Interventional Treatment Strategies in Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma and Perspectives for Combined Hepatocellular-Cholangiocarcinoma
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
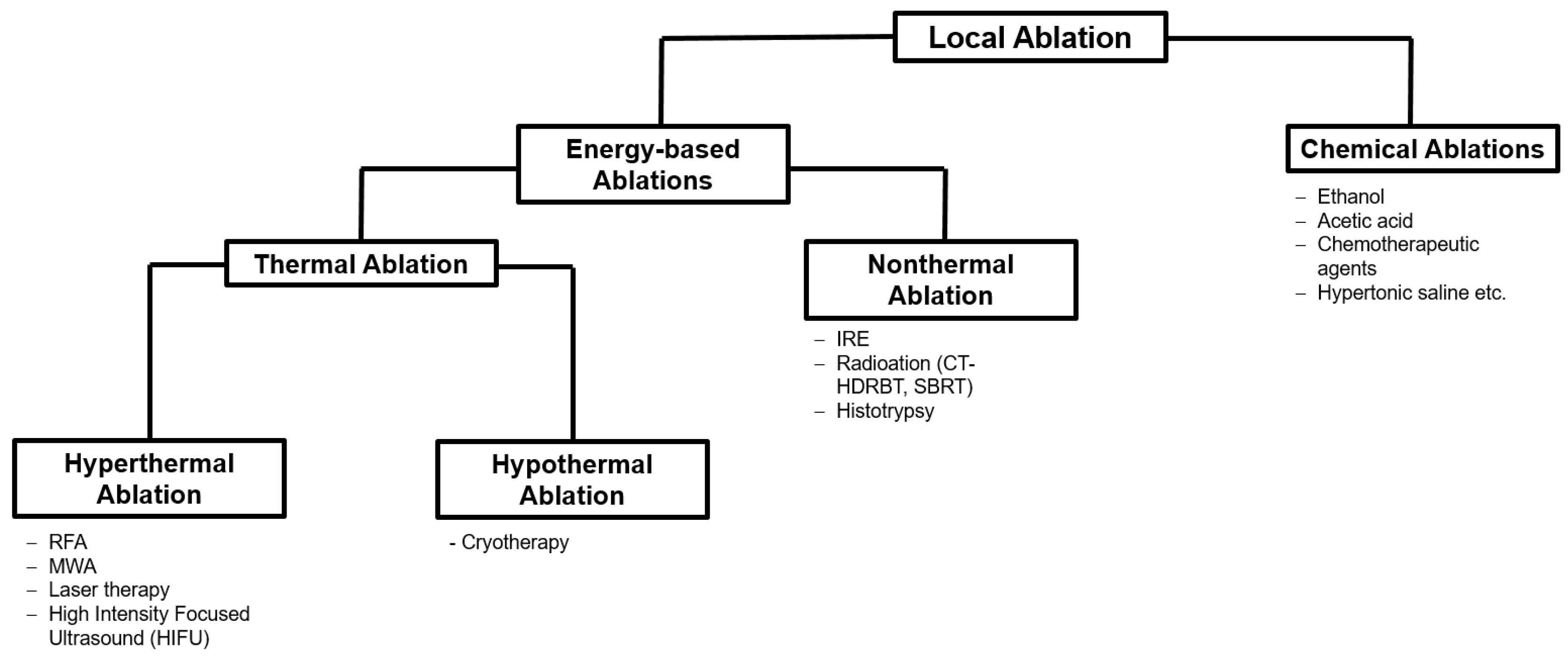
2. Ablation Procedures
2.1. Thermal Ablation
2.1.1. Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA)
2.1.2. Microwave Ablation (MWA)
2.1.3. Cryoablation
2.2. Non-Thermal Ablations
2.2.1. Computed Tomography High-Dose-Rate Brachytherapy (CT-HDRBT)
2.2.2. Irreversible Electroporation (IRE)
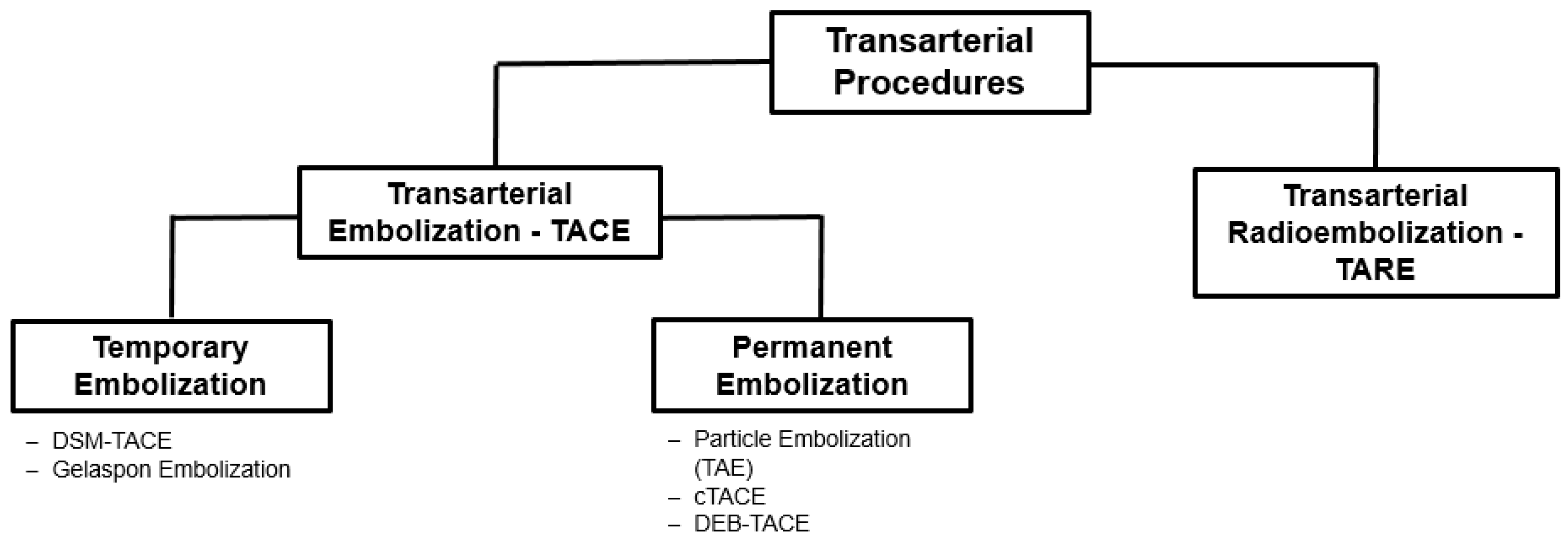
3. Transarterial Procedures
3.1. Transarterial Chemoembolization (TACE)
3.2. Transarterial Radioembolization (TARE)
4. Other Emerging Treatments
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Banales, J.M.; Cardinale, V.; Carpino, G.; Marzioni, M.; Andersen, J.B.; Invernizzi, P.; Lind, G.E.; Folseraas, T.; Forbes, S.J.; Fouassier, L.; et al. Expert consensus document: Cholangiocarcinoma: Current knowledge and future perspectives consensus statement from the European Network for the Study of Cholangiocarcinoma (ENS-CCA). Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 13, 261–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricci, A.D.; Rizzo, A.; Brandi, G. Immunotherapy in Biliary Tract Cancer: Worthy of a Second Look. Cancer Control 2020, 27, 1073274820948047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzo, A.; Brandi, G. Neoadjuvant therapy for cholangiocarcinoma: A comprehensive literature review. Cancer Treat. Res. Commun. 2021, 27, 100354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banales, J.M.; Marin, J.J.G.; Lamarca, A.; Rodrigues, P.M.; Khan, S.A.; Roberts, L.R.; Cardinale, V.; Carpino, G.; Andersen, J.B.; Braconi, C.; et al. Cholangiocarcinoma 2020: The next horizon in mechanisms and management. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 17, 557–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.A.; Thomas, H.C.; Davidson, B.R.; Taylor-Robinson, S.D. Cholangiocarcinoma. Lancet 2005, 366, 1303–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Florio, A.A.; Ferlay, J.; Znaor, A.; Ruggieri, D.; Alvarez, C.S.; Laversanne, M.; Bray, F.; McGlynn, K.A.; Petrick, J.L. Global trends in intrahepatic and extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma incidence from 1993 to 2012. Cancer 2020, 126, 2666–2678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krenzien, F.; Nevermann, N.; Krombholz, A.; Benzing, C.; Haber, P.; Fehrenbach, U.; Lurje, G.; Pelzer, U.; Pratschke, J.; Schmelzle, M.; et al. Treatment of Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma-A Multidisciplinary Approach. Cancers 2022, 14, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, Y.; Uemura, K.; Sudo, T.; Hashimoto, Y.; Nakashima, A.; Kondo, N.; Sakabe, R.; Ohge, H.; Sueda, T. Prognostic factors after surgical resection for intrahepatic, hilar, and distal cholangiocarcinoma. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2011, 18, 651–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohtsuka, M.; Ito, H.; Kimura, F.; Shimizu, H.; Togawa, A.; Yoshidome, H.; Miyazaki, M. Results of surgical treatment for intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma and clinicopathological factors influencing survival. Br. J. Surg. 2002, 89, 1525–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.K.; Zhu, A.X.; Fuchs, C.S.; Brooks, G.A. Forty-Year Trends in Cholangiocarcinoma Incidence in the U.S.: Intrahepatic Disease on the Rise. Oncologist 2016, 21, 594–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forner, A.; Vidili, G.; Rengo, M.; Bujanda, L.; Ponz-Sarvise, M.; Lamarca, A. Clinical