What Is Known about Breast Cancer in Young Women?
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Epidemiology
2.1. Geographic Variations
2.2. Ethnic/Racial Differences
2.3. Risk Factors
2.3.1. Lifestyle Risk Factors
2.3.2. Genetic Risk Factors
High-Penetrance Genes
Moderate-Penetrance Genes
Low-Penetrance Genes
2.3.3. Reproductive Risk Factors
3. Prognosis
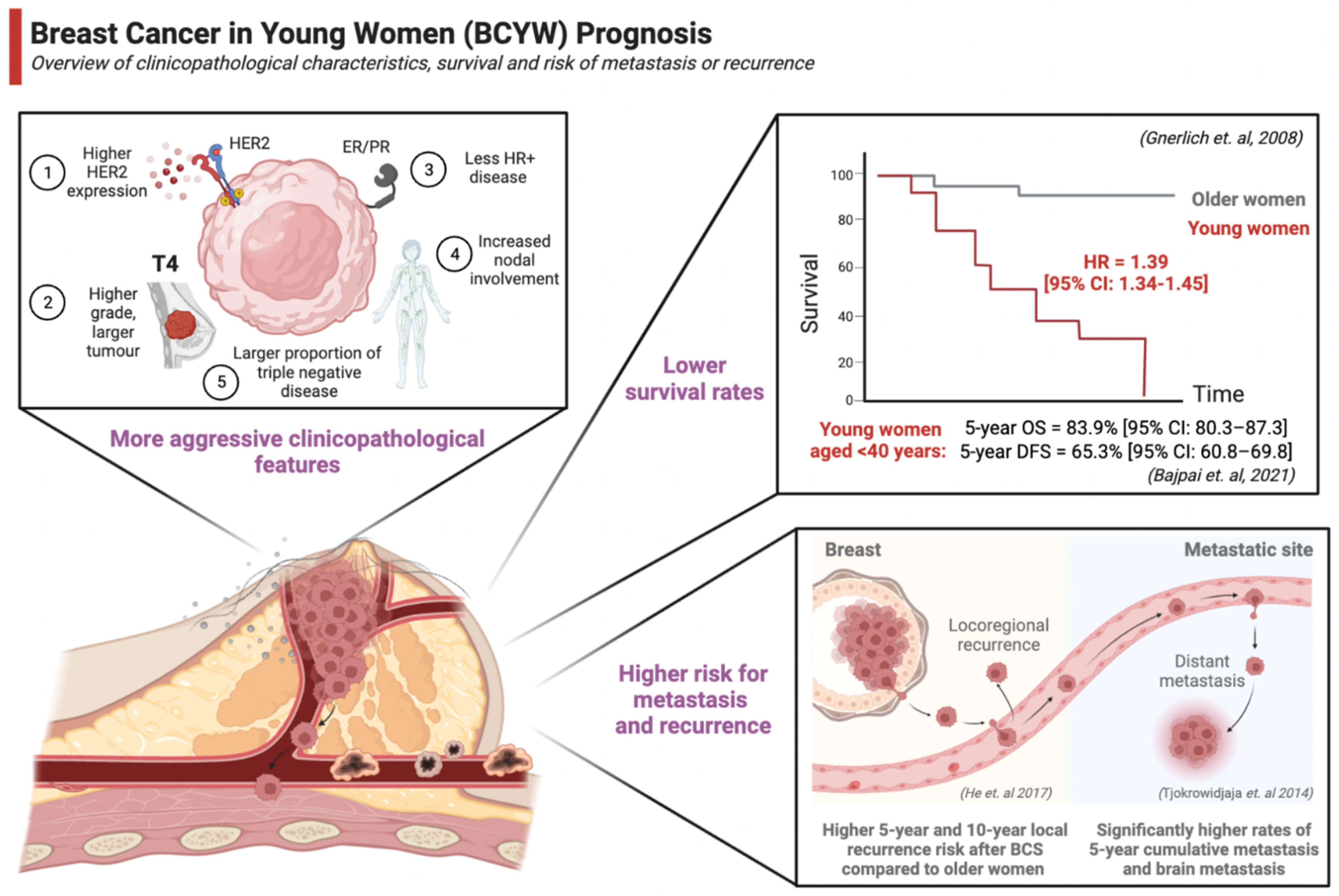
3.1. Clinicopathological Characteristics
3.2. Survival
3.3. Risk of Local Recurrence and Metastasis
4. Treatment
4.1. Locoregional Treatment
4.1.1. Surgical Management
4.1.2. Radiation Therapy
4.2. Systemic Treatment
4.2.1. Endocrine Treatment
4.2.2. Chemotherapy
4.2.3. Targeted Therapy
4.2.4. Chemotherapy for Loco-Regional Relapse and Metastasis
5. Special Considerations
5.1. Fertility
5.2. Breast Cancer during Pregnancy
5.3. Bone Health
6. Conclusions and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sopik, V. International variation in breast cancer incidence and mortality in young women. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2020, 186, 497–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, A.N.; Carroll, K.J.; Gerratana, L.; Lin, C.; Davis, A.A.; Zhang, Q.; Jacob, S.; Finkelman, B.; Zhang, Y.; Qiang, W.; et al. Circulating tumor cells, circulating tumor DNA, and disease characteristics in young women with metastatic breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2021, 187, 397–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anders, C.K.; Hsu, D.S.; Broadwater, G.; Acharya, C.R.; Foekens, J.A.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Marcom, P.K.; Marks, J.R.; Febbo, P.G.; et al. Young Age at Diagnosis Correlates With Worse Prognosis and Defines a Subset of Breast Cancers With Shared Patterns of Gene Expression. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 3324–3330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kataoka, A.; Iwamoto, T.; Tokunaga, E.; Tomotaki, A.; Kumamaru, H.; Miyata, H.; Niikura, N.; Kawai, M.; Anan, K.; Hayashi, N.; et al. Young adult breast cancer patients have a poor prognosis independent of prognostic clinicopathological factors: A study from the Japanese Breast Cancer Registry. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2016, 160, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paluch-Shimon, S.; Pagani, O.; Partridge, A.H.; Abulkhair, O.; Cardoso, M.-J.; Dent, R.A.; Gelmon, K.; Gentilini, O.; Harbeck, N.; Margulies, A.; et al. ESO-ESMO 3rd international consensus guidelines for breast cancer in young women (BCY3). Breast 2017, 35, 203–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, B.L.; Day, C.N.; Hoskin, T.L.; Habermann, E.B.; Boughey, J.C. Adolescents and Young Adults with Breast Cancer have More Aggressive Disease and Treatment Than Patients in Their Forties. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2019, 26, 3920–3930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pruessmann, J.; Pursche, T.; Hammersen, F.; Katalinic, A.; Fischer, D.; Waldmann, A. Conditional Disease-Free and Overall Survival of 1858 Young Women with Non-Metastatic Breast Cancer and with Participation in a Post-Therapeutic Rehab Programme according to Clinical Subtypes. Breast Care 2020, 16, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, R.H.; Hu, P.; Fan, C.; Anders, C.K. Gene expression in “young adult type” breast cancer: A retrospective analysis. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 13688–13702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredholm, H.; Magnusson, K.; Lindström, L.S.; Garmo, H.; Fält, S.E.; Lindman, H.; Bergh, J.; Holmberg, L.; Pontén, F.; Frisell, J.; et al. Long-term outcome in young women with breast cancer: A population-based study. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2016, 160, 131–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Azim, H.A.; Partridge, A.H. Biology of breast cancer in young women. Breast Cancer Res. 2014, 16, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malone, K.E.; Daling, J.R.; Neal, C.; Suter, N.M.; O’Brien, C.; Cushing-Haugen, K.; Jonasdottir, T.J.; Thompson, J.D.; Ostrander, E.A. Frequency of BRCA1/BRCA2 mutations in a population-based sample of young breast carcinoma cases. Cancer 2000, 88, 1393–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenup, R.; Buchanan, A.; Lorizio, W.; Rhoads, K.; Chan, S.; Leedom, T.; King, R.; McLennan, J.; Crawford, B.; Marcom, P.K.; et al. Prevalence of BRCA Mutations Among Women with Triple-Negative Breast Cancer (TNBC) in a Genetic Counseling Cohort. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2013, 20, 3254–3258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggard, M.A.; O’Connell, J.B.; Lane, K.E.; Liu, J.H.; Etzioni, D.A.; Ko, C.Y. Do young breast cancer patients have worse outcomes? J. Surg. Res. 2003, 113, 109–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroman, N.; Jensen, M.-B.; Wohlfahrt, J.; Mouridsen, H.T.; Andersen, P.K.; Melbye, M.; Tutt, A.; Ross, G. Factors influencing the effect of age on prognosis in breast cancer: Population based study. BMJ 2000, 320, 474–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiong, Q.; Valero, V.; Kau, V.; Kau, S.W.; Taylor, S.; Smith, T.L.; Buzdar, A.U.; Hortobagyi, G.N.; Theriault, R.L. Female patients with breast carcinoma age 30 years and younger have a poor prognosis: The M.D. Anderson Cancer Center experience. Cancer 2001, 92, 2523–2528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, P.; Cserni, G.; Van De Steene, J.; Vlastos, G.; Voordeckers, M.; Royce, M.; Lee, S.-J.; Vinh-Hung, V.; Storme, G. Modeling the effect of age in T1-2 breast cancer using the SEER database. BMC Cancer 2005, 5, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bollet, M.A.; Sigal-Zafrani, B.; Mazeau, V.; Savignoni, A.; de la Rochefordière, A.; Vincent-Salomon, A.; Salmon, R.; Campana, F.; Kirova, Y.M.; Dendale, R.; et al. Age remains the first prognostic factor for loco-regional breast cancer recurrence in young (<40 years) women treated with breast conserving surgery first. Radiother. Oncol. 2007, 82, 272–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, S.H.; Son, B.H.; Kim, S.W.; Kim, S.I.; Jeong, J.; Ko, S.-S.; Han, W. Poor Outcome of Hormone Receptor–Positive Breast Cancer at Very Young Age Is Due to Tamoxifen Resistance: Nationwide Survival Data in Korea—A Report From the Korean Breast Cancer Society. J. Clin. Oncol. 2007, 25, 2360–2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredholm, H.; Eaker, S.; Frisell, J.; Holmberg, L.; Fredriksson, I.; Lindman, H. Breast Cancer in Young Women: Poor Survival Despite Intensive Treatment. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e7695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Copson, E.; Eccles, B.; Maishman, T.; Gerty, S.; Stanton, L.; Cutress, R.I.; Altman, D.G.; Durcan, L.; Simmonds, P.; Lawrence, G.; et al. Prospective Observational Study of Breast Cancer Treatment Outcomes for UK Women Aged 18–40 Years at Diagnosis: The POSH Study. Gynecol. Oncol. 2013, 105, 978–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yeo, W.; Lee, H.-M.; Chan, A.; Chan, E.Y.; Chan, M.C.; Chan, K.-W.; Chan, S.W.; Cheung, F.-Y.; Cheung, P.S.; Choi, P.H.; et al. Risk factors and natural history of breast cancer in younger Chinese women. World J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 5, 1097–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narod, S.A. Breast cancer in young women. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 9, 460–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bellanger, M.; Zeinomar, N.; Tehranifar, P.; Terry, M.B. Are Global Breast Cancer Incidence and Mortality Patterns Related to Country-Specific Economic Development and Prevention Strategies? J. Glob. Oncol. 2018, 4, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, C.-Y.; Na Li, N.; Bin Lu, B.; Cai, J.; Lu, M.; Zhang, Y.-H.; Chen, H.-D.; Dai, M. Global and regional trends in incidence and mortality of female breast cancer and associated factors at national level in 2000 to 2019. Chin. Med. J. 2021, 135, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heer, E.; Harper, A.; Escandor, N.; Sung, H.; McCormack, V.; Fidler-Benaoudia, M.M. Global burden and trends in premenopausal and postmenopausal breast cancer: A population-based study. Lancet Glob. Health 2020, 8, e1027–e1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; White, M.C.; Sabatino, S.A.; Febo-Vázquez, I. Mammography use among women aged 18–39 years in the United States. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2017, 168, 687–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keating, N.L.; Pace, L.E. New Guidelines for Breast Cancer Screening in US Women. JAMA 2015, 314, 1569–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, H.D.; Pappas, M.; Cantor, A.; Griffin, J.; Daeges, M.; Humphrey, L. Harms of Breast Cancer Screening: Systematic Review to Update the 2009 U.S. Preventive Services Task Force Recommendation. Ann. Intern. Med. 2016, 164, 256–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- DeSantis, C.E.; Ma, J.; Jemal, A. Trends in stage at diagnosis for young breast cancer patients in the United States. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2018, 173, 743–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yip, C.H.; Anderson, B.O. The Breast Health Global Initiative: Clinical practice guidelines for management of breast cancer in low- and middle-income countries. Expert Rev. Anticancer Ther. 2007, 7, 1095–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smigal, C.; Jemal, A.; Ward, E.; Cokkinides, V.; Smith, R.; Howe, H.L.; Thun, M. Trends in Breast Cancer by Race and Ethnicity: Update 2006. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2006, 56, 168–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baquet, C.R.; Mishra, S.I.; Commiskey, P.; Ellison, G.L.; DeShields, M. Breast Cancer Epidemiology in Blacks and Whites: Disparities in Incidence, Mortality, Survival Rates and Histology. J. Natl. Med. Assoc. 2008, 100, 480–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gathani, T.; Reeves, G.; Broggio, J.; Barnes, I. Ethnicity and the tumour characteristics of invasive breast cancer in over 116,500 women in England. Br. J. Cancer 2021, 125, 611–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambertini, M.; Santoro, L.; Del Mastro, L.; Nguyen, B.; Livraghi, L.; Ugolini, D.; Peccatori, F.; Azim, H.A. Reproductive behaviors and risk of developing breast cancer according to tumor subtype: A systematic review and meta-analysis of epidemiological studies. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2016, 49, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidayat, K.; Yang, C.-M.; Shi, B.-M. Body fatness at a young age, body fatness gain and risk of breast cancer: Systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies. Obes. Rev. 2017, 19, 254–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collaborative Group on Hormonal Factors in Breast Cancer. Type and timing of menopausal hormone therapy and breast cancer risk: Individual participant meta-analysis of the worldwide epidemiological evidence. Lancet 2019, 394, 1159–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gathani, T.; Ali, R.; Balkwill, A.; Green, J.; Reeves, G.; Beral, V.; Moser, K.A.; on behalf of the Million Women Study Collaborators. Ethnic differences in breast cancer incidence in England are due to differences in known risk factors for the disease: Prospective study. Br. J. Cancer 2013, 110, 224–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shin, H.-R.; Joubert, C.; Boniol, M.; Hery, C.; Ahn, S.H.; Won, Y.-J.; Nishino, Y.; Sobue, T.; Chen, C.-J.; You, S.-L.; et al. Recent trends and patterns in breast cancer incidence among Eastern and Southeastern Asian women. Cancer Causes Control 2010, 21, 1777–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-H.; Yap, Y.S.; Lee, K.-H.; Im, S.-A.; Naito, Y.; Yeo, W.; Ueno, T.; Kwong, A.; Li, H.; Huang, S.-M.; et al. Contrasting Epidemiology and Clinicopathology of Female Breast Cancer in Asians vs the US Population. Gynecol. Oncol. 2019, 111, 1298–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, H.; Rosenberg, P.S.; Chen, W.-Q.; Hartman, M.; Lim, W.-Y.; Chia, K.S.; Mang, O.W.-K.; Chiang, C.-J.; Kang, D.; Ngan, R.K.-C.; et al. Female Breast Cancer Incidence Among Asian and Western Populations: More Similar Than Expected. Gynecol. Oncol. 2015, 107, djv107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Porter, P. “Westernizing” Women’s Risks? Breast Cancer in Lower-Income Countries. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 358, 213–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amadou, A.; Ferrari, P.; Muwonge, R.; Moskal, A.; Biessy, C.; Romieu, I.; Hainaut, P. Overweight, obesity and risk of premenopausal breast cancer according to ethnicity: A systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis. Obes. Rev. 2013, 14, 665–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoemaker, M.L.; White, M.C.; Wu, M.; Weir, H.K.; Romieu, I. Differences in breast cancer incidence among young women aged 20–49 years by stage and tumor characteristics, age, race, and ethnicity, 2004–2013. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2018, 169, 595–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, E.C.; Ziogas, A.; Anton-Culver, H. Delay in Surgical Treatment and Survival After Breast Cancer Diagnosis in Young Women by Race/Ethnicity. JAMA Surg. 2013, 148, 516–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dorgan, J.F.; Brown, C.; Barrett, M.; Splansky, G.L.; Kreger, B.E.; D’Agostino, R.B.; Albanes, D.; Schatzkin, A. Physical Activity and Risk of Breast Cancer in the Framingham Heart Study. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1994, 139, 662–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thune, I.; Brenn, T.; Lund, E.; Gaard, M. Physical Activity and the Risk of Breast Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 1997, 336, 1269–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerhan, J.; Chiu, B.C.-H.; Wallace, R.B.; Lemke, J.H.; Lynch, C.F.; Tomer, J.C.; Rubenstein, L.M. Physical Activity, Physical Function, and the Risk of Breast Cancer in a Prospective Study Among Elderly Women. J. Gerontol. Ser. A 1998, 53, M251–M256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rockhill, B.; Willett, W.C.; Hunter, D.J.; Manson, J.E.; Hankinson, S.E.; Spiegelman, D.; Colditz, G.A. Physical activity and breast cancer risk in a cohort of young women. Gynecol. Oncol. 1998, 90, 1155–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sesso, H.D.; Lee, I.-M.; Paffenbarger, R.S.P., Jr. Physical activity and breast cancer risk in the College Alumni Health Study (United States). Cancer Causes Control 1998, 9, 433–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rockhill, B.; Willett, W.C.; Hunter, D.J.; Manson, J.E.; Hankinson, S.E.; Colditz, G.A. A prospective study of recreational physical activity and breast cancer risk. Arch. Intern. Med. 1999, 159, 2290–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luoto, R.; Latikka, P.; Pukkala, E.; Hakulinen, T.; Vihko, V. The effect of physical activity on breast cancer risk: A cohort study of 30,548 women. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2000, 16, 973–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyrwich, K.W.; Wolinsky, F.D. Physical activity, disability, and the risk of hospitalization for breast cancer among older women. J. Gerontol. Ser. A 2000, 55, M418–M421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Breslow, R.A.; Ballard-Barbash, R.; Munoz, K.; Graubard, B.I. Long-term recreational physical activity and breast cancer in the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey I epidemiologic follow-up study. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2001, 10, 805–808. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, I.-M.; Rexrode, K.M.; Cook, N.R.; Hennekens, C.H.; Burin, J.E.; Buring, J.E. Physical activity and breast cancer risk: The Women’s Health Study (United States). Cancer Causes Control 2001, 12, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi, T.; Adami, H.-O.; Ekbom, A.; Wedrén, S.; Terry, P.; Floderus, B.; Lichtenstein, P. Physical activity and risk for breast cancer a prospective cohort study among Swedish twins. Int. J. Cancer 2002, 100, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rintala, P.E.; Pukkala, E.; Paakkulainen, H.T.; Vihko, V.J. Self-experienced physical workload and risk of breast cancer. Scand. J. Work Environ. Health 2002, 28, 158–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.V.; Calle, E.E.; Bernstein, L.; Wu, A.H.; Thun, M.J. Recreational physical activity and risk of postmenopausal breast cancer in a large cohort of US women. Cancer Causes Control 2003, 14, 519–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margolis, K.L.; Mucci, L.; Braaten, T.; Kumle, M.; Lagerros, Y.T.; Adami, H.-O.; Lund, E.; Weiderpass, E. Physical Activity in Different Periods of Life and the Risk of Breast Cancer: The Norwegian-Swedish Women’s Lifestyle and Health Cohort Study. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2005, 14, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardia, A.; Hartmann, L.C.; Vachon, C.M. Recreational Physical Activity and Risk of Postmenopausal Breast Cancer Based on Hormone Receptor Status. Arch. Intern. Med. 2006, 166, 2478–2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mertens, A.J.; Sweeney, C.; Shahar, E.; Rosamond, W.D.; Folsom, A.R. Physical activity and breast cancer incidence in middle-aged women: A prospective cohort study. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2005, 97, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silvera, S.A.N.; Jain, M.; Howe, G.R.; Miller, A.B.; Rohan, T.E. Energy balance and breast cancer risk: A prospective cohort study. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2005, 97, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tehard, B.; Friedenreich, C.M.; Oppert, J.