Conditioned Media from Head and Neck Cancer Cell Lines and Serum Samples from Head and Neck Cancer Patients Drive Catabolic Pathways in Cultured Muscle Cells
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Population
2.2. Clinical and Biological Nutritional Assessment
- Nutritional risk index (NRI) = 1.519 × blood albumin + (current weight/usual weight) × 41.7;
- Percent weight loss over the previous 3 months = [(usual weight-current weight)/current weight] × 100;
- Body mass index (BMI) = current weight/height2 (kg/m2).
2.3. Skeletal Muscle Mass Assessment
2.4. Serum Amino Acids Concentration
2.5. Plasma Elisa Test
2.6. Cell Culture
2.7. Myotube Morphology Analysis
2.8. Generation of Tumor Cell-Conditioned Medium (TCM)
2.9. RNA Isolation, Reverse Transcription, and Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-qPCR)
2.10. Protein Isolation and Western Blotting
2.11. Quantification of Autophagy Flux
2.12. Proteasome Activity Measurements
2.13. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Epidemiological Characteristics
3.2. Tumor CM Drove Atrophy on Differentiated Myotubes
3.2.1. Tumor CM Disrupted the Catabolic Pathway and Its Regulation
3.2.2. TCM Induced the Autophagy/Lysosome Pathway
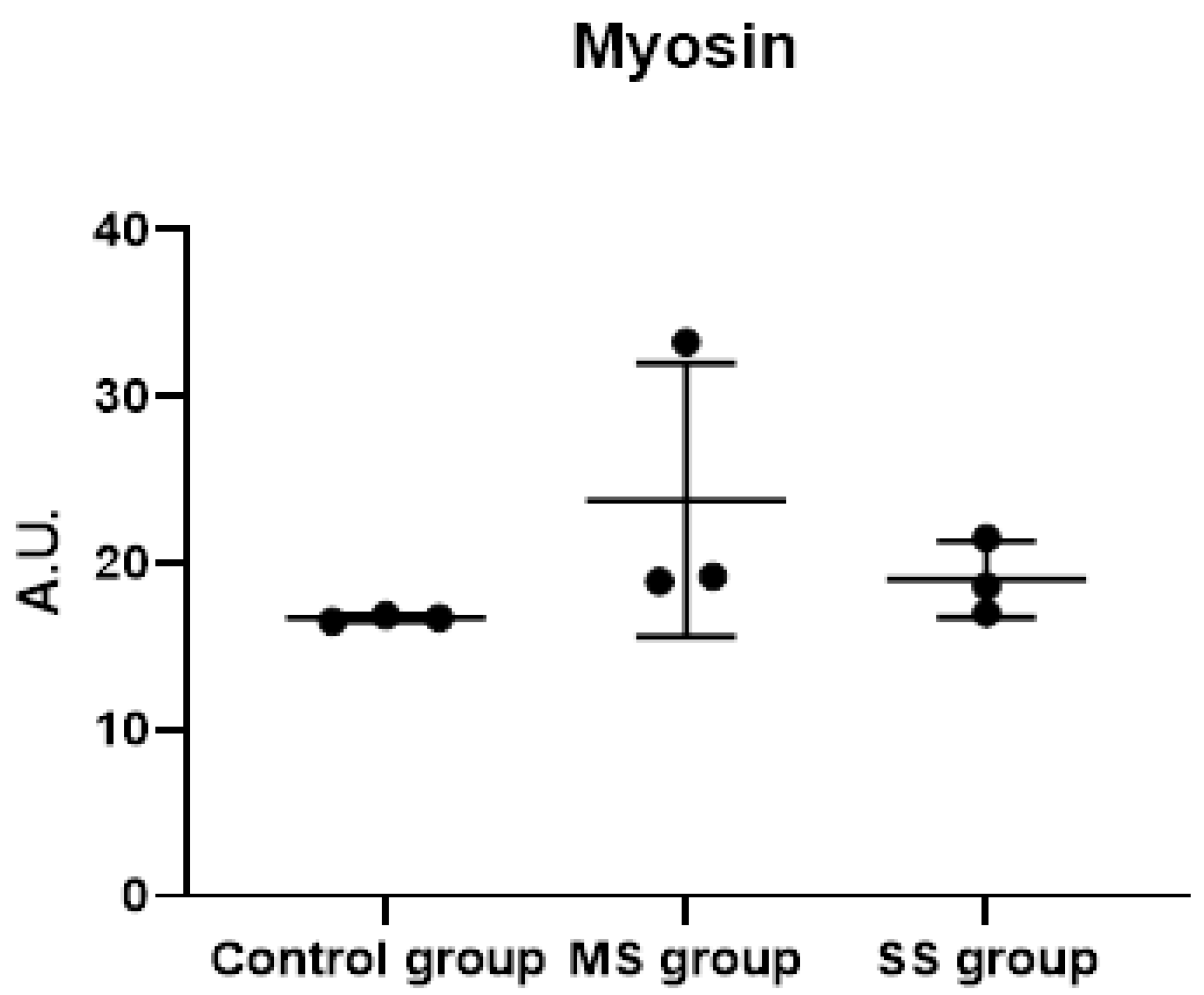
3.3. Sera from Cancer Patients Were Not Able to Drive Atrophy in Differentiated Myotubes but Changed Myotube Metabolism in the Same Way as Conditioned Media
3.3.1. Autophagy Genes
3.3.2. Proteasome Genes
3.3.3. Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress/Lipid Metabolism/Inflammation Genes
3.3.4. Proteasome Activity
3.3.5. Autophagy/Lysosomal Pathway
3.3.6. Synthesis of the Results
3.4. Blood Parameters That Could Explain the Serum Effect
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Primers | Forward Sequence | Reverse Sequence |
|---|---|---|
| P62 | GAGAGTGTGGCAGCTGCCCT | GGCAGCTTCCTTCAGCCCTG |
| LC3B | TCGAGAGCAGCATCCAACCAA | TGCTGTGTCCGTTCACCAAC |
| MurF1 | GAGCAGGGCTTTGAGAACATGG | CATCTGGGGGCCTCTCATTCAT |
| TRAF 6 | GTTGCTGAAATCGAAGCACA | CGGGTTTGCCAGTGTAGAAT |
| Fox O | AAACCTGTCCTACGCGGACC | AGGTTGTGCCGGATGGAGTT |
| MafBx | GCAGCAGCAGCTGAACAACA | AGGCACAAAGGCAGGTCAGT |
| PLIN 3 | CTTCGAGCCACCAAGCAG | AACGCCTTGCTTGACAGTTT |
| IL 6 | CCCACACAGACAGCCACTCA | TCTGCCAGTGCCTCTTTGCT |
References
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global Cancer Statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haeggblom, L.; Attoff, T.; Yu, J.; Holzhauser, S.; Vlastos, A.; Mirzae, L.; Ährlund-Richter, A.; Munck-Wikland, E.; Marklund, L.; Hammarstedt-Nordenvall, L.; et al. Changes in Incidence and Prevalence of Human Papillomavirus in Tonsillar and Base of Tongue Cancer during 2000-2016 in the Stockholm Region and Sweden. Head Neck 2019, 