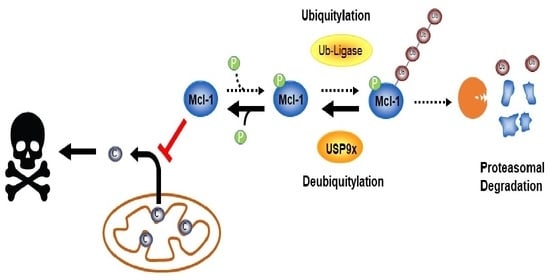
Protein Levels of Anti-Apoptotic Mcl-1 and the Deubiquitinase USP9x Are Cooperatively Upregulated during Prostate Cancer Progression and Limit Response of Prostate Cancer Cells to Radiotherapy
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Antibodies
2.2. Cells and Cell Culture
2.3. Transfection with siRNA
2.4. Flow Cytometric Analysis
2.5. Colony Formation Assay
2.6. Western Blot Analysis
2.7. Analysis of Mcl-1 and USP9x Gene Expression in Human Prostate Samples
2.8. Analysis of Mcl-1 and USP9x Protein Levels in Human Prostate Samples
2.9. Determination of Protein Stability
2.10. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Mcl-1 Protein Level but Not Gene Expression of MCL1 Is Elevated in Human Prostate Cancer Samples
3.2. Mcl-1 Protein Levels Change in LNCaP and PC3 Prostate Cancer Cells after Irradiation
3.3. Downregulation of Mcl-1 Protein Levels Sensitizes LNCaP and PC3 Prostate Cancer Cells to Ionizing Radiation-Induced Cell Death
3.4. Ionizing Radiation Affects Protein Stability of Mcl-1 in Prostate Cancer Cells
3.5. Knockdown of USP9x Expression Improves Response to Radiotherapy
3.6. Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL Regulate Prostate Cancer Cell Survival in Cooperation with Mcl-1
4. Discussion
4.1. Regulation of MCL1 Gene Expression and Mcl-1 Protein Stability in Prostate Cancer
4.2. Increased Mcl-1 Stability by USP9x Mediates Prostate Cancer Resistance to Radiotherapy
4.3. Bcl-2, Bcl-xL, and Mcl-1 Cooperatively Protect Prostate Cancer Cells from Apoptosis
4.4. Limits of the Study
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akakura, K.; Suzuki, H.; Ichikawa, T.; Fujimoto, H.; Maeda, O.; Usami, M.; Hirano, D.; Takimoto, Y.; Kamoto, T.; Ogawa, O.; et al. A randomized trial comparing radical prostatectomy plus endocrine therapy versus external beam radiotherapy plus endocrine therapy for locally advanced prostate cancer: Results at median follow-up of 102 months. Jpn. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 36, 789–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Amico, A.V.; Chen, M.H.; Renshaw, A.A.; Loffredo, M.; Kantoff, P.W. Androgen suppression and radiation vs radiation alone for prostate cancer: A randomized trial. JAMA 2008, 299, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uzzo, R.G.; Haas, N.B.; Crispen, P.L.; Kolenko, V.M. Mechanisms of apoptosis resistance and treatment strategies to overcome them in hormone-refractory prostate cancer. Cancer 2008, 112, 1660–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Dong, L.; Lii, M.F.; Lee, A.L.; de Crevoisier, R.; Mohan, R.; Cox, J.D.; Kuban, D.A.; Cheung, R. Implementation and validation of a three-dimensional deformable registration algorithm for targeted prostate cancer radiotherapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2005, 61, 725–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, L.; Fang, H.; Chen, C.; Wu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ge, H.; Wang, L.; Wan, Y.; He, H. Metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer: Academic insights and perspectives through bibliometric analysis. Medicine 2020, 99, e19760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morciano, G.; Giorgi, C.; Balestra, D.; Marchi, S.; Perrone, D.; Pinotti, M.; Pinton, P. Mcl-1 involvement in mitochondrial dynamics is associated with apoptotic cell death. Mol. Biol. Cell 2016, 27, 20–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollville, E.; Carroll, R.G.; Cullen, S.P.; Martin, S.J. Bcl-2 family proteins participate in mitochondrial quality control by regulating Parkin/PINK1-dependent mitophagy. Mol. Cell 2014, 55, 451–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, J.M.; Cory, S. The Bcl-2 apoptotic switch in cancer development and therapy. Oncogene 2007, 26, 1324–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youle, R.J.; Strasser, A. The BCL-2 protein family: Opposing activities that mediate cell death. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2008, 9, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, K.J.; Leung, H.Y. Evasion of cell death: A contributory factor in prostate cancer development and treatment resistance. Cancer Lett. 2021, 520, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krajewska, M.; Krajewski, S.; Epstein, J.I.; Shabaik, A.; Sauvageot, J.; Song, K.; Kitada, S.; Reed, J.C. Immunohistochemical analysis of bcl-2, bax, bcl-X, and mcl-1 expression in prostate cancers. Am. J. Pathol. 1996, 148, 1567–1576. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Soliman, L.; De Souza, A.; Srinivasan, P.; Danish, M.; Bertone, P.; El-Deiry, W.S.; Carneiro, B.A. The Role of BCL-2 Proteins in the Development of Castration-resistant Prostate Cancer and Emerging Therapeutic Strategies. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 44, 374–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiner, T.; de Las Pozas, A.; Parrondo, R.; Palenzuela, D.; Cayuso, W.; Rai, P.; Perez-Stable, C. Mcl-1 protects prostate cancer cells from cell death mediated by chemotherapy-induced DNA damage. Oncoscience 2015, 2, 703–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parrondo, R.; de Las Pozas, A.; Reiner, T.; Perez-Stable, C. ABT-737, a small molecule Bcl-2/Bcl-xL antagonist, increases antimitotic-mediated apoptosis in human prostate cancer cells. PeerJ 2013, 1, e144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamanaka, K.; Rocchi, P.; Miyake, H.; Fazli, L.; So, A.; Zangemeister-Wittke, U.; Gleave, M.E. Induction of apoptosis and enhancement of chemosensitivity in human prostate cancer LNCaP cells using bispecific antisense oligonucleotide targeting Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL genes. BJU Int. 2006, 97, 1300–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masilamani, A.P.; Dettmer-Monaco, V.; Monaco, G.; Cathomen, T.; Kuckuck, I.; Schultze-Seemann, S.; Huber, N.; Wolf, P. An Anti-PSMA Immunotoxin Reduces Mcl-1 and Bcl2A1 and Specifically Induces in Combination with the BAD-Like BH3 Mimetic ABT-737 Apoptosis in Prostate Cancer Cells. Cancers 2020, 12, 1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, S.W.; Derouet, M.; Howse, M.; Moots, R.J. Regulation of neutrophil apoptosis by Mcl-1. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2004, 32, 489–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Li, T.; Hu, M.; Wang, B.; Zhou, Q.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Duan, X.; Yang, J.; Liu, X.; et al. PHLPP1 deficiency ameliorates cardiomyocyte death and cardiac dysfunction through inhibiting Mcl-1 degradation. Cell. Signal. 2022, 92, 110281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, J.C.; Talab, F.; Zuzel, M.; Lin, K.; Slupsky, J.R. c-Abl regulates Mcl-1 gene expression in chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells. Blood 2011, 117, 2414–2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, S.; Oelsner, M.; Decker, T.; zum Buschenfelde, C.M.; Wagner, M.; Lutzny, G.; Kuhnt, T.; Schmidt, B.; Oostendorp, R.A.; Peschel, C.; et al. Sorafenib induces cell death in chronic lymphocytic leukemia by translational downregulation of Mcl-1. Leukemia 2011, 25, 838–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwickart, M.; Huang, X.; Lill, J.R.; Liu, J.; Ferrando, R.; French, D.M.; Maecker, H.; O’Rourke, K.; Bazan, F.; Eastham-Anderson, J.; et al. Deubiquitinase USP9X stabilizes MCL1 and promotes tumour cell survival. Nature 2010, 463, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flores, M.L.; Castilla, C.; Gasca, J.; Medina, R.; Pérez-Valderrama, B.; Romero, F.; Japón, M.A.; Sáez, C. Loss of PKCδ Induces Prostate Cancer Resistance to Paclitaxel through Activation of Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway and Mcl-1 Accumulation. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2016, 15, 1713–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, S.; Zhang, S.; Driss, A.; Liu, Z.R.; Kim, H.R.; Wang, Y.; Ritenour, C.; Zhau, H.E.; Kucuk, O.; Chung, L.W.; et al. PDGF upregulates Mcl-1 through activation of β-catenin and HIF-1α-dependent signaling in human prostate cancer cells. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, N.; Baek, H.S.; Chun, Y.J. Embelin-Induced Apoptosis of Human Prostate Cancer Cells Is Mediated through Modulation of Akt and β-Catenin Signaling. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0134760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, Y.H.; Yu, F.J.; Nassef, Y.; Liu, C.J.; Chen, Y.S.; Lin, C.Y.; Feng, J.L.; Wu, M.H. Targeting of Mcl-1 Expression by MiRNA-3614-5p Promotes Cell Apoptosis of Human Prostate Cancer Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasqualini, L.; Bu, H.; Puhr, M.; Narisu, N.; Rainer, J.; Schlick, B.; Schäfer, G.; Angelova, M.; Trajanoski, Z.; Börno, S.T.; et al. miR-22 and miR-29a Are Members of the Androgen Receptor Cistrome Modulating LAMC1 and Mcl-1 in Prostate Cancer. Mol. Endocrinol. 2015, 29, 1037–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Q.; He, X.; Hsu, J.M.; Xia, W.; Chen, C.T.; Li, L.Y.; Lee, D.F.; Liu, J.C.; Zhong, Q.; Wang, X.; et al. Degradation of Mcl-1 by beta-TrCP mediates glycogen synthase kinase 3-induced tumor suppression and chemosensitization. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2007, 27, 4006–4017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wertz, I.E.; Kusam, S.; Lam, C.; Okamoto, T.; Sandoval, W.; Anderson, D.J.; Helgason, E.; Ernst, J.A.; Eby, M.; Liu, J.; et al. Sensitivity to antitubulin chemotherapeutics is regulated by MCL1 and FBW7. Nature 2011, 471, 110–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Q.; Gao, W.; Du, F.; Wang, X. Mule/ARF-BP1, a BH3-only E3 ubiquitin ligase, catalyzes the polyubiquitination of Mcl-1 and regulates apoptosis. Cell 2005, 121, 1085–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inuzuka, H.; Shaik, S.; Onoyama, I.; Gao, D.; Tseng, A.; Maser, R.S.; Zhai, B.; Wan, L.; Gutierrez, A.; Lau, A.W.; et al. SCF(FBW7) regulates cellular apoptosis by targeting MCL1 for ubiquitylation and destruction. Nature 2011, 471, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivigno, D.; Essmann, F.; Huber, S.M.; Rudner, J. Deubiquitinase USP9x confers radioresistance through stabilization of Mcl-1. Neoplasia 2012, 14, 893–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfsperger, F.; Hogh-Binder, S.A.; Schittenhelm, J.; Psaras, T.; Ritter, V.; Bornes, L.; Huber, S.M.; Jendrossek, V.; Rudner, J. Deubiquitylating enzyme USP9x regulates radiosensitivity in glioblastoma cells by Mcl-1-dependent and -independent mechanisms. Cell Death Dis. 2016, 7, e2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maurer, U.; Charvet, C.; Wagman, A.S.; Dejardin, E.; Green, D.R. Glycogen synthase kinase-3 regulates mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization and apoptosis by destabilization of MCL-1. Mol. Cell 2006, 21, 749–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Molecular Taxonomy of Primary Prostate Cancer. Cell 2015, 163, 1011–1025. [CrossRef]
- Ketteler, J.; Panic, A.; Reis, H.; Wittka, A.; Maier, P.; Herskind, C.; Yagüe, E.; Jendrossek, V.; Klein, D. Progression-Related Loss of Stromal Caveolin 1 Levels Mediates Radiation Resistance in Prostate Carcinoma via the Apoptosis Inhibitor TRIAP1. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panic, A.; Reis, H.; Wittka, A.; Darr, C.; Hadaschik, B.; Jendrossek, V.; Klein, D. The Biomarker Potential of Caveolin-1 in Penile Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 606122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remmele, W.; Stegner, H.E. Recommendation for uniform definition of an immunoreactive score (IRS) for immunohistochemical estrogen receptor detection (ER-ICA) in breast cancer tissue. Pathologe 1987, 8, 138–140. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, R.; Emi, M.; Tanabe, K. Caspase-dependent and -independent cell death pathways after DNA damage (Review). Oncol. Rep. 2005, 14, 595–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudner, J.; Lepple-Wienhues, A.; Budach, W.; Berschauer, J.; Friedrich, B.; Wesselborg, S.; Schulze-Osthoff, K.; Belka, C. Wild-type, mitochondrial and ER-restricted Bcl-2 inhibit DNA damage-induced apoptosis but do not affect death receptor-induced apoptosis. J. Cell Sci. 2001, 114, 4161–4172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritter, V.; Krautter, F.; Klein, D.; Jendrossek, V.; Rudner, J. Bcl-2/Bcl-xL inhibitor ABT-263 overcomes hypoxia-driven radioresistence and improves radiotherapy. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, S.; Jonas, O.; Whitman, M.A.; Corey, E.; Balk, S.P.; Chen, S. Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors Increase MCL1 Degradation and in Combination with BCLXL/BCL2 Inhibitors Drive Prostate Cancer Apoptosis. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 5458–5470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of cancer: The next generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willis, S.N.; Adams, J.M. Life in the balance: How BH3-only proteins induce apoptosis. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2005, 17, 617–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anvari, K.; Seilanian Toussi, M.; Kalantari, M.; Naseri, S.; Karimi Shahri, M.; Ahmadnia, H.; Katebi, M.; Sedighi Pashaki, A.; Dayani, M.; Broumand, M. Expression of Bcl-2 and Bax in advanced or metastatic prostate carcinoma. Urol. J. 2012, 9, 381–388. [Google Scholar]
- Brinkmann, K.; Ng, A.P.; de Graaf, C.A.; Strasser, A. What can we learn from mice lacking pro-survival BCL-2 proteins to advance BH3 mimetic drugs for cancer therapy? Cell Death Differ. 2022, 29, 1079–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, B.; Xu, L.; Hui, H.; Sun, Y.; Wu, J. USP9X mRNA expression predicts clinical outcome for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma treated with cisplatin-based therapy. Clin. Res. Hepatol. Gastroenterol. 2020, 44, 932–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yang, B.; Cao, H.; Yang, C.X.; Ouyang, W.; Zhang, S.M.; Yang, G.F.; Zhou, F.X.; Zhou, Y.F.; et al. Elevated expression of USP9X correlates with poor prognosis in human non-small cell lung cancer. J. Thorac. Dis. 2015, 7, 672–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Li, S.; Huang, J.; Dong, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zheng, J. Down-Regulation of Ubiquitin-Specific Peptidase 9X Inhibited Proliferation, Migration and Invasion of Osteosarcoma via ERK1/2 and PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathways. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2022, 45, 1283–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murtaza, M.; Jolly, L.A.; Gecz, J.; Wood, S.A. La FAM fatale: USP9X in development and disease. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2015, 72, 2075–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuta, H.; Yoshihara, H.; Fukushima, T.; Yoneyama, Y.; Ito, A.; Worrall, C.; Girnita, A.; Girnita, L.; Yoshida, M.; Asano, T.; et al. IRS-2 deubiquitination by USP9X maintains anchorage-independent cell growth via Erk1/2 activation in prostate carcinoma cell line. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 33871–33883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Xu, X.; Lin, P.; He, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, B.; Zhang, Z.; Sethi, G.; Liu, J.; Zhou, X.; et al. Inhibition of the deubiquitinase USP9x induces pre-B cell homeobox 1 (PBX1) degradation and thereby stimulates prostate cancer cell apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 4572–4582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Kollipara, R.K.; Srivastava, N.; Li, R.; Ravindranathan, P.; Hernandez, E.; Freeman, E.; Humphries, C.G.; Kapur, P.; Lotan, Y.; et al. Ablation of the oncogenic transcription factor ERG by deubiquitinase inhibition in prostate cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 4251–4256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, B.; Sartor, O. Radiation-based approaches for therapy and palliation of advanced prostate cancer. Curr. Opin. Urol. 2012, 22, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gogna, N.K.; Baxi, S.; Hickey, B.; Baumann, K.; Burmeister, E.; Holt, T. Split-course, high-dose palliative pelvic radiotherapy for locally progressive hormone-refractory prostate cancer. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2012, 83, e205-211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, A.R.; Park, W. Radiotherapy in prostate cancer treatment: Results of the patterns of care study in Korea. Radiat. Oncol. J. 2017, 35, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alimirah, F.; Chen, J.; Basrawala, Z.; Xin, H.; Choubey, D. DU-145 and PC-3 human prostate cancer cell lines express androgen receptor: Implications for the androgen receptor functions and regulation. FEBS Lett. 2006, 580, 2294–2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, J.; Yue, P.; Deng, X.; Khuri, F.R.; Sun, S.Y. mTOR Complex 2 Stabilizes Mcl-1 Protein by Suppressing Its Glycogen Synthase Kinase 3-Dependent and SCF-FBXW7-Mediated Degradation. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2015, 35, 2344–2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindner, S.E.; Wissler, M.; Gründer, A.; Aumann, K.; Ottina, E.; Peintner, L.; Brauns-Schubert, P.; Preiss, F.; Herzog, S.; Borner, C.; et al. Increased leukocyte survival and accelerated onset of lymphoma in the absence of MCL-1 S159-phosphorylation. Oncogene 2014, 33, 5221–5224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boiani, M.; Daniel, C.; Liu, X.; Hogarty, M.D.; Marnett, L.J. The stress protein BAG3 stabilizes Mcl-1 protein and promotes survival of cancer cells and resistance to antagonist ABT-737. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 6980–6990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Xie, M.; Li, R.; Owonikoko, T.K.; Ramalingam, S.S.; Khuri, F.R.; Curran, W.J.; Wang, Y.; Deng, X. Role of Ku70 in deubiquitination of Mcl-1 and suppression of apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 2014, 21, 1160–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Cai, T.Y.; Zhu, H.; Yang, L.Q.; Jiang, H.; Dong, X.W.; Hu, Y.Z.; Lin, N.M.; He, Q.J.; Yang, B. Synergistic antitumor activity of gemcitabine and ABT-737 in vitro and in vivo through disrupting the interaction of USP9X and Mcl-1. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2011, 10, 1264–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yecies, D.; Carlson, N.E.; Deng, J.; Letai, A. Acquired resistance to ABT-737 in lymphoma cells that up-regulate MCL-1 and BFL-1. Blood 2010, 115, 3304–3313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Delft, M.F.; Wei, A.H.; Mason, K.D.; Vandenberg, C.J.; Chen, L.; Czabotar, P.E.; Willis, S.N.; Scott, C.L.; Day, C.L.; Cory, S.; et al. The BH3 mimetic ABT-737 targets selective Bcl-2 proteins and efficiently induces apoptosis via Bak/Bax if Mcl-1 is neutralized. Cancer Cell 2006, 10, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czabotar, P.E.; Lee, E.F.; van Delft, M.F.; Day, C.L.; Smith, B.J.; Huang, D.C.; Fairlie, W.D.; Hinds, M.G.; Colman, P.M. Structural insights into the degradation of Mcl-1 induced by BH3 domains. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 6217–6222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, W.; Sharma, K.; Lee, J.Y.; Maxim, N.T.; Hicks, M.A.; Vu, T.T.; Luu, A.; Yeudall, W.A.; Tanaka, N.; Harada, H. DNA damaging agent-induced apoptosis is regulated by MCL-1 phosphorylation and degradation mediated by the Noxa/MCL-1/CDK2 complex. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 36353–36365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Certo, M.; Del Gaizo Moore, V.; Nishino, M.; Wei, G.; Korsmeyer, S.; Armstrong, S.A.; Letai, A. Mitochondria primed by death signals determine cellular addiction to antiapoptotic BCL-2 family members. Cancer Cell 2006, 9, 351–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, V.; Saleh, T.; Min Lee, S.; Murray, G.; Reed, J.; Souers, A.; Faber, A.C.; Harada, H.; Gewirtz, D.A. Androgen-deprivation induced senescence in prostate cancer cells is permissive for the development of castration-resistance but susceptible to senolytic therapy. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2021, 193, 114765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corella, A.N.; Cabiliza Ordonio, M.V.A.; Coleman, I.; Lucas, J.M.; Kaipainen, A.; Nguyen, H.M.; Sondheim, D.; Brown, L.G.; True, L.D.; Lee, J.K.; et al. Identification of Therapeutic Vulnerabilities in Small-cell Neuroendocrine Prostate Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 1667–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pecina, P.; Borisenko, G.G.; Belikova, N.A.; Tyurina, Y.Y.; Pecinova, A.; Lee, I.; Samhan-Arias, A.K.; Przyklenk, K.; Kagan, V.E.; Hüttemann, M. Phosphomimetic substitution of cytochrome C tyrosine 48 decreases respiration and binding to cardiolipin and abolishes ability to trigger downstream caspase activation. Biochemistry 2010, 49, 6705–6714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krajewska, M.; Krajewski, S.; Banares, S.; Huang, X.; Turner, B.; Bubendorf, L.; Kallioniemi, O.P.; Shabaik, A.; Vitiello, A.; Peehl, D.; et al. Elevated expression of inhibitor of apoptosis proteins in prostate cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2003, 9, 4914–4925. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Carson, J.P.; Behnam, M.; Sutton, J.N.; Du, C.; Wang, X.; Hunt, D.F.; Weber, M.J.; Kulik, G. Smac is required for cytochrome c-induced apoptosis in prostate cancer LNCaP cells. Cancer Res. 2002, 62, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Berezovskaya, O.; Schimmer, A.D.; Glinskii, A.B.; Pinilla, C.; Hoffman, R.M.; Reed, J.C.; Glinsky, G.V. Increased expression of apoptosis inhibitor protein XIAP contributes to anoikis resistance of circulating human prostate cancer metastasis precursor cells. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 2378–2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








| Characteristics | Sub-Characteristics | Value (n %) |
|---|---|---|
| Age (range) | 68 ± 7.3 | |
| Surgical procedures | radical prostatectomy | 32 (44%) |
| palliative transurethral resection | 26 (35%) | |
| radical cystoprostatectomy | 6 (8%) | |
| transvesical prostatectomy | 4 (5%) | |
| transurethral resection | 6 (8%) | |
| Stage (pT) (n = 32 for Gleason scored specimen) | pT1 | 0 |
| pT2 | 23 (72%) | |
| pT3 | 9 (28%) | |
| Lymph node metastasis (pN) (n = 58; without benige specimen) | pN0 | 30 (52%) |
| pN1 | 13 (22%) | |
| pNX | 15 (26%) | |
| Distant metastasis (M) (n = 58; without benige specimen) | M0 (high and low GL) | 32 (57%) |
| M1 (all palliative) | 20 (33%) | |
| MX (palliative) | 6 (10%) | |
| USP9x scores (epithelium) | benige | 16 (21%) |
| low | 16 (21%) | |
| high | 16 (21%) | |
| palliative | 25 (33.6%) | |
| Mcl-1 scores (epithelium) | benige | 7 (9%) |
| low | 12 (16%) | |
| high | 14 (19%) | |
| palliative | 22 (29%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hogh-Binder, S.A.; Klein, D.; Wolfsperger, F.; Huber, S.M.; Hennenlotter, J.; Stenzl, A.; Rudner, J. Protein Levels of Anti-Apoptotic Mcl-1 and the Deubiquitinase USP9x Are Cooperatively Upregulated during Prostate Cancer Progression and Limit Response of Prostate Cancer Cells to Radiotherapy. Cancers 2023, 15, 2496. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15092496
Hogh-Binder SA, Klein D, Wolfsperger F, Huber SM, Hennenlotter J, Stenzl A, Rudner J. Protein Levels of Anti-Apoptotic Mcl-1 and the Deubiquitinase USP9x Are Cooperatively Upregulated during Prostate Cancer Progression and Limit Response of Prostate Cancer Cells to Radiotherapy. Cancers. 2023; 15(9):2496. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15092496
Chicago/Turabian StyleHogh-Binder, Sophia A., Diana Klein, Frederik Wolfsperger, Stephan M. Huber, Jörg Hennenlotter, Arnulf Stenzl, and Justine Rudner. 2023. "Protein Levels of Anti-Apoptotic Mcl-1 and the Deubiquitinase USP9x Are Cooperatively Upregulated during Prostate Cancer Progression and Limit Response of Prostate Cancer Cells to Radiotherapy" Cancers 15, no. 9: 2496. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15092496
APA StyleHogh-Binder, S. A., Klein, D., Wolfsperger, F., Huber, S. M., Hennenlotter, J., Stenzl, A., & Rudner, J. (2023). Protein Levels of Anti-Apoptotic Mcl-1 and the Deubiquitinase USP9x Are Cooperatively Upregulated during Prostate Cancer Progression and Limit Response of Prostate Cancer Cells to Radiotherapy. Cancers, 15(9), 2496. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15092496