Plant-Derived Polyphenols to Prevent and Treat Oral Mucositis Induced by Chemo- and Radiotherapy in Head and Neck Cancers Management
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Oral Mucositis (OM)
- Inflammatory/vascular phase: It is induced by chemotherapy and/or radiotherapy, which induce cytotoxicity in normal cells by directly damaging the DNA and leading to excessive ROS generation. This phenomenon acts as a trigger for the inflammatory process activating different signalling pathways such as proinflammatory cytokines (e.g., IL1 β, IL6, and TNF-α) and prostaglandins [21,22].
- Activation of transcription factors such as nuclear factor-κ B (NF-κB) and NF-E2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) which can be directly activated by the chemotherapeutic agents, e.g., 5-FU activates the NF-κB, thereby upregulating the genes encoding pro-inflammatory cytokines such as Tumour Necrosis Factor α (TNF-α), interleukin 1β (IL-1β), and IL-6, cyclooxygenase 2 (COX-2), and high-mobility group box 1 protein (HMGB1) or radiation, and indirectly through the ROS release, producing inflammatory mediators, which increase the tissue damage stimulating angiogenesis and vascular permeability [23].
- Up-regulation and signal amplification stage, leading to loss of the epithelium integrity and, hence, ulcer formation (beginning of OM evolution).
- Rich inflammatory infiltrate stage, containing macrophages, neutrophils, and mastocytes [24]. In addition, lesions are strongly subjected to bacterial colonization, which contributes to stimulating the innate immune system, thereby increasing the inflammatory response.
- The final healing phase, characterized by the proliferating and differentiating epithelial cells, leading to the restoration of the integrity of altered mucosa.
Polyphenols in the Prevention and Management of OM
3. Methodology
4. Curcuminoids
4.1. In Vivo Animal Studies
4.2. Clinical Trials
5. Flavonoids
5.1. Hesperidin
5.2. Epicatechin
5.3. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate
5.4. Apigenin
5.5. Quercetin
5.6. Flavonoids-Rich Plants and Their Use in OM
5.6.1. In Vivo Animal Studies
5.6.2. Clinical Trials
6. Conclusions and Future Prospectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vigneswaran, N.; Williams, M.D. Epidemiologic Trends in Head and Neck Cancer and Aids in Diagnosis. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. Clin. N. Am. 2014, 26, 123–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Argiris, A.; Karamouzis, M.V.; Raben, D.; Ferris, R.L. Head and Neck Cancer. Lancet 2008, 371, 1695–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panzarella, V.; Campisi, G.; Giardina, Y.; Maniscalco, L.; Capra, G.; Rodolico, V.; Di Fede, O.; Mauceri, R. Low Frequency of Human Papillomavirus in Strictly Site-coded Oral Squamous Cell Carcinomas, Using the Latest Nhi/Seer-icd Systems: A Pilot Observational Study and Critical Review. Cancers 2021, 13, 4595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, V.; Singh, A. Oral Mucositis. Natl. J. Maxillofac. Surg. 2020, 11, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mauceri, R.; Bazzano, M.; Coppini, M.; Tozzo, P.; Panzarella, V.; Campisi, G. Diagnostic Delay of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma and the Fear of Diagnosis: A Scoping Review. Front. Psychol. 2022, 13, 1009080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, M.P.; Kumar, V.; Agarwal, A.; Kumar, R.; Bhatt, M.L.B.; Misra, S. Clinico-Epidemiological Study of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Tertiary Care Centre Study in North India. J. Oral Biol. Craniofac. Res. 2016, 6, 32–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Prima, G.; Conigliaro, A.; De Caro, V. Mucoadhesive Polymeric Films to Enhance Barbaloin Penetration into Buccal Mucosa: A Novel Approach to Chemoprevention. AAPS PharmSciTech 2019, 20, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Caro, V.; Scaturro, A.L.; Di Prima, G.; Avellone, G.; Sutera, F.M.; Di Fede, O.; Campisi, G.; Giannola, L.I. Aloin Delivery on Buccal Mucosa: Ex Vivo Studies and Design of a New Locoregional Dosing System. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2015, 41, 1541–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamimi, A.; Tamimi, A.; Sorkheh, F.; Asl, S.M.; Ghafari, A.; Karimi, A.G.; Erabi, G.; Pourmontaseri, H.; Deravi, N. Monoclonal Antibodies for the Treatment of Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Literature Review. Cancer Rep. 2023, 6, e1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budach, W.; Hehr, T.; Budach, V.; Belka, C.; Dietz, K. A Meta-Analysis of Hyperfractionated and Accelerated Radiotherapy and Combined Chemotherapy and Radiotherapy Regimens in Unresected Locally Advanced Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck. BMC Cancer 2006, 6, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanemaaijer, S.H.; Kok, I.C.; Fehrmann, R.S.N.; van der Vegt, B.; Gietema, J.A.; Plaat, B.E.C.; van Vugt, M.A.T.M.; Vergeer, M.R.; Leemans, C.R.; Langendijk, J.A.; et al. Comparison of Carboplatin With 5-Fluorouracil vs. Cisplatin as Concomitant Chemoradiotherapy for Locally Advanced Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guigay, J.; Tahara, M.; Licitra, L.; Keilholz, U.; Friesland, S.; Witzler, P.; Mesía, R. The Evolving Role of Taxanes in Combination with Cetuximab for the Treatment of Recurrent and/or Metastatic Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck: Evidence, Advantages, and Future Directions. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinna, R.; Campus, G.; Cumbo, E.; Mura, I.; Milia, E. Xerostomia Induced by Radiotherapy: An Overview of the Physiopathology, Clinical Evidence, and Management of the Oral Damage. Ther. Clin. Risk Manag. 2015, 11, 171–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raber-Durlacher, J.E.; Elad, S.; Barasch, A. Oral Mucositis. Oral Oncol. 2010, 46, 452–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Caballero, A.; Torres-Lagares, D.; Robles-García, M.; Pachón-Ibáñez, J.; González-Padilla, D.; Gutiérrez-Pérez, J.L. Cancer Treatment-Induced Oral Mucositis: A Critical Review. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2012, 41, 225–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulito, C.; Cristaudo, A.; La Porta, C.; Zapperi, S.; Blandino, G.; Morrone, A.; Strano, S. Oral Mucositis: The Hidden Side of Cancer Therapy. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 39, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beech, N.; Robinson, S.; Porceddu, S.; Batstone, M. Dental Management of Patients Irradiated for Head and neck Cancer. Aust. Dent. J. 2014, 59, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpato, L.E.R.; Silva, T.C.; Oliveira, T.M.; Sakai, V.T.; Machado, M.A.A.M. Radiation Therapy and Chemotherapy-Induced Oral Mucositis. Braz. J. Otorhinolaryngol. 2007, 73, 562–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oronsky, B.; Goyal, S.; Kim, M.M.; Cabrales, P.; Lybeck, M.; Caroen, S.; Oronsky, N.; Burbano, E.; Carter, C.; Oronsky, A. A Review of Clinical Radioprotection and Chemoprotection for Oral Mucositis. Transl. Oncol. 2018, 11, 771–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonis, S.T. The Pathobiology of Mucositis. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2004, 4, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonis, S.T. Mucositis: The Impact, Biology and Therapeutic Opportunities of Oral Mucositis. Oral Oncol. 