miRNA Expression Profiling in G1 and G2 Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Tissue Collection
2.2. Sample Processing and RNA Isolation
2.3. Real-Time Quantitative Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-qPCR) for Quantification and NGS Validation
2.4. miRNA Expression Profiling from FFPE Samples by Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS)
2.5. Statistical– and Machine Learning Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Real-Time Quantitative Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-qPCR) Validation of miRNAs Found in Literature
3.2. miRNA Expression Profiling by Next-Generation Sequencing
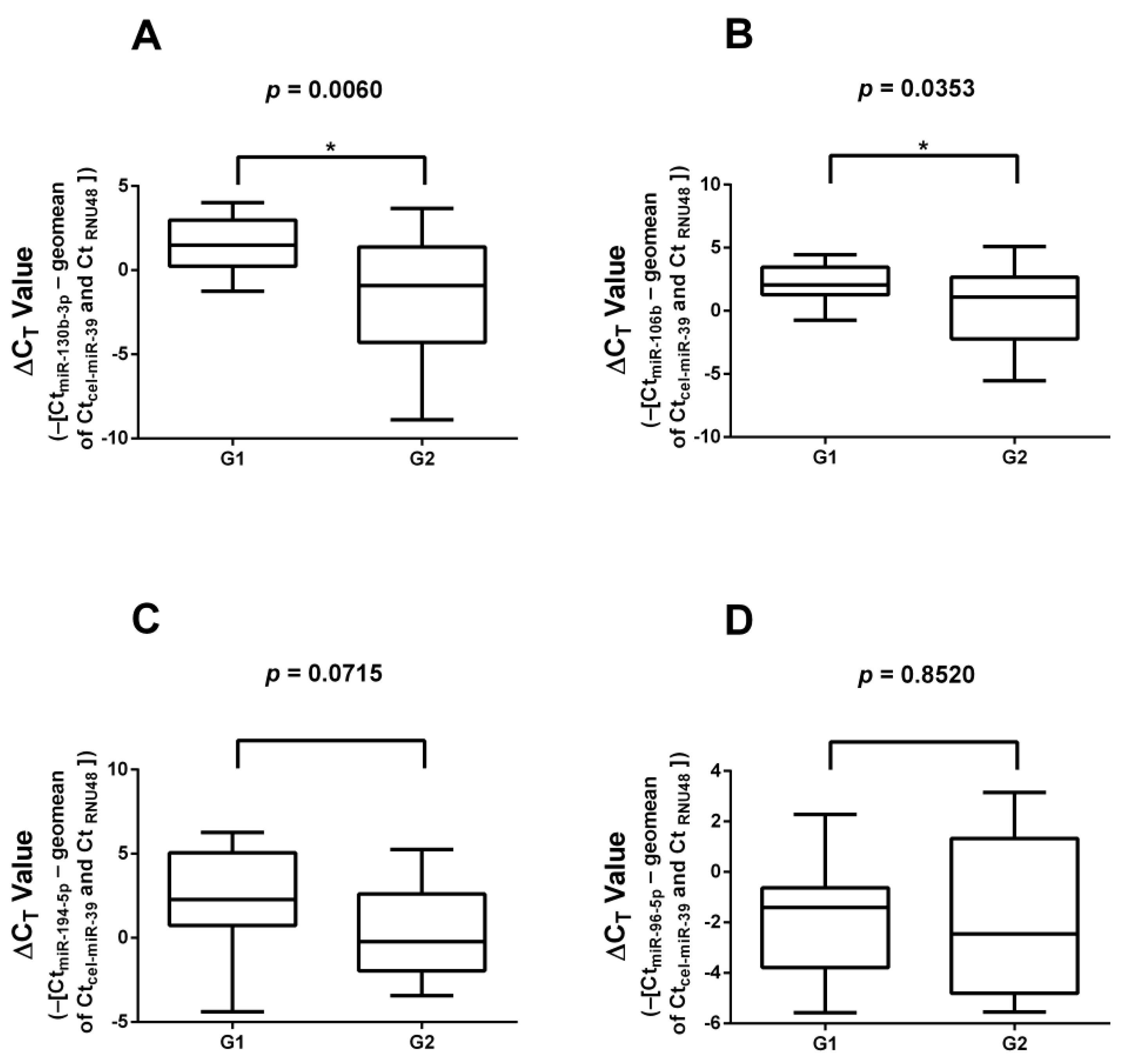
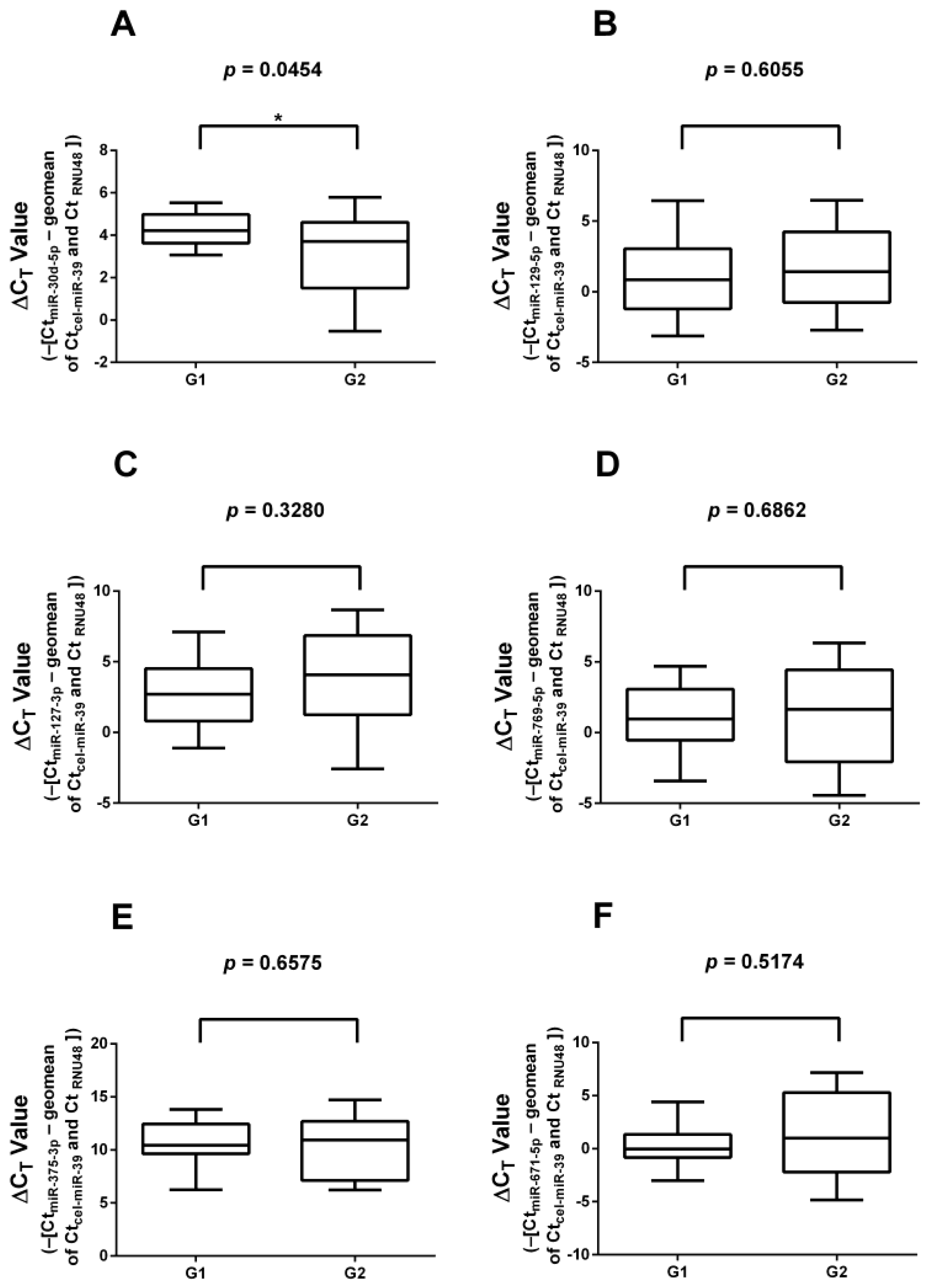
3.3. RT-qPCR Validation of Significantly Differentially Expressed miRNAs
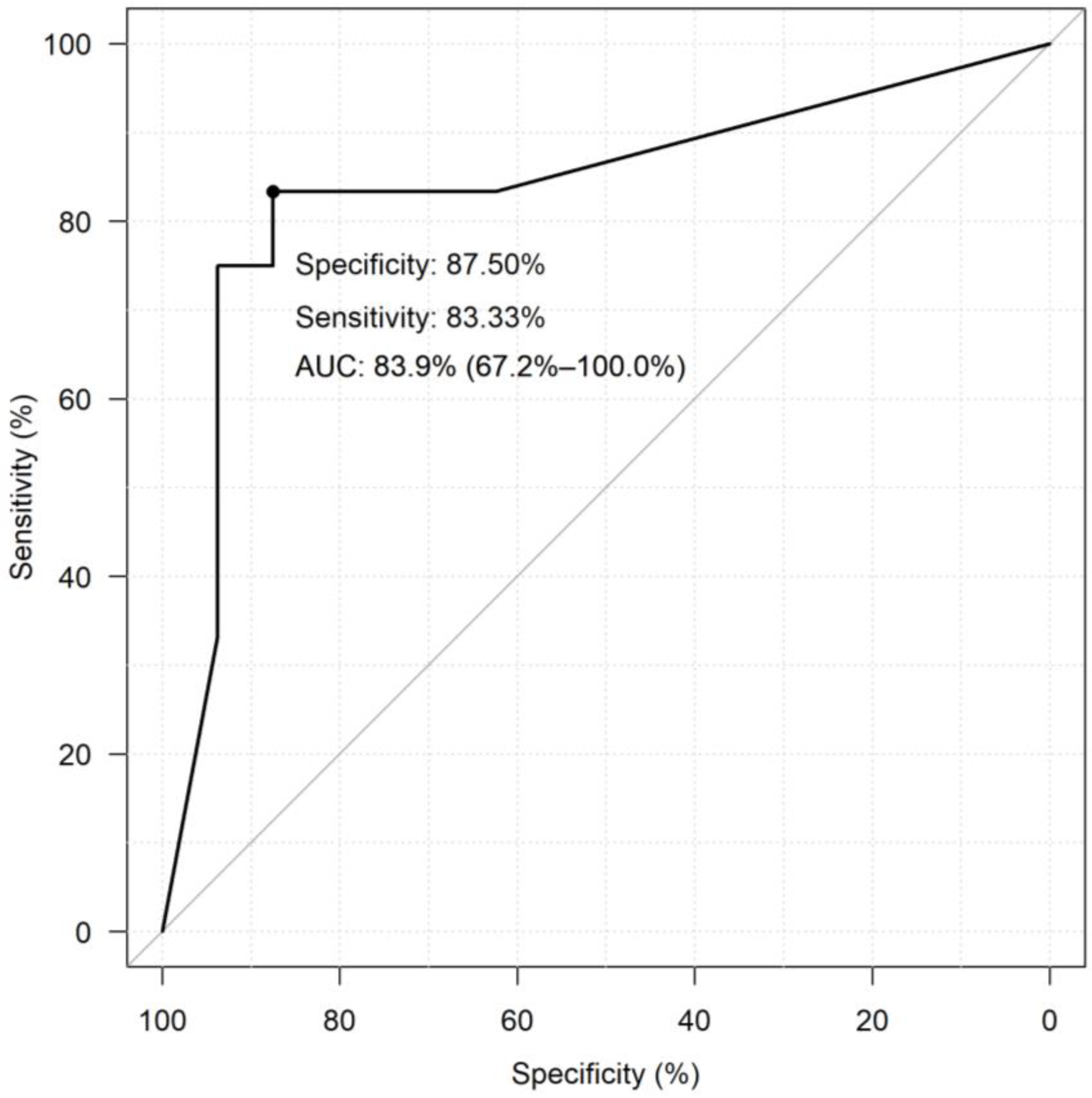
3.4. Diagnostic Performance of miRNAs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wyld, D.; Wan, M.H.; Moore, J.; Dunn, N.; Youl, P. Epidemiological trends of neuroendocrine tumours over three decades in Queensland, Australia. Cancer Epidemiol. 2019, 63, 101598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulkarni, R.; Anand, A.; Parikh, S.; Panchal, H.; Patel, A.; Mehta, D.; Patel, P. Clinical and epidemiological profile of neuroendocrine tumors: An experience from a regional cancer center from Western India. South Asian J. Cancer 2019, 8, 198–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rindi, G.; Mete, O.; Uccella, S.; Basturk, O.; La Rosa, S.; Brosens, L.A.A.; Ezzat, S.; de Herder, W.W.; Klimstra, D.S.; Papotti, M.; et al. Overview of the 2022 WHO Classification of Neuroendocrine Neoplasms. Endocr. Pathol. 2022, 33, 115–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofland, J.; Falconi, M.; Christ, E.; Castaño, J.P.; Faggiano, A.; Lamarca, A.; Perren, A.; Petrucci, S.; Prasad, V.; Ruszniewski, P.; et al. European Neuroendocrine Tumor Society 2023 guidance paper for functioning pancreatic neuroendocrine tumour syndromes. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2023, 35, e13318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uccella, S.; La Rosa, S.; Metovic, J.; Marchiori, D.; Scoazec, J.Y.; Volante, M.; Mete, O.; Papotti, M. Genomics of High-Grade Neuroendocrine Neoplasms: Well-Differentiated Neuroendocrine Tumor with High-Grade Features (G3 NET) and Neuroendocrine Carcinomas (NEC) of Various Anatomic Sites. Endocr. Pathol. 2021, 32, 192–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasari, A.; Shen, C.; Halperin, D.; Zhao, B.; Zhou, S.; Xu, Y.; Shih, T.; Yao, J.C. Trends in the incidence, prevalence, and survival outcomes in patients with neuroendocrine tumors in the United States. JAMA Oncol. 2017, 3, 1335–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falconi, M.; Eriksson, B.; Kaltsas, G.; Bartsch, D.K.; Capdevila, J.; Caplin, M.; Kos-Kudla, B.; Kwekkeboom, D.; Rindi, G.; Klöppel, G.; et al. ENETS consensus guidelines update for the management of patients with functional pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors and non-functional pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. Neuroendocrinology 2016, 103, 153–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kos-Kudła, B.; Castaño, J.P.; Denecke, T.; Grande, E.; Kjaer, A.; Koumarianou, A.; de Mestier, L.; Partelli, S.; Perren, A.; Stättner, S.; et al. European Neuroendocrine Tumour Society (ENETS) 2023 guidance paper for nonfunctioning pancreatic neuroendocrine tumours. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2023, 35, e13343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magi, L.; Marasco, M.; Rinzivillo, M.; Faggiano, A.; Panzuto, F. Management of Functional Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Neoplasms. Curr. Treat. Options Oncol. 2023, 24, 725–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marasco, M.; Dell’Unto, E.; Laviano, A.; Campana, D.; Panzuto, F. Gastrointestinal side effects of somatostatin analogs in neuroendocrine tumors: A focused review. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2024. ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calomino, N.; Poto, G.E.; Carbone, L.; Bagnacci, G.; Piccioni, S.; Andreucci, E.; Nenci, L.; Marano, L.; Verre, L.; Petrioli, R.; et al. Neuroendocrine tumors’ patients treated with somatostatin analogue could complicate with emergency cholecystectomy. Ann. Ital. Chir. 2023, 94, 518–522. [Google Scholar]
