Accumulation of 3-Monochloro-Propanediol Esters in Kidney Tissues of Patients with Human Renal Cell Carcinoma
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
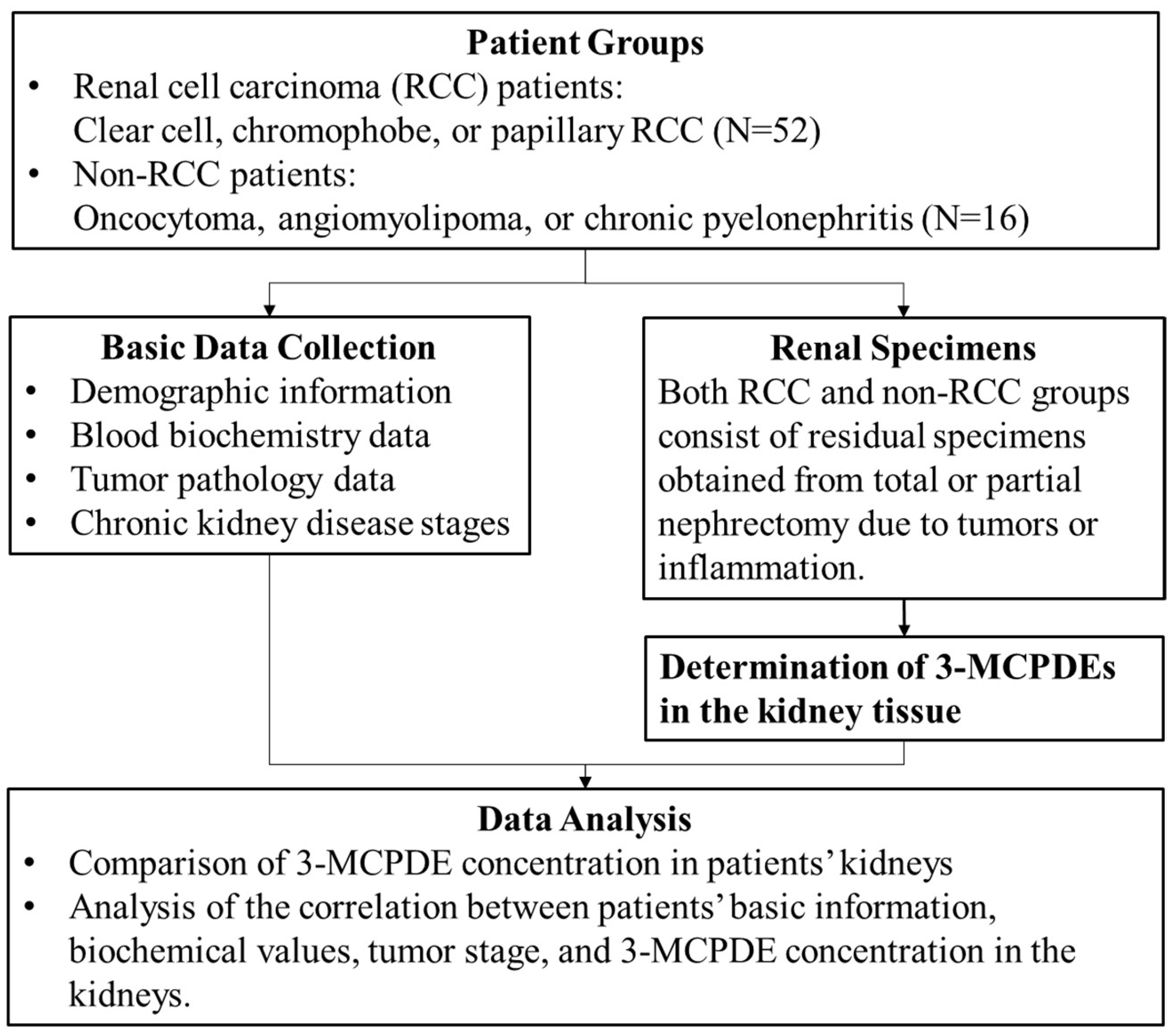
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Patients and Data Collection
2.3. Method Validation
2.4. Determinations of 3-MCPDEs in Human Renal Samples
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics of RCC Patients and Non-RCC Patients
3.2. Method Validation
3.3. Analysis of Cumulative 3-MCPDE Levels in Kidney Tissues
3.4. Analysis of Correlations between Cumulative 3-MCPDE Levels in Kidney Tissues and Basic Demographic Data and Biochemical Indicators
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Šmidrkal, J.; Tesařová, M.; Hrádková, I.; Berčíková, M.; Adamčíková, A.; Filip, V. Mechanism of formation of 3-chloropropan-1, 2-diol (3-MCPD) esters under conditions of the vegetable oil refining. Food Chem. 2016, 211, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, T.; Liu, W.; Zheng, Z.; Chen, Y.; Shen, M.; Li, C. Bibliometric analysis of research trends on 3-monochloropropane-1, 2-diol esters in foods. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 15347–15359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.W.; Li, C.I.; Huang, K.C.; Liu, C.S.; Chen, H.L.; Lee, C.C.; Chiou, Y.Y.; Chen, R.J. 3-MCPD and glycidol coexposure induces systemic toxicity and synergistic nephrotoxicity via NLRP3 inflammasome activation, necroptosis, and autophagic cell death. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 405, 124241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Tsao, C.H.; Chang, Y.H.; Lee, W.J. Occurrence of thermally induced glycidyl esters and 3-monochloropropane-1, 2-diol esters in refined oils and pressed oils manufactured by different processes and associated with human health risks in Taiwan. Food Chem. 2021, 360, 130053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, Y.H.; Liao, K.W.; Lin, Z.E.; Lee, W.J. Preliminary assessments of population exposure to glycidyl esters and 3-monochloropropane-1, 2-diol esters from miscellaneous oil-containing packaged foods in Taiwan. Food Chem. 2024, 430, 137055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wang, S.T.; Tan, C.H.; Lin, Z.E.; Lee, W.J. Occurrence and risk assessment of glycidyl and 3-monochloropropanediol esters in infant formulas marketed in Taiwan. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2024, 41, 352–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yabani, D.S.; Ofosu, I.W.; Ankar-Brewoo, G.M.; Lutterodt, H.E. Toxicity of dietary exposure to 3-monochloropropanediol, glycidol, and their fatty acid esters. J. Food Qual. 2024, 2024, 7913820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Destaillats, F.; Craft, B.D.; Sandoz, L.; Nagy, K. Formation mechanisms of monochloropropanediol (MCPD) fatty acid diesters in refined palm (Elaeis guineensis) oil and related fractions. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2012, 29, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inagaki, R.; Ito, F.; Shimamura, Y.; Masuda, S. Effect of chloride on the formation of 3-monochloro-1, 2-propanediol fatty acid diesters and glycidol fatty acid esters in fish, meats and acylglycerols during heating. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2019, 36, 236–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhiya, N.; Abraham, K.; Gürtler, R.; Appel, K.E.; Lampen, A. Toxicological assessment of 3-chloropropane-1, 2-diol and glycidol fatty acid esters in food. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2011, 55, 509–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Gao, B.Y.; Qin, F.; Wu, P.P.; Shi, H.M.; Luo, W.; Ma, A.N.; Jiang, R.Y.; Xu, X.B.; Yu, L.L. Acute oral toxicity of 3-MCPD mono-and di-palmitic esters in Swiss mice and their cytotoxicity in NRK-52E rat kidney cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2012, 50, 3785–3791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Huang, G.; Wang, T.T.; Sun, X.; Yu, L. 3-MCPD 1-palmitate induced tubular cell apoptosis in vivo via JNK/p53 pathways. Toxicol. Sci. 2016, 151, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwack, S.J.; Kim, S.S.; Choi, Y.W.; Rhee, G.S.; Lee, R.D.; Seok, J.H.; Chae, S.Y.; Won, Y.H.; Lim, K.J.; Choi, K.S.; et al. Mechanism of antifertility in male rats treated with 3-monochloro-1, 2-propanediol (3-MCPD). J. Toxicol. Environ. Health A 2004, 67, 2001–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, W.S.; Han, B.S.; Nam, K.T.; Park, K.; Choi, M.; Kim, S.H.; Jeong, J.; Jang, D.D. Carcinogenicity study of 3-monochloropropane-1, 2-diol in Sprague–Dawley rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2008, 46, 3172–3177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC). IARC Monographs–101: 3-Monochloro-1,2-Propanediol. 2012. Available online: https://publications.iarc.fr/_publications/media/download/5695/5a8db1ef7524cce85ad21b3836bea40ab9082535.pdf (accessed on 10 September 2024).
