Update on Calcitonin Screening for Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma and the Results of a Retrospective Analysis of 12,984 Patients with Thyroid Nodules
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
- To determine the spectrum of screening Ctn values and the current MTC prevalence in the Rhine–Ruhr area, the region with the highest population density in Germany;
- To examine the impact of stimulation tests (especially the calcium stimulation test) vs. different, sex-specific basal Ctn cut-off values on Ctn screening;
- To analyze the characteristics of the MTC cases detected by Ctn screening regarding Ctn values and sex distribution;
- To understand and discuss the basic problems of Ctn screening for MTC.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Eligibility Criteria
- ○
- The presence of at least one thyroid nodule that is detectable by ultrasonography (down to about 2 mm size);
- ○
- Age ≥ 18 years.
- ○
- Advanced kidney disease *;
- ○
- Known Ctn elevations **;
- ○
- Personal or family history of thyroid carcinoma or MEN **;
- ○
- Known mutations of the RET proto-oncogene **;
- ○
- (* Because in the case of advanced renal insufficiency, non-specific increased Ctn values are often measured even with a Ctn assay, which detects the mature (monomeric) Ctn form with high selectivity; ** in order to avoid a preselection bias, which would simulate an unrepresentatively high MTC prevalence in the examined patients).
2.2. Ctn Measurement
2.3. Stimulation Tests
2.4. Procedures for Clarifying Increased Ctn Values
- ○
- Ctn drops during follow-up or no increase within an observation period of several years;
- ○
- The confirmation test with the monomer-specific ICMA showed an inconspicuous Ctn value;