-M.; Clavel-Chapelon, F. Effect of Physical Activity on Women at Increased Risk of Breast Cancer: Results from the E3N Cohort Study. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2006, 15, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dallal, C.M.; Sullivan-Halley, J.; Ross, R.K.; Wang, Y.; Deapen, D.; Horn-Ross, P.L.; Reynolds, P.; Stram, D.O.; Clarke, C.A.; Anton-Culver, H.; et al. Long-term Recreational Physical Activity and Risk of Invasive and In Situ Breast Cancer. Arch. Intern. Med. 2007, 167, 408–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leitzmann, M.F.; Moore, S.C.; Peters, T.M.; Lacey, J.V.; Schatzkin, A.; Schairer, C.; Brinton, L.A.; Albanes, D. Prospective study of physical activity and risk of postmenopausal breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2008, 10, R92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maruti, S.S.; Willett, W.C.; Feskanich, D.; Rosner, B.; Colditz, G.A. A Prospective Study of Age-Specific Physical Activity and Premenopausal Breast Cancer. Gynecol. Oncol. 2008, 100, 728–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suzuki, S.; Kojima, M.; Tokudome, S.; Mori, M.; Sakauchi, F.; Fujino, Y.; Wakai, K.; Lin, Y.; Kikuchi, S.; Tamakoshi, K.; et al. Effect of Physical Activity on Breast Cancer Risk: Findings of the Japan Collaborative Cohort Study. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2008, 17, 3396–3401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Howard, R.A.; Leitzmann, M.F.; Linet, M.S.; Freedman, D.M. Physical activity and breast cancer risk among pre- and postmenopausal women in the U.S. Radiologic Technologists cohort. Cancer Causes Control 2008, 20, 323–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chang, S.-C.; Ziegler, R.G.; Dunn, B.; Stolzenberg-Solomon, R.; Lacey, J.V.; Huang, W.-Y.; Schatzkin, A.; Reding, D.; Hoover, R.N.; Hartge, P.; et al. Association of Energy Intake and Energy Balance with Postmenopausal Breast Cancer in the Prostate, Lung, Colorectal, and Ovarian Cancer Screening Trial. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2006, 15, 334–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schnohr, P.; Grønbaek, M.; Petersen, L.V.; Hein, H.O.; Sørensen, T.I.A. Physical activity in leisure-time and risk of cancer: 14-year follow-up of 28,000 Danish men and women. Scand. J. Public Health 2005, 33, 244–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McTiernan, A.; Kooperberg, C.L.; White, E.; Wilcox, S.; Coates, R.J.; Adams-Campbell, L.L.; Woods, N.F.; Ockene, J.K. Recreational Physical Activity and the Risk of Breast Cancer in Postmenopausal Women. JAMA 2003, 290, 1331–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhang, D.; Kang, S. Physical activity and risk of breast cancer: A meta-analysis of prospective studies. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2012, 137, 869–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardefeldt, P.J.; Penninkilampi, R.; Edirimanne, S.; Eslick, G.D. Physical Activity and Weight Loss Reduce the Risk of Breast Cancer: A Meta-analysis of 139 Prospective and Retrospective Studies. Clin. Breast Cancer 2018, 18, e601–e612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, Q.; Tan, X. Physical Activity and Risk of Breast Cancer: A Meta-Analysis of 38 Cohort Studies in 45 Study Reports. Value Health 2018, 22, 104–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Endicott, J.A.; Ling, V. The biochemistry of p-glycoprotein-mediated multidrug resistance. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1989, 58, 137–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottesman, M.M.; Hrycyna, C.A.; Schoenlein, P.V.; Germann, U.A.; Pastan, I. Genetic analysis of the multidrug transporter. Annu. Rev. Genet. 1995, 29, 607–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Germann, U. P-glycoprotein—A mediator of multidrug resistance in tumour cells. Eur. J. Cancer 1996, 32, 927–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catsburg, C.; Kirsh, V.A.; Soskolne, C.L.; Kreiger, N.; Bruce, E.; Ho, T.; Leatherdale, S.T.; Rohan, T.E. Associations between anthropometric characteristics, physical activity, and breast cancer risk in a Canadian cohort. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2014, 145, 545–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renehan, A.G.; Tyson, M.; Egger, M.; Heller, R.F.; Zwahlen, M. Body-mass index and incidence of cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective observational studies. Lancet 2008, 371, 569–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Brandt, P.A.; Spiegelman, N.; Yaun, S.-S.; Adami, H.-O.; Beeson, L.; Folsom, A.R.; Fraser, G.; Goldbohm, R.A.; Graham, S.; Kushi, L.; et al. Pooled Analysis of Prospective Cohort Studies on Height, Weight, and Breast Cancer Risk. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2000, 152, 514–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bergström, A.; Pisani, P.; Tenet, V.; Wolk, A.; Adami, H. Overweight as an avoidable cause of cancer in Europe. Int. J. Cancer 2000, 91, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ursin, G.; Longnecker, M.; Haik, R.W.; Greenland, S. A Meta-analysis of Body Mass Index and Risk of Premenopausal Breast Cancer. Epidemiology 1995, 6, 137–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoemaker, M.J.; Nichols, H.B.; Wright, L.B.; Brook, M.N.; Jones, M.E.; O’Brien, K.M.; Adami, H.-O.; Baglietto, L.; Bernstein, L.; The Premenopausal Breast Cancer Collaborative Group; et al. Association of Body Mass Index and Age with Subsequent Breast Cancer Risk in Premenopausal Women. JAMA Oncol. 2018, 4, e181771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Michels, K.B.; Terry, K.L.; Willett, W.C. Longitudinal Study on the Role of Body Size in Premenopausal Breast Cancer. Arch. Intern. Med. 2006, 166, 2395–2402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Harris, H.R.; Willett, W.C.; Terry, K.L.; Michels, K.B. Body Fat Distribution and Risk of Premenopausal Breast Cancer in the Nurses’ Health Study II. Gynecol. Oncol. 2010, 103, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rose, D.P.; Vona-Davis, L. Interaction between menopausal status and obesity in affecting breast cancer risk. Maturitas 2010, 66, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrieling, A.; Buck, K.; Kaaks, R.; Chang-Claude, J. Adult weight gain in relation to breast cancer risk by estrogen and progesterone receptor status: A meta-analysis. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2010, 123, 641–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eliassen, A.H.; Colditz, G.; Rosner, B.; Willett, W.C.; Hankinson, S.E. Adult Weight Change and Risk of Postmenopausal Breast Cancer. JAMA 2006, 296, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Emaus, M.J.; Van Gils, C.H.; Bakker, M.F.; Bisschop, C.N.S.; Monninkhof, E.M.; Bueno-De-Mesquita, H.B.; Travier, N.; Berentzen, T.L.; Overvad, K.; Tjonneland, A.; et al. Weight change in middle adulthood and breast cancer risk in the EPIC-PANACEA study. Int. J. Cancer 2014, 135, 2887–2899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosner, B.; Eliassen, A.H.; Toriola, A.T.; Hankinson, S.E.; Willett, W.C.; Natarajan, L.; Colditz, G.A. Short-term weight gain and breast cancer risk by hormone receptor classification among pre- and postmenopausal women. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2015, 150, 643–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hall, I.J.; Newman, B.; Millikan, R.C.; Moorman, P.G. Body size and breast cancer risk in black women and white women: The Carolina Breast Cancer Study. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2000, 151, 754–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, W.R.; Tse, C.K.; Olshan, A.F.; Troester, M.A. Body size across the life course and risk of premenopausal and postmenopausal breast cancer in Black women, the Carolina Breast Cancer Study, 1993–2001. Cancer Causes Control 2014, 25, 1101–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Swanson, C.A.; Coates, R.J.; Malone, K.E.; Gammon, M.D.; Schoenberg, J.B.; Brogan, D.J.; McAdams, M.; Potischman, N.; Hoover, R.N.; Brinton, L.A. Alcohol Consumption and Breast Cancer Risk among Women under Age 45 Years. Epidemiology 1997, 8, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Godinho-Mota, J.C.M.; Gonçalves, L.V.; Mota, J.F.; Soares, L.R.; Schincaglia, R.M.; Martins, K.A.; Freitas-Junior, R. Sedentary Behavior and Alcohol Consumption Increase Breast Cancer Risk Regardless of Menopausal Status: A Case-Control Study. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, S.M.; Lee, I.-M.; Manson, J.E.; Cook, N.R.; Willett, W.C.; Buring, J.E. Alcohol Consumption and Breast Cancer Risk in the Women’s Health Study. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2007, 165, 667–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.Y.; Rosner, B.; Hankinson, S.E.; Colditz, G.; Willett, W.C. Moderate Alcohol Consumption During Adult Life, Drinking Patterns, and Breast Cancer Risk. JAMA 2011, 306, 1884–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jung, S.; Wang, M.; Anderson, K.; Baglietto, L.; Bergkvist, L.; Bernstein, L.; Brandt, P.A.V.D.; Brinton, L.; Buring, J.E.; Eliassen, A.H.; et al. Alcohol consumption and breast cancer risk by estrogen receptor status: In a pooled analysis of 20 studies. Leuk. Res. 2015, 45, 916–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- World Cancer Research Fund. Diet, Nutrition, Physical Activity and Breast Cancer: A Global Perspective; World Cancer Research Fund: London, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- MacMahon, B.; Trichopoulos, D.; Cole, P.; Brown, J. Cigarette Smoking and Urinary Estrogens. N. Engl. J. Med. 1982, 307, 1062–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collaborative Group on Hormonal Factors in Breast Cancer. Alcohol, tobacco and breast cancer—Collaborative reanalysis of individual data from 53 epidemiological studies, including 58,515 women with breast cancer and 95,067 women without the disease. Br. J. Cancer 2002, 87, 1234–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, K.C. Accumulating evidence on passive and active smoking and breast cancer risk. Int. J. Cancer 2005, 117, 619–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slattery, M.L.; Curtin, K.; Giuliano, A.R.; Sweeney, C.; Baumgartner, R.; Edwards, S.; Wolff, R.K.; Baumgartner, K.B.; Byers, T. Active and passive smoking, IL6, ESR1, and breast cancer risk. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2007, 109, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, M.E.; Schoemaker, M.J.; Wright, L.B.; Ashworth, A.; Swerdlow, A.J. Smoking and risk of breast cancer in the Generations Study cohort. Breast Cancer Res. 2017, 19, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morabia, A.; Bemstein, M.; Héritier, S.; Khatchatrian, N. Relation of Breast Cancer with Passive and Active Exposure to Tobacco Smoke. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1996, 143, 918–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macacu, A.; Autier, P.; Boniol, M.; Boyle, P. Active and passive smoking and risk of breast cancer: A meta-analysis. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2015, 154, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, L.-Y.; Chen, L.-J.; Qi, M.-L.; Su, Y.; Su, F.-X.; Lin, Y.; Wang, K.-P.; Jia, W.-H.; Zhuang, Z.-X.; Ren, Z.-F. Effects of passive smoking on breast cancer risk in pre/post-menopausal women as modified by polymorphisms of PARP1 and ESR1. Gene 2013, 524, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winters, S.; Martin, C.; Murphy, D.; Shokar, N.K. Breast Cancer Epidemiology, Prevention, and Screening. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 2017, 151, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pudrovska, T.; Anikputa, B. The Role of Early-Life Socioeconomic Status in Breast Cancer Incidence and Mortality. J. Aging Health 2011, 24, 323–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hansen, J. Night Shift Work and Risk of Breast Cancer. Curr. Environ. Health Rep. 2017, 4, 325–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nooshinfar, E.; Safaroghli-Azar, A.; Bashash, D.; Akbari, M.E. Melatonin, an inhibitory agent in breast cancer. Breast Cancer 2016, 24, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegrzyn, L.R.; Tamimi, R.M.; Rosner, B.A.; Brown, S.B.; Stevens, R.G.; Eliassen, A.H.; Laden, F.; Willett, W.C.; Hankinson, S.E.; Schernhammer, E.S. Rotating Night-Shift Work and the Risk of Breast Cancer in the Nurses’ Health Studies. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2017, 186, 532–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Papantoniou, K.; Castaño-Vinyals, G.; Espinosa, A.; Aragones, N.; Pérez-Gómez, B.; Ardanaz, E.; Altzibar, J.M.; Sanchez, V.M.; Gomez-Acebo, I.; Llorca, J.; et al. Breast cancer risk and night shift work in a case–control study in a Spanish population. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2015, 31, 867–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schernhammer, E.S.; Laden, F.; Speizer, F.E.; Willett, W.C.; Hunter, D.J.; Kawachi, I.; Colditz, G.A. Rotating night shifts and risk of breast cancer in women participating in the nurses’ health study. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2001, 93, 1563–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cordina-Duverger, E.; Menegaux, F.; Popa, A.; Rabstein, S.; Harth, V.; Pesch, B.; Brüning, T.; Fritschi, L.; Glass, D.C.; Heyworth, J.S.; et al. Night shift work and breast cancer: A pooled analysis of population-based case–control studies with complete work history. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2018, 33, 369–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apostolou, P.; Fostira, F. Hereditary Breast Cancer: The Era of New Susceptibility Genes. BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 747318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Economopoulou, P.; Dimitriadis, G.; Psyrri, A. Beyond BRCA: New hereditary breast cancer susceptibility genes. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2015, 41, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rich, T.A.; Woodson, A.H.; Litton, J.; Arun, B. Hereditary breast cancer syndromes and genetic testing. J. Surg. Oncol. 2014, 111, 66–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorling, L.; Carvalho, S.; Allen, J.; González-Neira, A.; Luccarini, C.; Wahlström, C.; Pooley, K.A.; Parsons, M.T.; Fortuno, C.; Breast Cancer Association Consortium; et al. Breast Cancer Risk Genes—Association Analysis in More than 113,000 Women. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 428–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Hart, S.N.; Gnanaolivu, R.; Huang, H.; Lee, K.Y.; Na, J.; Gao, C.; Lilyquist, J.; Yadav, S.; Boddicker, N.J.; et al. A Population-Based Study of Genes Previously Implicated in Breast Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 440–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddig, A.; Din, T.T.; Nafi, S.M.; Yahya, M.; Sulong, S.; Rahman, W.W.A. The Unique Biology behind the Early Onset of Breast Cancer. Genes 2021, 12, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narod, S.A.; Foulkes, W. BRCA1 and BRCA2: 1994 and beyond. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2004, 4, 665–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copson, E.R.; Maishman, T.C.; Tapper, W.J.; Cutress, R.I.; Greville-Heygate, S.; Altman, D.G.; Eccles, B.; Gerty, S.; Durcan, L.T.; Jones, L.; et al. Germline BRCA mutation and outcome in young-onset breast cancer (POSH): A prospective cohort study. Lancet Oncol. 2018, 19, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Soussi, T.; Wiman, K.G. TP53: An oncogene in disguise. Cell Death Differ. 2015, 22, 1239–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Masciari, S.; Dillon, D.A.; Rath, M.; Robson, M.; Weitzel, J.N.; Balmana, J.; Gruber, S.B.; Ford, J.M.; Euhus, D.; Lebensohn, A.; et al. Breast cancer phenotype in women with TP53 germline mutations: A Li-Fraumeni syndrome consortium effort. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2012, 133, 1125–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, D.S.; Yoon, S.-Y.; Looi, L.M.; Kang, P.; Kang, I.N.; Sivanandan, K.; Ariffin, H.; Thong, M.K.; Chin, K.F.; Taib, N.A.M.; et al. Comparable frequency of BRCA1, BRCA2 and TP53 germline mutations in a multi-ethnic Asian cohort suggests TP53 screening should be offered together with BRCA1/2 screening to early-onset breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res. 2012, 14, R66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gonzalez, K.D.; Noltner, K.A.; Buzin, C.H.; Gu, D.; Wen-Fong, C.Y.; Nguyen, V.Q.; Han, J.H.; Lowstuter, K.; Longmate, J.; Sommer, S.S.; et al. Beyond Li Fraumeni Syndrome: Clinical Characteristics of Families With p53 Germline Mutations. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 1250–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damineni, S.; Rao, V.R.; Kumar, S.; Ravuri, R.R.; Kagitha, S.; Dunna, N.R.; Digumarthi, R.; Satti, V. Germline mutations of TP53 gene in breast cancer. Tumor Biol. 2014, 35, 9219–9227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouchawar, J.; Korch, C.; Byers, T.; Pitts, T.M.; Li, E.; McCredie, M.R.; Giles, G.G.; Hopper, J.L.; Southey, M.C. Population-Based Estimate of the Contribution of TP53 Mutations to Subgroups of Early-Onset Breast Cancer: Australian Breast Cancer Family Study. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 4795–4800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McCuaig, J.M.; Armel, S.R.; Novokmet, A.; Ginsburg, O.; Demsky, R.; Narod, S.A.; Malkin, D. Routine TP53 testing for breast cancer under age 30: Ready for prime time? Fam. Cancer 2012, 11, 607–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.S.; Salmena, L.; Pandolfi, P.P. The functions and regulation of the PTEN tumour suppressor. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2012, 13, 283–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulido, R. PTEN: A yin-yang master regulator protein in health and disease. Methods 2015, 77–78, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobert, J.A.; Eng, C. PTEN hamartoma tumor syndrome: An overview. Anesth. Analg. 