- Botling, J.; Lamarca, A.; Bajic, D.; Norlén, O.; Lönngren, V.; Kjaer, J.; Eriksson, B.; Welin, S.; Hellman, P.; Rindi, G.; et al. High-Grade Progression Confers Poor Survival in Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors. Neuroendocrinology 2020, 110, 891–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malumbres, M. miRNAs and cancer: An epigenetics view. Mol. Asp. Med. 2013, 34, 863–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grolmusz, V.K.; Kövesdi, A.; Borka, K.; Igaz, P.; Patócs, A. Prognostic relevance of proliferation-related miRNAs in pancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2018, 179, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavalcanti, E.; Galleggiante, V.; Coletta, S.; Stasi, E.; Chieppa, M.; Armentano, R.; Serino, G. Altered miRNAs Expression Correlates with Gastroenteropancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors Grades. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kövesdi, A.; Kurucz, P.A.; Nyírő, G.; Darvasi, O.; Patócs, A.; Butz, H. Circulating miRNA increases the diagnostic accuracy of chromogranin a in metastatic pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. Cancers 2020, 12, 2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorns, C.; Schurmann, C.; Gebauer, N.; Wallaschofski, H.; Kümpers, C.; Bernard, V.; Feller, A.C.; Keck, T.; Habermann, J.K.; Begum, N.; et al. Global MicroRNA profiling of pancreatic neuroendocrine Neoplasias. Anticancer Res. 2014, 34, 2249–2254. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vicentini, C.; Fassan, M.; D’Angelo, E.; Corbo, V.; Silvestris, N.; Nuovo, G.J.; Scarpa, A. Clinical application of microRNA testing in neuroendocrine tumors of the gastrointestinal tract. Molecules 2014, 19, 2458–2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, A.; Yu, J.; Kim, H.; Wolfgang, C.L.; Canto, M.I.; Hruban, R.H.; Goggins, M. MicroRNA array analysis finds elevated serum miR-1290 accurately distinguishes patients with low-stage pancreatic cancer from healthy and disease controls. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 3600–3610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turai, P.I.; Herold, Z.; Nyirő, G.; Borka, K.; Micsik, T.; Tőke, J.; Szücs, N.; Tóth, M.; Patócs, A.; Igaz, P. Tissue miRNA Combinations for the Differential Diagnosis of Adrenocortical Carcinoma and Adenoma Established by Artificial Intelligence. Cancers 2022, 14, 895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmittgen, T.D.; Livak, K.J. Analyzing real-time PCR data by the comparative CT method. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 1101–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavel, M.; Öberg, K.; Falconi, M.; Krenning, E.P.; Sundin, A.; Perren, A.; Berruti, A. Gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, 844–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panzuto, F.; Ramage, J.; Pritchard, D.M.; van Velthuysen, M.L.F.; Schrader, J.; Begum, N.; Sundin, A.; Falconi, M.; O’Toole, D. European Neuroendocrine Tumor Society (ENETS) 2023 guidance paper for gastroduodenal neuroendocrine tumours (NETs) G1–G3. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2023, 35, e13306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, S.Y.; Huang, X.X.; Li, N.M.; Lv, C.Y.; Lv, C.H.; Wei, M.L.; Gao, Z.; Zhang, Y.P. MiR-127-3p inhibits proliferation of ovarian cancer in rats through down-regulating MAPK4. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 24, 10383–10390. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fellenberg, J.; Kunz, P.; Lehner, B.; Saehr, H.; Schenker, A. Tumor suppressor function of mir-127-3p and mir-376a-3p in osteosarcoma cells. Cancers 2019, 11, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shenouda, S.K.; Alahari, S.K. MicroRNA function in cancer: Oncogene or a tumor suppressor? Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2009, 28, 369–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolmeson, C.; Esguerra, J.L.S.; Salehi, A.; Speidel, D.; Eliasson, L.; Cilio, C.M. Differences in islet-enriched miRNAs in healthy and glucose intolerant human subjects. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2011, 404, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmermann, N.; Knief, J.; Kacprowski, T.; Lazar-Karsten, P.; Keck, T.; Billmann, F.; Schmid, S.; Luley, K.; Lehnert, H.; Brabant, G.; et al. MicroRNA analysis of gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumors and metastases. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 28379–28390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghafouri-Fard, S.; Askari, A.; Hussen, B.M.; Rasul, M.F.; Hatamian, S.; Taheri, M.; Kiani, A. A review on the role of miR-671 in human disorders. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2022, 9, 1077968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Sample No. | Tumor Grade | Ki-67 Index | Sex | Age | Hormonal Activity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | 1 | 2% | M | 60 | NF |
| 2. | 1 | 2% | F | 34 | NF |
| 3. | 1 | <1% | F | 46 | Insulinoma |
| 4. | 1 | 1% | F | 42 | NF |
| 5. | 1 | 1% | F | 49 | Insulinoma |
| 6. | 1 | 3% | F | 70 | NF |
| 7. | 1 | 0% | F | 65 | NF |
| 8. | 1 | 1% | M | 69 | NF |
| 9. | 1 | <1% | F | 67 | NF |
| 10. | 1 | 2% | F | 74 | NF |
| 11. | 1 | <1% | F | 40 | NF |
| 12. | 1 | <1% | F | 53 | NF |
| 13. | 1 | 1% | F | 44 | Insulinoma |
| 14. | 1 | <2% | M | 70 | NF |
| 15. | 1 | <1% | M | 71 | NF |
| 16. | 1 | <1% | F | 79 | NF |
| 17. | 1 | 1% | F | 56 | NF |
| 18. | 2 | 20% | F | 48 | NF |
| 19. | 2 | 15% | F | 42 | NF |
| 20. | 2 | 10% | M | 69 | NF |
| 21. | 2 | 5% | F | 60 | NF |
| 22. | 2 | 1–3% | F | 62 | NF |
| 23. | 2 | 10% | F | 65 | NF |
| 24. | 2 | 5% | M | 66 | NF |
| 25. | 2 | 1–4% | M | 49 | NF |
| 26. | 2 | 5–8% | M | 44 | NF |
| 27. | 2 | 2.8–3.1% | F | 76 | NF |
| 28. | 2 | 5–10% | M | 54 | NF |
| 29. | 2 | 5% | M | 47 | NF |
| 30. | 2 | 5% | M | 48 | NF |
| 31. | 2 | 20% | F | 49 | NF |
| 32. | 2 | 5% | F | 74 | NF |
| 33. | 2 | 7% | F | 41 | NF |
| Model Combination | TP | FP | TN | FN | Specificity | Sensitivity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| miR_106b + miR_130b_3p + miR_127_3p + miR_129_5p + miR_30d_5p | 14.92 | 4.34 | 14.92 | 2.07 | 77.44 | 87.82 |
| miR_106b + miR_130b_3p + miR_127_3p + miR_129_5p + miR_671_5p + miR_30d_5p | 14.86 | 6.03 | 14.86 | 2.13 | 71.11 | 87.47 |
| miR_106b + miR_130b_3p + miR_127_3p + miR_769_5p + miR_671_5p + miR_30d_5p | 14.54 | 5.56 | 14.54 | 2.45 | 72.33 | 85.56 |
