide. Cancer Gene Ther. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ocio, E.M.; Fernández-Lázaro, D.; San-Segundo, L.; López-Corral, L.; Corchete, L.A.; Gutiérrez, N.C.; Garayoa, M.; Paíno, T.; García-Gómez, A.; Delgado, M.; et al. In vivo murine model of acquired resistance in myeloma reveals differential mechanisms for lenalidomide and pomalidomide in combination with dexamethasone. Leukemia 2015, 29, 705–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Hideshima, T.; Xing, L.; Wang, S.; Zhou, W.; Samur, M.K.; Sewastianik, T.; Ogiya, D.; An, G.; Gao, S.; et al. ERK signaling mediates resistance to immunomodulatory drugs in the bone marrow microenvironment. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabg2697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Shi, H.; He, X.; Liao, A. Downregulation of Chemokine CCL20 Involved in Myeloma Cells Resistant to Elotuzumab and Lenalidomide. OncoTargets Ther. 2021, 14, 2789–2795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Ma, D.; Wang, P.; Cao, L.; Lu, T.; Fang, Q.; Zhao, J.; Wang, J. Potential crosstalk of the interleukin-6–heme oxygenase-1-dependent mechanism involved in resistance to lenalidomide in multiple myeloma cells. FEBS J. 2016, 283, 834–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Colombo, M.; Garavelli, S.; Mazzola, M.; Platonova, N.; Giannandrea, D.; Colella, R.; Apicella, L.; Lancellotti, M.; Lesma, E.; Ancona, S.; et al. Multiple myeloma exploits Jagged1 and Jagged2 to promote intrinsic and bone marrow-dependent drug resistance. Haematologica 2020, 105, 1925–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, T.; Nakayama, J.; Yamamoto, Y.; Kuroda, M.; Hattori, Y.; Ochiya, T. SORT1/LAMP2-mediated extracellular vesicle secretion and cell adhesion are linked to lenalidomide resistance in multiple myeloma. Blood Adv. 2022, 6, 2480–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hattori, Y.; Futo, T.; Uozaki, R.; Ichikawa, D.; Yamaguchi, T.; Yamamoto, T.; Matsushita, M.; Hirao, M. Integrin β5 and β7 expression in lenalidomide-resistant multiple myeloma cells. Int. J. Hematol. 2022, 115, 605–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Pal, R.; Monaghan, S.A.; Schafer, P.; Ouyang, H.; Mapara, M.; Galson, D.L.; Lentzsch, S. IMiD immunomodulatory compounds block C/EBPβ translation through eIF4E down-regulation resulting in inhibition of MM. Blood 2011, 117, 5157–5165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.X.; Shi, C.-X.; Bruins, L.A.; Wang, X.; Riggs, D.L.; Porter, B.; Ahmann, J.M.; de Campos, C.B.; Braggio, E.; Bergsagel, P.L.; et al. Identification of lenalidomide resistance pathways in myeloma and targeted resensitization using cereblon replacement, inhibition of STAT3 or targeting of IRF4. Blood Cancer J. 2019, 9, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, J.D.; Correa, M.; Nagy, M.A.; Alexander, M.; Plantevin, V.; Grant, V.; Whitefield, B.; Huang, D.; Kercher, T.; Harris, R.; et al. Discovery of CRBN E3 Ligase Modulator CC-92480 for the Treatment of Relapsed and Refractory Multiple Myeloma. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 6648–6676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madan, S.; Lacy, M.Q.; Dispenzieri, A.; Gertz, M.A.; Buadi, F.; Hayman, S.R.; Detweiler-Short, K.; Dingli, D.; Zeldenrust, S.; Lust, J.; et al. Efficacy of retreatment with immunomodulatory drugs (IMiDs) in patients receiving IMiDs for initial therapy of newly diagnosed multiple myeloma. Blood 2011, 118, 1763–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rychak, E.; Mendy, D.; Shi, T.; Ning, Y.; Leisten, J.; Lu, L.; Miller, K.; Narla, R.K.; Orlowski, R.Z.; Raymon, H.K.; et al. Pomalidomide in combination with dexamethasone results in synergistic anti-tumour responses in pre-clinical models of lenalidomide-resistant multiple myeloma. Br. J. Haematol. 