The Role of Insulin-like Growth Factor Binding Protein (IGFBP)-2 in DNA Repair and Chemoresistance in Breast Cancer Cells
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. Treatment with Etoposide
2.3. IGFBP-2 Silencing Using siRNA
2.4. Cell Counting Experiments Using Trypan Blue Dye Exclusion
2.5. Western Blotting
2.6. Immunofluorescence Staining and Confocal Imaging
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
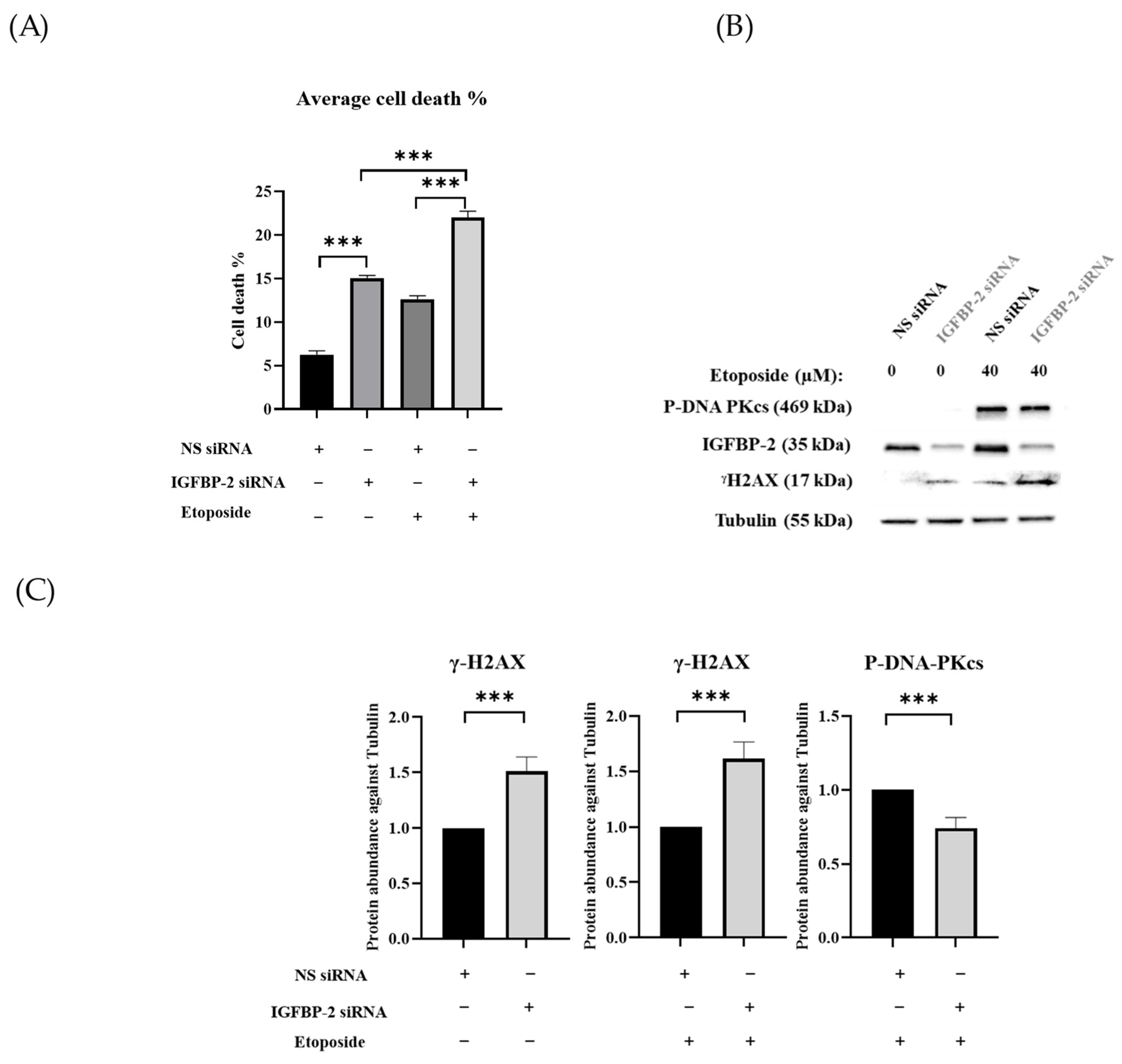
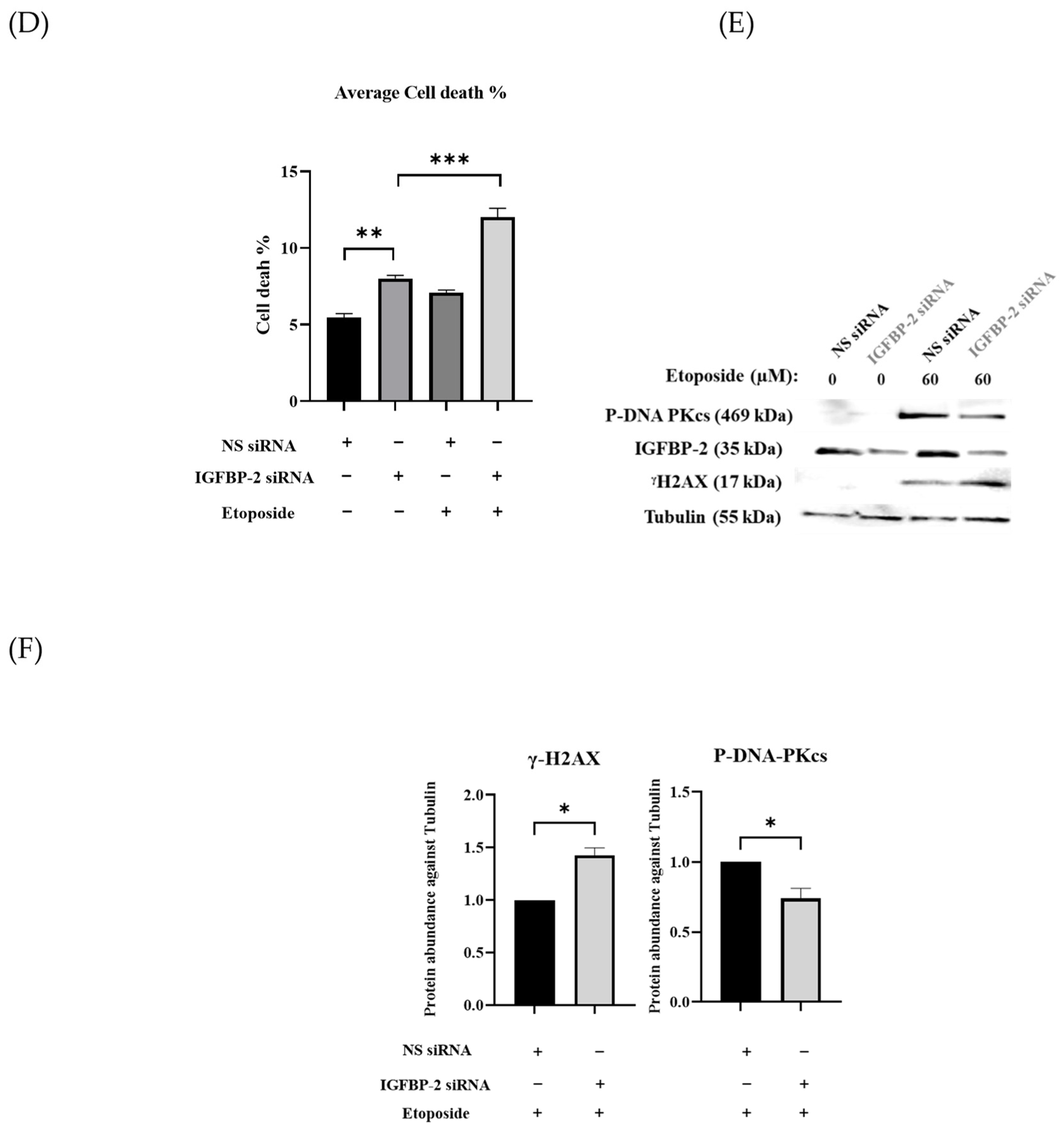
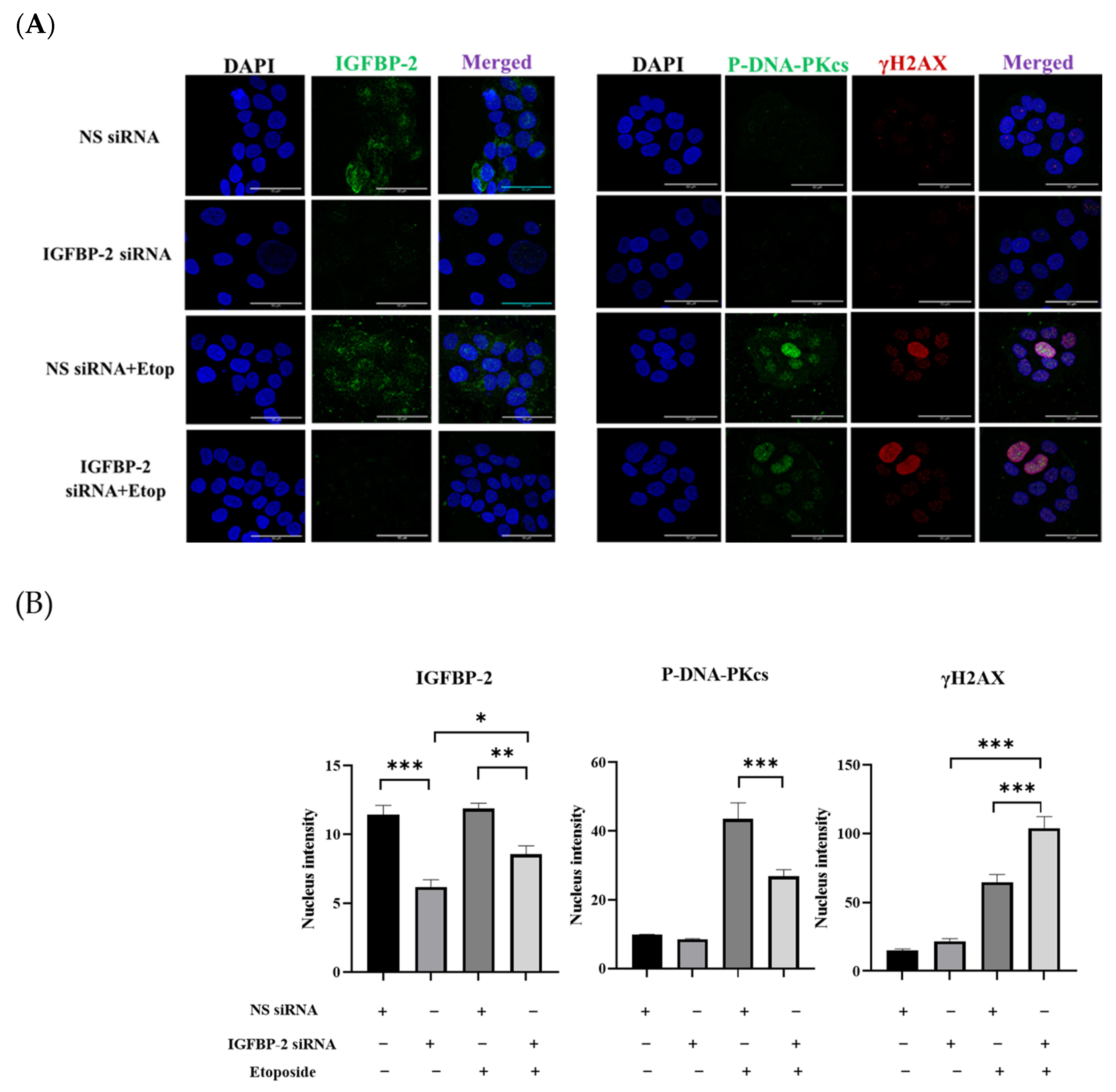
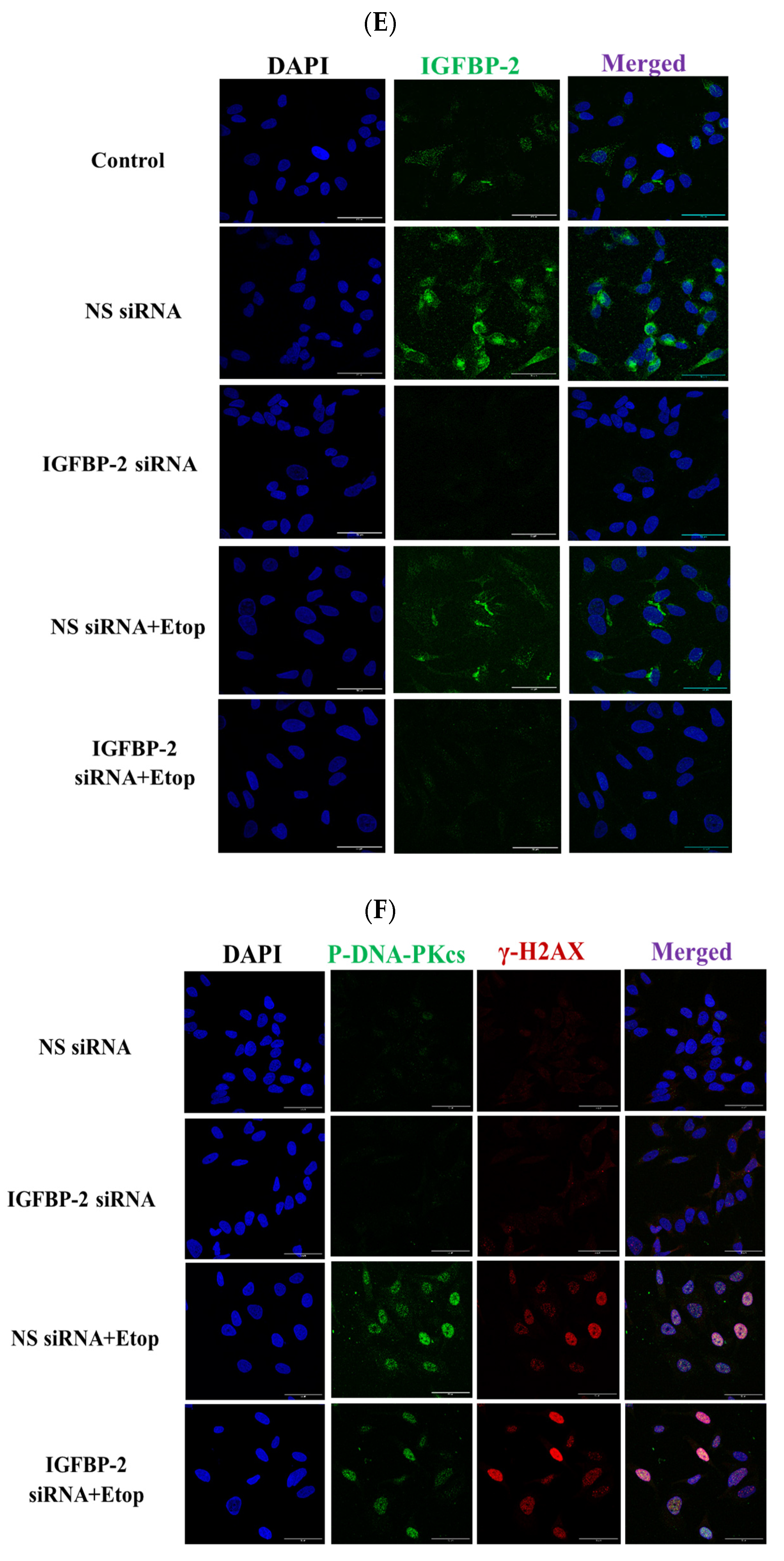
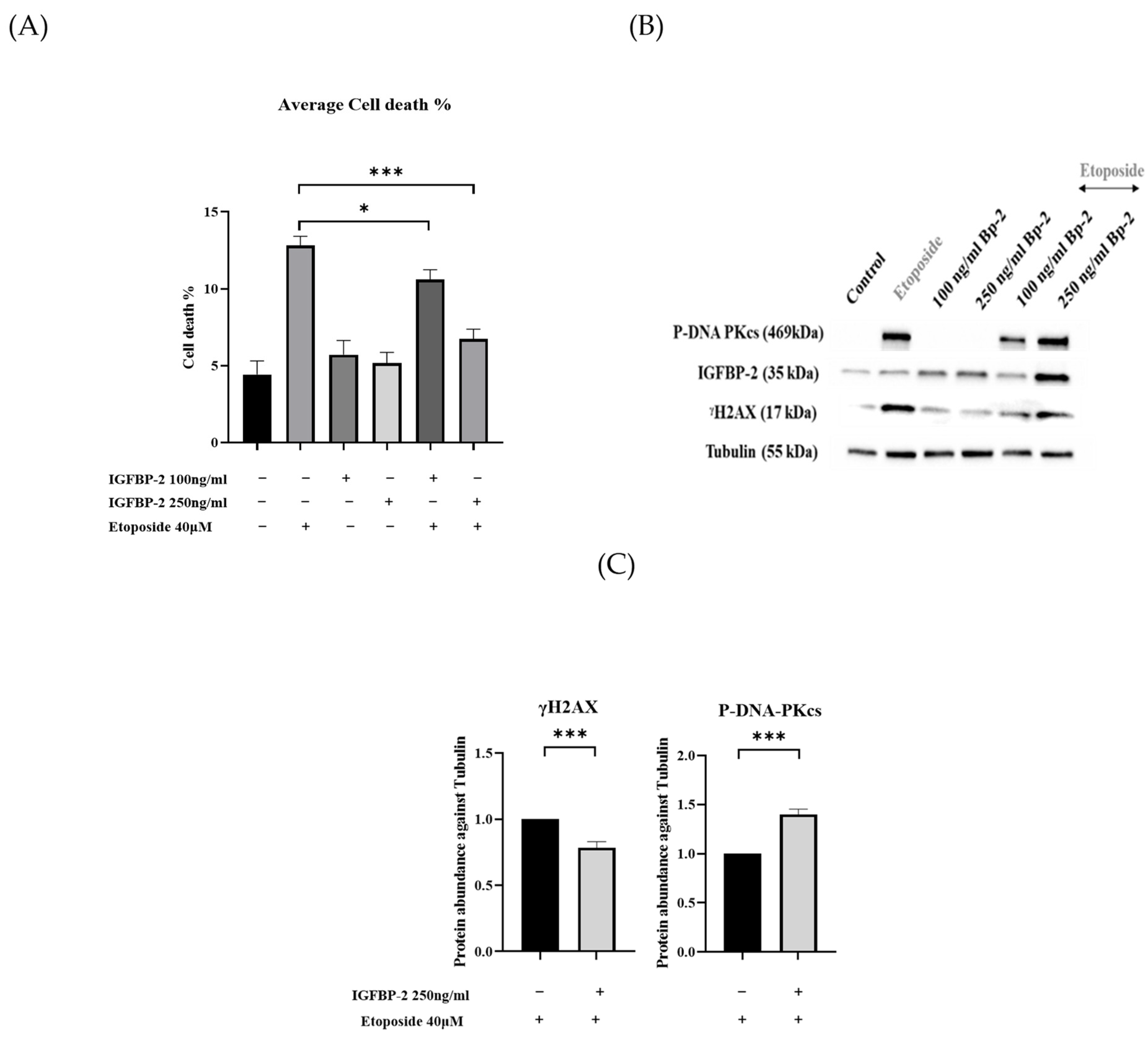
3.1. The Role of IGFBP-2 in DNA Damage in ER Positive Cells
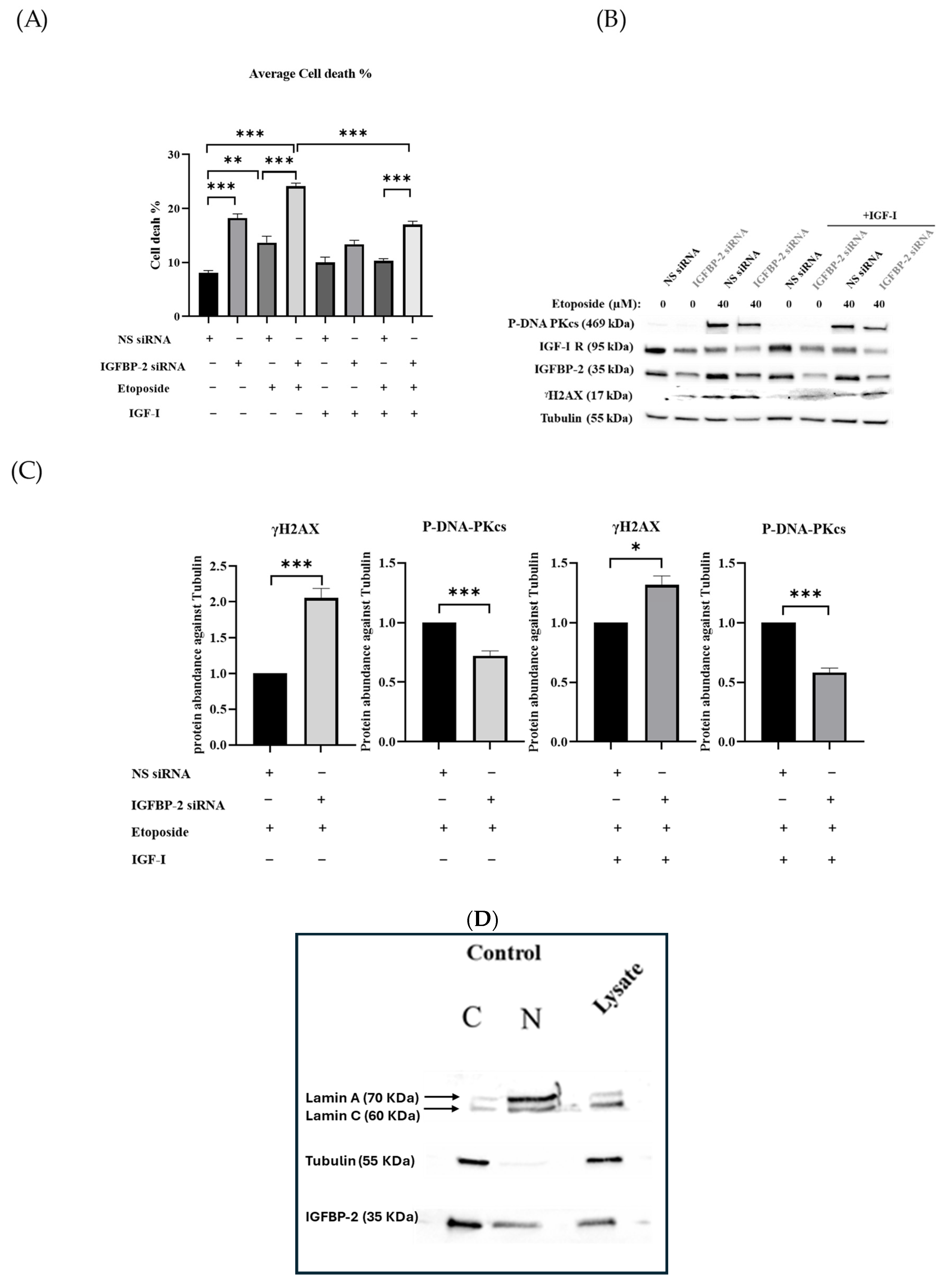
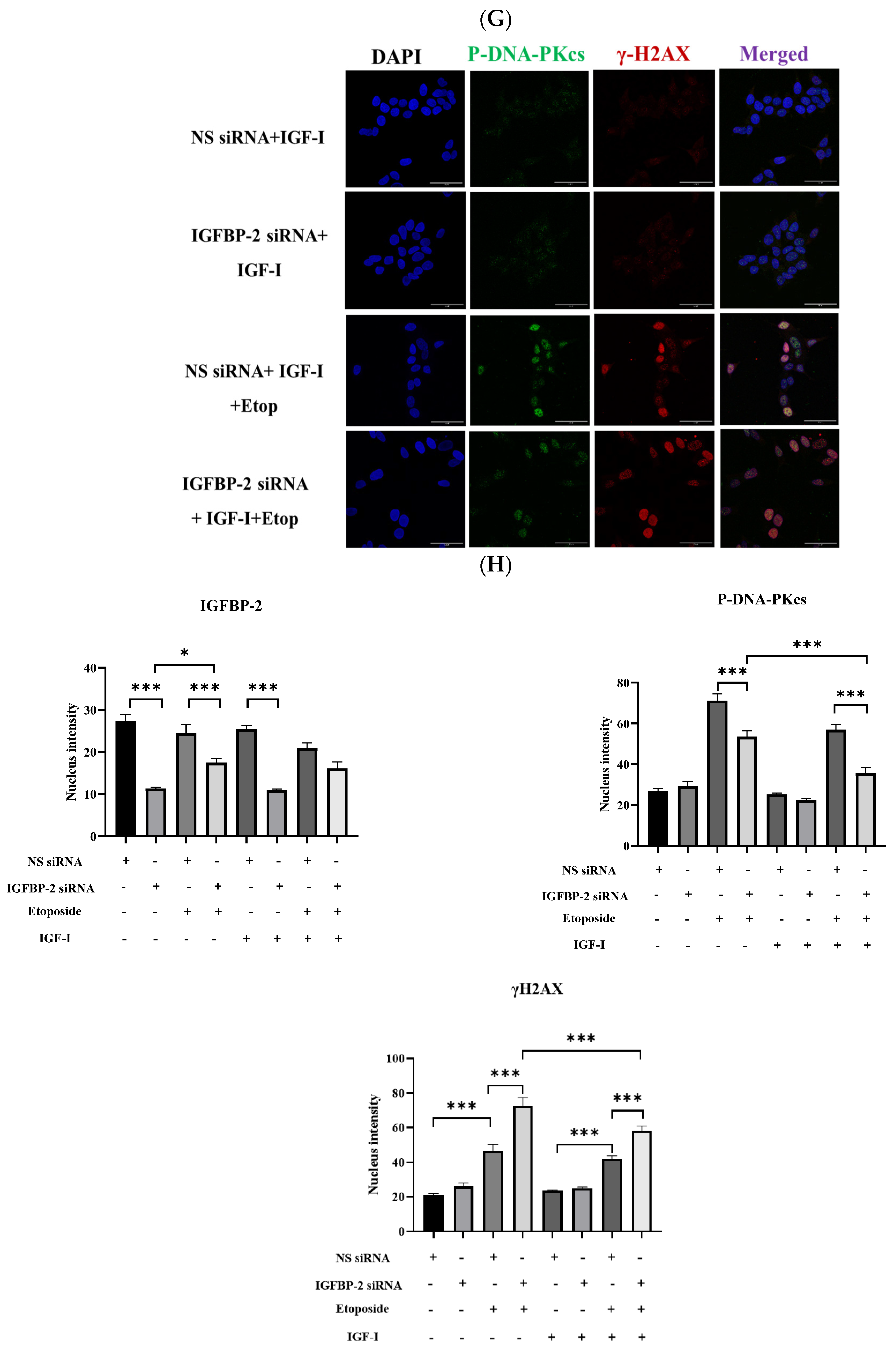
3.2. The Effect of IGF-I on the Role of IGFBP-2 in DNA Damage in MCF-7 Cells
3.3. The Role of IGFBP-2 in DNA Damage in ER-Negative MDA-MB-231 Cells
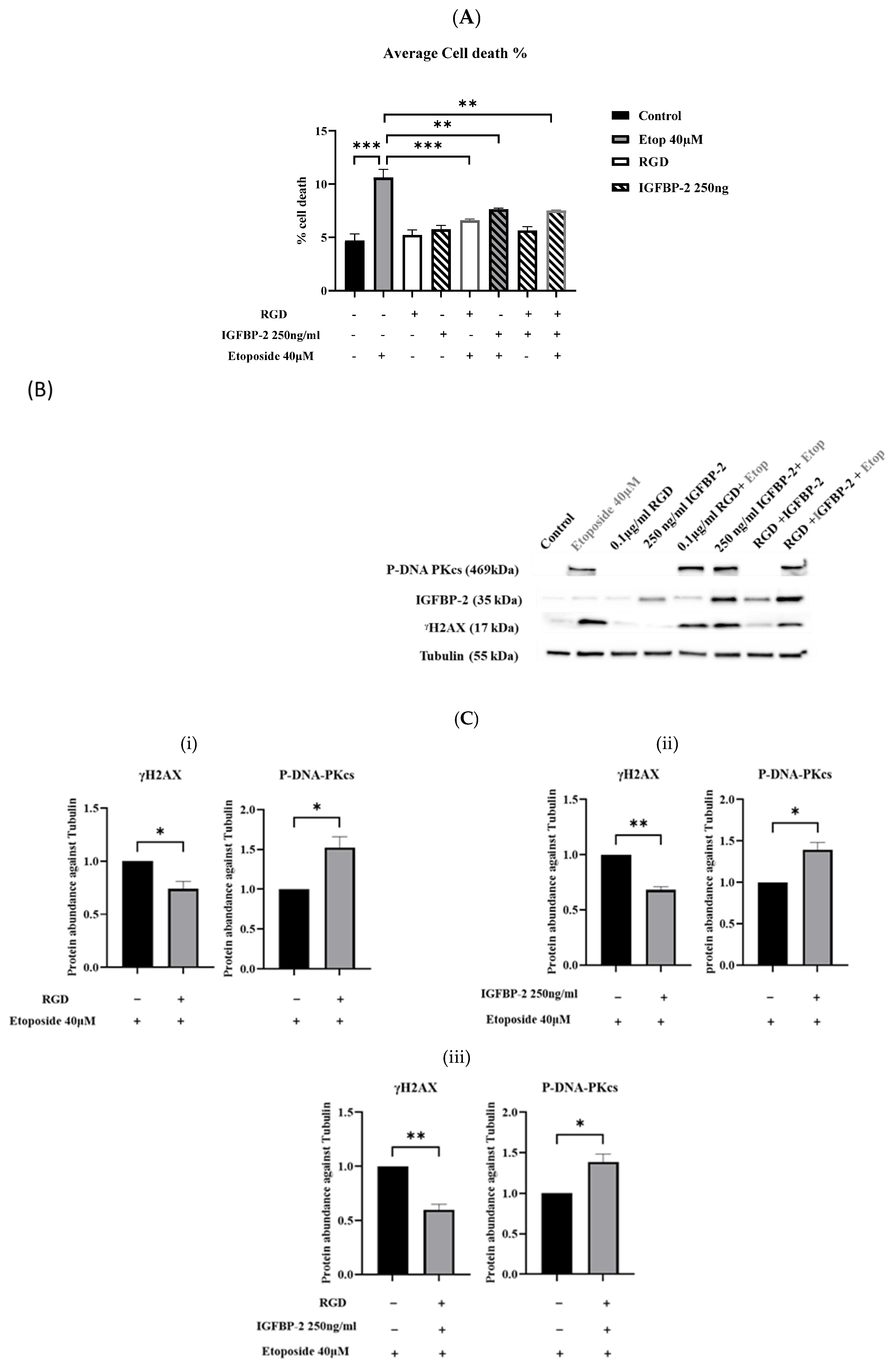
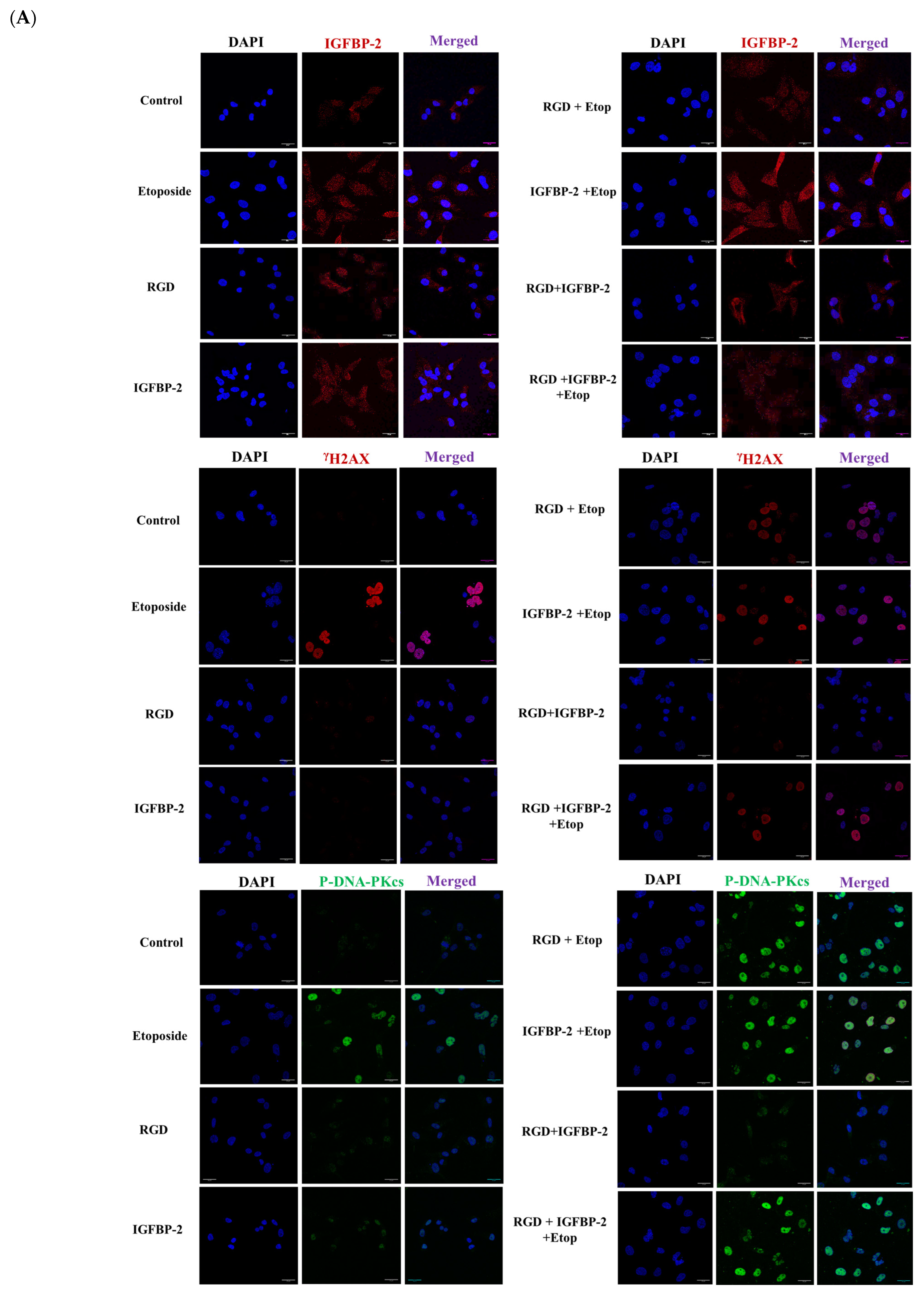
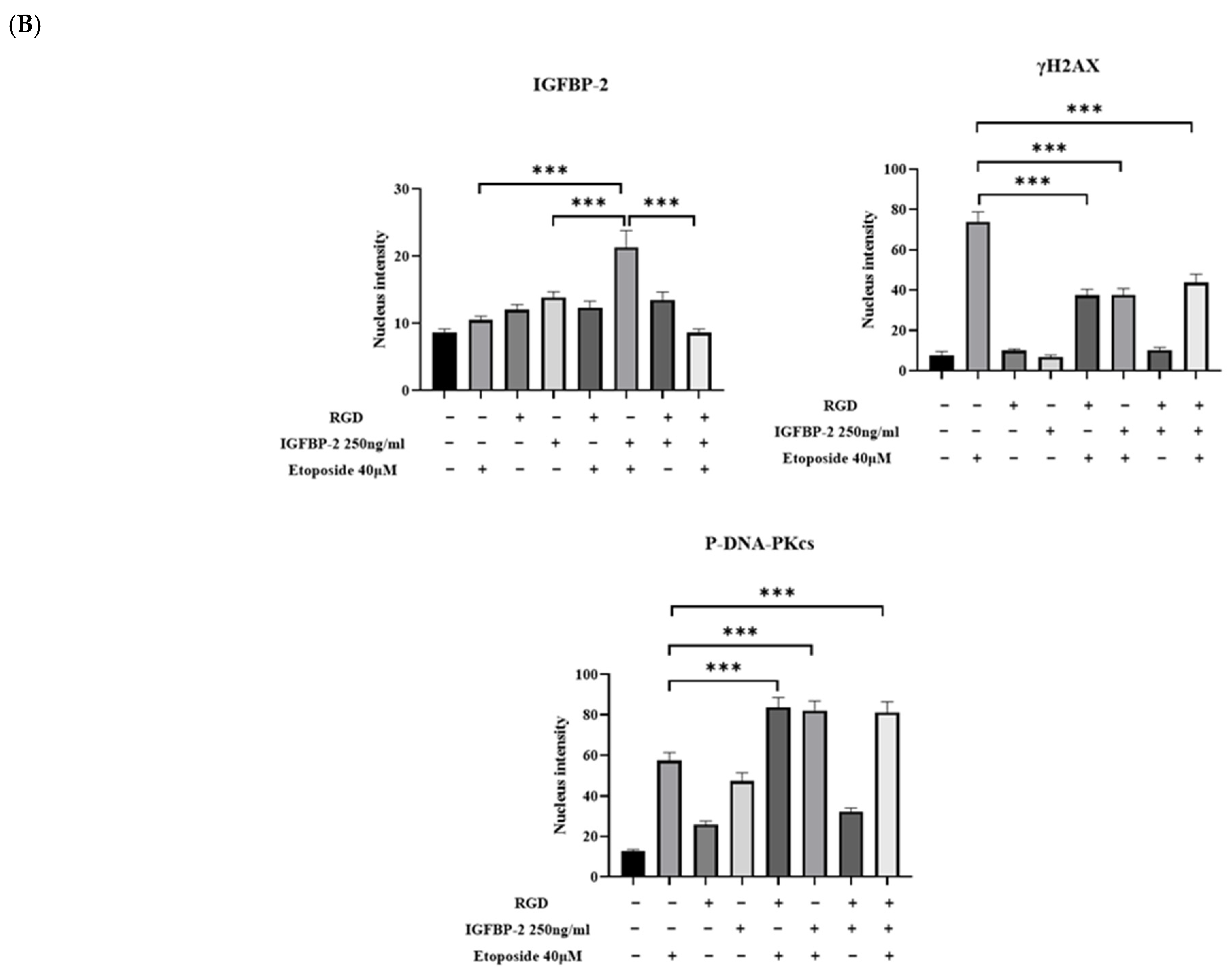
3.4. The Effect of an RGD-Containing Peptide on the Role of IGFBP-2 in DNA Damage in MDA-MB-231 Cells
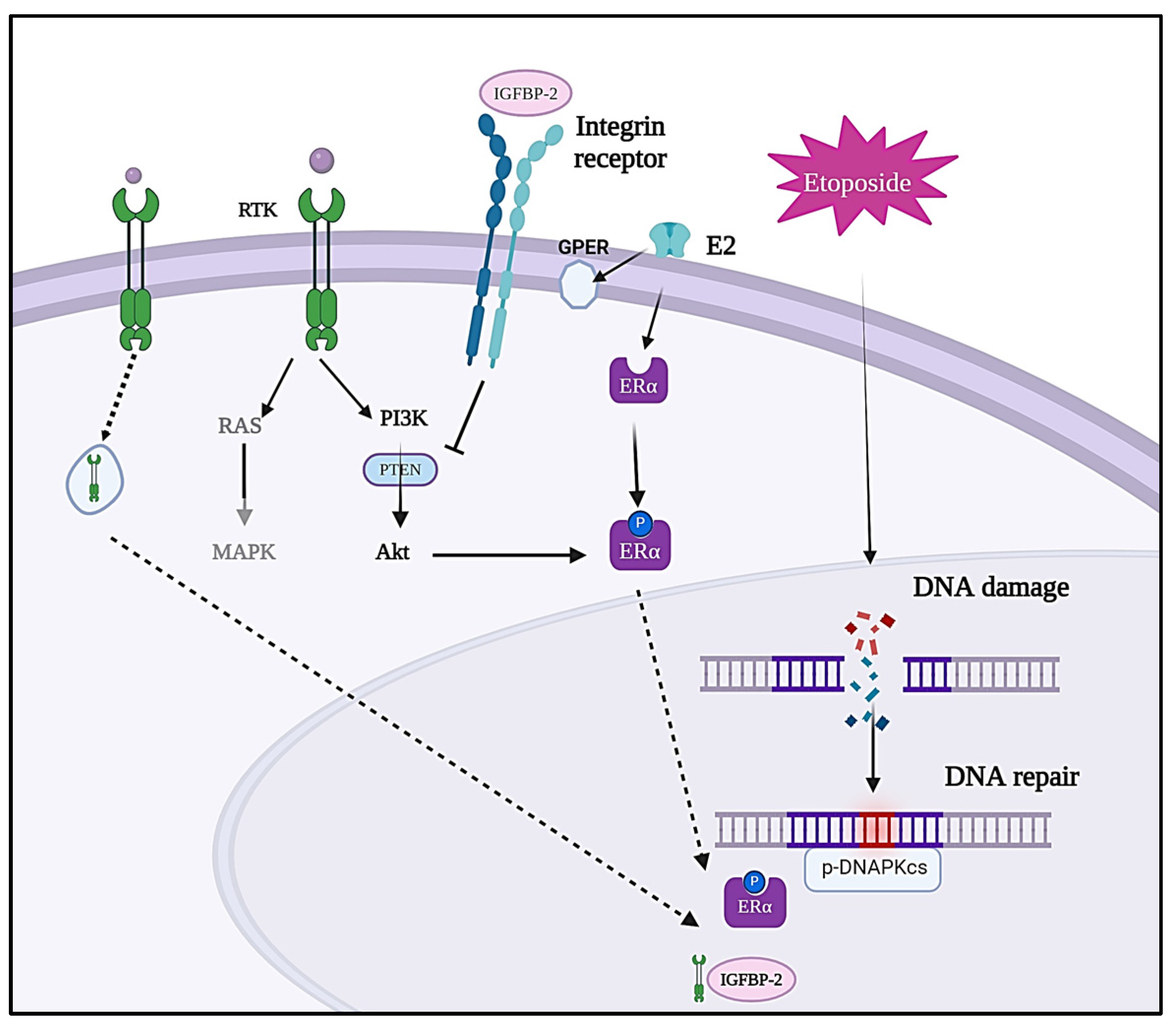
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yin, L.; Duan, J.-J.; Bian, X.-W.; Yu, S.-C. Triple-negative breast cancer molecular subtyping and treatment progress. Breast Cancer Res. BCR 2020, 22, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teixeira, A.C.; Dos Santos, R.A.; Poersch, A.; Carrara HH, A.; de Andrade, J.M.; Takahashi, C.S. DNA repair in Etoposide-induced DNA damage in lymphocytes of breast cancer patients and healthy women. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2009, 2, 280–288. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Urbani, L.; Sherwood, S.W.; Schimke, R.T. Dissociation of nuclear and cytoplasmic cell cycle progression by drugs employed in cell synchronization. Exp. Cell Res. 1995, 219, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, Z.; Bozzella, M.; Seluanov, A.; Gorbunova, V. Comparison of nonhomologous end joining and homologous recombination in human cells. DNA Repair 2008, 7, 1765–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douglas, P.; Moorhead, G.B.; Ye, R.; Lees-Miller, S.P. Protein phosphatases