Risk-Stratified Radiotherapy in Pediatric Cancer
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
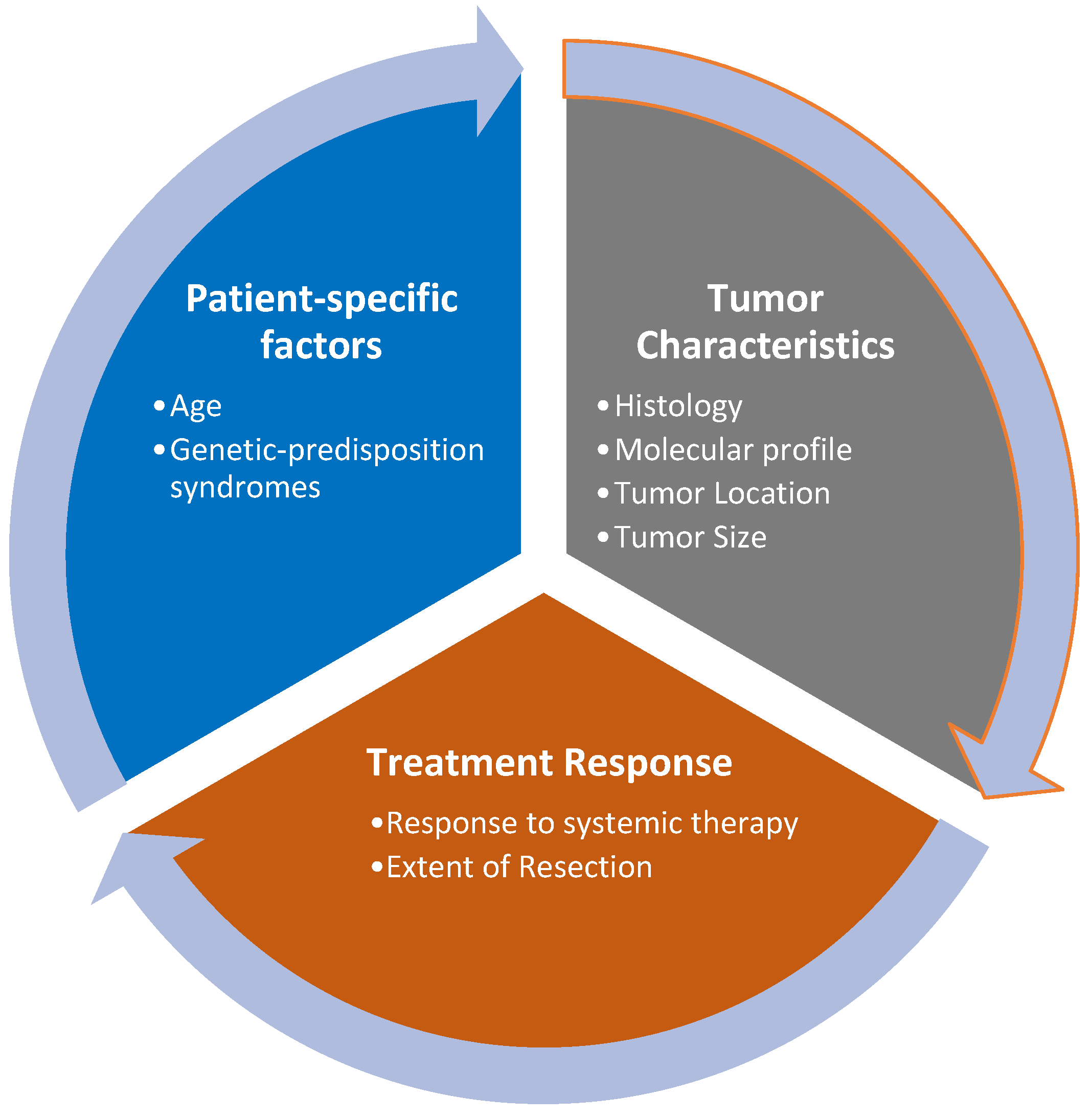
2. Assessment of Prognostic Factors
2.1. Tumor Characteristics
2.2. Patient-Specific Factors
3. De-Escalation of Radiotherapy Using Molecular Characterization
3.1. Medulloblastoma
3.2. Ependymomas
4. De-Escalation of Radiotherapy after Excellent Response to Chemotherapy
4.1. Hodgkin Lymphoma (HL)
4.2. Pediatric Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma
4.3. Intracranial Germ Cell Tumors (GCT)
4.4. Low-Grade Glioma
4.5. Wilms Tumor
5. Escalation of Radiotherapy Using Poor Response to Chemotherapy
5.1. Rhabdomyosarcoma
5.2. Ewing Sarcoma (ES)
6. Escalation of Radiotherapy Using Hypofractionation and SABR
7. Role of Modern Radiation Techniques
8. Conclusions and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Upadhyay, R.; Yadav, D.; Venkatesulu, B.P.; Singh, R.; Baliga, S.; Raval, R.R.; Lazow, M.A.; Salloum, R.; Fouladi, M.; Mardis, E.R.; et al. Risk of Secondary Malignant Neoplasms in Children Following Proton Therapy vs. Photon Therapy for Primary CNS Tumors: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 893855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyay, R.; Klamer, B.; Matsui, J.; Chakravarthy, V.B.; Scharschmidt, T.; Yeager, N.; Setty, B.A.; Cripe, T.P.; Roberts, R.D.; Aldrink, J.H.; et al. Disease Control and Toxicity Outcomes after Stereotactic Ablative Radiation Therapy for Recurrent and/or Metastatic Cancers in Young-Adult and Pediatric Patients. Cancers 2024, 16, 2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.; Valluri, A.; Didwania, P.; Lehrer, E.J.; Baliga, S.; Hiniker, S.; Braunstein, S.E.; Murphy, E.S.; Lazarev, S.; Tinkle, C.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy for Pediatric Malignancies: The LITE-SABR Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Adv. Radiat. Oncol. 2023, 8, 101123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, C.J.; Terezakis, S.A. The Evolving Role of Radiotherapy for Pediatric Cancers with Advancements in Molecular Tumor Characterization and Targeted Therapies. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 679701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, M.D.; Northcott, P.A.; Korshunov, A.; Remke, M.; Cho, Y.-J.; Clifford, S.C.; Eberhart, C.G.; Parsons, D.W.; Rutkowski, S.; Gajjar, A.; et al. Molecular Subgroups of Medulloblastoma: The Current Consensus. Acta Neuropathol. 2012, 123, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostrom, Q.T.; Price, M.; Neff, C.; Cioffi, G.; Waite, K.A.; Kruchko, C.; Barnholtz-Sloan, J.S. CBTRUS Statistical Report: Primary Brain and Other Central Nervous System Tumors Diagnosed in the United States in 2016–2020. Neuro Oncol. 2023, 25, iv1–iv99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Packer, R.J.; Sutton, L.N.; Elterman, R.; Lange, B.; Goldwein, J.; Nicholson, H.S.; Mulne, L.; Boyett, J.; D’Angio, G.; Wechsler-Jentzsch, K. Outcome for Children with Medulloblastoma Treated with Radiation and Cisplatin, CCNU, and Vincristine Chemotherapy. J. Neurosurg. 1994, 81, 690–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, R.M.; Richardson, S.; Schwalbe, E.C.; Hicks, D.; Lindsey, J.C.; Crosier, S.; Rafiee, G.; Grabovska, Y.; Wharton, S.B.; Jacques, T.S.; et al. Time, Pattern, and Outcome of Medulloblastoma Relapse and Their Association with Tumour Biology at Diagnosis and Therapy: A Multicentre Cohort Study. Lancet Child. Adolesc. Health 2020, 4, 865–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Packer, R.J.; Gajjar, A.; Vezina, G.; Rorke-Adams, L.; Burger, P.C.; Robertson, P.L.; Bayer, L.; LaFond, D.; Donahue, B.R.; Marymont, M.H.; et al. Phase III Study of Craniospinal Radiation Therapy Followed by Adjuvant Chemotherapy for Newly Diagnosed Average-Risk Medulloblastoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 24, 4202–4208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avizonis, V.N.; Fuller, D.B.; Thomson, J.W.; Walker, M.J.; Nilsson, D.E.; Menlove, R.L. Late Effects Following Central Nervous System Radiation in a Pediatric Population. Neuropediatrics 1992, 23, 228–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harbron, R.W.; Feltbower, R.G.; Glaser, A.; Lilley, J.; Pearce, M.S. Secondary Malignant Neoplasms Following Radiotherapy for Primary Cancer in Children and Young Adults. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 2014, 31, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eaton, B.R.; Esiashvili, N.; Kim, S.; Patterson, B.; Weyman, E.A.; Thornton, L.T.; Mazewski, C.; MacDonald, T.J.; Ebb, D.; MacDonald, S.M.; et al. Endocrine Outcomes with Proton and Photon Radiotherapy for Standard Risk Medulloblastoma. Neuro Oncol. 2016, 18, 881–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gajjar, A.; Chintagumpala, M.; Ashley, D.; Kellie, S.; Kun, L.E.; Merchant, T.E.; Woo, S.; Wheeler, G.; Ahern, V.; Krasin, M.J.; et al. Risk-Adapted Craniospinal Radiotherapy Followed by High-Dose Chemotherapy and Stem-Cell Rescue in Children with Newly Diagnosed Medulloblastoma (St Jude Medulloblastoma-96): Long-Term Results from a Prospective, Multicentre Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2006, 7, 813–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, P.R.; Deutsch, M.; Kepner, J.L.; Boyett, J.M.; Krischer, J.; Aronin, P.; Albright, L.; Allen, J.C.; Packer, R.J.; Linggood, R.; et al. Low-Stage Medulloblastoma: Final Analysis of Trial Comparing Standard-Dose with Reduced-Dose Neuraxis Irradiation. J. Clin. Oncol. 