2009, 45, 1015–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siomek, A.; Tujakowski, J.; Gackowski, D.; Rozalski, R.; Foksinski, M.; Dziaman, T.; Roszkowski, K.; Olinski, R. Severe Oxidatively Damaged DNA after Cisplatin Treatment of Cancer Patients. Int. J. Cancer 2006, 119, 2228–2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loboda, A.; Damulewicz, M.; Pyza, E.; Jozkowicz, A.; Dulak, J. Role of Nrf2/HO-1 System in Development, Oxidative Stress Response and Diseases: An Evolutionarily Conserved Mechanism. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2016, 73, 3221–3247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worthington, H.V.; Clarkson, J.E.; Bryan, G.; Furness, S.; Glenny, A.M.; Littlewood, A.; McCabe, M.G.; Meyer, S.; Khalid, T.; Riley, P. Interventions for Preventing Oral Mucositis for Patients with Cancer Receiving Treatment. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2011, 2021, CD000978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peña-Cardelles, J.F.; Salgado-Peralvo, A.O.; Garrido-Martínez, P.; Carretero, J.L.C.; Pozo-Kreilinger, J.J.; Moro-Rodríguez, J.E. Oral Mucositis. Is It Present in the Immunotherapy of the Immune Checkpoint Pd1/Pd-L1 against Oral Cancer? A Systematic Review. Med. Oral Patol. Oral Cir. Bucal. 2021, 26, e494–e501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa, A.; Kuten-Shorrer, M. Pathogenesis of Oral Toxicities Associated with Targeted Therapy and Immunotherapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 8188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miroddi, M.; Sterrantino, C.; Simonelli, I.; Ciminata, G.; Phillips, R.S.; Calapai, G. Risk of Grade 3-4 Diarrhea and Mucositis in Colorectal Cancer Patients Receiving Anti-EGFR Monoclonal Antibodies Regimens: A Meta-Analysis of 18 Randomized Controlled Clinical Trials. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2015, 96, 355–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amy, D.P.B.; Shalabi, A.; Finfter, O.; Birenzweig, Y.; Zadik, Y. Severe Chronic Nonlichenoid Oral Mucositis in Pembrolizumab-Treated Patients: New Cases and a Review of the Literature. Immunotherapy 2020, 12, 777–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalla, R.V.; Treister, N.; Sollecito, T.; Schmidt, B.; Patton, L.L.; Mohammadi, K.; Hodges, J.S.; Brennan, M.T. Oral Complications at 6 Months after Radiation Therapy for Head and Neck Cancer. Oral Dis. 2017, 23, 1134–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saunders, D.P.; Rouleau, T.; Cheng, K.; Yarom, N.; Kandwal, A.; Joy, J.; Bektas Kayhan, K.; van de Wetering, M.; Brito-Dellan, N.; Kataoka, T.; et al. Systematic Review of Antimicrobials, Mucosal Coating Agents, Anesthetics, and Analgesics for the Management of Oral Mucositis in Cancer Patients and Clinical Practice Guidelines. Support Care Cancer 2020, 28, 2473–2484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarom, N.; Hovan, A.; Bossi, P.; Ariyawardana, A.; Jensen, S.B.; Gobbo, M.; Saca-Hazboun, H.; Kandwal, A.; Majorana, A.; Ottaviani, G.; et al. Systematic Review of Natural and Miscellaneous Agents, for the Management of Oral Mucositis in Cancer Patients and Clinical Practice Guidelines—Part 2: Honey, Herbal Compounds, Saliva Stimulants, Probiotics, and Miscellaneous Agents. Support Care Cancer 2020, 28, 2457–2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowen, J.; Al-Dasooqi, N.; Bossi, P.; Wardill, H.; Van Sebille, Y.; Al-Azri, A.; Bateman, E.; Correa, M.E.; Raber-Durlacher, J.; Kandwal, A.; et al. The Pathogenesis of Mucositis: Updated Perspectives and Emerging Targets. Support Care Cancer 2019, 27, 4023–4033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varoni, E.M.; Lodi, G.; Sardella, A.; Carrassi, A.; Iriti, M. Plant Polyphenols and Oral Health: Old Phytochemicals for New Fields. Curr. Med. Chem. 2012, 19, 1706–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.M.; Wang, X.; Islam, M.R.; Akash, S.; Supti, F.A.; Mitu, M.I.; Harun-Or-Rashid, M.; Aktar, M.N.; Khatun Kali, M.S.; Jahan, F.I.; et al. Multifunctional Role of Natural Products for the Treatment of Parkinson’s Disease: At a Glance. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 976385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, H.; Pandey, M.; Hua, C.K.; Mun, C.S.; Jing, J.K.; Kong, L.; Ern, L.Y.; Ashraf, N.A.; Kit, S.W.; Yee, T.S.; et al. An Update on Natural Compounds in the Remedy of Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review. J. Tradit. Complement. Med. 2018, 8, 361–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.; Xiao, M.; Zhao, J.; Li, Z.; Xing, B.; Li, X.; Kong, M.; Li, L.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, Y.; et al. An Overview of Plant Phenolic Compounds and Their Importance in Human Nutrition and Management of Type 2 Diabetes. Molecules 2016, 21, 1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertelli, A.; Biagi, M.; Corsini, M.; Baini, G.; Cappellucci, G.; Miraldi, E. Polyphenols: From Theory to Practice. Foods 2021, 10, 2595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudrapal, M.; Khairnar, S.J.; Khan, J.; Dukhyil, A.B.; Ansari, M.A.; Alomary, M.N.; Alshabrmi, F.M.; Palai, S.; Deb, P.K.; Devi, R. Dietary Polyphenols and Their Role in Oxidative Stress-Induced Human Diseases: Insights into Protective Effects, Antioxidant Potentials and Mechanism(s) of Action. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 806470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsao, R. Chemistry and Biochemistry of Dietary Polyphenols. Nutrients 2010, 2, 1231–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, M.C.; Pinto, D.C.G.A.; Silva, A.M.S. Plant Flavonoids: Chemical Characteristics and Biological Activity. Molecules 2021, 26, 5377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vauzour, D. Effect of Flavonoids on Learning, Memory and Neurocognitive Performance: Relevance and Potential Implications for Alzheimer’s Disease Pathophysiology. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2014, 94, 1042–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panickar, K.S. Effects of Dietary Polyphenols on Neuroregulatory Factors and Pathways That Mediate Food Intake and Energy Regulation in Obesity. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2013, 57, 34–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sitheeque, M.A.M.; Panagoda, G.J.; Yau, J.; Amarakoon, A.M.T.; Udagama, U.R.N.; Samaranayake, L.P. Antifungal Activity of Black Tea Polyphenols (Catechins and Theaflavins) against Candida Species. Chemotherapy 2009, 55, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simonetti, G.; Brasili, E.; Pasqua, G. Antifungal Activity of Phenolic and Polyphenolic Compounds from Different Matrices of Vitis vinifera L. Against Human Pathogens. Molecules 2020, 25, 3748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magrone, T.; Magrone, M.; Russo, M.A.; Jirillo, E. Recent Advances on the Anti-Inflammatory and Antioxidant Properties of Red Grape Polyphenols: In Vitro and in Vivo Studies. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Si, H.; Jia, Z.; Liu, D. Dietary Anti-Aging Polyphenols and Potential Mechanisms. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanmugavadivu, A.; Balagangadharan, K.; Selvamurugan, N. Angiogenic and Osteogenic Effects of Flavonoids in Bone Regeneration. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2022, 119, 2313–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angellotti, G.; Di Prima, G.; Belfiore, E.; Campisi, G.; De Caro, V. Chemopreventive and Anticancer Role of Resveratrol against Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- do Carmo, M.A.V.; Pressete, C.G.; Marques, M.J.; Granato, D.; Azevedo, L. Polyphenols as Potential Antiproliferative Agents: Scientific Trends. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2018, 24, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Prima, G.; Belfiore, E.; Migliore, M.; Scarpaci, A.G.; Angellotti, G.; Restivo, I.; Allegra, M.; Arizza, V.; De Caro, V. Green Extraction of Polyphenols from Waste Bentonite to Produce Functional Antioxidant Excipients for Cosmetic and Pharmaceutical Purposes: A Waste-to-Market Approach. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 2493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewandowska, U.; Szewczyk, K.; Hrabec, E.; Janecka, A.; Gorlach, S. Overview of Metabolism and Bioavailability Enhancement of Polyphenols. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 12183–12199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukherjee, S.; Kar, S.K. Curcuminoids: The Novel Molecules of Nature. In Herbs and Spices. New Processing Technologies; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Priyadarsini, K.I. Photophysics, Photochemistry and Photobiology of Curcumin: Studies from Organic Solutions, Bio-Mimetics and Living Cells. J. Photochem. Photobiol. C Photochem. 2009, 10, 81–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lüer, S.; Troller, R.; Jetter, M.; Spaniol, V.; Aebi, C. Topical Curcumin Can Inhibit Deleterious Effects of Upper Respiratory Tract Bacteria on Human Oropharyngeal Cells in Vitro: Potential Role for Patients with Cancer Therapy Induced Mucositis? Support Care Cancer 2011, 19, 799–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimizu, K.; Funamoto, M.; Sunagawa, Y.; Shimizu, S.; Katanasaka, Y.; Miyazaki, Y.; Wada, H.; Hasegawa, K.; Morimoto, T. Anti-Inflammatory Action of Curcumin and Its Use in the Treatment of Lifestyle-Related Diseases. Eur. Cardiol. Rev. 2019, 14, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amalraj, A.; Varma, K.; Jacob, J.; Divya, C.; Kunnumakkara, A.B.; Stohs, S.J.; Gopi, S. A Novel Highly Bioavailable Curcumin Formulation Improves Symptoms and Diagnostic Indicators in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Two-Dose, Three-Arm, and Parallel-Group Study. J. Med. Food 2017, 20, 1022–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dohare, P.; Garg, P.; Sharma, U.; Jagannathan, N.R.; Ray, M. Neuroprotective Efficacy and Therapeutic Window of Curcuma Oil: In Rat Embolic Stroke Model. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2008, 8, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomeh, M.A.; Hadianamrei, R.; Zhao, X. A Review of Curcumin and Its Derivatives as Anticancer Agents. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, A.; Wu, R.; Zhou, M.; Wang, P. Mechanism of the Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Curcumin: PPAR-γ Activation. PPAR Res. 2007, 2007, 89369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binion, D.G.; Otterson, M.F.; Rafiee, P. Curcumin Inhibits VEGF-Mediated Angiogenesis in Human Intestinal Microvascular Endothelial Cells through COX-2 and MAPK Inhibition. Gut 2008, 57, 1509–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lüer, S.; Troller, R.; Aebi, C. Antibacterial and Antiinflammatory Kinetics of Curcumin as a Potential Antimucositis Agent in Cancer Patients. Nutr. Cancer 2012, 64, 975–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vareed, S.K.; Kakarala, M.; Ruffin, M.T.; Crowell, J.A.; Normolle, D.P.; Djuric, Z.; Brenner, D.E. Pharmacokinetics of Curcumin Conjugate Metabolites in Healthy Human Subjects. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2008, 17, 1411–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, T.R.; Curra, M.; Wagner, V.P.; Martins, M.A.T.; de Oliveira, A.C.; Batista, A.C.; Valadares, M.C.; Marreto, R.N.; Martins, M.D. Mucoadhesive Formulation Containing Curcuma longa L. Reduces Oral Mucositis Induced by 5-Fluorouracil in Hamsters. Phytother. Res. 2019, 33, 881–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dvoretskiy, S.; Pereira, S.L.; Das, T. Efficacy of Nutrients in Reducing the Symptoms of Radiation Induced Oral Mucositis in a Hamster Model. Nutr. Cancer 2022, 74, 1079–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Normando, A.G.C.; de Menêses, A.G.; de Toledo, I.P.; Borges, G.Á.; de Lima, C.L.; dos Reis, P.E.D.; Guerra, E.N.S. Effects of Turmeric and Curcumin on Oral Mucositis: A Systematic Review. Phytother. Res. 2019, 33, 1318–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, S.; Rath, H.; Sharma, G.; Senapati, S.N.; Mishra, E. Effectiveness of Curcumin Mouthwash on Radiation-Induced Oral Mucositis among Head and Neck Cancer Patients: A Triple-Blind, Pilot Randomised Controlled Trial. Indian J. Dent. Res. 2020, 31, 718–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Cássia Dias Viana Andrade, R.; Azevedo Reis, T.; Rosa, L.P.; de Oliveira Santos, G.P.; da CristinaSilva, F. Comparative Randomized Trial Study about the Efficacy of Photobiomodulation and Curcumin Antimicrobial Photodynamic Therapy as a Coadjuvant Treatment of Oral Mucositis in Oncologic Patients: Antimicrobial, Analgesic, and Degree Alteration Effect. Support Care Cancer 2022, 30, 7365–7371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fardad, F.; Ghasemi, K.; Ansarinejad, N.; Khodakarim, N.; Nasiripour, S.; Farasatinasab, M. A Comparative Study to Assess the Effectiveness of Curcumin, Mucosamin, and Chlorhexidine in Chemotherapy-Induced Oral Mucositis. Explore 2023, 19, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soni, T.P.; Gupta, A.K.; Sharma, L.M.; Singhal, H.; Sharma, S.; Gothwal, R.S. A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Study to Evaluate the Effect of Bio-Enhanced Turmeric Formulation on Radiation-Induced Oral Mucositis. ORL 2022, 84, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimi, H.R.; Nedaeinia, R.; Shamloo, S.S.; Sh, N. Novel Delivery System for Natural Products: Nano-Curcumin Formulations. Avicenna J. Phytomed. 2016, 6, 383–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahmasebi, S.; Saeed, B.Q.; Temirgalieva, E.; Yumashev, A.V.; El-Esawi, M.A.; Navashenaq, J.G.; Valizadeh, H.; Sadeghi, A.; Aslani, S.; Yousefi, M.; et al. Nanocurcumin Improves Treg Cell Responses in Patients with Mild and Severe SARS-CoV2. Life Sci. 2021, 276, 119437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delavarian, Z.; Pakfetrat, A.; Ghazi, A.; Jaafari, M.R.; Homaei Shandiz, F.; Dalirsani, Z.; Mohammadpour, A.H.; Rahimi, H.R. Oral Administration of Nanomicelle Curcumin in the Prevention of Radiotherapy-Induced Mucositis in Head and Neck Cancers. Spec. Care Dentist. 2019, 39, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kia, S.J.; Basirat, M.; Saedi, H.S.; Arab, S.A. Effects of Nanomicelle Curcumin Capsules on Prevention and Treatment of Oral Mucosits in Patients under Chemotherapy with or without Head and Neck Radiotherapy: A Randomized Clinical Trial. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2021, 21, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramezani, V.; Ghadirian, S.; Shabani, M.; Boroumand, M.A.; Daneshvar, R.; Saghafi, F. Efficacy of Curcumin for Amelioration of Radiotherapy-Induced Oral Mucositis: A Preliminary Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial. BMC Cancer 2023, 23, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.T.; Deng, J.L.; Jin, X.R.; Zhang, Z.Z.; Zhang, X.H.; Zhou, X. Effects of 9 Oral Care Solutions on the Prevention of Oral Mucositis: A Network Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Medicine 2020, 99, E19661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Sun, D.; Qin, N.; Liu, M.; Zhang, J.; Li, X. Comparative Prevention Potential of 10 Mouthwashes on Intolerable Oral Mucositis in Cancer Patients: A Bayesian Network Analysis. Oral Oncol. 