presentation, diagnosis and staging of cholangiocarcinoma. Liver Int. 2019, 39 (Suppl. S1), 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valle, J.W.; Kelley, R.K.; Nervi, B.; Oh, D.Y.; Zhu, A.X. Biliary tract cancer. Lancet 2021, 397, 428–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massarweh, N.N.; El-Serag, H.B. Epidemiology of Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma. Cancer Control 2017, 24, 1073274817729245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunt, E.; Aishima, S.; Clavien, P.A.; Fowler, K.; Goodman, Z.; Gores, G.; Gouw, A.; Kagen, A.; Klimstra, D.; Komuta, M.; et al. cHCC-CCA: Consensus terminology for primary liver carcinomas with both hepatocytic and cholangiocytic differentation. Hepatology 2018, 68, 113–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizrahi, J.D.; Shroff, R.T. New Treatment Options for Advanced Biliary Tract Cancer. Curr. Treat. Options Oncol. 2020, 21, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelley, R.K.; Bridgewater, J.; Gores, G.J.; Zhu, A.X. Systemic therapies for intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2020, 72, 353–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valle, J.W.; Lamarca, A.; Goyal, L.; Barriuso, J.; Zhu, A.X. New Horizons for Precision Medicine in Biliary Tract Cancers. Cancer Discov. 2017, 7, 943–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, D.Y.; Lee, K.H.; Lee, D.W.; Yoon, J.; Kim, T.Y.; Bang, J.H.; Nam, A.R.; Oh, K.S.; Kim, J.M.; Lee, Y.; et al. Gemcitabine and cisplatin plus durvalumab with or without tremelimumab in chemotherapy-naive patients with advanced biliary tract cancer: An open-label, single-centre, phase 2 study. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 7, 522–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NCCN Guidelines for Hepatobiliary Cancers. Version 3.2021; 15 June 2021. Available online: http://nccn.ir/Guidelines/Summary/hepatobiliary.html (accessed on 17 March 2023).
- Kamarajah, S.; Giovinazzo, F.; Roberts, K.J.; Punia, P.; Sutcliffe, R.P.; Marudanayagam, R.; Chatzizacharias, N.; Isaac, J.; Mirza, D.F.; Muiesan, P.; et al. The role of down staging treatment in the management of locally advanced intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: Review of literature and pooled analysis. Ann. Hepatobiliary Pancreat. Surg. 2020, 24, 6–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.; Solbiati, L.; Brace, C.L.; Breen, D.J.; Callstrom, M.R.; Charboneau, J.W.; Chen, M.H.; Choi, B.I.; de Baere, T.; Dodd, G.D., 3rd; et al. Image-guided tumor ablation: Standardization of terminology and reporting criteria—A 10-year update. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2014, 25, 1691–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Association for the Study of the Liver. Electronic address, e.e.e.; European Association for the Study of the, L. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines: Management of hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2018, 69, 182–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Y.; Yang, W.; Wu, W.; Yan, K.; Xing, B.C.; Chen, M.H. Radiofrequency ablation in the management of unresectable intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2012, 23, 642–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sweeney, J.; Parikh, N.; El-Haddad, G.; Kis, B. Ablation of Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma. Semin. Intervent Radiol. 2019, 36, 298–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, K.; Georgiades, C. Radiofrequency ablation: Mechanism of action and devices. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2010, 21, S179–S186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, S.N.; Gazelle, G.S.; Solbiati, L.; Livraghi, T.; Tanabe, K.K.; Hahn, P.F.; Mueller, P.R. Ablation of liver tumors using percutaneous RF therapy. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 1998, 170, 1023–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kis, B.; El-Haddad, G.; Sheth, R.A.; Parikh, N.S.; Ganguli, S.; Shyn, P.B.; Choi, J.; Brown, K.T. Liver-Directed Therapies for Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma. Cancer Control 2017, 24, 1073274817729244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, K.; Ko, H.K.; Kim, K.W.; Won, H.J.; Shin, Y.M.; Kim, P.N. Radiofrequency ablation in the treatment of unresectable intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: Systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2015, 26, 943–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, G.H.; Kim, P.H.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, P.N.; Won, H.J.; Shin, Y.M.; Choi, S.H. Thermal ablation in the treatment of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. Radiol. 2022, 32, 1205–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavros, M.N.; Economopoulos, K.P.; Alexiou, V.G.; Pawlik, T.M. Treatment and Prognosis for Patients With Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Surg. 2014, 149, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groot Koerkamp, B.; Fong, Y. Outcomes in biliary malignancy. J. Surg. Oncol. 2014, 110, 585–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satiya, J.; Schwartz, I.; Tabibian, J.H.; Kumar, V.; Girotra, M. Ablative therapies for hepatic and biliary tumors: Endohepatology coming of age. Transl. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 5, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hendriquez, R.; Keihanian, T.; Goyal, J.; Abraham, R.R.; Mishra, R.; Girotra, M. Radiofrequency ablation in the management of primary hepatic and biliary tumors. World J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2022, 14, 203–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van den Berg, P.M.; De Hoop, A.T.; Segal, A.; Praagman, N. A computational model of the electromagnetic heating of biological tissue with application to hyperthermic cancer therapy. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 1983, 30, 797–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreano, A.; Brace, C.L. A comparison of direct heating during radiofrequency and microwave ablation in ex vivo liver. Cardiovasc. Intervent Radiol. 2013, 36, 505–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Yu, J.; Yu, X.; Han, Z.; Cheng, Z.; Liu, F.; Liang, P. Clinical and survival outcomes of percutaneous microwave ablation for intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Int. J. Hyperthermia 2018, 34, 292–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Li, L.; Xu, W.; Du, C.; Yang, L.; Tong, J.; Yi, Y. Ultrasound-guided percutaneous microwave ablation versus surgical resection for recurrent intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: Intermediate-term results. Int. J. Hyperthermia 2019, 36, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.W.; Zhao, Q.; Qian, S.; Zhu, L.; Qu, X.D.; Zhang, W.; Yan, Z.P.; Cheng, J.M.; Liu, Q.X.; Liu, R.; et al. Percutaneous microwave ablation combined with simultaneous transarterial chemoembolization for the treatment of advanced intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Onco Targets Ther. 2015, 8, 1245–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.X.; Wang, Y.; Lu, M.D.; Liu, L.N. Percutaneous ultrasound-guided thermal ablation for intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Br. J. Radiol. 