2000, 18, 3004–3011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashley, D.M.; Merchant, T.E.; Strother, D.; Zhou, T.; Duffner, P.; Burger, P.C.; Miller, D.C.; Lyon, N.; Bonner, M.J.; Msall, M.; et al. Induction Chemotherapy and Conformal Radiation Therapy for Very Young Children with Nonmetastatic Medulloblastoma: Children’s Oncology Group Study P9934. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 3181–3186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deutsch, M. Radiotherapy for Primary Brain Tumors in Very Young Children. Cancer 1982, 50, 2785–2789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiltie, A.E.; Lashford, L.S.; Gattamaneni, H.R. Survival and Late Effects in Medulloblastoma Patients Treated with Craniospinal Irradiation under Three Years Old. Med. Pediatr. Oncol. 1997, 28, 348–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalski, J.M.; Janss, A.J.; Vezina, L.G.; Smith, K.S.; Billups, C.A.; Burger, P.C.; Embry, L.M.; Cullen, P.L.; Hardy, K.K.; Pomeroy, S.L.; et al. Children’s Oncology Group Phase III Trial of Reduced-Dose and Reduced-Volume Radiotherapy with Chemotherapy for Newly Diagnosed Average-Risk Medulloblastoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 2685–2697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aridgides, P.D.; Kang, G.; Mazewski, C.; Merchant, T.E. Outcomes after Radiation Therapy for Very Young Children with High-Risk Medulloblastoma or Supratentorial Primitive Neuroectodermal Tumor Treated on COG ACNS0334. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2019, 105, S109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, J.T.; Tinkle, C.L.; Huang, J.; Onar-Thomas, A.; Srinivasan, S.; Tumlin, P.; Becksfort, J.B.; Klimo, P.; Boop, F.A.; Robinson, G.W.; et al. Revised Clinical and Molecular Risk Strata Define the Incidence and Pattern of Failure in Medulloblastoma Following Risk-Adapted Radiotherapy and Dose-Intensive Chemotherapy: Results from a Phase III Multi-Institutional Study. Neuro Oncol. 2022, 24, 1166–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louis, D.N.; Perry, A.; Wesseling, P.; Brat, D.J.; Cree, I.A.; Figarella-Branger, D.; Hawkins, C.; Ng, H.K.; Pfister, S.M.; Reifenberger, G.; et al. The 2021 WHO Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System: A Summary. Neuro Oncol. 2021, 23, 1231–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Northcott, P.A.; Buchhalter, I.; Morrissy, A.S.; Hovestadt, V.; Weischenfeldt, J.; Ehrenberger, T.; Gröbner, S.; Segura-Wang, M.; Zichner, T.; Rudneva, V.A.; et al. The Whole-Genome Landscape of Medulloblastoma Subtypes. Nature 2017, 547, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gajjar, A.; Robinson, G.W.; Smith, K.S.; Lin, T.; Merchant, T.E.; Chintagumpala, M.; Mahajan, A.; Su, J.; Bouffet, E.; Bartels, U.; et al. Outcomes by Clinical and Molecular Features in Children with Medulloblastoma Treated with Risk-Adapted Therapy: Results of an International Phase III Trial (SJMB03). J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 822–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramaswamy, V.; Remke, M.; Bouffet, E.; Bailey, S.; Clifford, S.C.; Doz, F.; Kool, M.; Dufour, C.; Vassal, G.; Milde, T.; et al. Risk Stratification of Childhood Medulloblastoma in the Molecular Era: The Current Consensus. Acta Neuropathol. 2016, 131, 821–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, G.W.; Merchant, T.E.; Orr, B.A.; Bass, J.K.; Conklin, H.M.; Bag, A.; Dhanda, S.K.; Pinto, S.; Delaney, A.; Mikkelsen, M.; et al. MDB-92. Effect of Reduced-Dose Craniospinal Irradiation and Reduced-Dose Adjuvant Chemotherapy on Children and Adolescents with Wnt Medulloblastoma without Residual or Metastatic Disease: Results from the Sjmb12 Clinical Trial. Neuro Oncol. 2024, 26, 0. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, K.; Bandopadhayay, P.; Chi, S.; London, W.; Rodriguez, F.; Hawkins, C.; Yang, E.; Aguilera, D.; Castellino, R.; MacDonald, T.; et al. MEDU-34. Pilot Study of a Surgery and Chemotherapy-Only Approach in the Upfront Therapy of Children with Wnt-Positive Standard Risk Medulloblastoma. Neuro Oncol. 2019, 21, ii110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, E.M.; Ashley, D.; Landi, D. Current Medulloblastoma Subgroup Specific Clinical Trials. Transl. Pediatr. 2020, 9, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouffet, E.; Perilongo, G.; Canete, A.; Massimino, M. Intracranial Ependymomas in Children: A Critical Review of Prognostic Factors and a Plea for Cooperation. Med. Pediatr. Oncol. 1998, 30, 319–329; discussion 329–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merchant, T.E.; Li, C.; Xiong, X.; Kun, L.E.; Boop, F.A.; Sanford, R.A. Conformal Radiotherapy after Surgery for Paediatric Ependymoma: A Prospective Study. Lancet Oncol. 2009, 10, 258–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, L.; Pueschel, J.; Spetzler, R.; Shapiro, W.; Coons, S.; Thomas, T.; Speiser, B. Is Gross-Total Resection Sufficient Treatment for Posterior Fossa Ependymomas? J. Neurosurg. 2005, 102, 629–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, P.L.; Zeltzer, P.M.; Boyett, J.M.; Rorke, L.B.; Allen, J.C.; Geyer, J.R.; Stanley, P.; Li, H.; Albright, A.L.; McGuire-Cullen, P.; et al. Survival and Prognostic Factors Following Radiation Therapy and Chemotherapy for Ependymomas in Children: A Report of the Children’s Cancer Group. J. Neurosurg. 