Implementation of Machine Learning Models to Ensure Radiotherapy Quality for Multicenter Clinical Trials: Report from a Phase III Lung Cancer Study
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Initial Data Review and Selection
2.2. Model Training
2.3. Plan Quality Review by Models
3. Results
3.1. Final Model Settings
3.2. Proton KBP Model Evaluation
3.3. Plan Quality Review
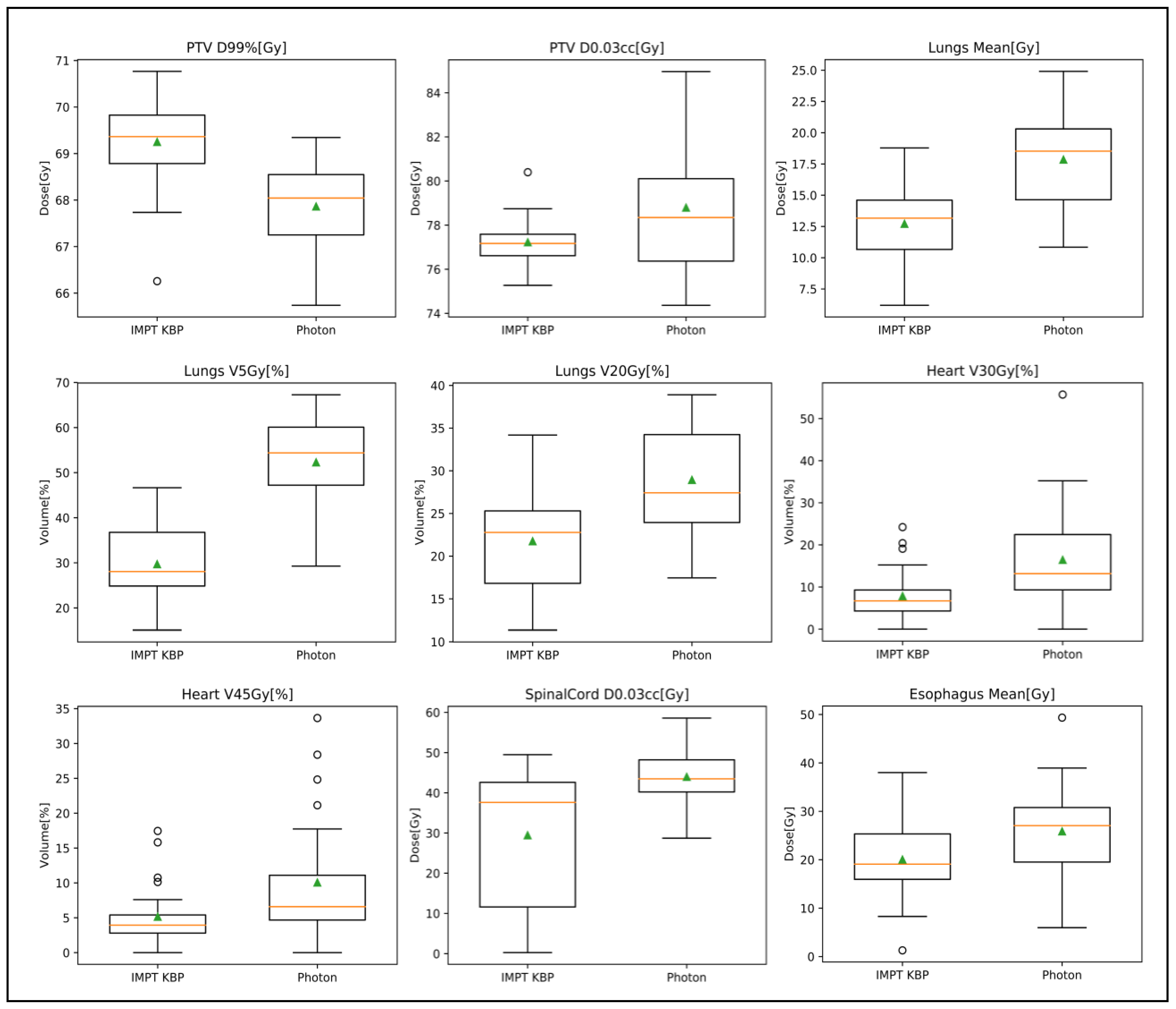
3.3.1. Photon Plan Quality Review
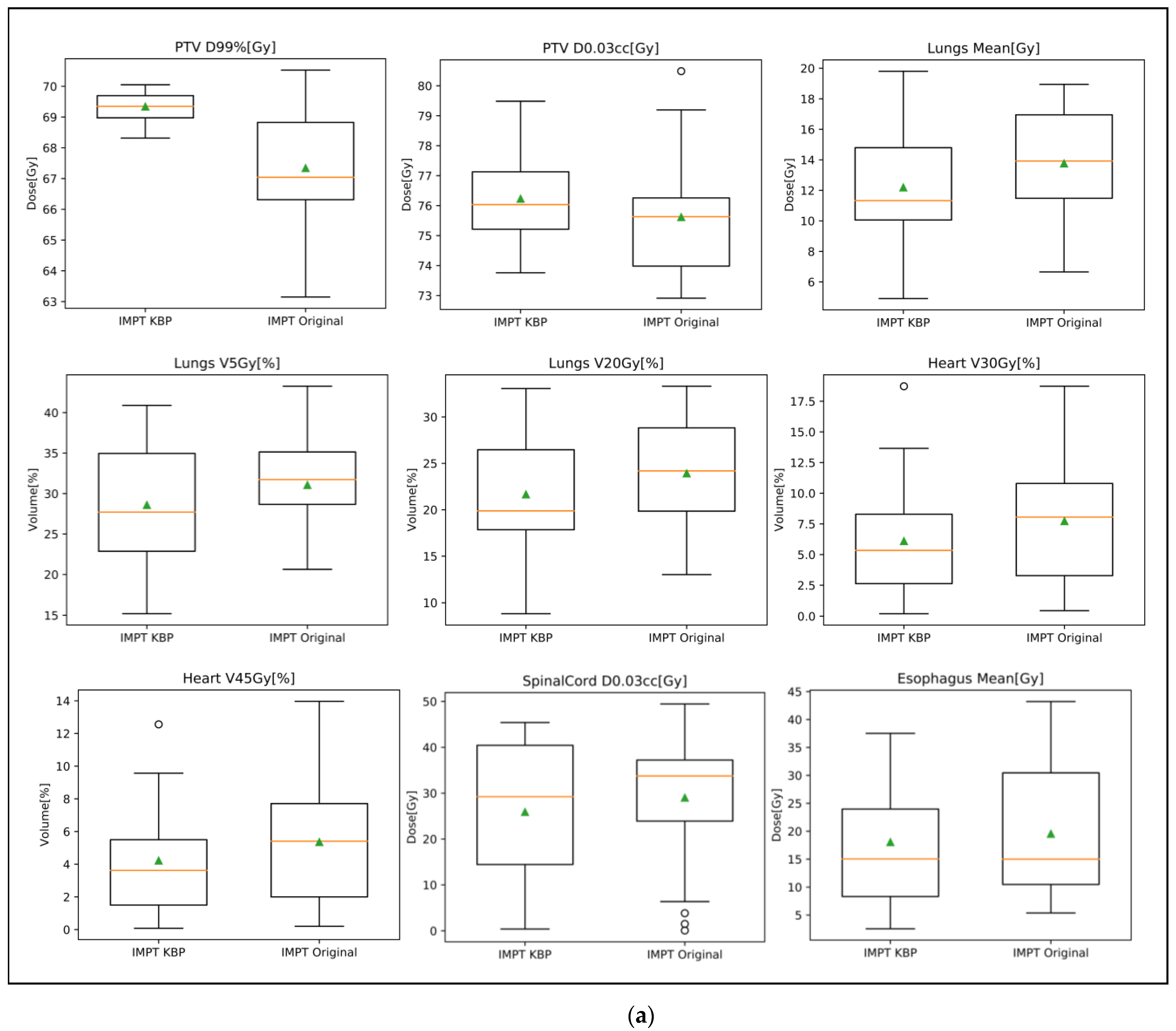
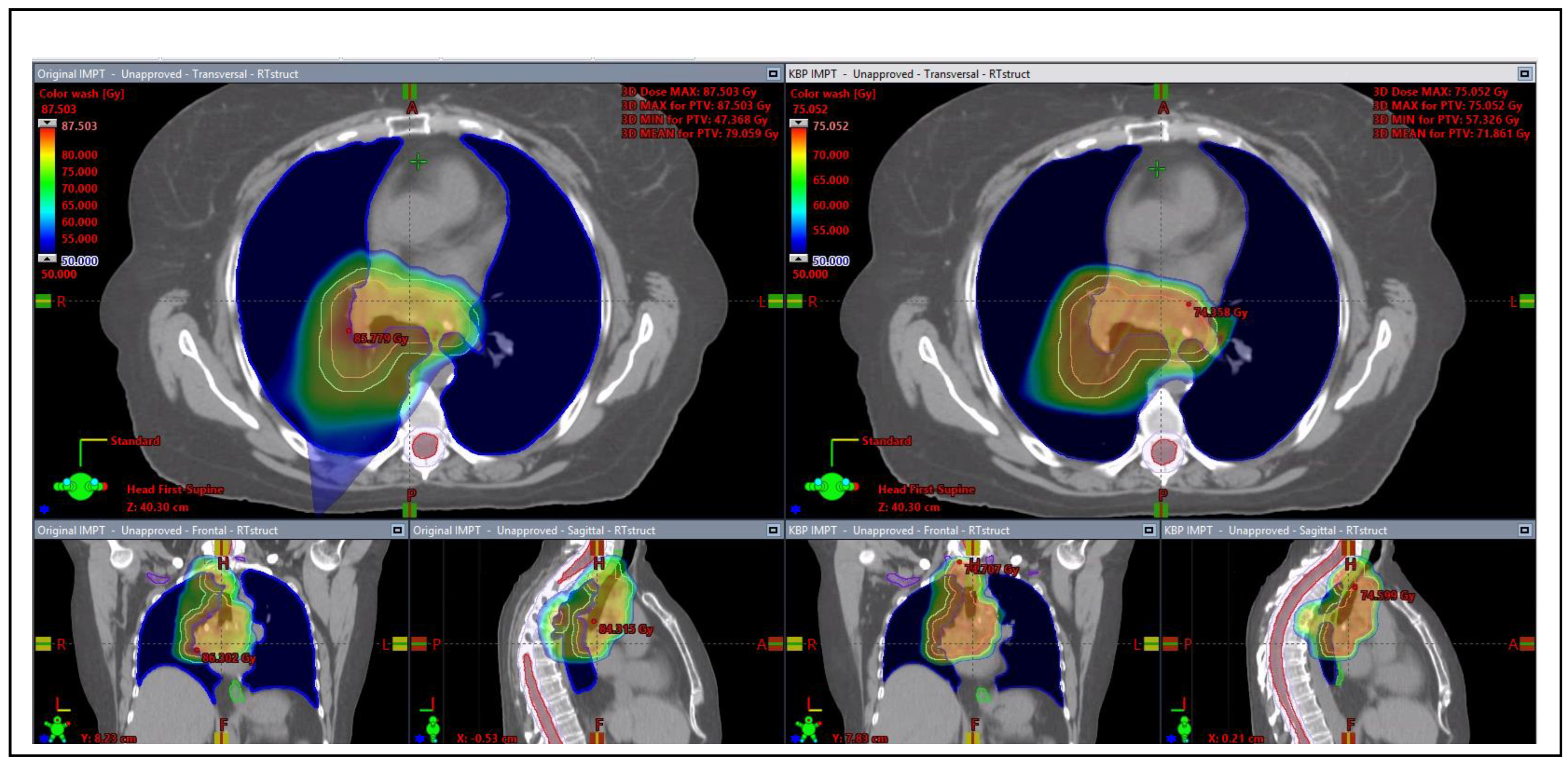
3.3.2. Proton Plan Quality Review
4. Discussions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Structure Name | Dose Point | Photon Original | IMPT KBP | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PTV | D95%[Gy] | 70 | 70.91 ± 0.52 | <0.001 |
| D0.03cc[Gy] | 78.80 ± 3.06 | 77.23 ± 1.16 | 0.0246 | |
| D99%[Gy] | 67.86 ± 0.98 | 69.25 ± 0.97 | <0.001 | |
| Heart | V45Gy[%] | 10.1% ± 9.2% | 5.2% ± 4.7% | 0.00166 |
| V30Gy[%] | 16.5% ± 12.9% | 7.8% ± 6.5% | <0.001 | |
| Mean[Gy] | 14.02 ± 8.66 | 5.80 ± 4.42 | <0.001 | |
| Lungs | V5Gy[%] | 52.3% ± 10.1% | 29.7% ± 8.2% | <0.001 |
| V20Gy[%] | 28.9% ± 6.2% | 21.8% ± 5.6% | <0.001 | |
| Mean[Gy] | 17.85 ± 3.69 | 12.72 ± 3.43 | <0.001 | |
| Esophagus | V74Gy[cc] | 0.20 ± 0.45 | 0.03 ± 0.06 | N/A |
| Spinal cord | D0.03cc[Gy] | 43.97 ± 7.04 | 29.44 ± 16.81 | <0.001 |
References
- Ohri, N.; Shen, X.; Dicker, A.P.; Doyle, L.A.; Harrison, A.S.; Showalter, T.N. Radiotherapy protocol deviations and clinical outcomes: A meta-analysis of cooperative group clinical trials. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2013, 105, 387–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FitzGerald, T.J. What We Have Learned: The Impact of Quality From a Clinical Trials Perspective. Semin. Radiat. Oncol. 