Impact of Novel Treatments in Patients with Melanoma Brain Metastasis: Real-World Data
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Selection
2.2. Data Collection and Definitions
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
3.2. Treatments over Time
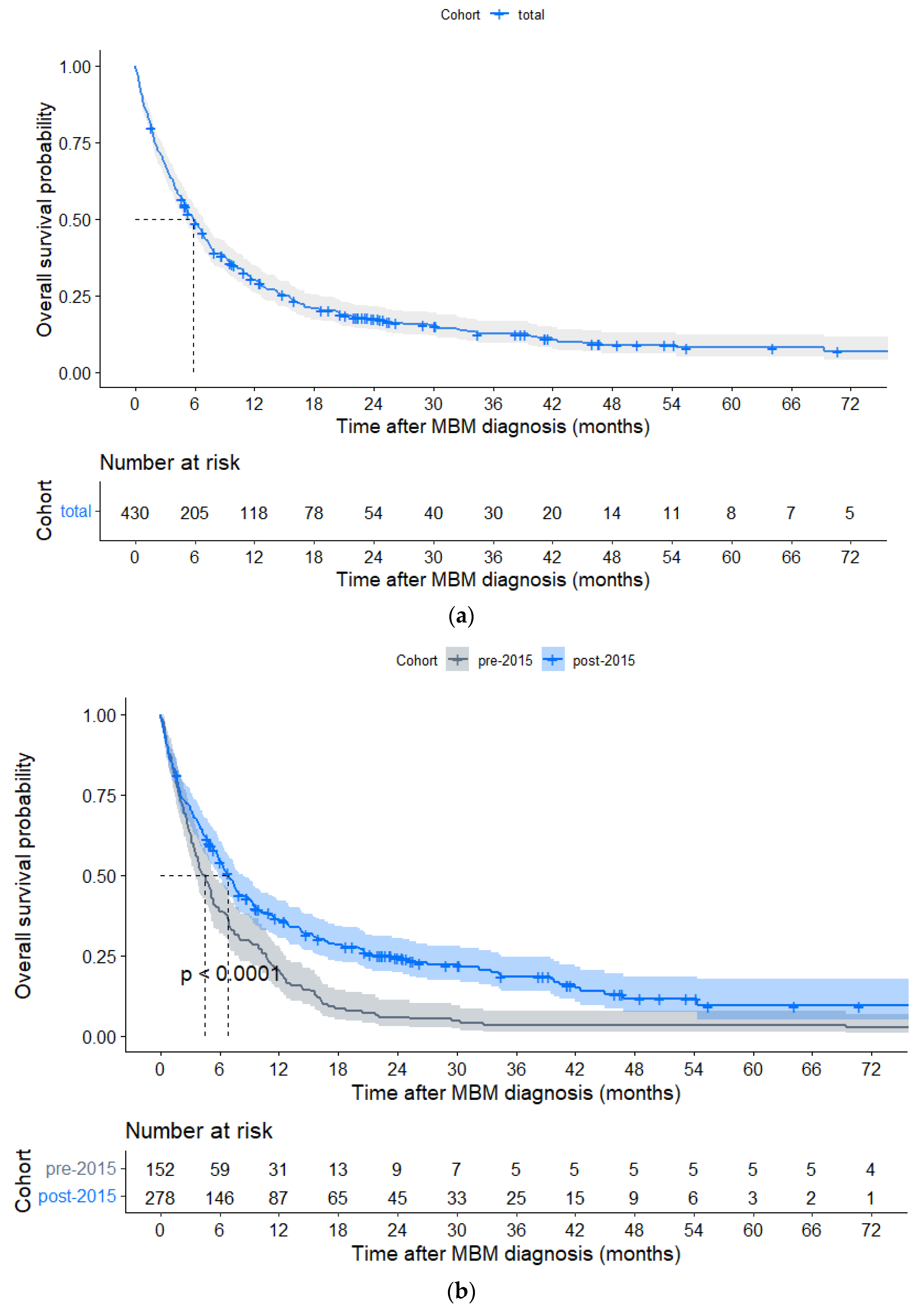
3.3. Overall Survival
3.3.1. Local Treatments Post-2015
3.3.2. Systemic Treatments Post-2015
3.4. Independent Prognostic Variables
3.5. Melanoma-molGPA
3.6. Switching from Targeted Therapy to Immune Checkpoint Inhibition
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A

| Year of Prescription | No. of Patients | Chemo-therapy | Targeted Therapy | Immune Checkpoint Inhibition | Stereotactic Radiotherapy | Whole Brain Radiotherapy | Surgical Resection |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2005 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 2007 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 3 |
| 2008 | 4 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 1 |
| 2009 | 22 | 8 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 19 | 4 |
| 2010 | 12 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 7 | 2 |
| 2011 | 20 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 5 | 13 | 4 |
| 2012 | 30 | 5 | 8 | 1 | 4 | 23 | 3 |
| 2013 | 21 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 9 | 13 | 3 |
| 2014 | 37 | 7 | 6 | 3 | 7 | 19 | 7 |
| 2015 | 33 | 0 | 12 | 9 | 5 | 17 | 2 |
| 2016 | 35 | 0 | 11 | 7 | 5 | 11 | 1 |
| 2017 | 47 | 0 | 17 | 17 | 9 | 12 | 9 |
| 2018 | 40 | 0 | 18 | 23 | 15 | 4 | 8 |
| 2019 | 60 | 0 | 38 | 40 | 17 | 2 | 11 |
| 2020 | 45 | 0 | 20 | 24 | 12 | 3 | 14 |
| 2021 * | 20 | 0 | 16 | 13 | 6 | 1 | 3 |


| Total Cohort | Pre-2015 Cohort | Post-2015 Cohort | HR [95%CI] (Ref. = Pre-2015 Cohort) | p-Value between Time Cohorts | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | Median OS (Months) | Median OS (Months) | Median OS (Months) | ||
| 5.88 | 4.44 | 6.87 | 0.626 [0.507–0.773] | <0.001 | |
| Symptoms of MBM | |||||
| Asymptomatic | 10.05 | 4.57 | 14.13 | 0.418 [0.255–0.684] | <0.001 |
| Symptomatic | 5.03 | 4.37 | 5.68 | 0.768 [0.607–0.971] | 0.027 |
| KPS | |||||
| ≤70 | 2.07 | 2.60 | 1.81 | 0.956 [0.659–1.389] | 0.816 |
| >70 | 9.04 | 6.77 | 11.30 | 0.516 [0.392–0.679] | <0.001 |
| LDH level | |||||
| ≤ULN | 9.36 | 7.00 | 10.05 | 0.720 [0.488–1.061] | 0.097 |
| >ULN | 3.55 | 2.73 | 4.67 | 0.627 [0.447–0.880] | 0.007 |
| ECM status | |||||
| None | 11.53 | 11.20 | 20.73 | 0.635 [0.374–1.078] | 0.092 |
| Synchronous MBM | 6.44 | 4.17 | 8.97 | 0.456 [0.329–0.634] | <0.001 |
| Metachronous MBM | 4.01 | 3.55 | 4.22 | 0.798 [0.563–1.130] | 0.210 |
| Number of MBMs | |||||
| <4 | 9.66 | 6.93 | 12.71 | 0.597 [0.439–0.813] | 0.001 |
| ≥4 | 3.94 | 2.99 | 5.19 | 0.621 [0.464–0.832] | 0.001 |
| Total Cohort | Pre-2015 Cohort | Post-2015 Cohort | HR [95%CI] (Ref. = Pre-2015 Cohort) | p-Value between Time Cohorts | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Median OS (Months) | Median OS (Months) | Median OS (Months) | |||
| Local treatments, <4 MBMs (n = 216) | |||||
| SRT | |||||
| Yes | 20.4 | 12.8 | 30.3 | 0.515 [0.272–0.974] | 0.04 |
| No | 6.8 | 6.0 | 7.6 | 0.620 [0.436–0.883] | 0.007 |
| Surgical resection | |||||
