Exo70 Promotes the Invasion of Pancreatic Cancer Cells via the Regulation of Exosomes
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Eligibility
2.2. Cell Culture
2.3. Antibodies and Reagents
2.4. Construction of Vectors and Stable Cell Lines
2.5. Cell Viability and Colony Formation
2.6. Western Blot
2.7. Transwell Assay
2.8. Exosomes Extraction
2.9. Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis
2.10. Immunofluorescence
2.11. Transmission Electron Microscopy
2.12. Fluorescent Labeling and Transfer of Exosomes
2.13. Animal Experiments
2.14. Evaluation of Immunohistochemical Staining
2.15. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
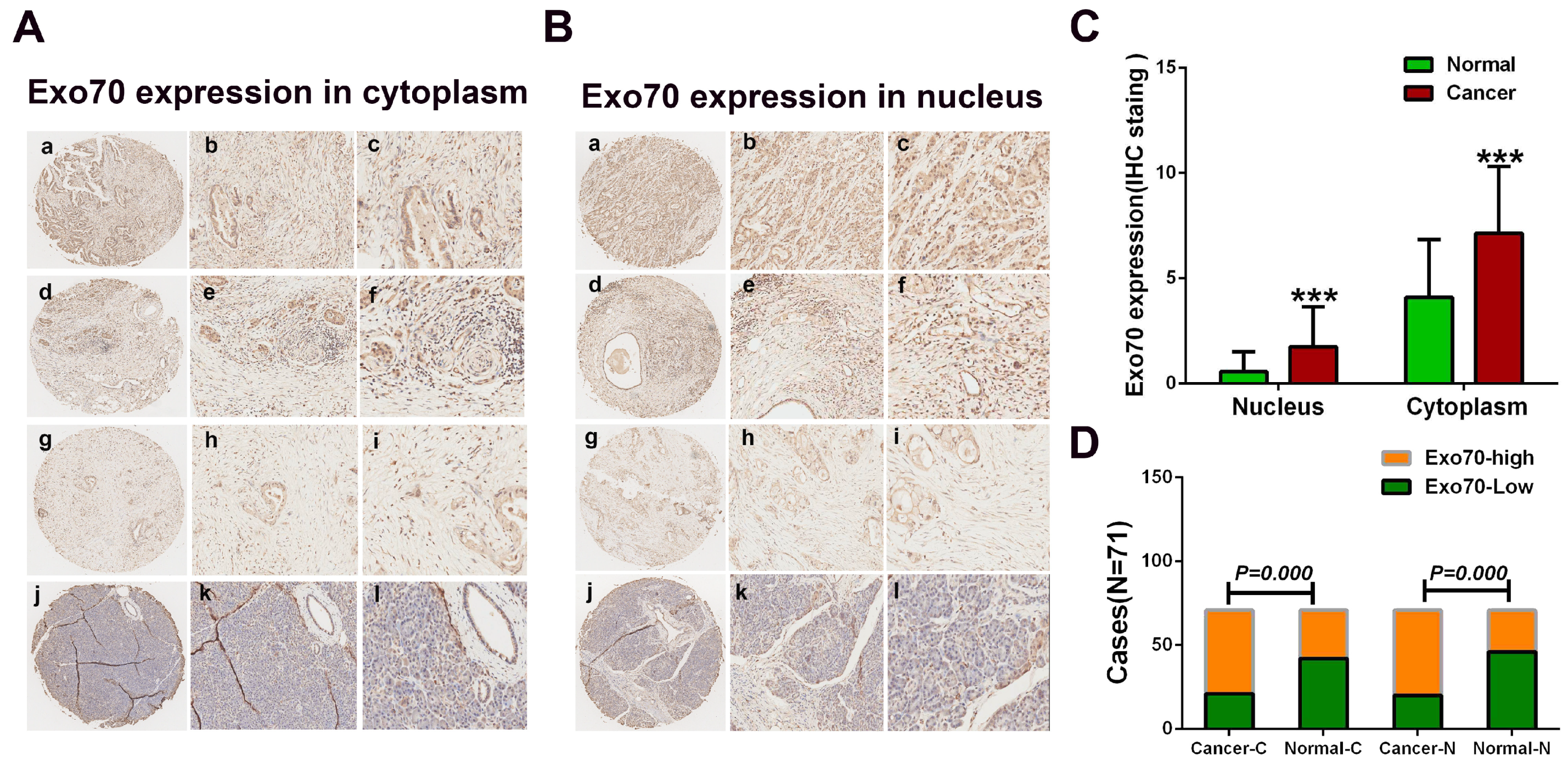
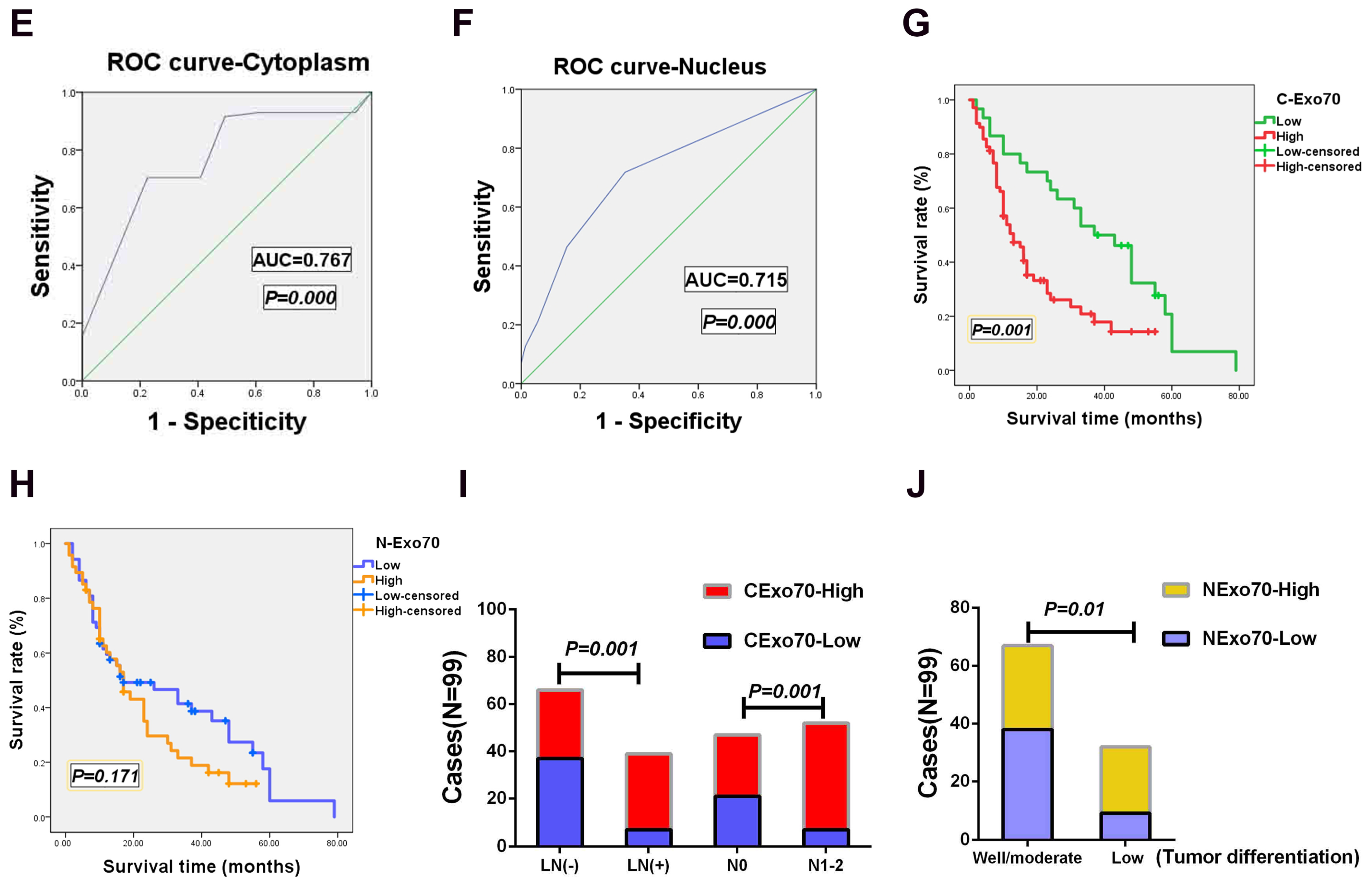
3.1. Exo70 Expression in Pancreatic Cancer Tissues Correlated with the Prognosis of Pancreatic Cancer Patients
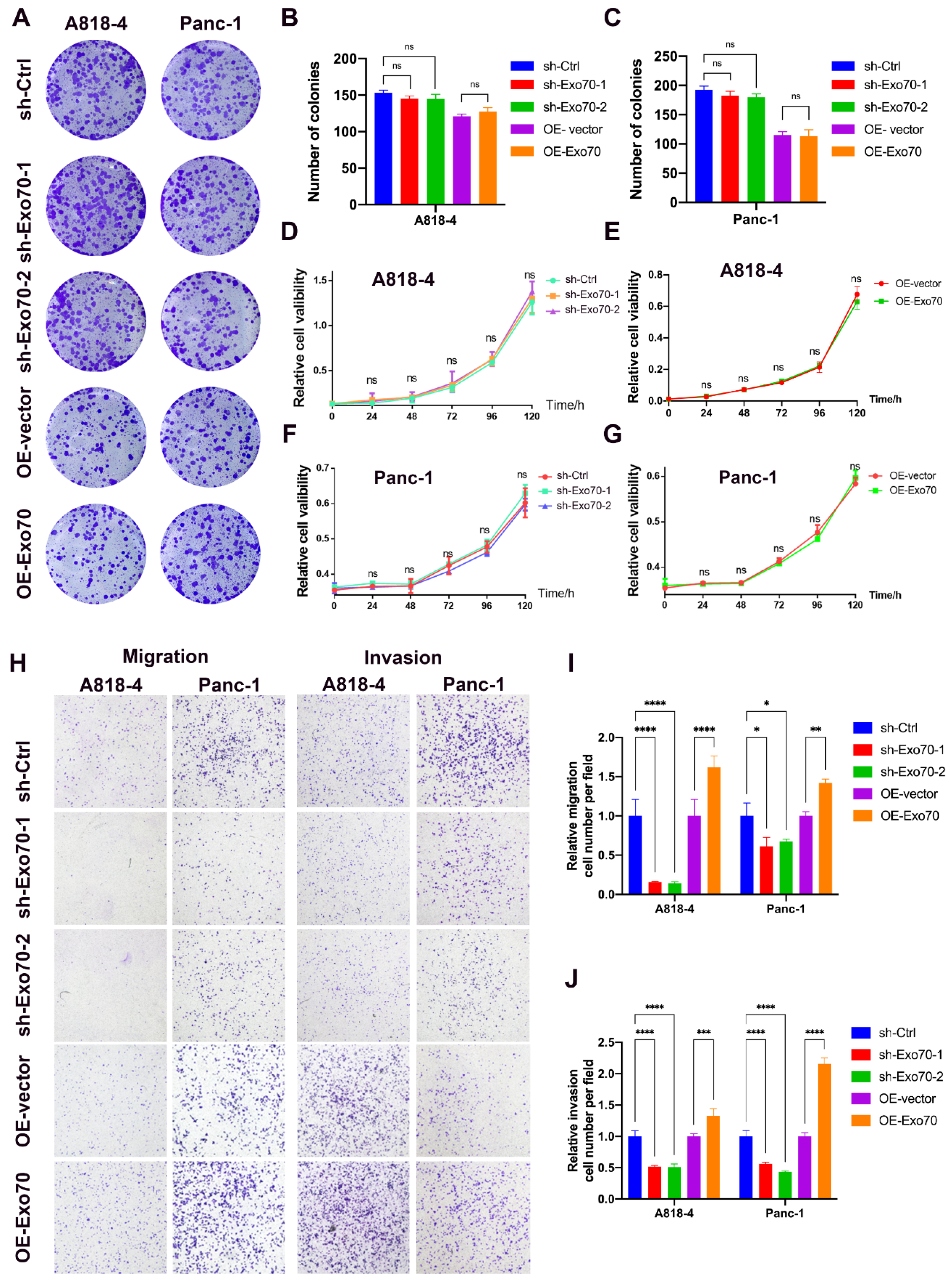
3.2. Exo70 Regulated the Invasion and Migration of Pancreatic Cancer Cells
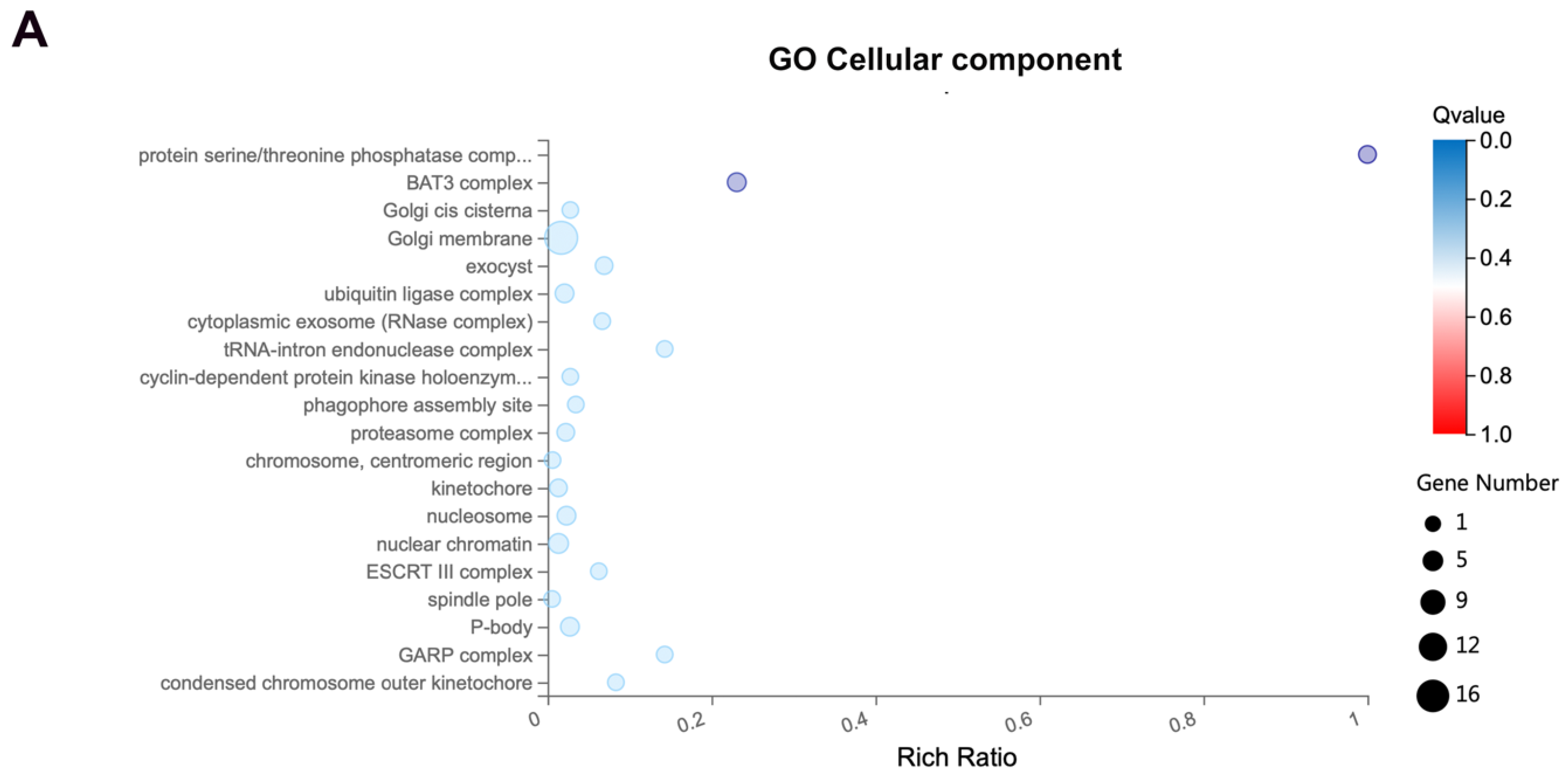
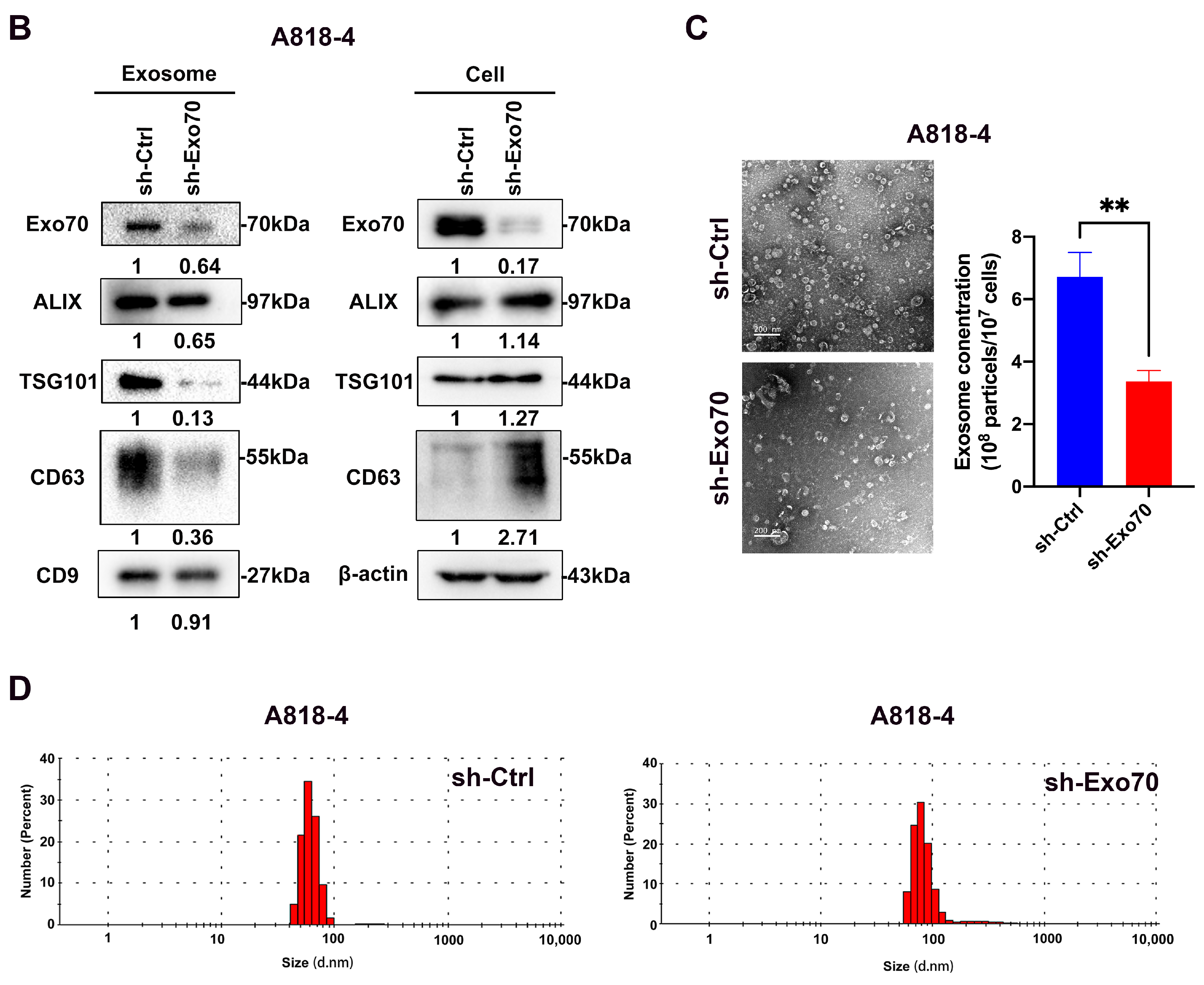
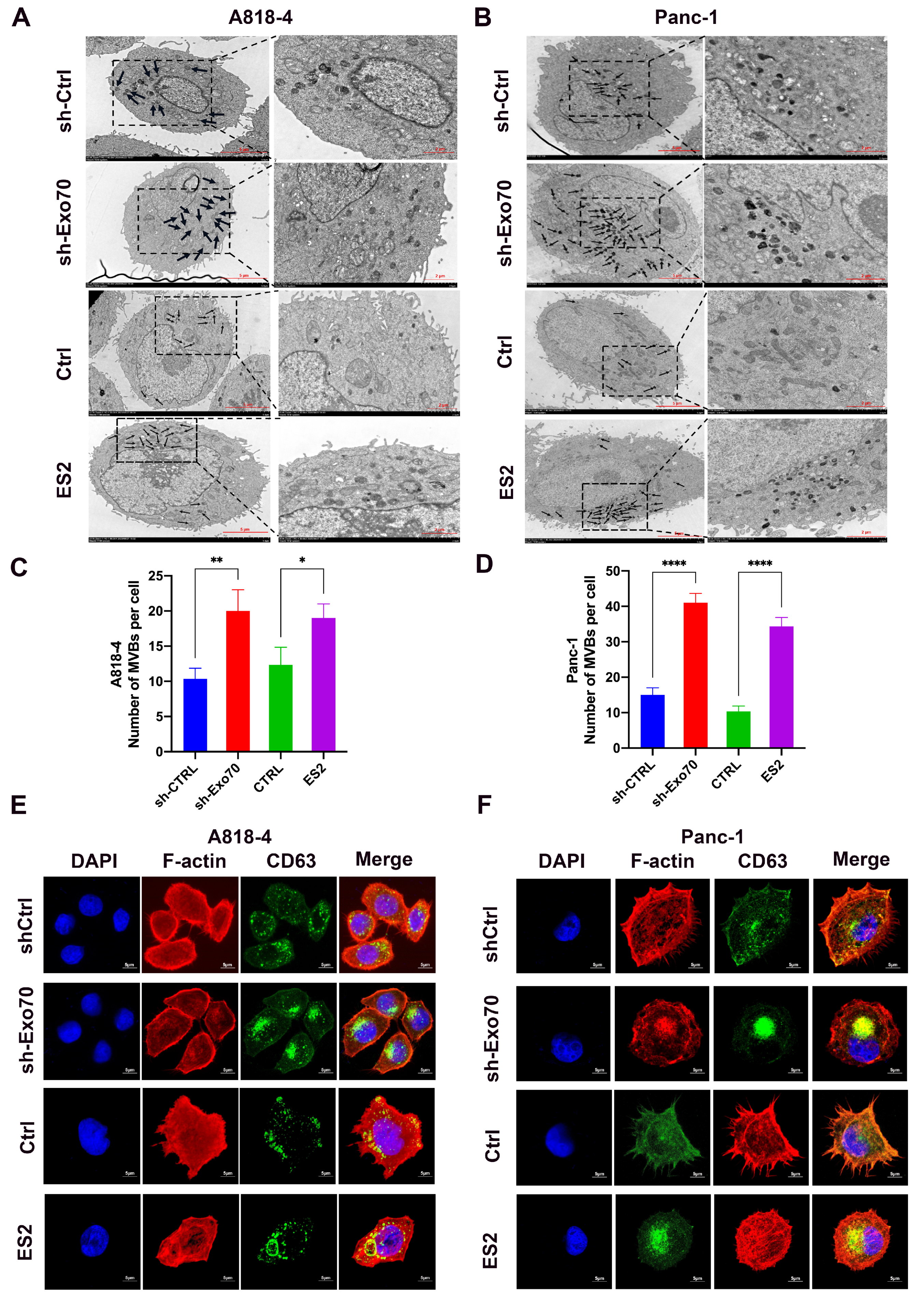
3.3. Exo70 Affected the Trafficking of Exosomes
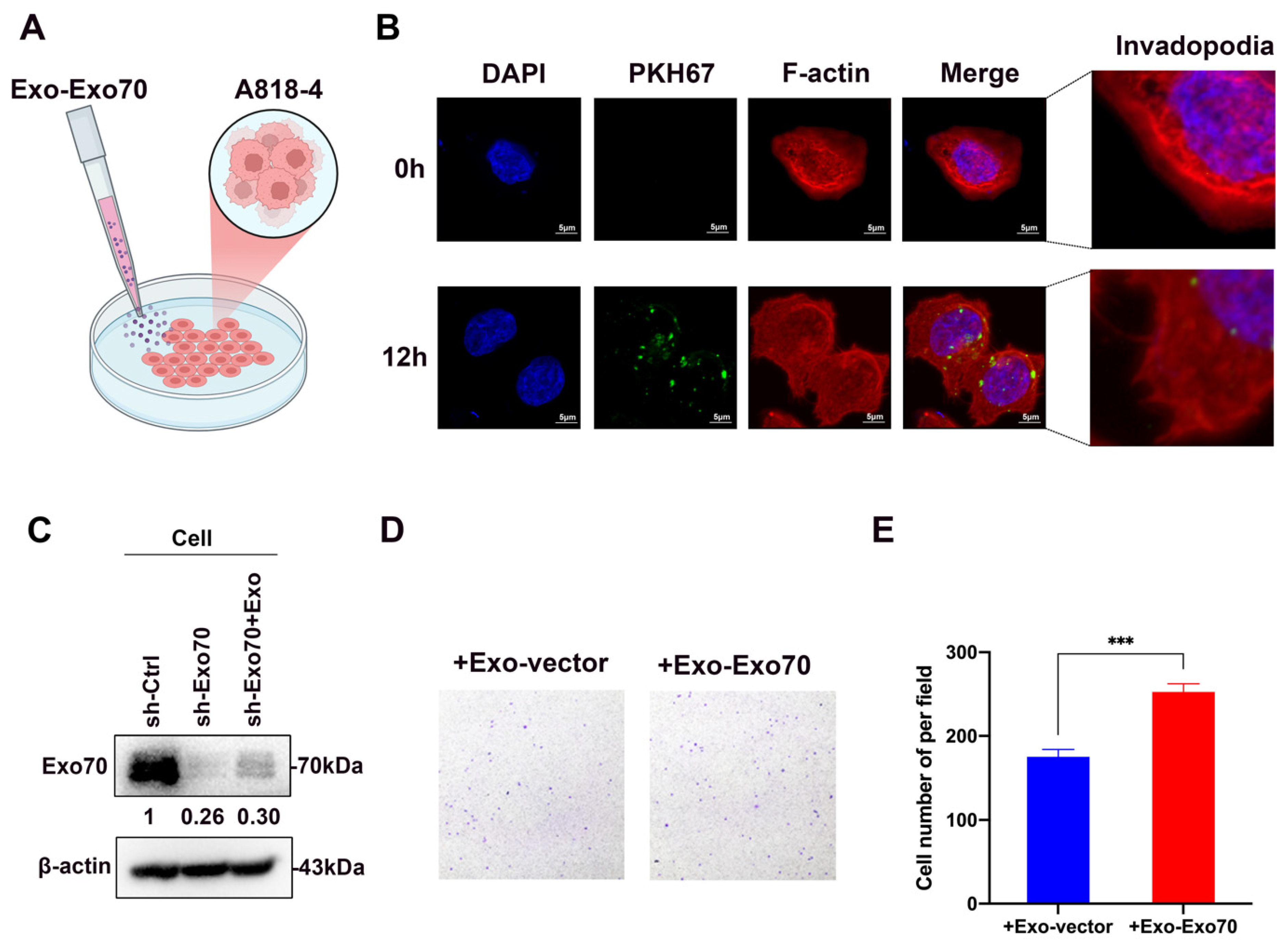
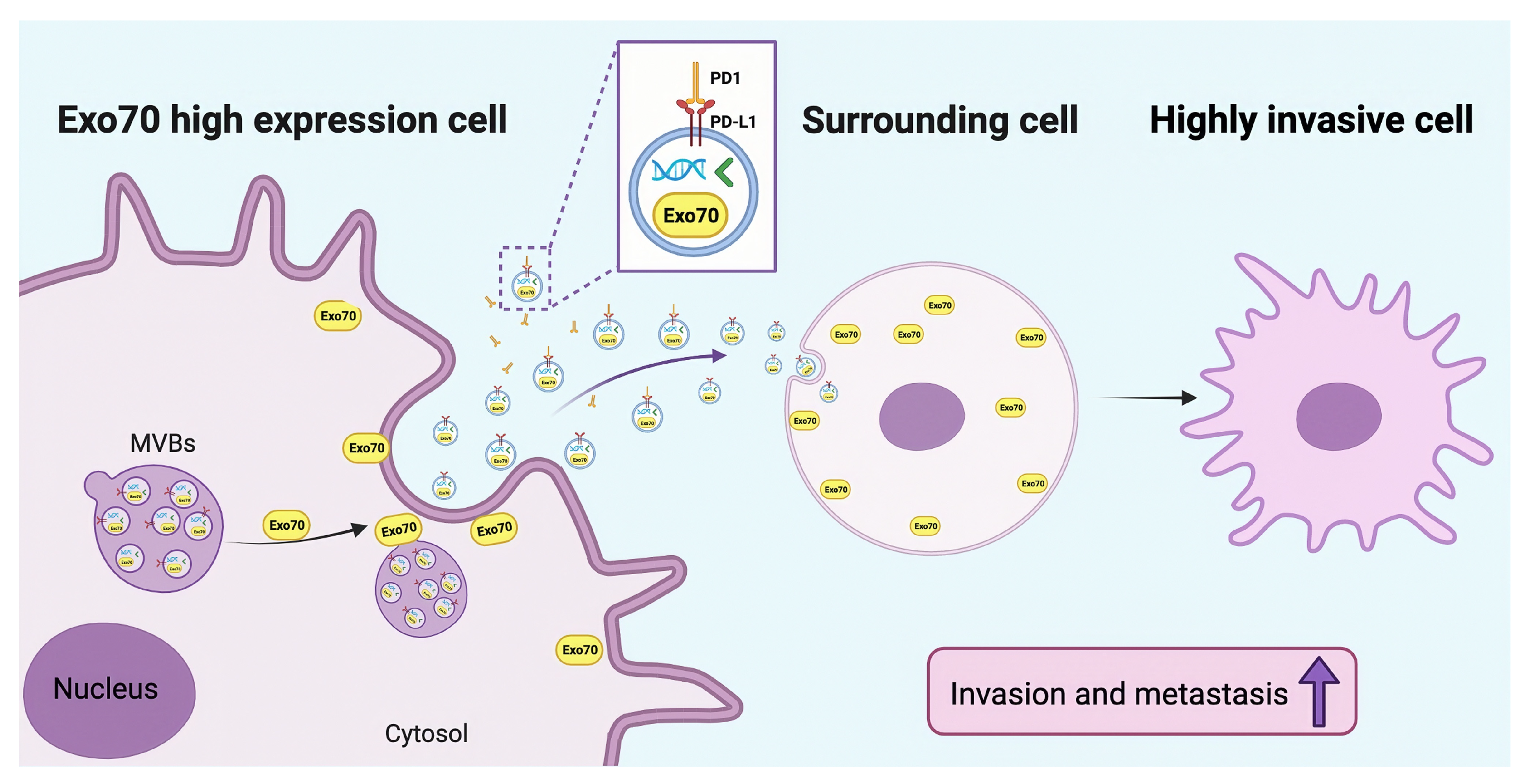
3.4. Exo70 Fused into the Exosomes to Promote Other PC Cells’ Invasion and Affected the Tumor Immune Microenvironment
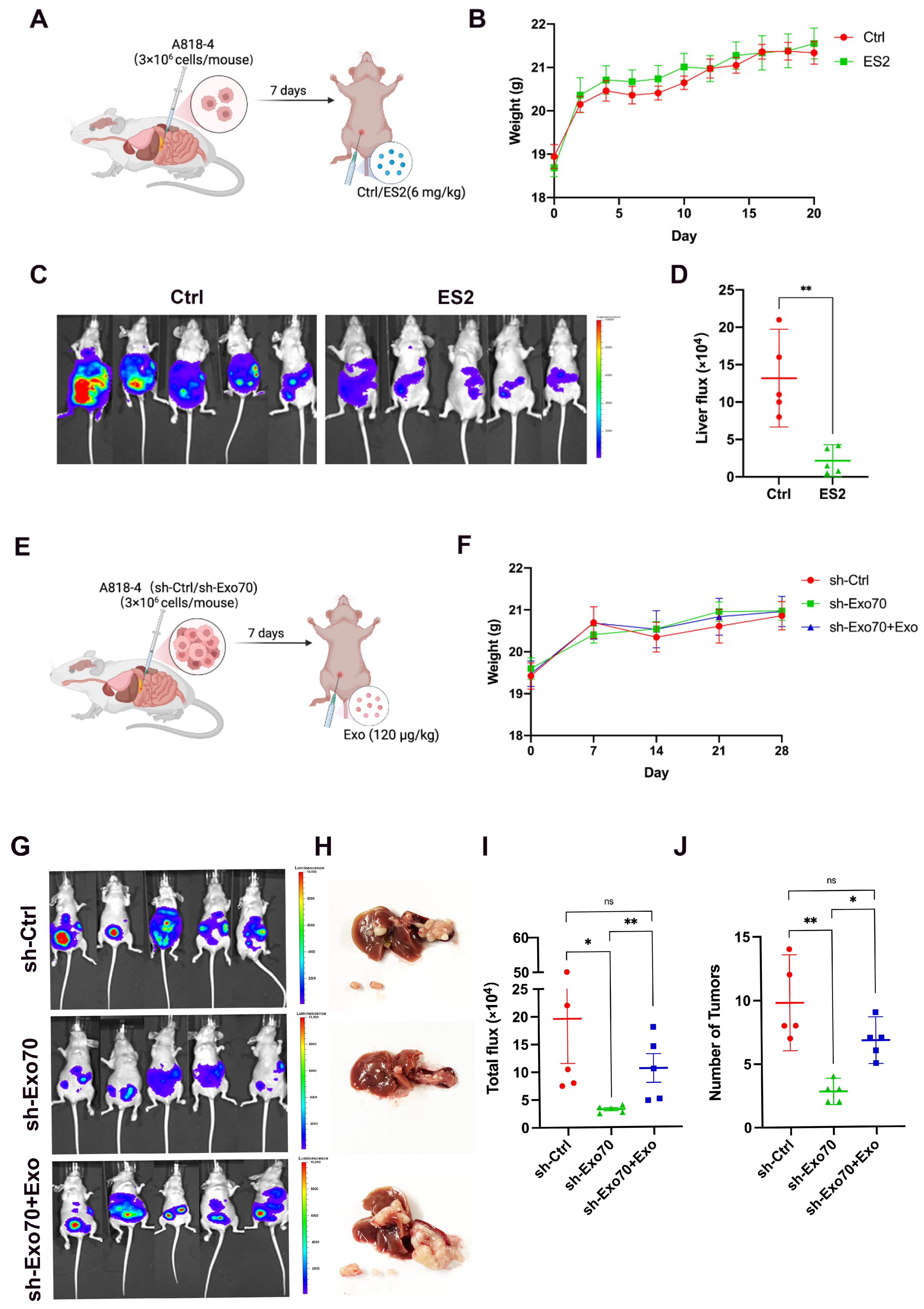
3.5. Exo70 Promoted Tumor Metastasis In Vivo
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Wagle, N.S.