An Isoxazoloquinone Derivative Inhibits Tumor Growth by Targeting STAT3 and Triggering Its Ubiquitin-Dependent Degradation
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. General Procedure for the Synthesis of 2a–2c and 10
2.2. 3-Ethylnaphtho[2,3-d]isoxazole-4,9-dione 4a
2.3. 3-(3,4,5-Trimethoxyphenyl)-naphtho[2,3-d]isoxazole-4,9-dione 4b
2.4. 3-(3,4,5-Trimethoxybenzyl)naphtho[2,3-d]isoxazole-4,9-dione 4c
2.5. 5,7-Dibromo-8-quinolinol 6
2.6. 7-Bromoquinoline-5,8-dione 7
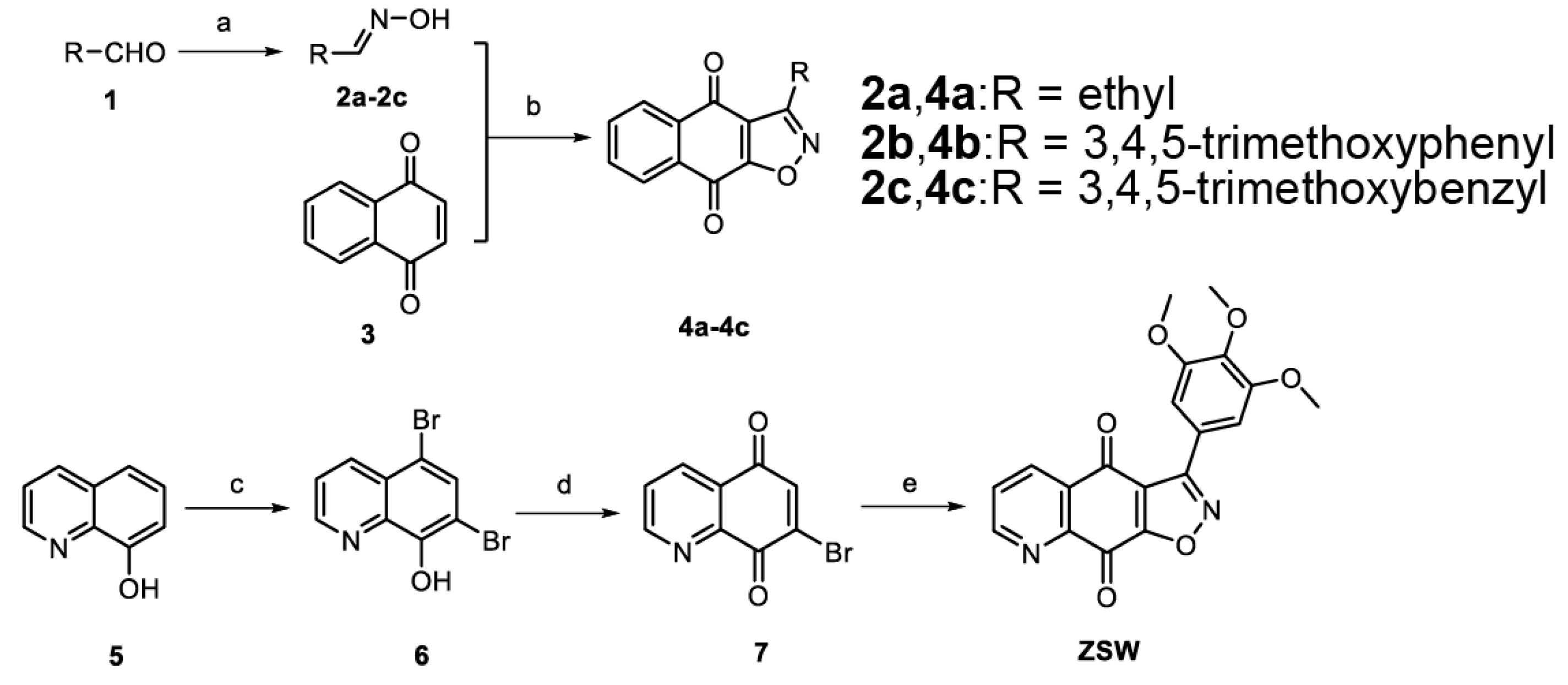
2.7. 3-(3,4,5-Trimethoxyphenyl)isoxazolo [4,5-g]quinoline-4,9-dione ZSW
2.8. 4-(3-Bromopropoxy)-3,5-dimethoxybenzaldehyde 9
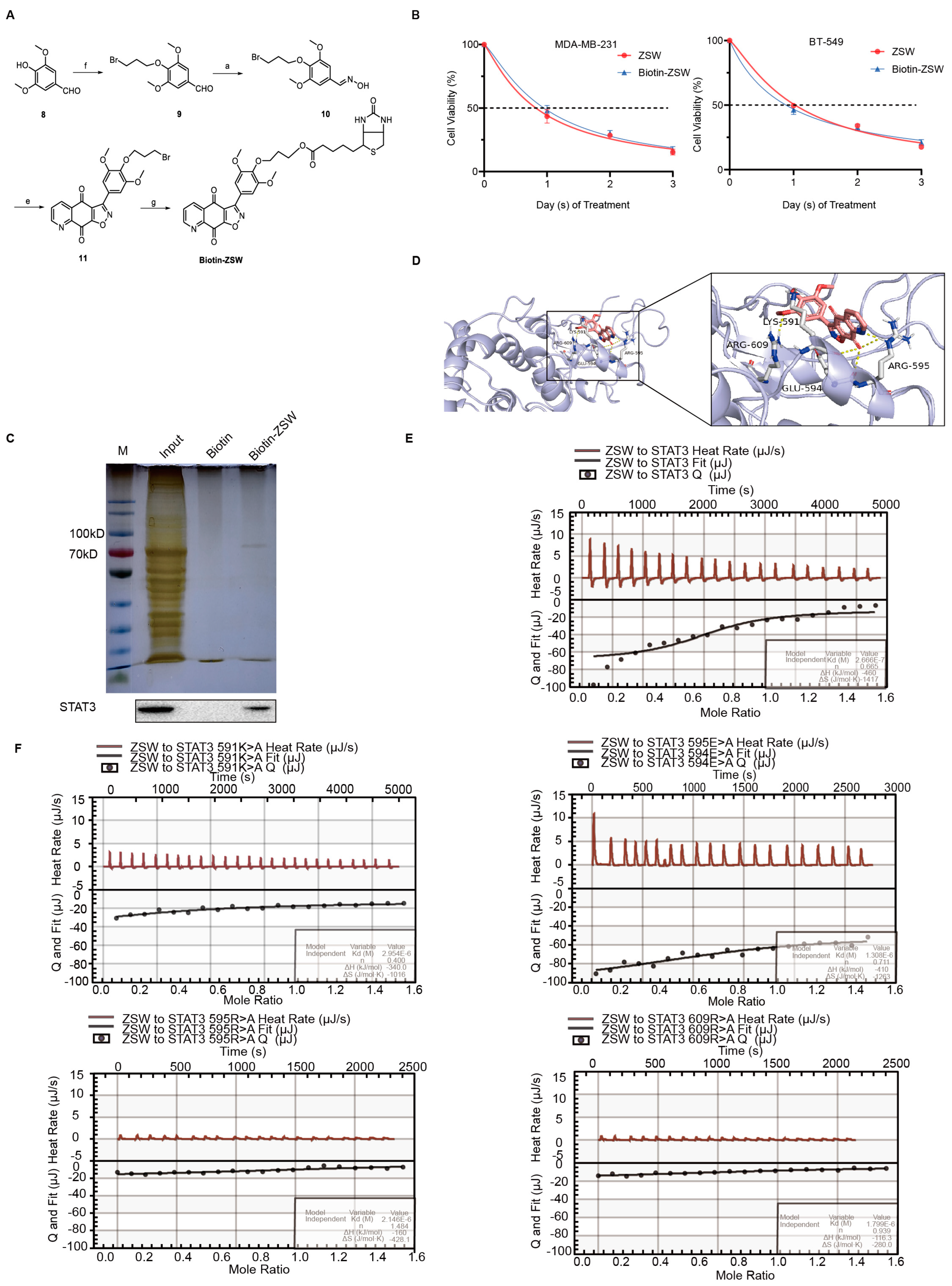
2.9. Synthesis of Biotin–ZSW
2.10. Cell Line Culture and Viability Assay