41, 1583–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillison, M.L.; Chaturvedi, A.K.; Anderson, W.F.; Fakhry, C. Epidemiology of Human Papillomavirus-Positive Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 3235–3242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirghani, H.; Bellera, C.; Delaye, J.; Dolivet, G.; Fakhry, N.; Bozec, A.; Garrel, R.; Malard, O.; Jegoux, F.; Maingon, P.; et al. Prevalence and Characteristics of HPV-Driven Oropharyngeal Cancer in France. Cancer Epidemiol. 2019, 61, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saroul, N.; Pastourel, R.; Mulliez, A.; Farigon, N.; Dupuch, V.; Mom, T.; Boirie, Y.; Gilain, L. Which Assessment Method of Malnutrition in Head and Neck Cancer? Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2018, 158, 1065–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fearon, K.C.H. Cancer Cachexia and Fat-Muscle Physiology. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 565–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubrak, C.; Olson, K.; Jha, N.; Jensen, L.; McCargar, L.; Seikaly, H.; Harris, J.; Scrimger, R.; Parliament, M.; Baracos, V.E. Nutrition Impact Symptoms: Key Determinants of Reduced Dietary Intake, Weight Loss, and Reduced Functional Capacity of Patients with Head and Neck Cancer before Treatment. Head Neck 2010, 32, 290–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fearon, K.; Strasser, F.; Anker, S.D.; Bosaeus, I.; Bruera, E.; Fainsinger, R.L.; Jatoi, A.; Loprinzi, C.; MacDonald, N.; Mantovani, G.; et al. Definition and Classification of Cancer Cachexia: An International Consensus. Lancet Oncol. 2011, 12, 489–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webster, J.M.; Kempen, L.J.A.P.; Hardy, R.S.; Langen, R.C.J. Inflammation and Skeletal Muscle Wasting During Cachexia. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 597675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Quan, X.-Q.; Yu, S. An Epidemiological Survey of Cachexia in Advanced Cancer Patients and Analysis on Its Diagnostic and Treatment Status. Nutr. Cancer 2015, 67, 1056–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossi, P.; Delrio, P.; Mascheroni, A.; Zanetti, M. The Spectrum of Malnutrition/Cachexia/Sarcopenia in Oncology According to Different Cancer Types and Settings: A Narrative Review. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.L.; Lee, D.E.; Rosa-Caldwell, M.E.; Brown, L.A.; Perry, R.A.; Haynie, W.S.; Huseman, K.; Sataranatarajan, K.; Van Remmen, H.; Washington, T.A.; et al. Protein Imbalance in the Development of Skeletal Muscle Wasting in Tumour-Bearing Mice. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2018, 9, 987–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Carson, J.A. Lewis Lung Carcinoma Regulation of Mechanical Stretch-Induced Protein Synthesis in Cultured Myotubes. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2016, 310, C66–C79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLean, J.B.; Moylan, J.S.; Andrade, F.H. Mitochondria Dysfunction in Lung Cancer-Induced Muscle Wasting in C2C12 Myotubes. Front. Physiol. 2014, 5, 503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.; Zhang, S.; Hu, W.; Lu, X.; Lou, N.; Yang, Z.; Chen, S.; Zhang, X.; Yang, H. Valproic Acid Attenuates Skeletal Muscle Wasting by Inhibiting C/EBPβ-Regulated Atrogin1 Expression in Cancer Cachexia. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2016, 311, C101–C115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sustova, H.; De Feudis, M.; Reano, S.; Alves Teixeira, M.; Valle, I.; Zaggia, I.; Agosti, E.; Prodam, F.; Filigheddu, N. Opposing Effects of 25-Hydroxy- and 1α,25-Dihydroxy-Vitamin D3 on pro-Cachectic Cytokine-and Cancer Conditioned Medium-Induced Atrophy in C2C12 Myotubes. Acta Physiol. 2019, 226, e13269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tisdale, M.J. Are Tumoral Factors Responsible for Host Tissue Wasting in Cancer Cachexia? Future Oncol. 2010, 6, 503–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yano, C.L.; Ventrucci, G.; Field, W.N.; Tisdale, M.J.; Gomes-Marcondes, M.C.C. Metabolic and Morphological Alterations Induced by Proteolysis-Inducing Factor from Walker Tumour-Bearing Rats in C2C12 Myotubes. BMC Cancer 2008, 8, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Liu, Z.; Ding, H.; Miao, H.; Garcia, J.M.; Li, Y.-P. Toll-like Receptor 4 Mediates Lewis Lung Carcinoma-Induced Muscle Wasting via Coordinate Activation of Protein Degradation Pathways. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guigni, B.A.; van der Velden, J.; Kinsey, C.M.; Carson, J.A.; Toth, M.J. Effects of Conditioned Media from Murine Lung Cancer Cells and Human Tumor Cells on Cultured Myotubes. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 318, E22–E32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaromina, A.; Quennet, V.; Zips, D.; Meyer, S.; Shakirin, G.; Walenta, S.; Mueller-Klieser, W.; Baumann, M. Co-Localisation of Hypoxia and Perfusion Markers with Parameters of Glucose Metabolism in Human Squamous Cell Carcinoma (HSCC) Xenografts. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2009, 85, 972–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meinzer, A.; Yaromina, A.; Hoinkis, C.; Zips, D.; Thames, H.D.; Petersen, C.; Baumann, M. Tumor Microenvironment during Fractionated Irradiation: First Results in UT-SCC-5 and UT-SCC-15 Tumors. Available online: https://inis.iaea.org/search/search.aspx?orig_q=RN:40067677 (accessed on 1 June 2019).
