Enabling Navigation and Augmented Reality in the Sitting Position in Posterior Fossa Surgery Using Intraoperative Ultrasound
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Cohort
2.2. Technical Equipment
2.3. Preoperative Planning
2.4. Patient Positioning and Registration Procedure
2.5. Intraoperative Navigated Ultrasound
2.6. Additional Postprocessing Using Rigid Image-Based Co-Registration
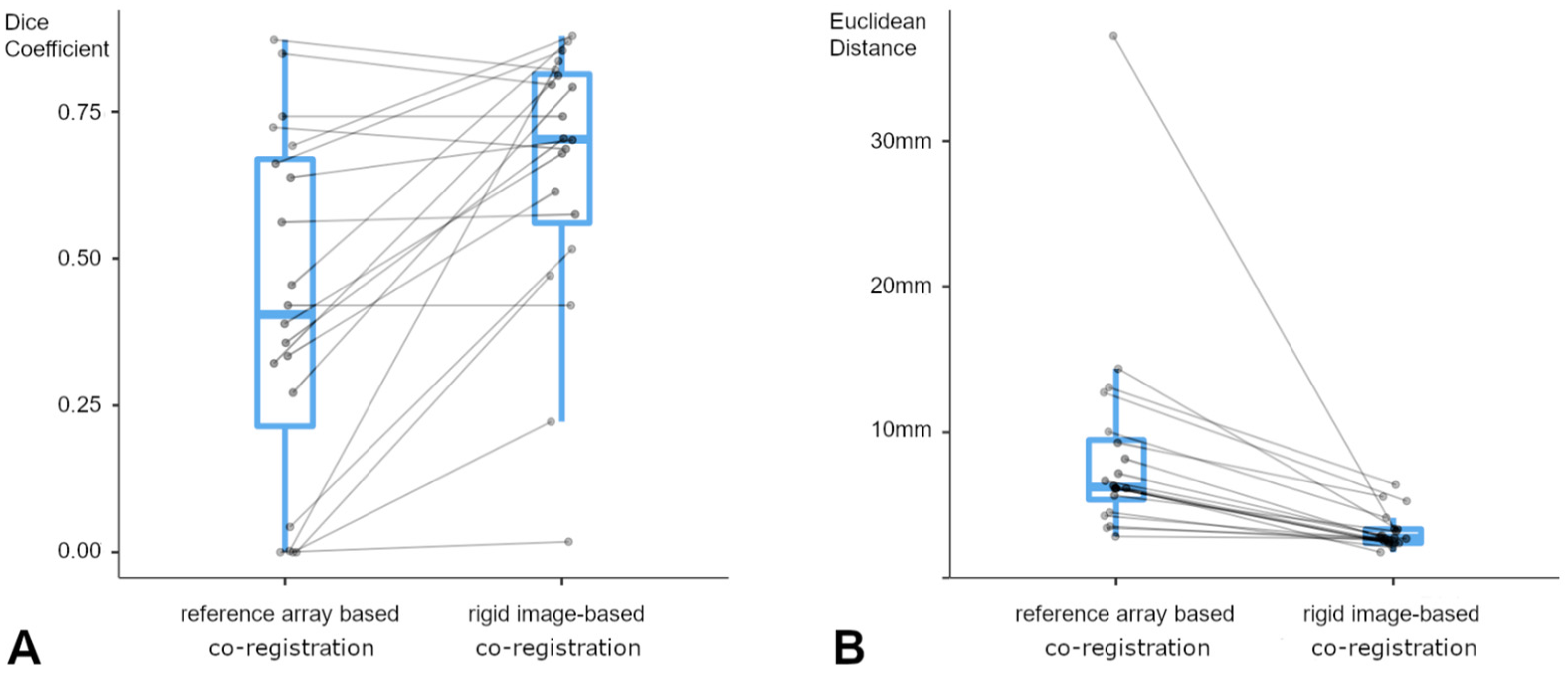
2.7. Quantification of Navigation Accuracy
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
3.2. Tumor Characteristics and Navigation Accuracy
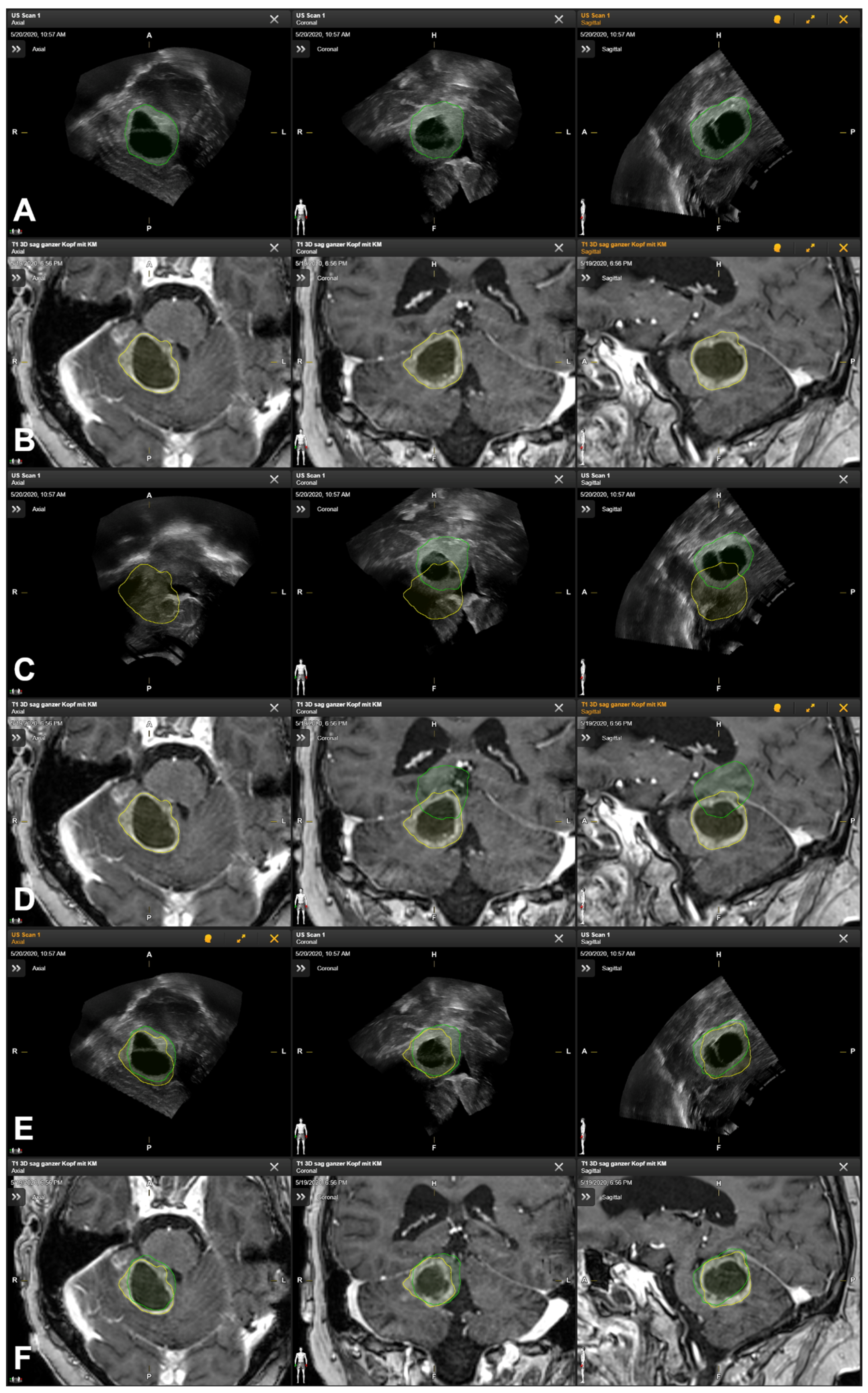
3.3. Lesion-Based Analysis
3.4. Landmark-Based Analysis
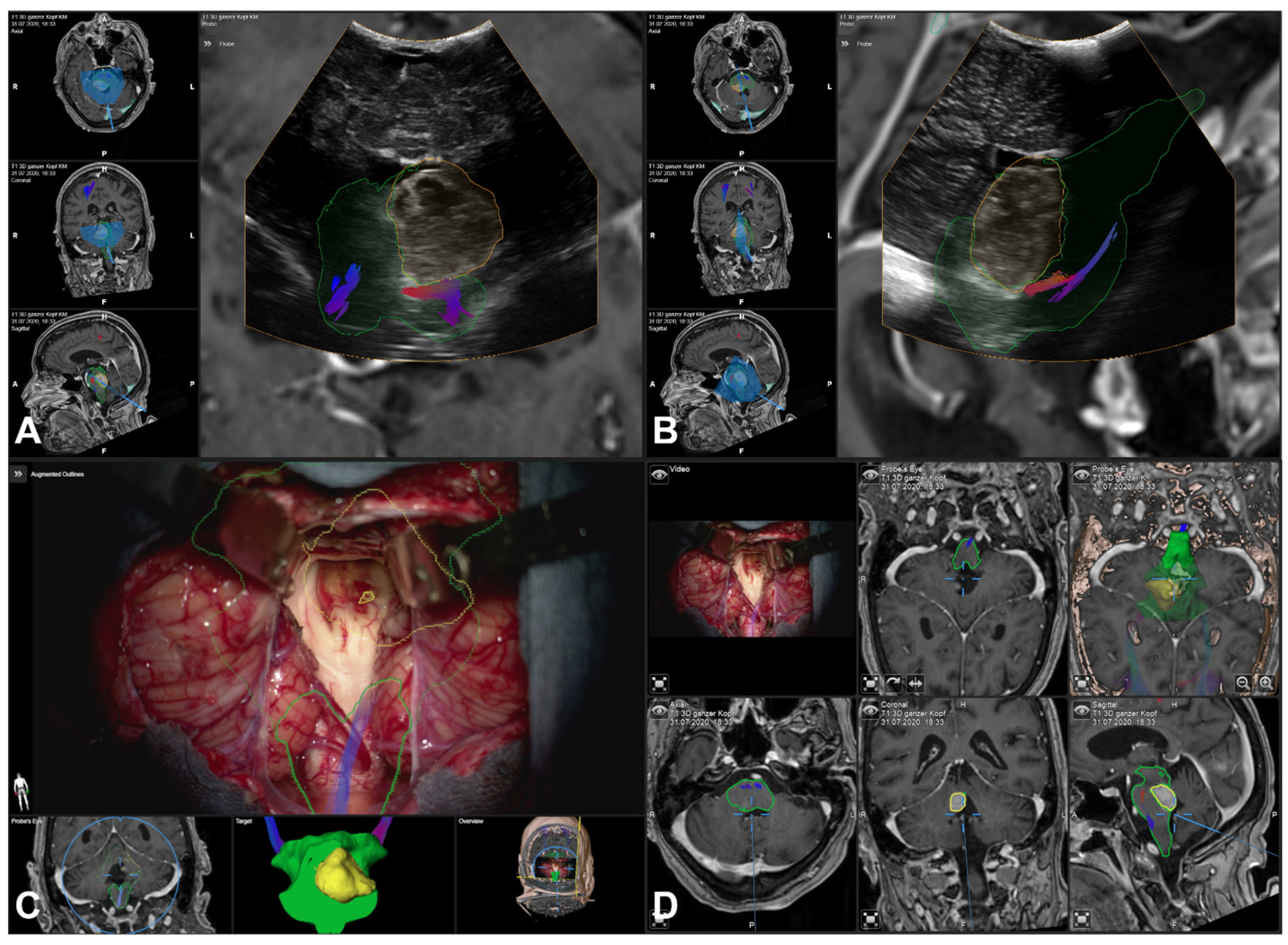
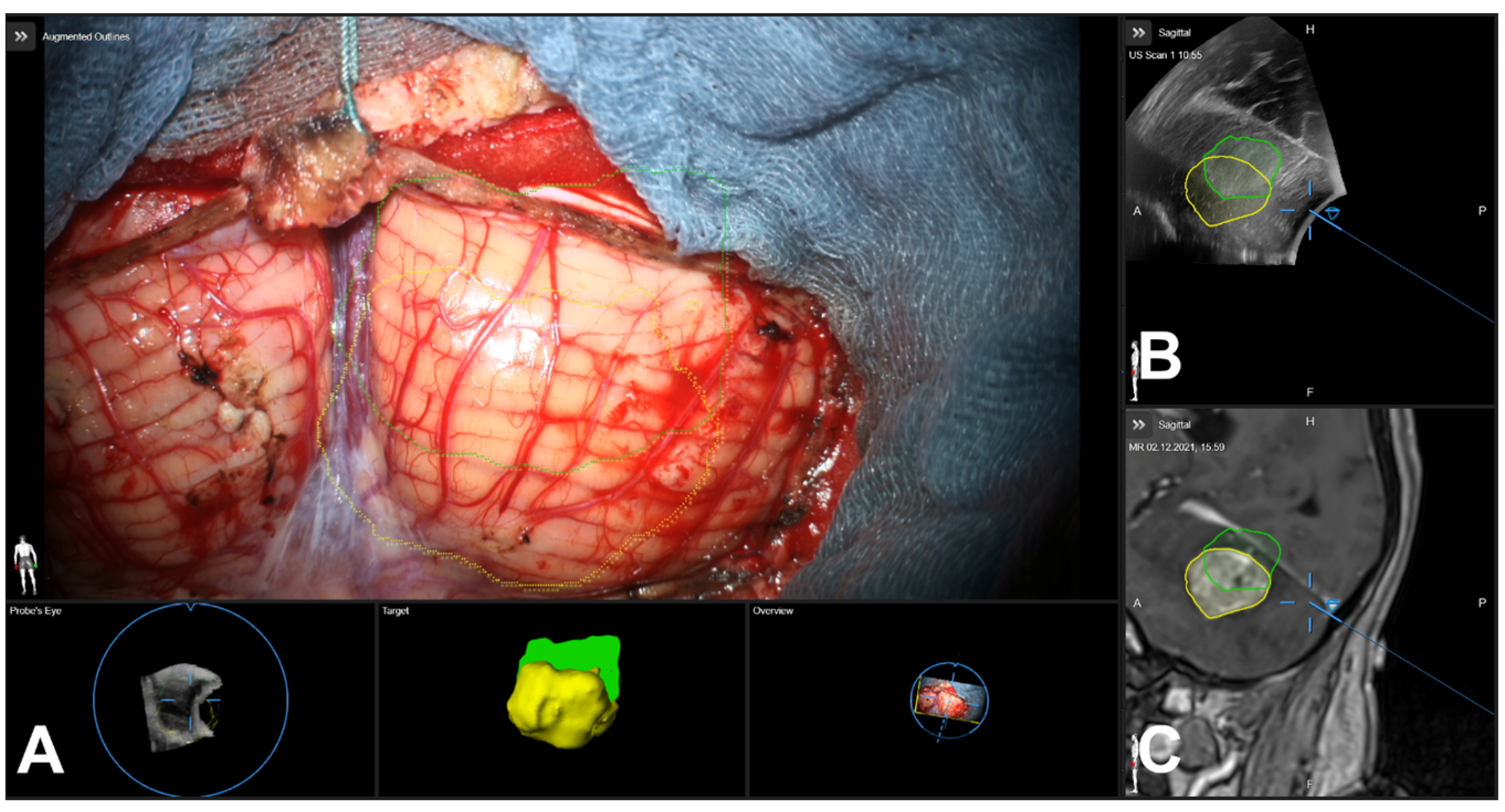
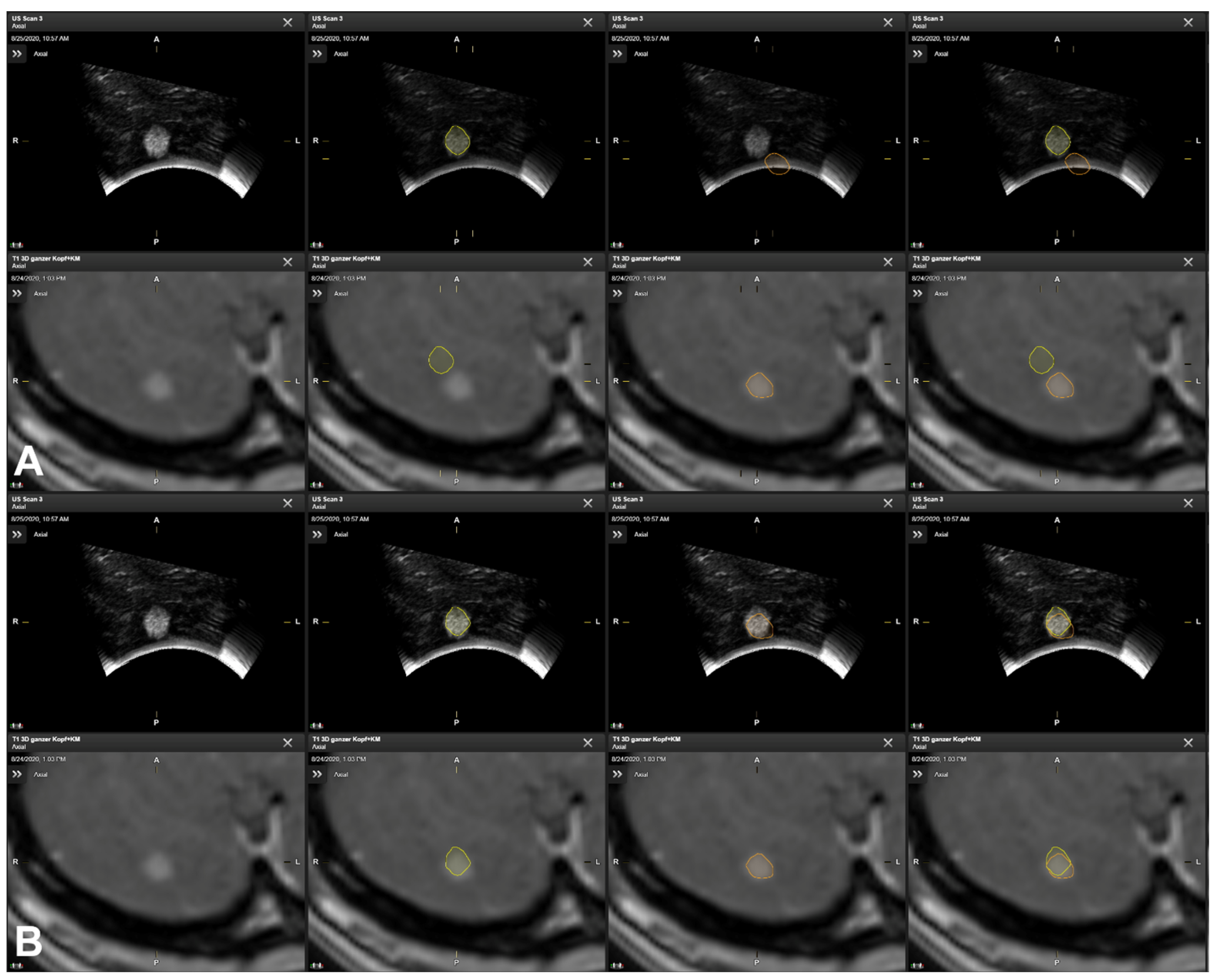
3.5. Illustrative Cases
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carl, B.; Bopp, M.; Sass, B.; Pojskic, M.; Gjorgjevski, M.; Voellger, B.; Nimsky, C. Reliable navigation registration in cranial and spine surgery based on intraoperative computed tomography. Neurosurg. Focus 2019, 47, E11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, Y.; Fujii, M.; Hayashi, Y.; Kimura, M.; Murai, Y.; Hata, M.; Sugiura, A.; Tsuzaka, M.; Wakabayashi, T. Evaluation of errors influencing accuracy in image-guided neurosurgery. Radiol. Phys. Technol. 2009, 2, 120–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stieglitz, L.H.; Fichtner, J.; Andres, R.; Schucht, P.; Krahenbuhl, A.K.; Raabe, A.; Beck, J. The silent loss of neuronavigation accuracy: A systematic retrospective analysis of factors influencing the mismatch of frameless stereotactic systems in cranial neurosurgery. Neurosurgery 2013, 72, 796–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kantelhardt, S.R.; Gutenberg, A.; Neulen, A.; Keric, N.; Renovanz, M.; Giese, A. Video-Assisted Navigation for Adjustment of Image-Guidance Accuracy to Slight Brain Shift. Oper. Neurosurg. 