- Jeong, J.; Han, B.S.; Cho, W.S.; Choi, M.; Ha, C.S.; Lee, B.S.; Kim, Y.B.; Son, W.C.; Kim, C.Y. Carcinogenicity study of 3-monochloropropane-1, 2-diol (3-MCPD) administered by drinking water to B6C3F1 mice showed no carcinogenic potential. Arch. Toxicol. 2010, 84, 719–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhamad Rosli, S.H.; Lau, M.S.; Khalid, T.; Maarof, S.K.; Jeyabalan, S.; Sirdar Ali, S.; Norhayati, M.K.; Md Noh, M.F.; Salleh, R.; Palaniveloo, L.; et al. Association between dietary 3-monochloropropane-1, 2-diol esters (3-MCPDE) and renal cancer in Peninsular Malaysia: Exposure assessment and matched case-control study. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2023, 40, 475–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meesters, R.; Voswinkel, S. Bioanalytical method development and validation: From the USFDA 2001 to the USFDA 2018 guidance for industry. J. Appl. Bioanal. 2018, 4, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Oil Chemists’ Society (AOCS). Official Methods and Recommended Practices of the AOCS, 7th ed.; American Oil Chemists’ Society: Champaign, IL, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Peired, A.J.; Campi, R.; Angelotti, M.L.; Antonelli, G.; Conte, C.; Lazzeri, E.; Becherucci, F.; Calistri, L.; Serni, S.; Romagnani, P. Sex and gender differences in kidney cancer: Clinical and experimental evidence. Cancers 2021, 13, 4588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, K.; Hielscher, J.; Kuhlmann, J.; Monien, B.H. Urinary excretion of 2/3-monochloropropanediol (2/3-MCPD) and 2, 3-dihydroxypropylmercapturic acid (DHPMA) after a single high dose of fatty acid esters of 2/3-MCPD and glycidol: A controlled exposure study in humans. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2021, 65, 2000735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braeuning, A.; Sawada, S.; Oberemm, A.; Lampen, A. Analysis of 3-MCPD-and 3-MCPD dipalmitate-induced proteomic changes in rat liver. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2015, 86, 374–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.; Liu, M.; Huang, G.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, T.T.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.; Yu, L. Absorption, distribution, metabolism and excretion of 3-MCPD 1-monopalmitate after oral administration in rats. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 2609–2614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, G.; Gao, B.; Xue, J.; Cheng, Z.; Sun, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, L.L. Toxicokinetics and metabolism of 3-monochloropropane 1, 2-diol dipalmitate in Sprague Dawley rats. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 11672–11680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zelinková, Z.; Novotný, O.; Schůrek, J.; Velíšek, J.; Hajšlová, J.; Doležal, M. Occurrence of 3-MCPD fatty acid esters in human breast milk. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2008, 25, 669–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becalski, A.; Zhao, T.; Granvogl, M.; Arbuckle, T. An investigation of presence of 2-and 3-monochloropropanediol fatty acid esters in Canadian human milk samples. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2018, 35, 1881–1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Li, J.; Feng, S.; Bian, L.; Liu, Z.; Ping, Y.; Wang, X.; Schepdael, A.V. Headspace solid-phase microextraction and on-fiber derivatization for the determination of 3-/2-MCPDE and GE in breast milk and infant formula by gas chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. LWT 2022, 154, 112575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Wang, Z.; Ren, M.; Feng, G.; Ye, B.; Wang, Y.; Fang, B.; Deng, X.; Guan, S. A 4-week study of four 3-monochloropropane-1, 2-diol diesters on lipid metabolism in C57BL/6J mice. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2015, 40, 453–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| All (n = 68) | Non-RCC (n = 16) | RCC (n = 52) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| n (%)/Median (Range) | |||