2012, 22, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcello, M.; Ebert, M.A.; Haworth, A.; Steigler, A.; Kennedy, A.; Bulsara, M.; Kearvell, R.; Joseph, D.J.; Denham, J.W.; Marcello, M.; et al. Association between measures of treatment quality and disease progression in prostate cancer radiotherapy: An exploratory analysis from the TROG 03.04 RADAR trial. J. Med. Imaging Radiat. Oncol. 2018, 62, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abrams, R.A.; Winter, K.A.; Regine, W.F.; Safran, H.; Hoffman, J.P.; Lustig, R.; Konski, A.A.; Benson, A.B.; Macdonald, J.S.; Rich, T.A.; et al. Failure to Adhere to Protocol Specified Radiation Therapy Guidelines was Associaated with Decreased Survival in RTOG 9704 -A Phase III Trial of Adjuvant Chemotherapy and Chemoradiotherapy for Patients with Resecyed Adenocarcinoma of the Pancreas. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2012, 82, 809–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, K.L.; Brame, R.S.; Low, D.A.; Mutic, S. Experience-based quality control of clinical intensity-modulated radiotherapy planning. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2011, 81, 545–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, K.L.; Schmidt, R.; Moiseenko, V.; Olsen, L.A.; Tan, J.; Xiao, Y.; Galvin, J.; Pugh, S.; Michael, J.; Dicker, A.P.; et al. Quantifying unnecessary normal tissue complication risks due to suboptimal planning: A secondary study on RTOG0126. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2015, 92, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Ge, Y.; Li, T.; Thongphiew, D.; Yin, F.-F.; Wu, Q.J. A planning quality evaluation tool for prostate adaptive IMRT based on machine learning. Med. Phys. 2011, 38, 719–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Ge, Y.; Lee, W.R.; Yin, F.F.; Kirkpatrick, J.P.; Wu, Q.J. Quantitative analysis of the factors which affect the interpatient organ-at-risk dose sparing variation in IMRT plans. Med. Phys. 2012, 39, 6868–6878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fogliata, A.; Nicolini, G.; Clivio, A.; Vanetti, E.; Laksar, S.; Tozzi, A.; Scorsetti, M.; Cozzi, L. A broad scope knowledge based model for optimization of VMAT in esophageal cancer: Validation and assessment of plan quality among different treatment centers. Radiat. Oncol. 