2009, 11, 687–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tan, M.-H.; Mester, J.L.; Ngeow, J.; Rybicki, L.A.; Orloff, M.S.; Eng, C. Lifetime Cancer Risks in Individuals with Germline PTEN Mutations. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 400–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pradella, L.M.; Evangelisti, C.; Ligorio, C.; Ceccarelli, C.; Neri, I.; Zuntini, R.; Amato, L.B.; Ferrari, S.; Martelli, A.M.; Gasparre, G.; et al. A novel deleterious PTEN mutation in a patient with early-onset bilateral breast cancer. BMC Cancer 2014, 14, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Turpin, A.; Cattan, S.; Leclerc, J.; Wacrenier, A.; Manouvrier-Hanu, S.; Buisine, M.-P.; Lejeune-Dumoulin, S. Prédisposition héréditaire aux cancers digestifs, mammaires, gynécologiques et gonadiques: État des lieux du syndrome de Peutz-Jeghers. Bull. du Cancer 2014, 101, 813–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hearle, N.; Schumacher, V.; Menko, F.H.; Olschwang, S.; Boardman, L.A.; Gille, J.J.; Keller, J.J.; Westerman, A.M.; Scott, R.J.; Lim, W.; et al. Frequency and Spectrum of Cancers in the Peutz-Jeghers Syndrome. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 3209–3215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pharoah, P.D.; Guilford, P.; Caldas, C.; International Gastric Cancer Linkage Consortium. Incidence of gastric cancer and breast cancer in CDH1 (E-cadherin) mutation carriers from hereditary diffuse gastric cancer families. Gastroenterology 2001, 121, 1348–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks-Wilson, A.R.; Kaurah, P.; Suriano, G.; Leach, S.; Senz, J.; Grehan, N.; Butterfield, Y.S.N.; Jeyes, J.; Schinas, J.; Bacani, J.; et al. Germline E-cadherin mutations in hereditary diffuse gastric cancer: Assessment of 42 new families and review of genetic screening criteria. J. Med. Genet. 2004, 41, 508–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suriano, G.; Yew, S.; Ferreira, P.; Senz, J.; Kaurah, P.; Ford, J.M.; Longacre, T.A.; Norton, J.A.; Chun, N.; Young, S.; et al. Characterization of a Recurrent Germ Line Mutation of the E-Cadherin Gene: Implications for Genetic Testing and Clinical Management. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 5401–5409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kluijt, I.; Sijmons, R.H.; Hoogerbrugge, N.; Plukker, J.T.; De Jong, D.; van Krieken, J.; Van Hillegersberg, R.; Ligtenberg, M.; Bleiker, E.; Cats, A. Familial gastric cancer: Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and periodic surveillance. Fam. Cancer 2012, 11, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Petridis, C.; Shinomiya, I.; Kohut, K.; Gorman, P.; Caneppele, M.; Shah, V.; Troy, M.; Pinder, S.E.; Hanby, A.; Tomlinson, I.; et al. Germline CDH1 mutations in bilateral lobular carcinoma in situ. Br. J. Cancer 2013, 110, 1053–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xie, Z.M.; Li, L.S.; Laquet, C.; Xie, X.M.; Penault-Llorca, F.; Uhrhammer, N.; Bignon, Y.J. Germline mutations of the E-cadherin gene in families with inherited invasive lobular breast carcinoma but no diffuse gastric cancer. Cancer 2011, 117, 3112–3117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrader, K.A.; Masciari, S.; Boyd, N.; Salamanca, C.; Senz, J.; Saunders, D.N.; Yorida, E.; Maines-Bandiera, S.; Kaurah, P.; Tung, N.; et al. Germline mutations in CDH1 are infrequent in women with early-onset or familial lobular breast cancers. J. Med. Genet. 2010, 48, 64–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Antoniou, A.C.; Casadei, S.; Heikkinen, T.; Barrowdale, D.; Pylkäs, K.; Roberts, J.; Lee, A.; Subramanian, D.; De Leeneer, K.; Fostira, F.; et al. Breast-Cancer Risk in Families with Mutations in PALB2. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Weischer, M.; Bojesen, S.E.; Ellervik, C.; Tybjærg-Hansen, A.; Nordestgaard, B.G. CHEK2*1100delC Genotyping for Clinical Assessment of Breast Cancer Risk: Meta-Analyses of 26,000 Patient Cases and 27,000 Controls. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 542–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rashid, M.U.; Muhammad, N.; Faisal, S.; Amin, A.; Hamann, U. Constitutional CHEK2mutations are infrequent in early-onset and familial breast/ovarian cancer patients from Pakistan. BMC Cancer 2013, 13, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, N.; Ding, H.; Liu, C.; Li, X.; Wei, L.; Yu, J.; Liu, M.; Ying, M.; Gao, W.; Jiang, H.; et al. A novel recurrent CHEK2 Y390C mutation identified in high-risk Chinese breast cancer patients impairs its activity and is associated with increased breast cancer risk. Oncogene 2015, 34, 5198–5205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, D.; Duedal, S.; Kirner, J.; McGuffog, L.; Last, J.; Reiman, A.; Byrd, P.; Taylor, M.; Easton, D.F. Cancer Risks and Mortality in Heterozygous ATM Mutation Carriers. Gynecol. Oncol. 2005, 97, 813–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maillet, P.; Bonnefoi, H.; Vaudan-Vutskits, G.; Pajk, B.; Cufer, T.; Foulkes, W.; Chappuis, P.O.; Sappino, A.-P. Constitutional alterations of the ATM gene in early onset sporadic breast cancer. J. Med. Genet. 2002, 39, 751–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Teraoka, S.N.; Malone, K.E.; Doody, D.; Suter, N.M.; Ostrander, E.; Daling, J.R.; Concannon, P. Increased frequency of ATM mutations in breast carcinoma patients with early onset disease and positive family history. Cancer 2001, 92, 479–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrell, D.; Cromartie, E.; Swift, M. Mortality and Cancer Incidence in 263 Patients With Ataxia-Telangiectasia2. Gynecol. Oncol. 1986, 77, 89–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, P.-H.; Kuo, W.-H.; Huang, A.-C.; Lu, Y.-S.; Lin, C.-H.; Kuo, S.-H.; Wang, M.-Y.; Liu, C.-Y.; Cheng, F.T.-F.; Yeh, M.-H.; et al. Multiple gene sequencing for risk assessment in patients with early-onset or familial breast cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 8310–8320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Izatt, L.; Greenman, J.; Hodgson, S.; Ellis, D.; Watts, S.; Scott, G.; Jacobs, C.; Liebmann, R.; Zvelebil, M.J.; Mathew, C.; et al. Identification of germline missense mutations and rare allelic variants in the ATM gene in early-onset breast cancer. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 1999, 26, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrnes, G.B.; Southey, M.C.; Hopper, J.L. Are the so-called low penetrance breast cancer genes, ATM, BRIP1, PALB2 and CHEK2, high risk for women with strong family histories? Breast Cancer Res. 2008, 10, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Churpek, J.E.; Walsh, T.; Zheng, Y.; Moton, Z.; Thornton, A.M.; Lee, M.K.; Casadei, S.; Watts, A.; Neistadt, B.; Churpek, M.M.; et al. Inherited predisposition to breast cancer among African American women. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2014, 149, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Couch, F.J.; Hart, S.N.; Sharma, P.; Toland, A.E.; Wang, X.; Miron, P.; Olson, J.E.; Godwin, A.K.; Pankratz, V.S.; Olswold, C.; et al. Inherited Mutations in 17 Breast Cancer Susceptibility Genes Among a Large Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cohort Unselected for Family History of Breast Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 304–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McInerney, N.M.; Miller, N.; Rowan, A.; Colleran, G.; Barclay, E.; Curran, C.; Kerin, M.; Tomlinson, I.P.; Sawyer, E. Evaluation of variants in the CHEK2, BRIP1 and PALB2 genes in an Irish breast cancer cohort. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2009, 121, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cao, A.-Y.; Huang, J.; Hu, Z.; Li, W.-F.; Ma, Z.-L.; Tang, L.-L.; Zhang, B.; Su, F.-X.; Zhou, J.; Di, G.-H.; et al. Mutation analysis of BRIP1/BACH1 in BRCA1/BRCA2 negative Chinese women with early onset breast cancer or affected relatives. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2008, 115, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stacey, S.N.; Sulem, P.; Johannsson, O.T.; Helgason, A.; Gudmundsson, J.; Kostic, J.P.; Kristjansson, K.; Jonsdottir, T.; Sigurdsson, H.; Hrafnkelsson, J.; et al. The BARD1 Cys557Ser Variant and Breast Cancer Risk in Iceland. PLoS Med. 2006, 3, e217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, G.; Wang, J.T.; Ma, B.L.; Geng, Z.L.; Ren, G.H.; Shan, M.H.; Ma, B.; Ma, L.L.; Wang, Y. Association between single nucleotide polymorphisms of BARD 1 gene and susceptibility of early-onset breast cancer in Uygur women in Xinjiang. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi 2012, 34, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, E.; Feng, B.J.; Stark, A.W.; Damiola, F.; Durand, G.; Forey, N.; Francy, T.C.; Gammon, A.; Kohlmann, W.K.; Kaphingst, K.A.; et al. Multigene testing of moderate-risk genes: Be mindful of the missense. J. Med. Genet. 2016, 53, 366–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghimenti, C.; Sensi, E.; Presciuttini, S.; Brunetti, I.M.; Conte, P.; Bevilacqua, G.; Caligo, M.A. Germline mutations of the BRCA1-associated ring domain (BARD1) gene in breast and breast/ovarian families negative for BRCA1 and BRCA2 alterations. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2002, 33, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karppinen, S.-M.; Heikkinen, K.; Rapakko, K.; Winqvist, R. Mutation screening of the BARD1 gene: Evidence for involvement of the Cys557Ser allele in hereditary susceptibility to breast cancer. J. Med. Genet. 2004, 41, e114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, X.; Song, H.; Leslie, G.; Engel, C.; Hahnen, E.; Auber, B.; Horváth, J.; Kast, K.; Niederacher, D.; Turnbull, C.; et al. Ovarian and Breast Cancer Risks Associated With Pathogenic Variants in RAD51C and RAD51D. Gynecol. Oncol. 2020, 112, 1242–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barnholtz-Sloan, J.S.; Shetty, P.B.; Guan, X.; Nyante, S.J.; Luo, J.; Brennan, D.J.; Millikan, R.C. FGFR2 and other loci identified in genome-wide association studies are associated with breast cancer in African-American and younger women. Carcinogenesis 2010, 31, 1417–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michailidou, K.; Beesley, J.; Lindstrom, S.; Canisius, S.; Dennis, J.; Lush, M.J.; Maranian, M.J.; Bolla, M.K.; Wang, Q.; Shah, M.; et al. Genome-wide association analysis of more than 120,000 individuals identifies 15 new susceptibility loci for breast cancer. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahsan, H.; Halpern, J.; Kibriya, M.G.; Pierce, B.L.; Tong, L.; Gamazon, E.; McGuire, V.; Felberg, A.; Shi, J.; Jasmine, F.; et al. A Genome-wide Association Study of Early-Onset Breast Cancer Identifies PFKM as a Novel Breast Cancer Gene and Supports a Common Genetic Spectrum for Breast Cancer at Any Age. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2014, 23, 658–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Si, S.; Boyle, T.; Heyworth, J.; Glass, D.; Saunders, C.; Fritschi, L. Lifetime physical activity and risk of breast cancer in pre-and post-menopausal women. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2015, 152, 449–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Masala, G.; Bendinelli, B.; Assedi, M.; Occhini, D.; Zanna, I.; Sieri, S.; Agnoli, C.; Sacerdote, C.; Ricceri, F.; Mattiello, A.; et al. Up to one-third of breast cancer cases in post-menopausal Mediterranean women might be avoided by modifying lifestyle habits: The EPIC Italy study. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2016, 161, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borghesan, D.H.P.; Agnolo, C.M.D.; Gravena, A.A.F.; Demitto, M.D.O.; Lopes, T.C.R.; Carvalho, M.D.D.B.; Pelloso, S.M. Risk Factors for Breast Cancer in Postmenopausal Women in Brazil. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2016, 17, 3587–3593. [Google Scholar]
- Conz, L.; Mota, B.S.; Bahamondes, L.; Dória, M.T.; Derchain, S.F.M.; Rieira, R.; Sarian, L.O. Levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine system and breast cancer risk: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Acta Obstet. Gynecol. Scand. 2020, 99, 970–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Henderson, K.D.; Sullivan-Halley, J.; Duan, L.; Marshall, S.F.; Ursin, G.; Horn-Ross, P.L.; Largent, J.; Deapen, D.M.; Lacey, J.V.; et al. Pregnancy-related factors and the risk of breast carcinoma in situand invasive breast cancer among postmenopausal women in the California Teachers Study cohort. Breast Cancer Res. 2010, 12, R35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Daniels, K.; Abma, J. Current Contraceptive Status among Women Aged 15–49: United States, 2015–2017; NCHS Data Brief, No 327; National Center for Health Statistics: Hyattsville, MD, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- The Collaborative Group on Hormonal Factors in Breast Cancer. Breast cancer and hormonal contraceptives: Collaborative reanalysis of individual data on 53 297 women with breast cancer and 100 239 women without breast cancer from 54 epidemiological studies. Lancet 1996, 347, 1713–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vaz-Luis, I.; Partridge, A.H. Exogenous reproductive hormone use in breast cancer survivors and previvors. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 15, 249–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mørch, L.S.; Skovlund, C.W.; Hannaford, P.C.; Iversen, L.; Fielding, S.; Lidegaard, Ø. Contemporary Hormonal Contraception and the Risk of Breast Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 2228–2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soini, T.; Hurskainen, R.; Grénman, S.; Mäenpää, J.; Paavonen, J.; Pukkala, E. Cancer Risk in Women Using the Levonorgestrel-Releasing Intrauterine System in Finland. Obstet. Gynecol. 2014, 124, 292–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zolfaroli, I.; Tarín, J.J.; Cano, A. Hormonal contraceptives and breast cancer: Clinical data. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 2018, 230, 212–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Familial Breast Cancer: Classification, Care and Managing Breast Cancer and Related Risks in People with a Family History of Breast Cancer | Guidance | NICE. Available online: https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/cg164 (accessed on 7 October 2022).
- MacMahon, B.; Cole, P.; Lin, T.M.; Lowe, C.R.; Mirra, A.P.; Ravnihar, B.; Salber, E.J.; Valaoras, V.G.; Yuasa, S. Age at first birth and breast cancer risk. Bull. World Health Organ. 1970, 43, 209–221. [Google Scholar]
- Albrektsen, G.; Heuch, I.; Hansen, S.; Kvåle, G. Breast cancer risk by age at birth, time since birth and time intervals between births: Exploring interaction effects. Br. J. Cancer 2004, 92, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dall, G.V.; Hawthorne, S.; Seyed-Razavi, Y.; Vieusseux, J.; Wu, W.; Gustafsson, J.-A.; Byrne, D.; Murphy, L.; Risbridger, G.P.; Britt, K.L. Estrogen receptor subtypes dictate the proliferative nature of the mammary gland. J. Endocrinol. 2018, 237, 323–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nichols, H.B.; Schoemaker, M.J.; Cai, J.; Xu, B.J.; Wright, M.L.B.; Brook, M.N.; Jones, M.E.; Adami, H.-O.; Baglietto, L.; Bertrand, S.K.A.; et al. Breast Cancer Risk After Recent Childbirth. Ann. Intern. Med. 2018, 170, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hall, I.J.; Moorman, P.G.; Millikan, R.C.; Newman, B. Comparative Analysis of Breast Cancer Risk Factors among African-American Women and White Women. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2005, 161, 40–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derks-Smeets, I.A.P.; Schrijver, L.H.; de Die-Smulders, C.E.M.; Tjan-Heijnen, V.C.G.; van Golde, R.J.T.; Smits, L.J.; Caanen, B.; van Asperen, C.J.; Ausems, M.; Collée, M.; et al. Ovarian stimulation for IVF and risk of primary breast cancer in BRCA1/2 mutation carriers. Br. J. Cancer 2018, 119, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huber, D.; Seitz, S.; Kast, K.; Emons, G.; Ortmann, O. Use of fertility treatments in BRCA1/2 mutation carriers and risk for ovarian and breast cancer: A systematic review. Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. 2020, 302, 715–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrosone, C.B.; Higgins, M.J. Relationships between Breast Feeding and Breast Cancer Subtypes: Lessons Learned from Studies in Humans and in Mice. Cancer Res. 2020, 80, 4871–4877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Britt, K.L.; Cuzick, J.; Phillips, K.-A. Key steps for effective breast cancer prevention. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2020, 20, 417–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collaborative Group on Hormonal Factors in Breast Cancer. Breast cancer and breastfeeding: Collaborative reanalysis of individual data from 47 epidemiological studies in 30 countries, including 50,302 women with breast cancer and 96,973 women without the disease. Lancet 2002, 360, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ursin, G.; Bernstein, L.; Lord, S.J.; Karim, R.; Deapen, D.; Press, M.F.; Daling, J.R.; Norman, S.A.; Liff, J.M.; Marchbanks, P.A.; et al. Reproductive factors and subtypes of breast cancer defined by hormone receptor and histology. Br. J. Cancer 2005, 93, 364–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Islami, F.; Liu, Y.; Jemal, A.; Zhou, J.; Weiderpass, E.; Colditz, G.; Boffetta, P.; Weiss, M. Breastfeeding and breast cancer risk by receptor status—A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann. Oncol. 2015, 26, 2398–2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Global Strategy for Infant and Young Child Feeding. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications-detail-redirect/9241562218 (accessed on 7 October 2022).