2016, 172, 889–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, P.G.; Hofmeister, C.C.; Raje, N.S.; Siegel, D.S.; Lonial, S.; Laubach, J.; Efebera, Y.A.; Vesole, D.H.; Nooka, A.K.; Rosenblatt, J.; et al. Pomalidomide, bortezomib and low-dose dexamethasone in lenalidomide-refractory and proteasome inhibitor-exposed myeloma. Leukemia 2017, 31, 2695–2701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, P.G.; Oriol, A.; Beksac, M.; Liberati, A.M.; Galli, M.; Schjesvold, F.; Lindsay, J.; Weisel, K.; White, D.; Facon, T.; et al. Pomalidomide, bortezomib, and dexamethasone for patients with relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma previously treated with lenalidomide (OPTIMISMM): A randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 781–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimopoulos, M.; Weisel, K.; Moreau, P.; Anderson, L.D.; White, D.; San-Miguel, J.; Sonneveld, P.; Engelhardt, M.; Jenner, M.; Corso, A.; et al. Pomalidomide, bortezomib, and dexamethasone for multiple myeloma previously treated with lenalidomide (OPTIMISMM): Outcomes by prior treatment at first relapse. Leukemia 2021, 35, 1722–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charlinski, G.; Grzasko, N.; Jurczyszyn, A.; Janczarski, M.; Szeremet, A.; Waszczuk-Gajda, A.; Bernatowicz, P.; Swiderska, A.; Guzicka-Kazimierczak, R.; Lech-Maranda, E.; et al. The efficacy and safety of pomalidomide in relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma in a “real-world” study: Polish Myeloma Group experience. Eur. J. Haematol. 2018, 101, 354–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, N.; Tucker, N.; Zahurak, M.; Wozney, J.; Borrello, I.; Huff, C.A. Clarithromycin overcomes resistance to lenalidomide and dexamethasone in multiple myeloma. Am. J. Hematol. 2014, 89, E116–E120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalff, A.; Khong, T.; Mithraprabhu, S.; Bergin, K.; Reynolds, J.; Bowen, K.M.; Thakurta, A.; Guzman, R.; Wang, M.; Couto, S.; et al. Oral azacitidine (CC-486) in combination with lenalidomide and dexamethasone in advanced, lenalidomide-refractory multiple myeloma (ROAR study). Leuk. Lymphoma 2019, 60, 2143–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khouri, J.; Faiman, B.M.; Grabowski, D.; Mahfouz, R.Z.; Khan, S.N.; Wei, W.; Valent, J.; Dean, R.; Samaras, C.; Jha, B.K.; et al. DNA methylation inhibition in myeloma: Experience from a phase 1b study of low-dose continuous azacitidine in combination with lenalidomide and low-dose dexamethasone in relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma. Semin. Hematol. 2021, 58, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alahmadi, M.; Masih-Khan, E.; Atenafu, E.G.; Chen, C.; Kukreti, V.; Tiedemann, R.; Trudel, S.; Reece, D.E. Addition of Cyclophosphamide “On Demand” to Lenalidomide and Corticosteroids in Patients With Relapsed/Refractory Multiple Myeloma—A Retrospective Review of a Single-center Experience. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2019, 19, e195–e203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelis, N.; Devos, T.; Dierickx, D.; Janssens, A.; Raddoux, J.; Verhoef, G.; Delforge, M. Treatment with lenalidomide (Revlimid®), cyclophosphamide (Endoxan®) and prednisone (REP) in relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma patients: Results of a single centre retrospective study. Acta Clin. Belg. 2014, 69, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hitz, F.; Kraus, M.; Pabst, T.; Hess, D.; Besse, L.; Silzle, T.; Novak, U.; Seipel, K.; Rondeau, S.; Stüdeli, S.; et al. Nelfinavir and lenalidomide/dexamethasone in patients with lenalidomide-refractory multiple myeloma. A phase I/II Trial (SAKK 39/10). Blood Cancer J. 2019, 9, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palumbo, A.; Chanan-Khan, A.; Weisel, K.; Nooka, A.K.; Masszi, T.; Beksac, M.; Spicka, I.; Hungria, V.; Munder, M.; Mateos, M.V.; et al. Daratumumab, Bortezomib, and Dexamethasone for Multiple Myeloma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 754–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attal, M.; Richardson, P.G.; Rajkumar, S.V.; San-Miguel, J.; Beksac, M.; Spicka, I.; Leleu, X.; Schjesvold, F.; Moreau, P.; Dimopoulos, M.A.; et al. Isatuximab plus pomalidomide and low-dose dexamethasone versus pomalidomide and low-dose dexamethasone in patients with relapsed and refractory multiple myeloma (ICARIA-MM): A randomised, multicentre, open-label, phase 3 study. Lancet 2019, 394, 2096–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimopoulos, M.A.; Dytfeld, D.; Grosicki, S.; Moreau, P.; Takezako, N.; Hori, M.; Leleu, X.; LeBlanc, R.; Suzuki, K.; Raab, M.S.; et al. Elotuzumab plus Pomalidomide and Dexamethasone for Multiple Myeloma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 1811–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimopoulos, M.A.; Moreau, P.; Palumbo, A.; Joshua, D.; Pour, L.; Hájek, R.; Facon, T.; Ludwig, H.; Oriol, A.; Goldschmidt, H.; et al. Carfilzomib and dexamethasone versus bortezomib and dexamethasone for patients with relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma (ENDEAVOR): A randomised, phase 3, open-label, multicentre study. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voorhees, P.M.; Suman, V.J.; Tuchman, S.A.; Laubach, J.P.; Hassoun, H.; Efebera, Y.A.; Mulkey, F.; Bova-Solem, M.; Santo, K.; Carlisle, D.; et al. A phase I/II study of ixazomib, pomalidomide, and dexamethasone for lenalidomide and proteasome inhibitor refractory multiple myeloma (Alliance A061202). Am. J. Hematol. 2021, 96, 1595–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimopoulos, M.A.; Schjesvold, F.; Doronin, V.; Vinogradova, O.; Quach, H.; Leleu, X.; Montes, Y.G.; Ramasamy, K.; Pompa, A.; Levin, M.-D.; et al. Oral ixazomib-dexamethasone vs oral pomalidomide-dexamethasone for lenalidomide-refractory, proteasome inhibitor-exposed multiple myeloma: A randomized Phase 2 trial. Blood Cancer J. 2022, 12, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimopoulos, M.; Quach, H.; Mateos, M.-V.; Landgren, O.; Leleu, X.; Siegel, D.; Weisel, K.; Yang, H.; Klippel, Z.; Zahlten-Kumeli, A.; et al. Carfilzomib, dexamethasone, and daratumumab versus carfilzomib and dexamethasone for patients with relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma (CANDOR): Results from a randomised, multicentre, open-label, phase 3 study. Lancet 2020, 396, 186–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawaji-Kanayama, Y.; Kobayashi, T.; Muramatsu, A.; Uchiyama, H.; Sasaki, N.; Uoshima, N.; Nakao, M.; Takahashi, R.; Shimura, K.; Kaneko, H.; et al. Prognostic impact of resistance to bortezomib and/or lenalidomide in carfilzomib-based therapies for relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma: The Kyoto Clinical Hematology Study Group, multicenter, pilot, prospective, observational study in Asian patients. Cancer Rep. 2022, 5, e1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Li, M.; Sanchez, E.; Soof, C.M.; Bujarski, S.; Ng, N.; Cao, J.; Hekmati, T.; Zahab, B.; Nosrati, J.D.; et al. JAK1/2 pathway inhibition suppresses M2 polarization and overcomes resistance of myeloma to lenalidomide by reducing TRIB1, MUC1, CD44, CXCL12, and CXCR4 expression. Br. J. Haematol. 2020, 188, 283–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berenson, J.R.; To, J.; Spektor, T.M.; Martinez, D.; Turner, C.; Sanchez, A.; Ghermezi, M.; Eades, B.M.; Swift, R.A.; Schwartz, G.; et al. A Phase I Study of Ruxolitinib, Lenalidomide, and Steroids for Patients with Relapsed/Refractory Multiple Myeloma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 2346–2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berenson, J.R.; Kim, C.; Bujarski, S.; To, J.; Spektor, T.M.; Martinez, D.; Turner, C.; Ghermezi, M.; Eades, B.M.; Swift, R.A.; et al. A phase 1 study of ruxolitinib, steroids and lenalidomide for relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma patients. Hematol. Oncol. 2022, 40, 906–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kulig, P.; Milczarek, S.; Bakinowska, E.; Szalewska, L.; Baumert, B.; Machaliński, B. Lenalidomide in Multiple Myeloma: Review of Resistance Mechanisms, Current Treatment Strategies and Future Perspectives. Cancers 2023, 15, 963. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15030963
Kulig P, Milczarek S, Bakinowska E, Szalewska L, Baumert B, Machaliński B. Lenalidomide in Multiple Myeloma: Review of Resistance Mechanisms, Current Treatment Strategies and Future Perspectives. Cancers. 2023; 15(3):963. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15030963
Chicago/Turabian StyleKulig, Piotr, Sławomir Milczarek, Estera Bakinowska, Laura Szalewska, Bartłomiej Baumert, and Bogusław Machaliński. 2023. "Lenalidomide in Multiple Myeloma: Review of Resistance Mechanisms, Current Treatment Strategies and Future Perspectives" Cancers 15, no. 3: 963. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15030963
APA StyleKulig, P., Milczarek, S., Bakinowska, E., Szalewska, L., Baumert, B., & Machaliński, B. (2023). Lenalidomide in Multiple Myeloma: Review of Resistance Mechanisms, Current Treatment Strategies and Future Perspectives. Cancers, 15(3), 963. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15030963




