Comparable Overall Survival in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma Diagnosed within and outside a Surveillance Programme: The Potential Impact of Liver Cirrhosis
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
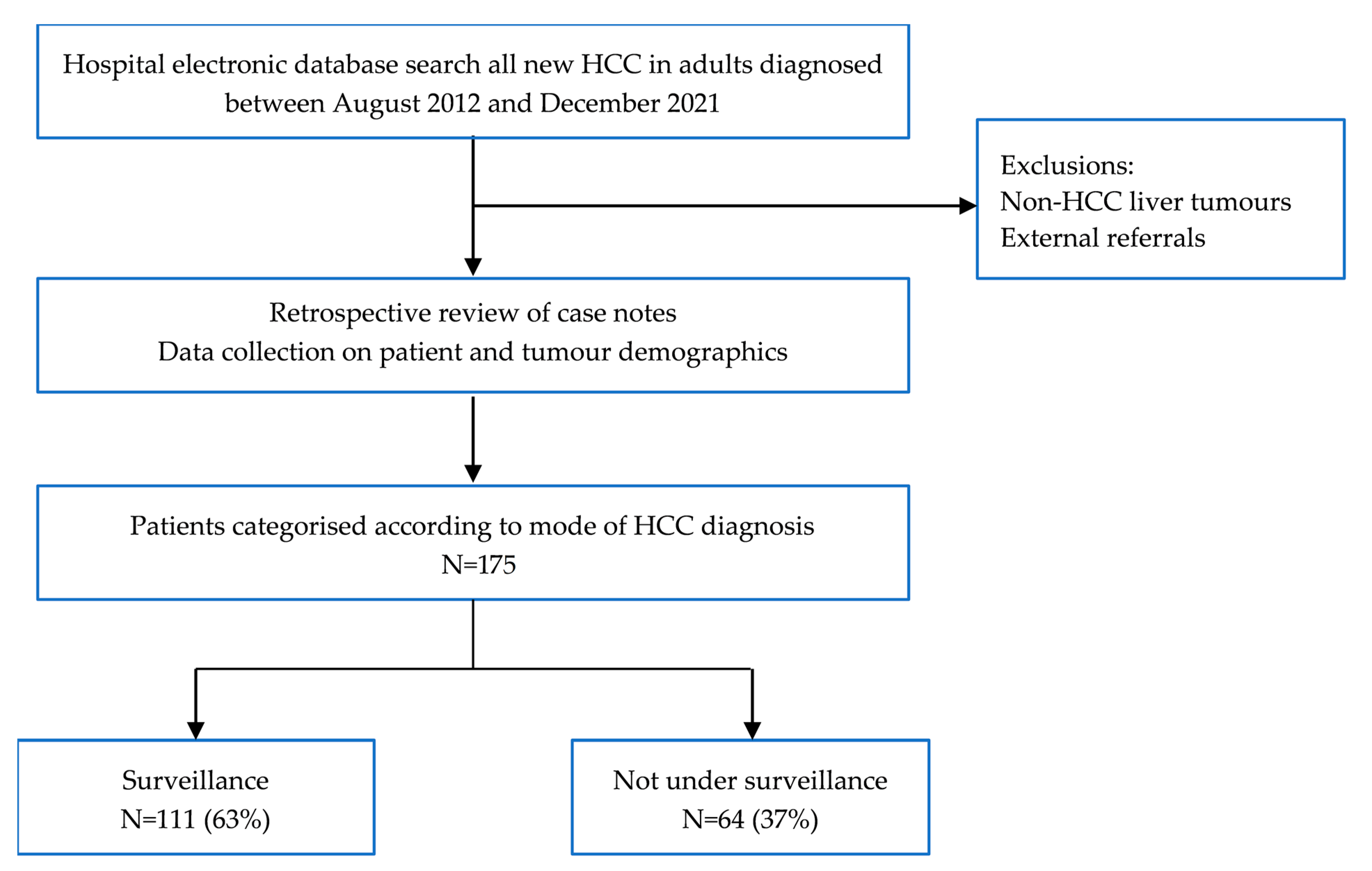
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient and Tumour Characteristics
3.2. HCC Treatment and Survival
3.3. Comparison of Cirrhotic and Non-Cirrhotic Patients in the Non-Surveillance Cohort
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dasgupta, P.; Henshaw, C.; Youlden, D.R.; Clark, P.J.; Aitken, J.F.; Baade, P.D. Global Trends in Incidence Rates of Primary Adult Liver Cancers: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cancer Research UK. Cancer Incidence for Common Cancers. 2021. Available online: https://www.cancerresearchuk.org/health-professional/cancer-statistics/incidence/common-cancers-compared#heading-Three (accessed on 27 October 2022).