1998, 88, 695–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zacharoulis, S.; Levy, A.; Chi, S.N.; Gardner, S.; Rosenblum, M.; Miller, D.C.; Dunkel, I.; Diez, B.; Sposto, R.; Ji, L.; et al. Outcome for Young Children Newly Diagnosed with Ependymoma, Treated with Intensive Induction Chemotherapy Followed by Myeloablative Chemotherapy and Autologous Stem Cell Rescue. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2007, 49, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merchant, T.E.; Bendel, A.E.; Sabin, N.D.; Burger, P.C.; Shaw, D.W.; Chang, E.; Wu, S.; Zhou, T.; Eisenstat, D.D.; Foreman, N.K.; et al. Conformal Radiation Therapy for Pediatric Ependymoma, Chemotherapy for Incompletely Resected Ependymoma, and Observation for Completely Resected, Supratentorial Ependymoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 974–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pajtler, K.W.; Witt, H.; Sill, M.; Jones, D.T.W.; Hovestadt, V.; Kratochwil, F.; Wani, K.; Tatevossian, R.; Punchihewa, C.; Johann, P.; et al. Molecular Classification of Ependymal Tumors across All CNS Compartments, Histopathological Grades, and Age Groups. Cancer Cell 2015, 27, 728–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramaswamy, V.; Hielscher, T.; Mack, S.C.; Lassaletta, A.; Lin, T.; Pajtler, K.W.; Jones, D.T.W.; Luu, B.; Cavalli, F.M.G.; Aldape, K.; et al. Therapeutic Impact of Cytoreductive Surgery and Irradiation of Posterior Fossa Ependymoma in the Molecular Era: A Retrospective Multicohort Analysis. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 2468–2477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witt, H.; Mack, S.C.; Ryzhova, M.; Bender, S.; Sill, M.; Isserlin, R.; Benner, A.; Hielscher, T.; Milde, T.; Remke, M.; et al. Delineation of Two Clinically and Molecularly Distinct Subgroups of Posterior Fossa Ependymoma. Cancer Cell 2011, 20, 143–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.; Onar-Thomas, A.; Ellison, D.; Owens-Pickle, E.; Wu, S.; Leary, S.E.S.; Fouladi, M.; Merchant, T.; Gajjar, A.; Foreman, N. EPEN-54. Acns0831, Phase III Randomized Trial of Post-Radiation Chemotherapy in Patients with Newly Diagnosed Ependymoma Ages 1 to 21 Years. Neuro Oncol. 2020, 22, iii318–iii319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodgson, D.C.; Hudson, M.M.; Constine, L.S. Pediatric Hodgkin Lymphoma: Maximizing Efficacy and Minimizing Toxicity. Semin. Radiat. Oncol. 2007, 17, 230–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudson, M.M.; Neglia, J.P.; Woods, W.G.; Sandlund, J.T.; Pui, C.-H.; Kun, L.E.; Robison, L.L.; Green, D.M. Lessons from the Past: Opportunities to Improve Childhood Cancer Survivor Care through Outcomes Investigations of Historical Therapeutic Approaches for Pediatric Hematological Malignancies. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2012, 58, 334–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nachman, J.B.; Sposto, R.; Herzog, P.; Gilchrist, G.S.; Wolden, S.L.; Thomson, J.; Kadin, M.E.; Pattengale, P.; Davis, P.C.; Hutchinson, R.J.; et al. Randomized Comparison of Low-Dose Involved-Field Radiotherapy and No Radiotherapy for Children with Hodgkin’s Disease Who Achieve a Complete Response to Chemotherapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2002, 20, 3765–3771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudson, M.M. Pediatric Hodgkin’s Therapy: Time for a Paradigm Shift. J. Clin. Oncol. 2002, 20, 3755–3757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, D.L.; Chen, L.; Wolden, S.; Buxton, A.; McCarten, K.; FitzGerald, T.J.; Kessel, S.; De Alarcon, P.A.; Chen, A.R.; Kobrinsky, N.; et al. Dose-Intensive Response-Based Chemotherapy and Radiation Therapy for Children and Adolescents with Newly Diagnosed Intermediate-Risk Hodgkin Lymphoma: A Report from the Children’s Oncology Group Study AHOD0031. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 3651–3658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keller, F.G.; Castellino, S.M.; Chen, L.; Pei, Q.; Voss, S.D.; McCarten, K.M.; Senn, S.L.; Buxton, A.B.; Bush, R.; Constine, L.S.; et al. Results of the AHOD0431 Trial of Response Adapted Therapy and a Salvage Strategy for Limited Stage, Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma: A Report from the Children’s Oncology Group. Cancer 2018, 124, 3210–3219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mauz-Körholz, C.; Landman-Parker, J.; Fernández-Teijeiro, A.; Attarbaschi, A.; Balwierz, W.; Bartelt, J.M.; Beishuizen, A.; Boudjemaa, S.; Cepelova, M.; Ceppi, F.; et al. Response-Adapted Omission of Radiotherapy in Children and Adolescents with Early-Stage Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma and an Adequate Response to Vincristine, Etoposide, Prednisone, and Doxorubicin (EuroNet-PHL-C1): A Titration Study. Lancet Oncol. 2023, 24, 252–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jhawar, S.R.; Rivera-Núñez, Z.; Drachtman, R.; Cole, P.D.; Hoppe, B.S.; Parikh, R.R. Association of Combined Modality Therapy vs Chemotherapy Alone with Overall Survival in Early-Stage Pediatric Hodgkin Lymphoma. JAMA Oncol. 2019, 5, 689–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oeffinger, K.C.; Stratton, K.L.; Hudson, M.M.; Leisenring, W.M.; Henderson, T.O.; Howell, R.M.; Wolden, S.L.; Constine, L.S.; Diller, L.R.; Sklar, C.A.; et al. Impact of Risk-Adapted Therapy for Pediatric Hodgkin Lymphoma on Risk of Long-Term Morbidity: A Report from the Childhood Cancer Survivor Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 2266–2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultan, I.; Casanova, M.; Ferrari, A.; Rihani, R.; Rodriguez-Galindo, C. Differential Features of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma in Children and Adults: A SEER Study. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2010, 55, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayan, I.; Kaytan, E.; Ayan, N. Childhood Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma: From Biology to Treatment. Lancet Oncol. 2003, 4, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheuk, D.K.L.; Billups, C.A.; Martin, M.G.; Roland, C.R.; Ribeiro, R.C.; Krasin, M.J.; Rodriguez-Galindo, C. Prognostic Factors and Long-Term Outcomes of Childhood Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. Cancer 2011, 117, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mertens, R.; Granzen, B.; Lassay, L.; Bucsky, P.; Hundgen, M.; Stetter, G.; Heimann, G.; Weiss, C.; Hess, C.F.; Gademann, G. Treatment of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma in Children and Adolescents: Definitive Results of a Multicenter Study (NPC-91-GPOH). Cancer 2005, 104, 1083–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahai, P.; Mohanti, B.K.; Sharma, A.; Thakar, A.; Bhasker, S.; Kakkar, A.; Sharma, M.C.; Upadhyay, A.D. Clinical Outcome and Morbidity in Pediatric Patients with Nasopharyngeal Cancer Treated with Chemoradiotherapy. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2017, 64, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribassin-Majed, L.; Marguet, S.; Lee, A.W.M.; Ng, W.T.; Ma, J.; Chan, A.T.C.; Huang, P.-Y.; Zhu, G.; Chua, D.T.T.; Chen, Y.; et al. What Is the Best Treatment of Locally Advanced Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma? An Individual Patient Data Network Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 498–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Galindo, C.; Wofford, M.; Castleberry, R.P.; Swanson, G.P.; London, W.B.; Fontanesi, J.; Pappo, A.S.; Douglass, E.C. Preradiation Chemotherapy with Methotrexate, Cisplatin, 5-Fluorouracil, and Leucovorin for Pediatric Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. Cancer 2005, 103, 850–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Galindo, C.; Krailo, M.D.; Krasin, M.J.; Huang, L.; McCarville, M.B.; Hicks, J.; Pashankar, F.; Pappo, A.S. Treatment of Childhood Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma with Induction Chemotherapy and Concurrent Chemoradiotherapy: Results of the Children’s Oncology Group ARAR0331 Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 3369–3376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buehrlen, M.; Zwaan, C.M.; Granzen, B.; Lassay, L.; Deutz, P.; Vorwerk, P.; Staatz, G.; Gademann, G.; Christiansen, H.; Oldenburger, F.; et al. Multimodal Treatment, Including Interferon Beta, of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma in Children and Young Adults: Preliminary Results from the Prospective, Multicenter Study NPC-2003-GPOH/DCOG. Cancer 2012, 118, 4892–4900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Römer, T.; Franzen, S.; Kravets, H.; Farrag, A.; Makowska, A.; Christiansen, H.; Eble, M.J.; Timmermann, B.; Staatz, G.; Mottaghy, F.M.; et al. Multimodal Treatment of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma in Children, Adolescents and Young Adults-Extended Follow-Up of the NPC-2003-GPOH Study Cohort and Patients of the Interim Cohort. Cancers 2022, 14, 1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Echevarría, M.E.; Fangusaro, J.; Goldman, S. Pediatric Central Nervous System Germ Cell Tumors: A Review. Oncologist 2008, 13, 690–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellie, S.J.; Boyce, H.; Dunkel, I.J.; Diez, B.; Rosenblum, M.; Brualdi, L.; Finlay, J.L. Intensive Cisplatin and Cyclophosphamide-Based Chemotherapy without Radiotherapy for Intracranial Germinomas: Failure of a Primary Chemotherapy Approach. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2004, 43, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, N.S.; Cappellano, A.M.; Diez, B.; Cavalheiro, S.; Gardner, S.; Wisoff, J.; Kellie, S.; Parker, R.; Garvin, J.; Finlay, J. Primary Chemotherapy for Intracranial Germ Cell Tumors: Results of the Third International CNS Germ Cell Tumor Study. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2010, 54, 377–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimaki, T. Central Nervous System Germ Cell Tumors: Classification, Clinical Features, and Treatment with a Historical Overview. J. Child. Neurol. 2009, 24, 1439–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldman, S.; Bouffet, E.; Fisher, P.G.; Allen, J.C.; Robertson, P.L.; Chuba, P.J.; Donahue, B.; Kretschmar, C.S.; Zhou, T.; Buxton, A.B.; et al. Phase II Trial Assessing the Ability of Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy with or without Second-Look Surgery to Eliminate Measurable Disease for Nongerminomatous Germ Cell Tumors: A Children’s Oncology Group Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 2464–2471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calaminus, G.; Frappaz, D.; Kortmann, R.D.; Krefeld, B.; Saran, F.; Pietsch, T.; Vasiljevic, A.; Garre, M.L.; Ricardi, U.; Mann, J.R.; et al. Outcome of Patients with Intracranial Non-Germinomatous Germ Cell Tumors-Lessons from the SIOP-CNS-GCT-96 Trial. Neuro Oncol. 2017, 19, 1661–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, E.S.; Dhall, G.; Fangusaro, J.; Bartels, U.; Fouladi, M.; Shaw, D.; Khatua, S.; Hughes, C.W.; Panigraphy, A.; Ioakeim-Ioannidou, M.; et al. A Phase 2 Trial of Response-Based Radiation Therapy for Localized Central Nervous System Germ Cell Tumors: Patterns of Failure and Radiation Dosimetry for Nongerminomatous Germ Cell Tumors. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2022, 113, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fangusaro, J.; Wu, S.; MacDonald, S.; Murphy, E.; Shaw, D.; Bartels, U.; Khatua, S.; Souweidane, M.; Lu, H.-M.; Morris, D.; et al. Phase II Trial of Response-Based Radiation Therapy for Patients with Localized CNS Nongerminomatous Germ Cell Tumors: A Children’s Oncology Group Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 3283–3290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fetcko, K.; Dey, M. Primary Central Nervous System Germ Cell Tumors: A Review and Update. Med. Res. Arch. 2018, 6, 1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, M.J.; Bartels, U.; Nishikawa, R.; Fangusaro, J.; Matsutani, M.; Nicholson, J.C. Consensus on the Management of Intracranial Germ-Cell Tumours. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, e470–e477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartels, U.; Onar-Thomas, A.; Patel, S.K.; Shaw, D.; Fangusaro, J.; Dhall, G.; Souweidane, M.; Bhatia, A.; Embry, L.; Trask, C.L.; et al. Phase II Trial of Response-Based Radiation Therapy for Patients with Localized Germinoma: A Children’s Oncology Group Study. Neuro Oncol. 2022, 24, 974–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stokland, T.; Liu, J.-F.; Ironside, J.W.; Ellison, D.W.; Taylor, R.; Robinson, K.J.; Picton, S.V.; Walker, D.A. A Multivariate Analysis of Factors Determining Tumor Progression in Childhood Low-Grade Glioma: A Population-Based Cohort Study (CCLG CNS9702). Neuro Oncol. 2010, 12, 1257–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsang, D.S.; Murphy, E.S.; Merchant, T.E. Radiation Therapy for Optic Pathway and Hypothalamic Low-Grade Gliomas in Children. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2017, 99, 642–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eaton, B.R.; Yock, T.I. Radiation for Pediatric Low-Grade Gliomas: Who Will Benefit and How Late Is Soon Enough? Neuro Oncol. 2020, 22, 1068–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitterman, D.S.; MacDonald, S.M.; Yock, T.I.; Tarbell, N.J.; Wright, K.D.; Chi, S.N.; Marcus, K.J.; Haas-Kogan, D.A. Revisiting the Role of Radiation Therapy for Pediatric Low-Grade Glioma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 3335–3339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ater, J.L.; Zhou, T.; Holmes, E.; Mazewski, C.M.; Booth, T.N.; Freyer, D.R.; Lazarus, K.H.; Packer, R.J.; Prados, M.; Sposto, R.; et al. Randomized Study of Two Chemotherapy Regimens for Treatment of Low-Grade Glioma in Young Children: A Report from the Children’s Oncology Group. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 2641–2647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chintagumpala, M.; Eckel, S.P.; Krailo, M.; Morris, M.; Adesina, A.; Packer, R.; Lau, C.; Gajjar, A. A Pilot Study Using Carboplatin, Vincristine, and Temozolomide in Children with Progressive/Symptomatic Low-Grade Glioma: A Children’s Oncology Group Study†. Neuro Oncol. 2015, 17, 1132–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gnekow, A.K.; Kortmann, R.-D.; Pietsch, T.; Emser, A. Low Grade Chiasmatic-Hypothalamic Glioma-Carboplatin and Vincristin Chemotherapy Effectively Defers Radiotherapy within a Comprehensive Treatment Strategy—Report from the Multicenter Treatment Study for Children and Adolescents with a Low Grade Glioma—HIT-LGG 1996—of the Society of Pediatric Oncology and Hematology (GPOH). Klin. Padiatr. 2004, 216, 331–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, G.T.; Conklin, H.M.; Huang, S.; Srivastava, D.; Sanford, R.; Ellison, D.W.; Merchant, T.E.; Hudson, M.M.; Hoehn, M.E.; Robison, L.L.; et al. Survival and Long-Term Health and Cognitive Outcomes after Low-Grade Glioma. Neuro Oncol. 2011, 13, 223–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, M.J.; Ullrich, N.J.; Manley, P.E.; Kieran, M.W.; Goumnerova, L.C.; Heidary, G. Long-Term Visual Outcomes of Optic Pathway Gliomas in Pediatric Patients without Neurofibromatosis Type 1. J. Neurooncol 2016, 129, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakotonjanahary, J.; De Carli, E.; Delion, M.; Kalifa, C.; Grill, J.; Doz, F.; Leblond, P.; Bertozzi, A.-I.; Rialland, X. Brain Tumor Committee of SFCE Mortality in Children with Optic Pathway Glioma Treated with Up-Front BB-SFOP Chemotherapy. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0127676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanania, A.N.; Paulino, A.C.; Ludmir, E.B.; Shah, V.S.; Su, J.M.; McGovern, S.L.; Baxter, P.A.; McAleer, M.F.; Grosshans, D.R.; Okcu, M.F.; et al. Early Radiotherapy Preserves Vision in Sporadic Optic Pathway Glioma. Cancer 2021, 127, 2358–2367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulino, A.C.; Mazloom, A.; Terashima, K.; Su, J.; Adesina, A.M.; Okcu, M.F.; Teh, B.S.; Chintagumpala, M. Intensity-Modulated Radiotherapy (IMRT) in Pediatric Low-Grade Glioma. Cancer 2013, 119, 2654–2659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherlow, J.M.; Shaw, D.W.W.; Margraf, L.R.; Bowers, D.C.; Huang, J.; Fouladi, M.; Onar-Thomas, A.; Zhou, T.; Pollack, I.F.; Gajjar, A.; et al. Conformal Radiation Therapy for Pediatric Patients with Low-Grade Glioma: Results from the Children’s Oncology Group Phase 2 Study ACNS0221. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2019, 103, 861–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dome, J.S.; Cotton, C.A.; Perlman, E.J.; Breslow, N.E.; Kalapurakal, J.A.; Ritchey, M.L.; Grundy, P.E.; Malogolowkin, M.; Beckwith, J.B.; Shamberger, R.C.; et al. Treatment of Anaplastic Histology Wilms’ Tumor: Results from the Fifth National Wilms’ Tumor Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 24, 2352–2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daw, N.C.; Chi, Y.