2012, 85, 1078–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.J.; Hu, P.; Wang, N.; Shen, Q.; Sun, A.X.; Kuang, M.; Qian, G.J. Thermal ablation versus repeated hepatic resection for recurrent intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2013, 20, 3596–3602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubinsky, B.; Lee, C.Y.; Bastacky, J.; Onik, G. The process of freezing and the mechanism of damage during hepatic cryosurgery. Cryobiology 1990, 27, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, F.T., Jr.; Chosy, S.G.; Littrup, P.J.; Warner, T.F.; Kuhlman, J.E.; Mahvi, D.M. CT-monitored percutaneous cryoablation in a pig liver model: Pilot study. Radiology 1999, 211, 687–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seifert, J.K.; Morris, D.L. World survey on the complications of hepatic and prostate cryotherapy. World J. Surg. 1999, 23, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orlacchio, A.; Bazzocchi, G.; Pastorelli, D.; Bolacchi, F.; Angelico, M.; Almerighi, C.; Masala, S.; Simonetti, G. Percutaneous cryoablation of small hepatocellular carcinoma with US guidance and CT monitoring: Initial experience. Cardiovasc. Intervent Radiol. 2008, 31, 587–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glazer, D.I.; Tatli, S.; Shyn, P.B.; Vangel, M.G.; Tuncali, K.; Silverman, S.G. Percutaneous Image-Guided Cryoablation of Hepatic Tumors: Single-Center Experience with Intermediate to Long-Term Outcomes. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2017, 209, 1381–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helling, T.S. Realistic expectations for cryoablation of liver tumors. J. Hepatobiliary Pancreat. Surg. 2000, 7, 510–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni Eochagain, A. Cryoshock following cryoablation for hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Clin. Anesth. 2022, 77, 110641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crocetti, L.; de Baere, T.; Lencioni, R. Quality improvement guidelines for radiofrequency ablation of liver tumours. Cardiovasc. Intervent Radiol. 2010, 33, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collettini, F.; Schreiber, N.; Schnapauff, D.; Denecke, T.; Wust, P.; Schott, E.; Hamm, B.; Gebauer, B. CT-guided high-dose-rate brachytherapy of unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. Strahlenther. Onkol. 2015, 191, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnapauff, D.; Denecke, T.; Grieser, C.; Collettini, F.; Seehofer, D.; Sinn, M.; Banzer, J.; Lopez-Hanninen, E.; Hamm, B.; Wust, P.; et al. Computed tomography-guided interstitial HDR brachytherapy (CT-HDRBT) of the liver in patients with irresectable intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Cardiovasc. Intervent Radiol. 2012, 35, 581–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamphues, C.; Seehofer, D.; Collettini, F.; Bahra, M.; Neuhaus, P.; Wust, P.; Denecke, T.; Gebauer, B.; Schnapauff, D. Preliminary experience with CT-guided high-dose rate brachytherapy as an alternative treatment for hepatic recurrence of cholangiocarcinoma. HPB 2012, 14, 791–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonczyk, M.; Collettini, F.; Schnapauff, D.; Geisel, D.; Boning, G.; Feldhaus, F.; Denecke, T.; Wieners, G.; Hamm, B.; Gebauer, B. Cholangiocarcinoma: CT-guided High-Dose Rate Brachytherapy (CT-HDRBT) for Limited (<4 cm) and Large (>4 cm) Tumors. Anticancer Res. 2018, 38, 