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2023, 73, 17–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Chen, H.; Lu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, B.; You, L.; Zhang, T.; Dai, M.; Zhao, Y. Advances in the epidemiology of pancreatic cancer: Trends, risk factors, screening, and prognosis. Cancer Lett. 2021, 520, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, A.; Donahue, T. Pancreatic Cancer. JAMA 2019, 322, 1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paskeh, M.D.A.; Entezari, M.; Mirzaei, S.; Zabolian, A.; Saleki, H.; Naghdi, M.J.; Sabet, S.; Khoshbakht, M.A.; Hashemi, M.; Hushmandi, K.; et al. Emerging role of exosomes in cancer progression and tumor microenvironment remodeling. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2022, 15, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Z.; Gao, Y.; Ho, C.; Li, L.; Jin, C.; Wang, X.; Zou, C.; Mao, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, Q.; et al. Exosome-delivered CD44v6/C1QBP complex drives pancreatic cancer liver metastasis by promoting fibrotic liver microenvironment. Gut 2022, 71, 568–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa-Silva, B.; Aiello, N.M.; Ocean, A.J.; Singh, S.; Zhang, H.; Thakur, B.K.; Becker, A.; Hoshino, A.; Mark, M.T.; Molina, H.; et al. Pancreatic cancer exosomes initiate pre-metastatic niche formation in the liver. Nat. Cell Biol. 2015, 17, 816–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhu, C.; Xu, J.; Chen, P.; Jiang, X.; Chen, Y.; Jiang, J.; Sun, C. Exosome-derived FGD5-AS1 promotes tumor-associated macrophage M2 polarization-mediated pancreatic cancer cell proliferation and metastasis. Cancer Lett. 2022, 548, 215751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Zu, F.; Chen, H.; Yin, X.; Tan, X. Exosomal DNAJB11 promotes the development of pancreatic cancer by modulating the EGFR/MAPK pathway. Cell Mol. Biol. Lett. 2022, 27, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Urdiroz, M.; Deeks, M.J.; Horton, C.G.; Dawe, H.R.; Jourdain, I. The Exocyst Complex in Health and Disease. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2016, 4, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, C.; Stalder, D.; Anderson, G.S.F.; Shun-Shion, A.S.; Houghton, J.; Antrobus, R.; Chapman, M.A.; Fazakerley, D.J.; Gershlick, D.C. The exocyst complex is an essential component of the mammalian constitutive secretory pathway. J. Cell Biol. 2023, 222, e202205137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, K.; Guo, W. The exocyst complex. Curr. Biol. 2018, 28, R922–R925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, B.; Guo, W. The exocyst complex in polarized exocytosis. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2009, 21, 537–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, H.; Liu, S.; Zhang, G.; Kwong, L.N.; Zhu, Y.; Miller, J.P.; Hu, Y.; Zhong, W.; Zeng, J.; Wu, L.; et al. Oncogenic BRAF-Mediated Melanoma Cell Invasion. Cell Rep. 2016, 15, 2012–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, L.; Zhan, Y.Y.; Wu, B.; Yu, Q.; Xu, L.; Hong, X.; Zhong, L.; Mi, P.; Xiao, L.; Wang, X.; et al. ULK1 phosphorylates Exo70 to suppress breast cancer metastasis. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Hong, X.; Chen, X.; Hu, C.; Lu, W.; Xie, B.; Zhong, L.; Zhang, W.; Cao, H.; Chen, B.; et al. Deregulation of Exo70 Facilitates Innate and Acquired Cisplatin Resistance in Epithelial Ovarian Cancer by Promoting Cisplatin Efflux. Cancers 2021, 13, 3467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Wu, B.; Guo, W. The role of Exo70 in exocytosis and beyond. Small GTPases 2019, 10, 