Efficacy and Safety of Bruton Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Monotherapy Compared with Combination Therapy for Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia and Small Lymphocytic Lymphoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Registration and Protocol
2.2. Data Sources and Search Strategies
2.3. Study Selection
2.4. Data Extraction Process and Risk of Bias Assessment
2.5. Study Outcome Evaluation
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
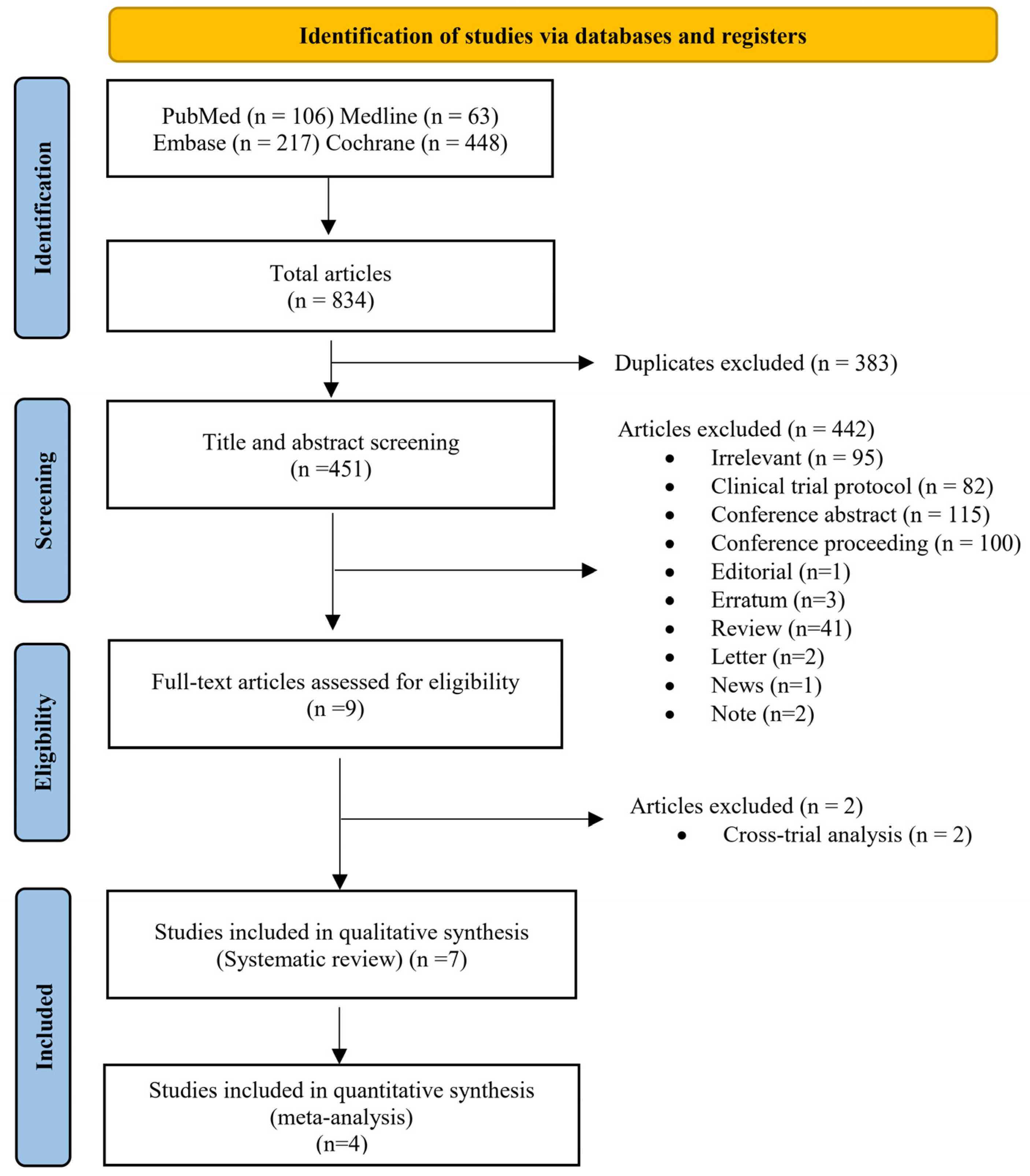
3.1. Literature Search and Study Selection
3.2. Study Features
3.3. Description of Patients
3.4. BTK Inhibitor Monotherapy versus Combination Therapy
3.5. Risk of Bias
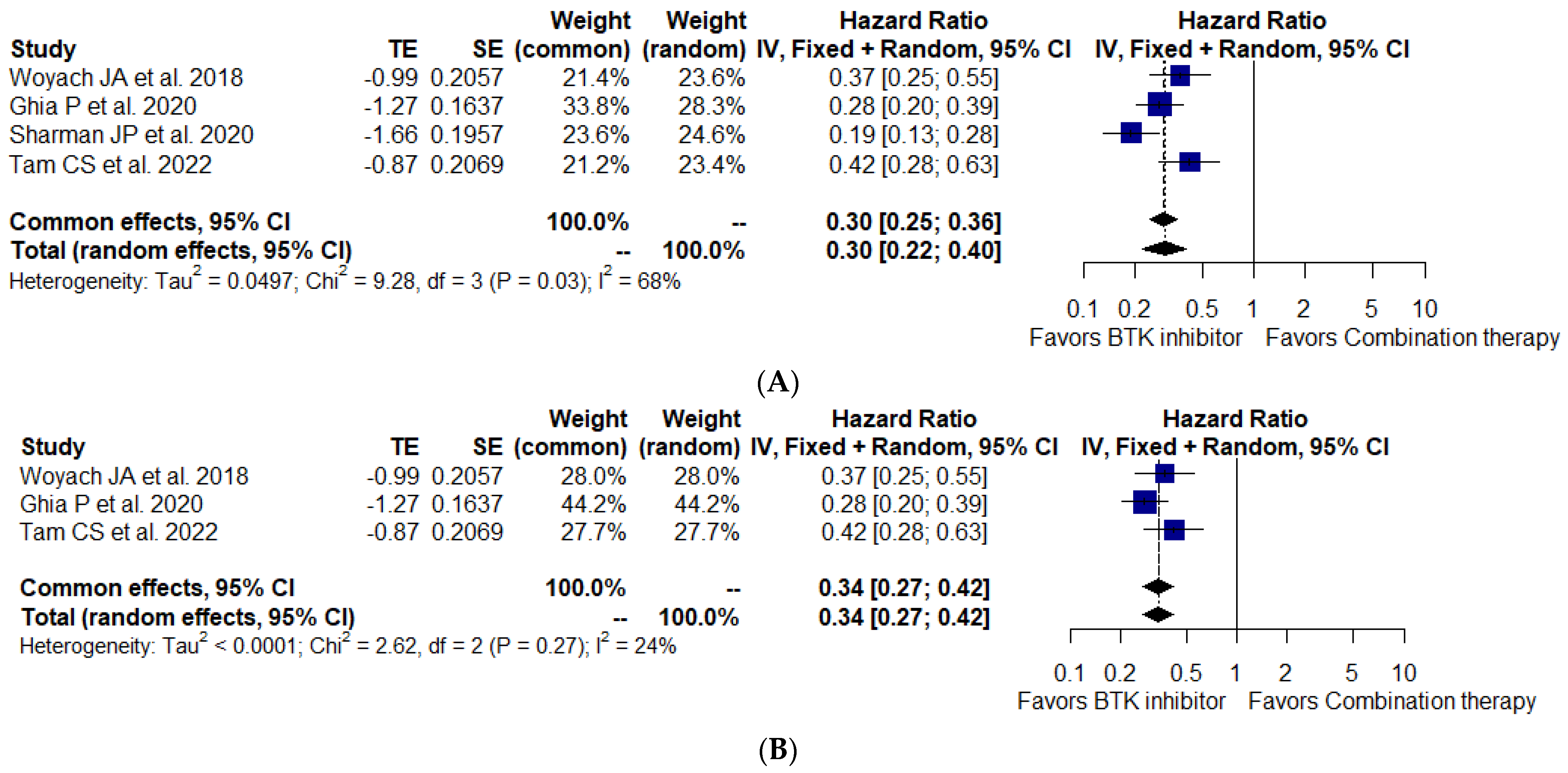
3.6. Primary Outcomes of Interest
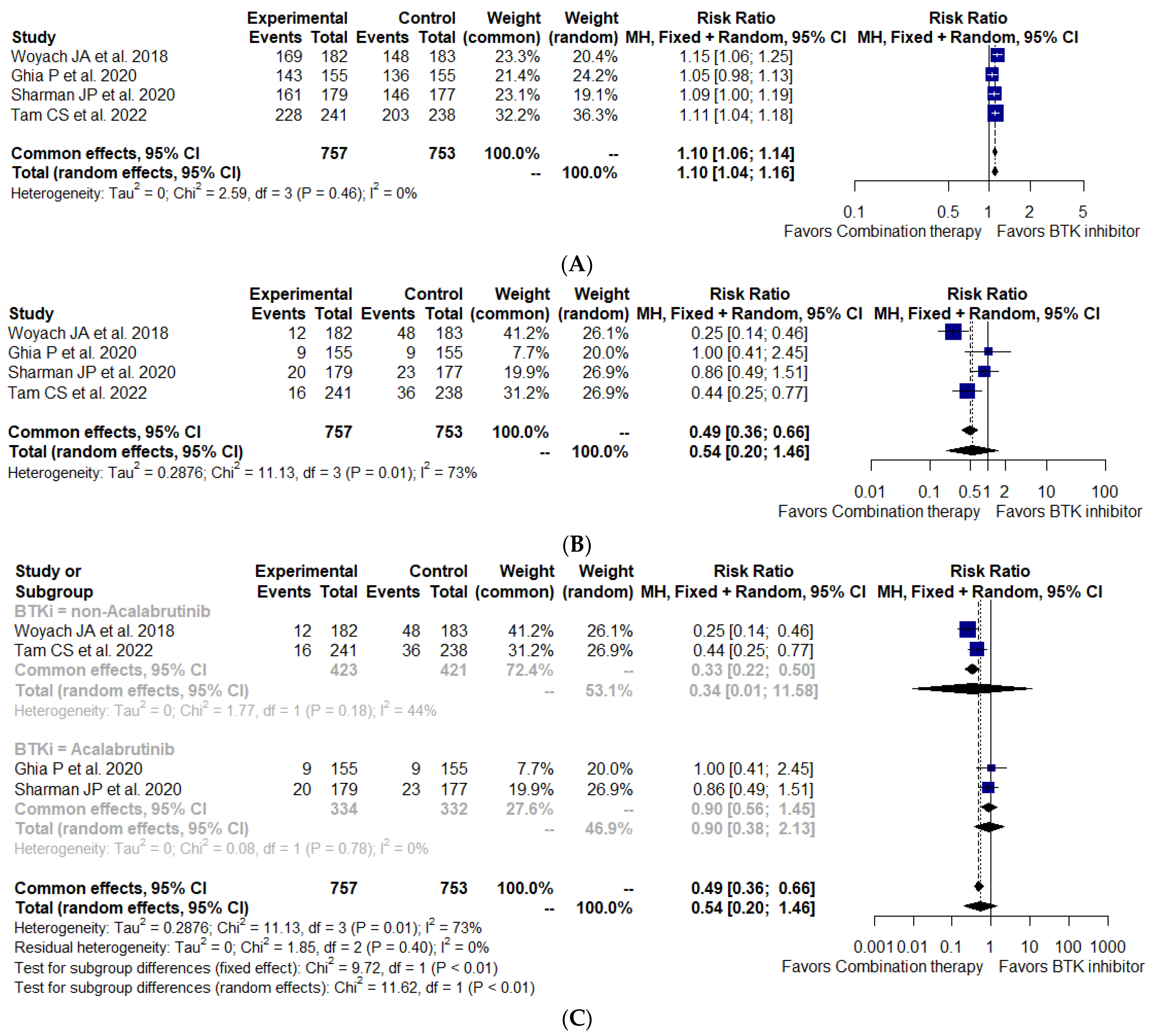
3.7. Secondary Outcomes of Interest
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hallek, M.; Cheson, B.D.; Catovsky, D.; Caligaris-Cappio, F.; Dighiero, G.; Döhner, H.; Hillmen, P.; Keating, M.; Montserrat, E.; Chiorazzi, N.J.B. iwCLL guidelines for diagnosis, indications for treatment, response assessment, and supportive management of CLL. J. Am. Soc. Hematol. 2018, 131, 2745–2760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, K.; Bahlo, J.; Fink, A.M.; Goede, V.; Herling, C.D.; Cramer, P.; Langerbeins, P.; Von Tresckow, J.; Engelke, A.; Maurer, C.J.B. Long-term remissions after FCR chemoimmunotherapy in previously untreated patients with CLL: Updated results of the CLL8 trial. J. Am. Soc. Hematol. 2016, 127, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallek, M.; Shanafelt, T.D.; Eichhorst, B. Chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Lancet 2018, 391, 1524–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, K.; Cramer, P.; Busch, R.; Stilgenbauer, S.; Bahlo, J.; Schweighofer, C.D.; Böttcher, S.; Staib, P.; Kiehl, M.; Eckart, M.J. Bendamustine combined with rituximab in patients with relapsed and/or refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia: A multicenter phase II trial of the German Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Study Group. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 3559–3566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furman, R.R.; Sharman, J.P.; Coutre, S.E.; Cheson, B.D.; Pagel, J.M.; Hillmen, P.; Barrientos, J.C.; Zelenetz, A.D.; Kipps, T.J.; Flinn, I. Idelalisib and rituximab in relapsed chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 997–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goede, V.; Fischer, K.; Busch, R.; Engelke, A.; Eichhorst, B.; Wendtner, C.M.; Chagorova, T.; De La Serna, J.; Dilhuydy, M.-S.; Illmer, T. Obinutuzumab plus chlorambucil in patients with CLL and coexisting conditions. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 1101–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seymour, J.F.; Kipps, T.J.; Eichhorst, B.; Hillmen, P.; D’Rozario, J.; Assouline, S.; Owen, C.; Gerecitano, J.; Robak, T.; De la Serna, J.; et al. Venetoclax-Rituximab in Relapsed or Refractory Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 1107–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sawaf, O.; Zhang, C.; Tandon, M.; Sinha, A.; Fink, A.M.; Robrecht, S.; Samoylova, O.; Liberati, A.M.; Pinilla-Ibarz, J.; Opat, S.; et al. Venetoclax plus obinutuzumab versus chlorambucil plus obinutuzumab for previously untreated chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (CLL14): Follow-up results from a multicentre, open-label, randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, 1188–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuneo, A.; Follows, G.; Rigolin, G.M.; Piciocchi, A.; Tedeschi, A.; Trentin, L.; Perez, A.M.; Coscia, M.; Laurenti, L.; Musuraca, G. Efficacy of bendamustine and rituximab as first salvage treatment in chronic lymphocytic leukemia and indirect comparison with ibrutinib: A gimema, eric and UK cll forum study. Haematologica 2018, 103, 1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mato, A.R.; Nabhan, C.; Barr, P.M.; Ujjani, C.S.; Hill, B.T.; Lamanna, N.; Skarbnik, A.P.; Howlett, C.; Pu, J.J.; Sehgal, A.R. Outcomes of CLL patients treated with sequential kinase inhibitor therapy: A real world experience. J. Am. Soc. Hematol. 2016, 128, 2199–2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mato, A.; Hill, B.; Lamanna, N.; Barr, P.; Ujjani, C.; Brander, D.; Howlett, C.; Skarbnik, A.; Cheson, B.; Zent, C.S. Optimal sequencing of ibrutinib, idelalisib, and venetoclax in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: Results from a multicenter study of 683 patients. Ann. Oncol. 2017, 28, 1050–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharman, J.P.; Coutre, S.E.; Furman, R.R.; Cheson, B.D.; Pagel, J.M.; Hillmen, P.; Barrientos, J.C.; Zelenetz, A.D.; Kipps, T.J.; Flinn, I.W. Final results of a randomized, phase III study of rituximab with or without idelalisib followed by open-label idelalisib in patients with relapsed chronic lymphocytic leukemia. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 1391–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamini, O.; Jain, P.; Trinh, L.; Qiao, W.; Strom, S.S.; Lerner, S.; Wang, X.; Burger, J.; Ferrajoli, A.; Kantarjian, H.J.L.; et al. Second cancers in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia who received frontline fludarabine, cyclophosphamide and rituximab therapy: Distribution and clinical outcomes. Leuk. Lymphoma 2015, 56, 1643–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Zhao, J. Frontline therapies for untreated chronic lymphoid leukemia. Exp. Hematol. Oncol. 