2015, 10, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fogliata, A.; Nicolini, G.; Bourgier, C.; Clivio, A.; De Rose, F.; Fenoglietto, P.; Lobefalo, F.; Mancosu, P.; Tomatis, S.; Vanetti, E.; et al. Performance of a Knowledge-Based Model for Optimization of Volumetric Modulated Arc Therapy Plans for Single and Bilateral Breast Irradiation. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0145137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Jiang, F.; Yue, H.; Zhang, H.; Wang, K.; Zhang, Y.; Bolan, C.; Zarepisheh, M.; Long, T.; Li, N.; et al. Applying a RapidPlan model trained on a technique and orientation to another: A feasibility and dosimetric evaluation. Radiat. Oncol. 2016, 11, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fogliata, A.; Wang, P.-M.; Belosi, F.; Clivio, A.; Nicolini, G.; Vanetti, E.; Cozzi, L. Assessment of a model based optimization engine for volumetric modulated arc therapy for patients with advanced hepatocellular cancer. Radiat. Oncol. 2014, 9, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, A.; Serban, M.; Abdulkarim, B.; Panet-Raymond, V.; Souhami, L.; Shenouda, G.; Sabri, S.; Jean-Claude, B.; Seuntjens, J. Performance of Knowledge-Based Radiation Therapy Planning for the Glioblastoma Disease Site. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2017, 99, 1021–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiraishi, S.; Tan, J.; Olsen, L.A.; Moore, K.L. Knowledge-based prediction of plan quality metrics in intracranial stereotactic radiosurgery. Med. Phys. Med. Phys 2015, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Gysen, K.; Kneebone, A.; Le, A.; Wu, K.; Haworth, A.; Bromley, R.; Hruby, G.; O’Toole, J.; Booth, J.; Brown, C.; et al. Evaluating the utility of knowledge-based planning for clinical trials using the TROG 08.03 post prostatectomy radiation therapy planning data. Phys. Imaging Radiat. Oncol. 