- Koi, L.; Bergmann, R.; Brüchner, K.; Pietzsch, J.; Pietzsch, H.-J.; Krause, M.; Steinbach, J.; Zips, D.; Baumann, M. Radiolabeled Anti-EGFR-Antibody Improves Local Tumor Control after External Beam Radiotherapy and Offers Theragnostic Potential. Radiother. Oncol. 2014, 110, 362–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, M.J.; Lasiter, J.C.; Misfeldt, M.L. Toll-like Receptors in Tonsillar Epithelial Cells. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2009, 73, 613–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Göttgens, E.-L.; Ansems, M.; Leenders, W.P.J.; Bussink, J.; Span, P.N. Genotyping and Characterization of HPV Status, Hypoxia, and Radiosensitivity in 22 Head and Neck Cancer Cell Lines. Cancers 2021, 13, 1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Landi, F.; Schneider, S.M.; Zúñiga, C.; Arai, H.; Boirie, Y.; Chen, L.-K.; Fielding, R.A.; Martin, F.C.; Michel, J.-P.; et al. Prevalence of and Interventions for Sarcopenia in Ageing Adults: A Systematic Review. Report of the International Sarcopenia Initiative (EWGSOP and IWGS). Age Ageing 2014, 43, 748–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freire, A.N.; Guerra, R.O.; Alvarado, B.; Guralnik, J.M.; Zunzunegui, M.V. Validity and Reliability of the Short Physical Performance Battery in Two Diverse Older Adult Populations in Quebec and Brazil. J. Aging Health 2012, 24, 863–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pichard, C.; Kyle, U.G. Body Composition Measurements during Wasting Diseases. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 1998, 1, 357–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, W.; Alexander, N.; Schipper, M.; Fig, L.; Feng, F.; Jolly, S. Characterization of Changes in Total Body Composition for Patients with Head and Neck Cancer Undergoing Chemoradiotherapy Using Dual-Energy x-Ray Absorptiometry. Head Neck 2014, 36, 1356–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyle, U.G.; Genton, L.; Karsegard, L.; Slosman, D.O.; Pichard, C. Single Prediction Equation for Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis in Adults Aged 20–94 Years. Nutrition 2001, 17, 248–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, I.; Heymsfield, S.B.; Baumgartner, R.N.; Ross, R. Estimation of Skeletal Muscle Mass by Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis. J. Appl. Physiol. 2000, 89, 465–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baracos, V.E.; Reiman, T.; Mourtzakis, M.; Gioulbasanis, I.; Antoun, S. Body Composition in Patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Contemporary View of Cancer Cachexia with the Use of Computed Tomography Image Analysis. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 91, 1133S–1137S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mourtzakis, M.; Prado, C.M.M.; Lieffers, J.R.; Reiman, T.; McCargar, L.J.; Baracos, V.E. A Practical and Precise Approach to Quantification of Body Composition in Cancer Patients Using Computed Tomography Images Acquired during Routine Care. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2008, 33, 997–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, J.; Tadokoro, N.; Watanabe, M.; Shinomiya, M. A Novel Method of Measuring Intra-Abdominal Fat Volume Using Helical Computed Tomography. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 2002, 26, 398–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsiopoulos, N.; Baumgartner, R.N.; Heymsfield, S.B.; Lyons, W.; Gallagher, D.; Ross, R. Cadaver Validation of Skeletal Muscle Measurement by Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Computerized Tomography. J. Appl. Physiol. 