2015, 11, 504–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, P.J.; Alker, G.J., Jr.; Goerss, S. Computer-assisted stereotactic microsurgery for the treatment of intracranial neoplasms. Neurosurgery 1982, 10, 324–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, D.W.; Strohbehn, J.W.; Hatch, J.F.; Murray, W.; Kettenberger, H. A frameless stereotaxic integration of computerized tomographic imaging and the operating microscope. J. Neurosurg. 1986, 65, 545–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannizzaro, D.; Zaed, I.; Safa, A.; Jelmoni, A.J.M.; Composto, A.; Bisoglio, A.; Schmeizer, K.; Becker, A.C.; Pizzi, A.; Cardia, A.; et al. Augmented Reality in Neurosurgery, State of Art and Future Projections. A Systematic Review. Front. Surg. 2022, 9, 864792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meola, A.; Cutolo, F.; Carbone, M.; Cagnazzo, F.; Ferrari, M.; Ferrari, V. Augmented reality in neurosurgery: A systematic review. Neurosurg. Rev. 2017, 40, 537–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leger, E.; Drouin, S.; Collins, D.L.; Popa, T.; Kersten-Oertel, M. Quantifying attention shifts in augmented reality image-guided neurosurgery. Healthc. Technol. Lett. 2017, 4, 188–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dho, Y.S.; Kim, Y.J.; Kim, K.G.; Hwang, S.H.; Kim, K.H.; Kim, J.W.; Kim, Y.H.; Choi, S.H.; Park, C.K. Positional effect of preoperative neuronavigational magnetic resonance image on accuracy of posterior fossa lesion localization. J. Neurosurg. 