Association Between Physical Activity and Pancreatic Cancer Risk and Mortality: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Literature Search
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
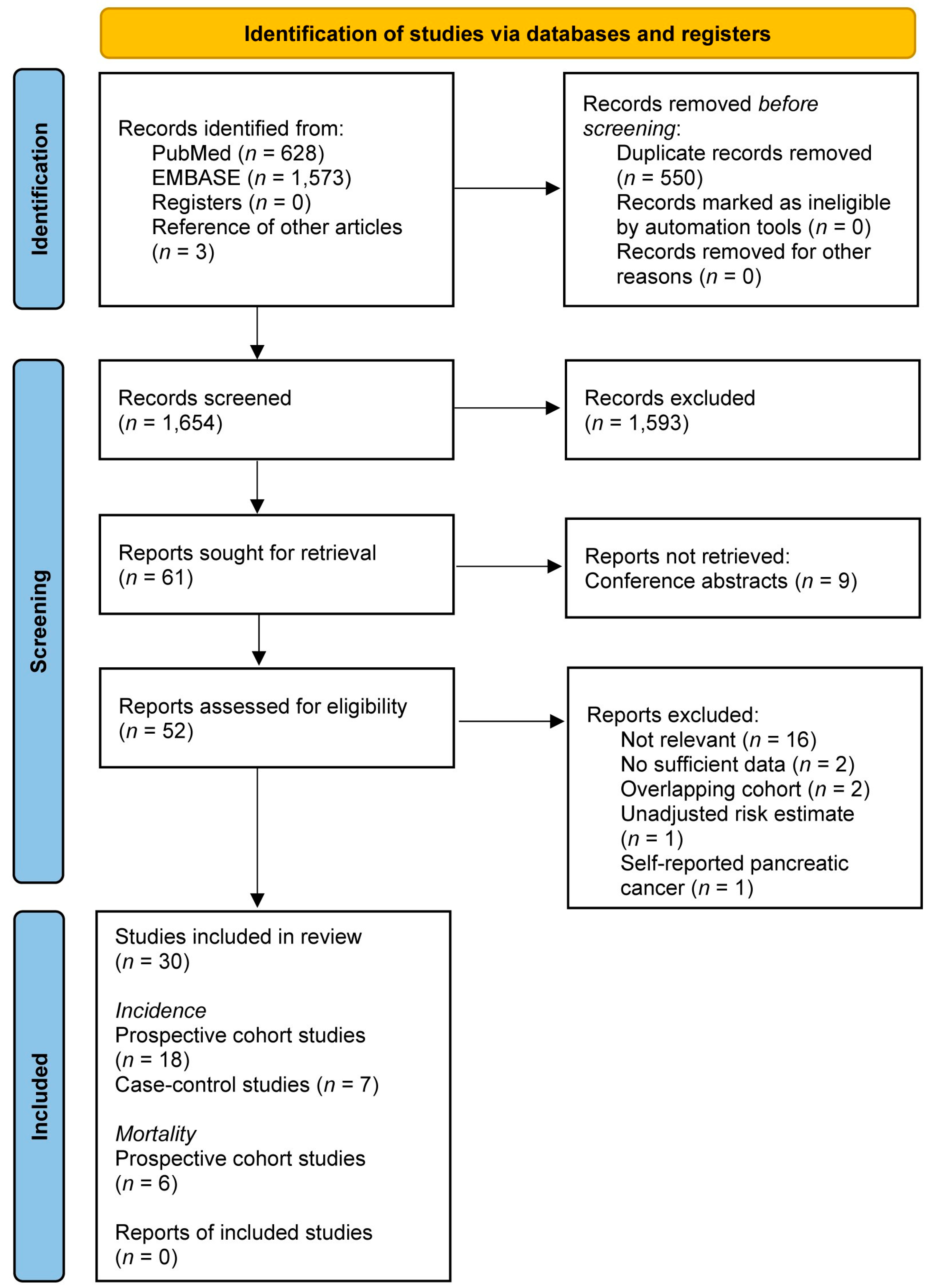
2.3. Study Selection
2.4. Quality Assessment
2.5. Data Collection
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Included Studies
3.2. Pancreatic Cancer Incidence
3.2.1. Study Characteristics
3.2.2. Primary Results
3.2.3. Subgroup Analysis Results
3.3. Pancreatic Cancer Mortality
3.3.1. Study Characteristics
3.3.2. Primary Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Laversanne, M.; Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA. Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 229–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, R.L.; Giaquinto, A.N.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2024. CA. Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 12–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizrahi, J.D.; Surana, R.; Valle, J.W.; Shroff, R.T. Pancreatic cancer. Lancet 2020, 395, 2008–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, A.P. Pancreatic cancer epidemiology: Understanding the role of lifestyle and inherited risk factors. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 18, 493–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McTiernan, A.; Friedenreich, C.M.; Katzmarzyk, P.T.; Powell, K.E.; Macko, R.; Buchner, D.; Pescatello, L.S.; Bloodgood, B.; Tennant, B.; Vaux-Bjerke, A.; et al. Physical Activity in Cancer Prevention and Survival: A Systematic Review. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2019, 51, 1252–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedenreich, C.M.; Ryder-Burbidge, C.; McNeil, J. Physical activity, obesity and sedentary behavior in cancer etiology: Epidemiologic evidence and biologic mechanisms. Mol. Oncol. 2021, 15, 790–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, E.A.; Dalamaga, M.; Magkos, F. The role of exercise in obesity-related cancers: Current evidence and biological mechanisms. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2023, 91, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.M.Y.; Wellberg, E.A.; Kopp, J.L.; Johnson, J.D. Hyperinsulinemia in Obesity, Inflammation, and Cancer. Diabetes Metab. J. 2021, 45, 285–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stolzenberg-Solomon, R.Z.; Graubard, B.I.; Chari, S.; Limburg, P.; Taylor, P.R.; Virtamo, J.; Albanes, D. Insulin, glucose, insulin resistance, and pancreatic cancer in male smokers. JAMA 2005, 294, 2872–2878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisani, P. Hyper-insulinaemia and cancer, meta-analyses of epidemiological studies. Arch. Physiol. Biochem. 