Molecular and Clinical Features of Pancreatic Acinar Cell Carcinoma: A Single-Institution Case Series
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Demographic Characteristics
3.2. Clinical and Molecular Characteristics of ACC
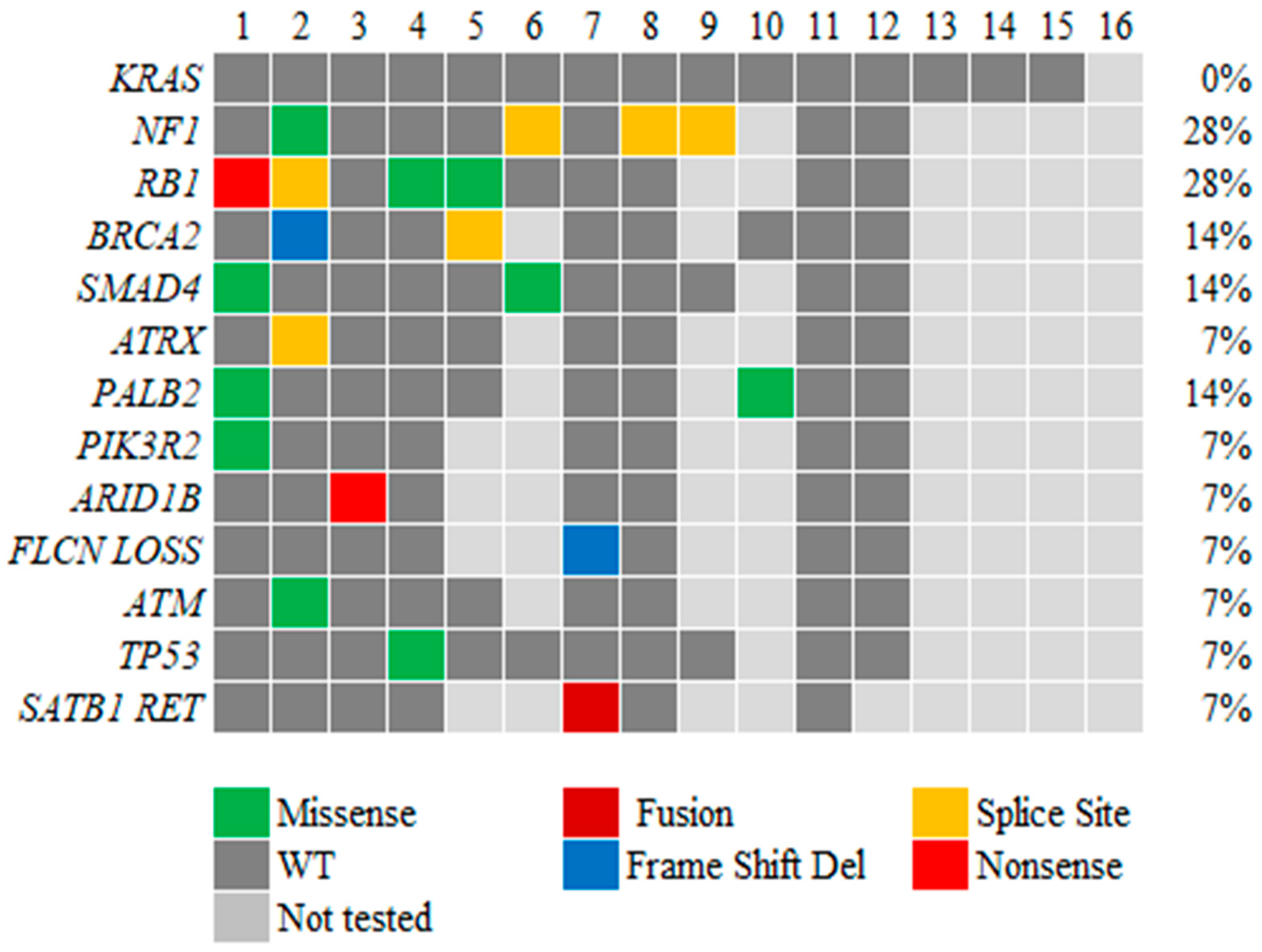
3.3. Genetic Alterations in ACC
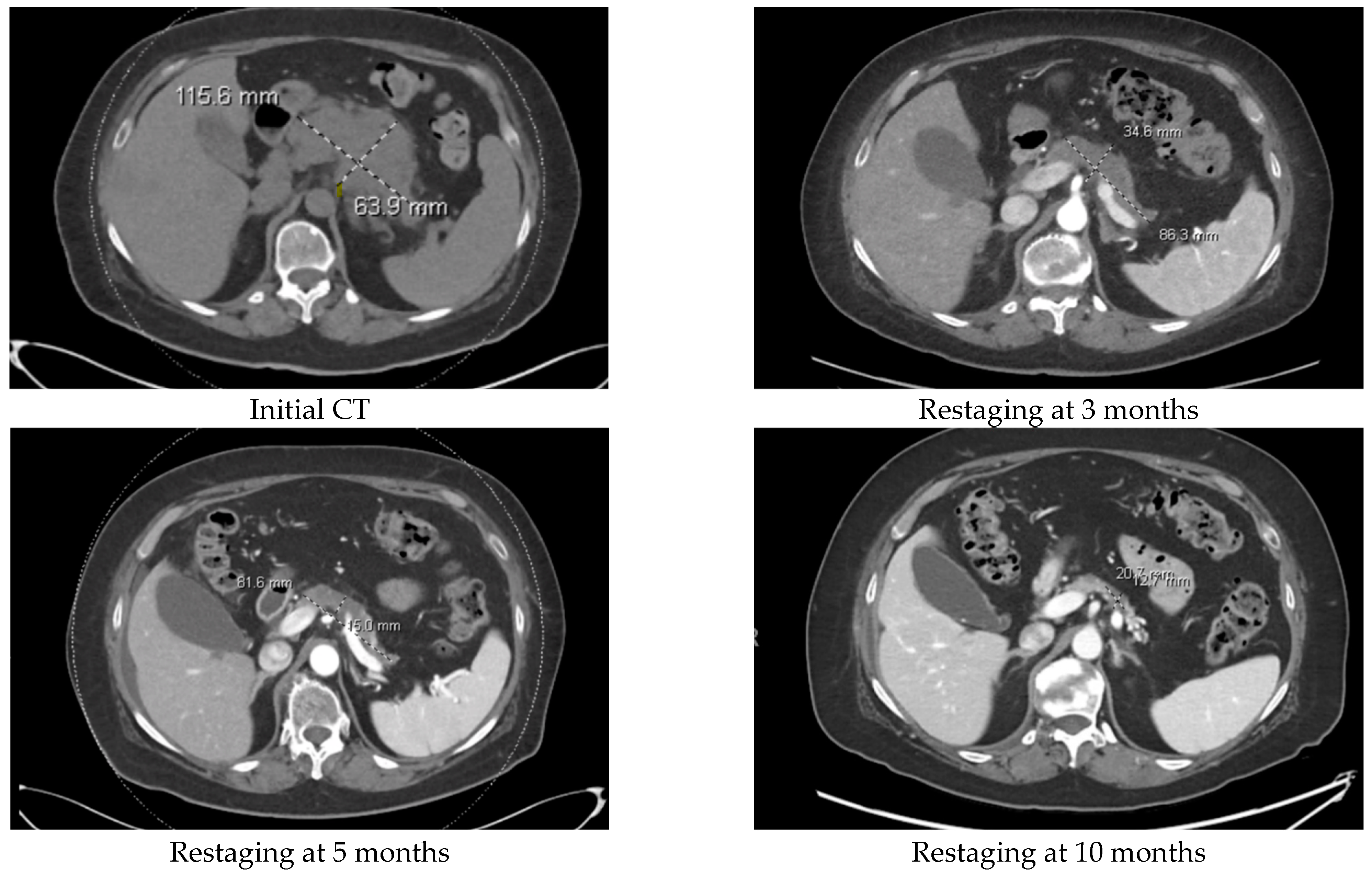
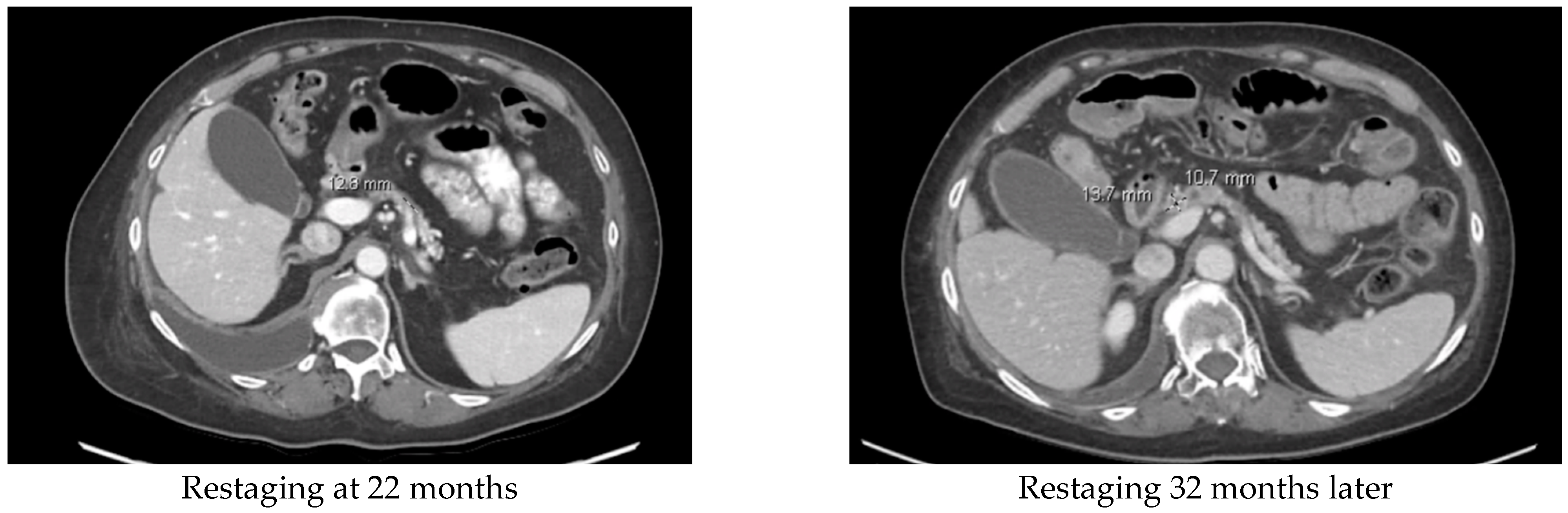
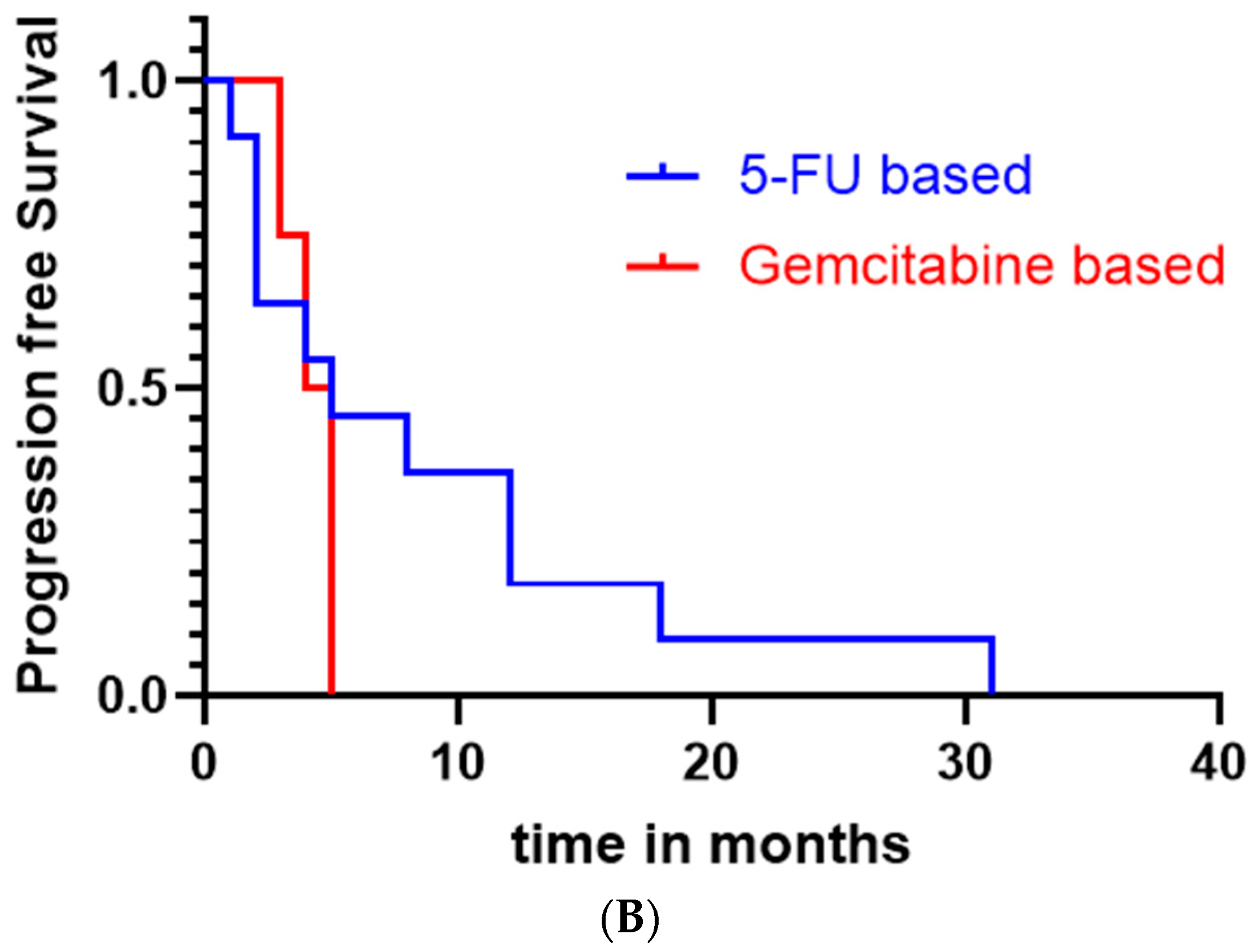
3.4. Treatment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Calimano-Ramirez, L.F.; Daoud, T.; Gopireddy, D.R.; Morani, A.C.; Waters, R.; Gumus, K.; Klekers, A.R.; Bhosale, P.R.; Virarkar, M.K. Pancreatic acinar cell carcinoma: A comprehensive review. World J. Gastroenterol. 2022, 28, 5827–5844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowery, M.A.; Klimstra, D.S.; Shia, J.; Yu, K.H.; Allen, P.J.; Brennan, M.F.; O’Reilly, E.M. Acinar Cell Carcinoma of the Pancreas: New Genetic and Treatment Insights into a Rare Malignancy. Oncologist 2011, 16, 1714–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pishvaian, M.J.; Blais, E.M.; Brody, J.R.; Lyons, E.; DeArbeloa, P.; Hendifar, A.; Mikhail, S.; Chung, V.; Sahai, V.; Sohal, D.P.S.; et al. Overall survival in patients with pancreatic cancer receiving matched therapies following molecular profiling: A retrospective analysis of the Know Your Tumor registry trial. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, 508–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakakida, T.; Ishikawa, T.; Doi, T.; Morita, R.; Kataoka, S.; Miyake, H.; Yamaguchi, K.; Moriguchi, M.; Sogame, Y.; Yasuda, H.; et al. Genomic landscape and clinical features of rare subtypes of pancreatic cancer: Analysis with the national database of Japan. J. Gastroenterol. 2023, 58, 575–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagaev, A.; Kotlov, N.; Nomie, K.; Svekolkin, V.; Gafurov, A.; Isaeva, O.; Osokin, N.; Kozlov, I.; Frenkel, F.; Gancharova, O.; et al. Conserved pan-cancer microenvironment subtypes predict response to immunotherapy. Cancer Cell 2021, 39, 845–865.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subbiah, V.; Wolf, J.; Konda, B.; Kang, H.; Spira, A.; Weiss, J.; Takeda, M.; Ohe, Y.; Khan, S.; Ohashi, K.; et al. Tumour-agnostic efficacy and safety of selpercatinib in patients with RET fusion-positive solid tumours other than lung or thyroid tumours (LIBRETTO-001): A phase 1/2, open-label, basket trial. Lancet Oncol. 2022, 23, 1261–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fricke, J.; Wang, J.; Gallego, N.; Mambetsariev, I.; Kim, P.; Babikian, R.; Chen, B.T.; Afkhami, M.; Subbiah, V.; Salgia, R. Selpercatinib and Pralsetinib Induced Chylous Ascites in RET-Rearranged Lung Adenocarcinoma: A Case Series. Clin. Lung Cancer 2023, 24, 666–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, Y.; Qi, C.; Peng, Z.; Shen, L.; Zhou, J. Patients With Acinar Cell Carcinoma of the Pancreas After 2005: A Large Population Study. Pancreas 2020, 49, 781–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing-Mao, Z.; Hong-Juan, Z.; Qing, L.; Qiang, H. Pancreatic acinar cell carcinoma-case report and literature review. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sridharan, V.; Mino-Kenudson, M.; Cleary, J.M.; Rahma, O.E.; Perez, K.; Clark, J.W.; Clancy, T.E.; Rubinson, D.A.; Goyal, L.; Bazerbachi, F.; et al. Pancreatic acinar cell carcinoma: A multi-center series on clinical characteristics and treatment outcomes. Pancreatology 2021, 21, 1119–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, S.; Motegi, H.; Kurihara, Y.; Shimbo, T.; Kikuchi, I.; Wakabayashi, T.; Sato, T. A resected case of acinar cell carcinoma of the pancreas with liver metastasis following chemotherapy using modified FOLFIRINOX. Surg. Case Rep. 2023, 9, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skacel, M.; Ormsby, A.H.; Petras, R.E.; McMahon, J.T.; Henricks, W.H. Immunohistochemistry in the differential diagnosis of acinar and endocrine pancreatic neoplasms. Appl. Immunohistochem. Mol. Morphol. 2000, 8, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holen, K.D.; Klimstra, D.S.; Hummer, A.; Gonen, M.; Conlon, K.; Brennan, M.; Saltz, L.B. Clinical Characteristics and Outcomes From an Institutional Series of Acinar Cell Carcinoma of the Pancreas and Related Tumors. J. Clin. Oncol. 2002, 20, 4673–4678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Said, S.; Kurtin, P.J.; Nasr, S.H.; Graham, R.P.; Dasari, S.; Vrana, J.A.; Yasir, S.; Torbenson, M.S.; Zhang, L.; Mounajjed, T.; et al. Carboxypeptidase A1 and regenerating islet-derived 1α as new markers for pancreatic acinar cell carcinoma. Hum. Pathol. 2020, 103, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishimoto-Namiki, U.; Ino, Y.; Esaki, M.; Shimada, K.; Saruta, M.; Hiraoka, N. Novel Insights into Immunohistochemical Analysis for Acinar Cell Neoplasm of the Pancreas: Carboxypeptidase A2, Carboxypeptidase A1, and Glycoprotein 2. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2023, 47, 525–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Rosa, S.; Adsay, V.; Albarello, L.; Asioli, S.; Casnedi, S.; Franzi, F.; Marando, A.; Notohara, K.; Sessa, F.; Vanoli, A.; et al. Clinicopathologic study of 62 acinar cell carcinomas of the pancreas: Insights into the morphology and immunophenotype and search for prognostic markers. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2012, 36, 1782–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strickler, J.H.; Satake, H.; George, T.J.; Yaeger, R.; Hollebecque, A.; Garrido-Laguna, I.; Schuler, M.; Burns, T.F.; Coveler, A.L.; Falchook, G.S.; et al. Sotorasib in KRAS p.G12C–Mutated Advanced Pancreatic Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousef, A.; Yousef, M.; Chowdhury, S.; Abdilleh, K.; Knafl, M.; Edelkamp, P.; Alfaro-Munoz, K.; Chacko, R.; Peterson, J.; Smaglo, B.G.; et al. Impact of KRAS mutations and co-mutations on clinical outcomes in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Npj Precis. Oncol. 2024, 8, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoorens, A.; Lemoine, N.R.; McLellan, E.; Morohoshi, T.; Kamisawa, T.; Heitz, P.U.; Stamm, B.; Ruschoff, J.; Wiedenmann, B.; Kloppel, G. Pancreatic acinar cell carcinoma. An analysis of cell lineage markers, p53 expression, and Ki-ras mutation. Am. J. Pathol. 1993, 143, 685–698. [Google Scholar]
