Tumor Suppression by Anti-Fibroblast Activation Protein Near-Infrared Photoimmunotherapy Targeting Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. Conjugation of Anti-FAP and Anti-PDPN Antibodies with IR700 Dye
2.3. In Vitro NIR-PIT
2.4. Mice
2.5. Mouse Tumor Models
2.6. In Vivo NIR-PIT
2.7. Bone Marrow Chimeras
2.8. In Vivo Depletion of FAP-TK+ Cells by Ganciclovir
2.9. Flow Cytometry
2.10. Histologic and Multiplex Immunofluorescence Staining
2.11. Digital Pathology Image Analysis
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
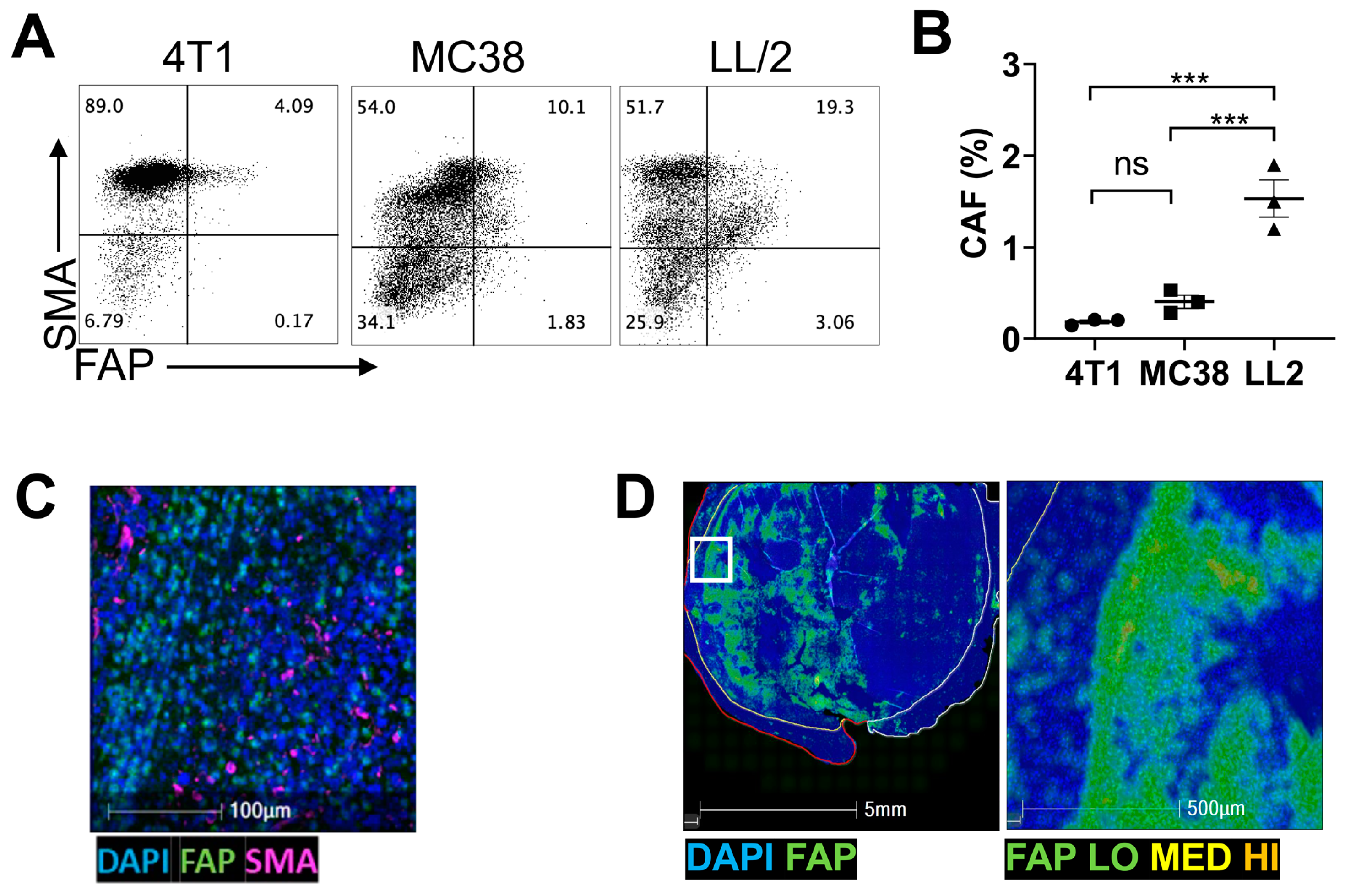
3.1. CAFs Are Present in the TME of Multiple Tumor Models
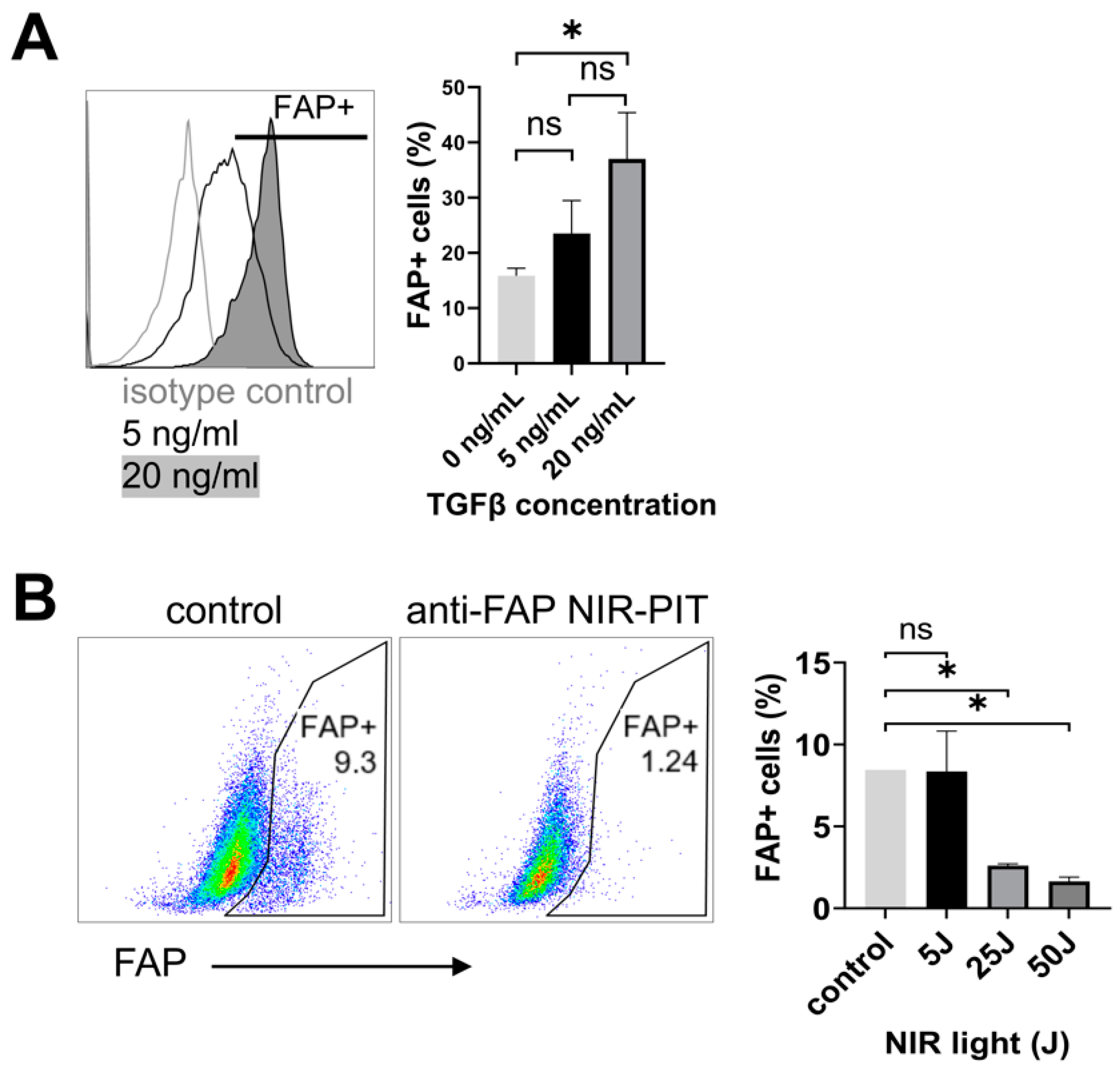
3.2. Anti-FAP-IR700 NIR-PIT Induces Cell Death of FAP-Expressing Fibroblasts In Vitro
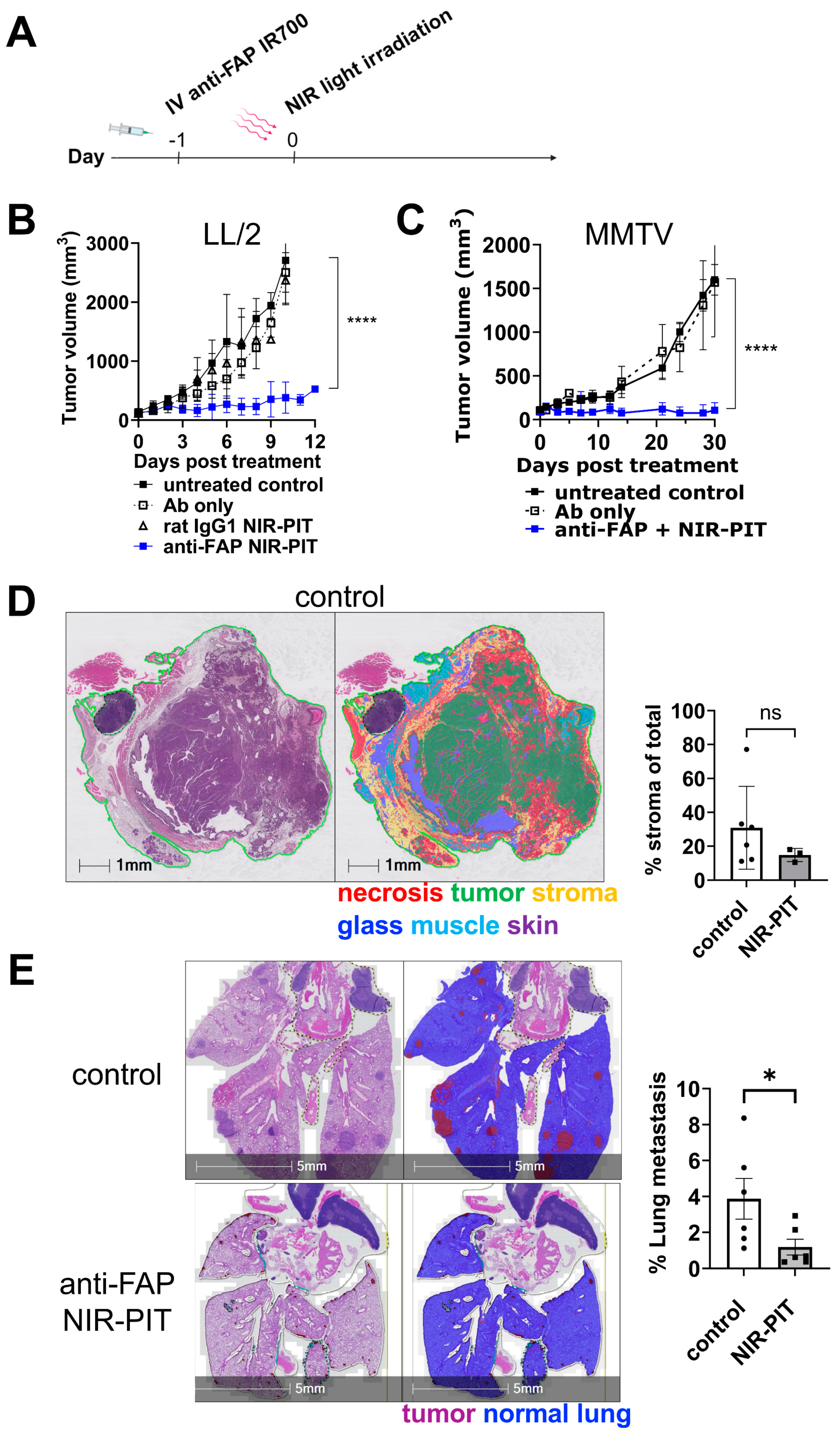
3.3. Anti-FAP NIR-PIT Suppresses Tumor Growth and Lung Metastasis In Vivo
3.4. Anti-PDPN-IR700 NIR-PIT Induces Cell Death of PDPN-Expressing Fibroblasts In Vitro but Did Not Suppress Tumor Growth In Vivo
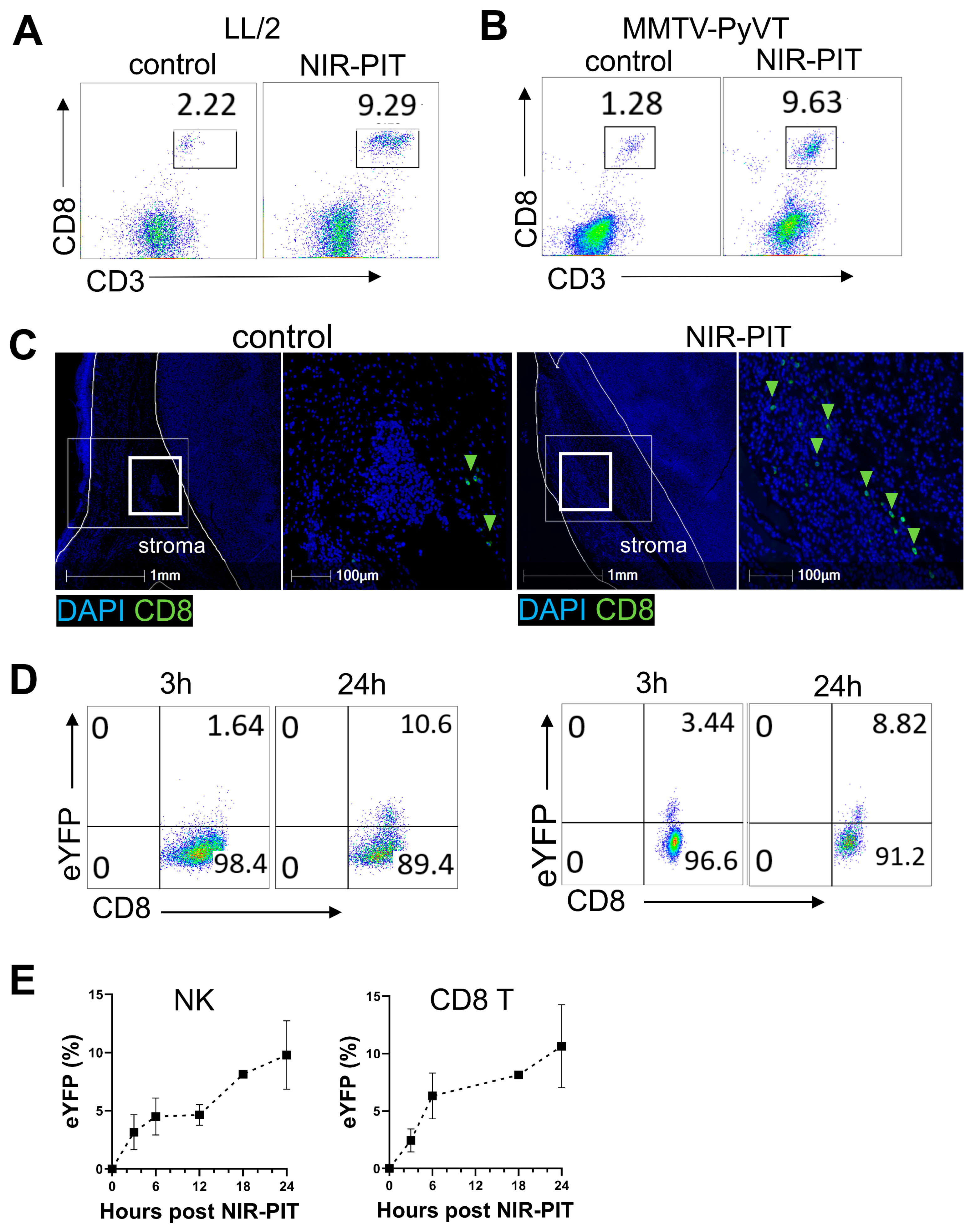
3.5. Anti-FAP NIR-PIT Increases Immune Effector Cells and Their IFN-γ Expression in the Tumor Microenvironment
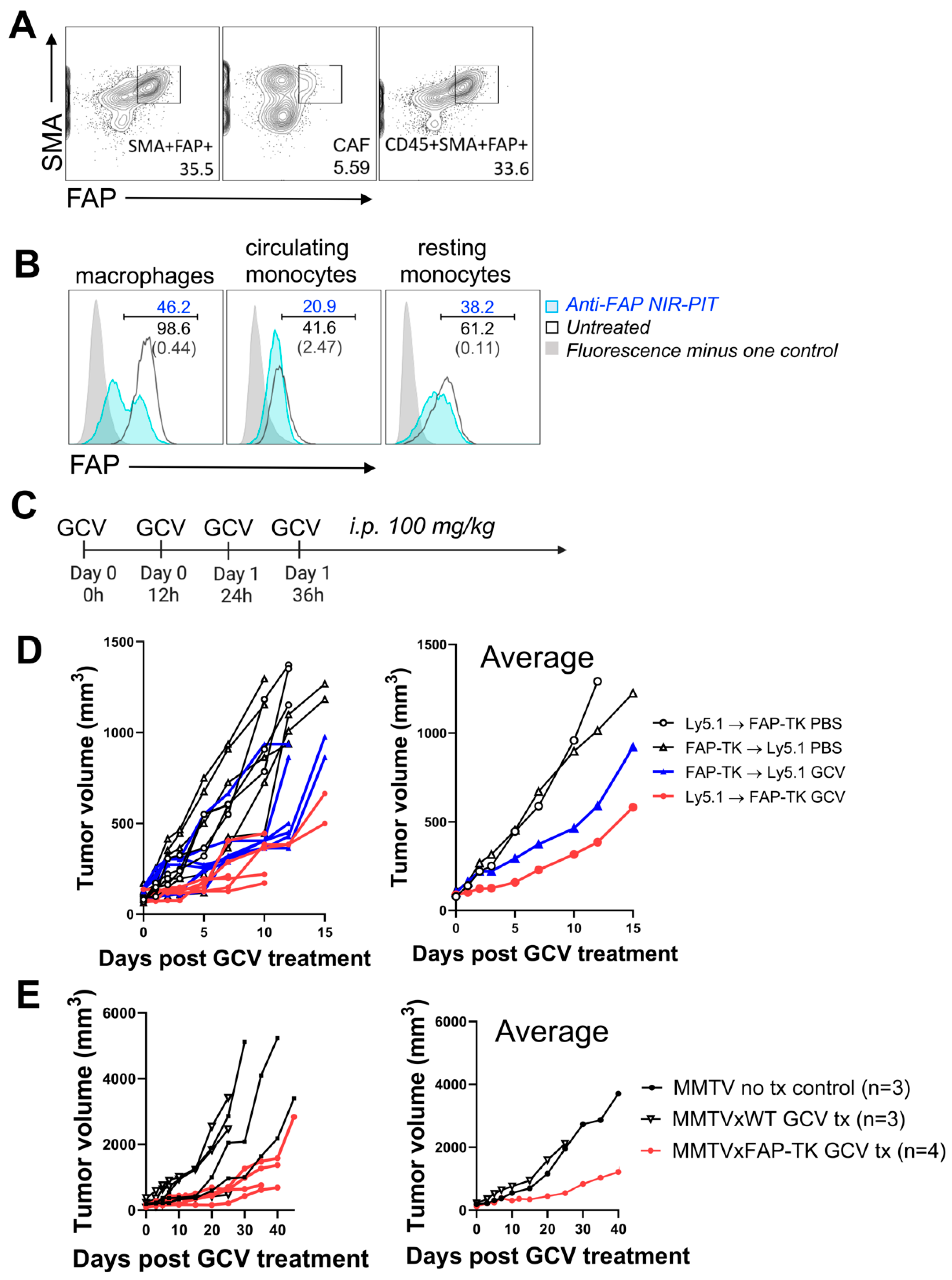
3.6. Depletion of FAP+ CAFs and FAP+ Hematopoietic Cells Both Contribute to Tumor Suppression in Anti-FAP NIR-PIT
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Adams, S.; Miller, G.T.; Jesson, M.I.; Watanabe, T.; Jones, B.; Wallner, B.P. PT-100, a small molecule dipeptidyl peptidase inhibitor, has potent antitumor effects and augments antibody-mediated cytotoxicity via a novel immune mechanism. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 5471–5480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monteran, L.; Erez, N. The Dark Side of Fibroblasts: Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts as Mediators of Immunosuppression in the Tumor Microenvironment. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toledo, B.; Picon-Ruiz, M.; Marchal, J.A.; Peran, M. Dual Role of Fibroblasts Educated by Tumour in Cancer Behavior and Therapeutic Perspectives. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, M.; Yao, J.; Cai, L.; Bachman, K.E.; van den Brule, F.; Velculescu, V.; Polyak, K. Distinct epigenetic changes in the stromal cells of breast cancers. Nat. Genet. 2005, 37, 899–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, M.; Su, G.; Casper, C.; He, R.; Rehrauer, W.; Friedl, A. Heterogeneity of gene expression in stromal fibroblasts of human breast carcinomas and normal breast. Oncogene 2010, 29, 1732–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.T.; Tan, Y.J.; Falasca, M.; Oon, C.E. Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts: Epigenetic Regulation and Therapeutic Intervention in Breast Cancer. Cancers 2020, 12, 2949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nurmik, M.; Ullmann, P.; Rodriguez, F.; Haan, S.; Letellier, E. In search of definitions: Cancer-associated fibroblasts and their markers. Int. J. Cancer 2020, 146, 895–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Li, H.; Liu, L.; Yu, J.; Ren, X. Fibroblast activation protein: A potential therapeutic target in cancer. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2012, 13, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niedermeyer, J.; Garin-Chesa, P.; Kriz, M.; Hilberg, F.; Mueller, E.; Bamberger, U.; Rettig, W.J.; Schnapp, A. Expression of the fibroblast activation protein during mouse embryo development. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 2001, 45, 445–447. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Wang, S.; Kelly, T. Seprase promotes rapid tumor growth and increased microvessel density in a mouse model of human breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 2712–2716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilvaer, T.K.; Rakaee, M.; Hellevik, T.; Ostman, A.; Strell, C.; Bremnes, R.M.; Busund, L.T.; Donnem, T.; Martinez-Zubiaurre, I. Tissue analyses reveal a potential immune-adjuvant function of FAP-1 positive fibroblasts in non-small cell lung cancer. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0192157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, T. Fibroblast activation protein-alpha and dipeptidyl peptidase IV (CD26): Cell-surface proteases that activate cell signaling and are potential targets for cancer therapy. Drug Resist. Updates 2005, 8, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernard, V.; Semaan, A.; Huang, J.; San Lucas, F.A.; Mulu, F.C.; Stephens, B.M.; Guerrero, P.A.; Huang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Kamyabi, N.; et al. Single-Cell Transcriptomics of Pancreatic Cancer Precursors Demonstrates Epithelial and Microenvironmental Heterogeneity as an Early Event in Neoplastic Progression. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 2194–2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.Y.; Kim, H.M.; Koo, J.S. Differential expression of cancer-associated fibroblast-related proteins according to molecular subtype and stromal histology in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2015, 149, 727–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.C.; Lo, A.; Scholler, J.; Sun, J.; Majumdar, R.S.; Kapoor, V.; Antzis, M.; Cotner, C.E.; Johnson, L.A.; Durham, A.C.; et al. Targeting fibroblast activation protein in tumor stroma with chimeric antigen receptor T cells can inhibit tumor growth and augment host immunity without severe toxicity. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2014, 2, 154–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saadi, A.; Shannon, N.B.; Lao-Sirieix, P.; O’Donovan, M.; Walker, E.; Clemons, N.J.; Hardwick, J.S.; Zhang, C.; Das, M.; Save, V.; et al. Stromal genes discriminate preinvasive from invasive disease, predict outcome, and highlight inflammatory pathways in digestive cancers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 2177–2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, M.; Qian, C.; Hu, Z.; Fei, B.; Zhou, H. Biomarkers in Tumor Microenvironment? Upregulation of Fibroblast Activation Protein-alpha Correlates with Gastric Cancer Progression and Poor Prognosis. OMICS 2017, 21, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Errarte, P.; Guarch, R.; Pulido, R.; Blanco, L.; Nunes-Xavier, C.E.; Beitia, M.; Gil, J.; Angulo, J.C.; Lopez, J.I.; Larrinaga, G. The Expression of Fibroblast Activation Protein in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinomas Is Associated with Synchronous Lymph Node Metastases. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0169105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, J.I.; Errarte, P.; Erramuzpe, A.; Guarch, R.; Cortes, J.M.; Angulo, J.C.; Pulido, R.; Irazusta, J.; Llarena, R.; Larrinaga, G. Fibroblast activation protein predicts prognosis in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Hum. Pathol. 2016, 54, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Qiu, X.; Wang, X.; He, J. FAP positive fibroblasts induce immune checkpoint blockade resistance in colorectal cancer via promoting immunosuppression. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 487, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, A.M.; Jung, J.; Aziz, N.; Kissil, J.L.; Pure, E. Targeting fibroblast activation protein inhibits tumor stromagenesis and growth in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 119, 3613–3625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mhawech-Fauceglia, P.; Yan, L.; Sharifian, M.; Ren, X.; Liu, S.; Kim, G.; Gayther, S.A.; Pejovic, T.; Lawrenson, K. Stromal Expression of Fibroblast Activation Protein Alpha (FAP) Predicts Platinum Resistance and Shorter Recurrence in patients with Epithelial Ovarian Cancer. Cancer Microenviron. 2015, 8, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, M.; Yu, D.H.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, C.Y.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Q.H.; Ni, C.R.; Zhu, M.H. Expression of fibroblast activation protein in human pancreatic adenocarcinoma and its clinicopathological significance. World J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 18, 840–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawase, T.; Yasui, Y.; Nishina, S.; Hara, Y.; Yanatori, I.; Tomiyama, Y.; Nakashima, Y.; Yoshida, K.; Kishi, F.; Nakamura, M.; et al. Fibroblast activation protein-alpha-expressing fibroblasts promote the progression of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. BMC Gastroenterol. 2015, 15, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorrentino, C.; Miele, L.; Porta, A.; Pinto, A.; Morello, S. Activation of the A2B adenosine receptor in B16 melanomas induces CXCL12 expression in FAP-positive tumor stromal cells, enhancing tumor progression. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 64274–64288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tulley, S.; Chen, W.T. Transcriptional regulation of seprase in invasive melanoma cells by transforming growth factor-beta signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 15280–15296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, D.; Hou, M.; Guan, Y.S.; Jiang, M.; Yang, Y.; Gou, H.F. Expression of HIF-1alpha and VEGF in colorectal cancer: Association with clinical outcomes and prognostic implications. BMC Cancer 2009, 9, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraman, M.; Bambrough, P.J.; Arnold, J.N.; Roberts, E.W.; Magiera, L.; Jones, J.O.; Gopinathan, A.; Tuveson, D.A.; Fearon, D.T. Suppression of antitumor immunity by stromal cells expressing fibroblast activation protein-alpha. Science 2010, 330, 827–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joyce, J.A.; Fearon, D.T. T cell exclusion, immune privilege, and the tumor microenvironment. Science 2015, 348, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, K.M.; Hsu, S.C.; Chu, Y.R.; Lin, M.Y.; Jiaang, W.T.; Chen, R.H.; Chen, X. Fibroblast activation protein (FAP) is essential for the migration of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells through RhoA activation. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e88772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeBeau, A.M.; Brennen, W.N.; Aggarwal, S.; Denmeade, S.R. Targeting the cancer stroma with a fibroblast activation protein-activated promelittin protoxin. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2009, 8, 1378–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eager, R.M.; Cunningham, C.C.; Senzer, N.; Richards, D.A.; Raju, R.N.; Jones, B.; Uprichard, M.; Nemunaitis, J. Phase II trial of talabostat and docetaxel in advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 21, 464–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eager, R.M.; Cunningham, C.C.; Senzer, N.N.; Stephenson, J., Jr.; Anthony, S.P.; O’Day, S.J.; Frenette, G.; Pavlick, A.C.; Jones, B.; Uprichard, M.; et al. Phase II assessment of talabostat and cisplatin in second-line stage IV melanoma. BMC Cancer 2009, 9, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofheinz, R.D.; al-Batran, S.E.; Hartmann, F.; Hartung, G.; Jager, D.; Renner, C.; Tanswell, P.; Kunz, U.; Amelsberg, A.; Kuthan, H.; et al. Stromal antigen targeting by a humanised monoclonal antibody: An early phase II trial of sibrotuzumab in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Onkologie 2003, 26, 44–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narra, K.; Mullins, S.R.; Lee, H.O.; Strzemkowski-Brun, B.; Magalong, K.; Christiansen, V.J.; McKee, P.A.; Egleston, B.; Cohen, S.J.; Weiner, L.M.; et al. Phase II trial of single agent Val-boroPro (Talabostat) inhibiting Fibroblast Activation Protein in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2007, 6, 1691–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, H.; Choyke, P.L. Near-Infrared Photoimmunotherapy of Cancer. Acc. Chem. Res. 2019, 52, 2332–2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsunaga, M.; Ogawa, M.; Kosaka, N.; Rosenblum, L.T.; Choyke, P.L.; Kobayashi, H. Cancer cell-selective in vivo near infrared photoimmunotherapy targeting specific membrane molecules. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 1685–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cognetti, D.M.; Johnson, J.M.; Curry, J.M.; Kochuparambil, S.T.; McDonald, D.; Mott, F.; Fidler, M.J.; Stenson, K.; Vasan, N.R.; Razaq, M.A.; et al. Phase 1/2a, open-label, multicenter study of RM-1929 photoimmunotherapy in patients with locoregional, recurrent head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Head Neck 2021, 43, 3875–3887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, K.; Sato, N.; Xu, B.; Nakamura, Y.; Nagaya, T.; Choyke, P.L.; Hasegawa, Y.; Kobayashi, H. Spatially selective depletion of tumor-associated regulatory T cells with near-infrared photoimmunotherapy. Sci. Transl. Med. 2016, 8, 352ra110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsube, R.; Noma, K.; Ohara, T.; Nishiwaki, N.; Kobayashi, T.; Komoto, S.; Sato, H.; Kashima, H.; Kato, T.; Kikuchi, S.; et al. Fibroblast activation protein targeted near infrared photoimmunotherapy (NIR PIT) overcomes therapeutic resistance in human esophageal cancer. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, H.; Noma, K.; Ohara, T.; Kawasaki, K.; Akai, M.; Kobayashi, T.; Nishiwaki, N.; Narusaka, T.; Komoto, S.; Kashima, H.; et al. Dual-targeted near-infrared photoimmunotherapy for esophageal cancer and cancer-associated fibroblasts in the tumor microenvironment. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 20152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, S.; Noma, K.; Ohara, T.; Kashima, H.; Sato, H.; Kato, T.; Urano, S.; Katsube, R.; Hashimoto, Y.; Tazawa, H.; et al. Photoimmunotherapy for cancer-associated fibroblasts targeting fibroblast activation protein in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2019, 20, 1234–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McAndrews, K.M.; Miyake, T.; Ehsanipour, E.A.; Kelly, P.J.; Becker, L.M.; McGrail, D.J.; Sugimoto, H.; LeBleu, V.S.; Ge, Y.; Kalluri, R. Dermal alphaSMA(+) myofibroblasts orchestrate skin wound repair via beta1 integrin and independent of type I collagen production. EMBO J. 2022, 41, e109470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reinhardt, R.L.; Liang, H.E.; Locksley, R.M. Cytokine-secreting follicular T cells shape the antibody repertoire. Nat. Immunol. 2009, 10, 385–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guy, C.T.; Cardiff, R.D.; Muller, W.J. Induction of mammary tumors by expression of polyomavirus middle T oncogene: A transgenic mouse model for metastatic disease. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1992, 12, 954–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, E.Y.; Jones, J.G.; Li, P.; Zhu, L.; Whitney, K.D.; Muller, W.J.; Pollard, J.W. Progression to malignancy in the polyoma middle T oncoprotein mouse breast cancer model provides a reliable model for human diseases. Am. J. Pathol. 2003, 163, 2113–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feig, C.; Jones, J.O.; Kraman, M.; Wells, R.J.; Deonarine, A.; Chan, D.S.; Connell, C.M.; Roberts, E.W.; Zhao, Q.; Caballero, O.L.; et al. Targeting CXCL12 from FAP-expressing carcinoma-associated fibroblasts synergizes with anti-PD-L1 immunotherapy in pancreatic cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 20212–20217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Lin, Y.; Shi, Y.; Li, B.; Liu, W.; Yin, W.; Dang, Y.; Chu, Y.; Fan, J.; He, R. FAP Promotes Immunosuppression by Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts in the Tumor Microenvironment via STAT3-CCL2 Signaling. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 4124–4135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attalla, S.; Taifour, T.; Bui, T.; Muller, W. Insights from transgenic mouse models of PyMT-induced breast cancer: Recapitulating human breast cancer progression in vivo. Oncogene 2021, 40, 475–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartoschek, M.; Oskolkov, N.; Bocci, M.; Lovrot, J.; Larsson, C.; Sommarin, M.; Madsen, C.D.; Lindgren, D.; Pekar, G.; Karlsson, G.; et al. Spatially and functionally distinct subclasses of breast cancer-associated fibroblasts revealed by single cell RNA sequencing. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 5150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.W.; Kwak, H.S.; Kang, M.H.; Park, Y.Y.; Jeong, G.S. Fibroblast-associated tumour microenvironment induces vascular structure-networked tumouroid. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyake, M.; Hori, S.; Morizawa, Y.; Tatsumi, Y.; Nakai, Y.; Anai, S.; Torimoto, K.; Aoki, K.; Tanaka, N.; Shimada, K.; et al. CXCL1-Mediated Interaction of Cancer Cells with Tumor-Associated Macrophages and Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts Promotes Tumor Progression in Human Bladder Cancer. Neoplasia 2016, 18, 636–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, K.U. Models of breast cancer: Quo vadis, animal modeling? Breast Cancer Res. 2004, 6, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hingorani, S.R.; Wang, L.; Multani, A.S.; Combs, C.; Deramaudt, T.B.; Hruban, R.H.; Rustgi, A.K.; Chang, S.; Tuveson, D.A. Trp53R172H and KrasG12D cooperate to promote chromosomal instability and widely metastatic pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma in mice. Cancer Cell 2005, 7, 469–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, A.M.; Wiseman, G.; Welt, S.; Adjei, A.; Lee, F.T.; Hopkins, W.; Divgi, C.R.; Hanson, L.H.; Mitchell, P.; Gansen, D.N.; et al. A Phase I dose-escalation study of sibrotuzumab in patients with advanced or metastatic fibroblast activation protein-positive cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2003, 9, 1639–1647. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kurebayashi, Y.; Olkowski, C.P.; Lane, K.C.; Vasalatiy, O.V.; Xu, B.C.; Okada, R.; Furusawa, A.; Choyke, P.L.; Kobayashi, H.; Sato, N. Rapid Depletion of Intratumoral Regulatory T Cells Induces Synchronized CD8 T- and NK-cell Activation and IFNgamma-Dependent Tumor Vessel Regression. Cancer Res. 2021, 81, 3092–3104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, J.; Barnett, J.D.; Krishnamachary, B.; Mironchik, Y.; Luo, C.K.; Kobayashi, H.; Bhujwalla, Z.M. Evaluating near-infrared photoimmunotherapy for targeting fibroblast activation protein-alpha expressing cells in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Sci. 2023, 114, 236–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glabman, R.A.; Choyke, P.L.; Sato, N. Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts: Tumorigenicity and Targeting for Cancer Therapy. Cancers 2022, 14, 3906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astarita, J.L.; Keerthivasan, S.; Husain, B.; Senbabaoglu, Y.; Verschueren, E.; Gierke, S.; Pham, V.C.; Peterson, S.M.; Chalouni, C.; Pierce, A.A.; et al. The neutrophil protein CD177 is a novel PDPN receptor that regulates human cancer-associated fibroblast physiology. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0260800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, T.; Furusawa, A.; Okada, R.; Inagaki, F.; Wakiyama, H.; Furumoto, H.; Fukushima, H.; Okuyama, S.; Choyke, P.L.; Kobayashi, H. Near-Infrared Photoimmunotherapy Targeting Podoplanin-Expressing Cancer Cells and Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2023, 22, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astarita, J.L.; Acton, S.E.; Turley, S.J. Podoplanin: Emerging functions in development, the immune system, and cancer. Front. Immunol. 