| Yes | 11.5 | 9.9 | 21.5 | 0.470 [0.249–0.890] | 0.02 |
| No | 7.6 | 6.5 | 9.4 | 0.617 [0.432–0.882] | 0.007 |
| Median OS (Months) | 1-Year Probability OS (%) | HR [95%CI] | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Treatments prior to diagnosis of MBM | ||||
| Systemic treatments (n = 278) | ||||
| No prior TTs 1 | 10.94 | 0.47 | ref. | |
| Prior TTs 1 | 1.95 | 0.11 | 2.670 [1.793–3.974] | <0.001 |
| No prior ICIs | 7.89 | 0.40 | ref. | |
| Prior ICIs | 4.24 | 0.24 | 1.665 [1.232–2.250] | <0.001 |
| Treatments directly after diagnosis of MBM | ||||
| Local treatments, <4 MBMs (n = 141) | ||||
| No SRT | 7.62 | 0.42 | ref. | |
| SRT | 30.33 | 0.72 | 0.456 [0.284–0.734] | <0.001 |
| No surgical resection | 9.36 | 0.47 | ref. | |
| Surgical resection | 21.49 | 0.66 | 0.769 [0.466–1.268] | 0.303 |
| Systemic treatments (n = 278) | ||||
| No TTs 1 | 7.41 | 0.42 | ref. | |
| TTs 1 | 7.79 | 0.36 | 1.154 [0.804–1.653] | 0.435 |
| No ICIs | 4.24 | 0.16 | ref. | |
| ICIs | 21.49 | 0.72 | 0.280 [0.205–0.384] | <0.001 |
| (a) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | Previous TTs (%) | No Previous TTs (%) | p-Value |
| 36 (100) | 121 (100) | ||
| Number of MBMs | 0.003 | ||
| 1–3 | 7 (19.4) | 57 (47.1) | |
| ≥4 | 29 (80.6) | 64 (52.9) | |
| ECM status | <0.001 | ||
| None | 1 (2.8) | 19 (15.7) | |
| Synchronous MBM | 1 (2.8) | 69 (57.0) | |
| Metachronous MBM | 33 (91.7) | 31 (25.6) | |
| Unknown 1 | 1 (2.8) | 2 (1.7) | |
| LDH status | 0.099 | ||
| ≤ULN | 15 (41.7) | 57 (47.1) | |
| >ULN | 20 (55.6) | 48 (39.7) | |
| Unknown 1 | 1 (2.8) | 16 (13.2) | |
| Symptomatic MBM | 0.040 | ||
| No | 6 (16.7) | 43 (35.5) | |
| Yes | 30 (83.3) | 78 (64.5) | |
| Previous ICIs | <0.001 | ||
| No | 15 (41.7) | 103 (85.1) | |
| Yes | 21 (58.3) | 18 (14.9) | |
| First line TTs | <0.001 | ||
| No | 28 (77.8) | 40 (33.1) | |
| Yes | 8 (22.2) | 81 (66.9) | |
| First line ICIs | 0.013 | ||
| No | 31 (86.1) | 77 (63.6) | |
| Yes | 5 (13.9) | 44 (36.4) | |
| Median time between primary diagnosis of ECM and MBM (months) 2 | 8.0 IQR (5.0–19.0) | 7.0 IQR (4.0–10.0) | 0.40 |
| (b) | |||
| Variables | Previous ICI (%) | No previous ICI (%) | p-Value |
| 70 (100) | 208 (100) | ||
| Number of MBMs | 0.10 | ||
| 1–3 | 29 (41.4) | 112 (53.8) | |
| ≥4 | 41 (58.6) | 96 (46.2) | |
| ECM status | <0.001 | ||
| None | 4 (5.7) | 40 (19.2) | |
| Synchronous MBM | 6 (8.6) | 116 (55.8) | |
| Metachronous MBM | 58 (82.9) | 46 (22.1) | |
| Unknown 1 | 2 (2.8) | 6 (2.9) | |
| LDH status | 0.018 | ||
| ≤ULN | 26 (37.1) | 96 (46.2) | |
| >ULN | 38 (54.3) | 75 (36.1) | |
| Unknown 1 | 6 (8.6) | 37 (17.8) | |
| Symptomatic MBM | 0.57 | ||
| No | 19 (27.1) | 66 (31.7) | |
| Yes | 51 (72.9) | 142 (68.3) | |
| Previous TTs | <0.001 | ||
| No | 49 (70.0) | 192 (92.3) | |
| Yes | 21 (30.0) | 16 (7.7) | |
| First line TTs | 0.22 | ||
| No | 51 (72.9) | 133 (63.9) | |
| Yes | 19 (27.1) | 75 (36.1) | |
| First line ICIs | <0.001 | ||
| No | 59 (84.3) | 121 (58.2) | |
| Yes | 11 (15.7) | 87 (41.8) | |
| Median time between primary diagnosis of ECM and primary diagnosis of MBM (months) 2 | 8.0 (IQR 6.0–19.0) | 7.5 (IQR 3.0–17.0) | 0.50 |




| Class | Number of Patients | % | Median OS | HR | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I (0–1) | 90 | 33.6 | 2.99 | ref. | <0.001 |