- Cancer Research UK. Cancer Mortality for Common Cancers. 2021. Available online: https://www.cancerresearchuk.org/health-professional/cancer-statistics/mortality/common-cancers-compared#heading-Three (accessed on 22 November 2022).
- Smittenaar, C.R.; Petersen, K.A.; Stewart, K.; Moitt, N. Cancer incidence and mortality projections in the UK until 2035. Br. J. Cancer 2016, 115, 1147–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prieto, J.; Melero, I.; Sangro, B. Immunological landscape and immunotherapy of hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 12, 681–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heimbach, J.K.; Kulik, L.M.; Finn, R.S.; Sirlin, C.B.; Abecassis, M.M.; Roberts, L.R.; Zhu, A.X.; Murad, M.H.; Marrero, J.A. AASLD guidelines for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2018, 67, 358–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines: Management of hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2018, 69, 182–236. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muñoz-Martínez, S.; Sapena, V.; Forner, A.; Nault, J.C.; Sapisochin, G.; Rimassa, L.; Sangro, B.; Bruix, J.; Sanduzzi-Zamparelli, M.; Hołówko, W.; et al. Assessing the impact of COVID-19 on liver cancer management (CERO-19). JHEP Rep. 2021, 3, 100260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esfeh, J.M.; Hajifathalian, K.; Ansari-Gilani, K. Sensitivity of ultrasound in detecting hepatocellular carcinoma in obese patients compared to explant pathology as the gold standard. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2020, 26, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, M.V.; Huo, Y.R.; Trieu, N.; Mitchelle, A.; George, J.; He, E.; Lee, A.U.; Chang, J.; Yang, J. Noncontrast MRI for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Detection: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis—A Potential Surveillance Tool? Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 20, 44–56.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Meer, S.; van Erpecum, K.J.; Sprengers, D.; Coenraad, M.J.; Klümpen, H.J.; Jansen, P.L.; JN, I.J.; Verheij, J.; van Nieuwkerk, C.M.; Siersema, P.D.; et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhotic versus noncirrhotic livers: Results from a large cohort in the Netherlands. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 28, 352–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gawrieh, S.; Dakhoul, L.; Miller, E.; Scanga, A.; deLemos, A.; Kettler, C.; Burney, H.; Liu, H.; Abu-Sbeih, H.; Chalasani, N.; et al. Characteristics, aetiologies and trends of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients without cirrhosis: A United States multicentre study. Aliment Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 50, 809–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalasani, N.; Younossi, Z.; Lavine, J.E.; Diehl, A.M.; Brunt, E.M.; Cusi, K.; Charlton, M.; Sanyal, A.J. The diagnosis and management of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Practice Guideline by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases, American College of Gastroenterology, and the American Gastroenterological Association. Hepatology 2012, 55, 2005–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singal, A.G.; Zhang, E.; Narasimman, M.; Rich, N.E.; Waljee, A.K.; Hoshida, Y.; Yang, J.D.; Reig, M.; Cabibbo, G.; Nahon, P.; et al. HCC surveillance improves early detection, curative treatment receipt, and survival in patients with cirrhosis: A meta-analysis. J. Hepatol. 2022, 77, 128–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duvoux, C.; Roudot-Thoraval, F.; Decaens, T.; Pessione, F.; Badran, H.; Piardi, T.; Francoz, C.; Compagnon, P.; Vanlemmens, C.; Dumortier, J.; et al. Liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma: A model including α-fetoprotein improves the performance of Milan criteria. Gastroenterology 2012, 143, 986–994.