| miR_769_5p + miR_375_3p + miR_30d_5p | 13.85 | 4.44 | 13.85 | 3.14 | 75.70 | 81.52 |
| miR_106b + miR_130b_3p + miR_127_3p + miR_769_5p + miR_30d_5p | 14.59 | 5.97 | 14.59 | 2.40 | 70.96 | 85.88 |
| miR_106b + mir_194_5p + miR_130b_3p + miR_127_3p + miR_129_5p + miR_30d_5p | 14.16 | 5.39 | 14.16 | 2.83 | 72.42 | 83.33 |
| miR_106b + miR_130b_3p + miR_127_3p + miR_769_5p + miR_671_5p | 14.00 | 5.29 | 14.00 | 2.99 | 72.567 | 82.4 |
| miR_106b + miR_130b_3p + miR_127_3p + miR_129_5p + miR_769_5p + miR_30d_5p | 14.65 | 6.84 | 14.65 | 2.34 | 68.14 | 86.19 |
| miR_106b + miR_130b_3p + miR_127_3p + miR_671_5p + miR_30d_5p | 14.20 | 6.12 | 14.20 | 2.79 | 69.85 | 83.53 |
| miR_106b + miR_130b_3p + miR_127_3p + miR_129_5p + miR_375_3p | 14.93 | 7.85 | 14.93 | 2.06 | 65.52 | 87.84 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nyirő, G.; Szeredás, B.K.; Decmann, Á.; Herold, Z.; Vékony, B.; Borka, K.; Dezső, K.; Zalatnai, A.; Kovalszky, I.; Igaz, P. miRNA Expression Profiling in G1 and G2 Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors. Cancers 2024, 16, 2528. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16142528
Nyirő G, Szeredás BK, Decmann Á, Herold Z, Vékony B, Borka K, Dezső K, Zalatnai A, Kovalszky I, Igaz P. miRNA Expression Profiling in G1 and G2 Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors. Cancers. 2024; 16(14):2528. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16142528
Chicago/Turabian StyleNyirő, Gábor, Bálint Kende Szeredás, Ábel Decmann, Zoltan Herold, Bálint Vékony, Katalin Borka, Katalin Dezső, Attila Zalatnai, Ilona Kovalszky, and Peter Igaz. 2024. "miRNA Expression Profiling in G1 and G2 Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors" Cancers 16, no. 14: 2528. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16142528
APA StyleNyirő, G., Szeredás, B. K., Decmann, Á., Herold, Z., Vékony, B., Borka, K., Dezső, K., Zalatnai, A., Kovalszky, I., & Igaz, P. (2024). miRNA Expression Profiling in G1 and G2 Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors. Cancers, 16(14), 2528. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16142528








