Low-Dose Bevacizumab for the Treatment of Focal Radiation Necrosis of the Brain (fRNB): A Single-Center Case Series
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Selection, Clinical Outcomes, and Adverse Events
2.2. Statistical Analysis
2.3. Imaging
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
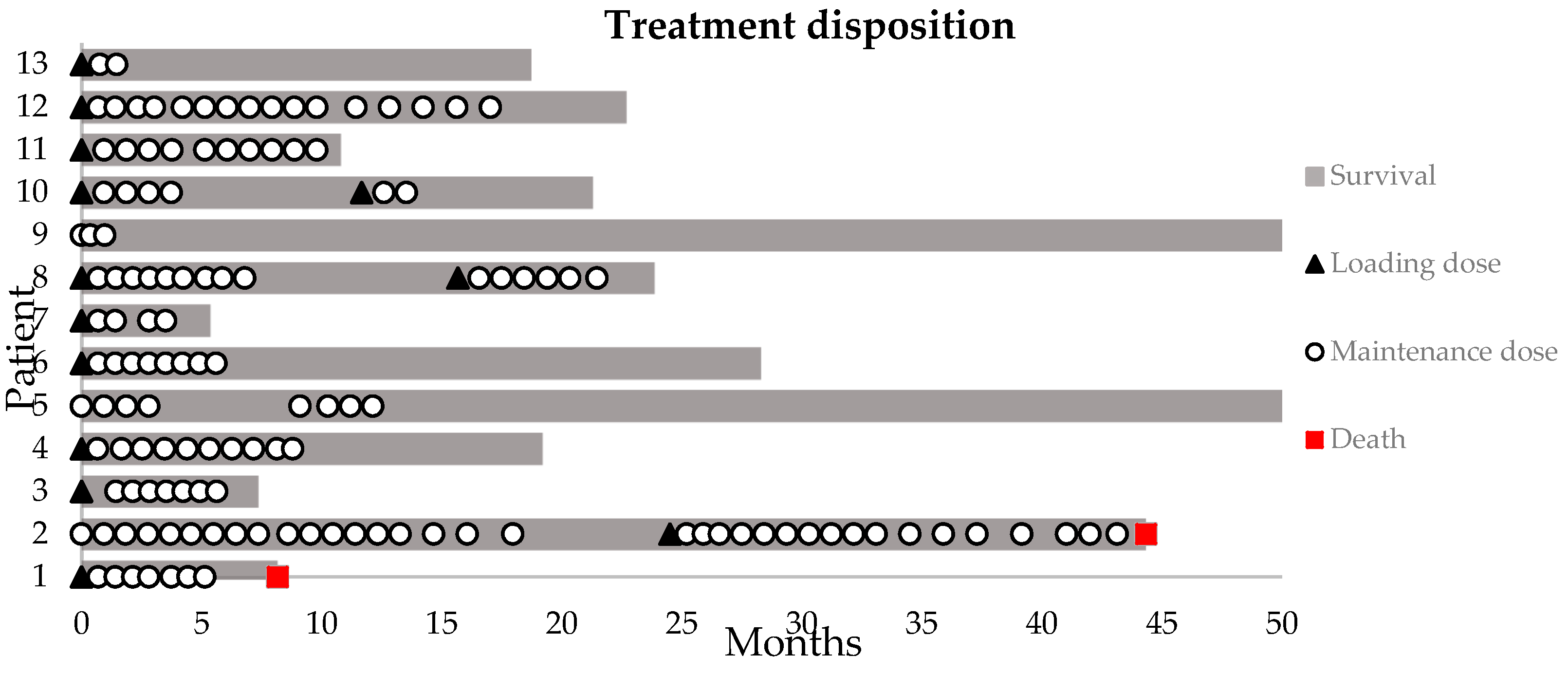
3.2. Treatment Disposition
3.3. Clinical Outcome
3.4. Objective Response on MRI of the Brain
3.5. Safety
3.6. Survival
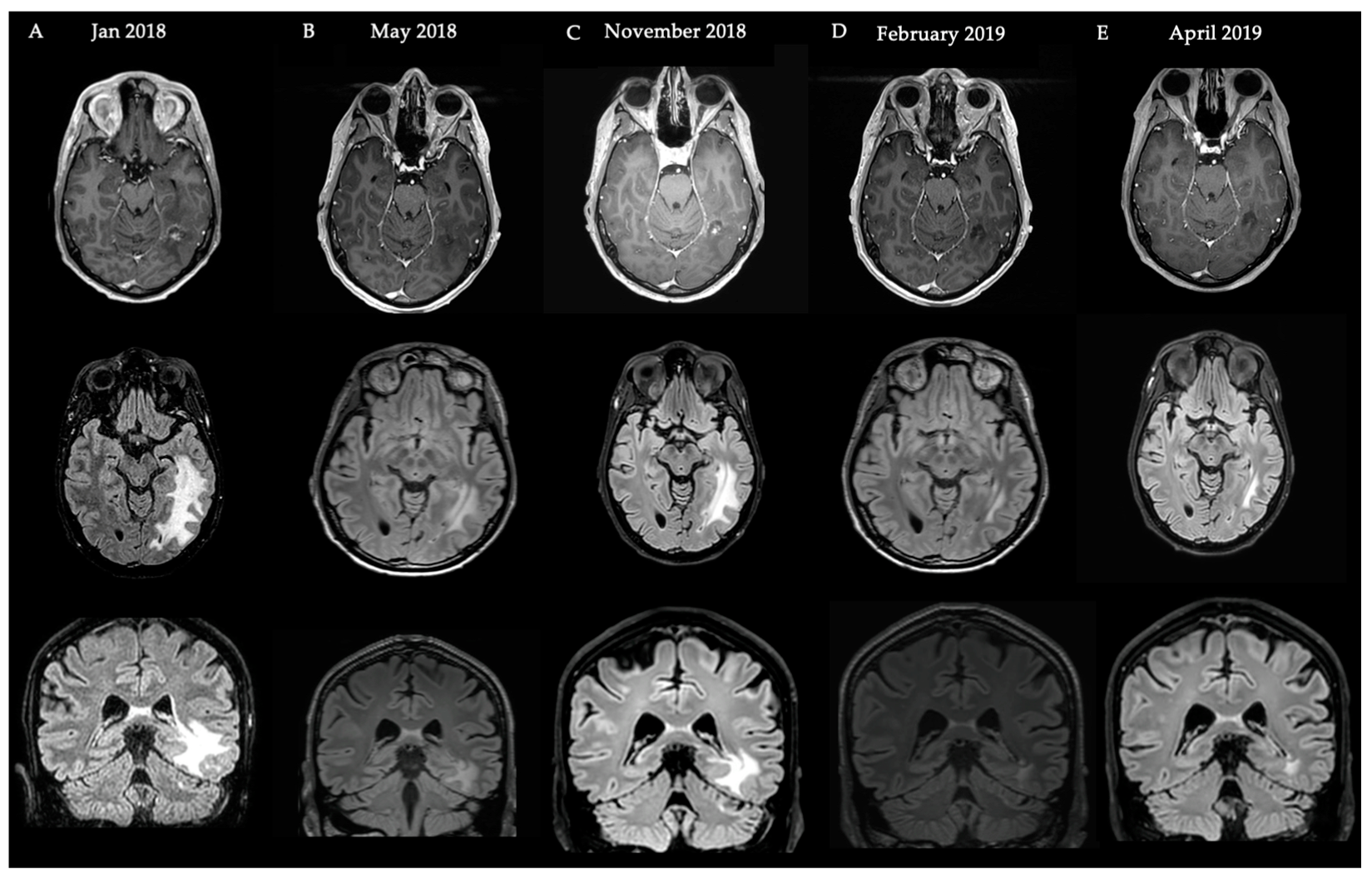
4. Case Illustrations
4.1. Case Illustration 1
4.2. Case Illustration 2
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vellayappan, B.; Tan, C.L.; Yong, C.; Khor, L.K.; Koh, W.Y.; Yeo, T.T.; Detsky, J.; Lo, S.; Sahgal, A. Diagnosis and Management of Radiation Necrosis in Patients with Brain Metastases. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, F.S.; Arevalo, O.; Zorofchian, S.; Patrizz, A.; Riascos, R.; Tandon, N.; Blanco, A.; Ballester, L.Y.; Esquenazi, Y. Cerebral Radiation Necrosis: Incidence, Pathogenesis, Diagnostic Challenges, and Future Opportunities. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2019, 21, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohutek, Z.A.; Yamada, Y.; Chan, T.A.; Brennan, C.W.; Tabar, V.; Gutin, P.H.; Jonathan Yang, T.; Rosenblum, M.K.; Ballangrud, Å.; Young, R.J.; et al. Long-term risk of radionecrosis and imaging changes after stereotactic radiosurgery for brain metastases. J. Neuro-Oncol. 2015, 125, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minniti, G.; Clarke, E.; Lanzetta, G.; Osti, M.F.; Trasimeni, G.; Bozzao, A.; Romano, A.; Enrici, R.M. Stereotactic radiosurgery for brain metastases: Analysis of outcome and risk of brain radionecrosis. Radiat. Oncol. 2011, 6, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varlotto, J.M.; Flickinger, J.C.; Niranjan, A.; Bhatnagar, A.K.; Kondziolka, D.; Lunsford, L.D. Analysis of tumor control and toxicity in patients who have survived at least one year after radiosurgery for brain metastases. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2003, 57, 452–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blonigen, B.J.; Steinmetz, R.D.; Levin, L.; Lamba, M.A.; Warnick, R.E.; Breneman, J.C. Irradiated volume as a predictor of brain radionecrosis after linear accelerator stereotactic radiosurgery. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2010, 77, 996–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, D.; Rong, X.; Chen, D.; Jiang, J.; Ng, W.T.; Mai, H.; Li, Y.; Li, H.; Cai, J.; Cheng, J.; et al. Mortality of early treatment for radiation-induced brain necrosis in head and neck cancer survivors: A multicentre, retrospective, registry-based cohort study. EClinicalMedicine 2022, 52, 101618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furuse, M.; Nonoguchi, N.; Kawabata, S.; Miyatake, S.; Kuroiwa, T. Delayed brain radiation necrosis: Pathological review and new molecular targets for treatment. Med. Mol. Morphol. 