Henry Gas Solubility Optimization Algorithm based Feature Extraction in Dermoscopic Images Analysis of Skin Cancer
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
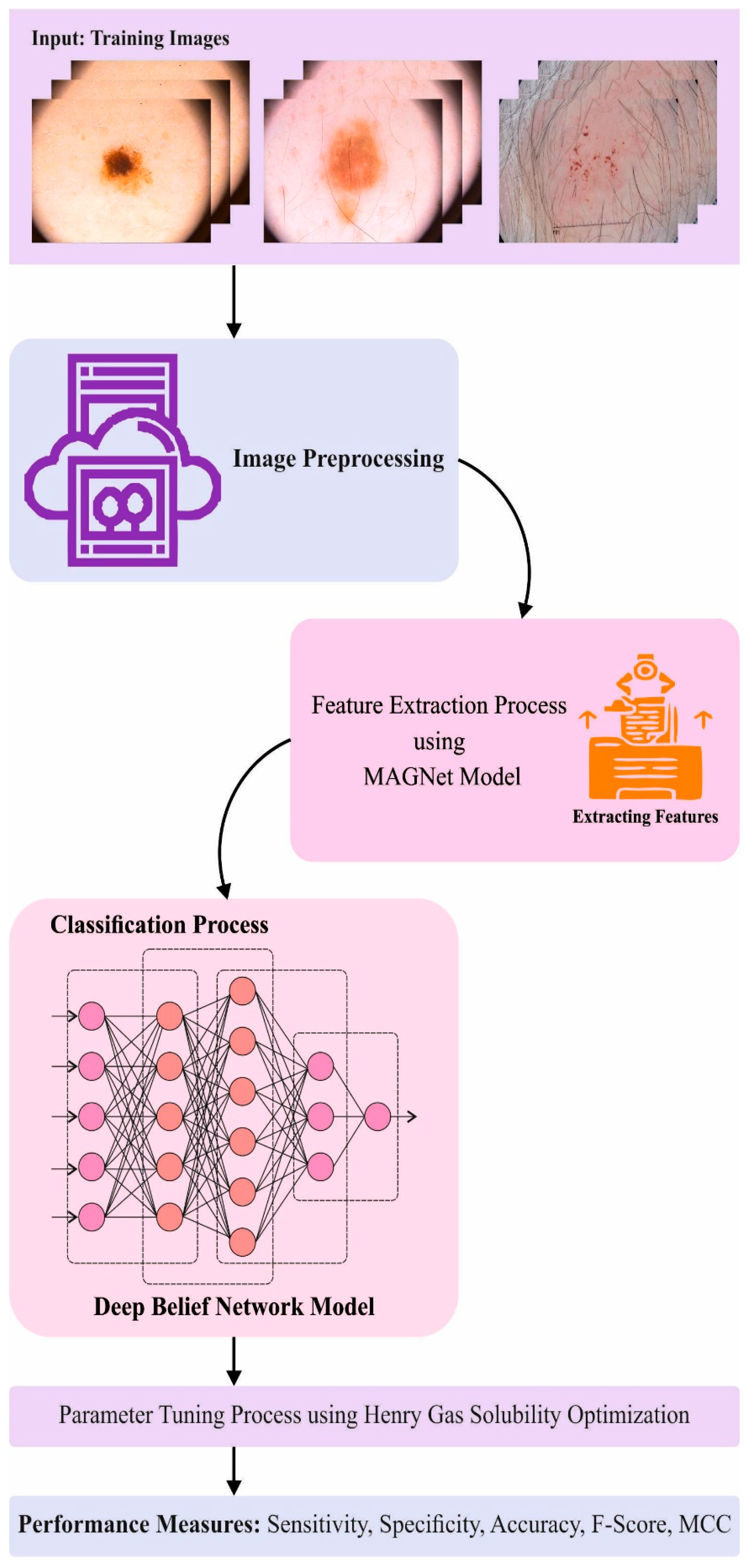
- An automated MAFCNN-SCD technique has been proposed in this study with pre-processing, MAFNet-based feature extraction, DBN classification, and HGSO-based hyperparameter tuning processes for skin cancer detection and classification. To the best of the authors’ knowledge, the proposed MAFCNN-SCD model is the first of its kind in this domain.