| Sex, male | 45 (66.18%) | 7 (43.75%) | 38 (73.07%) * |
| Age (years) | 63.5 (32~88) | 60 (32~81) | 65.5 (39~88) |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 25.3 (17.47~40) | 24.44 (19.50~40) | 26.36 (17.47~35.95) |
| eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m2) | 87.1 (6.13~183.61) | 86.4 (6.13~166.31) | 88.04 (6.6~183.61) |
| CKD stage | 2 (1~5) | 2 (1~5) | 2 (1~5) |
| AST (U/L) | 25 (12~122) | 23 (15~118) | 25.5 (12~122) |
| ALT (U/L) | 22 (5~199) | 15 (5~85) | 26 (10~199) |
| Tumor size (cm3) | - | - | 21.9 (3~931) |
| Tumor grade | - | - | 2 (1~4) |
| 3-MCPD-PP Equivalent Concentration (µg/mL) | Recovery (%) | RSD (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.05 | Intra-day | 101.16 ± 8.75 | 8.66 |
| Inter-day | 99.20 ± 3.92 | 3.95 | |
| 0.25 | Intra-day | 105.00 ± 3.83 | 3.65 |
| Inter-day | 100.72 ± 3.90 | 3.88 |
| n | 3-MCPDE Accumulation (µg/g) | Detection Rate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SD | Range | |||
| RCC | 52 | 0.22 ± 0.45 | ND~2.22 ** | 55.76% |
| Non-RCC | 16 | 0.01 ± 0.02 | ND~0.10 | 6.25% |
| 3-MCPDEs Accumulation | Sex | Age | BMI | eGFR | CKD Stage | AST | ALT | Tumor Size | Tumor Grade | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3-MCPDEs accumulation | 1 | |||||||||
| Sex | 0.174 | 1 | ||||||||
| Age | 0.086 | −0.208 | 1 | |||||||
| BMI | 0.178 | −0.087 | −0.11 | 1 | ||||||
| eGFR | −0.208 | −0.257 # | −0.216 | 0.151 | 1 | |||||
| CKD stage | 0.199 | 0.249 # | 0.267 # | −0.19 | −0.931 ** | 1 | ||||
| AST | 0.192 | 0.09 | −0.025 | −0.062 | 0.312 * | −0.328 * | 1 | |||
| ALT | 0.236 # | 0.249 # | −0.12 | 0.151 | 0.283 * | −0.257 # | 0.792 ** | 1 | ||
| Tumor size | −0.069 | −0.149 | 0.228 # | −0.158 | 0.143 | −0.119 | −0.388 ** | −0.364 ** | 1 | |
| Tumor grade | 0.127 | 0.263 # | −0.061 | −0.261 # | 0.085 | −0.08 | 0.13 | 0.058 | 0.232 # | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, C.-Y.; Wang, Y.-A.; Liao, K.-W.; Wu, H.-T.; Ou, C.-H.; Tan, C.H.; Lee, W.-J. Accumulation of 3-Monochloro-Propanediol Esters in Kidney Tissues of Patients with Human Renal Cell Carcinoma. Cancers 2024, 16, 3313. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16193313
Hu C-Y, Wang Y-A, Liao K-W, Wu H-T, Ou C-H, Tan CH, Lee W-J. Accumulation of 3-Monochloro-Propanediol Esters in Kidney Tissues of Patients with Human Renal Cell Carcinoma. Cancers. 2024; 16(19):3313. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16193313
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Che-Yuan, Yu-An Wang, Kai-Wei Liao, Hung-Tsung Wu, Chien-Hui Ou, Choon Hui Tan, and Wei-Ju Lee. 2024. "Accumulation of 3-Monochloro-Propanediol Esters in Kidney Tissues of Patients with Human Renal Cell Carcinoma" Cancers 16, no. 19: 3313. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16193313
APA StyleHu, C.-Y., Wang, Y.-A., Liao, K.-W., Wu, H.-T., Ou, C.-H., Tan, C. H., & Lee, W.-J. (2024). Accumulation of 3-Monochloro-Propanediol Esters in Kidney Tissues of Patients with Human Renal Cell Carcinoma. Cancers, 16(19), 3313. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16193313