| II (1,5–2) | 116 | 43.3 | 6.87 | 0.627 [0.463–0.849] | |
| III (2,5–3) | 47 | 17.5 | 24.51 | 0.290 [0.189–0.446] | |
| IV (3,5–4) | 15 | 5.6 | 30.33 | 0.203 [0.097–0.423] | |
| Unknown * | 10 |
| Variable | At Initiation of TTs n = 18 (100%) | At Initiation of ICIs (TTs Switched to ICIs) n = 18 (100%) | At First Progression 2 after Initiation of ICIs n = 18 (100%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Symptomatic MBM 1 | |||
| Yes | 16 (88.9) | 2 (11.1) | 7 (38.9) |
| No | 2 (11.1) | 13 (72.2) | 4 (22.2) |
| Unknown | 0 (0) | 3 (16.7) | 7 (38.9) |
| Performance status 1 | |||
| KPS ≤70 | 6 (33.3) | 2 (11.1) | 6 (33.3) |
| KPS >70 | 12 (66.7) | 15 (83.3) | 4 (22.2) |
| Unknown | 0 (0) | 1 (5.6) | 8 (44.4) |
| LDH 1 | |||
| ≤ULN | 13 (72.2) | 10 (55.6) | 3 (16.7) |
| >ULN | 3 (16.7) | 5 (27.8) | 9 (69.2) |
| Unknown | 2 (11.1) | 1 (5.6) | 6 (33.3) |
| BM status 1 | |||
| New/progressive | 18 (100) | 2 (11.1) | 13 (72.2) |
| Stable/response | 0 (0) | 12 (66.7) | 3 (16.7) |
| Mixed response | 0 (0) | 3 (16.7) | 1 (5.6) |
| Unknown | 0 (0) | 1 (5.6) | 1 (5.6) |
| ECM status 1 | |||
| New/progressive | 15 (83.3) | 4 (22.2) | 4 (22.2) |
| Stable/response | 1 (5.6) | 8 (44.4) | 9 (50.0) |
| Mixed response | 0 (0) | 2 (11.1) | 3 (16.7) |
| No ECM | 2 (11.1) | 2 (11.1) | 1 (5.6) |
| Unknown | 0 (0) | 2 (11.1) | 1 (5.6) |
| Systemic treatment | |||
| Dabrafenib + trametinib | 8 (44.4) | NA | 7 (38.9) |
| Vemurafenib + cobimetinib | 7 (38.9) | NA | 2 (11.1) |
| Dabrafenib | 2 (11.1) | NA | 0 (0) |
| Vemurafenib | 1 (5.6) | NA | 0 (0) |
| Encorafenib + binimetinib | 0 (0) | NA | 3 (16.7) |
| Nivolumab + ipilimumab | NA | 12 (66.7) | NA |
| Pembrolizumab | NA | 4 (22.2) | NA |
| Nivolumab | NA | 2 (11.1) | NA |
| No systemic treatment | NA | NA | 6 (33.3) |
Detailed Description Table A6: Switching from TT to ICI Treatment

References
- Cagney, D.N.; Martin, A.M.; Catalano, P.J.; Redig, A.J.; Lin, N.U.; Lee, E.Q.; Wen, P.Y.; Dunn, I.F.; Bi, W.L.; Weiss, S.E.; et al. Incidence and prognosis of patients with brain metastases at diagnosis of systemic malignancy: A population-based study. Neuro. Oncol. 2017, 19, 1511–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Davies, M.A.; Liu, P.; McIntyre, S.; Kim, K.B.; Papadopoulos, N.; Hwu, W.J.; Hwu, P.; Bedikian, A. Prognostic factors for survival in melanoma patients with brain metastases. Cancer 2011, 117, 1687–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J.V.; Tawbi, H.; Margolin, K.A.; Amravadi, R.; Bosenberg, M.; Brastianos, P.K.; Chiang, V.L.; de Groot, J.; Glitza, I.C.; Herlyn, M.; et al. Melanoma central nervous system metastases: Current approaches, challenges, and opportunities. Pigment. Cell Melanoma Res. 2016, 29, 627–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hauswald, H.; Dittmar, J.O.; Habermehl, D.; Rieken, S.; Sterzing, F.; Debus, J.; Combs, S.E. Efficacy and toxicity of whole brain radiotherapy in patients with multiple cerebral metastases from malignant melanoma. Radiat. Oncol. 