-Y.; Kalapurakal, J.A.; Kim, Y.; Hoffer, F.A.; Geller, J.I.; Perlman, E.J.; Ehrlich, P.F.; Mullen, E.A.; Warwick, A.B.; et al. Activity of Vincristine and Irinotecan in Diffuse Anaplastic Wilms Tumor and Therapy Outcomes of Stage II to IV Disease: Results of the Children’s Oncology Group AREN0321 Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 1558–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tobin, R.L.; Fontanesi, J.; Kun, L.E.; Fairclough, D.L.; Hustu, H.O.; Pao, W.J.; Douglass, E.C.; Wilimas, J.; Kumar, A.P.; Jenkins, J.J. Wilms’ Tumor: Reduced-Dose Radiotherapy in Advanced-Stage Wilms’ Tumor with Favorable Histology. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 1990, 19, 867–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dix, D.B.; Seibel, N.L.; Chi, Y.-Y.; Khanna, G.; Gratias, E.; Anderson, J.R.; Mullen, E.A.; Geller, J.I.; Kalapurakal, J.A.; Paulino, A.C.; et al. Treatment of Stage IV Favorable Histology Wilms Tumor with Lung Metastases: A Report from the Children’s Oncology Group AREN0533 Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 1564–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dix, D.B.; Fernandez, C.V.; Chi, Y.-Y.; Mullen, E.A.; Geller, J.I.; Gratias, E.J.; Khanna, G.; Kalapurakal, J.A.; Perlman, E.J.; Seibel, N.L.; et al. Augmentation of Therapy for Combined Loss of Heterozygosity 1p and 16q in Favorable Histology Wilms Tumor: A Children’s Oncology Group AREN0532 and AREN0533 Study Report. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 2769–2777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ognjanovic, S.; Linabery, A.M.; Charbonneau, B.; Ross, J.A. Trends in Childhood Rhabdomyosarcoma Incidence and Survival in the United States, 1975-2005. Cancer 2009, 115, 4218–4226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meza, J.L.; Anderson, J.; Pappo, A.S.; Meyer, W.H. Children’s Oncology Group Analysis of Prognostic Factors in Patients with Nonmetastatic Rhabdomyosarcoma Treated on Intergroup Rhabdomyosarcoma Studies III and IV: The Children’s Oncology Group. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 24, 3844–3851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hibbitts, E.; Chi, Y.-Y.; Hawkins, D.S.; Barr, F.G.; Bradley, J.A.; Dasgupta, R.; Meyer, W.H.; Rodeberg, D.A.; Rudzinski, E.R.; Spunt, S.L.; et al. Refinement of Risk Stratification for Childhood Rhabdomyosarcoma Using FOXO1 Fusion Status in Addition to Established Clinical Outcome Predictors: A Report from the Children’s Oncology Group. Cancer Med. 2019, 8, 6437–6448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parham, D.M.; Barr, F.G. Classification of Rhabdomyosarcoma and Its Molecular Basis. Adv. Anat. Pathol. 2013, 20, 387–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skapek, S.X.; Anderson, J.; Barr, F.G.; Bridge, J.A.; Gastier-Foster, J.M.; Parham, D.M.; Rudzinski, E.R.; Triche, T.; Hawkins, D.S. PAX-FOXO1 Fusion Status Drives Unfavorable Outcome for Children with Rhabdomyosarcoma: A Children’s Oncology Group Report. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2013, 60, 1411–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, M.A.; Anderson, J.R.; Gastier-Foster, J.M.; Barr, F.G.; Skapek, S.X.; Hawkins, D.S.; Raney, R.B.; Parham, D.M.; Teot, L.A.; Rudzinski, E.R.; et al. Histology, Fusion Status, and Outcome in Alveolar Rhabdomyosarcoma with Low-Risk Clinical Features: A Report from the Children’s Oncology Group. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2016, 63, 634–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolden, S.L.; Lyden, E.R.; Arndt, C.A.; Hawkins, D.S.; Anderson, J.R.; Rodeberg, D.A.; Morris, C.D.; Donaldson, S.S. Local Control for Intermediate-Risk Rhabdomyosarcoma: Results from D9803 According to Histology, Group, Site, and Size: A Report From the Children’s Oncology Group. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2015, 93, 1071–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucas, J.T.; Pappo, A.S.; Wu, J.; Indelicato, D.J.; Krasin, M.J. Excessive Treatment Failures in Patients with Parameningeal Rhabdomyosarcoma with Reduced-Dose Cyclophosphamide and Delayed Radiotherapy. J. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 2018, 40, 387–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, K.; Shulman, D.; Janeway, K.A.; DuBois, S.G. Comparison of Epidemiology, Clinical Features, and Outcomes of Patients with Reported Ewing Sarcoma and PNET over 40 Years Justifies Current WHO Classification and Treatment Approaches. Sarcoma 2018, 2018, 1712964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Indelicato, D.J.; Keole, S.R.; Shahlaee, A.H.; Shi, W.; Morris, C.G.; Gibbs, C.P.; Scarborough, M.T.; Marcus, R.B. Long-Term Clinical and Functional Outcomes after Treatment for Localized Ewing’s Tumor of the Lower Extremity. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2008, 70, 501–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuck, A.; Ahrens, S.; Paulussen, M.; Kuhlen, M.; Könemann, S.; Rübe, C.; Winkelmann, W.; Kotz, R.; Dunst, J.; Willich, N.; et al. Local Therapy in Localized Ewing Tumors: Results of 1058 Patients Treated in the CESS 81, CESS 86, and EICESS 92 Trials. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2003, 55, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laskar, S.; Sinha, S.; Chatterjee, A.; Khanna, N.; Manjali, J.J.; Puri, A.; Gulia, A.; Nayak, P.; Vora, T.; Chinnaswamy, G.; et al. Radiation Therapy Dose Escalation in Unresectable Ewing Sarcoma: Final Results of a Phase 3 Randomized Controlled Trial. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2022, 113, 996–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bronk, J.K.; McAleer, M.F.; McGovern, S.L.; Lassen-Ramshad, Y.; Safwat, A.; Daw, N.C.; Rainusso, N.; Mahajan, A.; Grosshans, D.R.; Paulino, A.C. Comprehensive Radiotherapy for Pediatric Ewing Sarcoma: Outcomes of a Prospective Proton Study. Radiother. Oncol. 2024, 195, 110270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.K.; Witten, B.G.; Harmsen, W.S.; Rose, P.S.; Krailo, M.; Marcus, K.J.; Randall, R.L.; DuBois, S.G.; Janeway, K.A.; Womer, R.B.; et al. Analysis of Local Control Outcomes and Clinical Prognostic Factors in Localized Pelvic Ewing Sarcoma Patients Treated with Radiation Therapy: A Report From the Children’s Oncology Group. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2023, 115, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uezono, H.; Indelicato, D.J.; Rotondo, R.L.; Mailhot Vega, R.B.; Bradfield, S.M.; Morris, C.G.; Bradley, J.A. Treatment Outcomes After Proton Therapy for Ewing Sarcoma of the Pelvis. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2020, 107, 974–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talleur, A.C.; Navid, F.; Spunt, S.L.; McCarville, M.B.; Wu, J.; Mao, S.; Davidoff, A.M.; Neel, M.D.; Krasin, M.J. Limited Margin Radiation Therapy for Children and Young Adults with Ewing Sarcoma Achieves High Rates of Local Tumor Control. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2016, 96, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohan, A.C.; Venkatramani, R.; Okcu, M.F.; Nuchtern, J.G.; Vasudevan, S.A.; Mahajan, A.; Rainusso, N.C.; Allen-Rhoades, W.; Chintagumpala, M.; Paulino, A.C. Local Therapy to Distant Metastatic Sites in Stage IV Rhabdomyosarcoma. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2018, 65, e26859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elledge, C.R.; Krasin, M.J.; Ladra, M.M.; Alcorn, S.R.; Han, P.; Gibbs, I.C.; Hiniker, S.M.; Laack, N.N.; Terezakis, S.A. A Multi-Institutional Phase 2 Trial of Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy in the Treatment of Bone Metastases in Pediatric and Young Adult Patients with Sarcoma. Cancer 2021, 127, 739–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haeusler, J.; Ranft, A.; Boelling, T.; Gosheger, G.; Braun-Munzinger, G.; Vieth, V.; Burdach, S.; van den Berg, H.; Juergens, H.; Dirksen, U. The Value of Local Treatment in Patients with Primary, Disseminated, Multifocal Ewing Sarcoma (PDMES). Cancer 2010, 116, 443–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smile, T.D.; Parsai, S.; Pflederer, T.M.; Murphy, E.S. Treatment Paradigms for Oligometastatic Pediatric Cancers: A Narrative Review with a Focus on Radiotherapy Approaches. Ann. Palliat. Med. 2021, 10, 6002015–6006015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eaton, B.R.; Esiashvili, N.; Kim, S.; Weyman, E.A.; Thornton, L.T.; Mazewski, C.; MacDonald, T.; Ebb, D.; MacDonald, S.M.; Tarbell, N.J.; et al. Clinical Outcomes Among Children with Standard-Risk Medulloblastoma Treated with Proton and Photon Radiation Therapy: A Comparison of Disease Control and Overall Survival. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2016, 94, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulsifer, M.B.; Duncanson, H.; Grieco, J.; Evans, C.; Tseretopoulos, I.D.; MacDonald, S.; Tarbell, N.J.; Yock, T.I. Cognitive and Adaptive Outcomes After Proton Radiation for Pediatric Patients with Brain Tumors. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2018, 102, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, J.P.; Powell, S.; Zelko, F.; Hartsell, W.; Goldman, S.; Fangusaro, J.; Lulla, R.R.; Smiley, N.P.; Chang, J.H.-C.; Gondi, V. Improved Neuropsychological Outcomes Following Proton Therapy Relative to X-Ray Therapy for Pediatric Brain Tumor Patients. Neuro Oncol. 2019, 21, 934–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahalley, L.S.; Douglas Ris, M.; Mahajan, A.; Fatih Okcu, M.; Chintagumpala, M.; Paulino, A.C.; Whitehead, W.E.; Minard, C.G.; Stancel, H.H.; Orobio, J.; et al. Prospective, Longitudinal Comparison of Neurocognitive Change in Pediatric Brain Tumor Patients Treated with Proton Radiotherapy versus Surgery Only. Neuro Oncol. 2019, 21, 809–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahalley, L.S.; Ris, M.D.; Grosshans, D.R.; Okcu, M.F.; Paulino, A.C.; Chintagumpala, M.; Moore, B.D.; Guffey, D.; Minard, C.G.; Stancel, H.H.; et al. Comparing Intelligence Quotient Change After Treatment with Proton Versus Photon Radiation Therapy for Pediatric Brain Tumors. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 1043–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howell, R.M.; Giebeler, A.; Koontz-Raisig, W.; Mahajan, A.; Etzel, C.J.; D’Amelio, A.M.; Homann, K.L.; Newhauser, W.D. Comparison of Therapeutic Dosimetric Data from Passively Scattered Proton and Photon Craniospinal Irradiations for Medulloblastoma. Radiat. Oncol. 2012, 7, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yock, T.I.; Yeap, B.Y.; Ebb, D.H.; Weyman, E.; Eaton, B.R.; Sherry, N.A.; Jones, R.M.; MacDonald, S.M.; Pulsifer, M.B.; Lavally, B.; et al. Long-Term Toxic Effects of Proton Radiotherapy for Paediatric Medulloblastoma: A Phase 2 Single-Arm Study. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 287–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paulino, A.C.; Ludmir, E.B.; Grosshans, D.R.; Su, J.M.; McGovern, S.L.; Okcu, M.F.; McAleer, M.F.; Baxter, P.A.; Mahajan, A.; Chintagumpala, M.M. Overall Survival and Secondary Malignant Neoplasms in Children Receiving Passively Scattered Proton or Photon Craniospinal Irradiation for Medulloblastoma. Cancer 2021, 127, 3865–3871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Diagnosis | Study | Description | Radiation Details |