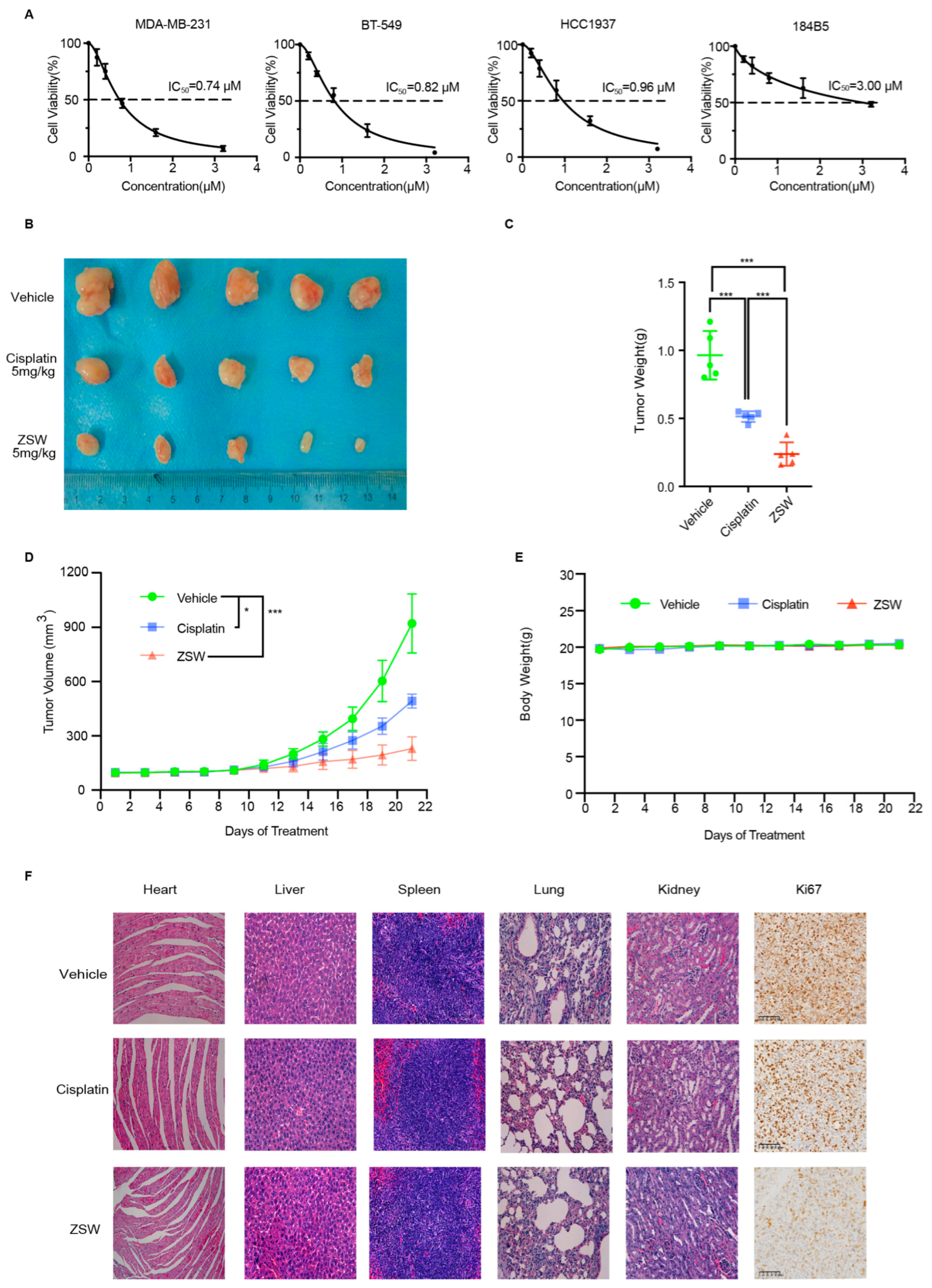
2.11. In Vivo Studies
2.12. Western Blot Analysis and Antibodies
2.13. Plasmids
2.14. Luciferase Assay
2.15. Isothermal Titration Calorimetry
2.16. Molecular Docking
2.17. ALDH1 Activity Assay
2.18. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
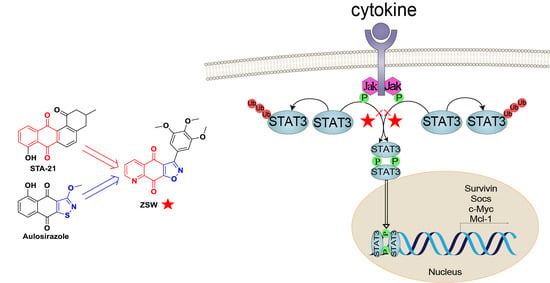
- The synthesis of isoxazoloquinone derivative ZSW:
- 2.
- Structure–activity relationship (SAR) analysis:
- 3.
- ZSW inhibits the proliferation of TNBC cells:
- 4.
- ZSW has a direct binding with STAT3:
- 5.
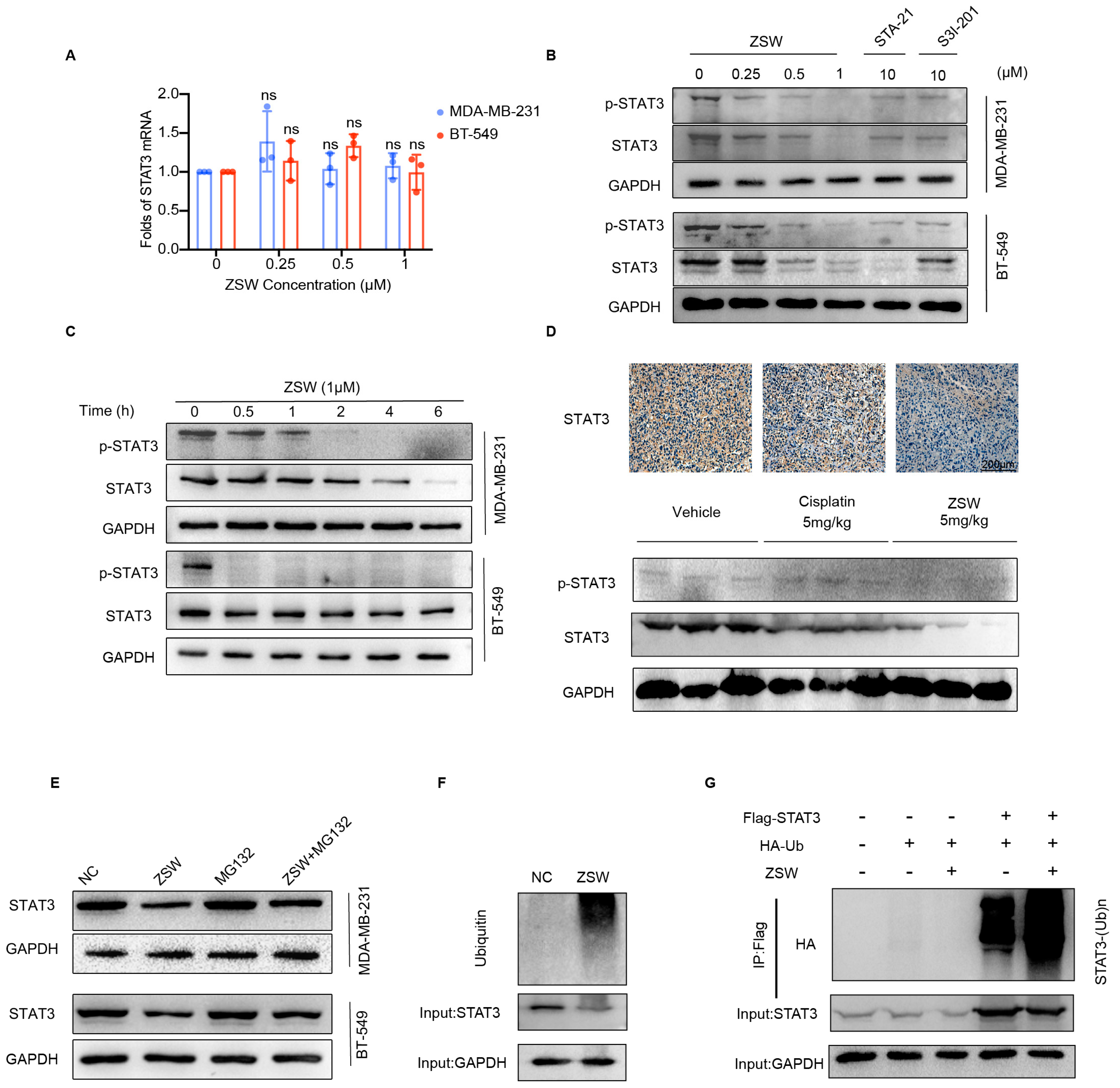
- ZSW promoted STAT3 degradation through ubiquitination:
- 6.
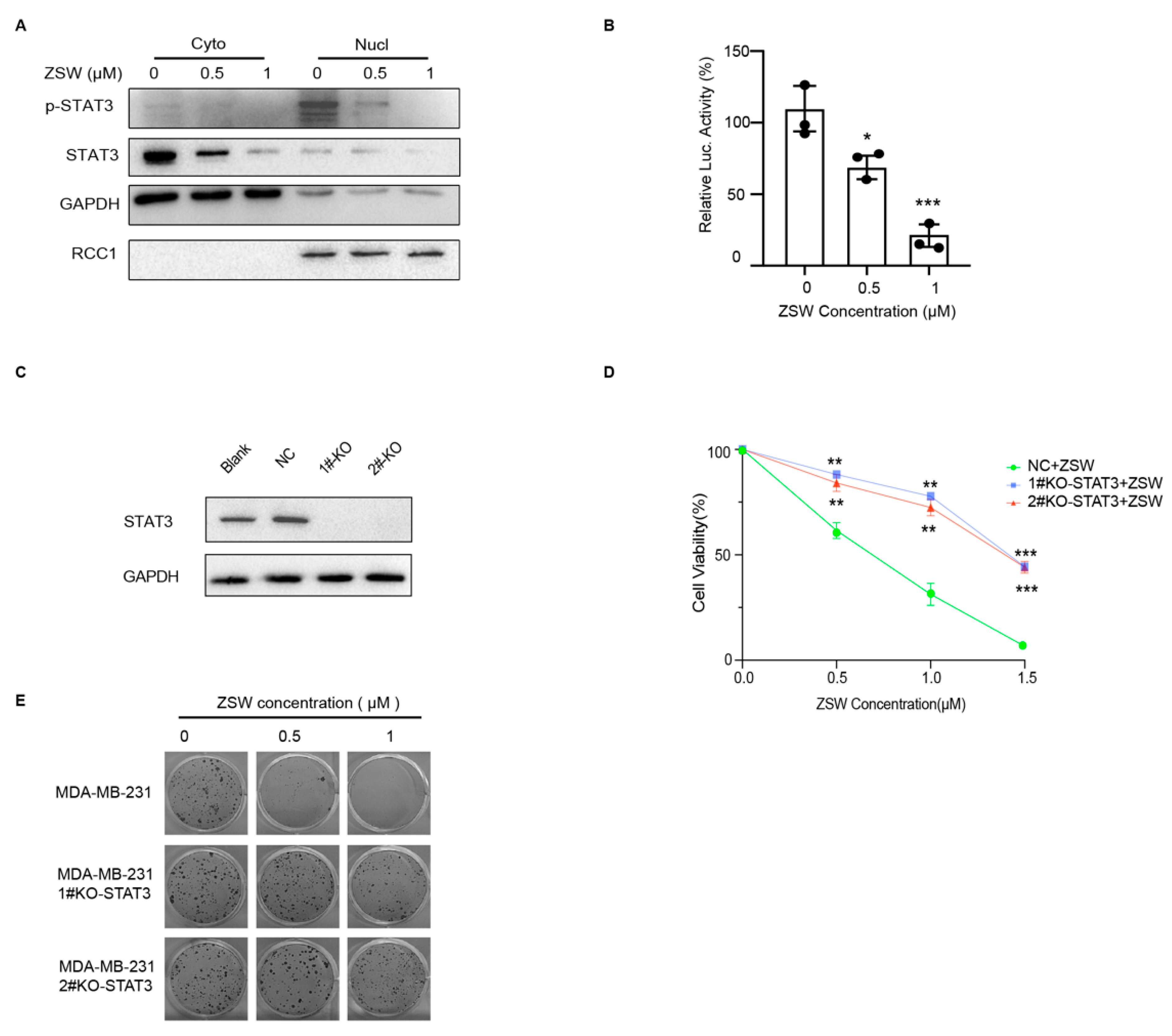
- ZSW exerts anti-tumor activity through STAT3:
- 7.