331–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, Y.; He, B.; Yang, C.; Svitkina, T.; Goldman, Y.E.; Guo, W. Exo70 stimulates the Arp2/3 complex for lamellipodia formation and directional cell migration. Curr. Biol. 2012, 22, 1510–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Zheng, K.; Lv, X.; Hou, J.; Xu, L.; Zhao, Y.; Song, F.; Fan, Y.; Cao, H.; Zhang, W.; et al. Exo70 is an independent prognostic factor in colon cancer. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Q.F.; Li, W.J.; Hu, K.S.; Gao, J.; Zhai, W.L.; Yang, J.H.; Zhang, S.J. Exosome biogenesis: Machinery, regulation, and therapeutic implications in cancer. Mol. Cancer 2022, 21, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eddy, R.J.; Weidmann, M.D.; Sharma, V.P.; Condeelis, J.S. Tumor Cell Invadopodia: Invasive Protrusions that Orchestrate Metastasis. Trends Cell Biol. 2017, 27, 595–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriksen, A.; Dyhl-Polk, A.; Chen, I.; Nielsen, D. Checkpoint inhibitors in pancreatic cancer. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2019, 78, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daassi, D.; Mahoney, K.M.; Freeman, G.J. The importance of exosomal PDL1 in tumour immune evasion. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2020, 20, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, S.; Hou, W.; Yao, Y.; Meng, J.; Wei, Y.; Hu, F.; Hu, X.; Wu, J.; Zhang, N.; Xu, R.; et al. Exocyst controls exosome biogenesis via Rab11a. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2022, 27, 535–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hessvik, N.P.; Llorente, A. Current knowledge on exosome biogenesis and release. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2018, 75, 193–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalluri, R.; LeBleu, V.S. The biology, function, and biomedical applications of exosomes. Science 2020, 367, eaau6977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Niel, G.; D’Angelo, G.; Raposo, G. Shedding light on the cell biology of extracellular vesicles. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2018, 19, 213–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.; Xue, C.; Li, X.; Ba, L.; Gu, J.; Sun, Z.; Han, Q.; Zhao, R.C. Effects of Gastric Cancer Cell-Derived Exosomes on the Immune Regulation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells by the NF-kB Signaling Pathway. Stem Cells Dev. 2019, 28, 464–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linton, S.S.; Abraham, T.; Liao, J.; Clawson, G.A.; Butler, P.J.; Fox, T.; Kester, M.; Matters, G.L. Tumor-promoting effects of pancreatic cancer cell exosomes on THP-1-derived macrophages. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0206759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Han, X. Anti-PD-1/PD-L1 therapy of human cancer: Past, present, and future. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 125, 3384–3391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Topalian, S.L.; Taube, J.M.; Anders, R.A.; Pardoll, D.M. Mechanism-driven biomarkers to guide immune checkpoint blockade in cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2016, 16, 275–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Diaz, A.; Shin, D.S.; Moreno, B.H.; Saco, J.; Escuin-Ordinas, H.; Rodriguez, G.A.; Zaretsky, J.M.; Sun, L.; Hugo, W.; Wang, X.; et al. Interferon Receptor Signaling Pathways Regulating PD-L1 and PD-L2 Expression. Cell Rep. 2017, 19, 1189–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Huang, A.C.