- ○
- Inconspicuous Ctn behavior in a stimulation test;
- ○
- Total thyroidectomy without histopathological evidence of MTC (if only a partial thyroid resection was performed without histopathological demonstration of a CCN, this was not considered as an MTC exclusion).
2.5. Postoperative Assessment of Confirmed MTC Cases
2.6. Statistics
3. Results
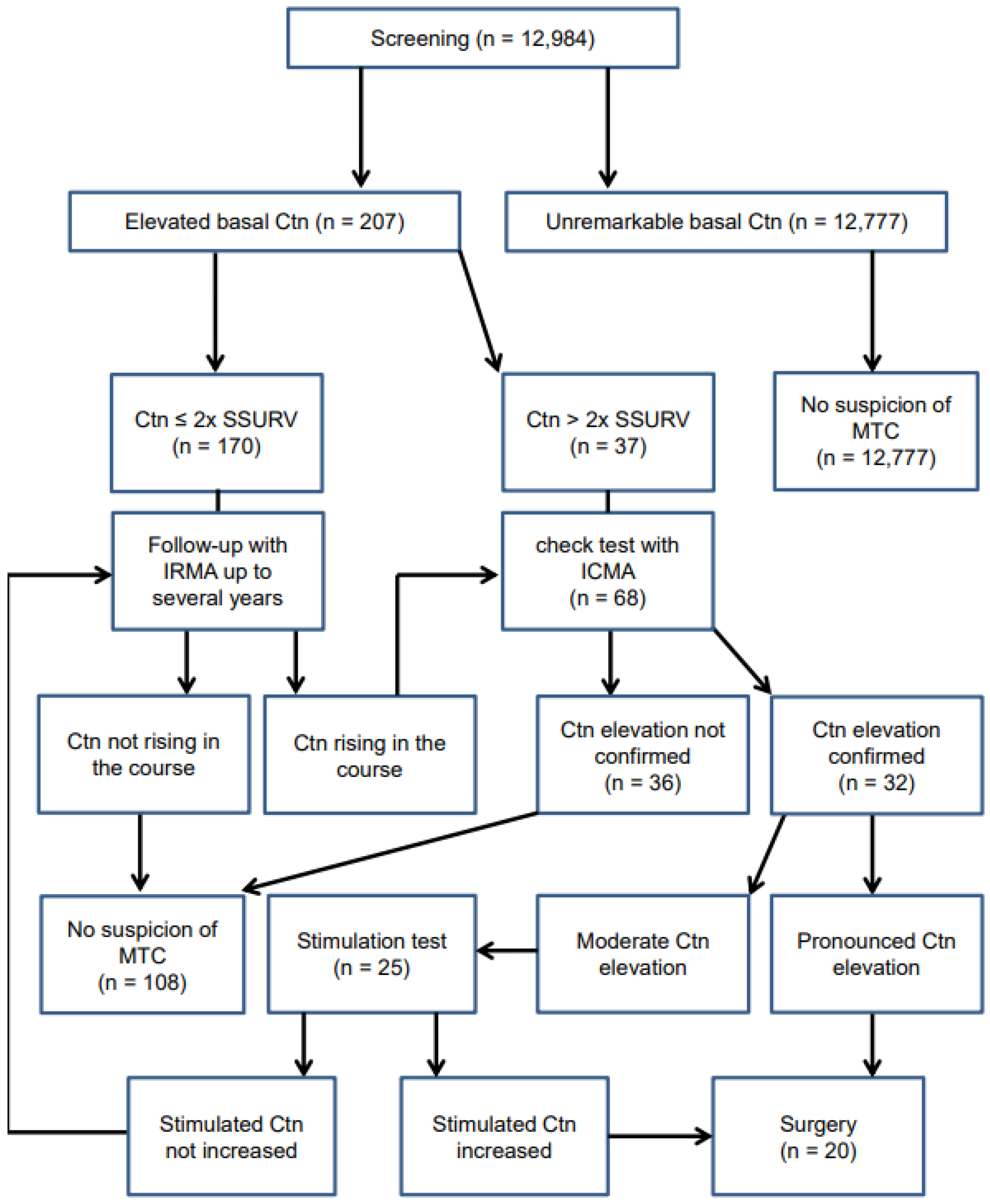
3.1. Spectrum of Screening Ctn Values and MTC Prevalence
3.2. Stimulation Tests vs. Sex-Specific Basal Ctn Cut-Off Values
- In 6/10 patients, the stimulation with calcium gluconate was strongly positive and led to total thyroidectomy, whereby histopathological examination revealed MTC only in four patients (peak stimulated Ctn (sCtn) values between 612 and >2000 pg/mL). The follicular variant of a PTC (m, bCtn 31.7 pg/mL at the time of the stimulation test and peak sCtn 703 pg/mL) or a CCH (m, bCtn 50 pg/mL and peak sCtn > 2000 pg/mL) was only seen in the remaining two patients.
- In 2/10 patients, the test produced no suspect Ctn stimulation (peak sCtn values were 9.9 and 64.0 pg/mL, respectively; MTC could be excluded in one case by non-increasing bCtn values during follow-up; in the other case MTC was histologically excluded).
- In another 2/10 patients, the test only produced a Ctn increase in the borderline pathological range. In two female patients, Ctn was increased from basal 10.9 to a maximum of 187 pg/mL (histologically no MTC but only CCH was detected, but the initial screening value was 51.6 pg/mL in the IRMA and 65.6 pg/mL in the ICMA) or from 10.9 pg/mL to a maximum of 180 pg/mL (in the long term, however, no increase in the bCtn values was observed).