|---|---|---|---|
| Medulloblastoma | ACNS1422 | A Phase 2 Study of Reduced Therapy for Newly Diagnosed Average-Risk WNT-Driven Medulloblastoma Patients | 18 Gy CSI with 36 Gy tumor bed boost |
| Ependymoma | ACNS0831 | Phase III Randomized Trial of Post-Radiation Chemotherapy in Patients with Newly Diagnosed Ependymoma Ages 1 to 21 years | 54–59.4 Gy |
| Intracranial Germ Cell Tumor | ACNS1123 | Phase 2 Trial of Response-Based Radiation Therapy for Patients with Localized Central Nervous System Germ Cell Tumors (CNS GCT) | 30.6 Gy Whole ventricular irradiation plus 23.4 Gy primary site boost |
| AGCT1531 | A Phase 3 Study of Active Surveillance for Low Risk and a Randomized Trial of Carboplatin vs. Cisplatin for Standard Risk Pediatric and Adult Patients with Germ Cell Tumors | No radiation | |
| ACNS2021 | A Phase 2 Trial of Chemotherapy followed by Response-Based Whole Ventricular and Spinal Canal Irradiation (WVSCI) for Patients with Localized Non-Germinomatous Central Nervous System Germ Cell Tumor | 30.6 Gy ventricular and spinal irradiation plus 23.4 Gy primary site boost | |
| Hodgkin Lymphoma | AHOD2131 | A Randomized Phase 3 Interim Response Adapted Trial Comparing Standard Therapy with Immuno-oncology Therapy for Children and Adults with Newly Diagnosed Stage I and II Classic Hodgkin Lymphoma | Involved site RT |
| AHOD1331 | A Randomized Phase 3 Study of Brentuximab Vedotin (SGN-35, IND #117117) for Newly Diagnosed High-Risk Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma (cHL) in Children and Young Adults | Involved site RT | |
| Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma | ARAR2221 | A Phase 2 Study Using Chemoimmunotherapy with Gemcitabine, Cisplatin and Nivolumab in Newly Diagnosed Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma (NPC) | 61.2 Gy in 34 daily fractions |
| Rhabdomyosarcoma | ARST1431 | A Randomized Phase 3 Study of Vincristine, Dactinomycin, Cyclophosphamide (VAC) Alternating with Vincristine and Irinotecan (VI) Versus VAC/VI Plus Temsirolimus (TORI, Torisel, NSC# 683864) in Patients with Intermediate Risk (IR) Rhabdomyosarcoma (RMS) | Site-dependent, 6.5 weeks |
| ARST2032 | A Prospective Phase 3 Study of Patients with Newly Diagnosed Very Low-risk and Low-risk Fusion Negative Rhabdomyosarcoma | Site-dependent, 6.5 weeks | |
| ARST1321 | Pazopanib Neoadjuvant Trial In Non-Rhabdomyosarcoma Soft Tissue Sarcomas (PAZNTIS): A Phase II/III Randomized Trial of Preoperative Chemoradiation or Preoperative Radiation Plus or Minus Pazopanib (NSC# 737754, IND# 118613) | 45 Gy preoperative radiotherapy; postoperative boost of 21.6 Gy for R2 resection or 16.2 Gy for R1 resection | |
| Ewing’s Sarcoma | AEWS0331 | European Ewing Tumor Working Initiative of National Groups Ewing Tumour Studies 1999 (EURO-E.W.I.N.G.99) | Definitive +/− metastatic site irradiation |
| AEWS1031 | A Phase III Randomized Trial of Adding Vincristine-Topotecan-Cyclophosphamide to Standard Chemotherapy in Initial Treatment of Non-metastatic Ewing Sarcoma | Definitive +/− metastatic site irradiation | |
| AEWS1221 | Randomized Phase 3 Trial Evaluating the Addition of the IGF-1R Monoclonal Antibody Ganitumab (AMG 479, NSC# 750008, IND# 120449) to Multiagent Chemotherapy for Patients with Newly Diagnosed Metastatic Ewing Sarcoma | Definitive +/− metastatic site irradiation | |
| Wilms Tumor | AREN1921 | Treatment of Newly Diagnosed Diffuse Anaplastic Wilms Tumors (DAWT) and Relapsed Favorable Histology Wilms Tumors (FHWT) | Flank and/or metastatic site radiation |
| AREN0532 | Treatment for Very-Low- and Standard-Risk Favorable Histology Wilms Tumor | Flank (10.8 Gy) or whole abdominal (10.5 Gy) radiation, with a 10.8 or 10.5 Gy boost to gross residual tumor, respectively | |
| AREN0533 | Treatment of Newly Diagnosed Higher-Risk Favorable Histology Wilms Tumors | 10.8 Gy flank RT for local stage III tumors, with 10.8 Gy boost for patients with gross residual disease after surgery, whole-lung RT 12 Gy for lung nodules, regardless of pulmonary metastatic lesion response at week 6 | |
| AREN0534 | Treatment for Patients with Bilateral, Multicentric, or Bilaterally Predisposed Unilateral Wilms Tumor | Flank radiation if indicated 10.8 Gy (19.8 Gy for ≥16 years old), Whole lung irradiation 12 Gy for patients with lung metastasis (10.5 Gy for <12 months old) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Upadhyay, R.; Paulino, A.C. Risk-Stratified Radiotherapy in Pediatric Cancer. Cancers 2024, 16, 3530. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16203530
Upadhyay R, Paulino AC. Risk-Stratified Radiotherapy in Pediatric Cancer. Cancers. 2024; 16(20):3530. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16203530
Chicago/Turabian StyleUpadhyay, Rituraj, and Arnold C. Paulino. 2024. "Risk-Stratified Radiotherapy in Pediatric Cancer" Cancers 16, no. 20: 3530. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16203530
APA StyleUpadhyay, R., & Paulino, A. C. (2024). Risk-Stratified Radiotherapy in Pediatric Cancer. Cancers, 16(20), 3530. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16203530





