Management of Relapsed–Refractory Multiple Myeloma in the Era of Advanced Therapies: Evidence-Based Recommendations for Routine Clinical Practice
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Definition of Relapsed and/or Refractory Disease
- ▪
- Serum monoclonal (M)-protein (absolute increase must be ≥0.5 g/dL). An M-protein increase of ≥1 g/dL indicates PD, if the lowest M-protein value is ≥5 g/dL.
- ▪
- Urine M-protein (absolute increase must be ≥200 mg/24 h).
- ▪
- Difference between the involved and uninvolved free light chains (FLC) (absolute increase must be >10 mg/dL). This criterion should only be used for patients who lack measurable M-protein in the serum and urine, which is defined as serum M-protein <1 g/dL and urine M-protein < 200 mg/24 h.
- ▪
- Bone marrow plasma cell percentage (absolute increase must be ≥10 percent). This criterion should only be used for patients who lack measurable serum and urine M-protein levels and additionally lack measurable involved FLC levels.
3. Available Therapeutic Modalities
3.1. Proteasome Inhibitors
3.2. Immunomodulators
3.3. Alkylating Agents
3.4. Targeted Therapies
3.5. Traditional Immunotherapy
3.5.1. Monoclonal Antibodies
3.5.2. Antibody Drug Conjugates
3.6. Advanced Immunotherapy
3.6.1. Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-Cell Therapy (CAR-T)
3.6.2. Bispecific Antibodies
3.7. Salvage Transplant
4. How to Approach Therapy Selection
4.1. General Approach
4.2. High Risk—Aggressive Disease
4.3. Comorbidities and Major Organ Dysfunction
4.4. Optimal Timing of Therapy Initiation
4.5. Previous Refractoriness and Timing of Relapse
4.5.1. First Relapse
4.5.2. Later Relapse
4.5.3. Relapse after CAR T-Cell Therapy
5. Supportive Care
5.1. Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis
5.2. Infection Prophylaxis
5.3. Management of MM-Related Bone Disease
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Howlader, N.; Noone, A.M.; Krapcho, M.; Miller, D.; Brest, A.; Yu, M.; Ruhl, J.; Tatalovich, Z.; Mariotto, A.; Lewis, D.R.; et al. SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975–2018; National Cancer Institute: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2022; Based on November 2020 SEER Data Submission, Posted to the SEER Web Site, 22 July 2022. Available online: https://seer.cancer.gov/archive/csr/1975_2018/ (accessed on 23 January 2023).
- Rajkumar, S.V.; Kumar, S. Multiple Myeloma Current Treatment Algorithms. Blood Cancer J. 2020, 10, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinto, V.; Bergantim, R.; Caires, H.R.; Seca, H.; Guimarães, J.E.; Vasconcelos, M.H. Multiple Myeloma: Available Therapies and Causes of Drug Resistance. Cancers 2020, 12, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cowan, A.J.; Green, D.J.; Kwok, M.; Lee, S.; Coffey, D.G.; Holmberg, L.A.; Tuazon, S.; Gopal, A.K.; Libby, E.N. Diagnosis and Management of Multiple Myeloma: A Review. JAMA 2022, 327, 464–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes, R.; Ferreira, B.V.; Caetano, J.; Barahona, F.; Carneiro, E.A.; João, C. Boosting Immunity against Multiple Myeloma. Cancers 2021, 13, 1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dima, D.; Jiang, D.; Singh, D.J.; Hasipek, M.; Shah, H.S.; Ullah, F.; Khouri, J.; Maciejewski, J.P.; Jha, B.K. Multiple Myeloma Therapy: Emerging Trends and Challenges. Cancers 2022, 14, 4082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Paiva, B.; Anderson, K.C.; Durie, B.; Landgren, O.; Moreau, P.; Munshi, N.; Lonial, S.; Bladé, J.; Mateos, M.-V.; et al. International Myeloma Working Group Consensus Criteria for Response and Minimal Residual Disease Assessment in Multiple Myeloma. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, e328–e346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, K.C.; Kyle, R.A.; Rajkumar, S.V.; Stewart, A.K.; Weber, D.; Richardson, P. Clinically Relevant End Points and New Drug Approvals for Myeloma. Leukemia 2008, 22, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Richardson, P.G.; Barlogie, B.; Berenson, J.; Singhal, S.; Jagannath, S.; Irwin, D.; Rajkumar, S.V.; Srkalovic, G.; Alsina, M.; Alexanian, R.; et al. A Phase 2 Study of Bortezomib in Relapsed, Refractory Myeloma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 348, 2609–2617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moreau, P.; Coiteux, V.; Hulin, C.; Leleu, X.; van de Velde, H.; Acharya, M.; Harousseau, J.-L. Prospective Comparison of Subcutaneous versus Intravenous Administration of Bortezomib in Patients with Multiple Myeloma. Haematologica 2008, 93, 1908–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Richardson, P.G.; Sonneveld, P.; Schuster, M.W.; Irwin, D.; Stadtmauer, E.A.; Facon, T.; Harousseau, J.-L.; Ben-Yehuda, D.; Lonial, S.; Goldschmidt, H.; et al. Bortezomib or High-Dose Dexamethasone for Relapsed Multiple Myeloma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 2487–2498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Richardson, P.G.; Weller, E.; Jagannath, S.; Avigan, D.E.; Alsina, M.; Schlossman, R.L.; Mazumder, A.; Munshi, N.C.; Ghobrial, I.M.; Doss, D.; et al. Multicenter, Phase I, Dose-Escalation Trial of Lenalidomide plus Bortezomib for Relapsed and Relapsed/Refractory Multiple Myeloma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 5713–5719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dimopoulos, M.A.; Beksac, M.; Benboubker, L.; Roddie, H.; Allietta, N.; Broer, E.; Couturier, C.; Mazier, M.-A.; Angermund, R.; Facon, T. Phase II Study of Bortezomib–Dexamethasone Alone or with Added Cyclophosphamide or Lenalidomide for Sub-Optimal Response as Second-Line Treatment for Patients with Multiple Myeloma. Haematologica 2013, 98, 1264–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, D.S.; Dimopoulos, M.A.; Ludwig, H.; Facon, T.; Goldschmidt, H.; Jakubowiak, A.; San-Miguel, J.; Obreja, M.; Blaedel, J.; Stewart, A.K. Improvement in Overall Survival with Carfilzomib, Lenalidomide, and Dexamethasone in Patients with Relapsed or Refractory Multiple Myeloma. JCO 2018, 36, 728–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, A.K.; Rajkumar, S.V.; Dimopoulos, M.A.; Masszi, T.; Špička, I.; Oriol, A.; Hájek, R.; Rosiñol, L.; Siegel, D.S.; Mihaylov, G.G.; et al. Carfilzomib, Lenalidomide, and Dexamethasone for Relapsed Multiple Myeloma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 142–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimopoulos, M.A.; Goldschmidt, H.; Niesvizky, R.; Joshua, D.; Chng, W.-J.; Oriol, A.; Orlowski, R.Z.; Ludwig, H.; Facon, T.; Hajek, R.; et al. Carfilzomib or Bortezomib in Relapsed or Refractory Multiple Myeloma (ENDEAVOR): An Interim Overall Survival Analysis of an Open-Label, Randomised, Phase 3 Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 1327–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimopoulos, M.A.; Moreau, P.; Palumbo, A.; Joshua, D.; Pour, L.; Hájek, R.; Facon, T.; Ludwig, H.; Oriol, A.; Goldschmidt, H.; et al. Carfilzomib and Dexamethasone versus Bortezomib and Dexamethasone for Patients with Relapsed or Refractory Multiple Myeloma (ENDEAVOR): A Randomised, Phase 3, Open-Label, Multicentre Study. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreau, P.; Masszi, T.; Grzasko, N.; Bahlis, N.J.; Hansson, M.; Pour, L.; Sandhu, I.; Ganly, P.; Baker, B.W.; Jackson, S.R.; et al. Oral Ixazomib, Lenalidomide, and Dexamethasone for Multiple Myeloma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 1621–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, P.G.; Kumar, S.K.; Masszi, T.; Grzasko, N.; Bahlis, N.J.; Hansson, M.; Pour, L.; Sandhu, I.; Ganly, P.; Baker, B.W.; et al. Final Overall Survival Analysis of the TOURMALINE-MM1 Phase III Trial of Ixazomib, Lenalidomide, and Dexamethasone in Patients With Relapsed or Refractory Multiple Myeloma. JCO 2021, 39, 2430–2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, P.G.; Oriol, A.; Beksac, M.; Liberati, A.M.; Galli, M.; Schjesvold, F.; Lindsay, J.; Weisel, K.; White, D.; Facon, T.; et al. Pomalidomide, Bortezomib, and Dexamethasone for Patients with Relapsed or Refractory Multiple Myeloma Previously Treated with Lenalidomide (OPTIMISMM): A Randomised, Open-Label, Phase 3 Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 781–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimopoulos, M.; Weisel, K.; Moreau, P.; Anderson, L.D.; White, D.; San-Miguel, J.; Sonneveld, P.; Engelhardt, M.; Jenner, M.; Corso, A.; et al. Pomalidomide, Bortezomib, and Dexamethasone for Multiple Myeloma Previously Treated with Lenalidomide (OPTIMISMM): Outcomes by Prior Treatment at First Relapse. Leukemia 2021, 35, 1722–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, J.J.; Stadtmauer, E.A.; Abonour, R.; Cohen, A.D.; Bensinger, W.I.; Gasparetto, C.; Kaufman, J.L.; Lentzsch, S.; Vogl, D.T.; Gomes, C.L.; et al. Carfilzomib, Pomalidomide, and Dexamethasone for Relapsed or Refractory Myeloma. Blood 2015, 126, 2284–2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonneveld, P.; Zweegman, S.; Cavo, M.; Nasserinejad, K.; Broijl, A.; Troia, R.; Pour, L.; Croockewit, S.; Corradini, P.; Patriarca, F.; et al. Carfilzomib, Pomalidomide, and Dexamethasone As Second-Line Therapy for Lenalidomide-Refractory Multiple Myeloma. Hemasphere 2022, 6, e786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonneveld, P.; Zweegman, S.; Cavo, M.; Nasserinejad, K.; Troia, R.; Pour, L.; Croockewit, S.; Corradini, P.; Patriarca, F.; Wu, K.; et al. Carfilzomib, Pomalidomide and Dexamethasone (KPd) in Patients with Multiple Myeloma Refractory to Bortezomib and Lenalidomide. the EMN011 Trial. Blood 2018, 132, 801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonneveld, P.; Zweegman, S.; Cavo, M.; Nasserinejad, K.; Broyl, A.; Troia, R.; Pour, L.; Croockewit, S.; Corradini, P.; Bos, G.M.J.; et al. Carfilzomib, Pomalidomide and Dexamethasone (KPd) in Patients with First Progression of Multiple Myeloma Refractory to Bortezomib and Lenalidomide. Final Report of the EMN011/HOVON114 Trial. Blood 2021, 138, 1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hájek, R.; Masszi, T.; Petrucci, M.T.; Palumbo, A.; Rosiñol, L.; Nagler, A.; Yong, K.L.; Oriol, A.; Minarik, J.; Pour, L.; et al. A Randomized Phase III Study of Carfilzomib vs. Low-Dose Corticosteroids with Optional Cyclophosphamide in Relapsed and Refractory Multiple Myeloma (FOCUS). Leukemia 2017, 31, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlowski, R.Z.; Moreau, P.; Niesvizky, R.; Ludwig, H.; Oriol, A.; Chng, W.J.; Goldschmidt, H.; Yang, Z.; Kimball, A.S.; Dimopoulos, M. Carfilzomib-Dexamethasone Versus Bortezomib-Dexamethasone in Relapsed or Refractory Multiple Myeloma: Updated Overall Survival, Safety, and Subgroups. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2019, 19, 522–530.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mateos, M.-V.; Goldschmidt, H.; San-Miguel, J.; Mikhael, J.; DeCosta, L.; Zhou, L.; Obreja, M.; Blaedel, J.; Szabo, Z.; Leleu, X. Carfilzomib in Relapsed or Refractory Multiple Myeloma Patients with Early or Late Relapse Following Prior Therapy: A Subgroup Analysis of the Randomized Phase 3 ASPIRE and ENDEAVOR Trials. Hematol. Oncol. 2018, 36, 463–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisel, K.; Mateos, M.