3.3. Characteristics of the Confirmed MTC Cases
4. Discussion
4.1. Spectrum of Screening Ctn Values and MTC Prevalence
4.2. Stimulation Tests vs. Sex-Specific Basal Ctn Cut-Off Values
| Females | |||||
| Source | bCtn Cut-Off | Sensitivity | Specificity | PPV | NPV |
| Colombo et al., 2012 [7] | >18.7 pg/mL | 100% | 100% | 100% | 100% |
| Mian et al., 2014 [48] | >26 pg/mL | 81.8% | 97.9% | 94.7% | 92% |
| Allelein et al., 2018 [49] | ≥35 pg/mL | 87.3% | 87.5% | 98% | 50% |
| Niederle et al., 2020 [50] | >23 pg/mL | 81% | 100% | 100% | 83% |
| Fugazzola et al., 2021 [45] | >30 pg/mL | 75.9% | 93.7% | 85% | 86.5% |
| Males | |||||
| Source | bCtn Cut-Off | Sensitivity | Specificity | PPV | NPV |
| Colombo et al., 2012 [7] | >68 pg/mL | 100% | 100% | 100% | 100% |
| Mian et al., 2014 [48] | >68 pg/mL | 83.3% | 100% | 100% | 92.9% |
| Allelein et al., 2018 [49] | ≥46 pg/mL | 93.6% | 95% | 97% | 90% |
| Niederle et al., 2020 [50] | >43 pg/mL | 53% | 100% | 100% | 83% |
| Fugazzola et al., 2021 [45] | >34 pg/mL | 88.9% | 95% | 88.9% | 92.7% |
4.3. Basic Problems of Ctn Screening for MTC
4.3.1. The Problem of False-Positive Cases
4.3.2. The Problem of True- and False-Negative Cases
4.3.3. The Problem of Assay Dependency of Measured Ctn Values
4.3.4. The Problem of Histopathological Examination as the “Gold Standard”
4.4. Limitations of Our Study
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bae, Y.J.; Schaab, M.; Kratzsch, J. Calcitonin as Biomarker for the Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma. In Recent Results in Cancer Research; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; Volume 204, pp. 117–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karges, W.; Dralle, H.; Raue, F.; Mann, K.; Reiners, C.; Grussendorf, M.; Hüfner, M.; Niederle, B.; Brabant, G.; German Society for Endocrinology (DGE)—Thyroid Section. Calcitonin measurement to detect medullary thyroid carcinoma in nodular goiter: German evidence-based consensus recommendation. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 2004, 112, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henry, J.F.; Denizot, A.; Puccini, M.; Gramatica, L.; Kvachenyuk, A.; Conte Devolx, B.; De Micco, C. Latent subclinical medullary thyroid carcinoma: Diagnosis and treatment. World J. Surg. 1998, 22, 752–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elisei, R.; Bottici, V.; Luchetti, F.; Di Coscio, G.; Romei, C.; Grasso, L.; Miccoli, P.; Iacconi, P.; Basolo, F.; Pinchera, A.; et al. Impact of routine measurement of serum calcitonin on the diagnosis and outcome of medullary thyroid cancer: Experience in 10,864 patients with nodular thyroid disorders. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2004, 89, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machens, A.; Dralle, H. Surgical cure rates of sporadic medullary thyroid cancer in the era of calcitonin screening. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2016, 175, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machens, A.; Lorenz, K.; Weber, F.; Dralle, H. Exceptionality of Distant Metastasis in Node-Negative Hereditary and Sporadic Medullary Thyroid Cancer: Lessons Learned. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 106, e2968–e2979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, C.; Verga, U.; Mian, C.; Ferrero, S.; Perrino, M.; Vicentini, L.; Dazzi, D.; Opocher, G.; Pelizzo, M.R.; Beck-Peccoz, P.; et al. Comparison of calcium and pentagastrin tests for the diagnosis and follow-up of medullary thyroid cancer. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 97, 905–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verburg, F.A.; Reiners, C.; Grelle, I.; Barth, H.; Fassnacht, M.; Luster, M. Calcium stimulated calcitonin measurement: A procedural proposal. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 2013, 121, 318–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fugazzola, L. Stimulated calcitonin cut-offs by different tests. Eur. Thyroid J. 2013, 2, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, K.; Elwerr, M.; Machens, A.; Abuazab, M.; Holzhausen, H.J.; Dralle, H. Hypercalcitoninemia in thyroid conditions other than medullary thyroid carcinoma: A comparative analysis of calcium and pentagastrin stimulation of serum calcitonin. Langenbecks Arch. Surg. 2013, 398, 403–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unluhizarci, K.; Akgun, H.; Oz, B.; Karaca, Z.; Tanriverdi, F.; Kelestimur, F. Patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma associated with high stimulated serum calcitonin levels. Endocrinol. Diabetes Metab. Case Rep. 2017, 2017, 17–0085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank-Raue, K.; Schott, M.; Raue, F.; im Namen der Sektion Schilddrüse der DGE. Empfehlung zum Calcitonin-Screening bei Struma nodosa [Recommendation for Calcitonin Screening in Nodular Goiter]. Dtsch. Med. Wochenschr. 2018, 143, 1065–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niederle, M.B.; Scheuba, C.; Riss, P.; Selberherr, A.; Koperek, O.; Niederle, B. Early Diagnosis of Medullary Thyroid Cancer: Are Calcitonin Stimulation Tests Still Indicated in the Era of Highly Sensitive Calcitonin Immunoassays? Thyroid 2020, 30, 974–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wells, S.A., Jr.; Asa, S.L.; Dralle, H.; Elisei, R.; Evans, D.B.; Gagel, R.F.; Lee, N.; Machens, A.; Moley, J.F.; Pacini, F.; et al. Revised American Thyroid Association guidelines for the management of medullary thyroid carcinoma. Thyroid 2015, 25, 567–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haugen, B.R.; Alexander, E.K.; Bible, K.C.; Doherty, G.M.; Mandel, S.J.; Nikiforov, Y.E.; Pacini, F.; Randolph, G.W.; Sawka, A.M.; Schlumberger, M.; et al. 2015 American Thyroid Association Management Guidelines for Adult Patients with Thyroid Nodules and Differentiated Thyroid Cancer: The American Thyroid Association Guidelines Task Force on Thyroid Nodules and Differentiated Thyroid Cancer. Thyroid 2016, 26, 1–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, K.; Roman, S.A.; Wang, T.S.; Walker, H.D.; Sosa, J.A. Calcitonin measurement in the evaluation of thyroid nodules in the United States: A cost-effectiveness and decision analysis. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2008, 93, 2173–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vardarli, I.; Weber, M.; Weidemann, F.; Führer, D.; Herrmann, K.; Görges, R. Diagnostic accuracy of routine calcitonin measurement for the detection of medullary thyroid carcinoma in the management of patients with nodular thyroid disease: A meta-analysis. Endocr. Connect. 2021, 10, 358–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guyétant, S.; Rousselet, M.C.; Durigon, M.; Chappard, D.; Franc, B.; Guerin, O.; Saint-André, J.P. Sex-related C cell hyperplasia in the normal human thyroid: A quantitative autopsy study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1997, 82, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bieglmayer, C.; Vierhapper, H.; Dudczak, R.; Niederle, B. Measurement of calcitonin by immunoassay analyzers. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2007, 45, 662–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, P.; Düren, C.; Nerlich, K.; Verburg, F.A.; Grelle, I.; Jahn, H.; Fassnacht, M.; Mäder, U.; Reiners, C.; Luster, M. Potency and tolerance of calcitonin stimulation with high-dose calcium versus pentagastrin in normal adults. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 94, 2970–2974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giovanella, L.; Avram, A.M.; Iakovou, I.; Kwak, J.; Lawson, S.A.; Lulaj, E.; Luster, M.; Piccardo, A.; Schmidt, M.; Tulchinsky, M.; et al. EANM practice guideline/SNMMI procedure standard for RAIU and thyroid scintigraphy. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2019, 46, 2514–2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Görges, R.; Kandror, T.; Kuschnerus, S.; Zimny, M.; Pink, R.; Palmedo, H.; Hach, A.; Rau, H.; Tanner, C.; Zaplatnikov, K.; et al. Szintigraphisch mehranreichernde Schilddrüsenknoten gehen überwiegend mit normwertigem TSH einher [Scintigraphically “hot” thyroid nodules mainly go hand in hand with a normal TSH]. Nuklearmedizin 2011, 50, 179–188. (In German) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giovanella, L.; D’Aurizio, F.; Campenni, A.; Ruggeri, R.M.; Baldari, S.; Verburg, F.A.; Trimboli, P.; Ceriani, L. Searching for the most effective thyrotropin (TSH) threshold to rule-out autonomously functioning thyroid nodules in iodine deficient regions. Endocrine 2016, 54, 757–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schenke, S.A.; Kreissl, M.C.; Grunert, M.; Hach, A.; Haghghi, S.; Kandror, T.; Peppert, E.; Rosenbaum-Krumme, S.; Ruhlmann, V.; Stahl, A.; et al. Distribution of Functional Status of Thyroid Nodules and Malignancy Rates of Hyperfunctioning and Hypofunctioning Thyroid Nodules in Germany. Nuklearmedizin 2022, 61, 376–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musholt, T.J.; Bockisch, A.; Clerici, T.; Dotzenrath, C.; Dralle, H.; Goretzki, P.E.; Hermann, M.; Holzer, K.; Karges, W.; Krude, H.; et al. Aktualisierung der S2k-Leitlinie: Operative Therapie benigner Schilddrüsenerkrankungen [Update of the S2k guidelines: Surgical treatment of benign thyroid diseases]. Chirurg 2018, 89, 699–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharib, H.; Papini, E.; Paschke, R.; Duick, D.S.; Valcavi, R.; Hegedüs, L.; Vitti, P.; Balafouta, S.T.; Baloch, Z.; Crescenzi, A.; et al. American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists, Associazione Medici Endocrinologi, and EuropeanThyroid Association Medical Guidelines for Clinical Practice for the Diagnosis and Management of Thyroid Nodules. Endocr. Pract. 2010, 16 (Suppl. S1), 1–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rink, T.; Truong, P.N.; Schroth, H.J.; Diener, J.; Zimny, M.; Grünwald, F. Calculation and validation of a plasma calcitonin limit for early detection of medullary thyroid carcinoma in nodular thyroid disease. Thyroid 2009, 19, 327–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrmann, B.L.; Schmid, K.W.; Görges, R.; Kemen, M.; Mann, K. Calcitonin screening and pentagastrin testing: Predictive value for the diagnosis of medullary carcinoma in nodular thyroid disease. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2010, 162, 1141–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, C.; Kobe, C.; Schmidt, M.; Kahraman, D.; Malchau, G.; Faust, M.; Schicha, H.; Dietlein, M. Calcitonin screening in patients with thyroid nodules. Diagnostic value. Nuklearmedizin 2012, 51, 228–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- d’Herbomez, M.; Caron, P.; Bauters, C.; Do Cao, C.; Schlienger, J.L.; Sapin, R.; Baldet, L.; Carnaille, B.; Wémeau, J.L.; French Group GTE (Groupe des Tumeurs Endocrines). Reference range of serum calcitonin levels in humans: Influence of calcitonin assays, sex, age, and cigarette smoking. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2007, 157, 749–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machens, A.; Hoffmann, F.; Sekulla, C.; Dralle, H. Importance of gender-specific calcitonin thresholds in screening for occult sporadic medullary thyroid cancer. Endocr.-Relat. Cancer 2009, 16, 1291–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guesgen, C.; Willms, A.; Zwad, A.; Waldeck, S.; Wieler, H.; Schwab, R. Investigation of factors potentially influencing calcitonin levels in the screening and follow-up for medullary thyroid carcinoma: A cautionary note. BMC Clin. Pathol. 2013, 13, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckelt, F.; Vogel, M.; Geserick, M.; Kirsten, T.; Bae, Y.J.; Baber, R.; Schaab, M.; Thiery, J.; Pfaeffle, R.; Raue, F.; et al. Calcitonin measurement in pediatrics: Reference ranges are sex-dependent, validation in medullary thyroid cancer and thyroid diseases. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2019, 57, 1242–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hahm, J.R.; Lee, M.S.; Min, Y.K.; Lee, M.K.; Kim, K.W.; Nam, S.J.; Yang, J.H.; Chung, J.H. Routine measurement of serum calcitonin is useful for early detection of medullary thyroid carcinoma in patients with nodular thyroid diseases. Thyroid 2001, 11, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vierhapper, H.; Niederle, B.; Bieglmayer, C.; Kaserer, K.; Baumgartner-Parzer, S. Early diagnosis and curative therapy of medullary thyroid carcinoma by routine measurement of serum calcitonin in patients with thyroid disorders. Thyroid 2005, 15, 1267–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costante, G.; Meringolo, D.; Durante, C.; Bianchi, D.; Nocera, M.; Tumino, S.; Crocetti, U.; Attard, M.; Maranghi, M.; Torlontano, M.; et al. Predictive value of serum calcitonin levels for preoperative diagnosis of medullary thyroid carcinoma in a cohort of 5817 consecutive patients with thyroid nodules. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 92, 450–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grani, G.; Nesca, A.; Del Sordo, M.; Calvanese, A.; Carbotta, G.; Bianchini, M.; Fumarola, A. Interpretation of serum calcitonin in patients with chronic autoimmune thyroiditis. Endocr.-Relat. Cancer 2012, 19, 345–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giovanella, L.; Verburg, F.A.; Imperiali, M.; Valabrega, S.; Trimboli, P.; Ceriani, L. Comparison of serum calcitonin and procalcitonin in detecting medullary thyroid carcinoma among patients with thyroid nodules. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2013, 51, 1477–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvestre, C.; Sampaio Matias, J.; Proença, H.; Bugalho, M.J. Calcitonin Screening in Nodular Thyroid Disease: Is There a Definitive Answer? Eur. Thyroid J. 2019, 8, 79–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valle, L.A.; Kloos, R.T. The prevalence of occult medullary thyroid carcinoma at autopsy. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 96, E109–E113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacini, F.; Fontanelli, M.; Fugazzola, L.; Elisei, R.; Romei, C.; Di Coscio, G.; Miccoli, P.; Pinchera, A. Routine measurement of serum calcitonin in nodular thyroid diseases allows the preoperative diagnosis of unsuspected sporadic medullary thyroid carcinoma. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1994, 78, 826–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iacobone, M.; Niccoli-Sire, P.; Sebag, F.; De Micco, C.; Henry, J.F. Can sporadic medullary thyroid carcinoma be biochemically predicted? Prospective analysis of 66 operated patients with elevated serum calcitonin levels. World J. Surg. 2002, 26, 886–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dralle, H.; Musholt, T.J.; Schabram, J.; Steinmüller, T.; Frilling, A.; Simon, D.; Goretzki, P.E.; Niederle, B.; Scheuba, C.; Clerici, T.; et al. German Association of Endocrine Surgeons practice guideline for the surgical management of malignant thyroid tumors. Langenbecks Arch. Surg. 2013, 398, 347–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elisei, R.; Romei, C. Calcitonin estimation in patients with nodular goiter and its significance for early detection of MTC: European comments to the guidelines of the American Thyroid Association. Thyroid Res. 2013, 6 (Suppl. S1), S2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fugazzola, L.; Di Stefano, M.; Censi, S.; Repaci, A.; Colombo, C.; Grimaldi, F.; Magri, F.; Pagotto, U.; Iacobone, M.; Persani, L.; et al. Basal and stimulated calcitonin for the diagnosis of medullary thyroid cancer: Updated thresholds and safety assessment. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2021, 44, 587–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiem, U.; Marculescu, R.; Cejka, D.; Gessl, A.; Borchhardt, K. Low-dose calcium versus pentagastrin for stimulation of calcitonin in chronic hemodialysis patients: A pilot study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 99, 4704–4711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannetta, E.; Guarnotta, V.; Altieri, B.; Sciammarella, C.; Guadagno, E.; Malandrino, P.; Puliani, G.; Feola, T.; Isidori, A.M.; Colao, A.A.L.; et al. ENDOCRINE TUMOURS: Calcitonin in thyroid and extra-thyroid neuroendocrine neoplasms: The two-faced Janus. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2020, 183, R197–R215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mian, C.; Perrino, M.; Colombo, C.; Cavedon, E.; Pennelli, G.; Ferrero, S.; De Leo, S.; Sarais, C.; Cacciatore, C.; Manfredi, G.I.; et al. Refining calcium test for the diagnosis of medullary thyroid cancer: Cutoffs, procedures, and safety. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 99, 1656–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allelein, S.; Ehlers, M.; Morneau, C.; Schwartz, K.; Goretzki, P.E.; Seppel, T.; Feldkamp, J.; Krieg, A.; Knoefel, W.T.; Kuebart, A.; et al. Measurement of Basal Serum Calcitonin for the Diagnosis of Medullary Thyroid Cancer. Horm. Metab. Res. 2018, 50, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niederle, M.B.; Riss, P.; Selberherr, A.; Koperek, O.; Kaserer, K.; Niederle, B.; Scheuba, C. Omission of lateral lymph node dissection in medullary thyroid cancer without a desmoplastic stromal reaction. Br. J. Surg. 2021, 108, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seifert, P.; Kloos, E.; Ritter, K.; Freesmeyer, M. Calcitonin Screening—Consideration of Heterophilic Antibody Interference in a Case of Obscure Hypercalcitoninemia. Nuklearmedizin 2020, 59, 35–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cvek, M.; Punda, A.; Brekalo, M.; Plosnić, M.; Barić, A.; Kaličanin, D.; Brčić, L.; Vuletić, M.; Gunjača, I.; Torlak Lovrić, V.; et al. Presence or severity of Hashimoto’s thyroiditis does not influence basal calcitonin levels: Observations from CROHT biobank. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2022, 45, 597–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leboeuf, R.; Langlois, M.F.; Martin, M.; Ahnadi, C.E.; Fink, G.D. “Hook effect” in calcitonin immunoradiometric assay in patients with metastatic medullary thyroid carcinoma: Case report and review of the literature. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2006, 91, 361–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fangous, M.S.; Kerspern, H.; Moineau, M.P.; Kerlan, V.; Alavi, Z.; Carré, J.L. The hook effect in calcitonin immunoradiometric assay: A case report. Ann. Endocrinol. 2012, 73, 552–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trimboli, P.; Giovanella, L. Serum calcitonin negative medullary thyroid carcinoma: A systematic review of the literature. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2015, 53, 1507–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.J.; Yun, H.J.; Shin, S.J.; Lee, Y.S.; Chang, H.S. Serum Calcitonin-Negative Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma: A Case Series of 19 Patients in a Single Center. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 747704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dora, J.M.; Canalli, M.H.; Capp, C.; Puñales, M.K.; Vieira, J.G.; Maia, A.L. Normal perioperative serum calcitonin levels in patients with advanced medullary thyroid carcinoma: Case report and review of the literature. Thyroid 2008, 18, 895–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frank-Raue, K.; Machens, A.; Leidig-Bruckner, G.; Rondot, S.; Haag, C.; Schulze, E.; Lorenz, A.; Kreissl, M.C.; Dralle, H.; Raue, F.; et al. Prevalence and clinical spectrum of nonsecretory medullary thyroid carcinoma in a series of 839 patients with sporadic medullary thyroid carcinoma. Thyroid 2013, 23, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trimboli, P.; Camponovo, C.; Ruinelli, L. The dilemma of routine testing for calcitonin thyroid nodule’s patients to detect or exclude medullary carcinoma: One single negative test should be valuable as rule-out strategy to avoid further calcitonin measurements over time. Endocrine 2022, 77, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kratzsch, J.; Petzold, A.; Raue, F.; Reinhardt, W.; Bröcker-Preuss, M.; Görges, R.; Mann, K.; Karges, W.; Morgenthaler, N.; Luster, M.; et al. Basal and stimulated calcitonin and procalcitonin by various assays in patients with and without medullary thyroid cancer. Clin. Chem. 2011, 57, 467–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatzl-Griesenhofer, M.; Pichler, R.; Bogner, S.; Wölfl, S.; Weinhäusel, A.; Hubert, H.; Weidinger, W.; Maschek, M. Results of calcitonin screening in a central upper Austrian region. Int. J. Disabil. Hum. Dev. 2002, 3, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papi, G.; Corsello, S.M.; Cioni, K.; Pizzini, A.M.; Corrado, S.; Carapezzi, C.; Fadda, G.; Baldini, A.; Carani, C.; Pontecorvi, A.; et al. Value of routine measurement of serum calcitonin concentrations in patients with nodular thyroid disease: A multicenter study. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2006, 29, 427–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Storani, M.E.; Bostico, S.T.; Subies, F.A.; Musich, M.; Oneto, A. Medición rutinaria de calcitonina sérica en nódulos tiroideos [Routine serum calcitonin measurement in thyroid nodules]. Medicina 2019, 79, 271–275. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]