2019, 133, 546–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermann, E.J.; Petrakakis, I.; Polemikos, M.; Raab, P.; Cinibulak, Z.; Nakamura, M.; Krauss, J.K. Electromagnetic navigation-guided surgery in the semi-sitting position for posterior fossa tumours: A safety and feasibility study. Acta Neurochir. 2015, 157, 1229–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganslandt, O.; Merkel, A.; Schmitt, H.; Tzabazis, A.; Buchfelder, M.; Eyupoglu, I.; Muenster, T. The sitting position in neurosurgery: Indications, complications and results. a single institution experience of 600 cases. Acta Neurochir. 2013, 155, 1887–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saladino, A.; Lamperti, M.; Mangraviti, A.; Legnani, F.G.; Prada, F.U.; Casali, C.; Caputi, L.; Borrelli, P.; DiMeco, F. The semisitting position: Analysis of the risks and surgical outcomes in a contemporary series of 425 adult patients undergoing cranial surgery. J. Neurosurg. 2017, 127, 867–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furuse, M.; Ikeda, N.; Kawabata, S.; Park, Y.; Takeuchi, K.; Fukumura, M.; Tsuji, Y.; Kimura, S.; Kanemitsu, T.; Yagi, R.; et al. Influence of surgical position and registration methods on clinical accuracy of navigation systems in brain tumor surgery. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bopp, M.H.A.; Corr, F.; Sass, B.; Pojskic, M.; Kemmling, A.; Nimsky, C. Augmented Reality to Compensate for Navigation Inaccuracies. Sensors 2022, 22, 9591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nimsky, C.; Ganslandt, O.; Cerny, S.; Hastreiter, P.; Greiner, G.; Fahlbusch, R. Quantification of, visualization of, and