regulate DNA-dependent protein kinase activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 18992–18998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huelsenbeck, S.C.; Schorr, A.; Roos, W.P.; Huelsenbeck, J.; Henninger, C.; Kaina, B.; Fritz, G. Rac1 protein signaling is required for DNA damage response stimulated by topoisomerase II poisons. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 38590–38599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podhorecka, M.; Skladanowski, A.; Bozko, P. H2AX Phosphorylation: Its Role in DNA Damage Response and Cancer Therapy. J. Nucleic Acids 2010, 2010, 920161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrivastav, M.; De Haro, L.P.; Nickoloff, J.A. Regulation of DNA double-strand break repair pathway choice. Cell Res. 2008, 18, 134–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papa, V.; Gliozzo, B.; Clark, G.M.; McGuire, W.L.; Moore, D.; Fujita-Yamaguchi, Y.; Vigneri, R.; Goldfine, I.D.; Pezzino, V. Insulin-like growth factor-I receptors are overexpressed and predict a low risk in human breast cancer. Cancer Res. 1993, 53, 3736–3740. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jones, R.A.; Campbell, C.I.; Gunther, E.J.; Chodosh, L.A.; Petrik, J.J.; Khokha, R.; Moorehead, R.A. Transgenic overexpression of IGF-IR disrupts mammary ductal morphogenesis and induces tumor formation. Oncogene 2007, 26, 1636–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chitnis, M.M.; Yuen JS, P.; Protheroe, A.S.; Pollak, M.; Macaulay, V.M. The type 1 insulin-like growth factor receptor pathway. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 6364–6370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christopoulos, P.F.; Msaouel, P.; Koutsilieris, M. The role of the insulin-like growth factor-1 system in breast cancer. Mol. Cancer 2015, 14, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poreba, E.; Durzynska, J. Nuclear localization and actions of the insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) system components: Transcriptional regulation and DNA damage response. Mutat. Res. Rev. Mutat. Res. 2020, 784, 108307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Zhou, X.A.; Zhang, N.; Wang, J. Evolving insights: How DNA repair pathways impact cancer evolution. Cancer