2019, 8, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burger, J.A.; Tedeschi, A.; Barr, P.M.; Robak, T.; Owen, C.; Ghia, P.; Bairey, O.; Hillmen, P.; Bartlett, N.L.; Li, J. Ibrutinib as initial therapy for patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 2425–2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrd, J.C.; Brown, J.R.; O’Brien, S.; Barrientos, J.C.; Kay, N.E.; Reddy, N.M.; Coutre, S.; Tam, C.S.; Mulligan, S.P.; Jaeger, U. Ibrutinib versus ofatumumab in previously treated chronic lymphoid leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrd, J.C.; Harrington, B.; O’Brien, S.; Jones, J.A.; Schuh, A.; Devereux, S.; Chaves, J.; Wierda, W.G.; Awan, F.T.; Brown, J.R. Acalabrutinib (ACP-196) in relapsed chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Yang, S.; Zhou, K.; Pan, L.; Li, Z.; Zhou, J.; Gao, S.; Zhou, D.; Hu, J.; Feng, R.; et al. Treatment of relapsed/refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma with the BTK inhibitor zanubrutinib: Phase 2, single-arm, multicenter study. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 13, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herman, S.E.; Mustafa, R.Z.; Gyamfi, J.A.; Pittaluga, S.; Chang, S.; Chang, B.; Farooqui, M.; Wiestner, A.J.B. Ibrutinib inhibits BCR and NF-κB signaling and reduces tumor proliferation in tissue-resident cells of patients with CLL. J. Am. Soc. Hematol. 2014, 123, 3286–3295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herman, S.E.; Mustafa, R.Z.; Jones, J.; Wong, D.H.; Farooqui, M.; Wiestner, A. Treatment with Ibrutinib Inhibits BTK-and VLA-4–Dependent Adhesion of Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Cells In VivoIbrutinib Inhibits VLA-4–Dependent Adhesion in CLL. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 4642–4651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponader, S.; Chen, S.-S.; Buggy, J.J.; Balakrishnan, K.; Gandhi, V.; Wierda, W.G.; Keating, M.J.; O’Brien, S.; Chiorazzi, N.; Burger, J.A.J.B. The Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor PCI-32765 thwarts chronic lymphocytic leukemia cell survival and tissue homing in vitro and in vivo. J. Am. Soc. Hematol. 2012, 119, 1182–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, S.; Furman, R.R.; Coutre, S.; Flinn, I.W.; Burger, J.A.; Blum, K.; Sharman, J.; Wierda, W.; Jones, J.; Zhao, W.J.B. Single-agent ibrutinib in treatment-naïve and relapsed/refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia: A 5-year experience. J. Am. Soc. Hematol. 2018, 131, 1910–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imbruvica® (ibrutinib) capsules, for oral use. Available online: https://www.Accessdata.Fda.Gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2015/205552s002lbl.Pdf (accessed on 1 January 2015).