5843–5852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chigurupalli, K.; Vashistha, A. Role of intraluminal brachytherapy as a palliative treatment modality in unresectable cholangiocarcinomas. J. Cancer Res. Ther. 2021, 17, 10–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogel, J.A.; van Veldhuisen, E.; Agnass, P.; Crezee, J.; Dijk, F.; Verheij, J.; van Gulik, T.M.; Meijerink, M.R.; Vroomen, L.G.; van Lienden, K.P.; et al. Time-Dependent Impact of Irreversible Electroporation on Pancreas, Liver, Blood Vessels and Nerves: A Systematic Review of Experimental Studies. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0166987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renzulli, M.; Ramai, D.; Singh, J.; Sinha, S.; Brandi, N.; Ierardi, A.M.; Albertini, E.; Sacco, R.; Facciorusso, A.; Golfieri, R. Locoregional Treatments in Cholangiocarcinoma and Combined Hepatocellular Cholangiocarcinoma. Cancers 2021, 13, 3336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, G.; Zhao, Q.; Chen, F.; Jiang, T.; Wang, W. Ablation of hepatic malignant tumors with irreversible electroporation: A systematic review and meta-analysis of outcomes. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 5853–5860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llovet, J.M.; Real, M.I.; Montana, X.; Planas, R.; Coll, S.; Aponte, J.; Ayuso, C.; Sala, M.; Muchart, J.; Sola, R.; et al. Arterial embolisation or chemoembolisation versus symptomatic treatment in patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: A randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2002, 359, 1734–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collettini, F.; Jonczyk, M.; Meddeb, A.; Wieners, G.; Geisel, D.; Schnapauff, D.; Gebauer, B. Feasibility and Safety of CT-Guided High-Dose-Rate Brachytherapy Combined with Transarterial Chemoembolization Using Irinotecan-Loaded Microspheres for the Treatment of Large, Unresectable Colorectal Liver Metastases. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2020, 31, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huppert, P.E.; Fierlbeck, G.; Pereira, P.; Schanz, S.; Duda, S.H.; Wietholtz, H.; Rozeik, C.; Claussen, C.D. Transarterial chemoembolization of liver metastases in patients with uveal melanoma. Eur. J. Radiol. 2010, 74, e38–e44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.Y.; Kim, J.H.; Yoon, H.J.; Lee, I.S.; Yoon, H.K.; Kim, K.P. Transarterial chemoembolization versus supportive therapy in the palliative treatment of unresectable intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Clin. Radiol. 2011, 66, 322–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiefer, M.V.; Albert, M.; McNally, M.; Robertson, M.; Sun, W.; Fraker, D.; Olthoff, K.; Christians, K.; Pappas, S.; Rilling, W.; et al. Chemoembolization of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma with cisplatinum, doxorubicin, mitomycin C, ethiodol, and polyvinyl alcohol: A 2-center study. Cancer 2011, 117, 1498–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogl, T.J.; Naguib, N.N.; Nour-Eldin, N.E.; Bechstein, W.O.; Zeuzem, S.; Trojan, J.; Gruber-Rouh, T. Transarterial chemoembolization in the treatment of patients with unresectable cholangiocarcinoma: Results and prognostic factors governing treatment success. Int. J. Cancer 2012, 131, 733–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kloeckner, R.; Weinmann, A.; Prinz, F.; Pinto dos Santos, D.; Ruckes, C.; Dueber, C.; Pitton, M.B. Conventional transarterial chemoembolization versus drug-eluting bead transarterial chemoembolization for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. BMC Cancer 2015, 15, 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bargellini, I.; Florio, F.; Golfieri, R.; Grosso, M.; Lauretti, D.L.; Cioni, R. Trends in utilization of transarterial treatments for hepatocellular carcinoma: Results of a survey by the Italian Society of Interventional Radiology. Cardiovasc. Intervent Radiol. 