- Florou, V.; Elliott, A.; Bailey, M.H.; Stone, D.; Affolter, K.; Soares, H.P.; Nevala-Plagemann, C.; Scaife, C.; Walker, P.; Korn, W.M.; et al. Comparative Genomic Analysis of Pancreatic Acinar Cell Carcinoma (PACC) and Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma (PDAC) Unveils New Actionable Genomic Aberrations in PACC. Clin. Cancer Res. 2023, 29, 3408–3417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Raimondo, M.; Wallace, M.B.; Mody, K.; Stauffer, J.A.; Zhang, L.; Ji, B.; Bi, Y. Exome Sequencing of Pancreatic Acinar Carcinoma Identified Distinctive Mutation Patterns. Pancreas 2021, 50, 1007–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furukawa, T.; Sakamoto, H.; Takeuchi, S.; Ameri, M.; Kuboki, Y.; Yamamoto, T.; Hatori, T.; Yamamoto, M.; Sugiyama, M.; Ohike, N.; et al. Whole exome sequencing reveals recurrent mutations in BRCA2 and FAT genes in acinar cell carcinomas of the pancreas. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.W.; Paravathaneni, M.; Knepper, T. KRAS Wild-Type and KRAS Mutant Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma: Are These One in the Same or Separate Entities? ASCO Daily News 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, H.; Keller, R.B.; Kapner, K.S.; Dilly, J.; Raghavan, S.; Yuan, C.; Cohen, E.F.; Tolstorukov, M.; Andrews, E.; Brais, L.K.; et al. Oncogenic Drivers and Therapeutic Vulnerabilities in KRAS Wild-Type Pancreatic Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2023, 29, 4627–4643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramakrishnan, G.; Parajuli, P.; Singh, P.; Friend, C.; Hurwitz, E.; Prunier, C.; Razzaque, M.S.; Xu, K.; Atfi, A. NF1 loss of function as an alternative initiating event in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Cell Rep. 2022, 41, 111623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Rosa, S.; Bernasconi, B.; Frattini, M.; Tibiletti, M.G.; Molinari, F.; Furlan, D.; Sahnane, N.; Vanoli, A.; Albarello, L.; Zhang, L.; et al. TP53 alterations in pancreatic acinar cell carcinoma: New insights into the molecular pathology of this rare cancer. Virchows Arch. Int. J. Pathol. 2016, 468, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chmielecki, J.; Hutchinson, K.E.; Frampton, G.M.; Chalmers, Z.R.; Johnson, A.; Shi, C.; Elvin, J.; Ali, S.M.; Ross, J.S.; Basturk, O.; et al. Comprehensive Genomic Profiling of Pancreatic Acinar Cell Carcinomas Identifies Recurrent RAF Fusions and Frequent Inactivation of DNA Repair Genes. Cancer Discov. 2014, 4, 1398–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandelker, D.; Marra, A.; Zheng-Lin, B.; Selenica, P.; Blanco-Heredia, J.; Zhu, Y.; Gazzo, A.; Wong, D.; Yelskaya, Z.; Rai, V.; et al. Genomic Profiling Reveals Germline Predisposition and Homologous Recombination Deficiency in Pancreatic Acinar Cell Carcinoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 5151–5162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, H.; Ikeda, M.; Shiba, S.; Imaoka, H.; Todaka, A.; Shioji, K.; Yane, K.; Kojima, Y.; Kobayashi, S.; Asagi, A.; et