2012, 3, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renart, J.; Carrasco-Ramirez, P.; Fernandez-Munoz, B.; Martin-Villar, E.; Montero, L.; Yurrita, M.M.; Quintanilla, M. New insights into the role of podoplanin in epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Int. Rev. Cell Mol. Biol. 2015, 317, 185–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki-Inoue, K.; Osada, M.; Ozaki, Y. Physiologic and pathophysiologic roles of interaction between C-type lectin-like receptor 2 and podoplanin: Partners from in utero to adulthood. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2017, 15, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, H.; Choyke, P.L. Super enhanced permeability and retention (SUPR) effects in tumors following near infrared photoimmunotherapy. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 12504–12509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, Y.; Mochida, A.; Choyke, P.L.; Kobayashi, H. Nanodrug Delivery: Is the Enhanced Permeability and Retention Effect Sufficient for Curing Cancer? Bioconjug. Chem. 2016, 27, 2225–2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolini, G.; Balzan, S.; Forini, F. Activated fibroblasts in cardiac and cancer fibrosis: An overview of analogies and new potential therapeutic options. Life Sci. 2023, 321, 121575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corsi, F.; Sorrentino, L.; Albasini, S.; Colombo, F.; Cigognini, M.; Massari, A.; Morasso, C.; Mazzucchelli, S.; Piccotti, F.; Ardizzone, S.; et al. Circulating Fibroblast Activation Protein as Potential Biomarker in Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 725726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, H.; Furusawa, A.; Rosenberg, A.; Choyke, P.L. Near-infrared photoimmunotherapy of cancer: A new approach that kills cancer cells and enhances anti-cancer host immunity. Int. Immunol. 2021, 33, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Pu, Y.; Huang, S.; Yang, C.; Yang, F.; Pu, Y.; Li, J.; Chen, L.; Huang, Y. FAPI-PET/CT in Cancer Imaging: A Potential Novel Molecule of the Century. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 854658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzgerald, A.A.; Weiner, L.M. The role of fibroblast activation protein in health and malignancy. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2020, 39, 783–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loktev, A.; Lindner, T.; Burger, E.M.; Altmann, A.; Giesel, F.; Kratochwil, C.; Debus, J.; Marme, F.; Jager, D.; Mier, W.; et al. Development of Fibroblast Activation Protein-Targeted Radiotracers with Improved Tumor Retention. J. Nucl. Med. 2019, 60, 1421–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loktev, A.; Lindner, T.; Mier, W.; Debus, J.; Altmann, A.; Jager, D.; Giesel, F.; Kratochwil, C.; Barthe, P.; Roumestand, C.; et al. A Tumor-Imaging Method Targeting Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts. J. Nucl. Med. 2018, 59, 1423–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Pang, Y.; Wu, J.; Zhao, L.; Hao, B.; Wu, J.; Wei, J.; Wu, S.; Zhao, L.; Luo, Z.; et al. Comparison of [(68)Ga]Ga-DOTA-FAPI-04 and [(18)F] FDG PET/CT for the diagnosis of primary and metastatic lesions in patients with various types of cancer. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2020, 47, 1820–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilardi, L.; Airo Farulla, L.S.; Demirci, E.; Clerici, I.; Omodeo Sale, E.; Ceci, F. Imaging Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts (CAFs) with FAPi PET. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnold, J.N.; Magiera, L.; Kraman, M.; Fearon, D.T. Tumoral immune suppression by macrophages expressing fibroblast activation protein-alpha and heme oxygenase-1. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2014, 2, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, E.W.; Deonarine, A.; Jones, J.O.; Denton, A.E.; Feig, C.; Lyons, S.K.; Espeli, M.; Kraman, M.; McKenna, B.; Wells, R.J.; et al. Depletion of stromal cells expressing fibroblast activation protein-alpha from skeletal muscle and bone marrow results in cachexia and anemia. J. Exp. Med. 2013, 210, 1137–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, E.; Chinnasamy, D.; Yu, Z.; Morgan, R.A.; Lee, C.C.; Restifo, N.P.; Rosenberg, S.A. Immune targeting of fibroblast activation protein triggers recognition of multipotent bone marrow stromal cells and cachexia. J. Exp. Med. 2013, 210, 1125–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagaya, T.; Okuyama, S.; Ogata, F.; Maruoka, Y.; Choyke, P.L.; Kobayashi, H. Endoscopic near infrared photoimmunotherapy using a fiber optic diffuser for peritoneal dissemination of gastric cancer. Cancer Sci. 2018, 109, 1902–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuyama, S.; Nagaya, T.; Sato, K.; Ogata, F.; Maruoka, Y.; Choyke, P.L.; Kobayashi, H. Interstitial near-infrared photoimmunotherapy: Effective treatment areas and light doses needed for use with fiber optic diffusers. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 11159–11169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Glabman, R.A.; Olkowski, C.P.; Minor, H.A.; Bassel, L.L.; Kedei, N.; Choyke, P.L.; Sato, N. Tumor Suppression by Anti-Fibroblast Activation Protein Near-Infrared Photoimmunotherapy Targeting Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts. Cancers 2024, 16, 449. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16020449
Glabman RA, Olkowski CP, Minor HA, Bassel LL, Kedei N, Choyke PL, Sato N. Tumor Suppression by Anti-Fibroblast Activation Protein Near-Infrared Photoimmunotherapy Targeting Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts. Cancers. 2024; 16(2):449. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16020449
Chicago/Turabian StyleGlabman, Raisa A., Colleen P. Olkowski, Hannah A. Minor, Laura L. Bassel, Noemi Kedei, Peter L. Choyke, and Noriko Sato. 2024. "Tumor Suppression by Anti-Fibroblast Activation Protein Near-Infrared Photoimmunotherapy Targeting Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts" Cancers 16, no. 2: 449. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16020449
APA StyleGlabman, R. A., Olkowski, C. P., Minor, H. A., Bassel, L. L., Kedei, N., Choyke, P. L., & Sato, N. (2024). Tumor Suppression by Anti-Fibroblast Activation Protein Near-Infrared Photoimmunotherapy Targeting Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts. Cancers, 16(2), 449. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16020449