-V.; Gay, F.; Delforge, M.; Cook, G.; Szabo, Z.; Desgraz, R.; DeCosta, L.; Moreau, P. Efficacy and Safety Profile of Deep Responders to Carfilzomib-Based Therapy: A Subgroup Analysis from ASPIRE and ENDEAVOR. Leukemia 2021, 35, 1732–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berenson, J.R.; Cartmell, A.; Bessudo, A.; Lyons, R.M.; Harb, W.; Tzachanis, D.; Agajanian, R.; Boccia, R.; Coleman, M.; Moss, R.A.; et al. CHAMPION-1: A Phase 1/2 Study of Once-Weekly Carfilzomib and Dexamethasone for Relapsed or Refractory Multiple Myeloma. Blood 2016, 127, 3360–3368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreau, P.; Mateos, M.-V.; Berenson, J.R.; Weisel, K.; Lazzaro, A.; Song, K.; Dimopoulos, M.A.; Huang, M.; Zahlten-Kumeli, A.; Stewart, A.K. Once Weekly versus Twice Weekly Carfilzomib Dosing in Patients with Relapsed and Refractory Multiple Myeloma (A.R.R.O.W.): Interim Analysis Results of a Randomised, Phase 3 Study. Lancet Oncol. 2018, 19, 953–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimopoulos, M.A.; Niesvizky, R.; Weisel, K.; Siegel, D.S.; Hajek, R.; Mateos, M.-V.; Cavo, M.; Huang, M.; Zahlten-Kumeli, A.; Moreau, P. Once-versus Twice-Weekly Carfilzomib in Relapsed and Refractory Multiple Myeloma by Select Patient Characteristics: Phase 3 A.R.R.O.W. Study Subgroup Analysis. Blood Cancer J. 2020, 10, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Auner, H.W.; Brown, S.R.; Walker, K.; Kendall, J.; Dawkins, B.; Meads, D.; Morgan, G.J.; Kaiser, M.F.; Cook, M.; Roberts, S.; et al. Ixazomib with Cyclophosphamide and Dexamethasone in Relapsed or Refractory Myeloma: MUKeight Phase II Randomised Controlled Trial Results. Blood Cancer J. 2022, 12, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimopoulos, M.A.; Schjesvold, F.; Doronin, V.; Vinogradova, O.; Quach, H.; Leleu, X.; Montes, Y.G.; Ramasamy, K.; Pompa, A.; Levin, M.-D.; et al. Oral Ixazomib-Dexamethasone vs. Oral Pomalidomide-Dexamethasone for Lenalidomide-Refractory, Proteasome Inhibitor-Exposed Multiple Myeloma: A Randomized Phase 2 Trial. Blood Cancer J. 2022, 12, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miguel, J.S.; Weisel, K.; Moreau, P.; Lacy, M.; Song, K.; Delforge, M.; Karlin, L.; Goldschmidt, H.; Banos, A.; Oriol, A.; et al. Pomalidomide plus Low-Dose Dexamethasone versus High-Dose Dexamethasone Alone for Patients with Relapsed and Refractory Multiple Myeloma (MM-003): A Randomised, Open-Label, Phase 3 Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2013, 14, 1055–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Holstein, S.A.; McCarthy, P.L. Immunomodulatory Drugs in Multiple Myeloma: Mechanisms of Action and Clinical Experience. Drugs 2017, 77, 505–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, P.G.; Siegel, D.S.; Vij, R.; Hofmeister, C.C.; Baz, R.; Jagannath, S.; Chen, C.; Lonial, S.; Jakubowiak, A.; Bahlis, N.; et al. Pomalidomide Alone or in Combination with Low-Dose Dexamethasone in Relapsed and Refractory Multiple Myeloma: A Randomized Phase 2 Study. Blood 2014, 123, 1826–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimopoulos, M.A.; Chen, C.; Spencer, A.; Niesvizky, R.; Attal, M.; Stadtmauer, E.A.; Petrucci, M.T.; Yu, Z.; Olesnyckyj, M.; Zeldis, J.B.; et al. Long-Term Follow-up on Overall Survival from the MM-009 and MM-010 Phase III Trials of Lenalidomide plus Dexamethasone in Patients with Relapsed or Refractory Multiple Myeloma. Leukemia 2009, 23, 2147–2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weber, D.M.; Chen, C.; Niesvizky, R.; Wang, M.; Belch, A.; Stadtmauer, E.A.; Siegel, D.; Borrello, I.; Rajkumar, S.V.; Chanan-Khan, A.A.; et al. Lenalidomide plus Dexamethasone for Relapsed Multiple Myeloma in North America. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 357, 2133–2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimopoulos, M.; Spencer, A.; Attal, M.; Prince, H.M.; Harousseau, J.-L.; Dmoszynska, A.; San Miguel, J.; Hellmann, A.; Facon, T.; Foà, R.; et al. Lenalidomide plus Dexamethasone for Relapsed or Refractory Multiple Myeloma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 357, 2123–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anderson, K.C.; Jagannath, S.; Jakubowiak, A.; Lonial, S.; Raje, N.; Alsina, M.; Ghobrial, I.; Knight, R.; Esseltine, D.; Richardson, P. Lenalidomide, Bortezomib, and Dexamethasone in Relapsed/Refractory Multiple Myeloma (MM): Encouraging Outcomes and Tolerability in a Phase II Study. JCO 2009, 27, 8536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, P.G.; Xie, W.; Jagannath, S.; Jakubowiak, A.; Lonial, S.; Raje, N.S.; Alsina, M.; Ghobrial, I.M.; Schlossman, R.L.; Munshi, N.C.; et al. A Phase 2 Trial of Lenalidomide, Bortezomib, and Dexamethasone in Patients with Relapsed and Relapsed/Refractory Myeloma. Blood 2014, 123, 1461–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, A.; Wu, Q.; Luo, S.; Warnick, G.S.; Zakai, N.A.; Libby, E.N.; Gage, B.F.; Garcia, D.A.; Lyman, G.H.; Sanfilippo, K.M. Derivation and Validation of a Risk Assessment Model for Immunomodulatory Drug-Associated Thrombosis Among Patients with Multiple Myeloma. J. Natl Compr. Cancer Netw. 2019, 17, 840–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sanfilippo, K.M.; Luo, S.; Wang, T.-F.; Fiala, M.; Schoen, M.; Wildes, T.M.; Mikhael, J.; Kuderer, N.M.; Calverley, D.C.; Keller, J.; et al. Predicting Venous Thromboembolism in Multiple Myeloma: Development and Validation of the IMPEDE VTE Score. Am. J. Hematol. 2019, 94, 1176–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richardson, P.G.; Hofmeister, C.C.; Siegel, D.; Lonial, S.; Zaki, M.; Hua, Y.; Shah, S.; Wang, J.; Anderson, K.C. MM-005: A Phase 1, Multicenter, Open-Label, Dose-Escalation Study to Determine the Maximum Tolerated Dose for the Combination of Pomalidomide, Bortezomib, and Low-Dose Dexamethasone in Subjects with Relapsed or Refractory Multiple Myeloma. Blood 2012, 120, 727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paludo, J.; Mikhael, J.R.; LaPlant, B.R.; Halvorson, A.E.; Kumar, S.; Gertz, M.A.; Hayman, S.R.; Buadi, F.K.; Dispenzieri, A.; Lust, J.A.; et al. Pomalidomide, Bortezomib, and Dexamethasone for Patients with Relapsed Lenalidomide-Refractory Multiple Myeloma. Blood 2017, 130, 1198–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Richardson, P.G.; Hofmeister, C.C.; Siegel, D.; Lonial, S.; Laubach, J.P.; Efebera, Y.A.; Vesole, D.H.; Nooka, A.K.; Rosenblatt, J.; Raje, N.; et al. MM-005: A Phase 1 Trial of Pomalidomide, Bortezomib, and Low-Dose Dexamethasone (PVD) in Relapsed and/Or Refractory Multiple Myeloma (RRMM). Blood 2013, 122, 1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soekojo, C.Y.; Kim, K.; Huang, S.-Y.; Chim, C.-S.; Takezako, N.; Asaoku, H.; Kimura, H.; Kosugi, H.; Sakamoto, J.; Gopalakrishnan, S.K.; et al. Pomalidomide and Dexamethasone Combination with Additional Cyclophosphamide in Relapsed/Refractory Multiple Myeloma (AMN001)—A Trial by the Asian Myeloma Network. Blood Cancer J. 2019, 9, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baz, R.C.; Martin, T.G.; Lin, H.-Y.; Zhao, X.; Shain, K.H.; Cho, H.J.; Wolf, J.L.; Mahindra, A.; Chari, A.; Sullivan, D.M.; et al. Randomized Multicenter Phase 2 Study of Pomalidomide, Cyclophosphamide, and Dexamethasone in Relapsed Refractory Myeloma. Blood 2016, 127, 2561–2568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garderet, L.; Kuhnowski, F.; Berge, B.; Roussel, M.; Escoffre-Barbe, M.; Lafon, I.; Facon, T.; Leleu, X.; Karlin, L.; Perrot, A.; et al. Pomalidomide, Cyclophosphamide, and Dexamethasone for Relapsed Multiple Myeloma. Blood 2018, 132, 2555–2563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Voorhees, P.M.; Suman, V.J.; Tuchman, S.A.; Laubach, J.P.; Hassoun, H.; Efebera, Y.A.; Mulkey, F.; Bova-Solem, M.; Santo, K.; Carlisle, D.; et al. A Phase I/II Study of Ixazomib, Pomalidomide, and Dexamethasone for Lenalidomide and Proteasome Inhibitor Refractory Multiple Myeloma (Alliance A061202). Am. J. Hematol. 2021, 96, 1595–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, A.; Kapoor, P.; Palmer, J.M.; Tsai, N.-C.; Kumar, S.; Lonial, S.; Htut, M.; Karanes, C.; Nathwani, N.; Rosenzweig, M.; et al. Phase I/II Trial of the Oral Regimen Ixazomib, Pomalidomide, and Dexamethasone in Relapsed/Refractory Multiple Myeloma. Leukemia 2018, 32, 1567–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateos, M.-V.; Ocio, E.M.; Sureda Balari, A.; Oriol, A.; Garcia, E.G.; Moreno, M.J.; Granell, M.; Escalante, F.; Gonzalez De La Calle, V.; Rosinol Dachs, L.; et al. Randomized Phase 2 Study of Weekly Carfilzomib 70 Mg/M2 and Dexamethasone Plus/Minus Cyclophosphamide in Relapsed and/or Refractory Multiple Myeloma (RRMM) Patients (GEM-KyCyDex). Blood 2020, 136, 8–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennipede, D.; Mohyuddin, G.R.; Hawkins, R.; Ganguly, S.; Shune, L.; Ahmed, N.; Mohan, M.; Cui, W.; Mahmoudjafari, Z.; McGuirk, J.; et al. Carfilzomib, Cyclophosphamide, and Dexamethasone (KCd) for the Treatment of Triple-Class Relapsed/Refractory Multiple Myeloma (RRMM). Eur. J. Haematol. 2021, 107, 602–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venner, C.P.; LeBlanc, R.; Sandhu, I.; White, D.; Belch, A.R.; Reece, D.E.; Chen, C.; Dolan, S.; Lalancette, M.; Louzada, M.; et al. Weekly Carfilzomib plus Cyclophosphamide and Dexamethasone in the Treatment of Relapsed/Refractory Multiple Myeloma: Final Results from the MCRN-003/MYX.1 Single Arm Phase II Trial. Am. J. Hematol. 2021, 96, 552–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.K.; Grzasko, N.; Delimpasi, S.; Jedrzejczak, W.W.; Grosicki, S.; Kyrtsonis, M.-C.; Spencer, A.; Gupta, N.; Teng, Z.; Byrne, C.; et al. Phase 2 Study of All-Oral Ixazomib, Cyclophosphamide and Low-Dose Dexamethasone for Relapsed/Refractory Multiple Myeloma. Br. J. Haematol. 2019, 184, 536–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodriguez-Otero, P.; Sirvent, M.; González-Rodríguez, A.P.; Lavilla, E.; de Coca, A.G.; Arguiñano, J.M.; Martí, J.M.; Cabañas, V.; Motlló, C.; de Cabo, E.; et al. Pomalidomide, Cyclophosphamide, and Dexamethasone for the Treatment of Relapsed/Refractory Multiple Myeloma: Real-World Analysis of the Pethema-GEM Experience. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2021, 21, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Donk, N.W.C.J.; Wittebol, S.; Minnema, M.C.; Lokhorst, H.M. Lenalidomide (Revlimid) Combined with Continuous Oral Cyclophosphamide (Endoxan) and Prednisone (REP) Is Effective in Lenalidomide/Dexamethasone-Refractory Myeloma. Br. J. Haematol. 2010, 148, 335–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nijhof, I.S.; Franssen, L.E.; Levin, M.-D.; Bos, G.M.J.; Broijl, A.; Klein, S.K.; Koene, H.R.; Bloem, A.C.; Beeker, A.; Faber, L.M.; et al. Phase 1/2 Study of Lenalidomide Combined with Low-Dose Cyclophosphamide and Prednisone in Lenalidomide-Refractory Multiple Myeloma. Blood 2016, 128, 2297–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sebag, M.; Bahlis, N.; Venner, C.P.; McCurdy, A.; Kouroukis, C.T.; Shustik, J.; White, D.J.; Kotb, R.; Stakiw, J.; Laferriere, N.B.; et al. A Randomized Phase II, Open Label, Study of Daratumumab, Weekly Low-Dose Oral Dexamethasone and Cyclophosphamide with or without Pomalidomide in Patients with Relapsed and Refractory Multiple Myeloma. Blood 2019, 134, 3121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knop, S.; Straka, C.; Haen, M.; Schwedes, R.; Hebart, H.; Einsele, H. The Efficacy and Toxicity of Bendamustine in Recurrent Multiple Myeloma after High-Dose Chemotherapy. Haematologica 2005, 90, 1287–1288. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.K.; Krishnan, A.; LaPlant, B.; Laumann, K.; Roy, V.; Zimmerman, T.; Gertz, M.A.; Buadi, F.K.; Stockerl Goldstein, K.; Birgin, A.; et al. Bendamustine, Lenalidomide, and Dexamethasone (BRD) Is Highly Effective with Durable Responses in Relapsed Multiple Myeloma. Am. J. Hematol. 2015, 90, 1106–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lentzsch, S.; O’Sullivan, A.; Kennedy, R.C.; Abbas, M.; Dai, L.; Pregja, S.L.; Burt, S.; Boyiadzis, M.; Roodman, G.D.; Mapara, M.Y.; et al. Combination of Bendamustine, Lenalidomide, and Dexamethasone (BLD) in Patients with Relapsed or Refractory Multiple Myeloma Is Feasible and Highly Effective: Results of Phase 1/2 Open-Label, Dose Escalation Study. Blood 2012, 119, 4608–4613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivaraj, D.; Green, M.M.; Kang, Y.; Long, G.D.; Rizzieri, D.A.; Li, Z.; Garrett, A.H.; McIntyre, J.L.; Chao, N.J.; Gasparetto, C. Bendamustine, Pomalidomide, and Dexamethasone for Relapsed and/or Refractory Multiple Myeloma. Blood Cancer J. 2018, 8, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ludwig, H.; Kasparu, H.; Leitgeb, C.; Rauch, E.; Linkesch, W.; Zojer, N.; Greil, R.; Seebacher, A.; Pour, L.; Weißmann, A.; et al. Bendamustine-Bortezomib-Dexamethasone Is an Active and Well-Tolerated Regimen in Patients with Relapsed or Refractory Multiple Myeloma. Blood 2014, 123, 985–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Offidani, M.; Corvatta, L.; Maracci, L.; Liberati, A.M.; Ballanti, S.; Attolico, I.; Caraffa, P.; Alesiani, F.; Caravita di Toritto, T.; Gentili, S.; et al. Efficacy and Tolerability of Bendamustine, Bortezomib and Dexamethasone in Patients with Relapsed-Refractory Multiple Myeloma: A Phase II Study. Blood Cancer J. 2013, 3, e162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cerchione, C.; Catalano, L.; Nappi, D.; Rocco, S.; Palmieri, S.; Pareto, A.E.; Musuraca, G.; Lucchesi, A.; Pane, F.; Ferrara, F.; et al. Bendamustine-Bortezomib-Dexamethasone (BVD) in Heavily Pretreated Multiple Myeloma: Old/New in NOVEL Agents’ Era. Blood 2020, 136, 2–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhakal, B.; D’Souza, A.; Hamadani, M.; Arce-Lara, C.; Schroeder, K.; Chhabra, S.; Shah, N.N.; Gauger, K.; Keaton, T.; Pasquini, M.; et al. Phase I/II Trial of Bendamustine, Ixazomib, and Dexamethasone in Relapsed/Refractory Multiple Myeloma. Blood Cancer J. 2019, 9, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gramatzki, M.; Guenther, A.; Offidani, M.; Engelhardt, M.M.; Montefusco, V.; Patriarca, F.; Angelucci, E.; Salvini, M.; Pönisch, W.; Spada, S.; et al. Carfilzomib, Bendamustine, and Dexamethasone (KBd) in Advanced Multiple Myeloma: The EMN09-Trial. JCO 2018, 36, 8019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, P.G.; Oriol, A.; Larocca, A.; Bladé, J.; Cavo, M.; Rodriguez-Otero, P.; Leleu, X.; Nadeem, O.; Hiemenz, J.W.; Hassoun, H.; et al. Melflufen and Dexamethasone in Heavily Pretreated Relapsed and Refractory Multiple Myeloma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 757–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schjesvold, F.H.; Dimopoulos, M.-A.; Delimpasi, S.; Robak, P.; Coriu, D.; Legiec, W.; Pour, L.; Špička, I.; Masszi, T.; Doronin, V.; et al. Melflufen or Pomalidomide plus Dexamethasone for Patients with Multiple Myeloma Refractory to Lenalidomide (OCEAN): A Randomised, Head-to-Head, Open-Label, Phase 3 Study. Lancet Haematol. 2022, 9, e98–e110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashyap, T.; Argueta, C.; Aboukameel, A.; Unger, T.J.; Klebanov, B.; Mohammad, R.M.; Muqbil, I.; Azmi, A.S.; Drolen, C.; Senapedis, W.; et al. Selinexor, a Selective Inhibitor of Nuclear Export (SINE) Compound, Acts through NF-ΚB Deactivation and Combines with Proteasome Inhibitors to Synergistically Induce Tumor Cell Death. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 78883–78895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chari, A.; Vogl, D.T.; Gavriatopoulou, M.; Nooka, A.K.; Yee, A.J.; Huff, C.A.; Moreau, P.; Dingli, D.; Cole, C.; Lonial, S.; et al. Oral Selinexor–Dexamethasone for Triple-Class Refractory Multiple Myeloma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 727–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosicki, S.; Simonova, M.; Spicka, I.; Pour, L.; Kriachok, I.; Gavriatopoulou, M.; Pylypenko, H.; Auner, H.W.; Leleu, X.; Doronin, V.; et al. Once-per-Week Selinexor, Bortezomib, and Dexamethasone versus Twice-per-Week Bortezomib and Dexamethasone in Patients with Multiple Myeloma (BOSTON): A Randomised, Open-Label, Phase 3 Trial. Lancet 2020, 396, 1563–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakubowiak, A.J.; Jasielec, J.K.; Rosenbaum, C.A.; Cole, C.E.; Chari, A.; Mikhael, J.; Nam, J.; McIver, A.; Severson, E.; Stephens, L.A.; et al. Phase 1 Study of Selinexor plus Carfilzomib and Dexamethasone for the Treatment of Relapsed/Refractory Multiple Myeloma. Br. J. Haematol. 2019, 186, 549–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gasparetto, C.; Lentzsch, S.; Schiller, G.; Callander, N.; Tuchman, S.; Chen, C.; White, D.; Kotb, R.; Sutherland, H.; Sebag, M.; et al. Selinexor, Daratumumab, and Dexamethasone in Patients with Relapsed or Refractory Multiple Myeloma. eJHaem 2021, 2, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Otero, P.; Gonzalez De La Calle, V.; Sureda, A.; De Arriba, F.; Reinoso Segura, M.; Ribas, P.; Gonzalez, A.P.; Gonzalez-Montes, Y.; Oriol, A.; Martínez-López, J.; et al. Selinexor in Combination with Daratumumab-Bortezomib and Dexamethasone for the Treatment of Relapse or Refractory Multiple Myeloma: Initial Results of the Phase 2, Open-Label, Multicenter GEM-Selibordara Study. Blood 2021, 138, 1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paner, A.; Patel, P.; Dhakal, B. The Evolving Role of Translocation t(11;14) in the Biology, Prognosis, and Management of Multiple Myeloma. Blood Rev. 2020, 41, 100643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slomp, A.; Peperzak, V. Role and Regulation of Pro-Survival BCL-2 Proteins in Multiple Myeloma. Front Oncol. 2018, 8, 533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, V.A.; Ackley, J.; Kaufman, J.L.; Boise, L.H. BCL2 Family Inhibitors in the Biology and Treatment of Multiple Myeloma. Blood Lymphat. Cancer 2021, 11, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaxman, I.; Sidiqi, M.H.; Gertz, M. Venetoclax for the Treatment of Multiple Myeloma. Expert Rev. Hematol. 2018, 11, 915–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davids, M.S.; Roberts, A.W.; Seymour, J.F.; Pagel, J.M.; Kahl, B.S.; Wierda, W.G.; Puvvada, S.; Kipps, T.J.; Anderson, M.A.; Salem, A.H.; et al. Phase I First-in-Human Study of Venetoclax in Patients With Relapsed or Refractory Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 826–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kumar, S.K.; Harrison, S.J.; Cavo, M.; de la Rubia, J.; Popat, R.; Gasparetto, C.; Hungria, V.; Salwender, H.; Suzuki, K.; Kim, I.; et al. Venetoclax or Placebo in Combination with Bortezomib and Dexamethasone in Patients with Relapsed or Refractory Multiple Myeloma (BELLINI): A Randomised, Double-Blind, Multicentre, Phase 3 Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, 1630–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, L.J.; Davies, F.E.; Monohan, G.P.; Kovacsovics, T.; Burwick, N.; Jakubowiak, A.; Kaufman, J.L.; Hong, W.-J.; Dail, M.; Salem, A.H.; et al. Phase 2 Study of Venetoclax plus Carfilzomib and Dexamethasone in Patients with Relapsed/Refractory Multiple Myeloma. Blood Adv. 2021, 5, 3748–3759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahlis, N.J.; Baz, R.; Harrison, S.J.; Quach, H.; Ho, S.-J.; Vangsted, A.J.; Plesner, T.; Moreau, P.; Gibbs, S.D.; Coppola, S.; et al. Phase I Study of Venetoclax Plus Daratumumab and Dexamethasone, With or Without Bortezomib, in Patients with Relapsed or Refractory Multiple Myeloma With and Without t(11;14). JCO 2021, 39, 3602–3612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overdijk, M.B.; Verploegen, S.; Bögels, M.; van Egmond, M.; Lammerts van Bueren, J.J.; Mutis, T.; Groen, R.W.J.; Breij, E.; Martens, A.C.M.; Bleeker, W.K.; et al. Antibody-Mediated Phagocytosis Contributes to the Anti-Tumor Activity of the Therapeutic Antibody Daratumumab in Lymphoma and Multiple Myeloma. MAbs 2015, 7, 311–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overdijk, M.B.; Jansen, J.H.M.; Nederend, M.; Lammerts van Bueren, J.J.; Groen, R.W.J.; Parren, P.W.H.I.; Leusen, J.H.W.; Boross, P. The Therapeutic CD38 Monoclonal Antibody Daratumumab Induces Programmed Cell Death via Fcγ Receptor-Mediated Cross-Linking. J. Immunol. 2016, 197, 807–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dima, D.; Dower, J.; Comenzo, R.L.; Varga, C. Evaluating Daratumumab in the Treatment of Multiple Myeloma: Safety, Efficacy and Place in Therapy. Cancer Manag. Res. 2020, 12, 7891–7903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lonial, S.; Weiss, B.M.; Usmani, S.Z.; Singhal, S.; Chari, A.; Bahlis, N.J.; Belch, A.; Krishnan, A.; Vescio, R.A.; Mateos, M.V.; et al. Daratumumab Monotherapy in Patients with Treatment-Refractory Multiple Myeloma (SIRIUS): An Open-Label, Randomised, Phase 2 Trial. Lancet 2016, 387, 1551–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plesner, T.; Arkenau, H.-T.; Gay, F.; Minnema, M.C.; Boccadoro, M.; Moreau, P.; Cavenagh, J.; Perrot, A.; Laubach, J.P.; Krejcik, J.; et al. Enduring Efficacy and Tolerability of Daratumumab in Combination with Lenalidomide and Dexamethasone in Patients with Relapsed or Relapsed/Refractory Multiple Myeloma (GEN503): Final Results of an Open-Label, Phase 1/2 Study. Br. J. Haematol. 2019, 186, e35–e39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Palumbo, A.; Chanan-Khan, A.; Weisel, K.; Nooka, A.K.; Masszi, T.; Beksac, M.; Spicka, I.; Hungria, V.; Munder, M.; Mateos, M.V.; et al. Daratumumab, Bortezomib, and Dexamethasone for Multiple Myeloma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 754–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Facon, T.; Kumar, S.; Plesner, T.; Orlowski, R.Z.; Moreau, P.; Bahlis, N.; Basu, S.; Nahi, H.; Hulin, C.; Quach, H.; et al. Daratumumab plus Lenalidomide and Dexamethasone for Untreated Myeloma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 2104–2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spencer, A.; Lentzsch, S.; Weisel, K.; Avet-Loiseau, H.; Mark, T.M.; Spicka, I.; Masszi, T.; Lauri, B.; Levin, M.-D.; Bosi, A.; et al. Daratumumab plus Bortezomib and Dexamethasone versus Bortezomib and Dexamethasone in Relapsed or Refractory Multiple Myeloma: Updated Analysis of CASTOR. Haematologica 2018, 103, 2079–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sonneveld, P.; Chanan-Khan, A.; Weisel, K.; Nooka, A.K.; Masszi, T.; Beksac, M.; Spicka, I.; Hungria, V.; Munder, M.; Mateos, M.-V.; et al. Overall Survival With Daratumumab, Bortezomib, and Dexamethasone in Previously Treated Multiple Myeloma (CASTOR): A Randomized, Open-Label, Phase III Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 41, 1600–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spencer, A.; Moreau, P.; Mateos, M.-V.; Goldschmidt, H.; Suzuki, K.; Levin, M.-D.; Sonneveld, P.; Yoon, S.-S.; Usmani, S.Z.; Weisel, K.; et al. Daratumumab (DARA) in Combination with Bortezomib plus Dexamethasone (D-Vd) or Lenalidomide plus Dexamethasone (D-Rd) in Relapsed or Refractory Multiple Myeloma (RRMM): Subgroup Analysis of the Phase 3 CASTOR and POLLUX Studies in Patients (Pts) with Early or Late Relapse after Initial Therapy. JCO 2022, 40, 8052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateos, M.