- Shanafelt, T.D.; Wang, X.V.; Kay, N.E.; Hanson, C.A.; O’Brien, S.; Barrientos, J.; Jelinek, D.F.; Braggio, E.; Leis, J.F.; Zhang, C.C. Ibrutinib–rituximab or chemoimmunotherapy for chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 432–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woyach, J.A.; Ruppert, A.S.; Heerema, N.A.; Zhao, W.; Booth, A.M.; Ding, W.; Bartlett, N.L.; Brander, D.M.; Barr, P.M.; Rogers, K.A.; et al. Ibrutinib Regimens versus Chemoimmunotherapy in Older Patients with Untreated CLL. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 2517–2528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellegrini, L.; Novak, U.; Andres, M.; Suter, T.; Nagler, M. Risk of bleeding complications and atrial fibrillation associated with ibrutinib treatment: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit. Rev. Oncol. 2021, 159, 103238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munir, T.; Brown, J.R.; O’Brien, S.; Barrientos, J.C.; Barr, P.M.; Reddy, N.M.; Coutre, S.; Tam, C.S.; Mulligan, S.P.; Jaeger, U. Final analysis from RESONATE: Up to six years of follow-up on ibrutinib in patients with previously treated chronic lymphocytic leukemia or small lymphocytic lymphoma. Am. J. Hematol. 2019, 94, 1353–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golay, J.; Ubiali, G.; Introna, M.J.H. The specific Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor acalabrutinib (ACP-196) shows favorable in vitro activity against chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells with CD20 antibodies. Haematologica 2017, 102, e400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Drug Administration. FDA Takes Second Action under International Collaboration, Approves New Treatment Option for Patients with Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. 2019. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/fda-takes-second-action-under-international-collaboration-approves-new-treatment-option-patients (accessed on 21 November 2019).
- Sharman, J.P.; Egyed, M.; Jurczak, W.; Skarbnik, A.; Pagel, J.M.; Flinn, I.W.; Kamdar, M.; Munir, T.; Walewska, R.; Corbett, G. Acalabrutinib with or without obinutuzumab versus chlorambucil and obinutuzumab for treatment-naive chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (ELEVATE-TN): A randomised, controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2020, 395, 1278–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Liu, Y.; Hu, N.; Yu, D.; Zhou, C.; Shi, G.; Zhang, B.; Wei, M.; Liu, J.; Luo, L. Discovery of zanubrutinib (BGB-3111), a novel, potent, and selective covalent inhibitor of Bruton’s tyrosine kinase. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 7923–7940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Zhou, K.; Zou, D.; Zhou, J.; Hu, J.; Yang, H.; Zhang, H.; Ji, J.; Xu, W.; Jin, J. Treatment of Patients with Relapsed or Refractory Mantle–Cell Lymphoma with Zanubrutinib, a Selective Inhibitor of Bruton’s Tyrosine KinaseZanubrutinib for Relapsed/Refractory MCL. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 4216–4224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, C.S.; Trotman, J.; Opat, S.; Burger, J.A.; Cull, G.; Gottlieb, D.; Harrup, R.; Johnston, P.B.; Marlton, P.; Munoz, J.J.B. Phase 1 study of the selective BTK inhibitor zanubrutinib in B-cell malignancies and safety and efficacy evaluation in CLL. J. Am. Soc. Hematol. 2019, 134, 851–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillmen, P.; Eichhorst, B.; Brown, J.R.; Lamanna, N.; O’Brien, S.; Tam, C.S.; Qiu, L.; Kazmierczak, M.; Zhou, K.; Šimkovič, M. First interim analysis of ALPINE study: Results of a phase 3 randomized study of zanubrutinib vs ibrutinib in patients with relapsed/refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma. In Proceedings of the 2021 European Hematology Association Virtual Congress, Virtual, 7 March 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. Br. Med. J. 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichhorst, B.; Robak, T.; Montserrat, E.; Ghia, P.; Niemann, C.; Kater, A.; Gregor, M.; Cymbalista, F.; Buske, C.; Hillmen, P. Chronic lymphocytic leukaemia: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2021, 32, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.; Thomas, J.; Chandler, J.; Cumpston, M.; Li, T.; Page, M.; Welch, V. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 6.3 (Updated February 2022); Cochrane. 2022. Available online: www.training.cochrane.org/handbook (accessed on 23 September 2019).