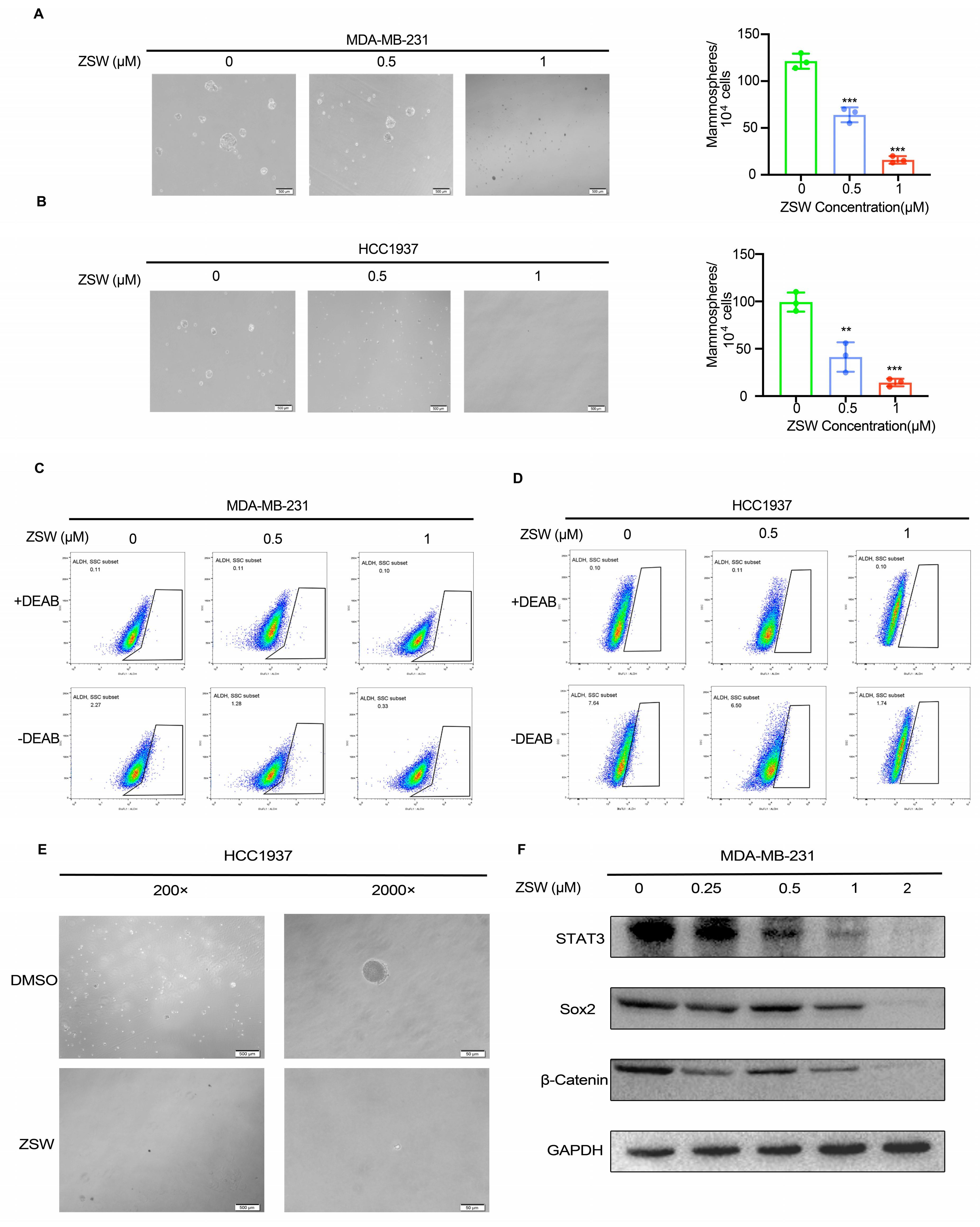
- ZSW suppresses the TNBC stem-cell-like properties
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Goldhirsch, A.; Wood, W.C.; Coates, A.S.; Gelber, R.D.; Thürlimann, B.; Senn, H.J. Strategies for subtypes—Dealing with the diversity of breast cancer: Highlights of the St. Gallen International Expert Consensus on the Primary Therapy of Early Breast Cancer 2011. Ann. Oncol. 2011, 22, 1736–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chavez, K.J.; Garimella, S.V.; Lipkowitz, S. Triple negative breast cancer cell lines: One tool in the search for better treatment of triple negative breast cancer. Breast Dis. 2010, 32, 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, M.; Ye, L.; Feng, X.; Shi, R.; Sun, Z.; Li, Z.; Liu, T. MicroRNA-590-3p inhibits invasion and metastasis in triple-negative breast cancer by targeting Slug. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2020, 10, 965–974. [Google Scholar]
- Fabbri, F.; Salvi, S.; Bravaccini, S. Know your enemy: Genetics, aging, exposomic and inflammation in the war against triple negative breast cancer. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2020, 60, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-H.; Hancock, B.A.; Solzak, J.P.; Brinza, D.; Scafe, C.; Miller, K.D.; Radovich, M. Next-generation sequencing of circulating tumor DNA to predict recurrence in triple-negative breast cancer patients with residual disease after neoadjuvant chemotherapy. NPJ Breast Cancer 2017, 3, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Ni, J.; Beretov, J.; Graham, P.; Li, Y. Cancer stem cell in breast cancer therapeutic resistance. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2018, 69, 152–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puglisi, C.; Giuffrida, R.; Borzì, G.; Di Mattia, P.; Costa, A.; Colarossi, C.; Deiana, E.; Picardo, M.C.; Colarossi, L.; Mare, M.; et al. Radiosensitivity of Cancer Stem Cells Has Potential Predictive Value for Individual Responses to Radiotherapy in Locally Advanced Rectal Cancer. Cancers 2020, 12, 3672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Q.; Zhong, Y.; Dong, H.; Zheng, Q.; Shi, S.; Zhu, K.; Qu, X.; Hu, W.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y. Revisiting signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) as an anticancer target and its inhibitor discovery: Where are we and where should we go? Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 187, 111922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, Y.-T.K.; Ramaiyer, M.; Johnson, D.E.; Grandis, J.R. Targeting STAT3 in Cancer with Nucleotide Therapeutics. Cancers 2019, 11, 1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Tweardy, D.J.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, X.; Landua, J.; Petrovic, I.; Bu, W.; Roarty, K.; Hilsenbeck, S.G.; Rosen, J.M.; et al. STAT3 signaling is activated preferentially in tumor-initiating cells in claudin-low models of human breast cancer. Stem Cells 2014, 32, 2571–2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, K.; Resat, H. Constitutive activation of STAT3 in breast cancer cells: A review. Int. J. Cancer 2016, 138, 2570–2578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.-J.; Yan, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, W.-D. STAT3 as a potential therapeutic target in triple negative breast cancer: A systematic review. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. CR 2019, 38, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brambilla, L.; Genini, D.; Laurini, E.; Merulla, J.; Perez, L.; Fermeglia, M.; Carbone, G.M.; Pricl, S.; Catapano, C.V. Hitting the right spot: Mechanism of action of OPB-31121, a novel and potent inhibitor of the Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 (STAT3). Mol. Oncol. 2015, 9, 1194–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerulli, R.A.; Shehaj, L.; Tosic, I.; Jiang, K.; Wang, J.; Frank, D.A.; Kritzer, J.A. Cytosolic delivery of peptidic STAT3 SH2 domain inhibitors. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2020, 28, 115542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hackermüller, J.; Reiche, K.; Otto, C.; Hösler, N.; Blumert, C.; Brocke-Heidrich, K.; Böhlig, L.; Nitsche, A.; Kasack, K.; Ahnert, P.; et al. Cell cycle, oncogenic and tumor suppressor pathways regulate numerous long and macro non-protein-coding RNAs. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, R48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Niu, G.; Kortylewski, M.; Burdelya, L.; Shain, K.; Zhang, S.; Bhattacharya, R.; Gabrilovich, D.; Heller, R.; Coppola, D.; et al. Regulation of the innate and adaptive immune responses by Stat-3 signaling in tumor cells. Nat. Med. 2004, 10, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Kortylewski, M.; Pardoll, D. Crosstalk between cancer and immune cells: Role of STAT3 in the tumour microenvironment. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2007, 7, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, S.; Tong, Q.; Liu, B.; Huang, W.; Tian, Y.; Fu, X. Targeting STAT3 in Cancer Immunotherapy. Mol. Cancer 2020, 19, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitamura, H.; Ohno, Y.; Toyoshima, Y.; Ohtake, J.; Homma, S.; Kawamura, H.; Takahashi, N.; Taketomi, A. Interleukin-6/STAT3 signaling as a promising target to improve the efficacy of cancer immunotherapy. Cancer Sci. 2017, 108, 1947–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, E.M.; Müller, C.E. Anthraquinones As Pharmacological Tools and Drugs. Med. Res. Rev. 2016, 36, 705–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, O.P.S.; Beteck, R.M.; Legoabe, L.J. Antimalarial application of quinones: A recent update. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 210, 113084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LA, T.H. Immunomodulation by quinones. A model for the use of quinones in the treatment of inflammation. Pharm. Weekbl. Sci. 1991, 13, 127–129. [Google Scholar]
- Kantarjian, H.; Short, N.J.; DiNardo, C.; Stein, E.M.; Daver, N.; Perl, A.E.; Wang, E.S.; Wei, A.; Tallman, M. Harnessing the benefits of available targeted therapies in acute myeloid leukaemia. Lancet. Haematol. 2021, 8, e922–e933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grünwald, V.; Karch, A.; Schuler, M.; Schöffski, P.; Kopp, H.G.; Bauer, S. Randomized Comparison of Pazopanib and Doxorubicin as First-Line Treatment in Patients With Metastatic Soft Tissue Sarcoma Age 60 Years or Older: Results of a German Intergroup Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 3555–3564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Yu, W.; Cai, G.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, C.; Li, S.; Guo, J.; Yin, G.; Chen, C.; Kong, L. A new synthetic derivative of cryptotanshinone KYZ3 as STAT3 inhibitor for triple-negative breast cancer therapy. Cell. Death Dis. 2018, 9, 1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamal, A.; Thao, L.; Sensintaffar, J.; Zhang, L.; Boehm, M.F.; Fritz, L.C.; Burrows, F.J. Burrows. A high-affinity conformation of Hsp90 confers tumour selectivity on Hsp90 inhibitors. Nature 2003, 425, 407–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stratmann, K.; Belli, J.; Jensen, C.M.; Moore, R.E.; Patterson, G.M.L. Aulosirazole, a novel solid tumor selective cytotoxin from the blue-green alga Aulosira fertilissima. J. Org. Chem. 1994, 59, 6279–6281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blunt, C.E.; Torcuk, C.; Liu, Y.; Lewis, W.; Siegel, D.; Ross, D.; Moody, C.J. Synthesis and Intracellular Redox Cycling of Natural Quinones and Their Analogues and Identification of Indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) as Potential Target for Anticancer Activity. Angew. Chem. (Int. Ed. Engl.) 2015, 54, 8740–8745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, F.A.; Hsu, P.D.; Wright, J.; Agarwala, V.; Scott, D.A.; Zhang, F. Genome engineering using the CRISPR-Cas9 system. Nat. Protoc. 2013, 8, 2281–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Li, Y.; Wei, W.; Wang, K.; Wang, L.; Wang, J. Design, synthesis, molecular docking studies and anti-HBV activity of phenylpropanoid derivatives. Chem.-Biol. Interact. 