2015, 48, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyatake, S.; Nonoguchi, N.; Furuse, M.; Yoritsune, E.; Miyata, T.; Kawabata, S.; Kuroiwa, T. Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Radiation Necrosis in the Brain. Neurol. Med. Chir. 2015, 55 (Suppl. 1), 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvo, W.; Hopewell, J.W.; Reinhold, H.S.; Yeung, T.K. Time- and dose-related changes in the white matter of the rat brain after single doses of X rays. Br. J. Radiol. 1988, 61, 1043–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinhold, H.S.; Calvo, W.; Hopewell, J.W.; van der Berg, A.P. Development of blood vessel-related radiation damage in the fimbria of the central nervous system. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 1990, 18, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyubimova, N.; Hopewell, J.W. Experimental evidence to support the hypothesis that damage to vascular endothelium plays the primary role in the development of late radiation-induced CNS injury. Br. J. Radiol. 2004, 77, 488–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sneed, P.K.; Mendez, J.; Vemer-van den Hoek, J.G.; Seymour, Z.A.; Ma, L.; Molinaro, A.M.; Fogh, S.E.; Nakamura, J.L.; McDermott, M.W. Adverse radiation effect after stereotactic radiosurgery for brain metastases: Incidence, time course, and risk factors. J. Neurosurg. 2015, 123, 373–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerschbaumer, J.; Demetz, M.; Krigers, A.; Nevinny-Stickel, M.; Thome, C.; Freyschlag, C.F. Risk Factors for Radiation Necrosis in Patients Undergoing Cranial Stereotactic Radiosurgery. Cancers 2021, 13, 4736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milano, M.T.; Grimm, J.; Niemierko, A.; Soltys, S.G.; Moiseenko, V.; Redmond, K.J.; Yorke, E.; Sahgal, A.; Xue, J.; Mahadevan, A.; et al. Single- and Multifraction Stereotactic Radiosurgery Dose/Volume Tolerances of the Brain. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2021, 110, 68–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du Four, S.; Janssen, Y.; Michotte, A.; Van Binst, A.M.; Van den Begin, R.; Duerinck, J.; Neyns, B. Focal radiation necrosis of the brain in patients with melanoma brain metastases treated with pembrolizumab. Cancer Med. 2018, 7, 4870–4879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, A.M.; Cagney, D.N.; Catalano, P.J.; Alexander, B.M.; Redig, A.J.; Schoenfeld, J.D.; Aizer, A.A. Immunotherapy and Symptomatic Radiation Necrosis in Patients With Brain Metastases Treated With Stereotactic Radiation. JAMA Oncol. 2018, 4, 1123–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du Four, S.; Wilgenhof, S.; Duerinck, J.; Michotte, A.; Van Binst, A.; De Ridder, M.; Neyns, B. Radiation necrosis of the brain in melanoma patients successfully treated with ipilimumab, three case studies. Eur. J. Cancer 2012, 48, 3045–3051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du Four, S.; Maenhout, S.K.; Niclou, S.P.; Thielemans, K.; Neyns, B.; Aerts, J.L. Combined VEGFR and CTLA-4 blockade increases the antigen-presenting function of intratumoral DCs and reduces the suppressive capacity of intratumoral MDSCs. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2016, 6, 2514–2531. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, P.; Jiang, W.; Allen, P.; Glitza, I.; Guha, N.; Hwu, P.; Ghia, A.; Phan, J.; Mahajan, A.; Tawbi, H.; et al. Radiation necrosis with stereotactic radiosurgery combined with CTLA-4 blockade and PD-1 inhibition for treatment of intracranial disease in metastatic melanoma. J. Neurooncol. 2017, 133, 595–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires da Silva, I.; Glitza, I.C.; Haydu, L.E.; Johnpulle, R.; Banks, P.D.; Grass, G.D.; Goldinger, S.M.A.; Smith, J.L.; Everett, A.S.; Koelblinger, P.; et al. Incidence, features and management of radionecrosis in melanoma patients treated with cerebral radiotherapy and anti-PD-1 antibodies. Pigment. Cell Melanoma Res. 2019, 32, 553–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furuse, M.; Nonoguchi, N.; Yamada, K.; Shiga, T.; Combes, J.D.; Ikeda, N.; Kawabata, S.; Kuroiwa, T.; Miyatake, S.I. Radiological diagnosis of brain radiation necrosis after cranial irradiation for brain tumor: A systematic review. Radiat. Oncol. 2019, 14, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galldiks, N.; Stoffels, G.; Filss, C.P.; Piroth, M.D.; Sabel, M.; Ruge, M.I.; Herzog, H.; Shah, N.J.; Fink, G.R.; Coenen, H.H.; et al. Role of O-(2-(18)F-fluoroethyl)-L-tyrosine PET for differentiation of local recurrent brain metastasis from radiation necrosis. J Nucl. Med. 2012, 53, 1367–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceccon, G.; Lohmann, P.; Stoffels, G.; Judov, N.; Filss, C.P.; Rapp, M.; Bauer, E.; Hamisch, C.; Ruge, M.I.; Kocher, M.; et al. Dynamic O-(2-18F-fluoroethyl)-L-tyrosine positron emission tomography differentiates brain metastasis recurrence from radiation injury after radiotherapy. Neuro-Oncology 2017, 19, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vellayappan, B.A.; McGranahan, T.; Graber, J.; Taylor, L.; Venur, V.; Ellenbogen, R.; Sloan, A.E.; Redmond, K.J.; Foote, M.; Chao, S.T.; et al. Radiation Necrosis from Stereotactic Radiosurgery-How Do We Mitigate? Curr. Treat. Options Oncol. 2021, 22, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, S.F.; Loebel, F.; Loeffler, J.; Batchelor, T.T.; Martinez-Lage, M.; Vajkoczy, P.; Dietrich, J. Treatment-induced brain tissue necrosis: A clinical challenge in neuro-oncology. Neuro-Oncology 2019, 21, 1118–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McPherson, C.M.; Warnick, R.E. Results of contemporary surgical management of radiation necrosis using frameless stereotaxis and intraoperative magnetic resonance imaging. J. Neurooncol. 