- Hallek, M.; Cheson, B.D.; Catovsky, D.; Caligaris-Cappio, F.; Dighiero, G.; Döhner, H.; Hillmen, P.; Keating, M.J.; Montserrat, E.; Rai, K.R.; et al. Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia: A report from the International Workshop on Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia updating the National Cancer Institute–Working Group 1996 guidelines. Blood 2008, 111, 5446–5456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheson, B.D.; Fisher, R.I.; Barrington, S.F.; Cavalli, F.; Schwartz, L.H.; Zucca, E.; Lister, T.A. Recommendations for initial evaluation, staging, and response assessment of Hodgkin and non-Hodgkin lymphoma: The Lugano classification. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 3059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tierney, J.F.; Stewart, L.A.; Ghersi, D.; Burdett, S.; Sydes, M.R. Practical methods for incorporating summary time-to-event data into meta-analysis. Trials 2007, 8, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruppert, A.S.; Booth, A.M.; Ding, W.; Bartlett, N.L.; Brander, D.M.; Coutre, S.; Brown, J.R.; Nattam, S.; Larson, R.A.; Erba, H.; et al. Adverse event burden in older patients with CLL receiving bendamustine plus rituximab or ibrutinib regimens: Alliance A041202. Leukemia 2021, 35, 2854–2861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghia, P.; Pluta, A.; Wach, M.; Lysak, D.; Kozak, T.; Simkovic, M.; Kaplan, P.; Kraychok, I.; Illes, A.; de la Serna, J.; et al. ASCEND: Phase III, Randomized Trial of Acalabrutinib Versus Idelalisib Plus Rituximab or Bendamustine Plus Rituximab in Relapsed or Refractory Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 2849–2861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghia, P.; Pluta, A.; Wach, M.; Lysak, D.; Šimkovič, M.; Kriachok, I.; Illés, Á.; De La Serna, J.; Dolan, S.; Campbell, P.; et al. Acalabrutinib Versus Investigator’s Choice in Relapsed/Refractory Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: Final ASCEND Trial Results. HemaSphere 2022, 6, E801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharman, J.P.; Egyed, M.; Jurczak, W.; Skarbnik, A.; Pagel, J.M.; Flinn, I.W.; Kamdar, M.; Munir, T.; Walewska, R.; Corbett, G.; et al. Efficacy and safety in a 4-year follow-up of the ELEVATE-TN study comparing acalabrutinib with or without obinutuzumab versus obinutuzumab plus chlorambucil in treatment-naïve chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leukemia 2022, 36, 1171–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, C.S.; Brown, J.R.; Kahl, B.S.; Ghia, P.; Giannopoulos, K.; Jurczak, W.; Šimkovič, M.; Shadman, M.; Österborg, A.; Laurenti, L.; et al. Zanubrutinib versus bendamustine and rituximab in untreated chronic lymphocytic leukaemia and small lymphocytic lymphoma (SEQUOIA): A randomised, controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2022, 23, 1031–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, I.E.; Tian, X.; Wiestner, A. Ibrutinib for chronic lymphocytic leukemia with TP53 alterations. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 498–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallek, M. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia: 2020 update on diagnosis, risk stratification and treatment. Am. J. Hematol. 2019, 94, 1266–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kipps, T.J.; Fraser, G.; Coutre, S.E.; Brown, J.R.; Barrientos, J.C.; Barr, P.M.; Byrd, J.C.; O’Brien, S.M.; Dilhuydy, M.-S.; Hillmen, P.; et al. Long-term studies assessing outcomes of ibrutinib therapy in patients with del (11q) chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2019, 19, 715–722.e716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, K.; Al-Sawaf, O.; Bahlo, J.; Fink, A.-M.; Tandon, M.; Dixon, M.; Robrecht, S.; Warburton, S.; Humphrey, K.; Samoylova, O. Venetoclax and obinutuzumab in patients with CLL and coexisting conditions. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 2225–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, C.; Greil, R.; Demirkan, F.; Tedeschi, A.; Anz, B.; Larratt, L.; Simkovic, M.; Samoilova, O.; Novak, J.; Ben-Yehuda, D.O. Ibrutinib plus obinutuzumab versus chlorambucil plus obinutuzumab in first-line treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (iLLUMINATE): A multicentre, randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burger, J.A.; Barr, P.M.; Robak, T.; Owen, C.; Ghia, P.; Tedeschi, A.; Bairey, O.; Hillmen, P.; Coutre, S.E.; Devereux, S.; et al. Long-term efficacy and safety of first-line ibrutinib treatment for patients with CLL/SLL: 5 years of follow-up from the phase 3 RESONATE-2 study. Leukemia 2020, 34, 787–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uminski, K.; Brown, K.; Bucher, O.; Hibbert, I.; Dhaliwal, D.H.; Johnston, J.B.; Geirnaert, M.; Dawe, D.E.; Banerji, V. Descriptive analysis of dosing and outcomes for patients with ibrutinib-treated relapsed or refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia in a Canadian centre. Curr. Oncol. 