2022, 22, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcello, M.; Ebert, M.; Haworth, A.; Steigler, A.; Kennedy, A.; Joseph, D.; Denham, J. Association between treatment planning and delivery factors and disease progression in prostate cancer radiotherapy: Results from the TROG 03.04 RADAR trial. Radiother. Oncol. 2018, 126, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giaddui, T.; Geng, H.; Chen, Q.; Linnemann, N.; Radden, M.; Lee, N.Y.; Xia, P.; Xiao, Y. Offline Quality Assurance for Intensity Modulated Radiation Therapy Treatment Plans for NRG-HN001 Head and Neck Clinical Trial Using Knowledge-Based Planning. Adv. Radiat. Oncol. 2020, 5, 1342–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, H.; Giaddui, T.; Cheng, C.; Zhong, H.; Ryu, S.; Liao, Z.; Yin, F.-F.; Gillin, M.; Mohan, R.; Xiao, Y. A comparison of two methodologies for radiotherapy treatment plan optimization and QA for clinical trials. J. Appl. Clin. Med. Phys. 2021, 22, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younge, K.C.; Marsh, R.B.; Owen, D.; Geng, H.; Xiao, Y.; Spratt, D.E.; Foy, J.; Suresh, K.; Wu, Q.J.; Yin, F.-F.; et al. Improving Quality and Consistency in NRG Oncology Radiation Therapy Oncology Group 0631 for Spine Radiosurgery via Knowledge-Based Planning. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2018, 100, 1067–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardcastle, N.; Cook, O.; Ray, X.; Moore, A.; Moore, K.L.; Pryor, D.; Rossi, A.; Foroudi, F.; Kron, T.; Siva, S. Personalising treatment plan quality review with knowledge-based planning in the TROG 15.03 trial for stereotactic ablative body radiotherapy in primary kidney cancer. Radiat. Oncol. 2021, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, D.; Moore, A.; Van Dyk, S.; Khaw, P. Why quality assurance is necessary in gynecologic radiation oncology. Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer 2022, 32, 402–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crellin, A.M.; Burnet, N.G. Proton Beam Therapy: The Context, Future Direction and Challenges Become Clearer. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 26, 736–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, D.C.; Trofimov, A.V.; Winey, B.A.; Liebsch, N.J.; Paganetti, H. Predicting patient-specific dosimetric benefits of proton therapy for skull-base tumors using a geometric knowledge-based method. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2017, 97, 1087–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grutters, J.P.C.; Kessels, A.G.H.; Pijls-Johannesma, M.; De Ruysscher, D.; Joore, M.A.; Lambin, P. Comparison of the effectiveness of radiotherapy with photons, protons and carbon-ions for non-small cell lung cancer: A meta-analysis. Radiother. Oncol. 2010, 95, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widder, J.; van der Schaaf, A.; Lambin, P.; Marijnen, C.A.M.; Pignol, J.P.; Rasch, C.R.; Slotman, B.J.; Verheij, M.; Langendijk, J.A. The Quest for Evidence for Proton Therapy: Model-Based Approach and Precision Medicine. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2016, 95, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delaney, A.R.; Verbakel, W.F.; Lindberg, J.; Koponen, T.K.; Slotman, B.J.; Dahele, M. Evaluation of an Automated Proton Planning Solution. Cureus 2018, 10, e3696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delaney, A.R.; Dong, L.; Mascia, A.; Zou, W.; Zhang, Y.; Yin, L.; Rosas, S.; Hrbacek, J.; Lomax, A.J.; Slotman, B.J.; et al. Automated knowledge-based intensity-modulated proton planning: An international multicenter benchmarking study. Cancers 2018, 10, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cozzi, L.; Vanderstraeten, R.; Fogliata, A.; Chang, F.L.; Wang, P.M. The role of a knowledge based dose–Volume histogram predictive model in the optimisation of intensity-modulated proton plans for hepatocellular carcinoma patients: Training and validation of a novel commercial system. Strahlenther. Onkol. 