compensation for brain shift using intraoperative magnetic resonance imaging. Neurosurgery 2000, 47, 1070–1079; discussion 1079–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinertsen, I.; Lindseth, F.; Askeland, C.; Iversen, D.H.; Unsgard, G. Intra-operative correction of brain-shift. Acta Neurochir. 2014, 156, 1301–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sastry, R.; Bi, W.L.; Pieper, S.; Frisken, S.; Kapur, T.; Wells, W., 3rd; Golby, A.J. Applications of Ultrasound in the Resection of Brain Tumors. J. Neuroimaging 2017, 27, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gronningsaeter, A.; Kleven, A.; Ommedal, S.; Aarseth, T.E.; Lie, T.; Lindseth, F.; Lango, T.; Unsgard, G. SonoWand, an ultrasound-based neuronavigation system. Neurosurgery 2000, 47, 1373–1379; discussion 1379–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bopp, M.H.A.; Emde, J.; Carl, B.; Nimsky, C.; Sass, B. Diffusion Kurtosis Imaging Fiber Tractography of Major White Matter Tracts in Neurosurgery. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sass, B.; Zivkovic, D.; Pojskic, M.; Nimsky, C.; Bopp, M.H.A. Navigated Intraoperative 3D Ultrasound in Glioblastoma Surgery: Analysis of Imaging Features and Impact on Extent of Resection. Front. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 883584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unsgaard, G.; Ommedal, S.; Muller, T.; Gronningsaeter, A.; Nagelhus Hernes, T.A. Neuronavigation by intraoperative three-dimensional ultrasound: Initial experience during brain tumor resection. Neurosurgery 2002, 50, 804–812; discussion 812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unsgaard, G.; Rygh, O.M.; Selbekk, T.; Muller, T.B.; Kolstad, F.; Lindseth, F.; Hernes, T.A. Intra-operative 3D ultrasound in neurosurgery. Acta Neurochir. 