2012, 7, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chang, E.L.; Wefel, J.S.; Hess, K.R.; Allen, P.K.; Lang, F.F.; Kornguth, D.G.; Arbuckle, R.B.; Swint, J.M.; Shiu, A.S.; Maor, M.H.; et al. Neurocognition in patients with brain metastases treated with radiosurgery or radiosurgery plus whole-brain irradiation: A randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2009, 10, 1037–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, J.; Atkinson, H.; A’Hern, R.; Lorentzos, A.; Gore, M.E. A phase II study of the sequential administration of dacarbazine and fotemustine in the treatment of cerebral metastases from malignant melanoma. Eur. J. Cancer 1994, 30, 2093–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, M.A.; Saiag, P.; Robert, C.; Grob, J.J.; Flaherty, K.T.; Arance, A.; Chiarion-Sileni, V.; Thomas, L.; Lesimple, T.; Mortier, L.; et al. Dabrafenib plus trametinib in patients with BRAF(V600)-mutant melanoma brain metastases (COMBI-MB): A multicentre, multicohort, open-label, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 863–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, G.V.; Atkinson, V.; Lo, S.; Sandhu, S.; Guminski, A.D.; Brown, M.P.; Wilmott, J.S.; Edwards, J.; Gonzalez, M.; Scolyer, R.A.; et al. Combination nivolumab and ipilimumab or nivolumab alone in melanoma brain metastases: A multicentre randomised phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2018, 19, 672–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, G.V.; Atkinson, V.G.; Lo, S.; Sandhu, S.K.; Brown, M.; Gonzalez, M.; Guminski, A.; Scolyer, R.A.; Emmett, L.; Menzies, A.M.; et al. 1311O—Long-term outcomes from the randomized phase II study of nivolumab (nivo) or nivo+ipilimumab (ipi) in patients (pts) with melanoma brain metastases (mets): Anti-PD1 brain collaboration (ABC). Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, v534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgina, V.L.; Victoria, A.; Serigne, L.; Alexander David, G.; Shahneen Kaur, S.; Michael Paul, B.; Maria, G.; Richard, A.S.; Louise, E.; Grant, A.M.; et al. Five-year overall survival from the anti-PD1 brain collaboration (ABC Study): Randomized phase 2 study of nivolumab (nivo) or nivo+ipilimumab (ipi) in patients (pts) with melanoma brain metastases (mets). J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 9508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawbi, H.A.; Forsyth, P.A.; Algazi, A.; Hamid, O.; Hodi, F.S.; Moschos, S.J.; Khushalani, N.I.; Lewis, K.; Lao, C.D.; Postow, M.A.; et al. Combined Nivolumab and Ipilimumab in Melanoma Metastatic to the Brain. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 722–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, G.V.; Trefzer, U.; Davies, M.A.; Kefford, R.F.; Ascierto, P.A.; Chapman, P.B.; Puzanov, I.; Hauschild, A.; Robert, C.; Algazi, A.; et al. Dabrafenib in patients with Val600Glu or Val600Lys BRAF-mutant melanoma metastatic to the brain (BREAK-MB): A multicentre, open-label, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2012, 13, 1087–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Giacomo, A.M.; Chiarion-Sileni, V.; Del Vecchio, M.; Ferrucci, P.F.; Guida, M.; Quaglino, P.; Guidoboni, M.; Marchetti, P.; Cutaia, O.; Amato, G.; et al. Primary Analysis and 4-Year Follow-Up of the Phase III NIBIT-M2 Trial in Melanoma Patients With Brain Metastases. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 27, 4737–4745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kluger, H.M.; Chiang, V.; Mahajan, A.; Zito, C.R.; Sznol, M.; Tran, T.; Weiss, S.A.; Cohen, J.V.; Yu, J.; Hegde, U.; et al. Long-Term Survival of Patients With Melanoma With Active Brain Metastases Treated With Pembrolizumab on a Phase II Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tawbi, H.A.; Forsyth, P.A.; Hodi, F.S.; Algazi, A.P.; Hamid, O.; Lao, C.D.; Moschos, S.J.; Atkins, M.B.; Lewis, K.; Postow, M.A.; et al. Long-term outcomes of patients with active melanoma brain metastases treated with combination nivolumab plus ipilimumab (CheckMate 204): Final results of an open-label, multicentre, phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2021, 22, 1692–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margolin, K.; Ernstoff, M.S.; Hamid, O.; Lawrence, D.; McDermott, D.; Puzanov, I.; Wolchok, J.D.; Clark, J.I.; Sznol, M.; Logan, T.F.; et al. Ipilimumab in patients with melanoma and brain metastases: An open-label, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2012, 13, 459–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sperduto, P.W.; Jiang, W.; Brown, P.D.; Braunstein, S.; Sneed, P.; Wattson, D.A.; Shih, H.A.; Bangdiwala, A.; Shanley, R.; Lockney, N.A.; et al. Estimating Survival in Melanoma Patients With Brain Metastases: An Update of the Graded Prognostic Assessment for Melanoma Using Molecular Markers (Melanoma-molGPA). Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2017, 99, 812–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sperduto, P.W.; Jiang, W.; Brown, P.D.; Braunstein, S.; Sneed, P.; Wattson, D.A.; Shih, H.A.; Bangdiwala, A.; Shanley, R.; Lockney, N.A.; et al. The Prognostic Value of BRAF, C-KIT, and NRAS Mutations in Melanoma Patients With Brain Metastases. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2017, 98, 1069–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sperduto, P.W.; Kased, N.; Roberge, D.; Xu, Z.; Shanley, R.; Luo, X.; Sneed, P.K.; Chao, S.T.; Weil, R.J.; Suh, J.; et al. Summary report on the graded prognostic assessment: An accurate and facile diagnosis-specific tool to estimate survival for patients with brain metastases. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 419–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Steindl, A.; Brunner, T.J.; Heimbach, K.; Schweighart, K.; Moser, G.M.; Niziolek, H.M.; Moor, E.; Kreminger, J.; Starzer, A.M.; Dieckmann, K.; et al. Changing characteristics, treatment approaches and survival of patients with brain metastasis: Data from six thousand and thirty-one individuals over an observation period of 30 years. Eur. J. Cancer 2022, 162, 170–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Breeschoten, J.; van den Eertwegh, A.J.M.; de Wreede, L.C.; Hilarius, D.L.; van Zwet, E.W.; Haanen, J.B.; Blank, C.U.; Aarts, M.J.B.; van den Berkmortel, F.W.P.J.; de Groot, J.W.B.; et al. Hospital Variation in Cancer Treatments and Survival OutComes of Advanced Melanoma Patients: Nationwide Quality Assurance in The Netherlands. Cancers 2021, 13, 5077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, M.; Serizawa, T.; Shuto, T.; Akabane, A.; Higuchi, Y.; Kawagishi, J.; Yamanaka, K.; Sato, Y.; Jokura, H.; Yomo, S.; et al. Stereotactic radiosurgery for patients with multiple brain metastases (JLGK0901): A multi-institutional prospective observational study. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Susko, M.S.; Garcia, M.A.; Ma, L.; Nakamura, J.L.; Raleigh, D.R.; Fogh, S.; Theodosopoulos, P.; McDermott, M.; Sneed, P.K.; Braunstein, S.E. Stereotactic Radiosurgery to More Than 10 Brain Metastases: Evidence to Support the Role of Radiosurgery for Ideal Hippocampal Sparing in the Treatment of Multiple Brain Metastases. World Neurosurg. 2020, 135, e174–e180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Rocha Dias, S.; Salmonson, T.; van Zwieten-Boot, B.; Jonsson, B.; Marchetti, S.; Schellens, J.H.; Giuliani, R.; Pignatti, F. The European Medicines Agency review of vemurafenib (Zelboraf®) for the treatment of adult patients with BRAF V600 mutation-positive unresectable or metastatic melanoma: Summary of the scientific assessment of the Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use. Eur. J. Cancer 2013, 49, 1654–1661. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, G.; McKee, A.E.; Ning, Y.M.; Hazarika, M.; Theoret, M.; Johnson, J.R.; Xu, Q.C.; Tang, S.; Sridhara, R.; Jiang, X.; et al. FDA approval summary: Vemurafenib for treatment of unresectable or metastatic melanoma with the BRAFV600E mutation. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 4994–5000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bander, E.D.; Yuan, M.; Carnevale, J.A.; Reiner, A.S.; Panageas, K.S.; Postow, M.A.; Tabar, V.; Moss, N.S. Melanoma brain metastasis presentation, treatment, and outcomes in the age of targeted and immunotherapies. Cancer 2021, 127, 2062–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, S.; Møller, S.; Donia, M.; Persson, G.F.; Svane, I.M.; Ellebaek, E. Real-world data on melanoma brain metastases and survival outcome. Melanoma Res. 2022, 32, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkins, M.B.; Lee, S.J.; Chmielowski, B.; Tarhini, A.A.; Cohen, G.I.; Truong, T.G.; Moon, H.H.; Davar, D.; O’Rourke, M.; Stephenson, J.J.; et al. Combination Dabrafenib and Trametinib Versus Combination Nivolumab and Ipilimumab for Patients With Advanced BRAF-Mutant Melanoma: The DREAMseq Trial-ECOG-ACRIN EA6134. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, JCO2201763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paolo Antonio, A.; Mario, M.; Pier Francesco, F.; Massimo, G.; Piotr, R.; Virginia, F.; Ana Maria, A.; Michele, G.; Evaristo, M.; Helen, G.; et al. Phase II study SECOMBIT (sequential combo immuno and target therapy study): A subgroup analysis with a longer follow-up. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 9535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakavand, H.; Wilmott, J.S.; Menzies, A.M.; Vilain, R.; Haydu, L.E.; Yearley, J.H.; Thompson, J.F.; Kefford, R.F.; Hersey, P.; Long, G.V.; et al. PD-L1 Expression and Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes Define Different Subsets of MAPK Inhibitor-Treated Melanoma Patients. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 3140–3148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]





| Patients (%) | ||||