2021, 197, 332–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celik, E.; Baues, C.; Claus, K.; Fogliata, A.; Scorsetti, M.; Marnitz, S.; Cozzi, L. Knowledge-based intensity-modulated proton planning for gastroesophageal carcinoma. Acta Oncol. 2021, 60, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hytönen, R.; Vergeer, M.R.; Vanderstraeten, R.; Koponen, T.K.; Smith, C.; Verbakel, W.F.A.R. Fast, Automated, Knowledge-Based Treatment Planning for Selecting Patients for Proton Therapy Based on Normal Tissue Complication Probabilities. Adv. Radiat. Oncol. 2022, 7, 100903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Structures | Dosimetric Points | Per Protocol Value | Acceptable Variation Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| PTV | D95%[Gy] | ≥Rx | ≥95% Rx |
| D0.03cc[Gy] | <=110% Rx | <=120% Rx | |
| D99%[Gy] | >=80% Rx | >=80% Rx | |
| Heart | V45Gy[%] | <=35 | <=40 |
| V30Gy[%] | <=50 | <=55 | |
| Lungs | Mean[Gy] | <=20 | <=22 |
| V20Gy[%] | <=37 | <=40 | |
| V5Gy[%] | <=60 | <=65 | |
| Esophagus | V74Gy[cc] | <=1 | <=1.5 |
| Spinal Cord | D0.03cc[Gy] | <=50 | <=52 |
| Structures | Objectives | Priorities |
|---|---|---|
| PTV | Dmin ≥ 103% Rx dose | 150 |
| Esophagus | Dmax ≤ 110% Rx dose | 100 |
| Dmax ≤ 70 Gy | 80 | |
| Line (preferring target) | Generated priority | |
| Brachial Plexus | Dmax ≤ 60 Gy | 80 |
| Heart | V30Gy ≤ Generated Value | Generated priority |
| Line (preferring target) | Generated priority | |
| Lungs | Dmax ≤ 65 Gy | 100 |
| Line (preferring target) | Generated priority | |
| Spinal cord | Dmax ≤ 45 G | 100 |
| Line (preferring target) | Generated priority |
| Structure Name | Dose Point | Manual | KBP | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PTV | D95%[Gy] | 69.43 ± 0.52 | 70.20 ± 0.29 | <0.0001 |
| D0.03cc[Gy] | 79.65 ± 1.37 | 79.73 ± 1.63 | 0.4345 | |
| D99%[Gy] | 67.74 ± 0.93 | 68.89 ± 0.74 | <0.0001 | |