2006, 148, 235–253; discussion 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohue, S.; Kumon, Y.; Nagato, S.; Kohno, S.; Harada, H.; Nakagawa, K.; Kikuchi, K.; Miki, H.; Ohnishi, T. Evaluation of intraoperative brain shift using an ultrasound-linked navigation system for brain tumor surgery. Neurol. Med. Chir. 2010, 50, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saß, B.; Carl, B.; Pojskic, M.; Nimsky, C.; Bopp, M. Navigated 3D Ultrasound in Brain Metastasis Surgery: Analyzing the Differences in Object Appearances in Ultrasound and Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 7798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sass, B.; Bopp, M.; Nimsky, C.; Carl, B. Navigated 3-Dimensional Intraoperative Ultrasound for Spine Surgery. World Neurosurg. 2019, 131, e155–e169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wein, W.; Brunke, S.; Khamene, A.; Callstrom, M.R.; Navab, N. Automatic CT-ultrasound registration for diagnostic imaging and image-guided intervention. Med. Image Anal. 2008, 12, 577–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wein, W.; Ladikos, A.; Fuerst, B.; Shah, A.; Sharma, K.; Navab, N. Global registration of ultrasound to MRI using the LC2 metric for enabling neurosurgical guidance. Med. Image Comput. Comput. Assist. Interv. 2013, 16, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dice, L.R. Measures of the Amount of Ecologic Association Between Species. Ecology 1945, 26, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Jamovi Project. Jamovi, 2.3; 2023. Available online: https://www.jamovi.org (accessed on 20 March 2024).