-V.; Sonneveld, P.; Hungria, V.; Nooka, A.K.; Estell, J.A.; Barreto, W.; Corradini, P.; Min, C.-K.; Medvedova, E.; Weisel, K.; et al. Daratumumab, Bortezomib, and Dexamethasone Versus Bortezomib and Dexamethasone in Patients with Previously Treated Multiple Myeloma: Three-Year Follow-up of CASTOR. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2020, 20, 509–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bahlis, N.J.; Dimopoulos, M.A.; White, D.J.; Benboubker, L.; Cook, G.; Leiba, M.; Ho, P.J.; Kim, K.; Takezako, N.; Moreau, P.; et al. Daratumumab plus Lenalidomide and Dexamethasone in Relapsed/Refractory Multiple Myeloma: Extended Follow-up of POLLUX, a Randomized, Open-Label, Phase 3 Study. Leukemia 2020, 34, 1875–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dimopoulos, M.; Quach, H.; Mateos, M.-V.; Landgren, O.; Leleu, X.; Siegel, D.; Weisel, K.; Yang, H.; Klippel, Z.; Zahlten-Kumeli, A.; et al. Carfilzomib, Dexamethasone, and Daratumumab versus Carfilzomib and Dexamethasone for Patients with Relapsed or Refractory Multiple Myeloma (CANDOR): Results from a Randomised, Multicentre, Open-Label, Phase 3 Study. Lancet 2020, 396, 186–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usmani, S.Z.; Quach, H.; Mateos, M.-V.; Landgren, O.; Leleu, X.; Siegel, D.S.; Weisel, K.; Yang, H.; Klippel, Z.K.; Zahlten-Kumeli, A.; et al. Carfilzomib, Dexamethasone, and Daratumumab Versus Carfilzomib and Dexamethasone for the Treatment of Patients with Relapsed or Refractory Multiple Myeloma (RRMM): Primary Analysis Results from the Randomized, Open-Label, Phase 3 Study Candor (NCT03158688). Blood 2019, 134, LBA-6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimopoulos, M.A.; Quach, H.; Mateos, M.-V.; Landgren, O.; Leleu, X.; Siegel, D.S.; Weisel, K.; Gavriatopoulou, M.; Oriol, A.; Rabin, N.K.; et al. Carfilzomib, Dexamethasone, and Daratumumab Versus Carfilzomib and Dexamethasone in Relapsed or Refractory Multiple Myeloma: Updated Efficacy and Safety Results of the Phase 3 Candor Study. Blood 2020, 136, 26–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usmani, S.Z.; Quach, H.; Mateos, M.-V.; Landgren, O.; Leleu, X.; Siegel, D.; Weisel, K.; Gavriatopoulou, M.; Oriol, A.; Rabin, N.; et al. Carfilzomib, Dexamethasone, and Daratumumab versus Carfilzomib and Dexamethasone for Patients with Relapsed or Refractory Multiple Myeloma (CANDOR): Updated Outcomes from a Randomised, Multicentre, Open-Label, Phase 3 Study. Lancet Oncol. 2022, 23, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimopoulos, M.A.; Terpos, E.; Boccadoro, M.; Delimpasi, S.; Beksac, M.; Katodritou, E.; Moreau, P.; Baldini, L.; Symeonidis, A.; Bila, J.; et al. Daratumumab plus Pomalidomide and Dexamethasone versus Pomalidomide and Dexamethasone Alone in Previously Treated Multiple Myeloma (APOLLO): An Open-Label, Randomised, Phase 3 Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2021, 22, 801–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yee, A.J.; Nadeem, O.; Rosenblatt, J.; Bianchi, G.; O’Donnell, E.; Branagan, A.R.; Harrington, C.C.; Agyemang, E.A.; Gammon, M.T.; Lively, K.J.; et al. A Phase II Study of Daratumumab with Weekly Carfilzomib, Pomalidomide, and Dexamethasone in Relapsed and Refractory Multiple Myeloma. JCO 2022, 40, 8012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasielec, J.; Zonder, J.; Derman, B.A.; Reece, D.E.; Cole, C.E.; Berdeja, J.G.; Wolfe, B.; Major, S.; Tinari, K.M.; Stefka, A.; et al. Daratumumab (DARA) Plus Carfilzomib, Pomalidomide, Dexamethasone (KPd) in Lenalidomide Refractory Multiple Myeloma (MM): A Multi-Center MMRC Study. Blood 2020, 136, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.D.; Padilla, M.; Liu, L.; Pu, M.; Pittman, E.; Tzachanis, D.; Larson, S.M.; Shah, N.; Mulroney, C.M.; Ball, E.D.; et al. Phase II Study of the Combination of Daratumumab, Ixazomib, Pomalidomide, and Dexamethasone as Salvage Therapy in Relapsed/Refractory Multiple Myeloma: Stage 2 Interim Results. JCO 2022, 40, 8041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attal, M.; Richardson, P.G.; Rajkumar, S.V.; San-Miguel, J.; Beksac, M.; Spicka, I.; Leleu, X.; Schjesvold, F.; Moreau, P.; Dimopoulos, M.A.; et al. Isatuximab plus Pomalidomide and Low-Dose Dexamethasone versus Pomalidomide and Low-Dose Dexamethasone in Patients with Relapsed and Refractory Multiple Myeloma (ICARIA-MM): A Randomised, Multicentre, Open-Label, Phase 3 Study. Lancet 2019, 394, 2096–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, P.G.; Perrot, A.; San-Miguel, J.; Beksac, M.; Spicka, I.; Leleu, X.; Schjesvold, F.; Moreau, P.; Dimopoulos, M.A.; Huang, J.S.-Y.; et al. Isatuximab plus Pomalidomide and Low-Dose Dexamethasone versus Pomalidomide and Low-Dose Dexamethasone in Patients with Relapsed and Refractory Multiple Myeloma (ICARIA-MM): Follow-up Analysis of a Randomised, Phase 3 Study. Lancet Oncol. 2022, 23, 416–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreau, P.; Dimopoulos, M.-A.; Mikhael, J.; Yong, K.; Capra, M.; Facon, T.; Hajek, R.; Špička, I.; Baker, R.; Kim, K.; et al. Isatuximab, Carfilzomib, and Dexamethasone in Relapsed Multiple Myeloma (IKEMA): A Multicentre, Open-Label, Randomised Phase 3 Trial. Lancet 2021, 397, 2361–2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimopoulos, M.; Bringhen, S.; Anttila, P.; Capra, M.; Cavo, M.; Cole, C.; Gasparetto, C.; Hungria, V.; Jenner, M.; Vorobyev, V.; et al. Isatuximab as Monotherapy and Combined with Dexamethasone in Patients with Relapsed/Refractory Multiple Myeloma. Blood 2021, 137, 1154–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bringhen, S.; Pour, L.; Vorobyev, V.; Vural, F.; Warzocha, K.; Benboubker, L.; Koh, Y.; Maisnar, V.; Karlin, L.; Pavic, M.; et al. Isatuximab plus Pomalidomide and Dexamethasone in Patients with Relapsed/Refractory Multiple Myeloma According to Prior Lines of Treatment and Refractory Status: ICARIA-MM Subgroup Analysis. Leuk. Res. 2021, 104, 106576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Facon, T.; Moreau, P.; Baker, R.; Pour, L.; Min, C.-K.; Leleu, X.; Mohty, M.; Karlin, L.; Rawlings, A.; Tekle, C.; et al. Isatuximab Plus Carfilzomib and Dexamethasone in Patients with Early Versus Late Relapsed Multiple Myeloma: Ikema Subgroup Analysis. Blood 2022, 140, 1820–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veillette, A.; Guo, H. CS1, a SLAM Family Receptor Involved in Immune Regulation, Is a Therapeutic Target in Multiple Myeloma. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2013, 88, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Sanchez, L.; Siegel, D.S.; Wang, M.L. Elotuzumab for the Treatment of Multiple Myeloma. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2016, 9, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lonial, S.; Dimopoulos, M.; Palumbo, A.; White, D.; Grosicki, S.; Spicka, I.; Walter-Croneck, A.; Moreau, P.; Mateos, M.-V.; Magen, H.; et al. Elotuzumab Therapy for Relapsed or Refractory Multiple Myeloma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 621–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dimopoulos, M.A.; Dytfeld, D.; Grosicki, S.; Moreau, P.; Takezako, N.; Hori, M.; Leleu, X.; LeBlanc, R.; Suzuki, K.; Raab, M.S.; et al. Elotuzumab plus Pomalidomide and Dexamethasone for Multiple Myeloma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 1811–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuchikama, K.; An, Z. Antibody-Drug Conjugates: Recent Advances in Conjugation and Linker Chemistries. Protein Cell 2018, 9, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, B.; Jiang, T.; Liu, D. BCMA-Targeted Immunotherapy for Multiple Myeloma. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 13, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, Y.-T.; Mayes, P.A.; Acharya, C.; Zhong, M.Y.; Cea, M.; Cagnetta, A.; Craigen, J.; Yates, J.; Gliddon, L.; Fieles, W.; et al. Novel Anti-B-Cell Maturation Antigen Antibody-Drug Conjugate (GSK2857916) Selectively Induces Killing of Multiple Myeloma. Blood 2014, 123, 3128–3138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Trudel, S.; Lendvai, N.; Popat, R.; Voorhees, P.M.; Reeves, B.; Libby, E.N.; Richardson, P.G.; Anderson, L.D.; Sutherland, H.J.; Yong, K.; et al. Targeting B-Cell Maturation Antigen with GSK2857916 Antibody-Drug Conjugate in Relapsed or Refractory Multiple Myeloma (BMA117159): A Dose Escalation and Expansion Phase 1 Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2018, 19, 1641–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trudel, S.; Lendvai, N.; Popat, R.; Voorhees, P.M.; Reeves, B.; Libby, E.N.; Richardson, P.G.; Hoos, A.; Gupta, I.; Bragulat, V.; et al. Antibody-Drug Conjugate, GSK2857916, in Relapsed/Refractory Multiple Myeloma: An Update on Safety and Efficacy from Dose Expansion Phase I Study. Blood Cancer J. 2019, 9, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lonial, S.; Lee, H.C.; Badros, A.; Trudel, S.; Nooka, A.K.; Chari, A.; Abdallah, A.-O.; Callander, N.; Lendvai, N.; Sborov, D.; et al. Belantamab Mafodotin for Relapsed or Refractory Multiple Myeloma (DREAMM-2): A Two-Arm, Randomised, Open-Label, Phase 2 Study. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, 207–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, P.G.; Lee, H.C.; Abdallah, A.-O.; Cohen, A.D.; Kapoor, P.; Voorhees, P.M.; Hoos, A.; Wang, K.; Baron, J.; Piontek, T.; et al. Single-Agent Belantamab Mafodotin for Relapsed/Refractory Multiple Myeloma: Analysis of the Lyophilised Presentation Cohort from the Pivotal DREAMM-2 Study. Blood Cancer J. 2020, 10, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lonial, S.; Lee, H.C.; Badros, A.; Trudel, S.; Nooka, A.K.; Chari, A.; Abdallah, A.-O.; Callander, N.; Sborov, D.; Suvannasankha, A.; et al. Longer Term Outcomes with Single-Agent Belantamab Mafodotin in Patients with Relapsed or Refractory Multiple Myeloma: 13-Month Follow-up from the Pivotal DREAMM-2 Study. Cancer 2021, 127, 4198–4212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suvannasankha, A.; Bahlis, N.J.; Trudel, S.; Weisel, K.; Koenecke, C.; Oriol Rocafiguera, A.; Voorhees, P.M.; Alonso, A.A.; Callander, N.S.; Mateos, M.-V.; et al. Safety and Clinical Activity of Belantamab Mafodotin with Pembrolizumab in Patients with Relapsed/Refractory Multiple Myeloma (RRMM): DREAMM-4 Study. JCO 2022, 40, 8018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lonial, S.; Grosicki, S.; Hus, M.; Song, K.W.; Facon, T.; Callander, N.S.; Ribrag, V.; Uttervall, K.; Quach, H.; Vorobyev, V.I.; et al. Synergistic Effects of Low-Dose Belantamab Mafodotin in Combination with a Gamma-Secretase Inhibitor (Nirogacestat) in Patients with Relapsed/Refractory Multiple Myeloma (RRMM): DREAMM-5 Study. JCO 2022, 40, 8019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nooka, A.K.; Stockerl-Goldstein, K.; Quach, H.; Forbes, A.; Mateos, M.-V.; Khot, A.; Tan, A.; Abonour, R.; Chopra, B.; Rogers, R.; et al. DREAMM-6: Safety and Tolerability of Belantamab Mafodotin in Combination with Bortezomib/Dexamethasone in Relapsed/Refractory Multiple Myeloma (RRMM). JCO 2020, 38, 8502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popat, R.; Nooka, A.; Stockerl-Goldstein, K.; Abonour, R.; Ramaekers, R.; Khot, A.; Forbes, A.; Lee, C.; Augustson, B.; Spencer, A.; et al. DREAMM-6: Safety, Tolerability and Clinical Activity of Belantamab Mafodotin (Belamaf) in Combination with Bortezomib/Dexamethasone (BorDex) in Relapsed/Refractory Multiple Myeloma (RRMM). Blood 2020, 136, 19–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trudel, S. Part 1 Results of a Dose Finding Study of Belantamab Mafodotin (GSK2857916) in Combination with Pomalidomide (POM) and Dexamethasone (DEX) for the Treatment of Relapsed/Refractory Multiple Myeloma (RRMM). Blood 2020, 136, 725. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.C.; Raje, N.S.; Landgren, O.; Upreti, V.V.; Wang, J.; Avilion, A.A.; Hu, X.; Rasmussen, E.; Ngarmchamnanrith, G.; Fujii, H.; et al. Phase 1 Study of the Anti-BCMA Antibody-Drug Conjugate AMG 224 in Patients with Relapsed/Refractory Multiple Myeloma. Leukemia 2021, 35, 255–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.K.; Migkou, M.; Bhutani, M.; Spencer, A.; Ailawadhi, S.; Kalff, A.; Walcott, F.; Pore, N.; Gibson, D.; Wang, F.; et al. Phase 1, First-in-Human Study of MEDI2228, a BCMA-Targeted ADC in Patients with Relapsed/Refractory Multiple Myeloma. Blood 2020, 136, 26–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willert, E.K.; Robinson, G.L.; Higgins, J.P.; Liu, J.; Lee, J.; Syed, S.; Zhang, Y.; Tavares, D.; Lublinsky, A.; Chattopadhyay, N.; et al. Abstract 2384: TAK-169, an Exceptionally Potent CD38 Targeted Engineered Toxin Body, as a Novel Direct Cell Kill Approach for the Treatment of Multiple Myeloma. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogl, D.T.; Kaufman, J.L.; Holstein, S.A.; Nadeem, O.; O’Donnell, E.; Suryanarayan, K.; Collins, S.; Parot, X.; Chaudhry, M. TAK-573, an Anti-CD38/Attenuated Ifnα Fusion Protein, Has Clinical Activity and Modulates the Ifnα Receptor (IFNAR) Pathway in Patients with Relapsed/Refractory Multiple Myeloma. Blood 2020, 136, 37–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherbenou, D.W.; Aftab, B.T.; Su, Y.; Behrens, C.R.; Wiita, A.; Logan, A.C.; Acosta-Alvear, D.; Hann, B.C.; Walter, P.; Shuman, M.A.; et al. Antibody-Drug Conjugate Targeting CD46 Eliminates Multiple Myeloma Cells. J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 126, 4640–4653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, N.N.; Krishnan, A.Y.; Shah, N.D.; Burke, J.M.; Melear, J.M.; Spira, A.I.; Popplewell, L.L.; Andreadis, C.B.; Chhabra, S.; Sharman, J.P.; et al. Preliminary Results of a Phase 1 Dose Escalation Study of the First-in-Class Anti-CD74 Antibody Drug Conjugate (ADC), STRO-001, in Patients with Advanced B-Cell Malignancies. Blood 2019, 134, 5329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadelain, M.; Brentjens, R.; Rivière, I. The Basic Principles of Chimeric Antigen Receptor Design. Cancer Discov. 2013, 3, 388–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lim, W.A.; June, C.H. The Principles of Engineering Immune Cells to Treat Cancer. Cell 2017, 168, 724–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Rivière, I. Clinical Manufacturing of CAR T Cells: Foundation of a Promising Therapy. Mol. Ther. Oncolytics 2016, 3, 16015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cohen, A.D.; Garfall, A.L.; Stadtmauer, E.A.; Melenhorst, J.J.; Lacey, S.F.; Lancaster, E.; Vogl, D.T.; Weiss, B.M.; Dengel, K.; Nelson, A.; et al. B Cell Maturation Antigen-Specific CAR T Cells Are Clinically Active in Multiple Myeloma. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 129, 2210–2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raje, N.; Berdeja, J.; Lin, Y.; Siegel, D.; Jagannath, S.; Madduri, D.; Liedtke, M.; Rosenblatt, J.; Maus, M.V.; Turka, A.; et al. Anti-BCMA CAR T-Cell Therapy Bb2121 in Relapsed or Refractory Multiple Myeloma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 1726–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munshi, N.C.; Anderson, L.D.; Shah, N.; Madduri, D.; Berdeja, J.; Lonial, S.; Raje, N.; Lin, Y.; Siegel, D.; Oriol, A.; et al. Idecabtagene Vicleucel in Relapsed and Refractory Multiple Myeloma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 705–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Otero, P.; Ailawadhi, S.; Arnulf, B.; Patel, K.; Cavo, M.; Nooka, A.K.; Manier, S.; Callander, N.; Costa, L.J.; Vij, R.; et al. Ide-Cel or Standard Regimens in Relapsed and Refractory Multiple Myeloma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 1002–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, D.K.; Sidana, S.; Peres, L.C.; Colin Leitzinger, C.; Shune, L.; Shrewsbury, A.; Gonzalez, R.; Sborov, D.W.; Wagner, C.; Dima, D.; et al. Idecabtagene Vicleucel for Relapsed/Refractory Multiple Myeloma: Real-World Experience from the Myeloma CAR T Consortium. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, JCO2201365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raje, N.S.; Shah, N.; Jagannath, S.; Kaufman, J.L.; Siegel, D.S.; Munshi, N.C.; Rosenblatt, J.; Lin, Y.; Jakubowiak, A.; Timm, A.; et al. Updated Clinical and Correlative Results from the Phase I CRB-402 Study of the BCMA-Targeted CAR T Cell Therapy Bb21217 in Patients with Relapsed and Refractory Multiple Myeloma. Blood 2021, 138, 548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berdeja, J.G.; Madduri, D.; Usmani, S.Z.; Jakubowiak, A.; Agha, M.; Cohen, A.D.; Stewart, A.K.; Hari, P.; Htut, M.; Lesokhin, A.; et al. Ciltacabtagene Autoleucel, a B-Cell Maturation Antigen-Directed Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-Cell Therapy in Patients with Relapsed or Refractory Multiple Myeloma (CARTITUDE-1): A Phase 1b/2 Open-Label Study. Lancet 2021, 398, 314–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usmani, S.Z.; Martin, T.G.; Berdeja, J.G.; Jakubowiak, A.J.; Agha, M.E.; Cohen, A.D.; Deol, A.; Htut, M.; Lesokhin, A.M.; Munshi, N.C.; et al. Phase 1b/2 Study of Ciltacabtagene Autoleucel, a BCMA-Directed CAR-T Cell Therapy, in Patients with Relapsed/Refractory Multiple Myeloma (CARTITUDE-1): Two Years Post-LPI. JCO 2022, 40, 8028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, T.; Usmani, S.Z.; Berdeja, J.G.; Agha, M.; Cohen, A.D.; Hari, P.; Avigan, D.; Deol, A.; Htut, M.; Lesokhin, A.; et al. Ciltacabtagene Autoleucel, an Anti–B-Cell Maturation Antigen Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-Cell Therapy, for Relapsed/Refractory Multiple Myeloma: CARTITUDE-1 2-Year Follow-Up. JCO 2022, 41, 1265–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansal, R.; Baksh, M.; Larsen, J.T.; Hathcock, M.; Dingli, D.; Stewart, K.; Kapoor, P.; Kourelis, T.; Hayman, S.R.; Warsame, R.M.; et al. Prognostic Value of Early Bone Marrow MRD Status in CAR-T Therapy for Myeloma. JCO 2022, 40, 8022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delforge, M.; Shah, N.; Miguel, J.S.F.; Braverman, J.; Dhanda, D.S.; Shi, L.; Guo, S.; Yu, P.; Liao, W.; Campbell, T.B.; et al. Health-Related Quality of Life with Idecabtagene Vicleucel in Relapsed and Refractory Multiple Myeloma. Blood Adv. 2022, 6, 1309–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costello, C.L.; Gregory, T.K.; Ali, S.A.; Berdeja, J.G.; Patel, K.K.; Shah, N.D.; Ostertag, E.; Martin, C.; Ghoddusi, M.; Shedlock, D.J.; et al. Phase 2 Study of the Response and Safety of P-Bcma-101 CAR-T Cells in Patients with Relapsed/Refractory (r/r) Multiple Myeloma (MM) (PRIME). Blood 2019, 134, 3184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frigault, M.J.; Rosenblatt, J.; Cook, D.; Cho, H.N.; Depinho, G.D.; Logan, E.; Liegel, J.; Prabhakar, Y.; Cornwell, C.; Banerjee, K.; et al. Phase 1 Study of CART-DdBCMA in Relapsed or Refractory Multiple Myeloma. JCO 2022, 40, 8003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, T.C.Y.; Xu, N.; Nordon, R.; Haber, M.; Micklethwaite, K.; Dolnikov, A. Donor T Cells for CAR T Cell Therapy. Biomark. Res. 2022, 10, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mailankody, S.; Matous, J.V.; Liedtke, M.; Sidana, S.; Malik, S.; Nath, R.; Oluwole, O.O.; Karski, E.E.; Lovelace, W.; Zhou, X.; et al. Universal: An Allogeneic First-in-Human Study of the Anti-Bcma ALLO-715 and the Anti-CD52 ALLO-647 in Relapsed/Refractory Multiple Myeloma. Blood 2020, 136, 24–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontermann, R.E.; Brinkmann, U. Bispecific Antibodies. Drug Discov. Today 2015, 20, 838–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lancman, G.; Sastow, D.L.; Cho, H.J.; Jagannath, S.; Madduri, D.; Parekh, S.S.; Richard, S.; Richter, J.; Sanchez, L.; Chari, A. Bispecific Antibodies in Multiple Myeloma: Present and Future. Blood Cancer Discov. 2021, 2, 423–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usmani, S.Z.; Garfall, A.L.; van de Donk, N.W.C.J.; Nahi, H.; San-Miguel, J.F.; Oriol, A.; Rosinol, L.; Chari, A.; Bhutani, M.; Karlin, L.; et al. Teclistamab, a B-Cell Maturation Antigen × CD3 Bispecific Antibody, in Patients with Relapsed or Refractory Multiple Myeloma (MajesTEC-1): A Multicentre, Open-Label, Single-Arm, Phase 1 Study. Lancet 2021, 398, 665–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreau, P.; Garfall, A.L.; van de Donk, N.W.C.J.; Nahi, H.; San-Miguel, J.F.; Oriol, A.; Nooka, A.K.; Martin, T.; Rosinol, L.; Chari, A.; et al. Teclistamab in Relapsed or Refractory Multiple Myeloma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 495–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Otero, P.; D’Souza, A.; Reece, D.E.; van de Donk, N.W.C.J.; Chari, A.; Krishnan, A.Y.; Martin, T.G.; Mateos, M.-V.; Morillo, D.; Hurd, D.D.; et al. A Novel, Immunotherapy-Based Approach for the Treatment of Relapsed/Refractory Multiple Myeloma (RRMM): Updated Phase 1b Results for Daratumumab in Combination with Teclistamab (a BCMA x CD3 Bispecific Antibody). JCO 2022, 40, 8032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, A.Y.; Nooka, A.K.; Chari, A.; Garfall, A.L.; Martin, T.G.; Nair, S.; Lin, X.; Qi, K.; Londhe, A.; Pei, L.; et al. Comparative Effectiveness of Teclistamab versus Real-World Treatments for Patients with Triple-Class Exposed (TCE), Relapsed/Refractory Multiple Myeloma (RRMM). JCO 2022, 40, 8036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateos, M.-V.; Bahlis, N.J.; Costa, L.J.; Perrot, A.; Pei, L.; Rubin, M.L.; Lantz, K.; Sun, W.; Jaffe, M.; Kobos, R.; et al. MajesTEC-3: Randomized, Phase 3 Study of Teclistamab plus Daratumumab versus Investigator’s Choice of Daratumumab, Pomalidomide, and Dexamethasone or Daratumumab, Bortezomib, and Dexamethasone in Patients with Relapsed/Refractory Multiple Myeloma. JCO 2022, 40, 1891–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chari, A.; Touzeau, C.; Schinke, C.; Minnema, M.C.; Berdeja, J.; Oriol, A.; Van De Donk, N.W.; Rodriguez Otero, P.; Askari, E.; Mateos, M.-V.; et al. Talquetamab, a G Protein-Coupled Receptor Family C Group 5 Member D x CD3 Bispecific Antibody, in Patients with Relapsed/Refractory Multiple Myeloma (RRMM): Phase 1/2 Results from MonumenTAL-1. Blood 2022, 140, 384–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minnema, M.C.; Krishnan, A.Y.; Berdeja, J.G.; Oriol Rocafiguera, A.; van de Donk, N.W.C.J.; Rodríguez-Otero, P.; Morillo, D.; Mateos, M.-V.; Costa, L.J.; Caers, J.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Talquetamab, a G Protein-Coupled Receptor Family C Group 5 Member D x CD3 Bispecific Antibody, in Patients with Relapsed/Refractory Multiple Myeloma (RRMM): Updated Results from MonumenTAL-1. JCO 2022, 40, 8015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chari, A.; Minnema, M.C.; Berdeja, J.G.; Oriol, A.; van de Donk, N.W.C.J.; Rodríguez-Otero, P.; Askari, E.; Mateos, M.