2004, 68, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, S.K.; Sheridan, A.D.; Rauch, P.J.; Yu, J.B.; Minja, F.J.; Vortmeyer, A.O.; Chiang, V.L. Significance of histology in determining management of lesions regrowing after radiosurgery. J. Neurooncol. 2014, 117, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tye, K.; Engelhard, H.H.; Slavin, K.V.; Nicholas, M.K.; Chmura, S.J.; Kwok, Y.; Ho, D.S.; Weichselbaum, R.R.; Koshy, M. An analysis of radiation necrosis of the central nervous system treated with bevacizumab. J. Neurooncol. 2014, 117, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, J.; Hurwitz, H.I.; Sandler, A.B.; Miles, D.; Coleman, R.L.; Deurloo, R.; Chinot, O.L. Bevacizumab (Avastin(R)) in cancer treatment: A review of 15 years of clinical experience and future outlook. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2020, 86, 102017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandes, A.A.; Bartolotti, M.; Tosoni, A.; Poggi, R.; Franceschi, E. Practical management of bevacizumab-related toxicities in glioblastoma. Oncologist 2015, 20, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, J.; Kumar, A.J.; Conrad, C.A.; Levin, V.A. Effect of bevacizumab on radiation necrosis of the brain. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol Phys 2007, 67, 323–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levin, V.A.; Bidaut, L.; Hou, P.; Kumar, A.J.; Wefel, J.S.; Bekele, B.N.; Grewal, J.; Prabhu, S.; Loghin, M.; Gilbert, M.R.; et al. Randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial of bevacizumab therapy for radiation necrosis of the central nervous system. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2011, 79, 1487–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, M.S.; Margolin, K.; Talpaz, M.; Sledge, G.W., Jr.; Holmgren, E.; Benjamin, R.; Stalter, S.; Shak, S.; Adelman, D. Phase I safety and pharmacokinetic study of recombinant human anti-vascular endothelial growth factor in patients with advanced cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2001, 19, 843–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abstract 371P: Low-dose bevacizumab for the treatment of focal post-radiation necrosis of the brain. In Proceedings of the European Society of Medical Oncology Congress, Lugano, Switzerland, 16–21 September 2021.
- Zhuang, H.; Zhuang, H.; Shi, S.; Wang, Y. Ultra-Low-Dose Bevacizumab for Cerebral Radiation Necrosis: A Prospective Phase II Clinical Study. OncoTargets Ther. 2019, 12, 8447–8453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Y.; Shen, J.; Zhang, L.; Fang, Z.; Xiao, F.; Zhang, C.; Fan, Z.; Huang, K.; Wang, L.; Huang, B.; et al. Low-Dosage Bevacizumab Treatment: Effect on Radiation Necrosis After Gamma Knife Radiosurgery for Brain Metastases. Front. Surg. 2021, 8, 720506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Pan, L.; Sheng, X.; Mao, Y.; Yao, Y.; Wang, E.; Zhang, N.; Dai, J. Reversal of cerebral radiation necrosis with bevacizumab treatment in 17 Chinese patients. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2012, 17, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boothe, D.; Young, R.; Yamada, Y.; Prager, A.; Chan, T.; Beal, K. Bevacizumab as a treatment for radiation necrosis of brain metastases post stereotactic radiosurgery. Neuro-Oncology 2013, 15, 1257–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuse, M.; Nonoguchi, N.; Kawabata, S.; Yoritsune, E.; Takahashi, M.; Inomata, T.; Kuroiwa, T.; Miyatake, S. Bevacizumab treatment for symptomatic radiation necrosis diagnosed by amino acid PET. Jpn. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 43, 337–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yonezawa, S.; Miwa, K.; Shinoda, J.; Nomura, Y.; Asano, Y.; Nakayama, N.; Ohe, N.; Yano, H.; Iwama, T. Bevacizumab treatment leads to observable morphological and metabolic changes in brain radiation necrosis. J. Neurooncol. 2014, 119, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadraei, N.H.; Dahiya, S.; Chao, S.T.; Murphy, E.S.; Osei-Boateng, K.; Xie, H.; Suh, J.H.; Peereboom, D.M.; Stevens, G.H.; Ahluwalia, M.S. Treatment of cerebral radiation necrosis with bevacizumab: The Cleveland clinic experience. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 38, 304–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, H.; Yuan, X.; Zheng, Y.; Li, X.; Chang, J.Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Yuan, Z.; Wang, P. A study on the evaluation method and recent clinical efficacy of bevacizumab on the treatment of radiation cerebral necrosis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Huang, X.; Jiang, J.; Hu, W.; Hu, J.; Cai, J.; Rong, X.; Cheng, J.; Xu, Y.; Wu, R.; et al. Clinical Variables for Prediction of the Therapeutic Effects of Bevacizumab Monotherapy in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Patients with Radiation-Induced Brain Necrosis. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2018, 100, 621–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Rong, X.; Hu, W.; Huang, X.; Li, Y.; Zheng, D.; Cai, Z.; Zuo, Z.; Tang, Y. Bevacizumab Monotherapy Reduces Radiation-induced Brain Necrosis in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Patients: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2018, 101, 1087–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alessandretti, M.; Buzaid, A.C.; Brandao, R.; Brandao, E.P. Low-dose bevacizumab is effective in radiation-induced necrosis. Case Rep. Oncol. 2013, 6, 598–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glitza, I.C.; Guha-Thakurta, N.; D’Souza, N.M.; Amaria, R.N.; McGovern, S.L.; Rao, G.; Li, J. Bevacizumab as an effective treatment for radiation necrosis after radiotherapy for melanoma brain metastases. Melanoma Res. 2017, 27, 580–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singnurkar, A.; Poon, R.; Detsky, J. 18F-FET-PET imaging in high-grade gliomas and brain metastases: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Neurooncol. 