- Letteboer, M.M.; Willems, P.W.; Viergever, M.A.; Niessen, W.J. Brain shift estimation in image-guided neurosurgery using 3-D ultrasound. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2005, 52, 268–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinmeier, R.; Rachinger, J.; Kaus, M.; Ganslandt, O.; Huk, W.; Fahlbusch, R. Factors influencing the application accuracy of neuronavigation systems. Stereotact. Funct. Neurosurg. 2000, 75, 188–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hastreiter, P.; Rezk-Salama, C.; Soza, G.; Bauer, M.; Greiner, G.; Fahlbusch, R.; Ganslandt, O.; Nimsky, C. Strategies for brain shift evaluation. Med. Image Anal. 2004, 8, 447–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nimsky, C.; Ganslandt, O.; Hastreiter, P.; Fahlbusch, R. Intraoperative compensation for brain shift. Surg. Neurol. 2001, 56, 357–364; discussion 364–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poggi, S.; Pallotta, S.; Russo, S.; Gallina, P.; Torresin, A.; Bucciolini, M. Neuronavigation accuracy dependence on CT and MR imaging parameters: A phantom-based study. Phys. Med. Biol. 2003, 48, 2199–2216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolfsberger, S.; Rossler, K.; Regatschnig, R.; Ungersbock, K. Anatomical landmarks for image registration in frameless stereotactic neuronavigation. Neurosurg. Rev. 2002, 25, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jonker, B.P. Image fusion pitfalls for cranial radiosurgery. Surg. Neurol. Int. 2013, 4, S123–S128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carl, B.; Bopp, M.; Benescu, A.; Sass, B.; Nimsky, C. Indocyanine Green Angiography Visualized by Augmented Reality in Aneurysm Surgery. World Neurosurg. 2020, 142, e307–e315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabavi, A.; Black, P.M.; Gering, D.T.; Westin, C.F.; Mehta, V.; Pergolizzi, R.S., Jr.; Ferrant, M.; Warfield, S.K.; Hata, N.; Schwartz, R.B.; et al. Serial intraoperative magnetic resonance imaging of brain shift. Neurosurgery 2001, 48, 787–797; discussion 797–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerard, I.J.; Kersten-Oertel, M.; Petrecca, K.; Sirhan, D.; Hall, J.A.; Collins, D.L. Brain shift in neuronavigation of brain tumors: A review. Med. Image Anal. 2017, 35, 403–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stieglitz, L.H. One of nature’s basic rules: The simpler the better-why this is also valid for neuronavigation. J. Neurosci. Rural Pract. 2014, 5, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stieglitz, L.H.; Raabe, A.; Beck, J. Simple Accuracy Enhancing Techniques in Neuronavigation. World Neurosurg. 2015, 84, 580–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golfinos, J.G.; Fitzpatrick, B.C.; Smith, L.R.; Spetzler, R.F. Clinical use of a frameless stereotactic arm: Results of 325 cases. J. Neurosurg. 1995, 83, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rozet, I.; Vavilala, M.S. Risks and benefits of patient positioning during neurosurgical care. Anesthesiol. Clin. 2007, 25, 631–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fathi, A.R.; Eshtehardi, P.; Meier, B. Patent foramen ovale and neurosurgery in sitting position: A systematic review. Br. J. Anaesth. 2009, 102, 588–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domaingue, C.M. Anaesthesia for neurosurgery in the sitting position: A practical approach. Anaesth. Intensive Care 2005, 33, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rachinger, J.; von Keller, B.; Ganslandt, O.; Fahlbusch, R.; Nimsky, C. Application accuracy of automatic registration in frameless stereotaxy. Stereotact. Funct. Neurosurg. 2006, 84, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nimsky, C.; Fujita, A.; Ganslandt, O.; von Keller, B.; Kohmura, E.; Fahlbusch, R. Frameless stereotactic surgery using intraoperative high-field magnetic resonance imaging. Neurol. Med. Chir. 2004, 44, 522–533; discussion 534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfisterer, W.K.; Papadopoulos, S.; Drumm, D.A.; Smith, K.; Preul, M.C. Fiducial versus nonfiducial neuronavigation registration assessment and considerations of accuracy. Neurosurgery 2008, 62, 201–207; discussion 207–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohlfing, T.; Maurer, C.R., Jr.; Dean, D.; Maciunas, R.J. Effect of changing patient position from supine to prone on the accuracy of a Brown-Roberts-Wells stereotactic head frame system. Neurosurgery 2003, 52, 610–618; discussion 617–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, D.R.; Zhu, X.; Tabesh, A.; Duffy, E.W.; Ramsey, D.A.; Brown, T.R. Structural Brain Changes following Long-Term 6 degrees Head-Down Tilt Bed Rest as an Analog for Spaceflight. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2015, 36, 2048–2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, M.J.; Erickson, R.K.; Levin, D.N.; Pelizzari, C.A.; Macdonald, R.L.; Dohrmann, G.J. Frameless stereotaxy with real-time tracking of patient head movement and retrospective patient-image registration. J. Neurosurg. 