1998, 85, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vesali, R.F.; Klaude, M.; Rooyackers, O.E.; TJäder, I.; Barle, H.; Wernerman, J. Longitudinal Pattern of Glutamine/Glutamate Balance across the Leg in Long-Stay Intensive Care Unit Patients. Clin. Nutr. 2002, 21, 505–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klaude, M.; Fredriksson, K.; Tjäder, I.; Hammarqvist, F.; Ahlman, B.; Rooyackers, O.; Wernerman, J. Proteasome Proteolytic Activity in Skeletal Muscle Is Increased in Patients with Sepsis. Clin. Sci. 2007, 112, 499–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Jin, B.; Li, Y.-P. C/EBPβ Mediates Tumour-Induced Ubiquitin Ligase Atrogin1/MAFbx Upregulation and Muscle Wasting. EMBO J. 2011, 30, 4323–4335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitagawa, M.; Haji, S.; Amagai, T. High Serum Essential Amino Acids as a Predictor of Skeletal Muscle Depletion in Patients With Cachexia and Advanced Gastrointestinal Cancers. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2017, 32, 645–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baracos, V.E.; Martin, L.; Korc, M.; Guttridge, D.C.; Fearon, K.C.H. Cancer-Associated Cachexia. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers. 2018, 4, 17105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aversa, Z.; Pin, F.; Lucia, S.; Penna, F.; Verzaro, R.; Fazi, M.; Colasante, G.; Tirone, A.; Rossi Fanelli, F.; Ramaccini, C.; et al. Autophagy Is Induced in the Skeletal Muscle of Cachectic Cancer Patients. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agustsson, T.; Wikrantz, P.; Rydén, M.; Brismar, T.; Isaksson, B. Adipose Tissue Volume Is Decreased in Recently Diagnosed Cancer Patients with Cachexia. Nutrition 2012, 28, 851–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.J.; Kim, H.J.; Yun, J.; Kim, K.H.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, S.-C.; Bae, S.B.; Kim, C.K.; Lee, N.S.; Lee, K.T.; et al. Pathophysiological Role of Hormones and Cytokines in Cancer Cachexia. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2012, 27, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerner, L.; Tao, J.; Liu, Q.; Nicoletti, R.; Feng, B.; Krieger, B.; Mazsa, E.; Siddiquee, Z.; Wang, R.; Huang, L.; et al. MAP3K11/GDF15 Axis Is a Critical Driver of Cancer Cachexia. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2016, 7, 467–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penafuerte, C.A.; Gagnon, B.; Sirois, J.; Murphy, J.; MacDonald, N.; Tremblay, M.L. Identification of Neutrophil-Derived Proteases and Angiotensin II as Biomarkers of Cancer Cachexia. Br. J. Cancer 2016, 114, 680–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loumaye, A.; de Barsy, M.; Nachit, M.; Lause, P.; Frateur, L.; van Maanen, A.; Trefois, P.; Gruson, D.; Thissen, J.-P. Role of Activin A and Myostatin in Human Cancer Cachexia. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 100, 2030–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batista, M.L.; Olivan, M.; Alcantara, P.S.M.; Sandoval, R.; Peres, S.B.; Neves, R.X.; Silverio, R.; Maximiano, L.F.; Otoch, J.P.; Seelaender, M. Adipose Tissue-Derived Factors as Potential Biomarkers in Cachectic Cancer Patients. Cytokine 2013, 61, 532–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burney, B.O.; Hayes, T.G.; Smiechowska, J.; Cardwell, G.; Papusha, V.; Bhargava, P.; Konda, B.; Auchus, R.J.; Garcia, J.M. Low Testosterone Levels and Increased Inflammatory Markers in Patients with Cancer and Relationship with Cachexia. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 97, E700–E709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felix, K.; Fakelman, F.; Hartmann, D.; Giese, N.A.; Gaida, M.M.; Schnölzer, M.; Flad, T.; Büchler, M.W.; Werner, J. Identification of Serum Proteins Involved in Pancreatic Cancer Cachexia. Life Sci. 2011, 88, 218–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krzystek-Korpacka, M.; Matusiewicz, M.; Diakowska, D.; Grabowski, K.; Blachut, K.; Kustrzeba-Wojcicka, I.; Banas, T. Impact of Weight Loss on Circulating IL-1, IL-6, IL-8, TNF-Alpha, VEGF-A, VEGF-C and Midkine in Gastroesophageal Cancer Patients. Clin. Biochem. 2007, 40, 1353–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uz, U.; Eskiizmir, G. Association Between Interleukin-6 and Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Systematic Review. Clin. Exp. Otorhinolaryngol. 2021, 14, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.-P.; Kao, H.-K.; Wu, C.-C.; Fang, K.-H.; Chang, Y.-L.; Huang, Y.-C.; Liu, S.-C.; Cheng, M.-H. Pretreatment Interleukin-6 Serum Levels Are Associated with Patient Survival for Oral Cavity Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2013, 148, 786–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, W.; Zhu, Y.; Zhou, H. Prognostic Value of Interleukin-6 and Interleukin-8 in Laryngeal Squamous Cell Cancer. Med. Oncol. 2013, 30, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Schutter, H.; Landuyt, W.; Verbeken, E.; Goethals, L.; Hermans, R.; Nuyts, S. The Prognostic Value of the Hypoxia Markers CA IX and GLUT 1 and the Cytokines VEGF and IL 6 in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma Treated by Radiotherapy +/− Chemotherapy. BMC Cancer 2005, 5, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moses, A.G.W.; Maingay, J.; Sangster, K.; Fearon, K.C.H.; Ross, J.A. Pro-Inflammatory Cytokine Release by Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells from Patients with Advanced Pancreatic Cancer: Relationship to Acute Phase Response and Survival. Oncol. Rep. 2009, 21, 1091–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ando, K.; Takahashi, F.; Kato, M.; Kaneko, N.; Doi, T.; Ohe, Y.; Koizumi, F.; Nishio, K.; Takahashi, K. Tocilizumab, a Proposed Therapy for the Cachexia of Interleukin6-Expressing Lung Cancer. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e102436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richey, L.M.; George, J.R.; Couch, M.E.; Kanapkey, B.K.; Yin, X.; Cannon, T.; Stewart, P.W.; Weissler, M.C.; Shores, C.G. Defining Cancer Cachexia in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 6561–6567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astradsson, T.; Sellberg, F.; Berglund, D.; Ehrsson, Y.T.; Laurell, G.F.E. Systemic Inflammatory Reaction in Patients With Head and Neck Cancer—An Explorative Study. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brady, G.; O’Regan, E.; Miller, I.; Ogungbowale, A.; Kapas, S.; Crean, S.J. Serum Levels of Insulin-like Growth Factors (IGFs) and Their Binding Proteins (IGFBPs), -1, -2, -3, in Oral Cancer. Int. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Surg. 2007, 36, 259–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Zhao, H.; Do, K.-A.; Johnson, M.M.; Dong, Q.; Hong, W.K.; Spitz, M.R. Serum Levels of Insulin Growth Factor (IGF-I) and IGF-Binding Protein Predict Risk of Second Primary Tumors in Patients with Head and Neck Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 3988–3995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, S.E.; Kari, F.W.; French, J.; Leininger, J.R.; Travlos, G.; Wilson, R.; Barrett, J.C. Dietary Restriction Reduces Insulin-like Growth Factor I Levels, Which Modulates Apoptosis, Cell Proliferation, and Tumor Progression in P53-Deficient Mice. Cancer Res. 1997, 57, 4667–4672. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Martín, A.I.; Priego, T.; Moreno-Ruperez, Á.; González-Hedström, D.; Granado, M.; López-Calderón, A. IGF-1 and IGFBP-3 in Inflammatory Cachexia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelmoez, A.M.; Sardón Puig, L.; Smith, J.A.B.; Gabriel, B.M.; Savikj, M.; Dollet, L.; Chibalin, A.V.; Krook, A.; Zierath, J.R.; Pillon, N.J. Comparative Profiling of Skeletal Muscle Models Reveals Heterogeneity of Transcriptome and Metabolism. Am. J. Physiol.-Cell Physiol. 2020, 318, C615–C626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pettersen, K.; Andersen, S.; Degen, S.; Tadini, V.; Grosjean, J.; Hatakeyama, S.; Tesfahun, A.N.; Moestue, S.; Kim, J.; Nonstad, U.; et al. Cancer Cachexia Associates with a Systemic Autophagy-Inducing Activity Mimicked by Cancer Cell-Derived IL-6 Trans-Signaling. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohnert, K.R.; Gallot, Y.S.; Sato, S.; Xiong, G.; Hindi, S.M.; Kumar, A. Inhibition of ER Stress and Unfolding Protein Response Pathways Causes Skeletal Muscle Wasting during Cancer Cachexia. FASEB J. 2016, 30, 3053–3068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puppa, M.J.; Gao, S.; Narsale, A.A.; Carson, J.A. Skeletal Muscle Glycoprotein 130’s Role in Lewis Lung Carcinoma-Induced Cachexia. FASEB J. 2014, 28, 998–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seto, D.N.; Kandarian, S.C.; Jackman, R.W. A Key Role for Leukemia Inhibitory Factor in C26 Cancer Cachexia. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 19976–19986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, K.A.S.; Dong, J.; Dong, Y.; Dong, Y.; Schor, N.; Tweardy, D.J.; Zhang, L.; Mitch, W.E. Inhibition of Stat3 Activation Suppresses Caspase-3 and the Ubiquitin-Proteasome System, Leading to Preservation of Muscle Mass in Cancer Cachexia. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 11177–11187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ottenheijm, C.A.C.; Heunks, L.M.A.; Li, Y.-P.; Jin, B.; Minnaard, R.; van Hees, H.W.H.; Dekhuijzen, P.N.R. Activation of the Ubiquitin-Proteasome Pathway in the Diaphragm in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2006, 174, 997–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Léger, B.; Vergani, L.; Sorarù, G.; Hespel, P.; Derave, W.; Gobelet, C.; D’Ascenzio, C.; Angelini, C.; Russell, A.P. Human Skeletal Muscle Atrophy in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Reveals a Reduction in Akt and an Increase in Atrogin-1. FASEB J. 2006, 20, 583–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, S.; Brault, J.J.; Gygi, S.P.; Glass, D.J.; Valenzuela, D.M.; Gartner, C.; Latres, E.; Goldberg, A.L. During Muscle Atrophy, Thick, but Not Thin, Filament Components Are Degraded by MuRF1-Dependent Ubiquitylation. J. Cell Biol. 2009, 185, 1083–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dworzak, F.; Ferrari, P.; Gavazzi, C.; Maiorana, C.; Bozzetti, F. Effects of Cachexia Due to Cancer on Whole Body and Skeletal Muscle Protein Turnover. Cancer 1998, 82, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, J.P.; Baynes, J.W.; Welle, S.L.; Kostek, M.C.; Matesic, L.E.; Sato, S.; Carson, J.A. The Regulation of Skeletal Muscle Protein Turnover during the Progression of Cancer Cachexia in the Apc(Min/+) Mouse. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e24650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodman, C.A.; Frey, J.W.; Mabrey, D.M.; Jacobs, B.L.; Lincoln, H.C.; You, J.-S.; Hornberger, T.A. The Role of Skeletal Muscle MTOR in the Regulation of Mechanical Load-Induced Growth. J. Physiol. 2011, 589, 5485–5501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| Cancer (Group 1) | Control (Group 2) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cancer (n = 20) | Control (n = 14) | p | |