2008, 114, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padoan, A.; Plebani, M.; Basso, D. Inflammation and Pancreatic Cancer: Focus on Metabolism, Cytokines, and Immunity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, Y.; Michaud, D.S. Physical activity and pancreatic cancer risk: A systematic review. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2008, 17, 2671–2682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Rorke, M.A.; Cantwell, M.M.; Cardwell, C.R.; Mulholland, H.G.; Murray, L.J. Can physical activity modulate pancreatic cancer risk? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Cancer 2010, 126, 2957–2968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farris, M.S.; Mosli, M.H.; McFadden, A.A.; Friedenreich, C.M.; Brenner, D.R. The Association between Leisure Time Physical Activity and Pancreatic Cancer Risk in Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2015, 24, 1462–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrens, G.; Jochem, C.; Schmid, D.; Keimling, M.; Ricci, C.; Leitzmann, M.F. Physical activity and risk of pancreatic cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2015, 30, 279–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, F.; You, Y.; Huang, J.; Guan, C.; Chen, Z.; Fang, M.; Yao, F.; Han, J. Association between physical activity and digestive-system cancer: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Sport. Health Sci. 2021, 10, 4–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedenreich, C.M.; Stone, C.R.; Cheung, W.Y.; Hayes, S.C. Physical Activity and Mortality in Cancer Survivors: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. JNCI Cancer Spectr. 2020, 4, pkz080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arem, H.; Moore, S.C.; Park, Y.; Ballard-Barbash, R.; Hollenbeck, A.; Leitzmann, M.; Matthews, C.E. Physical activity and cancer-specific mortality in the NIH-AARP Diet and Health Study cohort. Int. J. Cancer 2014, 135, 423–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, G.A.; Shea, B.; O’Connell, D.; Peterson, J.; Welch, V.; Losos, M.; Tugwell, P. The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) for Assessing the Quality of Nonrandomised Studies in Meta-Analyses. Available online: https://www.ohri.ca/programs/clinical_epidemiology/oxford.asp (accessed on 25 May 2024).