2014, 37, 438–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhlmann, J.B.; Euringer, W.; Spangenberg, H.C.; Breidert, M.; Blum, H.E.; Harder, J.; Fischer, R. Treatment of unresectable cholangiocarcinoma: Conventional transarterial chemoembolization compared with drug eluting bead-transarterial chemoembolization and systemic chemotherapy. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 24, 437–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.G.; Sun, Y.Y.; Li, D.S.; Xu, G.H.; Huang, X.Q. Efficacy and Safety of Drug-Eluting Beads Transarterial Chemoembolization Combining Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Unresectable Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma: A Propensity Score Matching Analysis. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 940009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auer, T.A.; Jonczyk, M.; Collettini, F.; Marth, A.; Wieners, G.; Hamm, B.; Gebauer, B. Trans-arterial chemoembolization with degradable starch microspheres (DSM-TACE) versus selective internal radiation therapy (SIRT) in multifocal hepatocellular carcinoma. Acta Radiol. 2021, 62, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forsberg, J.O. Transient blood flow reduction induced by intra-arterial injection of degradable starch microspheres. Experiments on rats. Acta Chir. Scand. 1978, 144, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gangi, A.; Shah, J.; Hatfield, N.; Smith, J.; Sweeney, J.; Choi, J.; El-Haddad, G.; Biebel, B.; Parikh, N.; Arslan, B.; et al. Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma Treated with Transarterial Yttrium-90 Glass Microsphere Radioembolization: Results of a Single Institution Retrospective Study. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2018, 29, 1101–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, R.T.; Paprottka, P.M.; Schon, A.; Bamberg, F.; Haug, A.; Durr, E.M.; Rauch, B.; Trumm, C.T.; Jakobs, T.F.; Helmberger, T.K.; et al. Transarterial hepatic yttrium-90 radioembolization in patients with unresectable intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: Factors associated with prolonged survival. Cardiovasc. Intervent Radiol. 2012, 35, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buettner, S.; Braat, A.; Margonis, G.A.; Brown, D.B.; Taylor, K.B.; Borgmann, A.J.; Kappadath, S.C.; Mahvash, A.; JNM, I.J.; Weiss, M.J.; et al. Yttrium-90 Radioembolization in Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma: A Multicenter Retrospective Analysis. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2020, 31, 1035–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallini, J.R.; Gabr, A.; Salem, R.; Lewandowski, R.J. Transarterial Radioembolization with Yttrium-90 for the Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Adv. Ther. 2016, 33, 699–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- SIRS-Spheres Yttrium-90 Microspheres Package Insert. Singapore Science Park SSM. Available online: https://www.sirtex.com/media/29845/ssl-us-10.pdf (accessed on 17 March 2023).
- CMN, T.Y.-m.p.i.K. TheraSphere Yttrium-90 Microspheres Package Insert. Kanata CMN—May 2023. Available online: https://www.bostonscientific.com/en-US/medical-specialties/interventional-radiology/interventional-oncology/therasphere.html (accessed on 17 March 2023).