| Total | Pre-2015 | Post-2015 | p-Value 1 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | 430 | 152 | 278 | |
| Age at diagnosis of MBM, years | 0.005 | |||
| Median (interquartile range) | 63.1 (52.3–71.7) | 60.6 (49.2–69.1) | 64.5 (53.4–72.9) | |
| Sex | 0.192 | |||
| Women | 173 (40.2) | 68 (44.7) | 105 (37.8) | |
| Men | 257 (59.8) | 84 (55.3) | 173 (62.2) | |
| Karnofsky performance status (KPS) | 0.722 | |||
| ≤70 | 133 (30.9) | 43 (28.3) | 90 (32.4) | |
| 80 | 141 (32.8) | 51 (33.6) | 90 (32.4) | |
| 90–100 | 131 (30.5) | 42 (27.6) | 89 (32.0) | |
| Unknown 2 | 25 (5.8) | 16 (10.5) | 9 (3.2) | |
| LDH at MBM diagnosis | 0.136 | |||
| ≤ULN | 162 (37.7) | 40 (26.3) | 122 (43.9) | |
| >ULN | 168 (39.1) | 55 (36.2) | 113 (47.8) | |
| Unknown 2 | 100 (23.3) | 57 (37.5) | 43 (15.5) | |
| BRAF mutational status | 0.013 | |||
| Wildtype | 145 (33.7) | 45 (29.6) | 100 (36.0) | |
| V600E+ or K | 192 (44.7) | 35 (23.0) | 157 (56.5) | |
| Other | 15 (3.5) | 2 (1.3) | 13 (4.7) | |
| Unknown 2 | 78 (18.1) | 70 (46.1) | 8 (2.9) | |
| Time between first diagnosis of melanoma and diagnosis of MBM, months | ||||
| Median (interquartile range) | 37.0 (11.0–68.0) | 36.5 (12.0–59.3) | 37.0 (10.0–70.0) | 0.720 |
| Time between first diagnosis of ECM and diagnosis of MBM, months 3 | ||||
| Median (interquartile range) | 8.0 (5.0–17.0) | 9.0 (4.0–15.0) | 8.0 (5.0–19.0) | 0.40 |
| Symptomatic MBM | 0.001 | |||
| Yes | 321 (74.6) | 128 (84.2) | 193 (69.4) | |
| No | 109 (25.3) | 24 (15.8) | 85 (30.6) | |
| Number of MBMs | 0.533 | |||
| 1 | 123 (28.6) | 38 (25.0) | 86 (30.9) | |
| 2 | 57 (13.3) | 23 (15.1) | 34 (12.2) | |
| 3 | 35 (8.1) | 14 (9.2) | 21 (7.6) | |
| ≥4 | 215 (50.0) | 77 (50.7) | 137 (49.3) | |
| Status of ECM | 0.391 | |||
| No ECM | 75 (17.4) | 31 (20.4) | 44 (15.8) | |
| MBM synchronous with ECM | 187 (43.5) | 65 (42.8) | 122 (43.9) | |
| MBM metachronous with ECM | 153 (35.6) | 49 (32.2) | 104 (37.4) | |
| Unknown 2 | 15 (3.5) | 7 (4.6) | 8 (2.9) | |
| Patients (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | Pre-2015 | Post-2015 | p-Value 1 | |
| Variable | 430 | 152 | 278 | |
| Treatments prior to MBM diagnosis | ||||
| Systemic treatments | ||||
| Chemotherapy | 0.008 | |||
| Yes | 14 (3.3) | 10 (6.6) | 4 (1.4) | |
| No | 416 (96.7) | 142 (93.4) | 274 (98.6) | |
| Targeted therapy | <0.001 | |||
| Yes | 42 (9.8) | 5 (3.3) | 37 (13.3) | |
| No | 388 (90.2) | 147 (96.7) | 241 (86.7) | |
| Immune checkpoint inhibition | <0.001 | |||
| Yes | 73 (17.0) | 3 (2.0) | 70 (25.2) | |
| No | 357 (83.0) | 149 (98.0) | 208 (74.8) | |
| Treatments directly after MBM diagnosis | ||||
| Local treatments | ||||
| SRT | 0.684 | |||
| Yes | 62 (14.4) | 20 (13.2) | 42 (15.1) | |
| No | 368 (85.6) | 132 (86.8) | 236 (84.9) | |
| WBRT | ||||
| Yes | 120 (27.9) | 84 (55.3) | 35 (12.6) | <0.001 |
| No | 310 (72.1) | 68 (44.7) | 243 (87.4) | |
| Surgical resection | 0.203 | |||
| Yes | 52 (12.1) | 23 (15.1) | 29 (10.4) | |
| No | 378 (87.9) | 129 (84.9) | 249 (89.6) | |
| Systemic treatments | ||||
| Chemotherapy | <0.001 | |||
| Yes | 22 (5.1) | 22 (14.5) | 4 (1.4) | |
| No | 408 (94.9) | 130 (85.5) | 274 (98.6) | |
| Targeted therapy | <0.001 | |||
| Yes | 110 (25.6) | 16 (10.5) | 94 (33.8) | |
| No | 320 (74.4) | 136 (89.5) | 184 (66.2) | |