2023, 161, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayo, Z.S.; Halima, A.; Broughman, J.R.; Smile, T.D.; Tom, M.C.; Murphy, E.S.; Suh, J.H.; Lo, S.S.; Barnett, G.H.; Wu, G.; et al. Radiation necrosis or tumor progression? A review of the radiographic modalities used in the diagnosis of cerebral radiation necrosis. J. Neurooncol. 2023, 161, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Characteristics | No. of Patients (%) Total (n = 13) |
|---|---|
| Median age, years (range) | 52 (33–68) |
| Sex | |
| Male | 7 (54%) |
| Female | 6 (46%) |
| Primary disease | |
| Melanoma | 6 (46%) |
| Non-small cell lung carcinoma | 3 (23%) |
| Breast cancer | 1 (8%) |
| Renal cell carcinoma | 1 (8%) |
| Medulloblastoma | 1 (8%) |
| Arteriovenous malformation | 1 (8%) |
| WHO-PS at inclusion | |
| 0 | 10 (77%) |
| 1 | 3 (23%) |
| Number of fRNB locations | |
| 1 | 9 (69%) |
| 2 | 3 (23%) |
| 3 | 1 (8%) |
| Prior radiation therapy | |
| Stereotactic radiosurgery | 6 (46%) |
| Stereotactic radiotherapy | 3 (23%) |
| Both | 4 (31%) |
| Corticosteroid treatment prior to initiation of bevacizumab | |
| Yes | 5 (39%) |
| No | 8 (62%) |
| Diagnosis of fRNB based on MRI supported by | |
| Histopathological examination of biopsy | 6 (46%) |
| 18F-FDG PET-CT | 6 (46%) |
| MRI-only | 3 (23%) |
| Symptoms at baseline | |
| Headache | 1 (8%) |
| Epileptic seizures | 6 (46%) |
| Focal neurological deficit | 9 (69%) |
| Patient | Primary Disease | Location of fRNB | Radiation Therapy | Prior ICI | Prior Chemotherapy | Time since SRS/SRT | WHO-PS Evolution | Time on Treatment | Re-challenge Needed | Steroids Prior | Symptomatic Improvement |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | NSCLC | Right frontal | SRS (1 × 20 Gy) | 23 | 1 -> 1 | 5 | N | Y1 | Y | ||
| 2 | MEL | Left parietal | SRS (1 × 20 Gy) | IPI + NIVO + PEMBRO | 43 | 0 -> 1 | 40 | Y | N | Y/N | |
| 3 | NSCLC | Bilateral parietal | SRS (20 Gy) | PEMBRO | 37 | 0 -> 1 | 5 | N | N | Y | |
| 4 | RCC | Right frontoparietal | SRS (20 Gy) + SRT (5 × 7.5 Gy) | NIVO | 58 | 0 -> 0 | 8 | N | N | Y | |
| 5 | MB | Left supratentorial | SRT (doses see case report 1) | Carboplatin + etoposide | 79 | 0 -> 0 | 11 | Y | N | Y | |
| 6 | AVM | Right parietal | SRS (1 × 20 Gy) | 79 | 0 -> 0 | 5 | N | N | Y | ||
| 7 | BC | Left temporal | SRS (1 × 20 Gy) + SRT (5 × 7 Gy) | Paclitaxel | 90 | 0 -> 0 | 3 | Y | N | Y | |
| 8 | MEL | Left frontoparietal | SRT+SRS (see case report 2) | IPI + NIVO | 18 | 1 -> 1 | 11 | Y | Y1 | Y | |
| 9 | MEL | Right frontal | SRS (1 × 20 Gy) | IPI + NIVO + PEMBRO | 60 | 0 -> 1 | 1 | N | Y1 | Y | |
| 10 | MEL | Bilateral frontoparietal | SRS (1 × 20 Gy) | IPI + NIVO | Temozolomide | 38 | 0 -> 0 | 4 | Y | N | Y |
| 11 | MEL | Left cerebellar | SRT (3 × 9 Gy) | 24 | 0 -> 0 | 10 | N | N | Y | ||
| 12 | MEL | Right cerebellum | SRT (4 × 8 Gy) | PEMBRO | 39 | 0 -> 0 | 20 | N | N | Y | |