- Schaarschmidt, B.M.; Kloeckner, R.; Dertnig, T.; Demircioglu, A.; Muller, L.; Auer, T.A.; Pinto Dos Santos, D.; Steinle, V.; Miederer, M.; Gebauer, B.; et al. Real-life experience in the treatment of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma by (90)Y radioembolization: A multicenter retrospective study. J. Nucl. Med. 2023, 64, 529–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schartz, D.A.; Porter, M.; Schartz, E.; Kallas, J.; Gupta, A.; Butani, D.; Cantos, A. Transarterial Yttrium-90 Radioembolization for Unresectable Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2022, 33, 679–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garin, E.; Palard, X.; Rolland, Y. Personalised Dosimetry in Radioembolisation for HCC: Impact on Clinical Outcome and on Trial Design. Cancers 2020, 12, 1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qadan, M.; Fong, Z.V.; Delman, A.M.; Gabr, A.; Salem, R.; Shah, S.A. Review of Use of Y90 as a Bridge to Liver Resection and Transplantation in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2021, 25, 2690–2699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guiu, B.; Garin, E.; Allimant, C.; Edeline, J.; Salem, R. TARE in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: From the Right to the Left of BCLC. Cardiovasc. Intervent Radiol. 2022, 45, 1599–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Procedures | Authors | Design | Endpoints * | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RFA/MWA | ||||
| RFA | Fu et al. (2012) [23] | Monocentric; Retrospective; n = 17 | Tumor necrosis | 96.2% |
| OS (median) | 33 months | |||
| RFS (median) | 17 months | |||
| 1Y-, 3Y-, 5Y-OS | 84.5%; 43.3%; 28.9% | |||
| RFA | Han et al. (2015) [28] | Meta-Analyses; Systematic Review; n = 84 | 1Y-, 3Y-, 5Y-OS | 82%; 47%; 24% (pooled) |
| Major complications | 2.3% | |||
| RFA/MWA | Kim et al. (2022) [29] | Meta-Analyses; Systematic Review; n = 917 | Technical efficacy | 91.9% |
| 1Y-, 3Y-, 5Y-OS | 82.4%; 41.1%; 28.5% | |||
| 1Y-, 3Y-RFS | 40%; 19.2% | |||
| 1Y-, 3Y-, 5Y-TTLTP | 79.3%; 59.5%; 58.2% | |||
| Major complications | 5.7% | |||
| MWA | Zhang at al. (2018) [36] | Monocentric; Retrospective; n = 107 | OS (median) | 28.0 months |
| 1Y-, 3Y-, 5Y-OS | 93.5%; 39.6%; 7.9% | |||
| 6 m-, 12 m-, 18 m-, 24 m-PFS | 67.4%; 41.5%; 18.2%; 8.7% | |||
| Major complications | 2.8% | |||
| MWA vs. SR | Xu et al. (2019) [37] | Monocentric; Retrospective; n = 121 | MWA: | |
| 5Y-OS (estimated) | 23.7% | |||
| 3Y-RFS (estimated) | 33.1% | |||
| Major complications | 5.3% (sign.) | |||
| Surgical resection: | ||||
| 5Y-OS (estimated) | 21.8% | |||
| 3Y-RFS (estimated) | 30.6% | |||
| Major Complications | 13.8% (sign.) | |||
| MWA + TACE | Yang et al. (2015) [38] | Monocentric; Retrospective; n = 26 | OS (median) | 19.2 months |
| PFS (median) | 6.2 months | |||
| 6 m-, 12 m-, 24 m-OS | 88.5%; 69.2%; 61.5% | |||
| Major complications | 0% | |||
| Cryoablation | ||||
| Currently no significant evidence available | ||||
| CT-HDRBT | ||||
| CT-HDRBT | Schnaauff et al. (2012) [50] | Monocentric; Retrospective; n = 15 | OS (median) | 14 months |
| LTC (median) | 11 months | |||
| CT-HDRBT | Kamphues et al. (2012) [51] | Monocentric; Retrospective; n = 10 | 1Y-, 5Y-OS | 77.1%; 51.4% |
| Major complications | 0% | |||
| CT-HDRBT | Jonczyk et al. (2018) [52] | Monocentric; Retrospective; n = 61 | iCCA < 4 cm: | |
| OS (median) | 15.5 months | |||
| LTC (median) | 8.0 months (sign.) | |||
| PFS (median) | 5.0 months | |||
| iCCA > 4 cm: | ||||
| OS (median) | 10.0 months | |||
| LTC (median) | 6.0 months (sign.) | |||
| PFS (median) | 3.0 months | |||
| IRE | ||||
| Currently no significant evidence available | ||||
| Procedures | Authors | Design | Endpoints * | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TACE | ||||
| cTACE vs. Supportive Care | Park et al. (2011) [60] | Monocentric; Retrospective; n = 155 | cTACE: | |