| Immune checkpoint inhibition | <0.001 | |||
| Yes | 101 (23.5) | 4 (2.6) | 98 (35.3) | |
| No | 329 (76.5) | 148 (97.4) | 180 (64.7) | |
| Best supportive care | 0.726 | |||
| Yes | 73 (17.0) | 24 (15.8) | 49 (17.6) | |
| No | 357 (83.0) | 128 (84.2) | 229 (82.4) | |
| Univariate Analysis | Multivariate Analysis | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | HR [95%CI] | p-Value | HR [95%CI] | p-Value |
| Age at MBM diagnosis | 1.012 [1.002–1.023] | 0.017 | - | - |
| Time between primary diagnosis melanoma and MBM | 1.001 [0.999–1.003] | 0.244 | - | - |
| Female sex (ref. male) | 0.945 [0.717–1.245] | 0.686 | - | - |
| LDH > ULN (ref. ≤ ULN) | 1.701 [1.269–2.279] | <0.001 | 1.305 [0.941–1.808] | 0.110 |
| KPS > 70 (ref. ≤ 70) | 0.331 [0.250–0.440] | <0.001 | 0.511 [0.371–0.703] | <0.001 |
| ≥4 MBMs (ref. 1–3) | 1.983 [1.509–2.606] | <0.001 | - | - |
| BRAF V600E+/K mutation (ref. wildtype) | 0.913 [0.686–1.215] | 0.546 | - | - |
| Symptomatic MBM (ref. no) | 1.918 [1.410–2.609] | <0.001 | 1.741 [1.210–2.504] | 0.003 |
| MBM synchronous with ECM (ref. no ECM) | 1.499 [0.978–2.298] | 0.063 | 1.412 [0.790–2.524] | 0.244 |
| MBM metachronous to ECM (ref. no ECM) | 2.815 [1.830–4.330] | <0.001 | 2.726 [1.501–4.951] | <0.001 |
| Previous TTs (ref. no) | 2.247 [1.565–3.225] | <0.001 | - | - |
| Previous ICIs (ref. no) | 1.665 [1.232–2.250] | <0.001 | 0.687 [0.456–1.035] | 0.072 |
| TTs after MBM diagnosis (ref. no) | 1.062 [0.803–1.404] | 0.673 | - | - |
| ICIs after MBM diagnosis (ref. no) | 0.280 [0.205–0.384] | <0.001 | 0.323 [0.221–0.472] | <0.001 |
| Surgical resection (ref. no) | 0.566 [0.357–0.899] | 0.009 | 0.656 [0.348–1.237] | 0.192 |
| SRT (ref. no) | 0.412 [0.271–0.626] | <0.001 | 0.493 [0.283–0.860] | 0.013 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Derks, S.H.A.E.; Jongen, J.L.M.; van der Meer, E.L.; Ho, L.S.; Slagter, C.; Joosse, A.; de Jonge, M.J.A.; Schouten, J.W.; Oomen-de Hoop, E.; van den Bent, M.J.; et al. Impact of Novel Treatments in Patients with Melanoma Brain Metastasis: Real-World Data. Cancers 2023, 15, 1461. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15051461
Derks SHAE, Jongen JLM, van der Meer EL, Ho LS, Slagter C, Joosse A, de Jonge MJA, Schouten JW, Oomen-de Hoop E, van den Bent MJ, et al. Impact of Novel Treatments in Patients with Melanoma Brain Metastasis: Real-World Data. Cancers. 2023; 15(5):1461. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15051461
Chicago/Turabian StyleDerks, Sophie H. A. E., Joost L. M. Jongen, Edgar L. van der Meer, Li Shen Ho, Cleo Slagter, Arjen Joosse, Maja J. A. de Jonge, Joost W. Schouten, Esther Oomen-de Hoop, Martin J. van den Bent, and et al. 2023. "Impact of Novel Treatments in Patients with Melanoma Brain Metastasis: Real-World Data" Cancers 15, no. 5: 1461. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15051461
APA StyleDerks, S. H. A. E., Jongen, J. L. M., van der Meer, E. L., Ho, L. S., Slagter, C., Joosse, A., de Jonge, M. J. A., Schouten, J. W., Oomen-de Hoop, E., van den Bent, M. J., & van der Veldt, A. A. M. (2023). Impact of Novel Treatments in Patients with Melanoma Brain Metastasis: Real-World Data. Cancers, 15(5), 1461. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15051461