| 13 | NSCLC | Right temporal | SRS (1 × 20 Gy) + SRT (5 × 7 Gy) | PEMBRO | Cisplatin + docetaxel | 32 | 1 -> 0 | 2 | N | Y | N |
| All AE | n = 6 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grade I | Grade II | Grade III | Grade IV | |
| Arterial Hypertension (n [%]) | 2 (15%) | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Headache (n [%]) | 1 (8%) | 1 (8%) | 0 | 0 |
| Alopecia (n [%]) | 2 (15%) | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Mucositis oral (n [%]) | 2 (15%) | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Diarrhea (n [%]) | 1 (8%) | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Epistaxis (n [%]) | 1 (8%) | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Proteinuria (n [%]) | 0 | 1 (8%) | 0 | 0 |
| Wound dehiscence (n [%]) | 0 | 1 (8%) | 0 | 0 |
| Citation | Study Design | No. of Patients | BEV Dose Regimen | Primary Pathologies (n) | Radiation (n) | Radiographic Response Rate (%) | Symptomatic Improvement (%) | Adverse Events Described (n) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gonzalez et al., 2007. USA. [32] | Retrospective | 8 | 5 mg/kg q2w or 7.5 mg/kg q3w | AOA (1), AOD (1), AA (1), HP (1), GBM (4) | RT/SRS | 100% | None | |
| Tye et al., 2014. USA. [29] | Review | 71 | 7.5 mg/kg q2w | GBM (22), Met (11), pG (15), Men (6), NPC (5), other (5), ponG (3), HP (2), AVM (2) | EBRT (57), SRS (9), BNCT (3), PT (2) | 100% | Small vessel thrombosis (3), sagittal sinus thrombosis (1), aspiration pneumonia (1), pneumonia with sepsis (1), pulmonary embolus (1) | |
| Levin et al., 2012. USA. [33] | Randomized controlled trial | 7 | 7.5 mg q3w | NPC (2), MS (1), A (1), ODG (1), SCC (1), PA (1) | RT (7) | 100% | 100% | Small vessel thrombosis (3), aspiration pneumonia (1), pulmonary embolus secondary from a deep vein thrombosis (1), superior sagittal sinus thrombosis (1) |
| Wang et al., 2012. China. [38] | Retrospective | 17 | 7.5 mg/kg q2w | GBM (7), Met (6), AA (1), AVM (1), Men (1), ODG (1) | EBRT (12), SRS (4), FSRT (2) | 100% | 94.1% | Hypertension (1), proteinuria (1), temporary fatigue (1) |
| Boothe et al., 2013. USA [39]. | Retrospective | 11 | 7.5 mg/kg q2w or 10 mg/kg q3w or 15 mg/kg q6w | Met (11) | SRS (11), WBRT (5) | 100% | 63.6% | None |
| Furuse et al., 2013. Japan. [40] | Retrospective | 11 | 5 mg/kg q2w | GBM (4), AM (3), Met (3), AA (1) | XRT (7), SRS (6), BNCT (3), SRT (1), | 100% | None | |
| Yonezawa et al., 2014. Japan. [41] | Non-randomized clinical trial | 9 | 5 mg/kg q2w | GBM (6), Met (2), ODG (1) | GTV (6), SRT(2), EL (1), SRT (1), WBRT (1) PT (1) | 100% | Anemia, thrombocytopenia, lymphocytopenia, and/or neutropenia (3) | |
| Sadraei et al., 2015. USA. [42] | Retrospective | 24 | 5 mg/kg q2w or 7.5 mg/kg q3w or 10 mg/kg q2w or 15 mg/kg q3w | Met (17), GBM (2), AVM (2), ODG (1), AE (1), TA (1) | WBRT (10), SRS (18), PT (1) | 95.8% | 95.8% | Grade 2 or less: hypertension, fatigue, urinary tract infection, and proteinuria (6). Grade 3: pulmonary embolism (1) |