- Adami, H.-O.; Malker, B.; Holmberg, L.; Persson, I.; Stone, B. The Relation between Survival and Age at Diagnosis in Breast Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 1986, 315, 559–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Saghir, N.S.; Seoud, M.; Khalil, M.K.; Charafeddine, M.; Salem, Z.K.; Geara, F.B.; Shamseddine, A.I. Effects of young age at presentation on survival in breast cancer. BMC Cancer 2006, 6, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Holli, K.; Isola, J. Effect of age on the survival of breast cancer patients. Eur. J. Cancer 1997, 33, 425–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, L.C.; Marotti, J.D.; Gelber, S.; Cole, K.; Ruddy, K.; Kereakoglow, S.; Brachtel, E.F.; Schapira, L.; Come, S.E.; Winer, E.P.; et al. Pathologic features and molecular phenotype by patient age in a large cohort of young women with breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2011, 131, 1061–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keegan, T.H.; DeRouen, M.C.; Press, D.J.; Kurian, A.W.; Clarke, C.A. Occurrence of breast cancer subtypes in adolescent and young adult women. Breast Cancer Res. 2012, 14, R55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lund, M.J.; Trivers, K.F.; Porter, P.L.; Coates, R.J.; Leyland-Jones, B.; Brawley, O.W.; Flagg, E.W.; O’Regan, R.M.; Gabram, S.G.A.; Eley, J.W. Race and triple negative threats to breast cancer survival: A population-based study in Atlanta, GA. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2008, 113, 357–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardo, I.; Lillemoe, H.A.; Blosser, R.J.; Choi, M.; Sauder, C.A.M.; Doxey, D.K.; Mathieson, T.; Hancock, B.A.; Baptiste, D.; Atale, R.; et al. Next-generation transcriptome sequencing of the premenopausal breast epithelium using specimens from a normal human breast tissue bank. Breast Cancer Res. 2014, 16, R26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Albain, K.S.; Allred, D.C.; Clark, G.M. Breast cancer outcome and predictors of outcome: Are there age differentials? J. Natl. Cancer Inst. Monogr. 1994, 16, 35–42. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, F.; Kuo, Y.-F.; Shih, Y.C.T.; Giordano, S.H.; Berenson, A.B. Trends in breast cancer mortality by stage at diagnosis among young women in the United States. Cancer 2018, 124, 3500–3509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De la Rochefordière, A.; Campana, F.; Fenton, J.; Vilcoq, J.; Fourquet, A.; Asselain, B.; Scholl, S.; Pouillart, P.; Durand, J.-C.; Magdelenat, H. Age as prognostic factor in premenopausal breast carcinoma. Lancet 1993, 341, 1039–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nixon, A.J.; Neuberg, D.; Hayes, D.F.; Gelman, R.; Connolly, J.L.; Schnitt, S.; Abner, A.; Recht, A.; Vicini, F.; Harris, J.R. Relationship of patient age to pathologic features of the tumor and prognosis for patients with stage I or II breast cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 1994, 12, 888–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnerlich, J.L.; Deshpande, A.D.; Jeffe, D.B.; Sweet, A.; White, N.; Margenthaler, J.A. Elevated Breast Cancer Mortality in Women Younger than Age 40 Years Compared with Older Women Is Attributed to Poorer Survival in Early-Stage Disease. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2009, 208, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Szollár, A.; Újhelyi, M.; Polgár, C.; Oláh, E.; Pukancsik, D.; Rubovszky, G.; Udvarhelyi, N.; Kovács, T.; Sávolt, Á.; Kenessey, I.; et al. A long-term retrospective comparative study of the oncological outcomes of 598 very young (≤35 years) and young (36–45 years) breast cancer patients. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. (EJSO) 2019, 45, 2009–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajpai, J.; Ventrapati, P.; Joshi, S.; Wadasadawala, T.; Rath, S.; Pathak, R.; Nandhana, R.; Mohanty, S.; Chougle, Q.; Engineer, M.; et al. Unique challenges and outcomes of young women with breast cancers from a tertiary care cancer centre in India. Breast 2021, 60, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez-Bañuelos, M.T.; Segura-Jaramillo, K.A.; Gómez-Rivera, E.D.C.; Alarcón-Rojas, C.A.; Morales-Romero, J.; Sampieri, C.L.; Guzmán-García, R.E. Age under 30 Years as a Predictor of Poor Survival in a Cohort of Mexican Women with Breast Cancer. Cancer Control 2021, 28, 10732748211047408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabiano, V.; Mandó, P.; Rizzo, M.; Ponce, C.; Coló, F.; Loza, M.; Loza, J.; Amat, M.; Mysler, D.; Costanzo, M.V.; et al. Breast Cancer in Young Women Presents With More Aggressive Pathologic Characteristics: Retrospective Analysis from an Argentine National Database. JCO Glob. Oncol. 2020, 6, 639–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van den Broek, A.J.; Schmidt, M.K.; van’t Veer, L.J.; Tollenaar, R.A.; van Leeuwen, F.E. Worse Breast Cancer Prognosis of BRCA1/BRCA2 Mutation Carriers: What’s the Evidence? A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0120189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eerola, H.; Heikkilä, P.; Tamminen, A.; Aittomäki, K.; Blomqvist, C.; Nevanlinna, H. Histopathological features of breast tumours in BRCA1, BRCA2 and mutation-negative breast cancer families. Breast Cancer Res. 2004, 7, R93–R100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Atchley, D.P.; Albarracin, C.T.; Lopez, A.; Valero, V.; Amos, C.I.; Gonzalez-Angulo, A.M.; Hortobagyi, G.N.; Arun, B.K. Clinical and Pathologic Characteristics of Patients With BRCA-Positive and BRCA-Negative Breast Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 4282–4288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodwin, P.J.; Phillips, K.-A.; West, D.W.; Ennis, M.; Hopper, J.L.; John, E.M.; O’Malley, F.P.; Milne, R.L.; Andrulis, I.L.; Friedlander, M.L.; et al. Breast Cancer Prognosis in BRCA1 and BRCA2 Mutation Carriers: An International Prospective Breast Cancer Family Registry Population-Based Cohort Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Spurdle, A.B.; Couch, F.J.; Parsons, M.T.; McGuffog, L.; Barrowdale, D.; Bolla, M.K.; Wang, Q.; Healey, S.; Schmutzler, R.K.; EMBRACE Group; et al. Refined histopathological predictors of BRCA1 and BRCA2mutation status: A large-scale analysis of breast cancer characteristics from the BCAC, CIMBA, and ENIGMA consortia. Breast Cancer Res. 2014, 16, 3419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vocka, M.; Zimovjanova, M.; Bielcikova, Z.; Tesarova, P.; Petruzelka, L.; Mateju, M.; Krizova, L.; Kotlas, J.; Soukupova, J.; Janatova, M.; et al. Estrogen Receptor Status Oppositely Modifies Breast Cancer Prognosis in BRCA1/BRCA2 Mutation Carriers Versus Non-Carriers. Cancers 2019, 11, 738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jonasson, J.G.; Stefansson, O.A.; Johannsson, O.T.; Sigurdsson, H.; Agnarsson, B.A.; Olafsdottir, G.H.; Alexiusdottir, K.K.; Stefansdottir, H.; Munoz Mitev, R.; Olafsdottir, K.; et al. Oestrogen receptor status, treatment and breast cancer prognosis in Icelandic BRCA2 mutation carriers. Br. J. Cancer 2016, 115, 776–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, M.K.; Van Den Broek, A.J.; Tollenaar, R.A.; Smit, V.T.; Westenend, P.; Brinkhuis, M.; Oosterhuis, W.J.W.; Wesseling, J.; Janssen-Heijnen, M.L.; Jobsen, J.J.; et al. Breast Cancer Survival of BRCA1/BRCA2 Mutation Carriers in a Hospital-Based Cohort of Young Women. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2017, 109, djw329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Metcalfe, K.; Lynch, H.T.; Foulkes, W.D.; Tung, N.; Olopade, O.I.; Eisen, A.; Lerner-Ellis, J.; Snyder, C.; Kim, S.J.; Sun, P.; et al. Oestrogen receptor status and survival in women with BRCA2-associated breast cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2019, 120, 398–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuchenbaecker, K.B.; Hopper, J.L.; Barnes, D.R.; Phillips, K.-A.; Mooij, T.M.; Roos-Blom, M.-J.; Jervis, S.; Van Leeuwen, F.E.; Milne, R.L.; Andrieu, N.; et al. Risks of Breast, Ovarian, and Contralateral Breast Cancer for BRCA1 and BRCA2 Mutation Carriers. JAMA 2017, 317, 2402–2416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mavaddat, N.; Peock, S.; Frost, D.; Ellis, S.; Platte, R.; Fineberg, E.; Evans, D.G.; Izatt, L.; Eeles, R.A.; Adlard, J.; et al. Cancer Risks for BRCA1 and BRCA2 Mutation Carriers: Results From Prospective Analysis of EMBRACE. Gynecol. Oncol. 2013, 105, 812–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Graeser, M.K.; Engel, C.; Rhiem, K.; Gadzicki, D.; Bick, U.; Kast, K.; Froster, U.G.; Schlehe, B.; Bechtold, A.; Arnold, N.; et al. Contralateral Breast Cancer Risk in BRCA1 and BRCA2 Mutation Carriers. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 5887–5892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkowitz, Z.; Rim, S.H.; Peipins, L.A. Characteristics and survival associated with ovarian cancer diagnosed as first cancer and ovarian cancer diagnosed subsequent to a previous cancer. Cancer Epidemiol. 2011, 35, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, L.C.; Lindor, N.M. The Role of Risk-Reducing Surgery in Hereditary Breast and Ovarian Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 454–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dullens, B.; de Putter, R.; Lambertini, M.; Toss, A.; Han, S.; Van Nieuwenhuysen, E.; Van Gorp, T.; Vanderstichele, A.; Van Ongeval, C.; Keupers, M.; et al. Cancer Surveillance in Healthy Carriers of Germline Pathogenic Variants in BRCA1/2: A Review of Secondary Prevention Guidelines. J. Oncol. 2020, 2020, 9873954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambertini, M.; Ceppi, M.; Hamy, A.-S.; Caron, O.; Poorvu, P.D.; Carrasco, E.; Grinshpun, A.; Punie, K.; Rousset-Jablonski, C.; Ferrari, A.; et al. Clinical behavior and outcomes of breast cancer in young women with germline BRCA pathogenic variants. npj Breast Cancer 2021, 7, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.-M.; Zou, D.-H. The association of young age with local recurrence in women with early-stage breast cancer after breast-conserving therapy: A meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Botteri, E.; Bagnardi, V.; Rotmensz, N.; Gentilini, O.; Disalvatore, D.; Bazolli, B.; Luini, A.; Veronesi, U. Analysis of local and regional recurrences in breast cancer after conservative surgery. Ann. Oncol. 2010, 21, 723–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arriagada, R.; Lê, M.G.; Contesso, G.; Guinebretière, J.M.; Rochard, F.; Spielmann, M. Predictive factors for local recurrence in 2006 patients with surgically resected small breast cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2002, 13, 1404–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurtz, J.M.; Jacquemier, J.; Amalric, R.; Brandone, H.; Ayme, Y.; Hans, D.; Bressac, C.; Spitalier, J.M. Why are local recurrences after breast-conserving therapy more frequent in younger patients? J. Clin. Oncol. 1990, 8, 591–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.; Kim, S.-W.; Oh, Y.-T.; Noh, O.; Jung, Y.; Chun, M.; Yoon, D. Local Recurrence in Young Women with Breast Cancer: Breast Conserving Therapy vs. Mastectomy Alone. Cancers 2021, 13, 2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maishman, T.; Cutress, R.I.; Hernandez, A.; Gerty, S.; Copson, E.R.; Durcan, L.; Eccles, D.M. Local Recurrence and Breast Oncological Surgery in Young Women With Breast Cancer. Ann. Surg. 2017, 266, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Quan, M.L.; Paszat, L.F.; Fernandes, K.A.; Sutradhar, R.; McCready, D.R.; Rakovitch, E.; Warner, E.; Wright, F.C.; Hodgson, N.; Brackstone, M.; et al. The effect of surgery type on survival and recurrence in very young women with breast cancer. J. Surg. Oncol. 2017, 115, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aalders, K.C.; Postma, E.L.; Strobbe, L.J.; Loo, M.V.D.H.-V.D.; Sonke, G.S.; Boersma, L.J.; van Diest, P.J.; Siesling, S.; van Dalen, T. Contemporary Locoregional Recurrence Rates in Young Patients With Early-Stage Breast Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 2107–2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Laar, C.; van der Sangen, M.; Poortmans, P.; Nieuwenhuijzen, G.; Roukema, J.; Roumen, R.; Tjan-Heijnen, V.; Voogd, A. Local recurrence following breast-conserving treatment in women aged 40years or younger: Trends in risk and the impact on prognosis in a population-based cohort of 1143 patients. Eur. J. Cancer 2013, 49, 3093–3101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; He, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, T.; Xie, Y.; Fan, Z.; Ouyang, T. Comparisons of breast conserving therapy versus mastectomy in young and old women with early-stage breast cancer: Long-term results using propensity score adjustment method. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2020, 183, 717–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.Q.; Truong, P.T.; Olivotto, I.A.; Olson, R.; Coulombe, G.; Keyes, M.; Weir, L.; Gelmon, K.; Bernstein, V.; Woods, R.; et al. Should Women Younger Than 40 Years of Age With Invasive Breast Cancer Have a Mastectomy?: 15-Year Outcomes in a Population-Based Cohort. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2014, 90, 509–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Wang, X.; Lin, H.; Wei, W.; Liu, P.; Xiao, X.; Xie, X.; Guan, X.; Yang, M.; Tang, J. Breast-Conserving Therapy: A Viable Option for Young Women with Early Breast Cancer—Evidence from a Prospective Study. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2014, 21, 2188–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Lu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, S.; Liu, H. Loco-regional recurrence trend and prognosis in young women with breast cancer according to molecular subtypes: Analysis of 1099 cases. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2021, 19, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millar, E.K.; Graham, P.H.; O’Toole, S.A.; McNeil, C.M.; Browne, L.; Morey, A.L.; Eggleton, S.; Beretov, J.; Theocharous, C.; Capp, A.; et al. Prediction of Local Recurrence, Distant Metastases, and Death After Breast-Conserving Therapy in Early-Stage Invasive Breast Cancer Using a Five-Biomarker Panel. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 4701–4708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowery, A.J.; Kell, M.R.; Glynn, R.W.; Kerin, M.J.; Sweeney, K.J. Locoregional recurrence after breast cancer surgery: A systematic review by receptor phenotype. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2011, 133, 831–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurberg, T.; Alsner, J.; Tramm, T.; Jensen, V.; Lyngholm, C.D.; Christiansen, P.M.; Overgaard, J. Impact of age, intrinsic subtype and local treatment on long-term local-regional recurrence and breast cancer mortality among low-risk breast cancer patients. Acta Oncol. 2016, 56, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnant, M.; Mlineritsch, B.; Stoeger, H.; Luschin-Ebengreuth, G.; Heck, D.; Menzel, C.; Jakesz, R.; Seifert, M.; Hubalek, M.; Pristauz, G.; et al. Adjuvant endocrine therapy plus zoledronic acid in premenopausal women with early-stage breast cancer: 62-month follow-up from the ABCSG-12 randomised trial. Lancet Oncol. 2011, 12, 631–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakesz, R.; Hausmaninger, H.; Kubista, E.; Gnant, M.; Menzel, C.; Bauernhofer, T.; Seifert, M.; Haider, K.; Mlineritsch, B.; Steindorfer, P.; et al. Randomized Adjuvant Trial of Tamoxifen and Goserelin Versus Cyclophosphamide, Methotrexate, and Fluorouracil: Evidence for the Superiority of Treatment With Endocrine Blockade in Premenopausal Patients With Hormone-Responsive Breast Cancer—Austrian Breast and Colorectal Cancer Study Group Trial 5. J. Clin. Oncol. 2002, 20, 4621–4627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tjokrowidjaja, A.; Lee, C.K.; Houssami, N.; Lord, S.J. Metastatic breast cancer in young women: A population-based cohort study to describe risk and prognosis. Intern. Med. J. 2014, 44, 764–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bock, G.H.; Putter, H.; Bonnema, J.; Van Der Hage, J.A.; Bartelink, H.; Van De Velde, C.J. The impact of loco-regional recurrences on metastatic progression in early-stage breast cancer: A multistate model. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2009, 117, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beadle, B.M.; Woodward, W.A.; Tucker, S.L.; Outlaw, E.D.; Allen, P.K.; Oh, J.L.; Strom, E.A.; Perkins, G.H.; Tereffe, W.; Yu, T.-K.; et al. Ten-Year Recurrence Rates in Young Women With Breast Cancer by Locoregional Treatment Approach. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2009, 73, 734–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rapiti, E.; Fioretta, G.; Verkooijen, H.M.; Vlastos, G.; Schäfer, P.; Sappino, A.-P.; Kurtz, J.; Neyroud-Caspar, I.; Bouchardy, C. Survival of young and older breast cancer patients in Geneva from 1990 to 2001. Eur. J. Cancer 2005, 41, 1446–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dabakuyo, T.S.; Bonnetain, F.; Roignot, P.; Poillot, M.-L.; Chaplain, G.; Altwegg, T.; Hedelin, G.; Arveux, P. Population-based study of breast cancer survival in Cote d’Or (France): Prognostic factors and relative survival. Ann. Oncol. 2007, 19, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kheirelseid, E.A.H.; Boggs, J.M.; Curran, C.; Glynn, R.W.; Dooley, C.; Sweeney, K.J.; Kerin, M.J. Younger age as a prognostic indicator in breast cancer: A cohort study. BMC Cancer 2011, 11, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Anders, C.K.; Fan, C.; Parker, J.S.; Carey, L.A.; Blackwell, K.L.; Klauber-Demore, N.; Perou, C. Breast Carcinomas Arising at a Young Age: Unique Biology or a Surrogate for Aggressive Intrinsic Subtypes? J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, e18–e20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Biganzoli, L.; Marotti, L.; Hart, C.D.; Cataliotti, L.; Cutuli, B.; Kühn, T.; Mansel, R.E.; Ponti, A.; Poortmans, P.; Regitnig, P.; et al. Quality indicators in breast cancer care: An update from the EUSOMA working group. Eur. J. Cancer 2017, 86, 59–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freedman, R.A.; Partridge, A.H. Emerging Data and Current Challenges for Young, Old, Obese, or Male Patients with Breast Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 2647–2654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Runowicz, C.D.; Leach, C.R.; Henry, N.L.; Henry, K.S.; Mackey, H.T.; Cowens-Alvarado, R.L.; Cannady, R.S.; Pratt-Chapman, M.; Edge, S.B.; Jacobs, L.A.; et al. American Cancer Society/American Society of Clinical Oncology Breast Cancer Survivorship Care Guideline. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2015, 66, 43–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vila, J.; Gandini, S.; Gentilini, O. Overall survival according to type of surgery in young (≤40 years) early breast cancer patients: A systematic meta-analysis comparing breast-conserving surgery versus mastectomy. Breast 2015, 24, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.C.; Yan, W.; Christos, P.J.; Nori, D.; Ravi, A. Equivalent Survival With Mastectomy or Breast-conserving Surgery Plus Radiation in Young Women Aged < 40 Years With Early-Stage Breast Cancer: A National Registry-based Stage-by-Stage Comparison. Clin. Breast Cancer 2015, 15, 390–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, P.; Li, L.; Xiu, B.; Zhang, L.; Yang, B.; Chi, Y.; Xue, J.; Wu, J. The Prognoses of Young Women with Breast Cancer (≤35 years) with Different Surgical Options: A Propensity Score Matching Retrospective Cohort Study. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 795023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartelink, H.; Maingon, P.; Poortmans, P.; Weltens, C.; Fourquet, A.; Jager, J.; Schinagl, D.; Oei, B.; Rodenhuis, C.; Horiot, J.