- The authors employed MAFNet as a feature extractor with DBN as a skin cancer detection and classification classifier.
- The hyperparameter optimization of the MAFNet model, using the HGSO algorithm with cross-validation, helped to boost the predictive outcomes of the proposed MAFCNN-SCD model for unseen data.
2. Literature Review
3. The Proposed Model
3.1. Image Pre-Processing
3.2. Feature Extraction Model
| Algorithm 1: Pseudocode of HGSO Algorithm. |
| Initialization: , number of gas kinds , and Split the population agent into a number of gas kinds (cluster) with a similar Henry’ constant value . Estimate every cluster Obtain the more suitable gas , better in all the clusters, and the better search agent While maximal iteration count, do For every search agent, do Upgrade the position of each search agent through Equations (9) and (10). End for Upgrade Henry’s coefficient of all the gas kinds based on Equation (7). Upgrade solubility of all the gases based on Equation (8). Select and Rank the amount of worst agents based on Equation (11). Upgrade the position of the worst agent based on Equation (12). Upgrade the more suitable Xi, better, and the better search agent Xbest. End while Return Xbest |
3.3. Skin Cancer Detection Model
4. Performance Evaluation
4.1. Dataset Used
4.2. Results Analysis
4.3. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Adegun, A.; Viriri, S. Deep learning techniques for skin lesion analysis and melanoma cancer detection: A survey of state-of-the-art. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2021, 54, 811–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadampur, M.A.; Al Riyaee, S. Skin cancer detection: Applying a deep learning based model driven architecture in the cloud for classifying dermal cell images. Inform. Med. Unlocked 2020, 18, 100282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jojoa Acosta, M.F.; Caballero Tovar, L.Y.; Garcia-Zapirain, M.B.; Percybrooks, W.S. Melanoma diagnosis using deep learning techniques on dermatoscopic images. BMC Med. Imaging 2021, 21, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hossin, M.A.; Rupom, F.F.; Mahi, H.R.; Sarker, A.; Ahsan, F.; Warech, S. Melanoma Skin Cancer Detection Using Deep Learning and Advanced Regularizer. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on Advanced Computer Science and Information Systems (ICACSIS), Depok City, Indonesia, 17–18 October 2020; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 89–94. [Google Scholar]
- Alazzam, M.B.; Alassery, F.; Almulihi, A. Diagnosis of melanoma using deep learning. Math. Probl. Eng. 2021, 2021, 1423605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahbod, A.; Tschandl, P.; Langs, G.; Ecker, R.; Ellinger, I. The effects of skin lesion segmentation on the performance of dermatoscopic image classification. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2020, 197, 105725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassani, S.H.; Kassani, P.H. A comparative study of deep learning architectures on melanoma detection. Tissue Cell 2019, 58, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ningrum, D.N.A.; Yuan, S.P.; Kung, W.M.; Wu, C.C.; Tzeng, I.S.; Huang, C.Y.; Li, J.Y.C.; Wang, Y.C. Deep learning classifier with patient’s metadata of dermoscopic images in malignant melanoma detection. J. Multidiscip. Healthc. 2021, 14, 877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahbod, A.; Schaefer, G.; Ellinger, I.; Ecker, R.; Pitiot, A.; Wang, C. Fusing fine-tuned deep features for skin lesion classification. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 2019, 71, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minaee, S.; Wang, Y.; Aygar, A.; Chung, S.; Wang, X.; Lui, Y.W.; Fieremans, E.; Flanagan, S.; Rath, J. MTBI identification from diffusion MR images using bag of adversarial visual features. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2019, 38, 2545–2555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shorfuzzaman, M. An explainable stacked ensemble of deep learning models for improved melanoma skin cancer detection. Multimed. Syst. 2022, 28, 1309–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhimavarapu, U.; Battineni, G. Skin Lesion Analysis for Melanoma Detection Using the Novel Deep Learning Model Fuzzy GC-SCNN. Healthcare 2022, 10, 962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafraxo, S.; Ansari, M.E.; Charfi, S. MelaNet: An effective deep learning framework for melanoma detection using dermoscopic images. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2022, 81, 16021–16045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Singh, S.K.; Chakraborty, A.; Das, A.; Bag, R. Melanoma diagnosis using deep learning and fuzzy logic. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daghrir, J.; Tlig, L.; Bouchouicha, M.; Sayadi, M. Melanoma Skin Cancer Detection Using Deep Learning and Classical Machine Learning Techniques: A Hybrid Approach. In Proceedings of the 2020 5th International Conference on Advanced Technologies for Signal and Image Processing (ATSIP), Sfax, Tunisia, 2–5 September 2020; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, T.Y.; Zhang, L.; Lim, C.P. Intelligent skin cancer diagnosis using improved particle swarm optimization and deep learning models. Appl. Soft Comput. 2019, 84, 105725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maniraj, S.P.; Maran, P.S. A hybrid deep learning approach for skin cancer diagnosis using subband fusion of 3D wavelets. J. Supercomput. 2022, 78, 12394–12409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malibari, A.A.; Alzahrani, J.S.; Eltahir, M.M.; Malik, V.; Obayya, M.; Al Duhayyim, M.; Neto, A.V.L.; de Albuquerque, V.H.C. Optimal deep neural network-driven computer aided diagnosis model for skin cancer. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2022, 103, 108318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.R.; Kang, S.H.; Lee, Y. Median modified wiener filter for improving the image quality of gamma camera images. Nucl. Eng. Technol. 2020, 52, 2328–2333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Jin, L.; Shen, T.; Huang, F. Skin Cancer Diagnosis Based on Improved Multiattention Convolutional Neural Network. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 5th Advanced Information Technology, Electronic and Automation Control Conference (IAEAC), Chongqing, China, 12–14 March 2021; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2021; Volume 5, pp. 761–765. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, S.; Lv, X.; Ding, W.; Fan, X. A Novel Multi-attention Fusion Convolution Neural Network for Blind Image Quality Assessment. Neural Process. Lett. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Song, T.; Gao, C.; Guo, T. M2FN: A Multilayer and Multiattention Fusion Network for Remote Sensing Image Scene Classification. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Han, J.; Liu, C.; Wang, Y.; Shen, H.; Li, L. A Deep-Learning Method for the Classification of Apple Varieties via Leaf Images from Different Growth Periods in Natural Environment. Symmetry 2022, 14, 1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Gao, J.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, Q. MAFNet: A Multi-Attention Fusion Network for RGB-T Crowd Counting. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2208.06761. [Google Scholar]