2019, 26, e610–e617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.R. How I treat CLL patients with ibrutinib. Blood 2018, 131, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mato, A.R.; Nabhan, C.; Thompson, M.C.; Lamanna, N.; Brander, D.M.; Hill, B.; Howlett, C.; Skarbnik, A.; Cheson, B.D.; Zent, C.J.H. Toxicities and outcomes of 616 ibrutinib-treated patients in the United States: A real-world analysis. Haematologica 2018, 103, 874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephens, D.M.; Spurgeon, S.E. Ibrutinib in mantle cell lymphoma patients: Glass half full? Evidence and opinion. Ther. Adv. Hematol. 2015, 6, 242–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barf, T.; Covey, T.; Izumi, R.; van de Kar, B.; Gulrajani, M.; van Lith, B.; van Hoek, M.; de Zwart, E.; Mittag, D.; Demont, D.; et al. Acalabrutinib (ACP-196): A covalent Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor with a differentiated selectivity and in vivo potency profile. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2017, 363, 240–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrd, J.C.; Hillmen, P.; Ghia, P.; Kater, A.P.; Chanan-Khan, A.; Furman, R.R.; O’Brien, S.; Yenerel, M.N.; Illés, A.; Kay, N.; et al. Acalabrutinib Versus Ibrutinib in Previously Treated Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: Results of the First Randomized Phase III Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 3441–3452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichhorst, B.; Fink, A.-M.; Bahlo, J.; Busch, R.; Kovacs, G.; Maurer, C.; Lange, E.; Köppler, H.; Kiehl, M.; Sökler, M.; et al. First-line chemoimmunotherapy with bendamustine and rituximab versus fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab in patients with advanced chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (CLL10): An international, open-label, randomised, phase 3, non-inferiority trial. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 928–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrd, J.C.; Owen, R.; O’Brien, S.M.; Brown, J.R.; Hillmen, P.; Bitman, B.; Chernyukhin, N.; Hamdy, A.; Izumi, R.; Patel, P.J.B. Pooled analysis of safety data from clinical trials evaluating acalabrutinib monotherapy in hematologic malignancies. Leukemia 2017, 130, 4326. [Google Scholar]
- Bond, D.A.; Huang, Y.; Fisher, J.L.; Ruppert, A.S.; Owen, D.H.; Bertino, E.M.; Rogers, K.A.; Bhat, S.A.; Grever, M.R.; Jaglowski, S.M.J.L. Second cancer incidence in CLL patients receiving BTK inhibitors. Leukemia 2020, 34, 3197–3205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beiggi, S.; Johnston, J.; Seftel, M.; Pitz, M.; Kumar, R.; Banerji, V.; J Griffith, E.; Gibson, S. Increased risk of second malignancies in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia patients as compared with follicular lymphoma patients: A Canadian population-based study. Br. J. Cancer 2013, 109, 1287–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lampson, B.L.; Yu, L.; Glynn, R.J.; Barrientos, J.C.; Jacobsen, E.D.; Banerji, V.; Jones, J.A.; Walewska, R.; Savage, K.J.; Michaud, G.F.J.B. Ventricular arrhythmias and sudden death in patients taking ibrutinib. J. Am. Soc. Hematol. 2017, 129, 2581–2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turakhia, M.P.; Shafrin, J.; Bognar, K.; Goldman, D.P.; Mendys, P.M.; Abdulsattar, Y.; Wiederkehr, D.; Trocio, J. Economic burden of undiagnosed nonvalvular atrial fibrillation in the United States. Am. J. Cardiol. 2015, 116, 733–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, C.S.; Opat, S.; D’Sa, S.; Jurczak, W.; Lee, H.-P.; Cull, G.; Owen, R.G.; Marlton, P.; Wahlin, B.E.; Sanz, R.G. A randomized phase 3 trial of zanubrutinib vs ibrutinib in symptomatic Waldenström macroglobulinemia: The ASPEN study. J. Am. Soc. Hematol. 2020, 136, 2038–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khouri, I.F.; Bassett, R.; Poindexter, N.; O’Brien, S.; Bueso-Ramos, C.E.; Hsu, Y.; Ferrajoli, A.; Keating, M.J.; Champlin, R.; Fernandez-Vina, M. Nonmyeloablative allogeneic stem cell transplantation in relapsed/refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia: Long-term follow-up, prognostic factors, and effect of human leukocyte histocompatibility antigen subtype on outcome. Cancer 2011, 117, 4679–4688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreger, P.; Schnaiter, A.; Zenz, T.; Böttcher, S.; Rossi, M.; Paschka, P.; Bühler, A.; Dietrich, S.; Busch, R.; Ritgen, M.; et al. TP53, SF3B1, and NOTCH1 mutations and outcome of allotransplantation for chronic lymphocytic leukemia: Six-year follow-up of the GCLLSG CLL3X trial. Blood 2013, 121, 3284–3288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, D.L.; Hwang, W.T.; Frey, N.V.; Lacey, S.F.; Shaw, P.A.; Loren, A.W.; Bagg, A.; Marcucci, K.T.; Shen, A.; Gonzalez, V.; et al. Chimeric antigen receptor T cells persist and induce sustained remissions in relapsed refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Sci. Transl. Med. 2015, 7, 303ra139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraietta, J.A.; Beckwith, K.A.; Patel, P.R.; Ruella, M.; Zheng, Z.; Barrett, D.M.; Lacey, S.F.; Melenhorst, J.J.; McGettigan, S.E.; Cook, D.R.; et al. Ibrutinib enhances chimeric antigen receptor T-cell engraftment and efficacy in leukemia. Blood 2016, 127, 1117–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nct. A Study of Pirtobrutinib (LOXO-305) Versus Bendamustine Plus Rituximab (BR) in Untreated Patients with Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL)/Small Lymphocytic Lymphoma (SLL). 2021. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT05023980 (accessed on 27 August 2021).