-C.; et al. Whole-breast irradiation with or without a boost for patients treated with breast-conserving surgery for early breast cancer: 20-year follow-up of a randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 16, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, A.; Oh, J.L.; Oswald, M.J.; Huang, E.; Strom, E.A.; Perkins, G.H.; Woodward, W.; Yu, T.K.; Tereffe, W.; Meric-Bernstam, F.; et al. Effect of Postmastectomy Radiotherapy in Patients <35 Years Old with Stage II-III Breast Cancer Treated with Doxorubicin-Based Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy and Mastectomy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2007, 69, 1478–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Darby, S.; McGale, P.; Correa, C.; Taylor, C.; Arriagada, R.; Clarke, M.; Cutter, D.; Davies, C.; Ewertz, M.; Early Breast Cancer Trialists’ Collaborative Group (EBCTCG); et al. Effect of radiotherapy after breast-conserving surgery on 10-year recurrence and 15-year breast cancer death: Meta-analysis of individual patient data for 10 801 women in 17 randomised trials. Lancet 2011, 378, 1707–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gray, R.G.; Rea, D.; Handley, K.; Bowden, S.J.; Perry, P.; Earl, H.M.; Poole, C.J.; Bates, T.; Chetiyawardana, S.; Dewar, J.A.; et al. aTTom: Long-term effects of continuing adjuvant tamoxifen to 10 years versus stopping at 5 years in 6953 women with early breast cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, C.; Pan, H.; Godwin, J.; Gray, R.; Arriagada, R.; Raina, V.; Abraham, M.; Medeiros Alencar, V.H.; Badran, A.; Bonfill, X.; et al. Long-term effects of continuing adjuvant tamoxifen to 10 years versus stopping at 5 years after diagnosis of oestrogen receptor-positive breast cancer: ATLAS, a randomised trial. Lancet 2013, 381, 805–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gnant, M.; Mlineritsch, B.; Schippinger, W.; Luschin-Ebengreuth, G.; Pöstlberger, S.; Menzel, C.; Jakesz, R.; Seifert, M.; Hubalek, M.; Bjelic-Radisic, V.; et al. Endocrine Therapy plus Zoledronic Acid in Premenopausal Breast Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 360, 679–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagani, O.; Regan, M.M.; Walley, B.A.; Fleming, G.F.; Colleoni, M.; Láng, I.; Gomez, H.L.; Tondini, C.; Burstein, H.J.; Perez, E.A.; et al. Adjuvant Exemestane with Ovarian Suppression in Premenopausal Breast Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Francis, P.A.; Regan, M.M.; Fleming, G.F.; Láng, I.; Ciruelos, E.; Bellet, M.; Bonnefoi, H.R.; Climent, M.A.; Da Prada, G.A.; Burstein, H.J.; et al. Adjuvant Ovarian Suppression in Premenopausal Breast Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 436–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bradley, R.; Braybrooke, J.; Gray, R.; Hills, R.K.; Liu, Z.; Pan, H.; Peto, R.; Dodwell, D.; McGale, P.; Taylor, C.; et al. Aromatase inhibitors versus tamoxifen in premenopausal women with oestrogen receptor-positive early-stage breast cancer treated with ovarian suppression: A patient-level meta-analysis of 7030 women from four randomised trials. Lancet Oncol. 2022, 23, 382–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huober, J.; Von Minckwitz, G.; Denkert, C.; Tesch, H.; Weiss, E.; Zahm, D.M.; Belau, A.; Khandan, F.; Hauschild, M.; Thomssen, C.; et al. Effect of neoadjuvant anthracycline–taxane-based chemotherapy in different biological breast cancer phenotypes: Overall results from the GeparTrio study. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2010, 124, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loibl, S.; Jackisch, C.; Lederer, B.; Untch, M.; Paepke, S.; Kümmel, S.; Schneeweiss, A.; Huober, J.B.; Hilfrich, J.; Hanusch, C.; et al. Outcome after neoadjuvant chemotherapy in young breast cancer patients: A pooled analysis of individual patient data from eight prospectively randomized controlled trials. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2015, 152, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spring, L.; Greenup, R.; Niemierko, A.; Schapira, L.; Haddad, S.; Jimenez, R.; Coopey, S.; Taghian, A.; Hughes, K.S.; Isakoff, S.J.; et al. Pathologic Complete Response after Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy and Long-Term Outcomes Among Young Women with Breast Cancer. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2017, 15, 1216–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zujewski, J.A.; Rubinstein, L. CREATE-X a role for capecitabine in early-stage breast cancer: An analysis of available data. npj Breast Cancer 2017, 3, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mayer, I.A.; Zhao, F.; Arteaga, C.L.; Symmans, W.F.; Park, B.H.; Burnette, B.L.; Tevaarwerk, A.J.; Garcia, S.F.; Smith, K.L.; Makower, D.F.; et al. Randomized Phase III Postoperative Trial of Platinum-Based Chemotherapy Versus Capecitabine in Patients with Residual Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Following Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy: ECOG-ACRIN EA1131. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 2539–2551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loibl, S.; Marmé, F.; Martin, M.; Untch, M.; Bonnefoi, H.; Kim, S.-B.; Bear, H.; McCarthy, N.; Olivé, M.M.; Gelmon, K.; et al. Palbociclib for Residual High-Risk Invasive HR-Positive and HER2-Negative Early Breast Cancer—The Penelope-B Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 1518–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparano, J.A.; Gray, R.J.; Makower, D.F.; Pritchard, K.I.; Albain, K.S.; Hayes, D.F.; Geyer, C.E., Jr.; Dees, E.C.; Goetz, M.P.; Olson, J.A.; et al. Adjuvant Chemotherapy Guided by a 21-Gene Expression Assay in Breast Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kalinsky, K.; Barlow, W.E.; Gralow, J.R.; Meric-Bernstam, F.; Albain, K.S.; Hayes, D.F.; Lin, N.U.; Perez, E.A.; Goldstein, L.J.; Chia, S.K.; et al. 21-Gene Assay to Inform Chemotherapy Benefit in Node-Positive Breast Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 2336–2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccart, M.; Veer, L.J.V.; Poncet, C.; Cardozo, J.M.N.L.; Delaloge, S.; Pierga, J.-Y.; Vuylsteke, P.; Brain, E.; Vrijaldenhoven, S.; Neijenhuis, P.A.; et al. 70-gene signature as an aid for treatment decisions in early breast cancer: Updated results of the phase 3 randomised MINDACT trial with an exploratory analysis by age. Lancet Oncol. 2021, 22, 476–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Laurentiis, M.; Cancello, G.; D’Agostino, D.; Giuliano, M.; Giordano, A.; Montagna, E.; Lauria, R.; Forestieri, V.; Esposito, A.; Silvestro, L.; et al. Taxane-Based Combinations As Adjuvant Chemotherapy of Early Breast Cancer: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Trials. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, P.; Cortes, J.; Pusztai, L.; McArthur, H.; Kümmel, S.; Bergh, J.; Denkert, C.; Park, Y.H.; Hui, R.; Harbeck, N.; et al. Pembrolizumab for Early Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 810–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loibl, S.; Untch, M.; Burchardi, N.; Huober, J.; Sinn, B.V.; Blohmer, J.-U.; Grischke, E.-M.; Furlanetto, J.; Tesch, H.; Hanusch, C.; et al. A randomised phase II study investigating durvalumab in addition to an anthracycline taxane-based neoadjuvant therapy in early triple-negative breast cancer: Clinical results and biomarker analysis of GeparNuevo study. Ann. Oncol. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Med. Oncol. 2019, 30, 1279–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bianchini, G.; Huang, C.-S.; Egle, D.; Bermejo, B.; Zamagni, C.; Thill, M.; Anton, A.; Zambelli, S.; Russo, S.; Ciruelos, E.; et al. LBA13 Tumour infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs), PD-L1 expression and their dynamics in the NeoTRIPaPDL1 trial. Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, S1145–S1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, R.; Braybrooke, J.; Gray, R.; Hills, R.; Liu, Z.; Peto, R.; Davies, L.; Dodwell, D.; McGale, P.; Pan, H.; et al. Trastuzumab for early-stage, HER2-positive breast cancer: A meta-analysis of 13 864 women in seven randomised trials. Lancet Oncol. 2021, 22, 1139–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Earl, H.M.; Hiller, L.; Vallier, A.-L.; Loi, S.; McAdam, K.; Hughes-Davies, L.; Harnett, A.N.; Ah-See, M.-L.; Simcock, R.; Rea, D.; et al. 6 vs. 12 months of adjuvant trastuzumab for HER2-positive early breast cancer (PERSEPHONE): 4-year disease-free survival results of a randomised phase 3 non-inferiority trial. Lancet 2019, 393, 2599–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Inno, A.; Barni, S.; Ghidini, A.; Zaniboni, A.; Petrelli, F. One year versus a shorter duration of adjuvant trastuzumab for HER2-positive early breast cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2018, 173, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccart, M.; Procter, M.; Fumagalli, D.; de Azambuja, E.; Clark, E.; Ewer, M.S.; Restuccia, E.; Jerusalem, G.; Dent, S.; Reaby, L.; et al. Adjuvant Pertuzumab and Trastuzumab in Early HER2-Positive Breast Cancer in the APHINITY Trial: 6 Years’ Follow-Up. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 1448–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Minckwitz, G.; Huang, C.-S.; Mano, M.S.; Loibl, S.; Mamounas, E.P.; Untch, M.; Wolmark, N.; Rastogi, P.; Schneeweiss, A.; Redondo, A.; et al. Trastuzumab Emtansine for Residual Invasive HER2-Positive Breast Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 617–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aebi, S.; Gelber, S.; Anderson, S.J.; Láng, I.; Robidoux, A.; Martín, M.; Nortier, J.W.R.; Paterson, A.H.G.; Rimawi, M.F.; Cañada, J.M.B.; et al. Chemotherapy for isolated locoregional recurrence of breast cancer (CALOR): A randomised trial. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wapnir, I.L.; Price, K.N.; Anderson, S.J.; Robidoux, A.; Martín, M.; Nortier, J.W.; Paterson, A.H.; Rimawi, M.F.; Láng, I.; Baena-Cañada, J.M.; et al. Efficacy of Chemotherapy for ER-Negative and ER-Positive Isolated Locoregional Recurrence of Breast Cancer: Final Analysis of the CALOR Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 1073–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaud, L.B.; Jones, K.L.; Buzdar, A.U. Combination Endocrine Therapy in the Management of Breast Cancer. Oncologist 2001, 6, 538–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Carlson, R.W.; Theriault, R.; Schurman, C.M.; Rivera, E.; Chung, C.T.; Phan, S.-C.; Arun, B.; Dice, K.; Chiv, V.Y.; Green, M.; et al. Phase II Trial of Anastrozole Plus Goserelin in the Treatment of Hormone Receptor–Positive, Metastatic Carcinoma of the Breast in Premenopausal Women. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 3917–3921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, K.-L.; Winterbottom, L.; Owers, R.; Robertson, J. Goserelin plus anastrozole as first-line endocrine therapy for premenopausal women with oestrogen receptor (ER) positive advanced breast cancer (ABC). J. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 23, 731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forward, D.P.; Cheung, K.L.; Jackson, L.; Robertson, J.F.R. Clinical and endocrine data for goserelin plus anastrozole as second-line endocrine therapy for premenopausal advanced breast cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2004, 90, 590–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nishimura, R.; Anan, K.; Yamamoto, Y.; Higaki, K.; Tanaka, M.; Shibuta, K.; Sagara, Y.; Ohno, S.; Tsuyuki, S.; Mase, T.; et al. Efficacy of goserelin plus anastrozole in premenopausal women with advanced or recurrent breast cancer refractory to an LH-RH analogue with tamoxifen: Results of the JMTO BC08-01 phase II trial. Oncol. Rep. 2013, 29, 1707–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Torrisi, R.; Bagnardi, V.; Pruneri, G.; Ghisini, R.; Bottiglieri, L.; Magni, E.; Veronesi, P.; D’Alessandro, C.; Luini, A.; Dellapasqua, S.; et al. Antitumour and biological effects of letrozole and GnRH analogue as primary therapy in premenopausal women with ER and PgR positive locally advanced operable breast cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2007, 97, 802–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortes, J.; O’Shaughnessy, J.; Loesch, D.; Blum, J.L.; Vahdat, L.T.; Petrakova, K.; Chollet, P.; Manikas, A.; Diéras, V.; Delozier, T.; et al. Eribulin monotherapy versus treatment of physician’s choice in patients with metastatic breast cancer (EMBRACE): A phase 3 open-label randomised study. Lancet 2011, 377, 914–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robson, M.; Im, S.A.; Senkus, E.; Xu, B.; Domchek, S.M.; Masuda, N.; Delaloge, S.; Li, W.; Tung, N.; Armstrong, A.; et al. Olaparib for Metastatic Breast Cancer in Patients with a Germline BRCA Mutation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 523–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litton, J.K.; Rugo, H.S.; Ettl, J.; Hurvitz, S.A.; Gonçalves, A.; Lee, K.-H.; Fehrenbacher, L.; Yerushalmi, R.; Mina, L.A.; Martin, M.; et al. Talazoparib in Patients with Advanced Breast Cancer and a Germline BRCA Mutation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 753–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baselga, J.; Cortés, J.; Kim, S.-B.; Im, S.-A.; Hegg, R.; Im, Y.-H.; Roman, L.; Pedrini, J.L.; Pienkowski, T.; Knott, A.; et al. Pertuzumab plus Trastuzumab plus Docetaxel for Metastatic Breast Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Verma, S.; Miles, D.; Gianni, L.; Krop, I.E.; Welslau, M.; Baselga, J.; Pegram, M.; Oh, D.-Y.; Diéras, V.; Guardino, E.; et al. Trastuzumab Emtansine for HER2-Positive Advanced Breast Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 367, 1783–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mahmood, U.; Morris, C.; Neuner, G.; Koshy, M.; Kesmodel, S.; Buras, R.; Chumsri, S.; Bao, T.; Tkaczuk, K.; Feigenberg, S. Similar Survival With Breast Conservation Therapy or Mastectomy in the Management of Young Women With Early-Stage Breast Cancer. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2012, 83, 1387–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroman, N.; Holtveg, H.; Wohlfahrt, J.; Jensen, M.-B.; Mouridsen, H.T.; Blichert-Toft, M.; Melbye, M. Effect of breast-conserving therapy versus radical mastectomy on prognosis for young women with breast carcinoma. Cancer 2004, 100, 688–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurian, A.W.; Lichtensztajn, D.Y.; Keegan, T.H.M.; Nelson, D.O.; Clarke, C.A.; Gomez, S.L. Use of and Mortality After Bilateral Mastectomy Compared With Other Surgical Treatments for Breast Cancer in California, 1998–2011. JAMA 2014, 312, 902–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Portschy, P.R.; Kuntz, K.M.; Tuttle, T.M. Survival Outcomes After Contralateral Prophylactic Mastectomy: A Decision Analysis. Gynecol. Oncol. 2014, 106, dju160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, U.; Hanlon, A.L.; Koshy, M.; Buras, R.; Chumsri, S.; Tkaczuk, K.H.; Cheston, S.B.; Regine, W.F.; Feigenberg, S.J. Increasing National Mastectomy Rates for the Treatment of Early Stage Breast Cancer. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2012, 20, 1436–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Didier, F.; Radice, D.; Gandini, S.; Bedolis, R.; Rotmensz, N.; Maldifassi, A.; Santillo, B.; Luini, A.; Galimberti, V.; Scaffidi, E.; et al. Does nipple preservation in mastectomy improve satisfaction with cosmetic results, psychological adjustment, body image and sexuality? Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2008, 118, 623–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Metcalfe, K.A.; Cil, T.; Semple, J.L.; Li, L.D.X.; Bagher, S.; Zhong, T.; Virani, S.; Narod, S.; Pal, T. Long-Term Psychosocial Functioning in Women with Bilateral Prophylactic Mastectomy: Does Preservation of the Nipple-Areolar Complex Make a Difference? Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2015, 22, 3324–3330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dongen, J.A.; Voogd, A.C.; Fentiman, I.S.; Legrand, C.; Sylvester, R.J.; Tong, D.; Van Der Schueren, E.; Helle, P.A.; Van Zijl, K.; Bartelink, H. Long-Term Results of a Randomized Trial Comparing Breast-Conserving Therapy With Mastectomy: European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer 10801 Trial. Gynecol. Oncol. 2000, 92, 1143–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fisher, B.; Anderson, S.; Bryant, J.; Margolese, R.G.; Deutsch, M.; Fisher, E.R.; Jeong, J.-H.; Wolmark, N. Twenty-Year Follow-up of a Randomized Trial Comparing Total Mastectomy, Lumpectomy, and Lumpectomy plus Irradiation for the Treatment of Invasive Breast Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 347, 1233–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Veronesi, U.; Cascinelli, N.; Mariani, L.; Greco, M.; Saccozzi, R.; Luini, A.; Aguilar, M.; Marubini, E. Twenty-Year Follow-up of a Randomized Study Comparing Breast-Conserving Surgery with Radical Mastectomy for Early Breast Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 347, 1227–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arriagada, R.; Lê, M.G.; Guinebretière, J.-M.; Dunant, A.; Rochard, F.; Tursz, T. Late local recurrences in a randomised trial comparing conservative treatment with total mastectomy in early breast cancer patients. Ann. Oncol. 2003, 14, 1617–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poggi, M.M.; Danforth, D.N.; Sciuto, L.C.; Smith, S.L.; Steinberg, S.M.; Liewehr, D.J.; Menard, C.; Lippman, M.E.; Lichter, A.S.; Altemus, R.M. Eighteen-year results in the treatment of early breast carcinoma with mastectomy versus breast conservation therapy. Cancer 2003, 98, 697–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blichert-Toft, M.; Nielsen, M.; Düring, M.; Møller, S.; Rank, F.; Overgaard, M.; Mouridsen, H.T. Long-term results of breast conserving surgery vs. mastectomy for early stage invasive breast cancer: 20-year follow-up of the Danish randomized DBCG-82TM protocol. Acta Oncol. 2008, 47, 672–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashworth, A.; Kong, W.; Whelan, T.; Mackillop, W.J. A Population-Based Study of the Fractionation of Postlumpectomy Breast Radiation Therapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2013, 86, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, B.D.; Bellon, J.R.; Blitzblau, R.; Freedman, G.; Haffty, B.; Hahn, C.; Halberg, F.; Hoffman, K.; Horst, K.; Moran, J.; et al. Radiation therapy for the whole breast: Executive summary of an American Society for Radiation Oncology (ASTRO) evidence-based guideline. Pract. Radiat. Oncol. 2018, 8, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shah, C.; Vicini, F.; Wazer, D.E.; Arthur, D.; Patel, R.R. The American Brachytherapy Society consensus statement for accelerated partial breast irradiation. Brachytherapy 2013, 12, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- The American Society of Breast Surgeons. Consensus Guideline on Accelerated Partial Breast Irradiation. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2019, 26, 3025–3031. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, B.D.; Arthur, D.W.; Buchholz, T.A.; Haffty, B.G.; Hahn, C.A.; Hardenbergh, P.H.; Julian, T.B.; Marks, L.B.; Todor, D.A.; Vicini, F.A.; et al. Accelerated Partial Breast Irradiation Consensus Statement From the American Society for Radiation Oncology (ASTRO). Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2009, 74, 987–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NSABP Foundation Inc. A Randomized Phase III Study of Conventional Whole Breast Irradiation (WBI) Versus Partial Breast Irradiation (PBI) for Women with Stage 0, I, or II Breast Cancer. 2022. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00103181 (accessed on 6 October 2022).