Biol. Med. 2020, 17, 805–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asleh, K.; Riaz, N.; Cheng, A.S.; Gao, D.; Leung SC, Y.; Anurag, M.; Nielsen, T.O. Proteomics-derived basal biomarker DNA-PKcs is associated with intrinsic subtype and long-term clinical outcomes in breast cancer. NPJ Breast Cancer 2021, 7, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chitnis, M.M.; Lodhia, K.A.; Aleksic, T.; Gao, S.; Protheroe, A.S.; Macaulay, V.M. IGF-1R inhibition enhances radiosensitivity and delays double-strand break repair by both non-homologous end-joining and homologous recombination. Oncogene 2014, 33, 5262–5273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, X.; Xi, G.; Maile, L.A.; Wai, C.; Rosen, C.J.; Clemmons, D.R. Insulin-like growth factor (IGF) binding protein 2 functions coordinately with receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase β and the IGF-I receptor to regulate IGF-I-stimulated signaling. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2012, 32, 4116–4130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renehan, A.G.; Frystyk, J.; Flyvbjerg, A. Obesity and cancer risk: The role of the insulin-IGF axis. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. TEM 2006, 17, 328–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foulstone, E.J.; Zeng, L.; Perks, C.M.; Holly, J.M.P. Insulin-Like Growth Factor Binding Protein 2 (IGFBP-2) Promotes Growth and Survival of Breast Epithelial Cells: Novel Regulation of the Estrogen Receptor. Endocrinology 2013, 154, 1780–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; Lu, H.; Zhu, S.; Gomaa, A.; Chen, Z.; Yan, J.; Washington, K.; El-Rifai, W.; Dang, C.; Peng, D. Activation of EGFR-DNA-PKcs pathway by IGFBP2 protects esophageal adenocarcinoma cells from acidic bile salts-induced DNA damage. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. CR 2019, 38, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holly, J.M.P.; Broadhurst, J.; Mansor, R.; Bahl, A.; Perks, C.M. Hyperglycemia Promotes TMPRSS2-ERG Gene Fusion in Prostate Cancer Cells via Upregulating Insulin-Like Growth Factor-Binding Protein-2. Front. Endocrinol. 2017, 8, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, L.; Zielinska, H.A.; Arshad, A.; Shield, J.P.; Bahl, A.; Holly, J.M.P.; Perks, C.M. Hyperglycaemia-induced chemoresistance in breast cancer cells: Role of the estrogen receptor. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2016, 23, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, L.; Biernacka, K.M.; Holly, J.M.P.; Jarrett, C.; Morrison, A.A.; Morgan, A.; Winters, Z.E.; Foulstone, E.J.; Shield, J.P.; Perks, C.M. Hyperglycaemia confers resistance to chemotherapy on breast cancer cells: The role of fatty acid synthase. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2010, 17, 539–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, L.; Jarrett, C.; Brown, K.; Gillespie, K.M.; Holly, J.M.; Perks, C.M. Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 (IGFBP-3) plays a role in the anti-tumorigenic effects of 5-Aza-2′-deoxycytidine (AZA) in breast cancer cells. Exp. Cell Res. 2013, 319, 2282–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gill, Z.P.; Perks, C.M.; Newcomb, P.V.; Holly, J.M. Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein (IGFBP-3) predisposes breast cancer cells to programmed cell death in a non-IGF-dependent manner. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 25602–25607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burrows, C.; Holly, J.M.P.; Laurence, N.J.; Vernon, E.G.; Carter, J.V.; Clark, M.A.; McIntosh, J.; McCaig, C.; Winters, Z.E.; Perks, C.M. Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 3 has opposing actions on malignant and nonmalignant breast epithelial cells that are each reversible and dependent upon cholesterol-stabilized integrin receptor complexes. Endocrinology 2006, 147, 3484–3500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeSantis, C.; Siegel, R.; Bandi, P.; Jemal, A. Breast cancer statistics. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2011, 61, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennecke, H.; Yerushalmi, R.; Woods, R.; Cheang, M.C.U.; Voduc, D.; Speers, C.H.; Nielsen, T.O.; Gelmon, K. Metastatic behavior of breast cancer subtypes. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 3271–3277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hande, K. Etoposide: Four decades of development of a topoisomerase II inhibitor. Eur. J. Cancer 1998, 34, 1514–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, L.; Perks, C.M.; Holly, J.M.P. IGFBP-2/PTEN: A critical interaction for tumours and for general physiology? Growth Horm. IGF Res. Off. J. Growth Horm. Res. Soc. Int. IGF Res. Soc. 2015, 25, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chua, C.Y.; Liu, Y.; Granberg, K.J.; Hu, L.; Haapasalo, H.; Annala, M.J.; Cogdell, D.E.; Verploegen, M.; Moore, L.M.; Fuller, G.N.; et al. IGFBP2 potentiates nuclear EGFR-STAT3 signaling. Oncogene 2016, 35, 738–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, S.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, X.; Hu, L.; Liu, Y.; Chua, C.Y.; Phillips, L.M.; Ren, H.; Fleming, J.B.; Wang, H.; et al. IGFBP2 activates the NF-κB pathway to Drive epithelial-mesenchymal transition and invasive character in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 6543–6554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azar, W.J.; Azar, S.H.X.; Higgins, S.; Hu, J.-F.; Hoffman, A.R.; Newgreen, D.F.; Werther, G.A.; Russo, V.C. IGFBP-2 enhances VEGF gene promoter activity and consequent promotion of angiogenesis by neuroblastoma cells. Endocrinology 2011, 152, 3332–3342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Qahtani, A.; Holly, J.; Perks, C. Hypoxia negates hyperglycaemia-induced chemo-resistance in breast cancer cells: The role of insulin-like growth factor binding protein 2. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 74635–74648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sehgal, P.; Kumar, N.; Praveen Kumar, V.R.; Patil, S.; Bhattacharya, A.; Vijaya Kumar, M.; Mukherjee, G.; Kondaiah, P. Regulation of protumorigenic pathways by insulin like growth factor binding protein2 and its association along with β-catenin in breast cancer lymph node metastasis. Mol. Cancer 2013, 12, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeggo, P.A. Identification of genes involved in repair of DNA double-strand breaks in mammalian cells. Radiat. Res. 1998, 150 (Suppl. 5), S80–S91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciszewski, W.M.; Tavecchio, M.; Dastych, J.; Curtin, N.J. DNA-PK inhibition by NU7441 sensitizes breast cancer cells to ionizing radiation and doxorubicin. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2014, 143, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medunjanin, S.; Weinert, S.; Schmeisser, A.; Mayer, D.; Braun-Dullaeus, R.C. Interaction of the double-strand break repair kinase DNA-PK and estrogen receptor-alpha. Mol. Biol. Cell 2010, 21, 1620–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ansari, S.M.R.; Hijazi, F.S.; Souchelnytskyi, S. Targeted and systemic insights into the crosstalk between DNA-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit and receptors of estrogen, progesterone and epidermal growth factor in the context of cancer. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2022, 49, 587–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mezi, S.; Botticelli, A.; Pomati, G.; Cerbelli, B.; Scagnoli, S.; Amirhassankhani, S.; d’Amati, G.; Marchetti, P. Standard of Care and Promising New Agents for the Treatment of Mesenchymal Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medunjanin, S.; Weinert, S.; Poitz, D.; Schmeisser, A.; Strasser, R.H.; Braun-Dullaeus, R.C. Transcriptional activation of DNA-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit gene expression by oestrogen receptor-alpha. EMBO Rep. 2010, 11, 208–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bleach, R.; Sherlock, M.; O’Reilly, M.W.; McIlroy, M. Growth Hormone/Insulin Growth Factor Axis in Sex Steroid Associated Disorders and Related Cancers. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 630503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perou, C.M.; Sørlie, T.; Eisen, M.B.; van de Rijn, M.; Jeffrey, S.S.; Rees, C.A.; Pollack, J.R.; Ross, D.T.; Johnsen, H.; Akslen, L.A.; et al. Molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature 2000, 406, 747–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickreuter, E.; Eke, I.; Krause, M.; Borgmann, K.; van Vugt, M.A.; Cordes, N. Targeting of β1 integrins impairs DNA repair for radiosensitization of head and neck cancer cells. Oncogene 2016, 35, 1353–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bates, R.C.; Lincz, L.F.; Burns, G.F. Involvement of integrins in cell survival. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 1995, 14, 191–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, J.I.; Doerr, M.E.; Clemmons, D.R. Cell migration: Interactions among integrins, IGFs and IGFBPs. Prog. Growth Factor Res. 1995, 6, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masuda, H.; Zhang, D.; Bartholomeusz, C.; Doihara, H.; Hortobagyi, G.N.; Ueno, N.T. Role of epidermal growth factor receptor in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2012, 136, 331–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, M.Z.; Marzec, K.A.; Martin, J.L.; Baxter, R.C. The role of insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 in the breast cancer cell response to DNA-damaging agents. Oncogene 2014, 33, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dittmann, K.; Mayer, C.; Fehrenbacher, B.; Schaller, M.; Raju, U.; Milas, L.; Chen, D.J.; Kehlbach, R.; Rodemann, H.P. Radiation-induced epidermal growth factor receptor nuclear import is linked to activation of DNA-dependent protein kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 31182–31189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Javvadi, P.; Makino, H.; Das, A.K.; Lin, Y.-F.; Chen, D.J.; Chen, B.P.; Nirodi, C.S. Threonine 2609 phosphorylation of the DNA-dependent protein kinase is a critical prerequisite for epidermal growth factor receptor-mediated radiation resistance. Mol. Cancer Res. MCR 2012, 10, 1359–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bandyopadhyay, D.; Mandal, M.; Adam, L.; Mendelsohn, J.; Kumar, R. Physical interaction between epidermal growth factor receptor and DNA-dependent protein kinase in mammalian cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 1568–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Segar, N.; Huang, C.; Zeng, P.; Tan, X.; Mao, L.; Chen, Z.; Haglund, F.; Larsson, O.; et al. Nuclear IGF1R interacts with NuMA and regulates 53BP1 dependent DNA double strand break repair in colorectal cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2021, 46, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, H.; Cheng, H.Y.; Cook, R.G.; Tweardy, D.J. Identification and characterization of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 recruitment sites within the epidermal growth factor receptor. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 3923–3930. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Park, O.K.; Schaefer, T.S.; Nathans, D. In vitro activation of Stat3 by epidermal growth factor receptor kinase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 13704–13708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coffer, P.J.; Kruijer, W. EGF receptor deletions define a region specifically mediating STAT transcription factor activation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1995, 210, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, H.-W.; Cao, X.; Zhu, H.; Ali-Osman, F. Cyclooxygenase-2 is a novel transcriptional target of the nuclear EGFR-STAT3 and EGFRvIII-STAT3 signaling axes. Mol. Cancer Res. MCR 2010, 8, 232–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaganathan, S.; Yue, P.; Paladino, D.C.; Bogdanovic, J.; Huo, Q.; Turkson, J. A functional nuclear epidermal growth factor receptor, SRC and Stat3 heteromeric complex in pancreatic cancer cells. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e19605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werner, H.; Sarfstein, R.; Laron, Z. The Role of Nuclear Insulin and IGF1 Receptors in Metabolism and Cancer. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mohammedali, A.; Biernacka, K.; Barker, R.M.; Holly, J.M.P.; Perks, C.M. The Role of Insulin-like Growth Factor Binding Protein (IGFBP)-2 in DNA Repair and Chemoresistance in Breast Cancer Cells. Cancers 2024, 16, 2113. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16112113
Mohammedali A, Biernacka K, Barker RM, Holly JMP, Perks CM. The Role of Insulin-like Growth Factor Binding Protein (IGFBP)-2 in DNA Repair and Chemoresistance in Breast Cancer Cells. Cancers. 2024; 16(11):2113. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16112113
Chicago/Turabian StyleMohammedali, Alaa, Kalina Biernacka, Rachel M. Barker, Jeff M. P. Holly, and Claire M. Perks. 2024. "The Role of Insulin-like Growth Factor Binding Protein (IGFBP)-2 in DNA Repair and Chemoresistance in Breast Cancer Cells" Cancers 16, no. 11: 2113. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16112113
APA StyleMohammedali, A., Biernacka, K., Barker, R. M., Holly, J. M. P., & Perks, C. M. (2024). The Role of Insulin-like Growth Factor Binding Protein (IGFBP)-2 in DNA Repair and Chemoresistance in Breast Cancer Cells. Cancers, 16(11), 2113. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16112113