2020, 107, 104751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dharman, S.; Maragathavalli, G.; Shanmugasundaram, K.; Shanmugam, R.K. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis on the Efficacy of Curcumin/Turmeric for the Prevention and Amelioration of Radiotherapy/Radiochemotherapy Induced Oral Mucositis in Head and Neck Cancer Patients. APJCP 2021, 22, 1671–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kharat, M.; Du, Z.; Zhang, G.; McClements, D.J. Physical and Chemical Stability of Curcumin in Aqueous Solutions and Emulsions: Impact of PH, Temperature, and Molecular Environment. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 1525–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panche, A.N.; Diwan, A.D.; Chandra, S.R. Flavonoids: An Overview. J. Nutr. Sci. 2016, 5, e47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Pandey, A.K. Chemistry and Biological Activities of Flavonoids: An Overview. Sci. World J. 2013, 2013, 162750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maleki, S.J.; Crespo, J.F.; Cabanillas, B. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Flavonoids. Food Chem. 2019, 299, 125124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopustinskiene, D.M.; Jakstas, V.; Savickas, A.; Bernatoniene, J. Flavonoids as Anticancer Agents. Nutrients 2020, 12, 457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scurria, A.; Sciortino, M.; Albanese, L.; Nuzzo, D.; Zabini, F.; Meneguzzo, F.; Alduina, R.; Presentato, A.; Pagliaro, M.; Avellone, G.; et al. Flavonoids in Lemon and Grapefruit IntegroPectin. ChemistryOpen 2021, 10, 1055–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Prima, G.; Scurria, A.; Angellotti, G.; Belfiore, E.; Pagliaro, M.; Meneguzzo, F.; De Caro, V.; Ciriminna, R. Grapefruit IntegroPectin Isolation via Spray Drying and via Freeze Drying: A Comparison. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2022, 29, 100816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshitomi, R.; Yamamoto, M.; Kumazoe, M.; Fujimura, Y.; Yonekura, M.; Shimamoto, Y.; Nakasone, A.; Kondo, S.; Hattori, H.; Haseda, A.; et al. The Combined Effect of Green Tea and α-Glucosyl Hesperidin in Preventing Obesity: A Randomized Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 19067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, P.; Jin, J.; Zou, G.; Sui, Y.; Han, Y.; Zhao, D.; Liu, L. Hesperidin Prevents Hyperglycemia in Diabetic Rats by Activating the Insulin Receptor Pathway. Exp. Ther. Med. 2020, 21, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mas-Capdevila, A.; Teichenne, J.; Domenech-Coca, C.; Caimari, A.; Bas, J.M.D.; Escoté, X.; Crescenti, A. Effect of Hesperidin on Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors: The Role of Intestinal Microbiota on Hesperidin Bioavailability. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parhiz, H.; Roohbakhsh, A.; Soltani, F.; Rezaee, R.; Iranshahi, M. Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Properties of the Citrus Flavonoids Hesperidin and Hesperetin: An Updated Review of Their Molecular Mechanisms and Experimental Models. Phytother. Res. 2015, 29, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wdowiak, K.; Walkowiak, J.; Pietrzak, R.; Bazan-Woźniak, A.; Cielecka-Piontek, J. Bioavailability of Hesperidin and Its Aglycone Hesperetin—Compounds Found in Citrus Fruits as A Parameter Conditioning the Pro-Health Potential (Neuroprotective and Antidiabetic Activity)—Mini-Review. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manach, C.; Williamson, G.; Morand, C.; Scalbert, A.; Rémésy, C. Bioavailability and Bioefficacy of Polyphenols in Humans. I. Review of 97 Bioavailability Studies1-3. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2005, 81, 230s–242s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.S.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, K.A. A Comparative Study of Hesperetin, Hesperidin and Hesperidin Glucoside: Antioxidant, Anti-Inflammatory, and Antibacterial Activities In Vitro. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshino, F.; Yoshida, A.; Toyama, T.; Wada-Takahashi, S.; Takahashi, S. suke α-Glucosyl Hesperidin Suppressed the Exacerbation of 5-Fluorouracil-Induced Oral Mucositis in the Hamster Cheek Pouch. J. Funct. Foods 2016, 21, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, J.D.; Elias, R.J. The Antioxidant and Pro-Oxidant Activities of Green Tea Polyphenols: A Role in Cancer Prevention. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2010, 501, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernatoniene, J.; Kopustinskiene, D.M. The Role of Catechins in Cellular Responses to Oxidative Stress. Molecules 2018, 23, 965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gopal, J.; Muthu, M.; Paul, D.; Kim, D.H.; Chun, S. Bactericidal Activity of Green Tea Extracts: The Importance of Catechin Containing Nano Particles. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 19710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakanishi, T.; Mukai, K.; Yumoto, H.; Hirao, K.; Hosokawa, Y.; Matsuo, T. Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Catechin on Cultured Human Dental Pulp Cells Affected by Bacteria-Derived Factors. Eur. J. Oral. Sci. 2010, 118, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spencer, J.P.E.; Schroeter, H.; Crossthwaithe, A.J.; Kuhnle, G.; Williams, R.J.; Rice-Evans, C. Contrasting Influences of Glucuronidation and O-Methylation of Epicatechin on Hydrogen Peroxide-Induced Cell Death in Neurons and Fibroblasts. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2001, 31, 1139–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnett, C.F.; Moreno-Ulloa, A.; Shiva, S.; Ramirez-Sanchez, I.; Taub, P.R.; Su, Y.; Ceballos, G.; Dugar, S.; Schreiner, G.; Villarreal, F. Pharmacokinetic, Partial Pharmacodynamic and Initial Safety Analysis of (-)-Epicatechin in Healthy Volunteers. Food Funct. 2015, 6, 824–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Ma, L.; Huang, Q. Advances in Nanodelivery of Green Tea Catechins to Enhance the Anticancer Activity. Molecules 2021, 26, 3301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, Y.S.; Shin, H.A.; Kang, S.U.; Kim, J.H.; Oh, Y.T.; Park, K.H.; Kim, C.H. Effect of Epicatechin against Radiation-Induced Oral Mucositis: In Vitro and In Vivo Study. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e69151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagle, D.G.; Ferreira, D.; Zhou, Y.D. Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate (EGCG): Chemical and Biomedical Perspectives. Phytochemistry 2006, 67, 1849–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.H.; Jeon, H.J.; Park, J.; Chang, M.S. Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate Prevents Oxidative Stress-Induced Cellular Senescence in Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells via Nrf2. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2016, 38, 1075–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tedeschi, E.; Menegazzi, M.; Yao, Y.; Suzuki, H.; Fö, U.; Kleinert, H. Green Tea Inhibits Human Inducible Nitric-Oxide Synthase Expression by Down-Regulating Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription-1 Activation. Mol. Pharmacol. 