| Men (%) | 19 (95) | 1(4) | <0.001 |
| Age (Years) | 60 ± 8 | 46 ± 14 | 0.003 |
| Weight (kg) | 66.1 ± 11.4 | 82.7 ± 21.4 | 0.007 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 22.0 ± 3.4 | 30.4 ± 7.0 | 0.003 |
| 3-month weight loss (%) | 5.6 ± 5.7 | −0.6 ± 1.4 | <0.001 |
| Handgrip strength (kg) | 33.6 ± 10.9 | 28.7 ± 7.7 | 0.23 |
| Kyle fat-free mass index (kg/m2) | 18.3 ± 2.4 | 21.0 ± 7.1 | 0.15 |
| Janssen muscular mass index (kg/m2) | 10.0 ± 1.6 | 9.4 ± 1.2 | 0.18 |
| L3MMI (cm2/m2) | 43.5 ± 7.8 | NA | NA |
| Serum albumin level (g/L) | 35 ± 5.9 | 38.2 ± 3.8 | 0.14 |
| Serum prealbumin (mg/mL) | 0.22 ± 0.08 | 0.24 ± 0.04 | 0.34 |
| Nutritional risk index | 92.5 ± 9.8 | 100.0 ± 5.7 | 0.02 |
| SPPB | 9.5 ± 3.6 | 11.6 ± 0.84 | 0.05 |
| n (%) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Site | Hypopharyngeal Oral Oropharyngeal Laryngeal CUP | 7 (35%) 4 (20%) 5 (25%) 3 (15%) 1 (5%) |
| Disease stage | I II III IVa IVb IVc | 0 2 (10%) 1 (5%) 11 (45%) 3 (15%) 3 (15%) |
| Non-malignant neck tumor | 5 (36%) |
| Thyroid disease (nodules or thyroiditis) | 9 (64%) |
| Surgery management | |
| Thyroidectomy | 9 (64%) |
| Parotidectomy | 3 (21%) |
| Paraganglioma | 1 (7%) |
| Submandibular gland removal | 1 (7%) |
| Biological Marker | Tumor Conditioned Media vs. Control Conditioned Media | Serum Patient Conditioned Media (Severely Sarcopenic Patient vs. Mild Sarcopenic Patient) |
|---|---|---|
| Myotubes size | ↘ | = |
| P62 | ↘ | ↘ |
| LC3 | = | = |
| Murf 1 | ↘ | ↘ |
| Fox | ↘ | ↘ |
| TRAF 6 | ↘ | ↘ |
| MafBx | = | = |
| DDIT | = | = |
| PLIN 3 | ↘ | ↗ |
| IL 6 | ↗ | ↗ |
| Proteasome activity | = | ↘ |
| Autophagy/lysosome pathway activity | ↗ | ↗ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Saroul, N.; Tardif, N.; Pereira, B.; Dissard, A.; Montrieul, L.; Sanchez, P.; Salles, J.; Petersen, J.E.; Jakobson, T.; Gilain, L.; et al. Conditioned Media from Head and Neck Cancer Cell Lines and Serum Samples from Head and Neck Cancer Patients Drive Catabolic Pathways in Cultured Muscle Cells. Cancers 2023, 15, 1843. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15061843
Saroul N, Tardif N, Pereira B, Dissard A, Montrieul L, Sanchez P, Salles J, Petersen JE, Jakobson T, Gilain L, et al. Conditioned Media from Head and Neck Cancer Cell Lines and Serum Samples from Head and Neck Cancer Patients Drive Catabolic Pathways in Cultured Muscle Cells. Cancers. 2023; 15(6):1843. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15061843
Chicago/Turabian StyleSaroul, Nicolas, Nicolas Tardif, Bruno Pereira, Alexis Dissard, Laura Montrieul, Phelipe Sanchez, Jérôme Salles, Jens Erik Petersen, Towe Jakobson, Laurent Gilain, and et al. 2023. "Conditioned Media from Head and Neck Cancer Cell Lines and Serum Samples from Head and Neck Cancer Patients Drive Catabolic Pathways in Cultured Muscle Cells" Cancers 15, no. 6: 1843. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15061843
APA StyleSaroul, N., Tardif, N., Pereira, B., Dissard, A., Montrieul, L., Sanchez, P., Salles, J., Petersen, J. E., Jakobson, T., Gilain, L., Mom, T., Boirie, Y., Rooyakers, O., & Walrand, S. (2023). Conditioned Media from Head and Neck Cancer Cell Lines and Serum Samples from Head and Neck Cancer Patients Drive Catabolic Pathways in Cultured Muscle Cells. Cancers, 15(6), 1843. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15061843