| OS (median (estimated)) | 12.2 months (sign.) | |||
| Supportive care: | ||||
| OS (median (estimated)) | 2.3 months (sign.) | |||
| cTACE | Kiefer et al. (2011) [61] | Bicentric; Retrospective; n = 62 | OS (median) | 20 months |
| 1Y-, 2Y-, 3Y-OS | 75%; 39%; 17% | |||
| PFS (median) | 8 months | |||
| 1Y-PFS | 28% | |||
| cTACE | Vogl et al. (2012) [62] | Monocentric; Retrospective; n = 155 | OS (mean) | 20.8 months |
| OS (median) | 13.0 months | |||
| 1Y-, 2Y-, 3Y-OS | 52%; 29%; 10% | |||
| cTACE vs. DEB-TACE vs. CTx | Kuhlmann at al. (2012) [65] | Monocentric; Retrospective; n = 67 | cTACE: | |
| OS | 5.7 months | |||
| PFS | 1.8 months | |||
| DEB-TACE: | ||||
| OS | 11.7 months | |||
| PFS | 3.9 months | |||
| CTx: | ||||
| OS: | 11.0 months | |||
| PFS: | 6.2 months | |||
| DEB-TACE + ICI vs. CTx | Yang et al. (2022) [66] | Monocentric; Retrospective; n = 49 | DEB-TACE + ICI: | |
| OS (median) | 13.2 months (sign.) | |||
| PFS (median) | 7.2 months (sign.) | |||
| Objective response rate | 55.0% (sign.) | |||
| Chemotherapy: | ||||
| OS (median) | 7.6 months (sign.) | |||
| PFS (median) | 5.7 months (sign.) | |||
| Objective response rate | 20.0% (sign.) | |||
| DSM-TACE | ||||
| Currently no significant evidence available | ||||
| TARE | ||||
| TARE | Hoffmann et al. (2012) [70] | Monocentric; Retrospective; n = 33 | OS (median) | 22 months |
| TTP (median) | 9.0 months | |||
| Gangi et al. (2018) [69] | Monocentric; Retrospective; n = 85 | OS (median) | 12.0 months | |
| Schaarschmidt et al. (2022) [75] | Multicentric; Retrospective; n = 128 | 1st-line Treatment: | ||
| OS (median) | 12 months | |||
| 3 m-, 6 m-, 12 m-disease control | 68.5%; 31.4%; 17.1% | |||
| 2nd-line Treatment: | ||||
| OS (median) | 11.8 months | |||
| 3 m-, 6 m-, 12 m-disease control | 52.8%; 15.1%; 5.7% | |||
| Salvage Treatment: | ||||
| OS (median) | 8.4 months | |||
| 3 m-, 6 m-, 12 m-disease control | 54.0%; 12.0%; 6.0% | |||
| Schartz et al. (2022) [76] | Meta-Analyses; Systematic Review; n = 921 | OS (median) | 12.7 months | |
| 3 m-, 6 m-, 12 m-, 18 m-, 24 m-, 30 m-, 36 m-OS | 84%; 69%; 47%; 31%; 30%; 21%; 5% | |||
| PFS (median) | 7.8 months | |||
| Disease control rate | 82.3% | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Auer, T.A.; Collettini, F.; Segger, L.; Pelzer, U.; Mohr, R.; Krenzien, F.; Gebauer, B.; Geisel, D.; Hosse, C.; Schöning, W.; et al. Interventional Treatment Strategies in Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma and Perspectives for Combined Hepatocellular-Cholangiocarcinoma. Cancers 2023, 15, 2655. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15092655
Auer TA, Collettini F, Segger L, Pelzer U, Mohr R, Krenzien F, Gebauer B, Geisel D, Hosse C, Schöning W, et al. Interventional Treatment Strategies in Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma and Perspectives for Combined Hepatocellular-Cholangiocarcinoma. Cancers. 2023; 15(9):2655. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15092655
Chicago/Turabian StyleAuer, Timo Alexander, Federico Collettini, Laura Segger, Uwe Pelzer, Raphael Mohr, Felix Krenzien, Bernhard Gebauer, Dominik Geisel, Clarissa Hosse, Wenzel Schöning, and et al. 2023. "Interventional Treatment Strategies in Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma and Perspectives for Combined Hepatocellular-Cholangiocarcinoma" Cancers 15, no. 9: 2655. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15092655
APA StyleAuer, T. A., Collettini, F., Segger, L., Pelzer, U., Mohr, R., Krenzien, F., Gebauer, B., Geisel, D., Hosse, C., Schöning, W., & Fehrenbach, U. (2023). Interventional Treatment Strategies in Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma and Perspectives for Combined Hepatocellular-Cholangiocarcinoma. Cancers, 15(9), 2655. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15092655