- Smith, B.D.; Bentzen, S.M.; Correa, C.R.; Hahn, C.A.; Hardenbergh, P.H.; Ibbott, G.S.; McCormick, B.; McQueen, J.R.; Pierce, L.J.; Powell, S.N.; et al. Fractionation for Whole Breast Irradiation: An American Society for Radiation Oncology (ASTRO) Evidence-Based Guideline. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2011, 81, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallgren, A.; Bonetti, M.; Gelber, R.; Goldhirsch, A.; Castiglione-Gertsch, M.; Holmberg, S.; Lindtner, J.; Thürlimann, B.; Fey, M.; Werner, I.; et al. Risk Factors for Locoregional Recurrence Among Breast Cancer Patients: Results From International Breast Cancer Study Group Trials I Through VII. J. Clin. Oncol. 2003, 21, 1205–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jagsi, R.; Raad, R.A.; Goldberg, S.; Sullivan, T.; Michaelson, J.; Powell, S.N.; Taghian, A.G. Locoregional recurrence rates and prognostic factors for failure in node-negative patients treated with mastectomy: Implications for postmastectomy radiation. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2005, 62, 1035–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yildirim, E.; Berberoglu, U. Can a Subgroup of Node-Negative Breast Carcinoma Patients With T1–2 Tumor Who May Benefit From Postmastectomy Radiotherapy be Identified? Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2007, 68, 1024–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overgaard, M.; Jensen, M.-B.; Overgaard, J.; Hansen, P.S.; Rose, C.; Andersson, M.; Kamby, C.; Kjaer, M.; Gadeberg, C.C.; Rasmussen, B.B.; et al. Postoperative radiotherapy in high-risk postmenopausal breast-cancer patients given adjuvant tamoxifen: Danish Breast Cancer Cooperative Group DBCG 82c randomised trial. Lancet 1999, 353, 1641–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overgaard, M.; Hansen, P.S.; Overgaard, J.; Rose, C.; Andersson, M.; Bach, F.; Kjaer, M.; Gadeberg, C.C.; Mouridsen, H.T.; Jensen, M.-B.; et al. Postoperative Radiotherapy in High-Risk Premenopausal Women with Breast Cancer Who Receive Adjuvant Chemotherapy. N. Engl. J. Med. 1997, 337, 949–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragaz, J.; Olivotto, I.A.; Spinelli, J.J.; Phillips, N.; Jackson, S.M.; Wilson, K.S.; Knowling, M.A.; Coppin, C.M.L.; Weir, L.; Gelmon, K.; et al. Locoregional Radiation Therapy in Patients With High-Risk Breast Cancer Receiving Adjuvant Chemotherapy: 20-Year Results of the British Columbia Randomized Trial. Gynecol. Oncol. 2005, 97, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ademuyiwa, F.; Cyr, A.; Ivanovich, J.; Thomas, M. Managing breast cancer in younger women: Challenges and solutions. Breast Cancer Targets Ther. 2015, 8, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Regan, M.M.; Francis, P.; Pagani, O.; Fleming, G.F.; Walley, B.A.; Viale, G.; Colleoni, M.; Láng, I.; Gomez, H.; Tondini, C.A.; et al. Absolute Benefit of Adjuvant Endocrine Therapies for Premenopausal Women With Hormone Receptor–Positive, Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2–Negative Early Breast Cancer: TEXT and SOFT Trials. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 2221–2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuda, N.; Sagara, Y.; Kinoshita, T.; Iwata, H.; Nakamura, S.; Yanagita, Y.; Nishimura, R.; Iwase, H.; Kamigaki, S.; Takei, H.; et al. Neoadjuvant anastrozole versus tamoxifen in patients receiving goserelin for premenopausal breast cancer (STAGE): A double-blind, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2012, 13, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwata, H.; Masuda, N.; Sagara, Y.; Kinoshita, T.; Nakamura, S.; Yanagita, Y.; Nishimura, R.; Iwase, H.; Kamigaki, S.; Takei, H.; et al. Analysis of Ki-67 expression with neoadjuvant anastrozole or tamoxifen in patients receiving goserelin for premenopausal breast cancer. Cancer 2012, 119, 704–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiavon, G.; Smith, I.E. Status of adjuvant endocrine therapy for breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2014, 16, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Biswas, T.; Efird, J.T.; Prasad, S.; Jindal, C.; Walker, P.R. The survival benefit of neoadjuvant chemotherapy and pCR among patients with advanced stage triple negative breast cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 112712–112719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paluch-Shimon, S.; Cardoso, F.; Partridge, A.; Abulkhair, O.; Azim, H.; Bianchi-Micheli, G.; Cardoso, M.-J.; Curigliano, G.; Gelmon, K.; Harbeck, N.; et al. ESO–ESMO 4th International Consensus Guidelines for Breast Cancer in Young Women (BCY4). Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, 674–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pluchino, L.A.; D’Amico, T.A. National Comprehensive Cancer Network Guidelines: Who Makes Them? What Are They? Why Are They Important? Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2020, 110, 1789–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnant, M.; Mlineritsch, B.; Stoeger, H.; Luschin-Ebengreuth, G.; Knauer, M.; Moik, M.; Jakesz, R.; Seifert, M.; Taucher, S.; Bjelic-Radisic, V.; et al. Zoledronic acid combined with adjuvant endocrine therapy of tamoxifen versus anastrozol plus ovarian function suppression in premenopausal early breast cancer: Final analysis of the Austrian Breast and Colorectal Cancer Study Group Trial 12. Ann. Oncol. 2014, 26, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Partridge, A.H.; Pagani, O.; Abulkhair, O.; Aebi, S.; Amant, F.; Azim, H.A.; Costa, A.; Delaloge, S.; Freilich, G.; Gentilini, O.D.; et al. First international consensus guidelines for breast cancer in young women (BCY1). Breast 2014, 23, 209–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldhirsch, A.; Winer, E.P.; Coates, A.S.; Gelber, R.D.; Piccart-Gebhart, M.; Thürlimann, B.; Senn, H.-J. Personalizing the treatment of women with early breast cancer: Highlights of the St Gallen International Expert Consensus on the Primary Therapy of Early Breast Cancer 2013. Ann. Oncol. 2013, 24, 2206–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junttila, T.T.; Li, G.; Parsons, K.; Phillips, G.L.; Sliwkowski, M.X. Trastuzumab-DM1 (T-DM1) retains all the mechanisms of action of trastuzumab and efficiently inhibits growth of lapatinib insensitive breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2010, 128, 347–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrow, M.; Van Zee, K.J.; Solin, L.J.; Houssami, N.; Chavez-MacGregor, M.; Harris, J.R.; Horton, J.; Hwang, S.; Johnson, P.L.; Marinovich, M.L.; et al. Society of Surgical Oncology–American Society for Radiation Oncology–American Society of Clinical Oncology Consensus Guideline on Margins for Breast-Conserving Surgery With Whole-Breast Irradiation in Ductal Carcinoma in Situ. Pract. Radiat. Oncol. 2016, 6, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gradishar, W.J.; Anderson, B.O.; Balassanian, R.; Blair, S.L.; Burstein, H.J.; Cyr, A.; Elias, A.D.; Farrar, W.B.; Forero, A.; Giordano, S.H.; et al. Breast Cancer Version 2.2015. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2015, 13, 448–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Croxtall, J.D.; McKeage, K. Fulvestrant: A review of its use in the management of hormone receptor-positive metastatic breast cancer in postmenopausal women. Drugs 2011, 71, 363–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Leo, A.; Jerusalem, G.; Petruzelka, L.; Torres, R.; Bondarenko, I.N.; Khasanov, R.; Verhoeven, D.; Pedrini, J.L.; Smirnova, I.; Lichinitser, M.R.; et al. Final Overall Survival: Fulvestrant 500 mg vs 250 mg in the Randomized CONFIRM Trial. Gynecol. Oncol. 2013, 106, djt337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Finn, R.S.; Dering, J.; Conklin, D.; Kalous, O.; Cohen, D.J.; Desai, A.J.; Ginther, C.; Atefi, M.; Chen, I.; Fowst, C.; et al. PD 0332991, a selective cyclin D kinase 4/6 inhibitor, preferentially inhibits proliferation of luminal estrogen receptor-positive human breast cancer cell lines in vitro. Breast Cancer Res. 2009, 11, R77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Eli Lilly and Company. MONARCH 2: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Phase 3 Study of Fulvestrant with or without Abemaciclib, a CDK4/6 Inhibitor, for Women with Hormone Receptor Positive, HER2 Negative Locally Advanced or Metastatic Breast Cancer. 2021. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02107703 (accessed on 6 October 2022).
- Novartis Pharmaceuticals. A Randomized Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study of LEE011 in Combination with Letrozole for the Treatment of Postmenopausal Women with Hormone Receptor Positive, HER2 Negative, Advanced Breast Cancer Who Received No Prior Therapy for Advanced Disease. 2022. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01958021 (accessed on 6 October 2022).
- Novartis Pharmaceuticals. A Phase III Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study of LEE011 or Placebo in Combination with Tamoxifen and Goserelin or a Non-Steroidal Aromatase Inhibitor (NSAI) and Goserelin for the Treatment of Premenopausal Women with Hormone Receptor Positive, HER2-Negative, Advanced Breast Cancer. 2022. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02278120 (accessed on 6 October 2022).
- Baselga, J.; Campone, M.; Piccart, M.; Burris, H.A., III; Rugo, H.S.; Sahmoud, T.; Noguchi, S.; Gnant, M.; Pritchard, K.I.; Lebrun, F.; et al. Everolimus in Postmenopausal Hormone-Receptor–Positive Advanced Breast Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 520–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bachelot, T.; Bourgier, C.; Cropet, C.; Ray-Coquard, I.; Ferrero, J.-M.; Freyer, G.; Abadie-Lacourtoisie, S.; Eymard, J.-C.; Debled, M.; Spaëth, D.; et al. Randomized Phase II Trial of Everolimus in Combination With Tamoxifen in Patients With Hormone Receptor–Positive, Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2–Negative Metastatic Breast Cancer With Prior Exposure to Aromatase Inhibitors: A GINECO Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 2718–2724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eng, L.G.; Dawood, S.; Dent, R. Palliative systemic therapy for young women with metastatic breast cancer. Curr. Opin. Support. Palliat. Care 2015, 9, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palomo, A.G. Therapeutic approaches in young women with advanced or metastatic breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2010, 123, 49–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Albain, K.S.; Nag, S.M.; Calderillo-Ruiz, G.; Jordaan, J.P.; Llombart, A.C.; Pluzanska, A.; Rolski, J.; Melemed, A.S.; Reyes-Vidal, J.M.; Sekhon, J.S.; et al. Gemcitabine Plus Paclitaxel Versus Paclitaxel Monotherapy in Patients With Metastatic Breast Cancer and Prior Anthracycline Treatment. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 3950–3957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Shaughnessy, J.; Miles, D.; Vukelja, S.; Moiseyenko, V.; Ayoub, J.-P.; Cervantes, G.; Fumoleau, P.; Jones, S.; Lui, W.-Y.; Mauriac, L.; et al. Superior Survival with Capecitabine Plus Docetaxel Combination Therapy in Anthracycline-Pretreated Patients with Advanced Breast Cancer: Phase III Trial Results. J. Clin. Oncol. 2002, 20, 2812–2823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oguz, A.; Babacan, T.; Dizdar, O.; Kucukoztas, N.; Rahatli, S.; Keskin, G.S.Y.; Altundag, O.; Altundag, K. Response rates of taxane rechallenge in metastatic breast cancer patients, previously treated with adjuvant taxanes. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlando, L.; Cardillo, A.; Rocca, A.; Balduzzi, A.; Ghisini, R.; Peruzzotti, G.; Goldhirsch, A.; D’Alessandro, C.; Cinieri, S.; Preda, L.; et al. Prolonged clinical benefit with metronomic chemotherapy in patients with metastatic breast cancer. Anticancer Drugs 2006, 17, 961–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pusztai, L.; Walters, R.S.; Valero, V.; Theriault, R.L.; Hortobagyi, G.N. Daily Oral Etoposide in Patients With Heavily Pretreated Metastatic Breast Cancer. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 1998, 21, 442–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traina, T.A.; Miller, K.; Yardley, D.A.; O’Shaughnessy, J.; Cortes, J.; Awada, A.; Kelly, C.M.; Trudeau, M.E.; Schmid, P.; Gianni, L.; et al. Results from a phase 2 study of enzalutamide (ENZA), an androgen receptor (AR) inhibitor, in advanced AR+ triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC). J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- André, F.; Zielinski, C.C. Optimal strategies for the treatment of metastatic triple-negative breast cancer with currently approved agents. Ann. Oncol. 2012, 23, vi46–vi51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swain, S.M.; Baselga, J.; Kim, S.-B.; Ro, J.; Semiglazov, V.; Campone, M.; Ciruelos, E.; Ferrero, J.-M.; Schneeweiss, A.; Heeson, S.; et al. Pertuzumab, Trastuzumab, and Docetaxel in HER2-Positive Metastatic Breast Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 724–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blackwell, K.L.; Burstein, H.J.; Storniolo, A.M.; Rugo, H.; Sledge, G.; Koehler, M.; Ellis, C.; Casey, M.; Vukelja, S.; Bischoff, J.; et al. Randomized Study of Lapatinib Alone or in Combination With Trastuzumab in Women With ErbB2-Positive, Trastuzumab-Refractory Metastatic Breast Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 1124–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geyer, C.E.; Forster, J.; Lindquist, D.; Chan, S.; Romieu, C.G.; Pienkowski, T.; Jagiello-Gruszfeld, A.; Crown, J.; Chan, A.; Kaufman, B.; et al. Lapatinib plus Capecitabine for HER2-Positive Advanced Breast Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 355, 2733–2743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Waddell, T.; Kotsori, A.; Constantinidou, A.; Yousaf, N.; Ashley, S.; Parton, M.; Allen, M.; Starling, N.; Papadopoulos, P.; O’Brien, M.; et al. Trastuzumab beyond progression in HER2-positive advanced breast cancer: The Royal Marsden experience. Br. J. Cancer 2011, 104, 1675–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mallet, A.; Lusque, A.; Levy, C.; Pistilli, B.; Brain, E.; Pasquier, D.; Debled, M.; Thery, J.C.; Gonçalves, A.; Desmoulins, I.; et al. Real-world evidence of the management and prognosis of young women (≤40 years) with de novo metastatic breast cancer. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2022, 14, 17588359211070362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christinat, A.; Pagani, O. Fertility after breast cancer. Maturitas 2012, 73, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berry, D.L.; Theriault, R.L.; Holmes, F.A.; Parisi, V.M.; Booser, D.J.; Singletary, S.E.; Buzdar, A.U.; Hortobagyi, G.N. Management of Breast Cancer During Pregnancy Using a Standardized Protocol. J. Clin. Oncol. 1999, 17, 855–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronn, R.; Holzer, H.E.G. Oncofertility in Canada: The Impact of Cancer on Fertility. Curr. Oncol. 2013, 20, 338–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Walshe, J.M.; Denduluri, N.; Swain, S.M. Amenorrhea in Premenopausal Women After Adjuvant Chemotherapy for Breast Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 24, 5769–5779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambertini, M.; Moore, H.C.; Leonard, R.C.; Loibl, S.; Munster, P.; Bruzzone, M.; Boni, L.; Unger, J.M.; Anderson, R.A.; Mehta, K.; et al. Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone Agonists During Chemotherapy for Preservation of Ovarian Function and Fertility in Premenopausal Patients With Early Breast Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Individual Patient–Level Data. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 1981–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, H.; Li, J.; Cui, T.; Hu, L. Adjuvant gonadotropin-releasing hormone analogues for the prevention of chemotherapy induced premature ovarian failure in premenopausal women. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2011, 11, CD008018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, H.C.; Unger, J.M.; Phillips, K.-A.; Boyle, F.; Hitre, E.; Porter, D.; Francis, P.A.; Goldstein, L.J.; Gomez, H.L.; Vallejos, C.S.; et al. Goserelin for Ovarian Protection during Breast-Cancer Adjuvant Chemotherapy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 923–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saunders, C.M.; Baum, M. Breast Cancer and Pregnancy: A Review. J. R. Soc. Med. 1993, 86, 162–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.M. Mammary cancers and pregnancy. BMJ 1979, 1, 1124–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Noyes, R.D.; Spanos, W.J.; Montague, E.D. Breast cancer in women aged 30 and under. Cancer 1982, 49, 1302–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toesca, A.A.; Gentilini, O.; Peccatori, F.; Azim, H.H.A.; Amant, F. Locoregional treatment of breast cancer during pregnancy. Gynecol. Surg. 2014, 11, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazonakis, M.; Varveris, H.; Damilakis, J.; Theoharopoulos, N.; Gourtsoyiannis, N. Radiation dose to conceptus resulting from tangential breast irradiation. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2003, 55, 386–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ring, A.E.; Smith, I.E.; Jones, A.; Shannon, C.; Galani, E.; Ellis, P.A. Chemotherapy for Breast Cancer during Pregnancy: An 18-Year Experience from Five London Teaching Hospitals. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 23, 4192–4197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hahn, K.M.; Johnson, P.H.; Gordon, N.; Kuerer, H.; Middleton, L.; Ramirez, M.; Yang, W.; Perkins, G.; Hortobagyi, G.N.; Theriault, R.L. Treatment of pregnant breast cancer patients and outcomes of children exposed to chemotherapy in utero. Cancer 2006, 107, 1219–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murthy, R.K.; Theriault, R.L.; Barnett, C.M.; Hodge, S.; Ramirez, M.M.; Milbourne, A.; Rimes, S.A.; Hortobagyi, G.N.; Valero, V.; Litton, J.K. Outcomes of children exposed in uteroto chemotherapy for breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2014, 16, 500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Azim, H.H.A.; Metzger-Filho, O.; de Azambuja, E.; Loibl, S.; Focant, F.; Gresko, E.; Arfi, M.; Piccart-Gebhart, M. Pregnancy occurring during or following adjuvant trastuzumab in patients enrolled in the HERA trial (BIG 01-01). Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2012, 133, 387–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azim, H.A.; Santoro, L.; Pavlidis, N.; Gelber, S.; Kroman, N.; Azim, H.; Peccatori, F. Safety of pregnancy following breast cancer diagnosis: A meta-analysis of 14 studies. Eur. J. Cancer 2011, 47, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroman, N.; Jensen, M.-B.; Wohlfahrt, J.; Ejlertsen, B.; Danish Breast Cancer Cooperative Group. Pregnancy after treatment of breast cancer—A population-based study on behalf of Danish Breast Cancer Cooperative Group. Acta Oncol. 2008, 47, 545–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valachis, A.; Tsali, L.; Pesce, L.; Polyzos, N.P.; Dimitriadis, C.; Tsalis, K.; Mauri, D. Safety of Pregnancy After Primary Breast Carcinoma in Young Women: A Meta-Analysis to Overcome Bias of Healthy Mother Effect Studies. Obstet. Gynecol. Surv. 2010, 65, 786–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ETOP IBCSG Partners Foundation. A Study Evaluating the Pregnancy Outcomes and Safety of Interrupting Endocrine Therapy for Young Women with Endocrine Responsive Breast Cancer Who Desire Pregnancy. 2022. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02308085 (accessed on 6 October 2022.).