| Sex m = Male f = Female | Age at Time of Surgery [Years] | bCtn IRMA [pg/mL] | Biochemical Reasons for the Indication for Thyroidectomy Because of a Strong Suspicion of C-cell Neoplasia | Histology |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| f | 64 | 10.1 | bCtn increasing to 25.1 pg/mL in 3.75 years, sCtn (Ca-test) peak >2000 pg/mL | MTC-16 |
| f | 29 | 14.6 | bCtn increasing to 71.6 pg/mL in 5.1 years, sCtn (Ca-test) peak >2000 pg/mL, CEA↑ | MTC-09 |
| m | 65 | 17.8 | bCtn increasing to 31.7 pg/mL in 8 months, sCtn (Ca-test) peak 703 pg/mL | PTC |
| f | 45 | 19.3 | bCtn moderately increased, sCtn (Ca-test) peak 612 pg/mL | MTC-03 |
| m | 73 | 30.5 | bCtn moderately increased, sCtn (Ca-test) peak 1616 pg/mL, CEA↑ | MTC-04 |
| f | 47 | 31.9 | bCtn moderately increased, sCtn (Pg-test) peak 1189 pg/mL | MTC-11 |
| m | 57 | 35.5 | bCtn moderately increased, sCtn (Ca-test) peak >2000 pg/mL | CCH |
| m | 69 | 47.2 | bCtn moderately increased, sCtn (Pg-test) peak 450 pg/mL, CEA↑ | CCH |
| m | 77 | 49.4 | bCtn moderately increased, sCtn (Ca-test) peak 1517 pg/mL, CEA↑ | MTC-13 |
| f | 45 | 51.6 | bCtn markedly increased | CCH |
| f | 38 | 53.0 | bCtn markedly increased, sCtn (Ca-test) peak >2000 pg/mL | MTC-01 |
| m | 44 | 90.4 | bCtn markedly increased, sCtn (Ca-test) peak 1336 pg/mL | MTC-06 |
| f | 78 | 128 | bCtn extremely increased, sCtn (Ca-test) peak >2000 pg/mL | MTC-12 |
| m | 47 | 227 | bCtn extremely increased, sCtn (Ca-test) peak 459 pg/mL | MTC-10 |
| f | 67 | 280 | bCtn extremely increased, sCtn (Pg-test) peak 5347 pg/mL, CEA↑ | MTC-08 |
| m | 72 | 291 | bCtn extremely increased, sCtn (Ca-test) peak >2000 pg/mL, CEA↑ | MTC-14 |
| f | 39 | 838 | bCtn extremely increased, CEA↑ | MTC-07 |
| f | 70 | 868 | bCtn extremely increased, sCtn (Ca-test) peak >2000 pg/mL, CEA↑ | MTC-02 |
| m | 72 | 1132 | bCtn extremely increased, CEA↑ | MTC-05 |
| f | 76 | 1276 | bCtn extremely increased, CEA↑ | MTC-15 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Broecker-Preuss, M.; Simon, D.; Fries, M.; Kornely, E.; Weber, M.; Vardarli, I.; Gilman, E.; Herrmann, K.; Görges, R. Update on Calcitonin Screening for Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma and the Results of a Retrospective Analysis of 12,984 Patients with Thyroid Nodules. Cancers 2023, 15, 2333. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15082333
Broecker-Preuss M, Simon D, Fries M, Kornely E, Weber M, Vardarli I, Gilman E, Herrmann K, Görges R. Update on Calcitonin Screening for Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma and the Results of a Retrospective Analysis of 12,984 Patients with Thyroid Nodules. Cancers. 2023; 15(8):2333. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15082333
Chicago/Turabian StyleBroecker-Preuss, Martina, Dietmar Simon, Mirka Fries, Elisabeth Kornely, Manuel Weber, Irfan Vardarli, Elena Gilman, Ken Herrmann, and Rainer Görges. 2023. "Update on Calcitonin Screening for Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma and the Results of a Retrospective Analysis of 12,984 Patients with Thyroid Nodules" Cancers 15, no. 8: 2333. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15082333
APA StyleBroecker-Preuss, M., Simon, D., Fries, M., Kornely, E., Weber, M., Vardarli, I., Gilman, E., Herrmann, K., & Görges, R. (2023). Update on Calcitonin Screening for Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma and the Results of a Retrospective Analysis of 12,984 Patients with Thyroid Nodules. Cancers, 15(8), 2333. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15082333