- Hashim, F.A.; Houssein, E.H.; Mabrouk, M.S.; Al-Atabany, W.; Mirjalili, S. Henry gas solubility optimization: A novel physics-based algorithm. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2019, 101, 646–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, D.; Abd Elaziz, M.; Moghdani, R.; Demir, E.; Mirjalili, S. Quantum Henry gas solubility optimization algorithm for global optimization. Eng. Comput. 2022, 38, 2329–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd Elaziz, M.; Attiya, I. An improved Henry gas solubility optimization algorithm for task scheduling in cloud computing. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2021, 54, 3599–3637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Hu, Z.; Yuan, W.; Wang, J. Pipeline leak detection based on empirical mode decomposition and deep belief network. Meas. Control. 2022, 56, 00202940221088713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; You, D.; Gao, X.; Katayama, S. Online monitoring of welding status based on a DBN model during laser welding. Engineering 2019, 5, 671–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, C.; Chen, S.; Xu, G.; Chen, Y. Defect detection method of carbon fiber sucker rod based on multi-sensor information fusion and DBN model. Sensors 2022, 22, 5189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Codella, N.C.; Gutman, D.; Celebi, M.E.; Helba, B.; Marchetti, M.A.; Dusza, S.W.; Kalloo, A.; Liopyris, K.; Mishra, N.; Kittler, H.; et al. Skin Lesion Analysis toward Melanoma Detection: A Challenge at the 2017 International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (isbi), Hosted by the International Skin Imaging Collaboration (isic). In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 15th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI 2018), Washington, DC, USA, 4–7 April 2018; IEEE: New York, NY, USA; pp. 168–172. [Google Scholar]
- Tschandl, P.; Rosendahl, C.; Kittler, H. The HAM10000 dataset, a large collection of multi-source dermatoscopic images of common pigmented skin lesions. Sci. Data 2018, 5, 180161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kousis, I.; Perikos, I.; Hatzilygeroudis, I.; Virvou, M. Deep Learning Methods for Accurate Skin Cancer Recognition and Mobile Application. Electronics 2022, 11, 1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.; Sharif, M.; Akram, T.; Damaševičius, R.; Maskeliunas, R. Skin Lesion-Segmentation and Multiclass Classification Using Deep Learning Features and Improved Moth Flame Optimization. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| ISIC 2017 Dataset | ||
|---|---|---|
| Label | Class | No. of Samples |
| Class-1 | Melanoma | 374 |
| Class-2 | Seborrheic Keratosis | 254 |
| Class-3 | Nevus | 1372 |
| Total Number of Dataset | 2000 | |
| HAM10000 Dataset | ||
|---|---|---|
| Description | Class | No. of Samples |
| Actinic Keratoses | AKIEC | 327 |
| Basal Cell Carcinoma | BCC | 541 |
| Benign Keratosis | BKL | 1099 |
| Dermatofibroma | DF | 155 |
| Melanocytic Nevus | NV | 6705 |
| Melanoma | MEL | 1113 |
| Vascular | VASC | 142 |
| Total No. of Dataset | 10,082 | |
| Labels | MCC | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Entire Dataset | |||||
| Class-1 | 94.4 | 71.66 | 99.63 | 82.72 | 80.84 |
| Class-2 | 95.75 | 68.9 | 99.66 | 80.46 | 79.56 |
| Class-3 | 90.25 | 99.2 | 70.7 | 93.32 | 77.39 |
| Average | 93.47 | 79.92 | 90 | 85.5 | 79.26 |
| Training Phase (70%) | |||||
| Class-1 | 94.71 | 72.9 | 99.74 | 83.77 | 82 |
| Class-2 | 96.29 | 71.86 | 99.59 | 82.19 | 81.22 |
| Class-3 | 91 | 99.18 | 72.49 | 93.86 | 78.77 |
| Average | 94 | 81.31 | 90.61 | 86.61 | 80.66 |
| Testing Phase (30%) | |||||