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llovet, J.M.; Brú, C.; Bruix, J. Prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma: The BCLC staging classification. Semin. Liver Dis. 1999, 19, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tretiakova, M.S.; Shabani-Rad, M.T.; Guggisberg, K.; Hart, J.; Anders, R.A.; Gao, Z.H. Genomic and immunophenotypical differences between hepatocellular carcinoma with and without cirrhosis. Histopathology 2010, 56, 683–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albillos, A.; Martin-Mateos, R.; Van der Merwe, S.; Wiest, R.; Jalan, R.; Álvarez-Mon, M. Cirrhosis-associated immune dysfunction. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 19, 112–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llovet, J.M.; Kelley, R.K.; Villanueva, A.; Singal, A.G.; Pikarsky, E.; Roayaie, S.; Lencioni, R.; Koike, K.; Zucman-Rossi, J.; Finn, R.S. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2021, 7, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Doorn, D.J.; Hendriks, P.; Burgmans, M.C.; Rietbergen, D.D.D.; Coenraad, M.J.; van Delden, O.M.; Bennink, R.J.; Labeur, T.A.; Klümpen, H.J.; Eskens, F.; et al. Liver Decompensation as Late Complication in HCC Patients with Long-Term Response following Selective Internal Radiation Therapy. Cancers 2021, 13, 5427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinyopornpanish, K.; Al-Yaman, W.; Dasarathy, S.; Romero-Marrero, C.; McCullough, A. Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Patients Without Cirrhosis: The Fibrosis Stage Distribution, Characteristics and Survival. Dig Dis. Sci. 2022, 67, 2677–2687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhlig, J.; Sellers, C.M.; Khan, S.A.; Cha, C.; Kim, H.S. Hepatocellular carcinoma: Impact of academic setting and hospital volume on patient survival. Surg. Oncol. 2019, 31, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haq, M.I.; Drake, T.M.; Goh, T.L.; Ahmed, A.; Forrest, E.; Barclay, S.; Gillespie, R.; Priest, M.; Evans, J.; Graham, J.; et al. Effect of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Surveillance Programmes on Overall Survival in a Mixed Cirrhotic UK Population: A Prospective, Longitudinal Cohort Study. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 2770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, C.R.; Garcia, R.T.; Trinh, H.N.; Lam, K.D.; Ha, N.B.; Nguyen, H.A.; Nguyen, K.K.; Levitt, B.S.; Nguyen, M.H. Adherence to screening for hepatocellular carcinoma among patients with cirrhosis or chronic hepatitis B in a community setting. Dig Dis. Sci. 2009, 54, 2712–2721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalton-Fitzgerald, E.; Tiro, J.; Kandunoori, P.; Halm, E.A.; Yopp, A.; Singal, A.G. Practice patterns and attitudes of primary care providers and barriers to surveillance of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with cirrhosis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 13, 791–798.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cucchetti, A.; Trevisani, F.; Pecorelli, A.; Erroi, V.; Farinati, F.; Ciccarese, F.; Rapaccini, G.L.; Di Marco, M.; Caturelli, E.; Giannini, E.G.; et al. Estimation of lead-time bias and its impact on the outcome of surveillance for the early diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2014, 61, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, J.C.; Covinsky, K.E.; Dodge, J.L.; Boscardin, W.J.; Segev, D.L.; Roberts, J.P.; Feng, S. Development of a novel frailty index to predict mortality in patients with end-stage liver disease. Hepatology 2017, 66, 564–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]





| Demographics | Surveillance (n = 111) | Non-Surveillance (n = 64) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years (range) | 66 (59.6–73.1) | 67 (24–87) | 0.6 |