2016, 251, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Yang, H.; Zhu, T.W.; Yu, L.M.; Chen, J.W.; Gu, L.Q.; Huang, Z.S.; An, L.K. Synthesis, cytotoxicity and structure-activity relationship of indolizinoquinolinedione derivatives as DNA topoisomerase IB catalytic inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 152, 195–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, K.; Wang, J.; Jiang, Y.; Xia, J.; Gou, L.; Liu, M.; Zhou, L.; He, T.; et al. Inhibitory effects of BMP9 on breast cancer cells by regulating their interaction with pre-adipocytes/adipocytes. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 35890–35901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, J.; Li, R.-J.; Cheng, M.-S.; Kim, Y.S. Alantolactone selectively suppresses STAT3 activation and exhibits potent anticancer activity in MDA-MB-231 cells. Cancer Lett. 2015, 357, 393–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Shi, T.; Qu, Z.; Zhang, A.; Wu, Z.; Zhao, H.; Zhao, H.; Chen, H. CircRNA_ACAP2 Suppresses EMT in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma by Targeting the miR-21-5p/STAT3 Signaling Axis. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 583682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hindupur, S.V.; Schmid, S.C.; Koch, J.A.; Youssef, A.; Baur, E.-M.; Wang, D.; Horn, T.; Slotta-Huspenina, J.; Gschwend, J.E.; Holm, P.S.; et al. STAT3/5 Inhibitors Suppress Proliferation in Bladder Cancer and Enhance Oncolytic Adenovirus Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tymoszuk, P.; Charoentong, P.; Hackl, H.; Spilka, R.; Müller-Holzner, E.; Trajanoski, Z.; Obrist, P.; Revillion, F.; Peyrat, J.-P.; Fiegl, H.; et al. High STAT1 mRNA levels but not its tyrosine phosphorylation are associated with macrophage infiltration and bad prognosis in breast cancer. BMC Cancer 2014, 14, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vikram, R.; Chou, W.C.; Hung, S.-C.; Shen, C.-Y. Tumorigenic and Metastatic Role of CD44(-/low)/CD24(-/low) Cells in Luminal Breast Cancer. Cancers 2020, 12, 1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Lu, P.; Zhang, H.; Luo, M.; Zhang, X.; Wei, X.; Gao, J.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, C. Oct-4 and Nanog promote the epithelial-mesenchymal transition of breast cancer stem cells and are associated with poor prognosis in breast cancer patients. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 10803–10815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czerwinska, P.; Rucinski, M.; Wlodarczyk, N.; Jaworska, A.; Grzadzielewska, I.; Gryska, K.; Galus, L.; Mackiewicz, J.; Mackiewicz, A. Therapeutic melanoma vaccine with cancer stem cell phenotype represses exhaustion and maintains antigen-specific T cell stemness by up-regulating BCL6. Oncoimmunology 2020, 9, 1710063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visvader, J.E.; Lindeman, G.J. Cancer stem cells: Current status and evolving complexities. Cell. Stem Cell. 2012, 10, 717–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, L.; Roberts, A.L.; Dunphy, K.A.; Bigelow, C.; Yan, H.; Jerry, D.J. Repression of mammary stem/progenitor cells by p53 is mediated by Notch and separable from apoptotic activity. Stem Cells 2011, 29, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Hong, L.; Yang, Z.; Tu, Y.; Xin, W.; Zha, M.; Tu, S.; Sun, G.; Li, Y.; Xiao, W. MicroRNA-148a-3p suppresses epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and stemness properties via Wnt1-mediated Wnt/β-catenin pathway in pancreatic cancer. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 13020–13035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-Y.; Kang, J.W.; Song, X.; Kim, B.K.; Yoo, Y.D.; Kwon, Y.T.; Lee, Y.J. Role of the IL-6-JAK1-STAT3-Oct-4 pathway in the conversion of non-stem cancer cells into cancer stem-like cells. Cell. Signal. 