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, G.; Wu, M.; Xu, W.; Yu, Z.; Yang, J.; Wang, B.; Sun, H.; et al. Exosomal PD-L1 contributes to immunosuppression and is associated with anti-PD-1 response. Nature 2018, 560, 382–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poggio, M.; Hu, T.; Pai, C.C.; Chu, B.; Belair, C.D.; Chang, A.; Montabana, E.; Lang, U.E.; Fu, Q.; Fong, L.; et al. Suppression of Exosomal PD-L1 Induces Systemic Anti-tumor Immunity and Memory. Cell 2019, 177, 414–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyenne, V.; Apaydin, A.; Rodriguez, D.; Spiegelhalter, C.; Hoff-Yoessle, S.; Diem, M.; Tak, S.; Lefebvre, O.; Schwab, Y.; Goetz, J.G.; et al. RAL-1 controls multivesicular body biogenesis and exosome secretion. J. Cell Biol. 2015, 211, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.A.; Tao, K.; Wu, B.; Yu, Z.; Szczepaniak, M.; Rames, M.; Yang, C.; Svitkina, T.; Zhu, Y.; Xu, F.; et al. A phosphoinositide switch mediates exocyst recruitment to multivesicular endosomes for exosome secretion. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 6883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Li, Y.; Wang, M.; Gu, J.; Xu, W.; Cai, H.; Fang, X.; Zhang, X. Exosomes as a new frontier of cancer liquid biopsy. Mol. Cancer 2022, 21, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo, S.A.; Luecke, L.B.; Kahlert, C.; Fernandez, A.F.; Gammon, S.T.; Kaye, J.; LeBleu, V.S.; Mittendorf, E.A.; Weitz, J.; Rahbari, N.; et al. Glypican-1 identifies cancer exosomes and detects early pancreatic cancer. Nature 2015, 523, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristic | N | Exo70 Expression in the Nucleus [n (%)] | p | Exo70 Expression in the Cytoplasm [n (%)] | p | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low | High | Low | High | ||||