| Heart | V45Gy[%] | 6.2 ± 6.1% | 4.9 ± 5.0% | <0.0001 |
| V30Gy[%] | 8.6 ± 7.5% | 7.0 ± 6.4% | <0.0001 | |
| Mean[Gy] | 6.35 ± 5.07 | 5.26 ± 4.34 | <0.0001 | |
| Lungs | V5Gy[%] | 31.8 ± 8.7% | 31.0 ± 8.9% | 0.0022 |
| V20Gy[%] | 23.0 ± 6.1% | 22.5 ± 6.4% | 0.0039 | |
| Mean[Gy] | 13.11 ± 3.38 | 12.81 ± 3.64 | 0.0028 | |
| Esophagus | V74Gy[cc] | 0 ± 0 | 0 ± 0 | N/A |
| Spinal Cord | D0.03cc[Gy] | 41.06 ± 9.80 | 40.58 ± 10.63 | 0.3579 |
| Structure Name | Dose Point | Photon Original | IMRT KBP | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PTV | D95%[Gy] | 70 | 70 | N/A |
| D0.03cc[Gy] | 78.80 ± 3.06 | 81.52 ± 2.31 | 0.447 | |
| D99%[Gy] | 67.86 ± 0.98 | 66.14 ± 1.47 | 0.7081 | |
| Heart | V45Gy[%] | 10.1% ± 9.2% | 13.1 ± 9.8% | 0.0074 |
| V30Gy[%] | 16.5% ± 12.9% | 21.9 ± 17.0 | 0.1029 | |
| Mean[Gy] | 14.02 ± 8.66 | 13.71 ± 12.31 | 0.0901 | |
| Lungs | V5Gy[%] | 52.3% ± 10.1% | 53.4 ± 13.1% | 0.1007 |
| V20Gy[%] | 28.9% ± 6.2% | 30.2 ±7.7% | 0.8153 | |
| Mean[Gy] | 17.85 ± 3.69 | 17.23 ± 3.39 | 0.0057 | |
| Esophagus | V74Gy[cc] | 0.20 ± 0.45 | 0 ± 0 | N/A |
| Spinal cord | D0.03cc[Gy] | 43.97 ± 7.04 | 42.44 ± 4.51 | 0.5377 |
| Structure | Dose Point | IMPT Original | IMPT KBP | p Value | PS Original | IMPT KBP | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PTV | D95%[Gy] | 69.60 ± 1.26 | 70.37 ± 0.16 | 0.0127 | 69.44 ± 3.39 | 70.30 ± 0.44 | 0.2497 |
| D0.03cc[Gy] | 75.62 ± 2.09 | 76.23 ± 1.54 | 0.2999 | 79.249 ± 3.97 | 76.11 ± 1.29 | 0.0053 | |
| D99%[Gy] | 67.34 ± 2.10 | 69.34 ± 0.48 | 0.0006 | 65.50 ± 5.08 | 69.14 ± 0.73 | 0.0044 | |
| Heart | V45Gy[%] | 5.4% ± 3.9% | 4.2% ± 3.3% | 0.0043 | 5.6% ± 5.5% | 4.2% ± 4.4% | 0.0001 |
| V30Gy[%] | 7.7% ± 5.2% | 6.1% ± 4.6% | 0.0048 | 7.6% ± 6.7% | 5.9% ± 5.6% | 0.0003 | |
| Mean[Gy] | 6.25 ± 4.07 | 4.92 ± 3.54 | 0.0032 | 5.46 ± 4.74 | 4.60 ± 4.12 | 0.0208 | |
| Lungs | V5Gy[%] | 31.1% ± 6.2% | 28.6% ± 7.6% | 0.0111 | 33.4% ± 10.8% | 28.8% ± 9.4% | <0.0001 |