2004, 65, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zawani, M.; Fauzi, M.B. Epigallocatechin Gallate: The Emerging Wound Healing Potential of Multifunctional Biomaterials for Future Precision Medicine Treatment Strategies. Polymers 2021, 13, 3656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandel, S.A.; Amit, T.; Weinreb, O.; Reznichenko, L.; Youdim, M.B.H. Simultaneous Manipulation of Multiple Brain Targets by Green Tea Catechins: A Potential Neuroprotective Strategy for Alzheimer and Parkinson Diseases. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2008, 14, 352–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.J.; Wang, K.L.; Chen, H.Y.; Chiang, Y.F.; Hsia, S.M. Protective Effects of Epigallocatechin Gallate (EGCG) on Endometrial, Breast, and Ovarian Cancers. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.-J.; Maliakal, P.; Chen, L.; Meng, X.; Bondoc, F.Y.; Prabhu, S.; Lambert, G.; Mohr, S.; Yang, C.S. Pharmacokinetics of Tea Catechins after Ingestion of Green Tea and (-)-Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate by Humans: Formation of Different Metabolites and Individual Variability. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2002, 11, 1025–1032. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, W.; Mei, H.; Jia, L.; Zhao, H.; Li, X.; Meng, X.; Zhao, X.; Ligang, X.; Yu, J. Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate Mouthwash Protects Mucosa from Radiation-Induced Mucositis in Head and Neck Cancer Patients: A Prospective, Non-Randomised, Phase 1 Trial. Investig. New Drugs 2020, 38, 1129–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, G.; Fong, R.Y.; Ensunsa, J.L.; Kimball, J.; Medici, V.; Ottaviani, J.I.; Crozier, A. Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism and Excretion of Apigenin and Its Glycosides in Healthy Male Adults. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2022, 185, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saima, S.; Anjum, I.; Mobashar, A.; Jahan, S.; Najm, S.; Nafidi, H.-A.; Bin Jardan, Y.A.; Bourhia, M. Spasmolytic and Uroprotective Effects of Apigenin by Downregulation of TGF-β and INOS Pathways and Upregulation of Antioxidant Mechanisms: In Vitro and In Silico Analysis. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolinski, A.T.; Pestka, J.J. Modulation of Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Proinflammatory Cytokine Production in Vitro and in Vivo by the Herbal Constituents Apigenin (Chamomile), Ginsenoside Rb1 (Ginseng) and Parthenolide (Feverfew). Food Chem. Toxicol. 2003, 41, 1381–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, B.; Venditti, A.; Sharifi-Rad, M.; Kręgiel, D.; Sharifi-Rad, J.; Durazzo, A.; Lucarini, M.; Santini, A.; Souto, E.B.; Novellino, E.; et al. The Therapeutic Potential of Apigenin. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molina Prats, P.; Gómez Garcia, F.; Martinez Diaz, F.; Amaral Mendes, R.; Lopez- Jornet, P. The Therapeutic Effects of Apigenin and Dexamethasone on 5-Fluorouracil-Induced Oral Mucositis—A Pilot Study Using a Syrian Hamster Model. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2017, 46, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Marzo, N.; Pérez-Sánchez, A.; Ruiz-Torres, V.; Martínez-Tébar, A.; Castillo, J.; Herranz-López, M.; Barrajón-Catalán, E. Antioxidant and Photoprotective Activity of Apigenin and Its Potassium Salt Derivative in Human Keratinocytes and Absorption in Caco-2 Cell Monolayers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Andrea, G. Quercetin: A Flavonol with Multifaceted Therapeutic Applications? Fitoterapia 2015, 106, 256–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mbikay, M.; Sirois, F.; Simoes, S.; Mayne, J.; Chrétien, M. Quercetin-3-Glucoside Increases Low-Density Lipoprotein Receptor (LDLR) Expression, Attenuates Proprotein Convertase Subtilisin/Kexin 9 (PCSK9) Secretion, and Stimulates LDL Uptake by Huh7 Human Hepatocytes in Culture. FEBS Open Bio 2014, 4, 755–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatahet, T.; Morille, M.; Hommoss, A.; Devoisselle, J.M.; Müller, R.H.; Bégu, S. Quercetin Topical Application, from Conventional Dosage Forms to Nanodosage Forms. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2016, 108, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rauf, A.; Imran, M.; Khan, I.A.; ur-Rehman, M.; Gilani, S.A.; Mehmood, Z.; Mubarak, M.S. Anticancer Potential of Quercetin: A Comprehensive Review. Phytother. Res. 2018, 32, 2109–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Meguid, A.; Hamdy, M.; Abd, M.; Ibrahem, E.-M. Management of Aphthous Ulceration with Topical Quercetin: A Randomized Clinical Trial. J. Contemp. Dent. Pract. 2010, 11, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angellotti, G.; Murgia, D.; Campisi, G.; De Caro, V. Quercetin-Based Nanocomposites as a Tool to Improve Dental Disease Management. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, Y.J.; Wang, L.; DiCenzo, R.; Morris, M.E. Quercetin Pharmacokinetics in Humans. Biopharm. Drug Dispos. 2008, 29, 205–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Hong, Y.; Liuyang, Z.; Li, H.; Jiang, Z.; Tao, J.; Liu, H.; Xie, A.; Feng, Y.; Dong, X.; et al. Quercetin Prevents Radiation-Induced Oral Mucositis by Upregulating BMI-1. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2021, 2021, 2231680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lotfi, M.; Kazemi, S.; Ebrahimpour, A.; Shirafkan, F.; Pirzadeh, M.; Hosseini, M.; Moghadamnia, A.A. Protective Effect of Quercetin Nanoemulsion on 5-Fluorouracil-Induced Oral Mucositis in Mice. J. Oncol. 2021, 2021, 5598230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kooshyar, M.M.; Mozafari, P.M.; Amirchaghmaghi, M.; Pakfetrat, A.; Karoos, P.; Mohasel, M.R.; Orafai, H.; Azarian, A.A. A Randomized Placebo-Controlled Double Blind Clinical Trial of Quercetin in the Prevention and Treatment of Chemotherapy-Induced Oral Mucositis. J. Dent. Res. Dent. Clin. Dent. Prospect. 2017, 11, ZC46–ZC50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkhouli, M.; Laflouf, M.; Alhaddad, M. Efficacy of Aloe-Vera Use for Prevention of Chemotherapy-Induced Oral Mucositis in Children with Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: A Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial. Compr. Child Adolesc. Nurs. 2021, 44, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazokopakis, E.E.; Vrentzos, G.E.; Papadakis, J.A.; Babalis, D.E.; Ganotakis, E.S. Wild Chamomile (Matricaria recutita L.) Mouthwashes in Methotrexate-Induced Oral Mucositis. Phytomedicine 2005, 12, 25–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavesi, V.C.S.; Lopez, T.C.C.; Martins, M.A.T.; Sant’ana Filho, M.; Bussadori, S.K.; Fernandes, K.P.S.; Mesquita-Ferrari, R.A.; Martins, M.D. Healing Action of Topical Chamomile on 5-Fluouracil Induced Oral Mucositis in Hamster. Support Care Cancer 2011, 19, 639–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayoobi, F.; Shamsizadeh, A.; Fatemi, I.; Vakilian, A.; Allahtavakoli, M.; Hassanshahi, G.; Moghadam-Ahmadi, A. Bio-Effectiveness of the Main Flavonoids of Achillea Millefolium in the Pathophysiology of Neurodegenerative Disorders—A Review. Iran. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2017, 20, 604–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Refai, A.S.; Al-Barazenchy, H.A.; Khalil, A.K. Immunohistochemical Study of the Effect of Green Tea Extract on Methotrexate- Induced Oral Mucositis in Albino Rats. J. Cytol. Histol. 2014, 5, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulrhman, M.; Samir El Barbary, N.; Ahmed Amin, D.; Saeid Ebrahim, R. Honey and a Mixture of Honey, Beeswax, and Olive Oilpropolis Extract in Treatment of Chemotherapy-Induced Oral Mucositis: A Randomized Controlled Pilot Study. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 2012, 29, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrokhi, F.; Tanideh, N.; Fekri, S.; Koohi-Hosseinabadi, O.; Tadbir, A.A.; Mardani, M. The Effect of Pistacia atlantica and Hypericum perforatum as a Healing Accelerator Remedy on Induced Oral Mucositis in Male Golden Hamster. Adv. Dent. Oral Health 2017, 4, 5555630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, L.; Zaiter, A.; Petit, J.; Zimmer, D.; Karam, M.C.; Baudelaire, E.; Scher, J.; Dicko, A. Improvement of Antioxidant Activity and Polyphenol Content of Hypericum perforatum and Achillea Millefolium Powders Using Successive Grinding and Sieving. Ind. Crops Prod. 2016, 87, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öztürk, N.; Korkmaz, S.; Öztürk, Y. Wound-Healing Activity of St. John’s Wort (Hypericum perforatum L.) on Chicken Embryonic Fibroblasts. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2007, 111, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bozorgi, M.; Memariani, Z.; Mobli, M.; Salehi Surmaghi, M.H.; Shams-Ardekani, M.R.; Rahimi, R. Five Pistacia Species (P. vera, P. atlantica, P. terebinthus, P. khinjuk, and P. lentiscus): A Review of Their Traditional Uses, Phytochemistry, and Pharmacology. Sci. World J. 2013, 2013, 219815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamidi, A.R.; Naeini, A.T.; Tanideh, N.; Nazifi, S. Effects of Pistacia atlantica (Subsp. Mutica) Oil Extracts on Antioxidant Activities during Experimentally Induced Cutaneous Wound Healing in Rats. Vet. Sci. Dev. 2015, 5, 5672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanideh, N.; Tavakoli, P.; Saghiri, M.A.; Garcia-Godoy, F.; Amanat, D.; Tadbir, A.A.; Samani, S.M.; Tamadon, A. Healing Acceleration in Hamsters of Oral Mucositis Induced by 5-Fluorouracil with Topical Calendula officinalis. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 2013, 115, 332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abudunia, A.M.; Marmouzi, I.; Faouzi, M.E.A.; Ramli, Y.; Taoufik, J.; El Madani, N.; Essassi, E.M.; Salama, A.; Khedid, K.; Ansar, M.; et al. Anticandidal, antibacterial, cytotoxic and antioxidant activities of Calendula arvensis flowers. J. Mycol. Med. 2017, 27, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, D.; Ferreira, M.S.; Sousa-Lobo, J.M.; Cruz, M.T.; Almeida, I.F. Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Calendula officinalis L. Flower Extract. Cosmetics 2021, 8, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babaee, N.; Moslemi, D.; Khalilpour, M.; Vejdani, F.; Moghadamnia, Y.; Bijani, A.; Baradaran, M.; Kazemi, M.T.; Khalilpour, A.; Pouramir, M.; et al. Antioxidant Capacity of Calendula officinalis Flowers Extract and Prevention of Radiation Induced Oropharyngeal Mucositis in Patients with Head and Neck Cancers: A Randomized Controlled Clinical Study. J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 21, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolaus, C.; Junghanns, S.; Hartmann, A.; Murillo, R.; Ganzera, M.; Merfort, I. In Vitro Studies to Evaluate the Wound Healing Properties of Calendula officinalis Extracts. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2017, 196, 94–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, A.N.; Bickford, P.C. Anthocyanins and Their Metabolites as Therapeutic Agents for Neurodegenerative Disease. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davarmanesh, M.; Miri, R.; Haghnegahdar, S.; Tadbir, A.A.; Tanideh, N.; Saghiri, M.A.; Garcia-Godoy, F.; Asatourian, A. Protective Effect of Bilberry Extract as a Pretreatment on Induced Oral Mucositis in Hamsters. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 2013, 116, 702–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tancharoen, S.; Shakya, P.; Narkpinit, S.; Dararat, P.; Kikuchi, K. Anthocyanins Extracted from Oryza sativa L. Prevent Fluorouracil-Induced Nuclear Factor-ΚB Activation in Oral Mucositis: In Vitro and in Vivo Studies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nizamutdinova, I.T.; Kim, Y.M.; Chung, J.I.; Shin, S.C.; Jeong, Y.K.; Seo, H.G.; Lee, J.H.; Chang, K.C.; Kim, H.J. Anthocyanins from Black Soybean Seed Coats Stimulate Wound Healing in Fibroblasts and Keratinocytes and Prevent Inflammation in Endothelial Cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2009, 47, 2806–2812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.C.; Chung, L.C.; Chen, Y.J.; Feng, T.H.; Chen, W.T.; Juang, H.H. Upregulation of B-Cell Translocation Gene 2 by Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate via P38 and ERK Signaling Blocks Cell Proliferation in Human Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cells. Cancer Lett. 2015, 360, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagai, K.; Jiang, M.H.; Hada, J.; Nagata, T.; Yajima, Y.; Yamamoto, S.; Nishizaki, T. Research Report (2)-Epigallocatechin Gallate Protects against NO Stress-Induced Neuronal Damage after Ischemia by Acting as an Anti-Oxidant. Brain Res. 2002, 956, 319–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amhed Saleh, H.; Hussein El-Rouby, D.; Raouf Amin, N. The Effect of Grape Seed Extract and Cetuximab Drug on Mucositis of Experimental Rats. J. Oral Health Dent. Manag. 2017, 16, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Miranzadeh, S.; Adib-Hajbaghery, M.; Soleymanpoor, L.; Ehsani, M. Effect of Adding the Herb Achillea Millefolium on Mouthwash Onchemotherapy Induced Oral Mucositis in Cancer Patients: Adouble-Blind Randomized Controlled Trial. Eur. J. Oncol. Nurs. 2015, 19, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, J.A.; Kasum, C.M. Dietary Flavonoids: Bioavailability, Metabolic Effects, and Safety. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2002, 22, 19–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enaru, B.; Socaci, S.; Farcas, A.; Socaciu, C.; Danciu, C.; Stanila, A.; Diaconeasa, Z. Novel Delivery Systems of Polyphenols and Their Potential Health Benefits. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopra, H.; Dey, P.S.; Das, D.; Bhattacharya, T.; Shah, M.; Mubin, S.; Maishu, S.P.; Akter, R.; Rahman, M.H.; Karthika, C.; et al. Curcumin Nanoparticles as Promising Therapeutic Agents for Drug Targets. Molecules 2021, 26, 4998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macedo, A.S.; Castro, P.M.; Roque, L.; Thomé, N.G.; Reis, C.P.; Pintado, M.E.; Fonte, P. Novel and Revisited Approaches in Nanoparticle Systems for Buccal Drug Delivery. J. Control. Release 2020, 320, 125–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Prima, G.; Angellotti, G.; Scarpaci, A.G.; Murgia, D.; D’agostino, F.; Campisi, G.; De Caro, V. Improvement of Resveratrol Permeation through Sublingual Mucosa: Chemical Permeation Enhancers versus Spray Drying Technique to Obtain Fast-Disintegrating Sublingual Mini-Tablets. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinesh Kumar, V.; Verma, P.R.P.; Singh, S.K. Development and Evaluation of Biodegradable Polymeric Nanoparticles for the Effective Delivery of Quercetin Using a Quality by Design Approach. LWT 2015, 61, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazmi, I.; Al-Abbasi, F.A.; Imam, S.S.; Afzal, M.; Nadeem, M.S.; Altayb, H.N.; Alshehri, S. Formulation and Evaluation of Apigenin-Loaded Hybrid Nanoparticles. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulaiman, G.M.; Waheeb, H.M.; Jabir, M.S.; Khazaal, S.H.; Dewir, Y.H.; Naidoo, Y. Hesperidin Loaded on Gold Nanoparticles as a Drug Delivery System for a Successful Biocompatible, Anti-Cancer, Anti-Inflammatory and Phagocytosis Inducer Model. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safwat, M.A.; Kandil, B.A.; Elblbesy, M.A.; Soliman, G.M.; Eleraky, N.E. Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate-Loaded Gold Nanoparticles: Preparation and Evaluation of Anticancer Efficacy in Ehrlich Tumor-Bearing Mice. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tie, S.; Tan, M. Current Advances in Multifunctional Nanocarriers Based on Marine Polysaccharides for Colon Delivery of Food Polyphenols. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 903–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murgia, D.; Angellotti, G.; Conigliaro, A.; Pavia, F.C.; D’agostino, F.; Contardi, M.; Mauceri, R.; Alessandro, R.; Campisi, G.; De Caro, V. Development of a Multifunctional Bioerodible Nanocomposite Containing Metronidazole and Curcumin to Apply on L-PRF Clot to Promote Tissue Regeneration in Dentistry. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Wei, Y.; Wang, Y.; Jin, Z.; Ma, G.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Hu, Z. Facile Preparation of Polyphenol-Crosslinked Chitosan-Based Hydrogels for Cutaneous Wound Repair. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 228, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Xu, Z.; Liu, G.; Wu, J. Polyphenols as a Versatile Component in Tissue Engineering. Acta Biomater. 2021, 119, 57–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angellotti, G.; Di Prima, G.; D’Agostino, F.; Peri, E.; Tricoli, M.R.; Belfiore, E.; Allegra, M.; Cancemi, P.; De Caro, V. Multicomponent Antibiofilm Lipid Nanoparticles as Novel Platform to Ameliorate Resveratrol Properties: Preliminary Outcomes on Fibroblast Proliferation and Migration. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 8382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angellotti, G.; Presentato, A.; Murgia, D.; Di Prima, G.; D’Agostino, F.; Scarpaci, A.G.; D’Oca, M.C.; Alduina, R.; Campisi, G.; De Caro, V. Lipid Nanocarriers-Loaded Nanocomposite as a Suitable Platform to Release Antibacterial and Antioxidant Agents for Immediate Dental Implant Placement Restorative Treatment. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bunte, K.; Hensel, A.; Beikler, T. Polyphenols in the Prevention and Treatment of Periodontal Disease: A Systematic Review of in Vivo, Ex Vivo and in Vitro Studies. Fitoterapia 2019, 132, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mauceri, R.; Panzarella, V.; Morreale, I.; Campisi, G. Medication-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw in a Cancer Patient Receiving Lenvatinib. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2019, 48, 1530–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Pei, X.; Duan, L.; Zhu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Chen, J.; Chen, T.; Ji, P.; Wan, Q.; Wang, J. A Mussel-Inspired Film for Adhesion to Wet Buccal Tissue and Efficient Buccal Drug Delivery. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
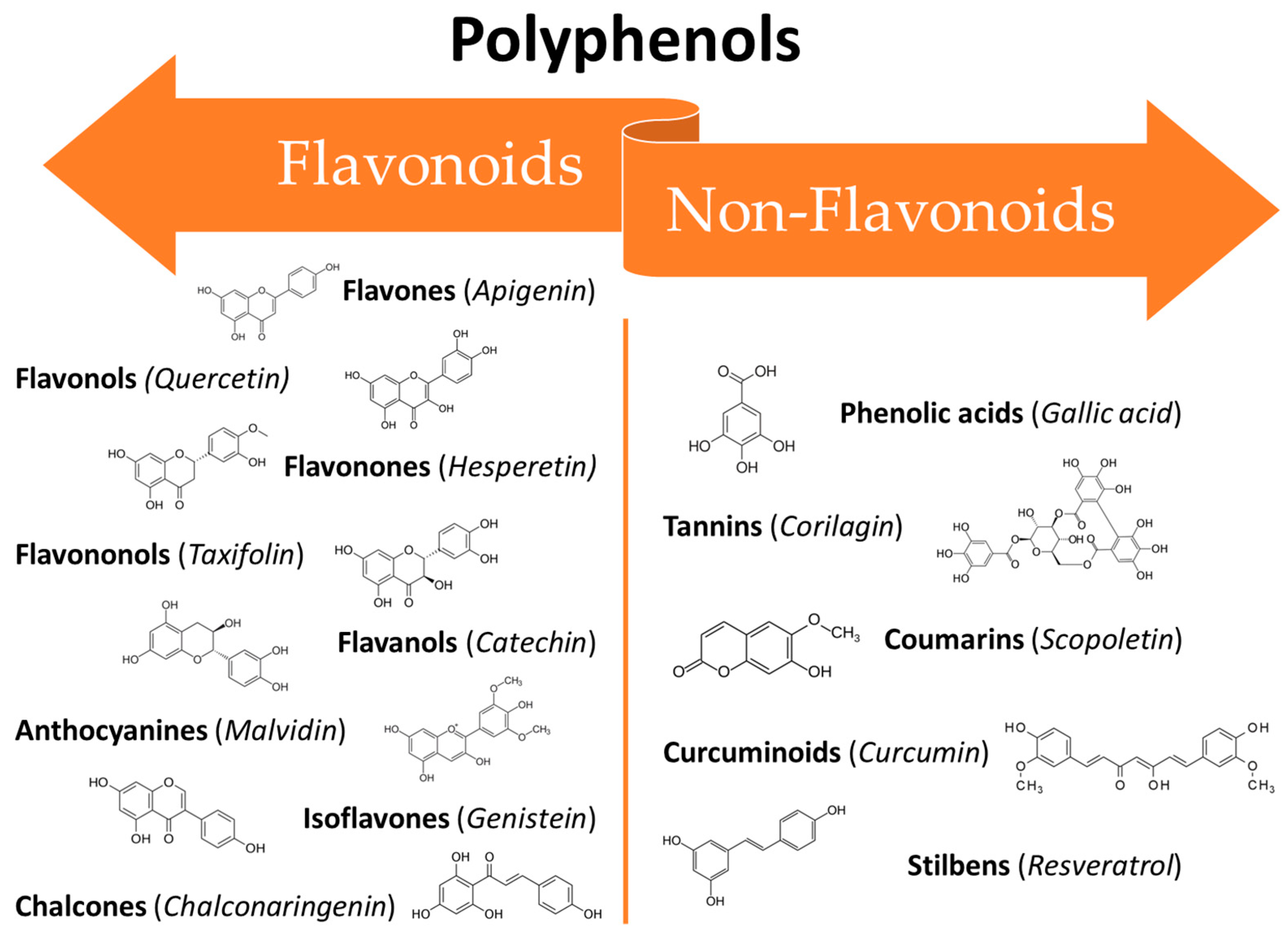









| Compound/Formulation, Route of Administration, Dose, and Regimen | Type of Study | Animals/ Participants | Model | Outcomes | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CUR (20 mg/mL) mucoadhesive gel; topical administration of 0.5 g twice a day for 2 weeks, compared to control, placebo, and C. recutita fluid extract | In vivo animal study | Golden Syrian hamsters | Chemotherapy-induced OM (5-FU) | Reduced angiogenesis, vascularization, and TGF-β1 labelling as well as rapid healing and reepithelization | Schmidt et al., 2019 [63] |
| CUR 50 or 100 μg/mL hydroalcoholic solution; topical administration of 0.25 mL/day, compared to control, placebo, QRC, and peptides, for 20 days. | In vivo animal study | Golden Syrian hamsters | Radiotherapy-induced OM (single dose: 40 Gy) | Massive reduction of OM severity in a dose-dependent manner | Dvoretskiy et al., 2022 [64] |
| CUR (0.1% w/v) mouthwash, topical administration of 10 mL 3 times/day for 6 weeks, compared to a commercial benzydamine mouthwash (0.15% w/v, COOLORA™) | Triple-blind clinical trial | Adult patients with OSCC | Radiotherapy-induced OM (60–70 Gy) | Delayed onset of OM by two weeks in half of the patients and no one displayed severe OM | Shah et al., 2020 [66] |
| CUR (7.5 mg in 10 mL) solution; topical administration once a week for 1 month in combination with photodynamic therapy (450 nm blue LED) compared to low-level laser irradiation (600 nm) and control | Clinical trial | Adult patients | Chemo- and radiotherapy-induced OM | Reduction of Candida albicans infection, together with less pain and lower OM scores | de Cássia Dias Viana Andrade et al., 2022 [67] |
| CUR gel (0.5% w/v); topical administration 4 times/day for 2 weeks compared to Mucosamin® oral spray (0.2% w/v) and Chlorhexidine mouthwash (0.5% w/v) | Double-blind clinical trial | Adult patients | Chemotherapy-induced OM | Reduction in OM severity (WHO and OMAS scores) and faster lesion restoration (within 4 days) compared with the other formulations | Fardad et al., 2022 [68] |
| Capsules containing curcuminoids and essential oil of turmeric (0,5 g); per os twice or 3 times/day (1 or 1.5 g/die) for 6 weeks, compared to placebo | Double-blind clinical trial | Adult patients | Chemotherapy-induced OM | Reduction of OM symptoms and severity in a dose-dependent manner | Soni et al., 2022 [69] |
| SinaCurcumin® capsules (80 mg CUR) per os once a day for 6 weeks, compared to placebo | Double-blind clinical trial | Adult patients | Radiotherapy-induced OM (50 Gy) | Delay in the OM onset (one week). Reduction in OM severity and lower weight loss | Delavarian et al., 2019 [72] |
| SinaCurcumin® capsules (80 mg CUR) per os twice a day for 7 weeks, compared to placebo | Clinical trial | Adult patients | Chemo- and/or radiotherapy-induced OM (30–50 mg Cisplatine or 640–750 mg 5-FU and/or 60–70 Gy) | Reduction of pain and OM signs, severity, and progression. The beneficial effects enhanced for patients receiving only chemotherapy. | Kia et al., 2021 [73] |
| SinaCurcumin® capsules (40 mg/die) per os 3 times/day, for 21 days compared to CUR mouthwash (0.1% w/v) topical administration 3 times/day, and placebo | Randomized clinical trial | Adult patients | Radiotherapy-induced OM | Complete ulcer restoration as well as reduction of OM severity, signs, and symptoms. No statistical difference in the two CUR groups was observed. | Ramezani et al., 2023 [74] |
| Tested Substance(s) | Dose, Regimen, and Route of Administration | Type of Study | Animals/ Participants | Model | Outcomes | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| α-glucosyl hesperidin (α-G-HSP) | α-G-HSP 1 mg/mL ad libitum, from 5 days before 5-FU treatment until 16 days. Oral administration | In vivo animal study | Golden Syrian hamsters | Chemotherapy-induced OM (5-FU 60 mg/kg by intraperitoneal injection) | Preventive effect leading to smaller ulceration areas due to inhibition of ROS and lipid peroxidase | Yoshino et al., 2016 [92] |
| (−)-Epicatechin (EC) | 100 μL/dose of a 2 mM EC solution three times a day compared to control for 23 days. Oral administration. | In vivo animal study | Sprague-Dawley rats | Radiotherapy-induced OM (30 Gy) | Inhibition of radiation-induced apoptosis, reduction of ROS, and NOX-e protein production. Improvement of animals’ viability. | Shin Y.S. et al., 2013 [100] |
| Epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) | 15 mL of EGCG-loaded mouthwash at increasing doses (from 440 to 2200 μM), 3 times/day for 8 weeks. Topical administration. | Clinical trial | Adult patients | Radio- and sometimes concurrent chemotherapy-induced OM (66–72 Gy) | Each dose was able to reduce pain and OM severity, resulting in no patients showing severe OM. The chosen recommended dose for a further phase II clinical trial is equal to 1760 μM. | Zhu et al., 2020 [108] |
| Apigenin (APG) | 40 mg/Kg of APG potassium salt solution by gavage compared to dexamethasone (1 mg/Kg) and control, for 14 days. Oral administration. | In vivo animal study | Golden Syrian hamsters | Chemotherapy-induced OM (5-FU 60 mg/kg by intraperitoneal injection) | Significant reduction of OM severity and acceleration of the normal wound-healing process | Molina Prats et al., 2017 [113] |
| Quercetin (QRC) | 0.25 mL/day of QRC in DMSO solutions 50 or 100 μg/mL compared to control, placebo, CUR and peptides, for 20 days. Topical administration. | In vivo animal study | Golden Syrian hamsters | Radiotherapy-induced OM (single dose: 40 Gy) | Both doses determined a strong reduction of OM severity but only the QRC 100 treatment was considered effective | Dvoretskiy et al., 2022 [64] |
| Quercetin (QRC) | 300 mg/Kg/day of QRC from one week before radiotherapy and until 8 days after radiotherapy. Oral administration. | In vivo animal study | C57BL/6 mice | Radiotherapy-induced OM (single dose—25 Gy or fractionated dose—8 Gy/day for 3 days) | Reduction of lesions’ size and mucosal damage. Protection against the radiation-induced reduction of Ki-67 and PCNA. Inhibition of P-21, P-16, and expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines. | Zhang J. et al., 2021 [122] |
| Quercetin (QRC) | 5 mg/kg/day of free QRC or QRC-loaded nanoemulsion as a pre-treatment or post-treatment, for 13 days. Oral administration. | In vivo animal study | Albino mice | Chemotherapy-induced OM (300 mg/kg) | Enhanced general health. Preservation of the mucosal integrity with reduction of inflammatory cell infiltration. Reduction of MDA and increase in SOD and CAT expressions. | Lotfi et al., 2021 [123] |
| Quercetin (QRC) | QRC hydrate-loaded capsules (250 mg/dose) compared to placebo, twice a day for 4 weeks. Oral administration. | Randomized placebo-controlled double-blind clinical trial | Adult patients | Chemotherapy-induced OM (predominately Cytarabine or Daunorubicin, but also Vincristine, Cyclophosphamide, Plasil, Idarubicin, Fludarabine, Adriamycin and L-asparaginase) | Reduction of OM incidence (from 60% to 30%) | Kooshyar et al., 2017 [124] |
| Hydro-alcoholic H. perforatum extract and P. atlantica oil extract | Hydro-alcoholic H. perforatum extract-loaded gel (10% w/v) or P. atlantica oil extract-loaded gel (10% w/v) or combination thereof for 18 days. Topical administration. | In vivo animal study | Golden Syrian hamsters | Chemotherapy-induced OM (60 mg/kg by intraperitoneal injections) | Lower micro- and macroscopic OM scores. Enhanced healing and reduced levels of oxidative stress markers. These effects are enhanced when the two extracts are administered in combination. | Farrokhi et al., 2017 [131] |
| Hydro-alcoholic C. officinalis extract | Hydro-alcoholic C. officinalis extract loaded mucoadhesive gel (5 or 10% w/v) once a day, compared to placebo and control for 17 days. Topical administration. | In vivo animal study | Golden Syrian hamsters | Chemotherapy-induced OM (60 mg/kg by intraperitoneal injections) | Reduction of haemorrhage, inflammatory cell infiltration, and ulceration. Dose-dependent wound healing properties. | Tanideh et al., 2013 [136] |
| Standardized bilberry extract containing 36% (w/v) of glycosylated Anthocyanins (ANTs) | 45 mg/mL (corresponding to 300 mg/kg) of aqueous solution containing the bilberry extract once a day by gavage for 7 days before chemotherapy. Oral administration. | In vivo animal study | Golden Syrian hamsters | Chemotherapy-induced OM (60 mg/kg by intraperitoneal injections) | The pre-treatment with the bilberry extract determined the enhancement of mice’s general health, together with a reduction of OM severity and signs | Davarmanesh et al., 2013 [142] |
| ANTs-rich Oryza sativa L. extract | 500 or 1000 mg/Kg of Oryza sativa L. extract once a day by gavage for 29 days compared to control. Oral administration. | In vivo animal study | Wistar rats | Chemotherapy-induced OM (60 mg/kg by intraperitoneal injections) | Dose-dependent wound healing properties due to reduction of p50, p65, NF-κB and HMGB1 markers | Tancharoen et al., 2018 [143] |
| Green tea extract | 40 mg/Kg of green tea extract by gavage once a day, compared to control for 5 days. Oral administration. | In vivo animal study | Albino rats | Chemotherapy-induced OM (MTX from 10 to 80 mg/kg by intraperitoneal injection) | No buccal mucosa damage and reduction of inflammatory cell infiltration. Normal Ki-67 expression together with up-regulation of Bcl-2. | Al-Refai et al., 2014 [129] |
| Grape seed extract | 20 mg/day of grape seed extract as a pre-treatment (from one week before chemotherapy) or in concomitance with chemotherapy, for 16 days, compared to control. Oral administration. | In vivo animal study | Rats | Chemotherapy-induced OM (0.25 mg of cetuximab by intraperitoneal injection) | Reduction of tongue damage, ROS levels, and susceptibility to bacterial infection. By the pre-treatment, a limited inflammatory stage and lower atrophic areas in the mucosa were observed. | Amhed Saleh et al., 2017 [147] |
| C. officinalis flowers ethanolic extract | 5 mL of a C. officinalis extract-loaded mouthwash gel (2% w/v) twice a day compared to placebo for 7 weeks. Topical administration. | Clinical trial | Adult patients with head and neck cancer | OM induced by radiotherapy (200 cGy-5 days/week) alone or in combination with chemotherapy (5-FU or Cisplatin) | Delayed OM onset and reduction of OM severity of OM Despite the presence of ethanol or irritation, no other serious side effects were observed | Babaee et al., 2013 [139] |
| A. millefolium distillate | 15 mL of A. millefolium distillate-loaded mouthwash (12 ppm) by gargling for 3 min daily compared to placebo for 14 days. Topical administration. | Clinical trial | Adult patients | Chemotherapy-induced OM | Remarkable regeneration of the injured mucosa and reduction in OM severity | Miranzadeh et al., 2015 [148] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Belfiore, E.; Di Prima, G.; Angellotti, G.; Panzarella, V.; De Caro, V. Plant-Derived Polyphenols to Prevent and Treat Oral Mucositis Induced by Chemo- and Radiotherapy in Head and Neck Cancers Management. Cancers 2024, 16, 260. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16020260
Belfiore E, Di Prima G, Angellotti G, Panzarella V, De Caro V. Plant-Derived Polyphenols to Prevent and Treat Oral Mucositis Induced by Chemo- and Radiotherapy in Head and Neck Cancers Management. Cancers. 2024; 16(2):260. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16020260
Chicago/Turabian StyleBelfiore, Elena, Giulia Di Prima, Giuseppe Angellotti, Vera Panzarella, and Viviana De Caro. 2024. "Plant-Derived Polyphenols to Prevent and Treat Oral Mucositis Induced by Chemo- and Radiotherapy in Head and Neck Cancers Management" Cancers 16, no. 2: 260. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16020260
APA StyleBelfiore, E., Di Prima, G., Angellotti, G., Panzarella, V., & De Caro, V. (2024). Plant-Derived Polyphenols to Prevent and Treat Oral Mucositis Induced by Chemo- and Radiotherapy in Head and Neck Cancers Management. Cancers, 16(2), 260. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16020260