al. Multicenter Retrospective Analysis of Chemotherapy for Advanced Pancreatic Acinar Cell Carcinoma: Potential Efficacy of Platinum- and Irinotecan-Containing Regimens. Pancreas 2021, 50, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunami, T.; Yamada, A.; Kondo, T.; Kanai, M.; Nagai, K.; Uchida, Y.; Yokode, M.; Matsumori, T.; Uza, N.; Murakami, H.; et al. Exceptional Response of Pancreatic Acinar Cell Carcinoma and Bile Duct Cancer to Platinum-Based Chemotherapy in a Family with a Germline BRCA2 Variant. Pancreas 2022, 51, 1258–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.-Y.; Guan, W.-L.; Lu, S.-X.; Wei, X.-L.; Shi, W.-J.; Ren, C.; Li, Y.-H.; Li, S.-P.; Qiu, M.-Z.; Wang, F.-H. Optimizing Chemotherapy of Pancreatic Acinar Cell Carcinoma: Our Experiences and Pooled Analysis of Literature. Clin. Med. Insights Oncol. 2022, 16, 11795549221090186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundy, J.; McKay, O.; Croagh, D.; Ganju, V. Exceptional Response to Olaparib and Pembrolizumab for Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma with Germline BRCA1 Mutation and High Tumor Mutation Burden: Case Report and Literature Review. JCO Precis. Oncol. 2022, 6, e2100437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, E.; Hicks, J.K.; Blue, K.; Kim, R.D.; Carballido, E.M.; Kim, D.W. Efficacy of olaparib therapy in metastatic pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) with homologous recombination deficiency (HRD). J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39 (Suppl. S15), e16266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Mou, Y.; Hou, S.; Cao, D.; Li, A. Response of germline BRCA2-mutated advanced pancreatic acinar cell carcinoma to olaparib: A case report. Medicine 2018, 97, e13113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsubayashi, H.; Todaka, A.; Tsushima, T.; Kiyozumi, Y.; Harada, R.; Ishihara, E.; Higashigawa, S.; Ohike, N.; Sakamoto, H.; Sato, J.; et al. The response of pancreatic acinar cell carcinoma to platinum and olaparib therapy in a germline BRCA2 variant carrier: Case report and literature review. Fam. Cancer 2024, 23, 393–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lelong, M.; Raoul, J.L.; Touchefeu, Y.; Berthelot, J.M.; Arnolfo, P.; Matysiak-Budnik, T.; Senellart, H. Prolonged response on olaparib maintenance in metastatic pancreatic acinar cell carcinoma associated with a germline BRCA 2 mutation, revealed by severe panniculitis. Clin. Case Rep. 2022, 10, e6718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreikhausen, L.; Schulte, N.; Belle, S.; Weidner, P.; Moersdorf, J.; Reissfelder, C.; Ebert, M.P.; Zhan, T. Pancreatic Acinar Cell Carcinoma with Germline BRCA2 Mutation and Severe Pancreatic Panniculitis: A Case Report. Visc. Med. 2021, 37, 447–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duke, E.S.; Bradford, D.; Marcovitz, M.; Amatya, A.K.; Mishra-Kalyani, P.S.; Nguyen, E.; Price, L.S.L.; Fourie Zirkelbach, J.; Li, Y.; Bi, Y.; et al. FDA Approval Summary: Selpercatinib for the treatment of advanced RET fusion-positive solid tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2023, 29, 3573–3578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, A.; Brown, I.S.; Kumarasinghe, M.P.; Perren, A.; Riley, D.; Kim, Y.; Pajic, M.; Steinmann, A.; Rathi, V.; Jamieson, N.B.; et al. RET gene rearrangements occur in a subset of pancreatic acinar cell carcinomas. Mod. Pathol. 