1996, 85, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schnaudigel, S.; Preul, C.; Ugur, T.; Mentzel, H.J.; Witte, O.W.; Tittgemeyer, M.; Hagemann, G. Positional brain deformation visualized with magnetic resonance morphometry. Neurosurgery 2010, 66, 376–384; discussion 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monea, A.G.; Verpoest, I.; Vander Sloten, J.; Van der Perre, G.; Goffin, J.; Depreitere, B. Assessment of relative brain-skull motion in quasistatic circumstances by magnetic resonance imaging. J. Neurotrauma 2012, 29, 2305–2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogiwara, T.; Goto, T.; Aoyama, T.; Nagm, A.; Yamamoto, Y.; Hongo, K. Bony surface registration of navigation system in the lateral or prone position: Technical note. Acta Neurochir. 2015, 157, 2017–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, E.; Mayanagi, Y.; Kosugi, Y.; Manaka, S.; Takakura, K. Open surgery assisted by the neuronavigator, a stereotactic, articulated, sensitive arm. Neurosurgery 1991, 28, 792–799; discussion 799–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Negwer, C.; Hiepe, P.; Meyer, B.; Krieg, S.M. Elastic Fusion Enables Fusion of Intraoperative Magnetic Resonance Imaging Data with Preoperative Neuronavigation Data. World Neurosurg. 2020, 142, e223–e228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riva, M.; Hiepe, P.; Frommert, M.; Divenuto, I.; Gay, L.G.; Sciortino, T.; Nibali, M.C.; Rossi, M.; Pessina, F.; Bello, L. Intraoperative Computed Tomography and Finite Element Modelling for Multimodal Image Fusion in Brain Surgery. Oper. Neurosurg. 2020, 18, 531–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dixon, L.; Lim, A.; Grech-Sollars, M.; Nandi, D.; Camp, S. Intraoperative ultrasound in brain tumor surgery: A review and implementation guide. Neurosurg. Rev. 2022, 45, 2503–2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pino, M.A.; Imperato, A.; Musca, I.; Maugeri, R.; Giammalva, G.R.; Costantino, G.; Graziano, F.; Meli, F.; Francaviglia, N.; Iacopino, D.G.; et al. New Hope in Brain Glioma Surgery: The Role of Intraoperative Ultrasound. A Review. Brain Sci. 2018, 8, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eljamel, M.S.; Mahboob, S.O. The effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of intraoperative imaging in high-grade glioma resection; a comparative review of intraoperative ALA, fluorescein, ultrasound and MRI. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther. 2016, 16, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prada, F.; Del Bene, M.; Mattei, L.; Lodigiani, L.; DeBeni, S.; Kolev, V.; Vetrano, I.; Solbiati, L.; Sakas, G.; DiMeco, F. Preoperative magnetic resonance and intraoperative ultrasound fusion imaging for real-time neuronavigation in brain tumor surgery. Ultraschall Med. 2015, 36, 174–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lunn, K.E.; Paulsen, K.D.; Roberts, D.W.; Kennedy, F.E.; Hartov, A.; West, J.D. Displacement estimation with co-registered ultrasound for image guided neurosurgery: A quantitative in vivo porcine study. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2003, 22, 1358–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coburger, J.; Konig, R.W.; Scheuerle, A.; Engelke, J.; Hlavac, M.; Thal, D.R.; Wirtz, C.R. Navigated high frequency ultrasound: Description of technique and clinical comparison with conventional intracranial ultrasound. World Neurosurg. 2014, 82, 366–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aleo, D.; Elshaer, Z.; Pfnur, A.; Schuler, P.J.; Fontanella, M.M.; Wirtz, C.R.; Pala, A.; Coburger, J. Evaluation of a Navigated 3D Ultrasound Integration for Brain Tumor Surgery: First Results of an Ongoing Prospective Study. Curr. Oncol. 2022, 29, 6594–6609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shetty, P.; Yeole, U.; Singh, V.; Moiyadi, A. Navigated ultrasound-based image guidance during resection of gliomas: Practical utility in intraoperative decision-making and outcomes. Neurosurg. Focus 2021, 50, E14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, R.J.; Perrin, D.P.; Vasilyev, N.V.; Marx, G.R.; Del Nido, P.J.; Howe, R.D. Real-time image-based rigid registration of three-dimensional ultrasound. Med. Image Anal. 2012, 16, 402–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coupe, P.; Hellier, P.; Morandi, X.; Barillot, C. 3D Rigid Registration of Intraoperative Ultrasound and Preoperative MR Brain Images Based on Hyperechogenic Structures. Int. J. Biomed. Imaging 2012, 2012, 531319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Y.; Rivaz, H.; Chabanas, M.; Fortin, M.; Machado, I.; Ou, Y.; Heinrich, M.P.; Schnabel, J.A.; Zhong, X.; Maier, A.; et al. Evaluation of MRI to Ultrasound Registration Methods for Brain Shift Correction: The CuRIOUS2018 Challenge. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2020, 39, 777–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzucchi, E.; Hiepe, P.; Langhof, M.; La Rocca, G.; Pignotti, F.; Rinaldi, P.; Sabatino, G. Automatic rigid image Fusion of preoperative MR and intraoperative US acquired after craniotomy. Cancer Imaging 2023, 23, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastos, D.C.A.; Juvekar, P.; Tie, Y.; Jowkar, N.; Pieper, S.; Wells, W.M.; Bi, W.L.; Golby, A.; Frisken, S.; Kapur, T. Challenges and Opportunities of Intraoperative 3D Ultrasound With Neuronavigation in Relation to Intraoperative MRI. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 656519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, J.W.; Lam, D.; Cai, B.; Hugo, G.D. Robustness and reproducibility of an artificial intelligence-assisted online segmentation and adaptive planning process for online adaptive radiation therapy. J. Appl. Clin. Med. Phys. 2022, 23, e13702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherer, M.V.; Lin, D.; Elguindi, S.; Duke, S.; Tan, L.T.; Cacicedo, J.; Dahele, M.; Gillespie, E.F. Metrics to evaluate the performance of auto-segmentation for radiation treatment planning: A critical review. Radiother. Oncol. 2021, 160, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozak, J.; Nesper, M.; Fischer, M.; Lutze, T.; Goggelmann, A.; Hassfeld, S.; Wetter, T. Semiautomated registration using new markers for assessing the accuracy of a navigation system. Comput. Aided Surg. 2002, 7, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farnia, P.; Ahmadian, A.; Shabanian, T.; Serej, N.D.; Alirezaie, J. A hybrid method for non-rigid registration of intra-operative ultrasound images with pre-operative MR images. Annu. Int. Conf. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Soc. 2014, 2014, 5562–5565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farnia, P.; Ahmadian, A.; Shabanian, T.; Serej, N.D.; Alirezaie, J. Brain-shift compensation by non-rigid registration of intra-operative ultrasound images with preoperative MR images based on residual complexity. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 2015, 10, 555–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, I.; Toews, M.; Luo, J.; Unadkat, P.; Essayed, W.; George, E.; Teodoro, P.; Carvalho, H.; Martins, J.; Golland, P.; et al. Non-rigid registration of 3D ultrasound for neurosurgery using automatic feature detection and matching. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 2018, 13, 1525–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Agostino, E.; Maes, F.; Vandermeulen, D.; Suetens, P. A viscous fluid model for multimodal non-rigid image registration using mutual information. Med. Image Anal. 2003, 7, 565–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrant, M.; Nabavi, A.; Macq, B.; Jolesz, F.A.; Kikinis, R.; Warfield, S.K. Registration of 3-D intraoperative MR images of the brain using a finite-element biomechanical model. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2001, 20, 1384–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeole, U.; Singh, V.; Mishra, A.; Shaikh, S.; Shetty, P.; Moiyadi, A. Navigated intraoperative ultrasonography for brain tumors: A pictorial essay on the technique, its utility, and its benefits in neuro-oncology. Ultrasonography 2020, 39, 394–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Patient No. | Age | Sex | Diagnosis |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 42.70 | M | Anaplastic astrocytic tumor |
| 2 | 76.56 | F | Hematoma (brainstem) |
| 3 | 71.00 | F | Metastasis (colon) 1 |
| 4 | 62.04 | M | Metastasis (lung) 2 |
| 5 | 67.55 | F | Metastasis (neuroendocrine carcinoma) |
| 6 | 53.91 | F | Metastasis (ovary) |
| 7 | 61.53 | M | Metastasis (colon) |
| 8 | 63.08 | F | Meningioma |
| 9 | 45.00 | F | Low-grade glioma |
| 10 | 59.93 | M | Metastasis (gastrointestinal) |
| 11 | 59.43 | M | Metastasis (colon) |
| 12 | 68.71 | F | Metastasis (ovary) 1 |
| 13 | 64.91 | M | Cavernoma |
| 14 | 51.08 | F | Subependymoma, WHO°I |
| 15 | 56.60 | F | Arteriovenous malformation |
| Patient No. | Tumor Volume MRI [cm³] | Tumor Volume iUS [cm3] | iUS Probe | iUS #Slices/Slice Thickness |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 13.10 | 13.40 | N13C5 | 178/0.5 mm |
| 2 | 5.40 | 5.55 | 8862 | 98/0.5 mm |
| 3 | 8.54 | 8.60 | 8862 | 125/0.5 mm |
| 0.09 | 0.08 | 36/0.5 mm | ||
| 4 | 4.45 | 3.76 | N13C5 | 155/0.5 mm |
| 0.08 | 0.10 | |||
| 0.45 | 0.48 | |||
| 2.44 | 2.27 | |||
| 5 | 30.50 | 26.40 | 8862 | 175/0.5 mm |
| 6 | 10.50 | 10.40 | N13C5 | 110/0.5 mm |
| 7 | 22.10 | 21.80 | N13C5 | 120/0.5 mm |
| 8 | 21.30 | 21.30 | N13C5 | 128/0.5 mm |
| 9 | 0.43 | 0.51 | 8862 | 81/0.4 mm |
| 10 | 29.40 | 29.50 | N13C5 | 176/0.4 mm |
| 11 | 18.90 | 14.60 | N13C5 | 101/0.5 mm |
| 12 | 24.00 | 17.80 | N13C5 | 206/0.5 mm |
| 0.60 | 0.52 | 60/0.5 mm | ||
| 13 | 13.10 | 13.40 | N13C5 | 134/0.5 mm |
| 14 | 5.40 | 5.55 | N13C5 | 76/0.4 mm |
| 15 | 8.54 | 8.60 | N13C5 | 159/0.5 mm |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bopp, M.H.A.; Grote, A.; Gjorgjevski, M.; Pojskic, M.; Saß, B.; Nimsky, C. Enabling Navigation and Augmented Reality in the Sitting Position in Posterior Fossa Surgery Using Intraoperative Ultrasound. Cancers 2024, 16, 1985. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16111985
Bopp MHA, Grote A, Gjorgjevski M, Pojskic M, Saß B, Nimsky C. Enabling Navigation and Augmented Reality in the Sitting Position in Posterior Fossa Surgery Using Intraoperative Ultrasound. Cancers. 2024; 16(11):1985. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16111985
Chicago/Turabian StyleBopp, Miriam H. A., Alexander Grote, Marko Gjorgjevski, Mirza Pojskic, Benjamin Saß, and Christopher Nimsky. 2024. "Enabling Navigation and Augmented Reality in the Sitting Position in Posterior Fossa Surgery Using Intraoperative Ultrasound" Cancers 16, no. 11: 1985. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16111985
APA StyleBopp, M. H. A., Grote, A., Gjorgjevski, M., Pojskic, M., Saß, B., & Nimsky, C. (2024). Enabling Navigation and Augmented Reality in the Sitting Position in Posterior Fossa Surgery Using Intraoperative Ultrasound. Cancers, 16(11), 1985. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16111985