| Class-1 | 93.67 | 68.75 | 99.39 | 80.21 | 78.1 |
| Class-2 | 94.5 | 63.22 | 99.81 | 76.92 | 76.28 |
| Class-3 | 88.5 | 99.25 | 66.83 | 92.02 | 74.32 |
| Average | 92.22 | 77.07 | 88.67 | 83.05 | 76.23 |
| Labels | MCC | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Entire Dataset | |||||
| AKIEC | 99.52 | 92.35 | 99.76 | 92.64 | 92.39 |
| BCC | 99.27 | 92.42 | 99.65 | 93.11 | 92.73 |
| BKL | 99.56 | 99 | 99.63 | 98.02 | 97.78 |
| DF | 99.62 | 87.1 | 99.82 | 87.66 | 87.47 |
| NV | 98.64 | 99 | 97.93 | 98.98 | 96.95 |
| MEL | 99.58 | 98.38 | 99.73 | 98.12 | 97.88 |
| VASC | 99.55 | 77.46 | 99.87 | 83.02 | 83.01 |
| Average | 99.39 | 92.25 | 99.49 | 93.08 | 92.6 |
| Training Phase (70%) | |||||
| AKIEC | 99.53 | 93.33 | 99.74 | 92.72 | 92.48 |
| BCC | 99.35 | 92.78 | 99.7 | 93.56 | 93.22 |
| BKL | 99.6 | 99.09 | 99.67 | 98.21 | 97.99 |
| DF | 99.66 | 87.85 | 99.84 | 88.68 | 88.51 |
| NV | 98.7 | 99.03 | 98.03 | 99.03 | 97.06 |
| MEL | 99.52 | 98.19 | 99.68 | 97.81 | 97.54 |
| VASC | 99.56 | 76.53 | 99.89 | 82.87 | 82.94 |
| Average | 99.42 | 92.4 | 99.51 | 93.27 | 92.82 |
| Testing Phase (30%) | |||||
| AKIEC | 99.5 | 90.2 | 99.83 | 92.46 | 92.24 |
| BCC | 99.07 | 91.71 | 99.54 | 92.22 | 91.73 |
| BKL | 99.47 | 98.77 | 99.56 | 97.58 | 97.29 |
| DF | 99.54 | 85.42 | 99.76 | 85.42 | 85.18 |
| NV | 98.51 | 98.94 | 97.7 | 98.87 | 96.7 |
| MEL | 99.74 | 98.83 | 99.85 | 98.83 | 98.68 |
| VASC | 99.54 | 79.55 | 99.83 | 83.33 | 83.2 |
| Average | 99.34 | 91.92 | 99.44 | 92.67 | 92.15 |
| ISIC 2017 Dataset | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Methods | Accuracy | Sensitivity | Specificity | F-Score |
| MAFCNN-SCD | 92.22 | 77.07 | 88.67 | 83.05 |
| Naïve Bayes | 89.77 | 74.7 | 84.02 | 81.37 |
| KELM | 88.04 | 77.03 | 84.49 | 83.2 |
| MSVM | 87.15 | 75.44 | 83.19 | 81.45 |
| MobileNet | 85.03 | 74.17 | 87.98 | 81.18 |
| DenseNet169 | 89.42 | 76.83 | 86.28 | 83.27 |
| ISIC 2017 Dataset | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Methods | Accuracy | Sensitivity | Specificity | F-Score |
| MAFCNN-SCD | 92.22 | 77.07 | 88.67 | 83.05 |
| Naïve Bayes | 89.77 | 74.7 | 84.02 | 81.37 |
| KELM | 88.04 | 77.03 | 84.49 | 83.2 |
| MSVM | 87.15 | 75.44 | 83.19 | 81.45 |
| MobileNet | 85.03 | 74.17 | 87.98 | 81.18 |
| DenseNet169 | 89.42 | 76.83 | 86.28 | 83.27 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Obayya, M.; Alhebri, A.; Maashi, M.; S. Salama, A.; Mustafa Hilal, A.; Alsaid, M.I.; Osman, A.E.; Alneil, A.A. Henry Gas Solubility Optimization Algorithm based Feature Extraction in Dermoscopic Images Analysis of Skin Cancer. Cancers 2023, 15, 2146. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15072146
Obayya M, Alhebri A, Maashi M, S. Salama A, Mustafa Hilal A, Alsaid MI, Osman AE, Alneil AA. Henry Gas Solubility Optimization Algorithm based Feature Extraction in Dermoscopic Images Analysis of Skin Cancer. Cancers. 2023; 15(7):2146. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15072146
Chicago/Turabian StyleObayya, Marwa, Adeeb Alhebri, Mashael Maashi, Ahmed S. Salama, Anwer Mustafa Hilal, Mohamed Ibrahim Alsaid, Azza Elneil Osman, and Amani A. Alneil. 2023. "Henry Gas Solubility Optimization Algorithm based Feature Extraction in Dermoscopic Images Analysis of Skin Cancer" Cancers 15, no. 7: 2146. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15072146
APA StyleObayya, M., Alhebri, A., Maashi, M., S. Salama, A., Mustafa Hilal, A., Alsaid, M. I., Osman, A. E., & Alneil, A. A. (2023). Henry Gas Solubility Optimization Algorithm based Feature Extraction in Dermoscopic Images Analysis of Skin Cancer. Cancers, 15(7), 2146. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15072146