2020, 33, 657–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, S.C.; Wu, T.T.; Hruban, R.H.; Lee, J.H.; Yeo, C.J.; Conlon, K.; Brennan, M.; Cameron, J.L.; Klimstra, D.S. Genetic and immunohistochemical analysis of pancreatic acinar cell carcinoma: Frequent allelic loss on chromosome 11p and alterations in the APC/beta-catenin pathway. Am. J. Pathol. 2002, 160, 953–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Shia, J.; Gönen, M.; Lowery, M.A.; O’Reilly, E.M.; Klimstra, D.S. DNA mismatch repair abnormalities in acinar cell carcinoma of the pancreas: Frequency and clinical significance. Pancreas 2014, 43, 1264–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drilon, A.; Laetsch, T.W.; Kummar, S.; DuBois, S.G.; Lassen, U.N.; Demetri, G.D.; Nathenson, M.; Doebele, R.C.; Farago, A.F.; Pappo, A.S.; et al. Efficacy of Larotrectinib in TRK Fusion–Positive Cancers in Adults and Children. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 731–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, D.S.; Bauer, T.M.; Lee, J.J.; Dowlati, A.; Brose, M.S.; Farago, A.F.; Taylor, M.; Shaw, A.T.; Montez, S.; Meric-Bernstam, F.; et al. Larotrectinib in adult patients with solid tumours: A multi-centre, open-label, phase I dose-escalation study. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, M.; Sherrow, C.; Krone, M.E.; Blais, E.M.; Pishvaian, M.J.; Petricoin, E.F.; Matrisian, L.M.; DeArbeloa, P.; Gregory, G.; Brown, A.; et al. Targeting the NTRK Fusion Gene in Pancreatic Acinar Cell Carcinoma: A Case Report and Review of the Literature. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2021, 19, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Wang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Shu, Y.; Dong, H.; Zhao, Q.; Yang, C.; Li, J.; Duan, X.; Zhou, Q. A unified DNA- and RNA-based NGS strategy for the analysis of multiple types of variants at the dual nucleic acid level in solid tumors. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2023, 37, e24977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heydt, C.; Wölwer, C.B.; Velazquez Camacho, O.; Wagener-Ryczek, S.; Pappesch, R.; Siemanowski, J.; Rehker, J.; Haller, F.; Agaimy, A.; Worm, K.; et al. Detection of gene fusions using targeted next-generation sequencing: A comparative evaluation. BMC Med. Genom. 2021, 14, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, K.; Yoo, Y.J.; Torre-Healy, L.A.; Rao, M.; Fassler, D.; Wang, P.; Caponegro, M.; Gao, M.; Kim, J.; Sasson, A.; et al. Coordinated single-cell tumor microenvironment dynamics reinforce pancreatic cancer subtype. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 5226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, W.C.; Lee, D.E.; Kang, H.W.; Kim, M.J.; Kim, M.; Kim, J.H.; Fang, S.; Kim, H.J.; Park, J.S. CD74 Promotes a Pro-Inflammatory Tumor Microenvironment by Inducing S100A8 and S100A9 Secretion in Pancreatic Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 12993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaels, A.D.; Newhook, T.E.; Adair, S.J.; Morioka, S.; Goudreau, B.J.; Nagdas, S.; Mullen, M.G.; Persily, J.B.; Bullock, T.N.J.; Slingluff, C.L., Jr.; et al. CD47 Blockade as an Adjuvant Immunotherapy for Resectable Pancreatic Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 1415–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilmi, M.; Delaye, M.; Muzzolini, M.; Nicolle, R.; Cros, J.; Hammel, P.; Cardot-Ruffino, V.; Neuzillet, C. The immunological landscape in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma and overcoming resistance to immunotherapy. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 8, 1129–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bear, A.S.; Vonderheide, R.H.; O’Hara, M.H. Challenges and Opportunities for Pancreatic Cancer Immunotherapy. Cancer Cell 2020, 38, 788–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.; Tandurella, J.A.; Gai, J.; Zhu, Q.; Lim, S.J.; Thomas, D.L.; Xia, T.; Mo, G.; Mitchell, J.T.; Montagne, J.; et al. Multi-omic analyses of changes in the tumor microenvironment of pancreatic adenocarcinoma following neoadjuvant treatment with anti-PD-1 therapy. Cancer Cell 2022, 40, 1374–1391.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gebauer, F.; Wicklein, D.; Horst, J.; Sundermann, P.; Maar, H.; Streichert, T.; Tachezy, M.; Izbicki, J.R.; Bockhorn, M.; Schumacher, U. Carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecules (CEACAM) 1, 5 and 6 as biomarkers in pancreatic cancer. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e113023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopetz, S.; Boni, V.; Kato, K.; Raghav, K.P.S.; Pallis, A.; Habermehl, C.; Galipelli, S.; Courlet, P.; Rivera, I.R. First-in-human trial of M9140, an anti-CEACAM5 antibody drug conjugate (ADC) with exatecan payload, in patients (pts) with metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC). J. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 42 (Suppl. S16), 3000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Han, X.; Fang, Y.; Han, S.; Cai, Y.; Kuang, T.; Lou, W.; Wang, D. Clinical Analysis of Acinar Cell Carcinoma of the Pancreas: A Single-Center Experience of 45 Consecutive Cases. Cancer Control 2020, 27, 1073274820969447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goeppert, B.; Ernst, C.; Baer, C.; Roessler, S.; Renner, M.; Mehrabi, A.; Hafezi, M.; Pathil, A.; Warth, A.; Stenzinger, A.; et al. Cadherin-6 is a putative tumor suppressor and target of epigenetically dysregulated miR-429 in cholangiocarcinoma. Epigenetics 2016, 11, 780–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casal, J.I.; Bartolomé, R.A. Beyond N-Cadherin, Relevance of Cadherins 5, 6 and 17 in Cancer Progression and Metastasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Lin, R.; Liao, X.; Li, D.; Qin, Y. Identification and verification of the molecular mechanisms and prognostic values of the cadherin gene family in gastric cancer. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 23674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, A.; Li, C.-P.; Buza, E.L.; Blomberg, R.; Govindaraju, P.; Avery, D.; Monslow, J.; Hsiao, M.; Puré, E. Fibroblast activation protein augments progression and metastasis of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. JCI Insight 2017, 2, e92232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

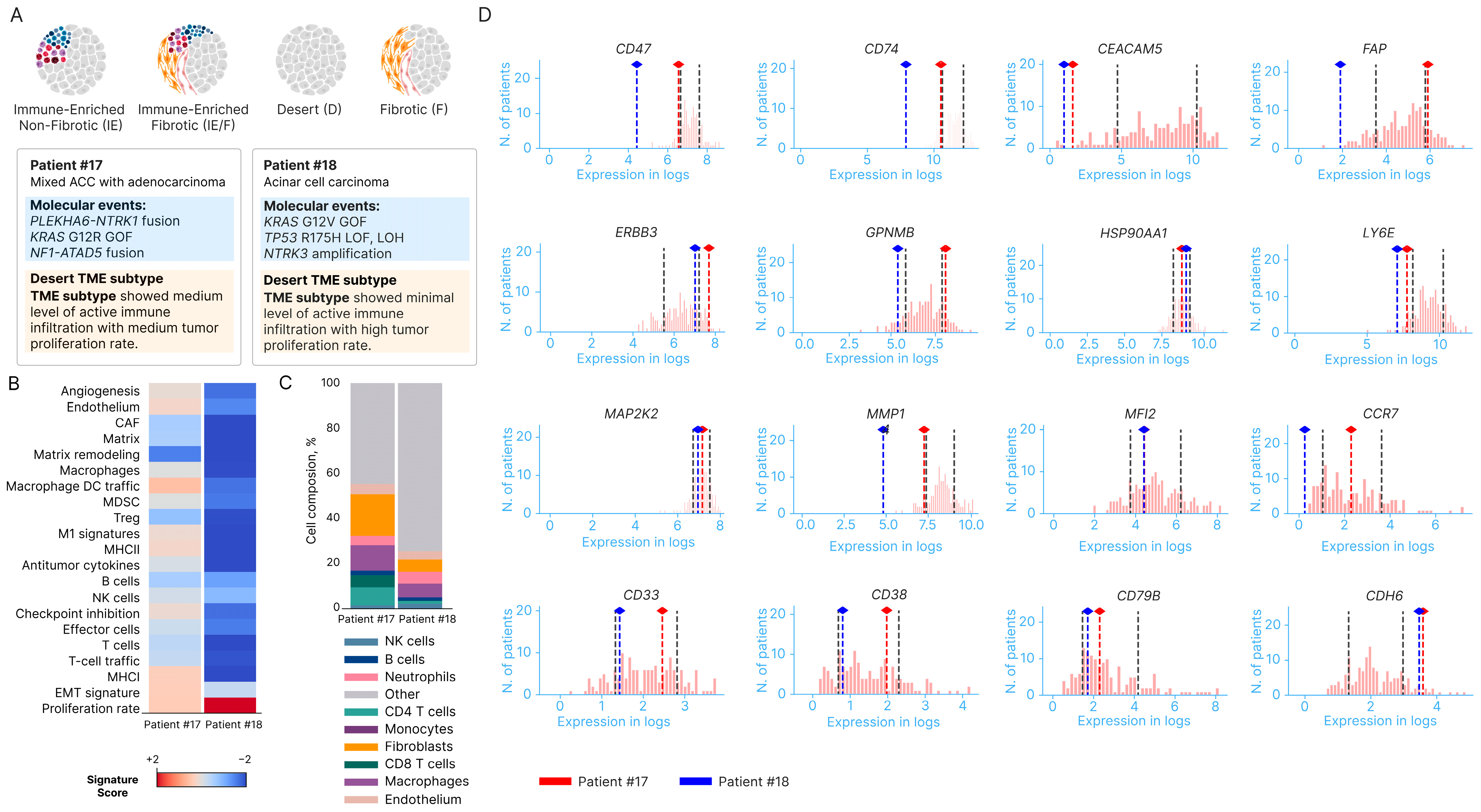
| Characteristics | Number of Patients (%) |
|---|---|
| Sex | |
| Male | 13 (81) |
| Female | 3 (19) |
| Median age at diagnosis, years | 62.5 |
| Race | |
| White | 14 (88) |
| Hispanic | 1 (6) |
| Asian | 1 (6) |
| Primary tumor location | |
| Head of pancreas | 8 (50) |
| Body of pancreas | 5 (31) |
| Tail of pancreas | 2 (13) |
| Body and head of pancreas | 1 (6) |
| Tumor status at initial diagnosis | |
| Resectable/borderline resectable | 2 (12) |
| Metastatic | 14 (88) |
| Smoking status (current/former smoker) | 9 (56) |
| Alcohol status (current/former drinker) | 10 (63) |
| Characteristic | Number of Patients |
|---|---|
| Histology | |
| Pure acinar cell carcinoma | 14 |
| Mixed acinar-neuroendocrine | 1 |
| Mixed acinar and adenocarcinoma | 1 |
| Marker positivity | (N of positive/tested) |
| Trypsin | 9/9 |
| Chymotrypsin | 2/2 |
| Synaptophysin | 5/12 |
| BCL-10 | 2/2 |
| Cytokeratin 7 | 8/9 |
| Alpha 1-antichymotrypsin | 2/2 |
| Chromogranin | 3/13 |
| Alpha 1 antitrypsin | 1/2 |
| BCL-2 | 2/2 |
| First Line | Second Line | Third Line and Beyond | OS | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 67/M | Gemcitabine/nab-paclitaxel/Xeloda POD at 5 mo. | Pt DOD prior to next line rx. | 7 | |
| 70/M | FOLFOX 3 mo followed by Xelox 1 mo and XRT to liver and then surveillance until POD at 18 mo. | Xelox, after 2 cycles switched to FOLFOX due to severe HFM for 1 mo with POD. | Everolimus, SD until POD in 10 mo. Gem/Abraxane for 2 mo with POD. 5-FU/Onivyde 3 mo with POD and DOD. | 46 |
| 72/M | Folfirinox 4 mo with PR and lost to follow-up. | 15 | ||
| 61/M | Folfirinox 3 mo and Folfiri 3 mo, maintenance Xeloda for 6 mo with PR 3 mo, 6 mo, and 9 mo, and POD at 12 mo. | Gem/Abraxane 2 mo with POD. | Folfiri 2 mo with POD, clinical trial recommended, and LTFU. | 24 |
| 59/M | Xelox for 6 mo with partial response at 3 and 6 mo, maintenance Xeloda for 2 mo with PR and LTFU. | 22 | ||
| 53/M | Folfox 2 mo with POD. | Folfirinox for 2 mo with POD. | Gem/Abraxane for 3 mo with SD. Xeloda added, PR at 2 mo and 4 mo, POD at 6 mo and DOD. | 29 |
| 58/F | Folfirinox 1 mo switch when RET-1 gene fusion identified. | Selpercatinib. Continuing to show PR. | 26 | |
| 52/M | Folfox 2 mo with POD. | Xeloda + XRT with PR f/u by surveillance for 3 mo, but POD with new mets. | FOLFIRINOX 2 mo with POD. Gem/Abraxane with SD at 2 mo and 6 mo, POD at 8 mo. Erlotinib + Avastin 3 mo with POD. Pembrolizumab 1 mo with POD and DOD. | 24 |