| Male (%) | 81 (73%) | 53 (83%) | 0.13 |
| BMI median (IQR) | 28 (24–34) | 30.8 (19.3–46.9) | <0.05 |
| WHO performance status 0 1 2 3 4 Unavailable | 94 (85%) 11 (10%) 4 (3%) 2 (2%) 0 0 | 37 (58%) 14 (22%) 5 (8%) 6 (9%) 1 (1.5%) 1(1.5%) | <0.05 <0.05 0.14 <0.05 - - |
| Aetiology NASH Alcohol Hepatitis C Hepatitis B Autoimmune Haemochromatosis Cryptogenic Other No liver disease | 25 (22.6%) 30 (27%) 30 (27%) 10 (9%) 10 (9%) 2 (1.8%) 0 4 (3.6%) 0 | 20 (31%) 8 (13%) 4 (6%) 3 (5%) 2 (3%) 2 (3%) 2 (3%) 3 (5%) 20 (31%) | 0.25 <0.05 <0.05 0.34 0.13 0.83 - 0.76 - |
| Cirrhosis present | 101 (91%) | 29 (45%) | <0.05 |
| Childs Pugh Score A B C | n = 101 91 (90%) 10 (10%) 0 | n = 29 22 (76%) 7 (24%) 0 | <0.05 <0.05 - |
| AFP median (IQR) | 6 (3–36) | 5 (3–25) | 0.99 |
| Douvoux score | 0 (0–1) | 1 (0–4) | <0.05 |
| Size of largest tumour at diagnosis (cm) | 2.9 (95%CI 2.5–3.3) | 5.3 (95%CI 4.4–6.1) | <0.05 |
| BCLC stage A B C D Unavailable | 93 (83.8%) 14 (12.6%) 1 (0.9%) 1 (0.9%) 2 (1.8%) | 41 (64%) 16 (25%) 5 (8%) 1 (1.5%) 1 (1.5%) | <0.05 0.07 0.23 0.77 0.58 |
| HCC treatment * Ablation Liver transplant SABR Surgical resection Systemic therapy TACE Best supportive care | 24 (22%) 12 (11%) 22 (20%) 5 (5%) 10 (9%) 48 (43%) 10 (9%) | 5 (8%) 2 (3%) 11 (17%) 18 (28%) 15 (23%) 19 (30%) 12 (19%) | <0.05 0.06 0.62 <0.05 <0.05 0.1 0.06 |
| Demographics | Non-Surveillance No Cirrhosis (N =35) | Non-Surveillance Cirrhosis (N = 29) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) median (IQR) | 72 (60–76) | 68 (62–75) | 0.22 |
| Male (%) | 27 (77%) | 26 (90%) | 0.17 |
| BMI median (IQR) | 30 (25–36) | 31 (27–34) | 0.88 |
| Aetiology NASH Alcohol Hepatitis C Hepatitis B Hemochromatosis Autoimmune Other Cryptogenic No liver disease | 9 (25.7%) 0 1 (2.9%) 0 1 (2.9%) 1 (2.9%) 3 (8.6%) 0 20 (57%) | 11 (37.9%) 8 (27.6%) 3 (10.4%) 3 (10.4%) 1 (3.4%) 1 (3.4%) 0 2 (6.9%) 0 | 0.06 <0.05 0.25 0.06 1 1 - - - |
| AFP median (IQR) | 5 (2–18) | 7 (3–42) | 0.41 |
| Douvoux score | 2.5 (0–4) | 1 (0–3) | 0.2 |
| Size of largest tumour at diagnosis (cm) | 7 (95%CI 5.6–8.4) | 4.5 (95%CI 3.6–5.4) | <0.05 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Faulkes, R.E.; Rehman, Z.; Palanichamy, S.; Zakeri, N.; Coldham, C.; Dasari, B.V.M.; Perera, M.T.P.R.; Rajoriya, N.; Shetty, S.; Shah, T. Comparable Overall Survival in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma Diagnosed within and outside a Surveillance Programme: The Potential Impact of Liver Cirrhosis. Cancers 2023, 15, 978. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15030978
Faulkes RE, Rehman Z, Palanichamy S, Zakeri N, Coldham C, Dasari BVM, Perera MTPR, Rajoriya N, Shetty S, Shah T. Comparable Overall Survival in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma Diagnosed within and outside a Surveillance Programme: The Potential Impact of Liver Cirrhosis. Cancers. 2023; 15(3):978. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15030978
Chicago/Turabian StyleFaulkes, Rosemary E., Zaira Rehman, Swetha Palanichamy, Nekisa Zakeri, Chris Coldham, Bobby V. M. Dasari, M. Thamara P. R. Perera, Neil Rajoriya, Shishir Shetty, and Tahir Shah. 2023. "Comparable Overall Survival in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma Diagnosed within and outside a Surveillance Programme: The Potential Impact of Liver Cirrhosis" Cancers 15, no. 3: 978. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15030978
APA StyleFaulkes, R. E., Rehman, Z., Palanichamy, S., Zakeri, N., Coldham, C., Dasari, B. V. M., Perera, M. T. P. R., Rajoriya, N., Shetty, S., & Shah, T. (2023). Comparable Overall Survival in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma Diagnosed within and outside a Surveillance Programme: The Potential Impact of Liver Cirrhosis. Cancers, 15(3), 978. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15030978