| Sex | |||||||
| Men | 63 | 32 | 31 | 0.681 | 18 | 45 | 0.933 |
| Women | 36 | 20 | 16 | 10 | 26 | ||
| Age, years | |||||||
| ≤61 | 51 | 25 | 26 | 0.548 | 14 | 37 | 0.851 |
| >61 | 48 | 27 | 21 | 14 | 34 | ||
| Degree of tumor differentiation | |||||||
| High/Medium grade | 67 | 29 | 38 | 0.01 a | 19 | 48 | 0.981 |
| Low grade | 32 | 9 | 23 | 11 | 21 | ||
| Lymphovascular invasion | |||||||
| No | 60 | 30 | 30 | 0.545 | 31 | 29 | 0.001 a |
| Yes | 39 | 22 | 17 | 7 | 32 | ||
| T stage | |||||||
| T1/2 | 78 | 40 | 38 | 0.806 | 20 | 58 | 0.283 |
| T3/4 | 21 | 12 | 9 | 8 | 13 | ||
| N stage (Lymph node metastasis) | |||||||
| 0 | 47 | 25 | 22 | 0.530 | 21 | 26 | 0.001 a |
| 1 + 2 | 52 | 27 | 25 | 7 | 45 | ||
| Variable | OS | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Hazard Ratio | 95% CI | p | |
| Age, years | |||
| ≤61 vs. >61 | 1.379 | 0.559–1.417 | 0.624 |
| Sex | |||
| Men vs. Women | 1.156 | 0.719–1.881 | 0.560 |
| Degree of tumor differentiation | |||
| High/Medium vs. Low | 1.628 | 1.010–2.622 | 0.045 a |
| T stage | |||
| T1–T2 vs. T3–T4 | 0.984 | 0.556–1.742 | 0.957 |
| N stage | |||
| N0 vs. N1–2 | 1.056 | 0.666–1.673 | 0.817 |
| Lymphovascular invasion | |||
| Yes vs. No | 1.178 | 0.737–1.883 | 0.494 |
| Exo70 in the nucleus | |||
| Low vs. High | 2.343 | 1.355–4.052 | 0.001 a |
| Exo70 in the cytoplasm | |||
| Low vs. High | 1.379 | 0.859–2.214 | 0.181 |
| Variable | OS | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Hazard Ratio | 95% CI | p | |