-V.; Costa, L.J.; Caers, J.; et al. Talquetamab, a T-Cell–Redirecting GPRC5D Bispecific Antibody for Multiple Myeloma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 2232–2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Topp, M.S.; Duell, J.; Zugmaier, G.; Attal, M.; Moreau, P.; Langer, C.; Krönke, J.; Facon, T.; Salnikov, A.V.; Lesley, R.; et al. Anti-B-Cell Maturation Antigen BiTE Molecule AMG 420 Induces Responses in Multiple Myeloma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 775–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahlis, N.J.; Raje, N.S.; Costello, C.; Dholaria, B.R.; Solh, M.M.; Levy, M.Y.; Tomasson, M.H.; Dube, H.; Liu, F.; Liao, K.H.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Elranatamab (PF-06863135), a B-Cell Maturation Antigen (BCMA)-CD3 Bispecific Antibody, in Patients with Relapsed or Refractory Multiple Myeloma (MM). JCO 2021, 39, 8006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesokhin, A.M.; Arnulf, B.; Niesvizky, R.; Mohty, M.; Bahlis, N.J.; Tomasson, M.H.; Rodríguez-Otero, P.; Quach, H.; Raje, N.S.; Iida, S.; et al. Initial Safety Results for MagnetisMM-3: A Phase 2 Trial of Elranatamab, a B-Cell Maturation Antigen (BCMA)-CD3 Bispecific Antibody, in Patients (Pts) with Relapsed/Refractory (R/R) Multiple Myeloma (MM). JCO 2022, 40, 8006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Souza, A.; Shah, N.; Rodriguez, C.; Voorhees, P.M.; Weisel, K.; Bueno, O.F.; Pothacamury, R.K.; Freise, K.J.; Yue, S.; Ross, J.A.; et al. A Phase I First-in-Human Study of ABBV-383, a B-Cell Maturation Antigen × CD3 Bispecific T-Cell Redirecting Antibody, in Patients With Relapsed/Refractory Multiple Myeloma. JCO 2022, 40, 3576–3586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldschmidt, H.; Baertsch, M.-A.; Schlenzka, J.; Becker, N.; Habermehl, C.; Hielscher, T.; Raab, M.-S.; Hillengass, J.; Sauer, S.; Müller-Tidow, C.; et al. Salvage Autologous Transplant and Lenalidomide Maintenance vs. Lenalidomide/Dexamethasone for Relapsed Multiple Myeloma: The Randomized GMMG Phase III Trial ReLApsE. Leukemia 2021, 35, 1134–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baertsch, M.-A.; Schlenzka, J.; Christina, H.; Hielscher, T.; Raab, M.S.; Hillengass, J.; Müller-Tidow, C.; Luntz, S.; Jauch, A.; Brossart, P.; et al. Subgroup Analyses of the Randomized GMMG Phase III Multicenter Trial Relapse Suggest Survival Benefit of Salvage Autologous Transplant Primarily in Low Risk Multiple Myeloma. Blood 2018, 132, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, G.; Ashcroft, A.J.; Cairns, D.A.; Williams, C.D.; Brown, J.M.; Cavenagh, J.D.; Snowden, J.A.; Parrish, C.; Yong, K.; Cavet, J.; et al. The Effect of Salvage Autologous Stem-Cell Transplantation on Overall Survival in Patients with Relapsed Multiple Myeloma (Final Results from BSBMT/UKMF Myeloma X Relapse [Intensive]): A Randomised, Open-Label, Phase 3 Trial. Lancet Haematol. 2016, 3, e340–e351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dhakal, B.; D’Souza, A.; Kleman, A.; Chhabra, S.; Mohan, M.; Hari, P. Salvage Second Transplantation in Relapsed Multiple Myeloma. Leukemia 2021, 35, 1214–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baertsch, M.-A.; Fougereau, M.; Hielscher, T.; Sauer, S.; Breitkreutz, I.; Jordan, K.; Müller-Tidow, C.; Goldschmidt, H.; Raab, M.-S.; Hillengass, J.; et al. Carfilzomib, Lenalidomide, and Dexamethasone Followed by Salvage Autologous Stem Cell Transplant with or without Maintenance for Relapsed or Refractory Multiple Myeloma. Cancers 2021, 13, 4706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, G.; Bal, S.; Rodriguez, C.; Chhabra, S.; Bayer, R.; Costa, L.; Lambird, J.; Ferrer, C.; Parascondola, A.; Marcello, L.; et al. P-216: Daratumumab, Carfilzomib, Lenalidomide, & Dexamethasone for Relapsed/Refractory Myeloma with Salvage Autologous Hematopoietic Cell Transplant: Interim Analysis of the Multicenter 2nd Chance Protocol. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2021, 21, S158–S159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giralt, S.; Garderet, L.; Durie, B.; Cook, G.; Gahrton, G.; Bruno, B.; Hari, P.; Lokhorst, H.; McCarthy, P.; Krishnan, A.; et al. American Society of Blood and Marrow Transplantation, European Society of Blood and Marrow Transplantation, Blood and Marrow Transplant Clinical Trials Network, and International Myeloma Working Group Consensus Conference on Salvage Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation in Patients with Relapsed Multiple Myeloma. Biol. Blood Marrow Transpl. 2015, 21, 2039–2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moreau, P.; Kumar, S.K.; San Miguel, J.; Davies, F.; Zamagni, E.; Bahlis, N.; Ludwig, H.; Mikhael, J.; Terpos, E.; Schjesvold, F.; et al. Treatment of Relapsed and Refractory Multiple Myeloma: Recommendations from the International Myeloma Working Group. Lancet Oncol. 2021, 22, e105–e118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Offidani, M.; Corvatta, L.; Gentili, S. Triplet vs. Doublet Drug Regimens for Managing Multiple Myeloma. Expert Opin. Pharm. 2018, 19, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terpos, E.; Gobbi, M.; Potamianou, A.; Lahaye, M.; Couturier, C.; Cavo, M. Retreatment and Prolonged Therapy with Subcutaneous Bortezomib in Patients with Relapsed Multiple Myeloma: A Randomized, Controlled, Phase III Study. Eur. J. Haematol. 2018, 100, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulin, C.; de la Rubia, J.; Dimopoulos, M.A.; Terpos, E.; Katodritou, E.; Hungria, V.; De Samblanx, H.; Stoppa, A.; Aagesen, J.; Sargin, D.; et al. Bortezomib Retreatment for Relapsed and Refractory Multiple Myeloma in Real-world Clinical Practice. Health Sci. Rep. 2018, 2, e104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreau, P.; Siegel, D.S.; Goldschmidt, H.; Niesvizky, R.; Bringhen, S.; Orlowski, R.Z.; Blaedel, J.; Yang, Z.; Dimopoulos, M.A. Subgroup Analysis of Patients with Biochemical or Symptomatic Relapse at the Time of Enrollment in the Endeavor Study. Blood 2018, 132, 3243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiedemann, R.E.; Gonzalez-Paz, N.; Kyle, R.A.; Santana-Davila, R.; Price-Troska, T.; Van Wier, S.A.; Chng, W.J.; Ketterling, R.P.; Gertz, M.A.; Henderson, K.; et al. Genetic Aberrations and Survival in Plasma Cell Leukemia. Leukemia 2008, 22, 1044–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Usmani, S.Z.; Heuck, C.; Mitchell, A.; Szymonifka, J.; Nair, B.; Hoering, A.; Alsayed, Y.; Waheed, S.; Haider, S.; Restrepo, A.; et al. Extramedullary Disease Portends Poor Prognosis in Multiple Myeloma and Is Over-Represented in High-Risk Disease Even in the Era of Novel Agents. Haematologica 2012, 97, 1761–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pour, L.; Sevcikova, S.; Greslikova, H.; Kupska, R.; Majkova, P.; Zahradova, L.; Sandecka, V.; Adam, Z.; Krejci, M.; Kuglik, P.; et al. Soft-Tissue Extramedullary Multiple Myeloma Prognosis Is Significantly Worse in Comparison to Bone-Related Extramedullary Relapse. Haematologica 2014, 99, 360–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, S.; Mahmood, S.T.; Lacy, M.Q.; Dispenzieri, A.; Hayman, S.R.; Buadi, F.K.; Dingli, D.; Rajkumar, S.V.; Litzow, M.R.; Gertz, M.A. Impact of Early Relapse after Auto-SCT for Multiple Myeloma. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2008, 42, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bygrave, C.; Pawlyn, C.; Davies, F.; Craig, Z.; Cairns, D.; Hockaday, A.; Jenner, M.; Cook, G.; Drayson, M.; Owen, R.; et al. Early Relapse after High-Dose Melphalan Autologous Stem Cell Transplant Predicts Inferior Survival and Is Associated with High Disease Burden and Genetically High-Risk Disease in Multiple Myeloma. Br. J. Haematol. 2021, 193, 551–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greipp, P.R.; San Miguel, J.; Durie, B.G.M.; Crowley, J.J.; Barlogie, B.; Bladé, J.; Boccadoro, M.; Child, J.A.; Avet-Loiseau, H.; Harousseau, J.-L.; et al. International Staging System for Multiple Myeloma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 23, 3412–3420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Palumbo, A.; Avet-Loiseau, H.; Oliva, S.; Lokhorst, H.M.; Goldschmidt, H.; Rosinol, L.; Richardson, P.; Caltagirone, S.; Lahuerta, J.J.; Facon, T.; et al. Revised International Staging System for Multiple Myeloma: A Report from International Myeloma Working Group. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 2863–2869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Agostino, M.; Lahuerta, J.-J.; Wester, R.; Waage, A.; Bertsch, U.; Zamagni, E.; Mateos, M.-V.; Larocca, A.; Dall’Olio, D.; van de Donk, N.W.C.J.; et al. A New Risk Stratification Model (R2-ISS) in Newly Diagnosed Multiple Myeloma: Analysis of Mature Data from 7077 Patients Collected By European Myeloma Network within Harmony Big Data Platform. Blood 2020, 136, 34–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Agostino, M.; Cairns, D.A.; Lahuerta, J.J.; Wester, R.; Bertsch, U.; Waage, A.; Zamagni, E.; Mateos, M.-V.; Dall’Olio, D.; van de Donk, N.W.C.J.; et al. Second Revision of the International Staging System (R2-ISS) for Overall Survival in Multiple Myeloma: A European Myeloma Network (EMN) Report Within the HARMONY Project. JCO 2022, 40, 4032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tandon, N.; Rajkumar, S.V.; LaPlant, B.; Pettinger, A.; Lacy, M.Q.; Dispenzieri, A.; Buadi, F.K.; Gertz, M.A.; Hayman, S.R.; Leung, N.; et al. Clinical Utility of the Revised International Staging System in Unselected Patients with Newly Diagnosed and Relapsed Multiple Myeloma. Blood Cancer J. 2017, 7, e528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lakshman, A.; Painuly, U.; Rajkumar, S.V.; Ketterling, R.P.; Kapoor, P.; Greipp, P.T.; Dispenzieri, A.; Gertz, M.A.; Buadi, F.K.; Lacy, M.Q.; et al. Impact of Acquired Del(17p) in Multiple Myeloma. Blood Adv. 2019, 3, 1930–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yee, A.J.; Laubach, J.; Campagnaro, E.L.; Lipe, B.; Nadeem, O.; Cole, C.; O’Donnell, E.; Schlossman, R.L.; Bianchi, G.; Branagan, A.R.; et al. A Phase II Study of Elotuzumab in Combination with Pomalidomide, Bortezomib, and Dexamethasone in Relapsed and Refractory Multiple Myeloma. JCO 2018, 36, 8012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Donk, N.W.C.J.; Agha, M.E.; Cohen, A.D.; Cohen, Y.C.; Anguille, S.; Kerre, T.; Roeloffzen, W.; Schecter, J.M.; De Braganca, K.C.; Varsos, H.; et al. Biological Correlative Analyses and Updated Clinical Data of Ciltacabtagene Autoleucel (Cilta-Cel), a BCMA-Directed CAR-T Cell Therapy, in Patients with Multiple Myeloma (MM) and Early Relapse after Initial Therapy: CARTITUDE-2, Cohort B. JCO 2022, 40, 8029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Einsele, H.; Cohen, A.; Delforge, M.; Hillengass, J.; Goldschmidt, H.; Weisel, K.; Raab, M.-S.; Scheid, C.; Schecter, J.; De Braganca, K.; et al. P08: CARTITUDE-2 UPDATE: Ciltacabtagene autoleucel, a b-cell maturation antigen–directed chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy, in lenalidomide-refractory patients with progressive multiple myeloma after 1-3 prior lines of therapy. Hemasphere 2022, 6, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usmani, S.; Patel, K.; Hari, P.; Berdeja, J.; Alsina, M.; Vij, R.; Raje, N.; Leleu, X.; Dhodapkar, M.; Reshef, R.; et al. KarMMa-2 Cohort 2a: Efficacy and Safety of Idecabtagene Vicleucel in Clinical High-Risk Multiple Myeloma Patients with Early Relapse after Frontline Autologous Stem Cell Transplantation. Blood 2022, 140, 875–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhodapkar, M.; Alsina, M.; Berdeja, J.; Patel, K.; Vij, R.; Leleu, X.; Truppel-Hartmann, A.; Basudhar, D.; Thompson, E.; Zheng, X.; et al. KarMMa-2 Cohort 2c: Efficacy and Safety of Idecabtagene Vicleucel in Patients with Clinical High-Risk Multiple Myeloma Due to Inadequate Response to Frontline Autologous Stem Cell Transplantation. Blood 2022, 140, 7441–7443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshman, A.; Singh, P.P.; Rajkumar, S.V.; Dispenzieri, A.; Lacy, M.Q.; Gertz, M.A.; Buadi, F.K.; Dingli, D.; Hwa, Y.L.; Fonder, A.L.; et al. Efficacy of VDT PACE-like Regimens in Treatment of Relapsed/Refractory Multiple Myeloma. Am. J. Hematol. 2018, 93, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, P.T.; Ho, V.Q.; Fulp, W.; Nishihori, T.; Shain, K.H.; Alsina, M.; Baz, R.C. A Comparison of Salvage Infusional Chemotherapy Regimens for Recurrent/Refractory Multiple Myeloma. Cancer 2015, 121, 3622–3630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerrie, A.S.; Mikhael, J.R.; Cheng, L.; Jiang, H.; Kukreti, V.; Panzarella, T.; Reece, D.; Stewart, K.A.; Trieu, Y.; Trudel, S.; et al. D(T)PACE as Salvage Therapy for Aggressive or Refractory Multiple Myeloma. Br. J. Haematol. 2013, 161, 802–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadacaridou, M.; Papanicolaou, X.; Maltesas, D.; Megalakaki, C.; Patos, P.; Panteli, K.; Repousis, P.; Mitsouli-Mentzikof, C. Dexamethasone, Cyclophosphamide, Etoposide and Cisplatin (DCEP) for Relapsed or Refractory Multiple Myeloma Patients. J. BUON 2007, 12, 41–44. [Google Scholar]