- Shapiro, C.; Halabi, S.; Hars, V.; Archer, L.; Weckstein, D.; Kirshner, J.; Sikov, W.; Winer, E.; Burstein, H.; Hudis, C.; et al. Zoledronic acid preserves bone mineral density in premenopausal women who develop ovarian failure due to adjuvant chemotherapy: Final results from CALGB trial 79809. Eur. J. Cancer 2011, 47, 683–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sverrisdóttir, A.; Fornander, T.; Jacobsson, H.; Von Schoultz, E.; Rutqvist, L. Bone Mineral Density Among Premenopausal Women with Early Breast Cancer in a Randomized Trial of Adjuvant Endocrine Therapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2004, 22, 3694–3699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gnant, M.; Mlineritsch, B.; Luschin-Ebengreuth, G.; Kainberger, F.; Kässmann, H.; Piswanger-Sölkner, J.C.; Seifert, M.; Ploner, F.; Menzel, C.; Dubsky, P.; et al. Adjuvant endocrine therapy plus zoledronic acid in premenopausal women with early-stage breast cancer: 5-year follow-up of the ABCSG-12 bone-mineral density substudy. Lancet Oncol. 2008, 9, 840–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brufsky, A.M.; Harker, W.G.; Beck, J.T.; Bosserman, L.; Vogel, C.L.; Seidler, C.; Jin, L.; Warsi, G.; Argonza-Aviles, E.; Hohneker, J.; et al. Final 5-year results of Z-FAST trial: Adjuvant zoledronic acid maintains bone mass in postmenopausal breast. Cancer 2011, 118, 1192–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.R.; Egerdie, B.; Toriz, N.H.; Feldman, R.; Tammela, T.L.; Saad, F.; Heracek, J.; Szwedowski, M.; Ke, C.; Kupic, A.; et al. Denosumab in Men Receiving Androgen-Deprivation Therapy for Prostate Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 745–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ellis, G.K.; Bone, H.G.; Chlebowski, R.; Paul, D.; Spadafora, S.; Smith, J.; Fan, M.; Jun, S. Randomized Trial of Denosumab in Patients Receiving Adjuvant Aromatase Inhibitors for Nonmetastatic Breast Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 4875–4882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnant, M.F.; Mlineritsch, B.; Luschin-Ebengreuth, G.; Grampp, S.; Kaessmann, H.; Schmid, M.; Menzel, C.; Piswanger-Soelkner, J.C.; Galid, A.; Mittlboeck, M.; et al. Zoledronic Acid Prevents Cancer Treatment–Induced Bone Loss in Premenopausal Women Receiving Adjuvant Endocrine Therapy for Hormone-Responsive Breast Cancer: A Report from the Austrian Breast and Colorectal Cancer Study Group. J. Clin. Oncol. 2007, 25, 820–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, R.; Cameron, D.; Dodwell, D.; Bell, R.; Wilson, C.; Rathbone, E.; Keane, M.; Gil, M.; Burkinshaw, R.; Grieve, R.; et al. Adjuvant zoledronic acid in patients with early breast cancer: Final efficacy analysis of the AZURE (BIG 01/04) randomised open-label phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, 997–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnant, M.; Pfeiler, G.; Dubsky, P.C.; Hubalek, M.; Greil, R.; Jakesz, R.; Wette, V.; Balic, M.; Haslbauer, F.; Melbinger, E.; et al. Adjuvant denosumab in breast cancer (ABCSG-18): A multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2015, 386, 433–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokal, A.; Elefant, E.; Leturcq, T.; Beghin, D.; Mariette, X.; Seror, R. Pregnancy and newborn outcomes after exposure to bisphosphonates: A case-control study. Osteoporos. Int. 2018, 30, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, M.; Olivotto, I.; Baxter, N.; Friedenreich, C.; Metcalfe, K.; Warner, E.; MacLennan, K.; Stephen, J.; Akbari, M.; Howell, D.; et al. A Pan-Canadian Prospective Study of Young Women with Breast Cancer: The Rationale and Protocol Design for the RUBY Study. Curr. Oncol. 2020, 27, 516–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
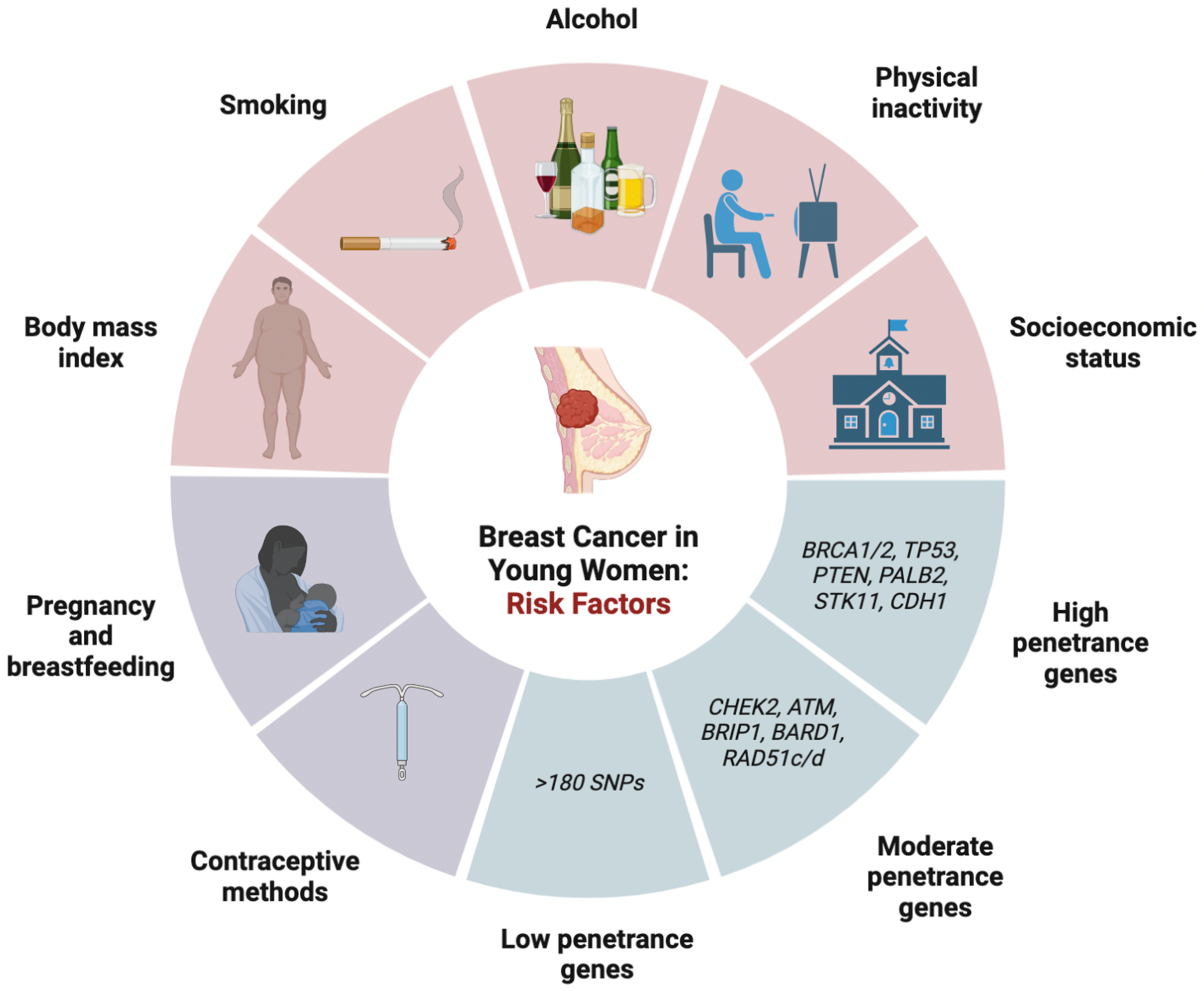
| Breast Cancer Susceptibility Gene | Study, Year | Patient Population (Age Group) | Odds Ratio | 95% Confidence Interval | Penetrance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BRCA1 | Breast Cancer Association Consortium, 2021 [118] | 175 cases, 10 controls with mutation (<40 years) | 32.8 | 16.9–63.4 | High |
| Hu et al., 2021 [119] | 209 cases, 27 controls with mutation (<45 years) | 8.63 | 5.63–13.89 | High | |
| BRCA2 | Breast Cancer Association Consortium, 2021 [118] | 156 cases, 20 controls with mutation (<40 years) | 11.9 | 7.33–19.4 | High |
| Hu et al., 2021 [119] | 296 cases, 38 controls with mutation (<45 years) | 7.65 | 5.47–11.02 | High | |
| PALB2 | Breast Cancer Association Consortium, 2021 [118] | 26 cases, 8 controls with mutation (<40 years) | 5.36 | 2.26–12.7 | High |
| Hu et al., 2021 [119] | 15 cases, 5 controls with mutation (<45 years) | 3.99 | 2.50–6.67 | High | |
| CHD1 | Hu et al., 2021 [119] | 89 cases, 22 controls with mutation (<45 years) | 2.66 * | 1.00–8.38 | High |
| TP53 | Hu et al., 2021 [119] Breast Cancer Association Consortium, 2021 [118] | NA † | NA † | NA † | High |
| PTEN | Hu et al., 2021 [119] Breast Cancer Association Consortium, 2021 [118] | NA † | NA † | NA † | High |
| STK11 | Hu et al., 2021 [119] Breast Cancer Association Consortium, 2021 [118] | NA † | NA † | NA † | High |
| CHEK2 | Breast Cancer Association Consortium, 2021 [118] | 77 cases, 28 controls with mutation (<40 years) | 4.54 | 2.87–7.17 | Moderate |
| Hu et al., 2021 [119] | 218 cases, 72 controls with mutation (<45 years) | 3.06 | 2.32–4.08 | Moderate | |
| ATM | Breast Cancer Association Consortium, 2021 [118] | 21 cases, 17 controls with mutation (<40 years) | 1.77 | 0.87–3.59 | Moderate |
| Hu et al., 2021 [119] | 162 cases, 80 controls with mutation (<45 years) | 1.89 | 1.43–2.53 | Moderate | |
| BARD1 | Breast Cancer Association Consortium, 2021 [118] | 6 cases, 3 controls with the mutation (<40 years) | 4.30 | 1.05–17.7 | Moderate |
| Hu et al., 2021 [119] | 33 cases, 22 controls with the mutation (<45 years) | 1.37 | 0.78–2.43 | Moderate | |
| RAD51C | Breast Cancer Association Consortium, 2021 [118] | 4 cases, 1 control with the mutation (<40 years) | 4.83 | 0.52–45.2 | Moderate |
| Hu et al., 2021 [119] | 26 cases, 20 controls with the mutation (<45 years) | 1.26 | 0.69–2.35 | Moderate | |
| RAD51D | Breast Cancer Association Consortium, 2021 [118] | 4 cases, 3 controls with the mutation (<40 years) | 1.76 | 0.38–8.17 | Moderate |
| Hu et al., 2021 [119] | 16 cases, 6 controls with the mutation (<45 years) | 2.41 | 0.91–7.60 | Moderate | |
| BRIP1 | Hu et al., 2021 [119] | 41 cases, 35 controls with the mutation (<45 years) | 1.22 * | 0.75–1.99 | Moderate |
| RAD51B | Hu et al., 2021 [119] Breast Cancer Association Consortium, 2021 [118] | NA † | NA † | NA † | Moderate |
| XRCC2 | Hu et al., 2021 [119] | 21 cases, 13 controls with the mutation (<45 years) | 1.37 * | 0.69–2.83 | Moderate |
| XRCC3 | Hu et al., 2021 [119] Breast Cancer Association Consortium, 2021 [118] | NA † | NA † | NA † | Moderate |
| Pre-Menopausal Women | Post-Menopausal Women | |
|---|---|---|
| Lifestyle Risk Factors | ||
| Physical Exercise | Reduces risk of breast cancer | Reduces risk of breast cancer [168] |
| BMI | Increasing BMI has a modest protective effect against breast cancer | Increasing BMI associated with increased risk of breast cancer |
| Alcohol Consumption | Increases risk of breast cancer | Increases risk of breast cancer [169] |
| Smoking | Increases risk of breast cancer, Higher risk in younger age of initiation | Increases risk of breast cancer [105] |
| Socioeconomic status (SES) | Increasing risk with higher SES | Increasing risk with higher SES |
| Occupational related long-term night shifts | Increases risk of breast cancer | Increases risk of breast cancer |
| Reproductive Factors | ||
| Oral contraceptive pills (OCPs) | Increases risk of breast cancer | Increases risk of breast cancer [170] |
| Levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine system (LNG-IUS) | Increases risk of breast cancer | Increases risk of breast cancer [171] |
| Menopausal hormonal therapy (MHT) | NA | Does not increase the risk of breast cancer |
| Age of pregnancy | Parity before 20 years of age is associated with reduced risk of breast cancer, Parity after 35 years of age is associated with increased risk | Older age of first pregnancy is associated with higher risk of breast cancer [172] |
| Fertility preservation techniques | Does not increase the risk of breast cancer | Does not increase the risk of breast cancer |
| Breastfeeding | Reduces risk of breast cancer | Reduces risk of breast cancer |
| Classification | Treatment | Study, Year | Population | Intervention | Control | Key Findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Locoregional treatment | Surgery | Vila et al., 2015 [253] | 22,598 patients aged ≤40 years | BCS | Mastectomy | No significant difference in risk of death, HR = 0.90 [95%CI: 0.81–1.00] |
| Ye et al., 2015 [254] | 7665 women aged <40 years | BCS | Mastectomy | No significant differences in 10-year BCSS or 10-year OS 10-year BCSS = 87.7% [95%CI: 86.5–88.9%] for BCS vs. 85.4% [95%CI: 83.8–87.9%] for mastectomy 10-year OS = 85.9% [95% CI: 84.5–87.3%] for BCS vs. 83.5% [95%CI: 81.9–85.1%] for mastectomy | ||
| Li et al., 2022 [255] | 1520 patients aged ≤35 years | BCS | Mastectomy | Significantly improved 5-year DFS and 5-year OS for BCS compared to mastectomy 5-year DFS: HR = 0.45 [95% CI: 0.28–0.73], p = 0.001 5-year OS: HR = 0.41 [95% CI 0.21–0.80], p = 0.009 | ||
| Radiation therapy | Bartelink et al., 2015 [256] | 449 women aged ≤40 years with stage I and II breast cancer | Whole-breast irradiation (50 Gy in 5 weeks) with 16 Gy boost | Whole-breast irradiation (50 Gy in 5 weeks) alone | Significantly lower 20-year ipsilateral breast tumour recurrence: HR = 0.56 [99% CI 0.34–0.92], p = 0.003 | |
| Garg et al., 2007 [257] | 107 women aged ≤35 years with stage II or III breast cancer | Mastectomy + postmastectomy radiotherapy (PMRT) | Mastectomy alone | Significantly improved 5-year locoregional control: 88% vs. 63%, p = 0.001 Significantly improved 5-year OS: 67% vs. 48%, p = 0.03 | ||
| Systemic treatment | Endocrine therapy | Early Breast Cancer Trialists’ Collaborative Group (EBCTCG), 2005 [258] | 2027 women aged <50 years of age with ER+ breast cancer | 6 months of anthracycline-based chemotherapy + 5 years adjuvant tamoxifen | 6 months of anthracycline-based chemotherapy alone | 57% reduction in annual breast cancer mortality rate |
| Gray et al., 2013 (aTTOM trial) [259] | 6953 women with ER+ or ER-untested BC | 10 years of tamoxifen treatment | 5 years of tamoxifen treatment | Continued tamoxifen reduced breast cancer recurrence (p = 0.003) Recurrence rate ratio (RRR) = 0.99 [95% CI: 0.86–1.15] during years 5–9 RRR = 0.75 [95%CI: 0.66–0.86] at ≥10 years | ||
| Davies et al., 2013 (ATLAS trial) [260] | 6846 women with ER+ early BC | 10 years of tamoxifen treatment | 5 years of tamoxifen treatment | Continued tamoxifen reduced risk of breast cancer recurrence (p = 0.002) RRR = 0.90 [95% CI: 0.79–1.02] during years 5–9 RRR = 0.75 [95% CI: 0.62–0.90] ≥10 years Breast cancer mortality RR = 0.97 [95% CI: 0.79–1.18] during years 5–9 Breast cancer mortality RR = 0.71 [95%CI: 0.58–0.88] ≥10 years | ||
| Gnant et al., 2009 [261] | 1803 premenopausal women with stage I or II ER/PR+ breast cancer | Anastrozole | Tamoxifen | No significant difference in disease-free survival (DFS): 92.0% vs. 92.8% | ||
| Pagani et al., 2014 (TEXT trial) [262] Francis et al., 2015 (SOFT trial) [263] | 4690 premenopausal women with hormone- receptor–positive early breast cancer | 5 years of tamoxifen plus ovarian suppression, or exemestane plus ovarian suppression | 5 years of tamoxifen | Significantly higher 8-year DFS for exemestane + OFS compared to tamoxifen + OFS group: 86.8% vs. 82.8%, HR (recurrence, a second invasive cancer, or death) = 0.77 [95% CI: 0.67–0.90], p < 0.001 Significantly higher 8-year OS for tamoxifen + OS vs. tamoxifen alone: 93.3% vs. 91.5%, p = 0.01 | ||
| Early Breast Cancer Trialists’ Collaborative Group (EBCTCG), 2022 [264] | 7030 premenopausal women with ER+ tumours | Aromatase inhibitors (anastrozole, exemestane, or letrozole) and ovarian suppression | Tamoxifen and ovarian suppression | Lower breast cancer recurrence for women who received AI and ovarian suppression: RR = 0.79 [95% CI 0.69–0.90], p = 0.0005 Highest benefit in years 0–4 and no significant difference at >5 years | ||
| Chemotherapy (neoadjuvant) | Huober et al., 2010 [265] | 2072 patients with operable or locally advanced breast cancer | 6–8 cycles of docetaxel, doxorubicin, and cyclophosphamide (TAC) | 2 cycles of TAC followed by 4 cycles of vinorelbine and capecitabine | Highest pathological complete response (pCR) rate in women aged <40 years with TNBC or grade 3 tumours compared to women aged ≥40 years: 57.0% vs. 34.0%, p < 0.0001 Women <40 years had double the odds of pCR at surgery compared to those ≥40 years: OR = 2.02 [95% CI: 1.569–2.610] p < 0.0001 | |