- Brown, J.R.; Eichhorst, B.; Hillmen, P.; Jurczak, W.; Kaźmierczak, M.; Lamanna, N.; O’Brien, S.M.; Tam, C.S.; Qiu, L.; Zhou, K.; et al. Zanubrutinib or Ibrutinib in Relapsed or Refractory Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 319–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachaine, J.; Beauchemin, C.; Guinan, K.; Thebault, P.; Aw, A.; Banerji, V.; Fleury, I.; Owen, C. Impact of Oral Targeted Therapy on the Economic Burden of Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia in Canada. Curr. Oncol. 2021, 28, 332–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dyke, D.L.; Werner, L.; Rassenti, L.Z.; Neuberg, D.; Ghia, E.; Heerema, N.A.; Dal Cin, P.; Dell Aquila, M.; Sreekantaiah, C.; Greaves, A.W.; et al. The Dohner fluorescence in situ hybridization prognostic classification of chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (CLL): The CLL Research Consortium experience. Br. J. Haematol. 2016, 173, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stilgenbauer, S.; Schnaiter, A.; Paschka, P.; Zenz, T.; Rossi, M.; Döhner, K.; Bühler, A.; Böttcher, S.; Ritgen, M.; Kneba, M.; et al. Gene mutations and treatment outcome in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: Results from the CLL8 trial. Blood 2014, 123, 3247–3254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zenz, T.; Fröhling, S.; Mertens, D.; Döhner, H.; Stilgenbauer, S. Moving from prognostic to predictive factors in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (CLL). Best Pract. Res. Clin. Haematol. 2010, 23, 71–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quijada-Álamo, M.; Hernández-Sánchez, M.; Alonso-Pérez, V.; Rodríguez-Vicente, A.E.; García-Tuñón, I.; Martín-Izquierdo, M.; Hernández-Sánchez, J.M.; Herrero, A.B.; Bastida, J.M.; San Segundo, L.; et al. CRISPR/Cas9-generated models uncover therapeutic vulnerabilities of del(11q) CLL cells to dual BCR and PARP inhibition. Leukemia 2020, 34, 1599–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woyach, J.A.; Ruppert, A.S.; Guinn, D.; Lehman, A.; Blachly, J.S.; Lozanski, A.; Heerema, N.A.; Zhao, W.; Coleman, J.; Jones, D.; et al. BTK(C481S)-Mediated Resistance to Ibrutinib in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 1437–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinquenel, A.; Fornecker, L.M.; Letestu, R.; Ysebaert, L.; Fleury, C.; Lazarian, G.; Dilhuydy, M.S.; Nollet, D.; Guieze, R.; Feugier, P.; et al. Prevalence of BTK and PLCG2 mutations in a real-life CLL cohort still on ibrutinib after 3 years: A FILO group study. Blood 2019, 134, 641–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woyach, J.; Huang, Y.; Rogers, K.; Bhat, S.A.; Grever, M.R.; Lozanski, A.; Doong, T.-J.; Blachly, J.S.; Lozanski, G.; Jones, D.J.B. Resistance to acalabrutinib in CLL is mediated primarily by BTK mutations. Blood 2019, 134, 504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Alliance Woyach JA et al. 2018 [25] | Ascend Ghia P et al. 2020 [42] | Elevate-TN Sharman JP et al. 2020 [30] | Sequoia Tam CS et al. 2022 [45] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Study design | Phase III, MC, OL | Phase III, MC, OL | Phase III, MC, OL | Phase III, MC, OL |
| Enrolled period | December 2013–May 2016 | February 2017–January 2018 | September 2015–February 2017 | October 2017–July 2019 |
| ClinicalTrials.gov ID | NCT01886872 | NCT02970318 | NCT02475681 | NCT03336333 |
| Method of analysis | ITT | ITT | ITT | ITT |
| Response definition | iwCLL 2008 criteria | iwCLL 2008 criteria | iwCLL 2008 criteria | iwCLL 2008 criteria (CLL) or Lugano classification (SLL) |
| Safety assessment | NR | CTCAE v4.03 | CTCAE v4.03 | CTCAE v4.03 |
| Inclusion criteria | Treatment-naive patients | Relapsed or refractory patients | Treatment-naive patients | Treatment-naive patients |
| Randomization | 1:1 | 1:1 | 1:1 | 1:1 |
| Masking | No | No | No | No |
| Randomization stratification | Risk factors for CLL | Presence or absence of del[17p] status, ECOG PS score, and lines of prior therapy received | Presence or absence of del[17p], ECOG PS score, and geographic region | Based on age, Binet stage, IGHV mutational status, and geographical region |
| Primary outcome | PFS | PFS | PFS | PFS |
| Secondary outcome | OS, ORR, CR, safety, etc | ORR, OS, DOR, safety, etc | ORR, OS, CR, safety, etc | ORR, OS, safety, etc |
| Definition PFS | The interval time from randomization until disease progression or death from any cause | The time from randomization until disease progression or death | The time from randomization until disease progression or death | The time from randomization until disease progression or death |
| Intervention arm | Ibrutinib 420 mg/day | Acalabrutinib 200 mg/day | Acalabrutinib 200 mg/day | Zanubrutinib 320 mg/day |
| Standard of care arm | Bendamustine 90 mg/m2 + Rituximab (375 mg/m2) | Bendamustine 70 mg/m2 or Idelalisib 300 mg/day + Rituximab (500 mg/m2) | Chlorambucil (0.5 mg/kg on day 1 and day 15) + Obinutuzumab (1000 mg) | Bendamustine 90 mg/m2 + Rituximab (500 mg/m2) |
| Sample size | 365 | 310 | 356 | 479 |
| Time of initial response assessment | NR | NR | Week 12 | Week 12 |