- Bansal, R.; Rakshit, S.; Kumar, S. Extramedullary Disease in Multiple Myeloma. Blood Cancer J. 2021, 11, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Short, K.D.; Rajkumar, S.V.; Larson, D.; Buadi, F.; Hayman, S.; Dispenzieri, A.; Gertz, M.; Kumar, S.; Mikhael, J.; Roy, V.; et al. Incidence of Extramedullary Disease in Patients with Multiple Myeloma in the Era of Novel Therapy, and the Activity of Pomalidomide on Extramedullary Myeloma. Leukemia 2011, 25, 906–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, X.; Flüchter, P.; Nickel, K.; Meckel, K.; Messerschmidt, J.; Böckle, D.; Knorz, S.; Steinhardt, M.J.; Krummenast, F.; Danhof, S.; et al. Carfilzomib Based Treatment Strategies in the Management of Relapsed/Refractory Multiple Myeloma with Extramedullary Disease. Cancers 2020, 12, 1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Siegel, D.S.; Martin, T.; Wang, M.; Vij, R.; Jakubowiak, A.J.; Lonial, S.; Trudel, S.; Kukreti, V.; Bahlis, N.; Alsina, M.; et al. A Phase 2 Study of Single-Agent Carfilzomib (PX-171-003-A1) in Patients with Relapsed and Refractory Multiple Myeloma. Blood 2012, 120, 2817–2825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Waxman, A.J.; Clasen, S.; Hwang, W.-T.; Garfall, A.; Vogl, D.T.; Carver, J.; O’Quinn, R.; Cohen, A.D.; Stadtmauer, E.A.; Ky, B.; et al. Carfilzomib-Associated Cardiovascular Adverse Events: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. JAMA Oncol. 2018, 4, e174519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimopoulos, M.A.; Cheung, M.C.; Roussel, M.; Liu, T.; Gamberi, B.; Kolb, B.; Derigs, H.G.; Eom, H.; Belhadj, K.; Lenain, P.; et al. Impact of Renal Impairment on Outcomes with Lenalidomide and Dexamethasone Treatment in the FIRST Trial, a Randomized, Open-Label Phase 3 Trial in Transplant-Ineligible Patients with Multiple Myeloma. Haematologica 2016, 101, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Borrello, I. Lenalidomide in Renal Insufficiency–Balancing the Risks and Benefits. Br. J. Haematol. 2009, 144, 446–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nakaya, A.; Fujita, S.; Satake, A.; Nakanishi, T.; Azuma, Y.; Tsubokura, Y.; Hotta, M.; Yoshimura, H.; Ishii, K.; Ito, T.; et al. Realistic Lenalidomide Dose Adjustment Strategy for Transplant-Ineligible Elderly Patients with Relapsed/Refractory Multiple Myeloma: Japanese Real-World Experience. Acta Haematol. 2017, 138, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, A.C.; Aneja, E.; Boyer, A.; Jayabalan, D.; Mark, T.M.; Pearse, R.; Pekle, K.; Perry, A.; Coleman, M.; Niesvizky, R. Effect of Renal and Hepatic Function on Pomalidomide Dose in Patients with Relapsed/Refractory Multiple Myeloma. Blood 2014, 124, 4754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavriatopoulou, M.; Terpos, E.; Dimopoulos, M.A. IMiDs for Myeloma Induced Renal Impairment. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 35476–35477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidana, S.; Peres, L.; Hashmi, H.; Hosoya, H.; Ferreri, C.; Atrash, S.; Khouri, J.; Voorhees, P.M.; Dima, D.; Simmons, G.L.; et al. Idecabtagene Vicleucel (Ide-Cel) Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-Cell Therapy for Relapsed/Refractory Multiple Myeloma (RRMM) with Renal Impairment: Real World Experience. JOC 2022, 40, 8042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidana, S.; Peres, L.C.; Hashmi, H.; Hosoya, H.; Ferreri, C.J.; Atrash, S.; Khouri, J.; Voorhees, P.M.; Dima, D.; Simmons, G.; et al. Idecabtagene Vicleucel Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-Cell Therapy for Relapsed/Refractory Multiple Myeloma with Renal Insufficiency: Real World Experience. Blood 2022, 140, 10377–10379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capra, M.; Martin, T.; Moreau, P.; Baker, R.; Pour, L.; Min, C.-K.; Leleu, X.; Mohty, M.; Segura, M.R.; Turgut, M.; et al. Isatuximab plus Carfilzomib and Dexamethasone versus Carfilzomib and Dexamethasone in Relapsed Multiple Myeloma Patients with Renal Impairment: IKEMA Subgroup Analysis. Haematologica 2022, 107, 1397–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimopoulos, M.A.; Leleu, X.; Moreau, P.; Richardson, P.G.; Liberati, A.M.; Harrison, S.J.; Miles Prince, H.; Ocio, E.M.; Assadourian, S.; Campana, F.; et al. Isatuximab plus Pomalidomide and Dexamethasone in Relapsed/Refractory Multiple Myeloma Patients with Renal Impairment: ICARIA-MM Subgroup Analysis. Leukemia 2021, 35, 562–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niewinski, M.; Chin-Hon, J.; Akerman, M.; Davies, F.; Morgan, G.; Braunstein, M.J. Safety and Efficacy of Daratumumab Use in Patients with Renal Impairment and Hemodialysis. JCO 2022, 40, 8026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzume, A.; Tabata, R.; Terao, T.; Tsushima, T.; Miura, D.; Narita, K.; Takeuchi, M.; Matsue, K. Safety and Efficacy of Daratumumab in Patients with Multiple Myeloma and Severe Renal Failure. Br. J. Haematol. 2021, 193, e33–e36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monge, J.; Solomon, R.S.; Flicker, K.; Jayabalan, D.S.; Guo, J.; Contreras, J.; Pogonowski, K.; Agudo, N.; Guarneri, D.; Liotta, B.; et al. Daratumumab in Patients with Multiple Myeloma and Renal Impairment-Real-World Data from a Single-Center Institution. Blood 2019, 134, 5563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kastritis, E.; Terpos, E.; Symeonidis, A.; Delimpasi, S.; Cavo, M.; Zamagni, E.; Katodritou, E.; Rivolti, E.; Kyrtsonis, M.-C.; Gavriatopoulou, M.; et al. Daratumumab with Dexamethasone in Patients with Relapsed/Refractory Multiple Myeloma and Severe Renal Impairment: Results on Efficacy and Safety of the Phase 2 Dare Study. Blood 2020, 136, 48–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smyth, E.; Glavey, S.; Melotti, D.; Thornton, P.; Sargent, J.; Conlon, P.; Murphy, P.; Quinn, J. Dialysis Independence Following Single-Agent Daratumumab in Refractory Myeloma with Renal Failure. Ir. J. Med. Sci. 2019, 188, 1079–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeyaraman, P.; Bhasin, A.; Dayal, N.; Pathak, S.; Naithani, R. Daratumumab in Dialysis-Dependent Multiple Myeloma. Blood Res. 2020, 55, 65–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gandhi, U.H.; Cornell, R.F.; Lakshman, A.; Gahvari, Z.J.; McGehee, E.; Jagosky, M.H.; Gupta, R.; Varnado, W.; Fiala, M.A.; Chhabra, S.; et al. Outcomes of Patients with Multiple Myeloma Refractory to CD38-Targeted Monoclonal Antibody Therapy. Leukemia 2019, 33, 2266–2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nooka, A.K.; Joseph, N.S.; Kaufman, J.L.; Heffner, L.T.; Gupta, V.A.; Gleason, C.; Boise, L.H.; Lonial, S. Clinical Efficacy of Daratumumab, Pomalidomide, and Dexamethasone in Patients with Relapsed or Refractory Myeloma: Utility of Re-Treatment with Daratumumab among Refractory Patients. Cancer 2019, 125, 2991–3000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, M.J.; Robinson, M.M.; Hamadeh, I.; Arnall, J.; Bhutani, M.; Atrash, S.; Friend, R.; Pineda-Roman, M.; Symanowski, J.T.; Usmani, S.Z.; et al. Daratumumab, Pomalidomide and Dexamethasone Combination Therapy in Daratumumab and/or Pomalidomide Refractory Multiple Myeloma. Br. J. Haematol. 2019, 186, 140–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavriatopoulou, M.; Kastritis, E.; Ntanasis-Stathopoulos, I.; Fotiou, D.; Roussou, M.; Migkou, M.; Ziogas, D.C.; Kanellias, N.; Terpos, E.; Dimopoulos, M.A. The Addition of IMiDs for Patients with Daratumumab-Refractory Multiple Myeloma Can Overcome Refractoriness to Both Agents. Blood 2018, 131, 464–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdallah, A.-O.; Mahmoudjafari, Z.; Ahmed, N.; Cui, W.; Shune, L.; McGuirk, J.; Mohan, M.; Mohyuddin, G.R.; Afrough, A.; Alkharabsheh, O.; et al. Clinical Efficacy of Retreatment of Daratumumab-Based Therapy (D2) in Daratumumab-Refractory Multiple Myeloma. Eur. J. Haematol. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grajales-Cruz, A.F.; Rodriguez Arocho, C.I.; Rose, A.; Shapiro, J.; Finley-Oliver, E.; Shain, K.H.; Brayer, J.B.; Nishihori, T.; Ochoa, L.; Castaneda Puglianini, O.A.; et al. Elotuzumab in Combination with an Immunomodulatory Agent (IMID) in Patients with Multiple Myeloma Refractory to Imids and/or Daratumumab: A Single-Institution Analysis. Blood 2019, 134, 3183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhael, J.; Belhadj-Merzoug, K.; Hulin, C.; Vincent, L.; Moreau, P.; Gasparetto, C.; Pour, L.; Spicka, I.; Vij, R.; Zonder, J.; et al. A Phase 2 Study of Isatuximab Monotherapy in Patients with Multiple Myeloma Who Are Refractory to Daratumumab. Blood Cancer J. 2021, 11, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashmi, H.; Hansen, D.K.; Peres, L.C.; Castaneda Puglianini, O.A.; Freeman, C.L.; De Avila, G.; Sidana, S.; Shune, L.O.; Sborov, D.W.; Davis, J.; et al. Factors Associated with Refractoriness or Early Progression after Idecabtagene Vicleucel (Ide-Cel) in Patients with Relapsed/Refractory Multiple Myeloma (RRMM): U.S. Myeloma CAR T Consortium Real World Experience. Blood 2022, 140, 4642–4645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreri, C.J.; Hildebrandt, M.A.T.; Hashmi, H.; Shune, L.O.; McGuirk, J.P.; Sborov, D.W.; Wagner, C.B.; Kocoglu, M.H.; Atrash, S.; Voorhees, P.M.; et al. Idecabtagene Vicleucel (Ide-Cel) Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR) T-Cell Therapy in Patients with Relapsed/Refractory Multiple Myeloma (RRMM) Who Have Received a Prior BCMA-Targeted Therapy: Real World, Multi-Institutional Experience. Blood 2022, 140, 1856–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, A.D.; Garfall, A.L.; Dogan, A.; Lacey, S.F.; Martin, C.; Lendvai, N.; Vogl, D.T.; Spear, M.; Lesokhin, A.M. Serial Treatment of Relapsed/Refractory Multiple Myeloma with Different BCMA-Targeting Therapies. Blood Adv. 2019, 3, 2487–2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Oekelen, O.; Mouhieddine, T.H.; Pan, D.; Metzger, M.; Agte, S.; Aleman, A.; Melnekoff, D.T.; Lancman, G.; Lagana, A.; Richard, S.; et al. Clinical Outcomes and Treatment Strategies for Relapsed/Refractory Myeloma Patients after Relapse on BCMA-Targeted CAR T. Blood 2021, 138, 2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oekelen, O.V.; Mouhieddine, T.; Pan, D.; Metzger, M.; Agte, S.; Aleman, A.; Melnekoff, D.; Lancman, G.; Lagana, A.; Richard, S.; et al. OAB-053: Clinical Outcomes of Relapsed/Refractory Multiple Myeloma Patients after BCMA-Targeted CAR T Therapy. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2021, 21, S38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes, K.R.; Liu, Y.C.; Huang, C.Y.; Banerjee, R.; Martin, T.; Shah, N.; Wong, S.W.; Wolf, J.L.; Arora, S.; Chung, A. Salvage Therapies and Clinical Outcomes After Relapse Following BCMA CAR-T in Patients with Relapsed/Refractory Multiple Myeloma. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Myeloma Society Annual Meeting and Exposition, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 25–27 September 2022. Abstract OAB-051. [Google Scholar]