| Zhuang et al. China. 2016. [36] | Non-randomized clinical trial | 21 | 1 mg/kg q3w | Met (21) | SRS (16), WBRT (5) | 95.2% | 81% | Allergy (1), hypertension (1) |
| Zhuang et al. China. 2016. [43] | Retrospective | 14 | 5 mg/kg q3-4w | Met (14) | STI (10), WBRT (4) | 92.9% | 83.3% | Allergy (1), hypertension (1) |
| Weng et al., 2021. China. [37] | Retrospective | 22 | 3 mg/kg q2w | Met (22) | SRS (22) | 100% | None | |
| Li et al., 2017. China. [44] | Retrospective | 50 | 5mg/kg q2w | NPC | RT | 76% | Not collected | |
| Xu et al., 2018. China. [45] | Randomized, open label clinical trial | 58 | 5 mg/kg q2w | NPC | RT | 51.8% | 62.1% | Hypertension (12), fatigue (7), infection (4), hemorrhage (4), insomnia (3), headache (3), rash (3), fever (2), blurred vision (1), hyperglycemia (1), stroke (1) |
| Alessandretti et al., 2021. Brazil. [46] | Retrospective | 2 | 5 mg/kg q2w | Met (2) | SRS (2) | 100% | 50% | None |
| Glitza et al., 2017 USA. [47] | Retrospective | 7 | 5, 7.5, 10 mg/kg | Melanoma | SRS/WBRT | 57.4% | 71.5% | Arthralgia (1), dysgeusia (1) |
| This study | Retrospective | 13 | 400 mg loading dose, 100 mg q4w maintenance dose | Met (11), MB (1), AVM (1) | SRS (8), SRT (5) | 100% | 11 | Hypertension (2), headache (2), mucositis oral (2), alopecia (2), diarrhea (1), epistaxis (1), proteinuria (1), wound dehiscence (1) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tijtgat, J.; Calliauw, E.; Dirven, I.; Vounckx, M.; Kamel, R.; Vanbinst, A.M.; Everaert, H.; Seynaeve, L.; Van Den Berge, D.; Duerinck, J.; et al. Low-Dose Bevacizumab for the Treatment of Focal Radiation Necrosis of the Brain (fRNB): A Single-Center Case Series. Cancers 2023, 15, 2560. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15092560
Tijtgat J, Calliauw E, Dirven I, Vounckx M, Kamel R, Vanbinst AM, Everaert H, Seynaeve L, Van Den Berge D, Duerinck J, et al. Low-Dose Bevacizumab for the Treatment of Focal Radiation Necrosis of the Brain (fRNB): A Single-Center Case Series. Cancers. 2023; 15(9):2560. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15092560
Chicago/Turabian StyleTijtgat, Jens, Evan Calliauw, Iris Dirven, Manon Vounckx, Randa Kamel, Anne Marie Vanbinst, Hendrik Everaert, Laura Seynaeve, Dirk Van Den Berge, Johnny Duerinck, and et al. 2023. "Low-Dose Bevacizumab for the Treatment of Focal Radiation Necrosis of the Brain (fRNB): A Single-Center Case Series" Cancers 15, no. 9: 2560. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15092560
APA StyleTijtgat, J., Calliauw, E., Dirven, I., Vounckx, M., Kamel, R., Vanbinst, A. M., Everaert, H., Seynaeve, L., Van Den Berge, D., Duerinck, J., & Neyns, B. (2023). Low-Dose Bevacizumab for the Treatment of Focal Radiation Necrosis of the Brain (fRNB): A Single-Center Case Series. Cancers, 15(9), 2560. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15092560