| Degree of tumor differentiation | |||
| High/Medium vs. Low | 2.057 | 1.249–3.386 | 0.005 a |
| T stage | |||
| T1–T2 vs. T3–T4 | 0.980 | 0.543–1.771 | 0.948 |
| N stage | |||
| N0 vs. N1–2 | 1.031 | 0.647–1.644 | 0.897 |
| Lymphovascular invasion | |||
| Yes vs. No | 1.315 | 0.805–2.148 | 0.274 |
| Exo70 in the nucleus | |||
| Low vs. High | 2.788 | 1.539–5.048 | 0.001 a |
| Exo70 in the cytoplasm | |||
| Low vs. High | 1.068 | 0.639–1.787 | 0.801 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiang, J.; Zheng, B.; Zhao, L.; He, Y.; Lou, F.; Li, R.; Fu, M.; Huang, X.; Zhang, W.; Hong, X.; et al. Exo70 Promotes the Invasion of Pancreatic Cancer Cells via the Regulation of Exosomes. Cancers 2024, 16, 336. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16020336
Xiang J, Zheng B, Zhao L, He Y, Lou F, Li R, Fu M, Huang X, Zhang W, Hong X, et al. Exo70 Promotes the Invasion of Pancreatic Cancer Cells via the Regulation of Exosomes. Cancers. 2024; 16(2):336. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16020336
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiang, Jingzhou, Bowen Zheng, Lingying Zhao, Yuting He, Fanzhuoran Lou, Runyang Li, Miao Fu, Xintian Huang, Wenqing Zhang, Xiaoting Hong, and et al. 2024. "Exo70 Promotes the Invasion of Pancreatic Cancer Cells via the Regulation of Exosomes" Cancers 16, no. 2: 336. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16020336
APA StyleXiang, J., Zheng, B., Zhao, L., He, Y., Lou, F., Li, R., Fu, M., Huang, X., Zhang, W., Hong, X., Xiao, L., & Hu, T. (2024). Exo70 Promotes the Invasion of Pancreatic Cancer Cells via the Regulation of Exosomes. Cancers, 16(2), 336. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16020336