| Crossover design | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Study (First Author, Year) | BTK Inhibitor Group/Investigator’s Choice of Combination Therapy Group | Patient, n | Patient ≥ 65 years old | Patient age, median (range) | Sex, male, n (%) | ECOG PS (0–1), n (%) | ECOG PS (2), n (%) | High-Risk Disease (Rai/Binet Stage), n (%) | Treatment-Naïve Patients, n (%) | Relapsed or Refractory Patients, n (%) | Unmutated IGHV, n (%) | Del(17p), n (%) | Del(11q), n (%) | TP53 Mutation, n (%) | Complex Karyotype, n (%) | Follow-Up, Month, Median (Range) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Woyach JA et al. 2018 [25] | Ibrutinib Bendamustine + Rituximab | 182 183 | 182 183 | 71 (65–89) 70 (65–86) | 123 (68) 119 (65) | 177 (97) 173 (95) | 5 (3) 10 (5) | 99 (54) 99 (54) | 182 (100) 183 (100) | 0 (0) 0 (0) | 77/122 (63) 71/123 (58) | 9/181 (5) 14/181 (8) | 35/181 (19) 33/181 (18) | 15/168 (9) 16/174 (9) | 39/165 (24) 44/166 (27) | 38 38 |
| Ghia P et al. 2020 [42] | Acalabrutinib Bendamustine/Idelalisib +Rituximab | 155 155 | 97 98 | 68 (32–89) 67 (34–90) | 108 (70) 100 (65) | 136 (88) 134 (86) | 19 (12) 21 (14) | 65 (42) 64 (41) | 0 (0) 0 (0) | 155 (100) 155 (100) | 118/154 (77) 125/153 (82) | 28/155 (18) 21/154 (14) | 39/155 (25) 44/155 (29) | 39/152 (26) 34/153 (22) | 50/154 (32) 46/153 (30) | 46.5 45.7 |
| Sharman JP et al. 2020 [30] | Acalabrutinib Chlorambucil + Obinutuzumab | 179 177 | 151 153 | 70 (66–75) 71 (67–76) | 111 (62) 106 (59.9) | 165 (92.2) 167 (94.4) | 14 (7.8) 10 (5.6) | 87 (48.6) 78 (44.1) | 179 (100) 177 (100) | 0 (0) 0 (0) | 119 (66.5) 116 (65.5) | 16 (8.9) 16 (9.0) | 31 (17.3) 33 (18.6) | 19 (10.6) 21 (11.9) | 31 (17.3) 32 (18.1) | 46.9 46.9 |
| Tam CS et al. 2022 [45] | Zanubrutinib Bendamustine + Rituximab | 241 238 | 196 192 | 70 (66–75) 70 (66–74) | 154 (64) 144 (61) | 226 (96) 218 (92) | 15 (6) 20 (8) | 70 (29) 70 (29) | 241 (100) 238 (100) | 0 (0) 0 (0) | 125/234 (53) 121/231 (52) | 2 (1) 0 (0) | 43 (18) 46 (19) | 15/232 (6) 13/223 (6) | NR | 26.2 26.2 |
| Study | Bias arising from the Randomization Process | Bias due to Deviations from Intended Interventions | Bias due to Missing Outcome Data | Bias in the Measurement of the Outcome | Bias in the Selection of the Reported Result | The Overall Risk of Bias |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Woyach JA et al. 2018 [25] |  |  |  |  |  |  |
| Ghia P et al. 2020 [42] |  |  |  |  |  |  |
| Sharman JP et al. 2020 [30] |  |  |  |  |  |  |
| Tam CS et al. 2022 [45] |  |  |  |  |  |  |
 —Low risk;
—Low risk;  —Some concerns;
—Some concerns;  —High risk.
—High risk.| Adverse Events | BTK Inhibitor | Combination Therapy | Risk Ratio | 95% Confident Interval | I2 (%) | p -Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Events | Total | Event | Total | |||||
| AE any grade | 543 | 573 | 530 | 549 | 0.98 | 0.91–1.06 | 51 | 0.13 |
| AE of grade 3 or higher | 452 | 753 | 535 | 725 | 0.82 | 0.55–1.23 | 92 | <0.01 |
| AE of grade 3 or higher subgroup | 319 | 573 | 424 | 549 | 0.73 | 0.54–0.98 | 64 | 0.06 |
| Anemia | 54 | 753 | 49 | 725 | 1.06 | 0.45–2.49 | 30 | 0.23 |
| Arthralgia | 7 | 753 | 3 | 725 | 1.79 | 0.58–5.57 | 0 | 0.81 |
| Diarrhea | 11 | 753 | 42 | 725 | 1.58 | 0.22–11.56 | 43 | 0.15 |
| Fatigue | 16 | 753 | 12 | 725 | 1.29 | 0.92–1.82 | 0 | 0.97 |
| Hemorrhage | 21 | 753 | 8 | 752 | 2.01 | 0.54–7.44 | 0 | 0.40 |
| Infection | 150 | 753 | 127 | 725 | 1.18 | 0.68–2.03 | 52 | 0.10 |
| Neutropenia | 103 | 753 | 315 | 725 | 0.32 | 0.18–0.58 | 70 | 0.02 |
| Neutropenia subgroup | 74 | 599 | 257 | 572 | 0.28 | 0.14–0.55 | 44 | 0.17 |
| Pneumonia | 23 | 573 | 26 | 549 | 0.85 | 0.18–4.05 | 30 | 0.24 |
| Sepsis | 14 | 753 | 25 | 725 | 0.55 | 0.32–0.93 | 0 | 0.86 |
| SPM | 45 | 753 | 20 | 725 | 2.09 | 1.01–4.36 | 0 | 0.53 |
| Thrombocytopenia | 27 | 753 | 73 | 725 | 0.37 | 0.20–0.70 | 0 | 0.48 |
| URTI | 17 | 753 | 22 | 725 | 0.77 | 0.51–1.16 | 0 | 0.91 |
| UTI | 14 | 753 | 13 | 725 | 1.03 | 0.21–4.95 | 22 | 0.28 |
| Cardiac adverse events | 35 | 573 | 23 | 549 | 1.50 | 0.17–13.49 | 62 | 0.07 |
| Atrial fibrillation | 22 | 753 | 10 | 725 | 1.74 | 0.30–9.96 | 32 | 0.22 |
| Ventricular tachycardia | 2 | 753 | 0 | 725 | - | - | - | - |
| Sudden death | 7 | 420 | 2 | 403 | - | - | - | - |
| Hypertension | 80 | 753 | 43 | 725 | 1.64 | 0.60–4.51 | 36 | 0.19 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nguyen, T.T.; Nhu, N.T.; Tran, V.K.; Nguyen, T.T.H.; Lin, C.-F. Efficacy and Safety of Bruton Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Monotherapy Compared with Combination Therapy for Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia and Small Lymphocytic Lymphoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cancers 2023, 15, 1996. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15071996
Nguyen TT, Nhu NT, Tran VK, Nguyen TTH, Lin C-F. Efficacy and Safety of Bruton Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Monotherapy Compared with Combination Therapy for Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia and Small Lymphocytic Lymphoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cancers. 2023; 15(7):1996. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15071996
Chicago/Turabian StyleNguyen, Thi Thuy, Nguyen Thanh Nhu, Van Khoi Tran, Tran Thuc Huan Nguyen, and Chiou-Feng Lin. 2023. "Efficacy and Safety of Bruton Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Monotherapy Compared with Combination Therapy for Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia and Small Lymphocytic Lymphoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Cancers 15, no. 7: 1996. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15071996
APA StyleNguyen, T. T., Nhu, N. T., Tran, V. K., Nguyen, T. T. H., & Lin, C.-F. (2023). Efficacy and Safety of Bruton Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Monotherapy Compared with Combination Therapy for Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia and Small Lymphocytic Lymphoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cancers, 15(7), 1996. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15071996