| Loibl et al., 2015 [266] | 1453 breast cancer patients | Neoadjuvant chemotherapy in women aged <40 years | Neoadjuvant chemotherapy in women aged 40–49 and >50 | A significantly higher pathological complete remission in the young (< 40 years) group compared with older groups: 20.9 vs. 17.7 vs. 13.7%, p < 0.001 Young women with HR+/HER2- and TNBC disease were more likely to achieve pCR after NAC compared to older women: 11 % vs. 5.8 %, p < 0.001 in HR+/HER2- and 39.3 % vs. 25.2 %, p < 0.001 in TNBC Older women (≥50 years) had significantly better survival outcomes with improved OS (HR = 0.87; 95% CI: 0.74–1.02; p = 0.079), LRFS (HR = 0.64; 95% CI: 0.52–0.79; p < 0.001), and DFS (HR = 0.81; 95% CI: 0.71–0.92; p = 0.001) compared to young women <40 years | ||
| Ahn et al., 2007 [19] | 1444 women aged <35 years with breast cancer | NA | NA | Young women were less likely to benefit from adjuvant hormone therapy with higher de novo tamoxifen resistance compared to older women | ||
| Spring et al., 2017 [267] | 170 young women aged ≤40 years | Received neoadjuvant chemotherapy and achieved pCR | Received neoadjuvant chemotherapy and did not achieve pCR | Attaining pCR was associated with significantly improved 5-year DFS: 91% vs. 60% for those without pCR, HR = 0.12 [95% CI: 0.04–0.39] p < 0.001 Achievement of pCR was associated with significantly improved 5-year OS for patients with pCR compared to those who did not: 95% vs. 75%, HR = 0.19 [95% CI: 0.06–0.62], p = 0.006 for all receptor subtypes | ||
| Zujewski et al., 2017 [268] | 910 patients | Capecitabine | No additional therapy | Capecitabine had a statistically significant survival advantage compared with no additional therapy | ||
| Mayer et al., 2021 [269] | 775 patients with clinical stage II or III TNBC | Platinum agent | Capecitabine | Platinum agents do not improve outcomes in patients with basal subtype TNBC RD post-NAC and are associated with more severe toxicity when compared with capecitabine | ||
| Loibl et al., 2021 [270] | 1250 patients with hormone receptor-positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative primary breast cancer without a pathological complete response after taxane-containing NACT and at high risk of relapse | Palbociclib | Placebo | Palbociclib for 1 year in addition to ET did not improve iDFS in women with residual invasive disease after NACT | ||
| Chemotherapy (adjuvant) | Sparano et al., 2018 [271] | 10,273 women with HR+, HER2-, axillary node-negative breast cancer | Chemoendocrine therapy | Endocrine therapy alone | Adjuvant endocrine therapy and chemoendocrine therapy had similar efficacy Exploratory subgroup analyses of women aged ≤50 years who received chemoendocrine treatment with intermediate RS of 16–25 found a 5-year distant recurrence benefit = 0.8–3.2% and 9-year = 1.6–6.5% No significant difference in overall survival | |
| Kalinsky et al., 2021 [272] | 5015 women with HR+, HER2- breast cancer, one to three positive axillary lymph nodes, and a recurrence score of 25 or lower | Chemoendocrine therapy | Endocrine therapy only | Among premenopausal women, those who received chemoendocrine therapy had longer iDFS and distant relapse-free survival than those who received endocrine-only therapy | ||
| Piccart et al., 2021 [273] | 6693 women aged 18–70 years with localized breast cancer (stage T1, T2, or operable T3) with up to three positive lymph nodes | Chemotherapy | No chemotherapy | 8-year distant metastasis-free survival rates for those classified as high clinical risk and low genomic risk = 92.0% [95%: CI 89.6–93.8] for the chemotherapy cohort vs. 89.4% [95%CI: 86.8–91.5] for no chemotherapy, HR = 0.66 [95% CI:0. 48–0.92] | ||
| Early Breast Cancer Trialists’ Collaborative Group (EBCTCG) 2022 [264] | 7030 premenopausal women with ER+ tumours | Aromatase inhibitors (anastrozole, exemestane, or letrozole) and ovarian suppression | Tamoxifen and ovarian suppression | Anthracycline-based chemotherapy was associated with a larger reduction in the annual breast cancer death rate in younger compared to older women: 38% vs. 20% (independent of hormone-receptor status, tamoxifen use, nodal status, and other tumour features) | ||
| De Laurentiis et al., 2008 [274] | 22,903 patients | Taxanes and anthracycline-based chemotherapy | Anthracycline-based chemotherapy | Adding taxanes to anthracycline-based chemotherapy was associated with improved disease-free survival (pooled HR = 0.83; 95% CI: 0.79–0.87; p < 0.00001) and overall survival (pooled HR = 0.85; 95% CI: 0.79–0.91; p < 0.00001) in both younger and older women with high-risk early stage breast cancer | ||
| Kroman et al., 2000 [15] | 10,356 patient, <50 years | NA | NA | No age-specific differences in survival among women who received chemotherapy. However, younger women who did not receive chemotherapy aged <40 years had a higher relative risk of death at 10-ten years of follow-up compared to those aged 45–49 years (RR = 1.40; 95% CI: 1.10–1.78 for ages 35–39 and RR = 2.18; 95% CI: 1.64–2.89 for age <35) | ||
| Targeted therapy | Schmid et al., 2020 [275] | 602 patients | Pembrolizumab and chemotherapy | Placebo and chemotherapy | Pembrolizumab (PD-L1 inhibitor) and neoadjuvant chemotherapy was significantly more effective compared to placebo and neoadjuvant chemotherapy in young patients (64.8% vs. 51.2% pCR; p < 0.01) | |
| Loibl et al., 2019 [276] | 174 patients | Durvalumab and nab-paclitaxel followed by standard EC | Placebo and nab-paclitaxel followed by standard EC | Durvalumab (PD-L1 inhibitor) and chemotherapy was significantly more effective compared to placebo and chemotherapy | ||
| Bianchini et al., 2020 [277] | 280 patients nab-paclitaxel/carbo (CT) or with atezolizumab (CT/A) | Atezolizumab (CT/A) | Nab-paclitaxel/carbo (CT) | No significant difference in the pCR (42.3% for placebo vs. 47.1% for atezolizumab group; p = 0.66) in 279 patients with early-stage TNBC randomized to receive neoadjuvant chemotherapy alone versus with atezolizumab for the general population | ||
| Early Breast Cancer Trialists’ Collaborative group (EBCTCG) 2021 [278] | 13,864 patients | Trastuzumab and chemotherapy | chemotherapy | The addition of trastuzumab to chemotherapy reduced recurrence rates and breast cancer-related mortality by approximately a third, irrespective of patient age and tumour characteristics | ||
| Earl et al., 2019 [279] | 2045 patients | Six-month trastuzumab treatment | Twelve-month trastuzumab treatment | Six-month trastuzumab treatment is not inferior to twelve-month treatment in patients with HER2-positive early breast cancer | ||
| Inno et al., 2019 [280] | 11,381 patients | Shorter trastuzumab treatment | Standard trastuzumab treatment | One-year adjuvant trastuzumab is correlated with better DFS and OS compared with shorter durations. | ||
| Piccart et al., 2021 [281] | 4805 patients (13.6% of patients aged <40 years in each treatment arm) | 1-year pertuzumab added to standard adjuvant chemotherapy and 1-year trastuzumab. | Placebo added to standard adjuvant chemotherapy and 1-year trastuzumab. | Adjuvant pertuzumab in addition to trastuzumab and standard chemotherapy was associated with a significant improvement in the 3-year rate of invasive-disease–free survival compared to trastuzumab and chemotherapy alone (92.0% vs. 90.2%; invasive-disease event HR = 0.77; 95% CI: 0.62–0.96; p = 0.02) among patients with HER2+, node-positive breast cancer | ||
| von Minckwitz et al., 2019 [282] | 1486 patients (20% of patients aged <40 years in each treatment arm) | Adjuvant Trastuzumab-DM1 | Trastuzumab | Significantly improved 3-year invasive disease-free survival by 11.3% in T-DM1 group (invasive disease or death HR of 0.50; 95% CI: 0.39–0.64; p < 0.001) | ||
| Metastatic setting | Aebi et al., 2014 [283] Wapnir et al., 2018 [284] | 162 patients | Chemotherapy | No chemotherapy | Improved 5-year DFS in women who received chemotherapy for isolated locoregional recurrence (ILRR) after surgical removal with negative margins: 5-year DFS of 69% (95% CI 56–79) with chemotherapy versus 57% (95%CI: 44–67) without chemotherapy (HR = 0.59; 95% CI: 0.35–0.99; p = 0.046) | |
| Michaud et al., 2001 [285] | Meta Analysis of 4 trials involving 464 premenopausal patients | Combined endocrine therapy | Monotherapy | Significant improved median survival (2.9 years with combination vs. 2.5 years with LHRH agonist alone; p = 0.02) and median PFS with combined therapy versus monotherapy (8.7 vs. 5.4 months, p = 0.0003) | ||
| Carlson et al., 2010 [286] | 32 patients | Goserelin plus anastrozole | NA | Goserelin plus anastrozole has substantial antitumour activity in the treatment of premenopausal patients | ||
| Cheung et al., 2005 [287] | 36 premenopausal patients with metastatic and locally advanced disease | Goserelin plus anastrozole | NA | The combinations of ovarian function suppression (Goserelin) and Aromatase inhibitors produced sustained clinical benefit and minimal side effects in premenopausal women | ||
| Forward et al., 2004 [288] | 16 premenopausal women with metastatic breast cancer or locally advanced primary breast cancer | Goserelin and Anastrozole | NA | The combination of goserelin and anastrozole as second-line endocrine therapy produced a significant clinical response | ||
| Nishimura et al., 2013 [289] | 37 premenopausal women with estrogen receptor (ER)-positive and/or progesterone-receptor positive, advanced or recurrent breast cancer refractory to an LH-RH analogue plus tamoxifen | Goserelin and Anastrozole | NA | The combination of goserelin and anastrozole is a safe effective treatment for premenopausal women with hormone receptor-positive, recurrent, or advanced breast cancer | ||
| Torrisi et al., 2007 [290] | 32 premenopausal women with T2-T4 N0-N2 breast cancer, whose tumours expressed oestrogen and progesterone receptors. | Letrozole in combination with GnRH analogue | NA | Preoperative letrozole and GnRH analogue are effective in premenopausal women | ||
| Cortes et al., 2011 [291] | 762 women with heavily pretreated metastatic breast cancer | Eribulin | Treatment of physician’s choice | Improved overall survival in the eribulin group compared with treatment of physician’s choice (median OS of 13 vs. 11 months; HR = 0.81, 95% CI: 0.66–0.99; p = 0.041) | ||
| Schmid et al., 2020 [275] | 1174 patients with previously untreated stage II or stage III triple-negative breast cancer | Pembrolizumab, paclitaxel, and carboplatin | Placebo, paclitaxel, and carboplatin | Significantly improved PFS with median PFS of 9.7 months vs. 5.6 months (HR = 0.65; 95% CI: 0.49, 0.86; p = 0.0012) | ||
| Robson et al., 2017 [292] | 302 patients with a germline BRCA mutation and (HER2)-negative metastatic breast cancer | Olaparib monotherapy | Standard therapy | Superior PFS of olaparib with OS benefit of 7.9 months (22.6 vs. 14.7 months) and a more favourable toxicity profile for patients who did not receive chemotherapy in the metastatic setting | ||
| Litton et al., 2018 [293] | 431 patients with advanced breast cancer and a germline BRCA1/2 mutation | Talazoparib | Standard single-agent therapy of the physician’s choice | Superiority of talazoparib with a significantly improved PFS (8.6 months vs. 5.6 months; HR = 0.54; 95% CI: 0.41–0.71; p < 0.001) compared to standard single-agent therapy | ||
| Baselga et al., 2012 [294] | 808 patients with HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer | Pertuzumab, trastuzumab, and docetaxel | Placebo, and trastuzumab, and docetaxel | Median OS = 56.5 vs. 40.8 months (survival benefit of 15.7 months) in the pertuzumab added group | ||
| Verma et al., 2012 [295] | 991 patients with HER2-positive advanced breast cancer, who had previously been treated with trastuzumab and a taxane | Trastuzumab emtansine (T-DM1) | Lapatinib plus capecitabine | OS benefit for T-DM1: 30.9 vs. 25.1 months with less toxicity |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, J.W.; Charkhchi, P.; Adekunte, S.; Akbari, M.R. What Is Known about Breast Cancer in Young Women? Cancers 2023, 15, 1917. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15061917
Zhu JW, Charkhchi P, Adekunte S, Akbari MR. What Is Known about Breast Cancer in Young Women? Cancers. 2023; 15(6):1917. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15061917
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Jie Wei, Parsa Charkhchi, Shadia Adekunte, and Mohammad R. Akbari. 2023. "What Is Known about Breast Cancer in Young Women?" Cancers 15, no. 6: 1917. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15061917
APA StyleZhu, J. W., Charkhchi, P., Adekunte, S., & Akbari, M. R. (2023). What Is Known about Breast Cancer in Young Women? Cancers, 15(6), 1917. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15061917