2013, 25, 961–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Jin, Z.; Zhou, H.; Ou, X.; Xu, Y.; Li, H.; Liu, C.; Li, B. Suppression of prostate cancer progression by cancer cell stemness inhibitor napabucasin. Cancer Med. 2016, 5, 1251–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Sun, P.; Guo, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, A.; Meng, L.; Ding, C. Discovery of Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase 1 (IDO-1) Inhibitors Based on Ortho-Naphthaquinone-Containing Natural Product. Molecules 2019, 24, 1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schust, J.; Sperl, B.; Hollis, A.; Mayer, T.U.; Berg, T. Stattic: A small-molecule inhibitor of STAT3 activation and dimerization. Chem. Biol. 2006, 13, 1235–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resetca, D.; Haftchenary, S.; Gunning, P.T.; Wilson, D.J. Changes in signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) dynamics induced by complexation with pharmacological inhibitors of Src homology 2 (SH2) domain dimerization. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 32538–32547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yue, P.; Fletcher, S.; Zhao, W.; Gunning, P.T.; Turkson, J. A novel small-molecule disrupts Stat3 SH2 domain-phosphotyrosine interactions and Stat3-dependent tumor processes. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2010, 79, 1398–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.; Zhou, H.; Xu, R.; Zhao, Y.; Chinnaswamy, K.; McEachern, D.; Chen, J.; Yang, C.Y.; Liu, Z.; Wang, M.; et al. A Potent and Selective Small-Molecule Degrader of STAT3 Achieves Complete Tumor Regression In Vivo. Cancer Cell. 2019, 36, 498–511.e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Huang, S.; Li, H.; Li, Y.; Zeng, H.; Hu, J.; Lin, Y.; Cai, H.; Deng, P.; Song, T.; et al. STAT3 inhibitor BBI608 reduces patient-specific primary cell viability of cervical and endometrial cancer at a clinical-relevant concentration. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2023, 25, 662–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, D.; Kurzrock, R.; Kim, Y.; Woessner, R.; Younes, A.; Nemunaitis, J.; Fowler, N.; Zhou, T.; Schmidt, J.; Jo, M.; et al. AZD9150, a next-generation antisense oligonucleotide inhibitor of STAT3 with early evidence of clinical activity in lymphoma and lung cancer. Sci. Transl. Med. 2015, 7, 314ra185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Compound | MDA-MB-231 (IC50 a in µM) | MDA-MB-231-Doxorubicin Resistance (IC50 a in µM) | BT-549 (IC50 a in µM) | HCC1937 (IC50 a in µM) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4a | 5.14 ± 0.43 | 4.45 ± 0.73 | 4.35 ± 0.95 | 4.27 ± 0.65 |
| 4b | 2.38 ± 0.23 | 2.56 ± 0.75 | 1.95 ± 0.45 | 1.96 ± 0.24 |
| 4c | >10 | >10 | >10 | >10 |
| ZSW | 0.74 ± 0.06 | 0.48 ± 0.07 | 0.82 ± 0.06 | 0.96 ± 0.09 |
| STA-21 | >10 | >10 | >10 | >10 |
| S3I-201 Doxorubicin | >10 0.38 ± 0.04 | >10 1.18 ± 0.24 | >10 0.37 ± 0.03 | >10 0.49 ± 0.09 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xie, Y.; Zhu, S.; Chen, L.; Liu, H.; Peng, T.; Ming, Z.; Zou, Z.; Hu, X.; Luo, W.; Peng, K.; et al. An Isoxazoloquinone Derivative Inhibits Tumor Growth by Targeting STAT3 and Triggering Its Ubiquitin-Dependent Degradation. Cancers 2023, 15, 2424. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15092424
Xie Y, Zhu S, Chen L, Liu H, Peng T, Ming Z, Zou Z, Hu X, Luo W, Peng K, et al. An Isoxazoloquinone Derivative Inhibits Tumor Growth by Targeting STAT3 and Triggering Its Ubiquitin-Dependent Degradation. Cancers. 2023; 15(9):2424. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15092424
Chicago/Turabian StyleXie, Yuanzhu, Shuaiwen Zhu, Ling Chen, Hongdou Liu, Ting Peng, Zhengnan Ming, Zizheng Zou, Xiyuan Hu, Wensong Luo, Kunjian Peng, and et al. 2023. "An Isoxazoloquinone Derivative Inhibits Tumor Growth by Targeting STAT3 and Triggering Its Ubiquitin-Dependent Degradation" Cancers 15, no. 9: 2424. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15092424
APA StyleXie, Y., Zhu, S., Chen, L., Liu, H., Peng, T., Ming, Z., Zou, Z., Hu, X., Luo, W., Peng, K., Nie, Y., Luo, T., Ma, D., Liu, S., & Luo, Z. (2023). An Isoxazoloquinone Derivative Inhibits Tumor Growth by Targeting STAT3 and Triggering Its Ubiquitin-Dependent Degradation. Cancers, 15(9), 2424. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15092424