| V20Gy[%] | 23.9% ± 6.0% | 21.6% ± 6.6% | 0.0063 | 25.9% ± 7.9% | 22.04% ± 8.14% | <0.0001 | |
| Mean[Gy] | 13.76 ± 3.61 | 12.19 ± 3.98 | 0.002 | 14.64 ± 4.43 | 12.68 ± 4.43 | <0.0001 | |
| Esophagus | V74Gy[cc] | 0.05 ± 0.22 | 0.01 ± 0.04 | N/A | 0.80 ± 2.48 | 0.01 ± 0.03 | N/A |
| Spinal Cord | D0.03cc[Gy] | 29.02 ± 14.80 | 25.90 ± 15.52 | 0.2197 | 27.26 ± 16.55 | 33.20 ± 13.75 | 0.0466 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Geng, H.; Liao, Z.; Nguyen, Q.-N.; Berman, A.T.; Robinson, C.; Wu, A.; Nichols Jr, R.C.; Willers, H.; Mohammed, N.; Mohindra, P.; et al. Implementation of Machine Learning Models to Ensure Radiotherapy Quality for Multicenter Clinical Trials: Report from a Phase III Lung Cancer Study. Cancers 2023, 15, 1014. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15041014
Geng H, Liao Z, Nguyen Q-N, Berman AT, Robinson C, Wu A, Nichols Jr RC, Willers H, Mohammed N, Mohindra P, et al. Implementation of Machine Learning Models to Ensure Radiotherapy Quality for Multicenter Clinical Trials: Report from a Phase III Lung Cancer Study. Cancers. 2023; 15(4):1014. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15041014
Chicago/Turabian StyleGeng, Huaizhi, Zhongxing Liao, Quynh-Nhu Nguyen, Abigail T. Berman, Clifford Robinson, Abraham Wu, Romaine Charles Nichols Jr, Henning Willers, Nasiruddin Mohammed, Pranshu Mohindra, and et al. 2023. "Implementation of Machine Learning Models to Ensure Radiotherapy Quality for Multicenter Clinical Trials: Report from a Phase III Lung Cancer Study" Cancers 15, no. 4: 1014. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15041014
APA StyleGeng, H., Liao, Z., Nguyen, Q.-N., Berman, A. T., Robinson, C., Wu, A., Nichols Jr, R. C., Willers, H., Mohammed, N., Mohindra, P., & Xiao, Y. (2023). Implementation of Machine Learning Models to Ensure Radiotherapy Quality for Multicenter Clinical Trials: Report from a Phase III Lung Cancer Study. Cancers, 15(4), 1014. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15041014