| 65/F | Gemcitabine/cisplatin 4 mo with POD. | Folfox 2 mo with POD. | Gem/Abraxane 4 mo with PR, and added, Xeloda 9 mo with PR at 3 mo, and SD at 6 and 9 mo. LTFU. | 39 |
| 49 /M | Folfirinox for 7 mo with PR at 3 mo, SD at 5 and 7 mo, Xeloda maintenance for 24 mo with PR. | 31 | ||
| 70/F | Surgery, no neoadj or adj chemo, on surveillance for 3 yrs. | Recurrence—surgery adj chemo Xeloda 3 mo and surveillance for 5 yrs. | Recurrence as peritoneal carcinomatosis rxed with Gem/Abraxane with rapid POD and pt DOD. | 92 |
| 66/M | Neoadj Folfirinox 4 mo followed by Xeloda + XRT and surgery followed by adj chemo folfirinox 2 mo. | Recurrence with pleural mets rxed with Gem/Abr 2 mo with POD and phase I referral. DOD | 21 | |
| 59/M | Xelox 1 mo, b/l UE thrombosis, and lost central IV access. | Gem/Xeloda 1 mo + Xeloda XRT, POD at 2 mo. | FOLFIRI 4 mo with POD and reference to phase I. DOD | 17 |
| 62/M | Gemcitabine/Cisplatin 3 mo with POD. | Gemcitabine/Erlotinib with POD. | Phase 1, SD for 11 mo followed by POD and DOD. | 17 |
| 66/M | Folfirinox 5 mo with SD at 3 mo, POD at 5 mo. | Gem/Tazarotene/xeloda for 5 mo, SD—Rx break 6 mo per pt preference, restaging with POD. LTFU. | 33 | |
| 55/M | Neoadj Gemcitabine + Abraxane + Cisplatin 2 mo f/u by surgery—prolonged post-op recovery and post-op restaging with early relapse at 5 mo. | Adj FOLFIRINOX 3 cycles (1 mo) with POD. | Gem/Abraxane/5-FU and Cisplatin for 5 mo with SD at 2 mo and PR at 5 mo. Erlotinib added POD 7th mo and referral to Phase I. POD within 3 mo in Phase I. DOD. | 24 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Balachandran Pillai, A.; Yousef, M.; Yousef, A.; Alfaro-Munoz, K.D.; Smaglo, B.G.; Willis, J.; Wolff, R.A.; Pant, S.; Hurd, M.W.; Maitra, A.; et al. Molecular and Clinical Features of Pancreatic Acinar Cell Carcinoma: A Single-Institution Case Series. Cancers 2024, 16, 3421. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16193421
Balachandran Pillai A, Yousef M, Yousef A, Alfaro-Munoz KD, Smaglo BG, Willis J, Wolff RA, Pant S, Hurd MW, Maitra A, et al. Molecular and Clinical Features of Pancreatic Acinar Cell Carcinoma: A Single-Institution Case Series. Cancers. 2024; 16(19):3421. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16193421
Chicago/Turabian StyleBalachandran Pillai, Ashwathy, Mahmoud Yousef, Abdelrahman Yousef, Kristin D. Alfaro-Munoz, Brandon G. Smaglo, Jason Willis, Robert A. Wolff, Shubham Pant, Mark W. Hurd, Anirban Maitra, and et al. 2024. "Molecular and Clinical Features of Pancreatic Acinar Cell Carcinoma: A Single-Institution Case Series" Cancers 16, no. 19: 3421. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16193421
APA StyleBalachandran Pillai, A., Yousef, M., Yousef, A., Alfaro-Munoz, K. D., Smaglo, B. G., Willis, J., Wolff, R. A., Pant, S., Hurd, M. W., Maitra, A., Wang, H., Katz, M. H. G., Prakash, L. R., Tzeng, C.-W. D., Snyder, R., Castelnovo, L. F., Chen, A., Kravets, A., Kudriavtseva, K., ... Zhao, D. (2024). Molecular and Clinical Features of Pancreatic Acinar Cell Carcinoma: A Single-Institution Case Series. Cancers, 16(19), 3421. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16193421