- Chari, A.; Vogl, D.T.; Jagannath, S.; Jasielec, J.; Unger, T.J.; DeCastro, A.; Shah, J.; Kauffman, M.; Shacham, S.; Jakubowiak, A. Selinexor-Based Regimens for the Treatment of Myeloma Refractory to Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cell Therapy. Br. J. Haematol. 2020, 189, e126–e130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dima, D.; Li, A.; Granat, L.M.; Dhillon, P.; Chamseddine, F.; Yalamanchali, A.; Mirzai, S.; Wei, W.; Samaras, C.J.; Valent, J.; et al. External Validation of the SAVED Score for Venous Thromboembolism Risk Stratification in Patients with Multiple Myeloma Receiving Immunomodulatory Drugs. Br. J. Haematol. 2023. online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drayson, M.T.; Bowcock, S.; Planche, T.; Iqbal, G.; Pratt, G.; Yong, K.; Wood, J.; Raynes, K.; Higgins, H.; Dawkins, B.; et al. Levofloxacin Prophylaxis in Patients with Newly Diagnosed Myeloma (TEAMM): A Multicentre, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Randomised, Phase 3 Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 1760–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raje, N.S.; Anaissie, E.; Kumar, S.K.; Lonial, S.; Martin, T.; Gertz, M.A.; Krishnan, A.; Hari, P.; Ludwig, H.; O’Donnell, E.; et al. Consensus Guidelines and Recommendations for Infection Prevention in Multiple Myeloma: A Report from the International Myeloma Working Group. Lancet Haematol. 2022, 9, e143–e161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, H.; Boccadoro, M.; Moreau, P.; San-Miguel, J.; Cavo, M.; Pawlyn, C.; Zweegman, S.; Facon, T.; Driessen, C.; Hajek, R.; et al. Recommendations for Vaccination in Multiple Myeloma: A Consensus of the European Myeloma Network. Leukemia 2021, 35, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terpos, E.; Zamagni, E.; Lentzsch, S.; Drake, M.T.; García-Sanz, R.; Abildgaard, N.; Ntanasis-Stathopoulos, I.; Schjesvold, F.; de la Rubia, J.; Kyriakou, C.; et al. Treatment of Multiple Myeloma-Related Bone Disease: Recommendations from the Bone Working Group of the International Myeloma Working Group. Lancet Oncol. 2021, 22, e119–e130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, G.J.; Child, J.A.; Gregory, W.M.; Szubert, A.J.; Cocks, K.; Bell, S.E.; Navarro-Coy, N.; Drayson, M.T.; Owen, R.G.; Feyler, S.; et al. Effects of Zoledronic Acid versus Clodronic Acid on Skeletal Morbidity in Patients with Newly Diagnosed Multiple Myeloma (MRC Myeloma IX): Secondary Outcomes from a Randomised Controlled Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2011, 12, 743–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raje, N.; Terpos, E.; Willenbacher, W.; Shimizu, K.; García-Sanz, R.; Durie, B.; Legieć, W.; Krejčí, M.; Laribi, K.; Zhu, L.; et al. Denosumab versus Zoledronic Acid in Bone Disease Treatment of Newly Diagnosed Multiple Myeloma: An International, Double-Blind, Double-Dummy, Randomised, Controlled, Phase 3 Study. Lancet Oncol. 2018, 19, 370–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diel, I.J.; Body, J.-J.; Stopeck, A.T.; Vadhan-Raj, S.; Spencer, A.; Steger, G.; von Moos, R.; Goldwasser, F.; Feng, A.; Braun, A. The Role of Denosumab in the Prevention of Hypercalcaemia of Malignancy in Cancer Patients with Metastatic Bone Disease. Eur. J. Cancer 2015, 51, 1467–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, L.S.; Gordon, D.; Kaminski, M.; Howell, A.; Belch, A.; Mackey, J.; Apffelstaedt, J.; Hussein, M.A.; Coleman, R.E.; Reitsma, D.J.; et al. Long-Term Efficacy and Safety of Zoledronic Acid Compared with Pamidronate Disodium in the Treatment of Skeletal Complications in Patients with Advanced Multiple Myeloma or Breast Carcinoma: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Multicenter, Comparative Trial. Cancer 2003, 98, 1735–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Major, P.; Lortholary, A.; Hon, J.; Abdi, E.; Mills, G.; Menssen, H.D.; Yunus, F.; Bell, R.; Body, J.; Quebe-Fehling, E.; et al. Zoledronic Acid Is Superior to Pamidronate in the Treatment of Hypercalcemia of Malignancy: A Pooled Analysis of Two Randomized, Controlled Clinical Trials. J. Clin. Oncol. 2001, 19, 558–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

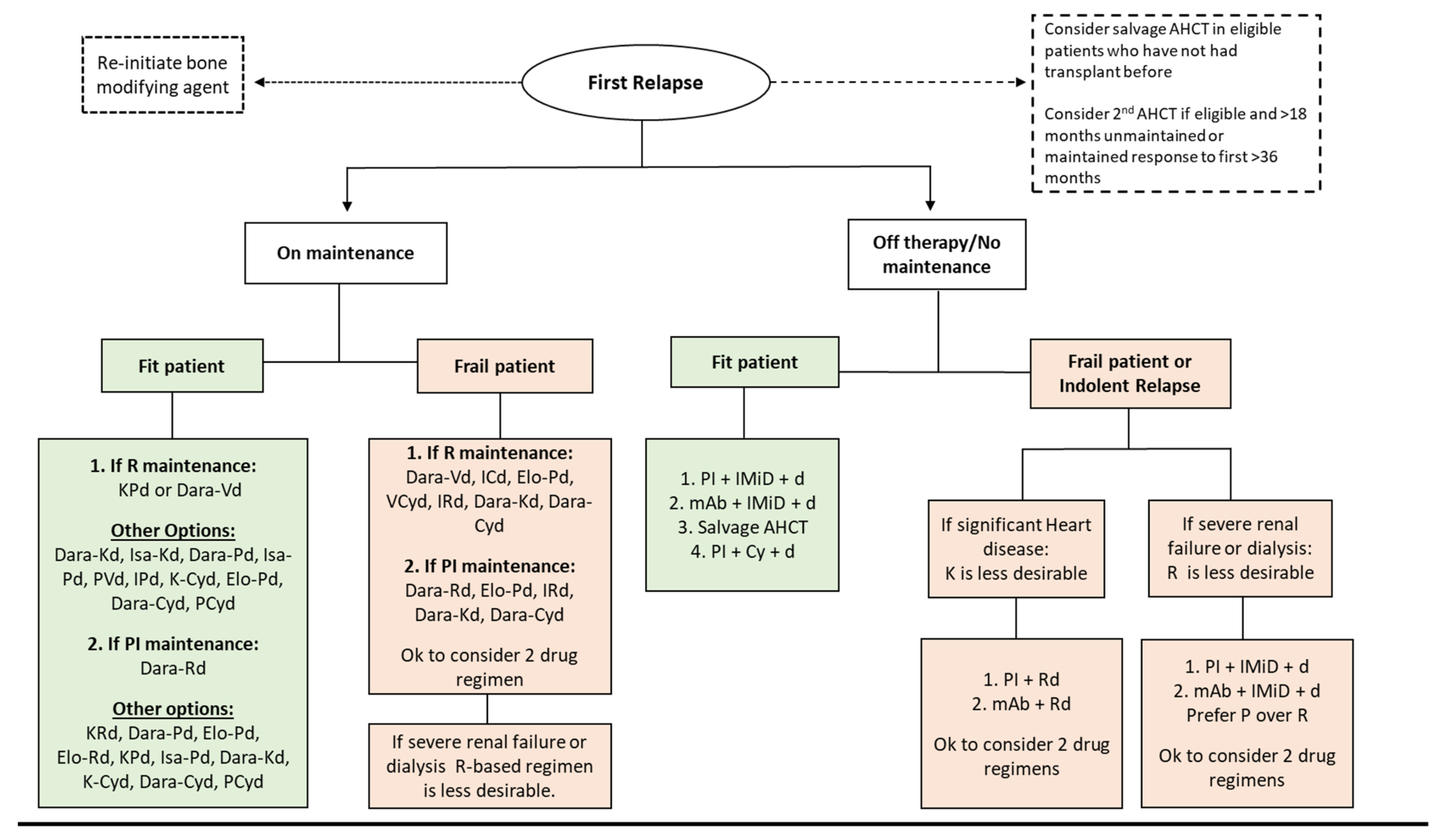

| Name (NCT Number) | Phase | Regimen | N | Study Population | Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ASPIRE NCT01080391 | III | KRd vs. Rd | 792 | • Median 2 prior Tx • Exposed to V: 67% • Refractory to V: 0% | ORR: 87.1% vs. 66.7% ≥VGPR at 38% vs. 31% mPFS: 26.3 vs. 17.6 mo, p < 0.0001 AEs were more common in the K arm mOS: 48.3 vs. 40.4 mo, p = 0.0045 AEs: HF in 6.4% of the K arm [14,15] Subgroup Analysis of OS: • 1st relapse: 11.4 mo longer for K arm • 1st relapse with prior V-exposure: 12 mo longer for K arm • 1st relapse with prior AHCT: 18.6 mo Longer for K arm • ≥2 prior therapies: 6.5 mo longer for K arm |
| ENDEAVOR NCT01568866 | III | Kd vs. Vd | 929 | • Exposed to V: 54% • Exposed to IMiD: ~75% | ORR: 77% vs. 63% mPFS 18.7 vs. 9.4 mo, p < 0.0001 [16,17] mOS: 47.8 vs. 38.8 mo, p = 0.0017 |
| Tourmaline-MM1 NCT01564537 | III | IRd vs. Rd | 722 | • Exposed to V: 70% • Refractory to R or PI: 0% | ORR: 78% vs. 72% (p = 0.04) ≥VGPR: 48% vs. 39% [18] mPFS: 20.6 vs. 14.7 mo, p = 0.01 mOS: 53.6 vs. 51.6 mo, p = 0.495 [19] |
| OPTIMISMM NCT01734928 | III | PVd vs. Vd | 559 | • Median 2 prior Tx • Prior AHCT: 57% • Exposed to R: 100% • Refractory to R: 70% | mPFS: 11.2 vs. 7.10 mo, p < 0.0001 [20] mPFS of R-ref pts: 9.5 vs. 5.6 mo, p = 0.0008 mPFS at 1st relapse: 20.7 vs. 11.6 mo, p = 0.0027 [21] mOS: not available |
| EMN011/ HOVON114 EudraCT 2013-003265-34 | II | PKd | 112 | • 1st relapse or primary refractory disease: 100% • Refractory to V + R: 100% | ORR: 92%, ≥VGPR 75% mPFS: 26 mo, mOS was 67 mo, 42% underwent first sAHCT, indicating that this regimen can be used as re-induction prior to delayed sAHCT [22,23,24,25] |
| MAb | Trial | Phase | N | Regimen | Study Population | m-Prior Tx | Refractoriness | Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DARA | SIRUS | II | 106 | Dara single agent | • ≥3 prior Tx inc a PI and an IMiD or refractory to both PI + IMiD • Excluded pts with anti-CD38 exposure | 5 | • P: 63% • K: 48% • V & R: 82% • Triple: 66% | ORR: 29.2% CR: 2.8%, VGPR: 9.4%, PR: 18% m-duration of response: 7.4 months mPFS: 3.7 months 12-month OS: 64.8% mOS: 17.5 months |
| CASTOR | III | 498 | Dara-Vd vs. Vd | • ≥1 prior Tx • Prior AHCT 61.2% • Excluded pts refractory to PI | 2 | • IMiD: ~33% | ORR: 83.8% vs. 63.2%, p < 0.0001 ≥CR: 28.8% vs. 9.8%, p < 0.0001 ≥VGPR: 62.1% vs. 29.1%, p < 0.0001 mPFS: 16.7 vs. 7.1 months, p < 0.0001 mOS: 49.6 vs. 38.5 months, p = 0.0075 MRD (−) rate: 14% vs. 2%, p < 0.0001 | |
| POLLUX | III | 569 | Dara-Rd vs. Rd | • ≥1 prior therapies • Excluded pts refractory to R | 1 | • PI: ~18% • IMiD: ~5.5% | ORR: 92.9% vs. 76.4%, p < 0.0001 ≥CR: 56.6% vs. 23.2%, p < 0.0001 ≥VGPR: 80.4% vs. 49.3%, p < 0.0001 mPFS: 44.5 vs. 17.5 months, p < 0.0001 MRD (−) rate: 30.4% vs. 5.3%, p < 0.0001 | |
| CANDOR | III | 446 | Dara-Kd vs. Kd | • 1–3 prior Tx | 2 | • R: 33% • V: 29% | ORR: 84% vs. 75%, p = 0.0080 ≥CR: 33% vs. 13%, ≥VGPR: 69% vs. 47% mPFS: 28.6 vs. 15.2 months, p < 0.0001 12-month MRD (−) rate: 18% vs. 4%, p < 0.0001 | |
| APOLLO | III | 304 | Dara-Pd vs. Pd | • ≥2 prior Tx inc R and PI • Excluded pts refractory to P, or exposed to anti-CD38 | 2 | • R: 80% • PI: 48% • PI & R: 42% | ORR: 69% vs. 46%, p < 0.0001 ≥CR: 25 vs. 4%, p < 0.0001 ≥VGPR: 51% vs. 20% <0.0001 mPFS: 12.4 vs. 6.9 months, p = 0.0018 MRD (−) rate: 9% vs. 2%, p = 0.010 | |
| ISA | ICARIA | III | 307 | Isa-Pd vs. Pd | • ≥2 prior Tx inc R and a PI • Excluded pts refractory to anti-CD38 | 3 | • R: 92.5% • PI: ~75% • PI & R: ~71% | ORR: 60% vs. 35%, p < 0.0001 ≥VGPR: 32% vs. 9%, p < 0.0001 mPFS: 11.5 vs. 6.5 months, p = 0.001 mOS: 24.6 vs. 17.7 months, p = 0.028 MRD (−) rate: 7% vs. 0% |
| IKEMA | II | 302 | Isa-Kd vs. Kd | • 1–3 prior Tx • Excluded pts previously esposed to K and pts refractory to anti-CD38 | 2 | • R: ~32% • PI: ~33% | CR: 40% vs. 28% ≥VGPR: 73% vs. 56%, p = 0.0011 mPFS: 19.1 months vs. NR, p = 0.0007 MRD (−) rate: 30% vs. 13% p = 0.0004 | |
| ELO | ELOQUE NT-2 | III | 321 | Elo-Rd vs. Rd | • 1–3 prior Tx | 2 | Most recent line of Tx: • V: 22% • T: 10% | ORR: 79%, vs. 66%, p < 0.001 ≥VGPR: 33% vs. 28% mPFS: 19.4 vs. 14.9 months, p < 0.001 mOS: 48.3 vs. 39.6 months, p = 0.0408 |
| ELOQUE NT-3 | II | 117 | Elo-Pd vs. Pd | • ≥2 prior Tx inc R and a PI • Excluded pts refractory to P | 3 | • R: ~87% • PI: ~80% • PI & R: ~70% | ORR: 53% vs. 26% mPFS: 10.3 vs. 4.7 months, p = 0.008 mOS: 29.8 mo vs. 17.4 mo, p = 0.0217 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dima, D.; Ullah, F.; Mazzoni, S.; Williams, L.; Faiman, B.; Kurkowski, A.; Chaulagain, C.; Raza, S.; Samaras, C.; Valent, J.; et al. Management of Relapsed–Refractory Multiple Myeloma in the Era of Advanced Therapies: Evidence-Based Recommendations for Routine Clinical Practice. Cancers 2023, 15, 2160. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15072160
Dima D, Ullah F, Mazzoni S, Williams L, Faiman B, Kurkowski A, Chaulagain C, Raza S, Samaras C, Valent J, et al. Management of Relapsed–Refractory Multiple Myeloma in the Era of Advanced Therapies: Evidence-Based Recommendations for Routine Clinical Practice. Cancers. 2023; 15(7):2160. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15072160
Chicago/Turabian StyleDima, Danai, Fauzia Ullah, Sandra Mazzoni, Louis Williams, Beth Faiman, Austin Kurkowski, Chakra Chaulagain, Shahzad Raza, Christy Samaras, Jason Valent, and et al. 2023. "Management of Relapsed–Refractory Multiple Myeloma in the Era of Advanced Therapies: Evidence-Based Recommendations for Routine Clinical Practice" Cancers 15, no. 7: 2160. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15072160
APA StyleDima, D., Ullah, F., Mazzoni, S., Williams, L., Faiman, B., Kurkowski, A., Chaulagain, C., Raza, S., Samaras, C., Valent, J., Khouri, J., & Anwer, F. (2023). Management of Relapsed–Refractory Multiple Myeloma in the Era of Advanced Therapies: Evidence-Based Recommendations for Routine Clinical Practice. Cancers, 15(7), 2160. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15072160