- Lanza, A.; Ravaud, P.; Riveros, C.; Dechartres, A. Comparison of Estimates between Cohort and Case-Control Studies in Meta-Analyses of Therapeutic Interventions: A Meta-Epidemiological Study. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0154877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.P.; Thompson, S.G. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat. Med. 2002, 21, 1539–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egger, M.; Davey Smith, G.; Schneider, M.; Minder, C. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ 1997, 315, 629–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viechtbauer, W. Conducting Meta-Analyses in R with the metafor Package. J. Stat. Soft. 2010, 36, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, M.; Yamamoto, S.; Kurahashi, N.; Iwasaki, M.; Sasazuki, S.; Tsugane, S.; Japan Public Health Center-based Prospective Study, G. Daily total physical activity level and total cancer risk in men and women: Results from a large-scale population-based cohort study in Japan. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2008, 168, 391–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stolzenberg-Solomon, R.Z.; Adams, K.; Leitzmann, M.; Schairer, C.; Michaud, D.S.; Hollenbeck, A.; Schatzkin, A.; Silverman, D.T. Adiposity, physical activity, and pancreatic cancer in the National Institutes of Health-AARP Diet and Health Cohort. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2008, 167, 586–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kollarova, H.; Azeem, K.; Tomaskova, H.; Horakova, D.; Prochazka, V.; Martinek, A.; Shonova, O.; Sevcikova, J.; Sevcikova, V.; Janout, V. Is physical activity a protective factor against pancreatic cancer? Bratisl. Lek. Listy. 2014, 115, 474–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, I.M.; Paffenbarger, R.S., Jr. Physical activity and its relation to cancer risk: A prospective study of college alumni. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 1994, 26, 831–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaud, D.S.; Giovannucci, E.; Willett, W.C.; Colditz, G.A.; Stampfer, M.J.; Fuchs, C.S. Physical activity, obesity, height, and the risk of pancreatic cancer. JAMA 2001, 286, 921–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keum, N.; Bao, Y.; Smith-Warner, S.A.; Orav, J.; Wu, K.; Fuchs, C.S.; Giovannucci, E.L. Association of Physical Activity by Type and Intensity with Digestive System Cancer Risk. JAMA Oncol. 2016, 2, 1146–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berrington de Gonzalez, A.; Spencer, E.A.; Bueno-de-Mesquita, H.B.; Roddam, A.; Stolzenberg-Solomon, R.; Halkjaer, J.; Tjonneland, A.; Overvad, K.; Clavel-Chapelon, F.; Boutron-Ruault, M.C.; et al. Anthropometry, physical activity, and the risk of pancreatic cancer in the European prospective investigation into cancer and nutrition. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2006, 15, 879–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calton, B.A.; Stolzenberg-Solomon, R.Z.; Moore, S.C.; Schatzkin, A.; Schairer, C.; Albanes, D.; Leitzmann, M.F. A prospective study of physical activity and the risk of pancreatic cancer among women (United States). BMC Cancer 2008, 8, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinen, M.M.; Verhage, B.A.; Goldbohm, R.A.; Lumey, L.H.; van den Brandt, P.A. Physical activity, energy restriction, and the risk of pancreatic cancer: A prospective study in the Netherlands. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 94, 1314–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, L.; Mitrou, P.N.; Reedy, J.; Graubard, B.I.; Hollenbeck, A.R.; Schatzkin, A.; Stolzenberg-Solomon, R. A combined healthy lifestyle score and risk of pancreatic cancer in a large cohort study. Arch. Intern. Med. 2009, 169, 764–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Iwasaki, M.; Inoue, M.; Sasazuki, S.; Otani, T.; Ye, W.; Tsugane, S.; Group, J.S. Body mass index, physical activity and the risk of pancreatic cancer in relation to smoking status and history of diabetes: A large-scale population-based cohort study in Japan--the JPHC study. Cancer Causes Control 2007, 18, 603–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luu, H.N.; Paragomi, P.; Wang, R.; Jin, A.; Brand, R.E.; Koh, W.P.; Yuan, J.M. Composite Score of Healthy Lifestyle Factors and the Risk of Pancreatic Cancer in a Prospective Cohort Study. Cancer Prev. Res. 2022, 15, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsen, T.I.; Vatten, L.J. A prospective study of lifestyle factors and the risk of pancreatic cancer in Nord-Trondelag, Norway. Cancer Causes Control 2000, 11, 645–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noor, N.M.; Banim, P.J.; Luben, R.N.; Khaw, K.T.; Hart, A.R. Investigating Physical Activity in the Etiology of Pancreatic Cancer: The Age at Which This Is Measured Is Important and Is Independent of Body Mass Index. Pancreas 2016, 45, 388–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nöthlings, U.; Wilkens, L.R.; Murphy, S.P.; Hankin, J.H.; Henderson, B.E.; Kolonel, L.N. Body mass index and physical activity as risk factors for pancreatic cancer: The Multiethnic Cohort Study. Cancer Causes Control 2007, 18, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.V.; Rodriguez, C.; Bernstein, L.; Chao, A.; Thun, M.J.; Calle, E.E. Obesity, recreational physical activity, and risk of pancreatic cancer in a large U.S. Cohort. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2005, 14, 459–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinner, P.J.; Schmitz, K.H.; Anderson, K.E.; Folsom, A.R. Lack of association of physical activity and obesity with incident pancreatic cancer in elderly women. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2005, 14, 1571–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Bjorge, T.; Teleka, S.; Engeland, A.; Wennberg, P.; Haggstrom, C.; Stocks, T. Interaction of leisure-time physical activity with body mass index on the risk of obesity-related cancers: A pooled study. Int. J. Cancer 2022, 151, 859–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Zheng, W.; Xiang, Y.B.; Gao, Y.T.; Li, H.L.; Cai, H.; Shu, X.O. Physical Activity and Pancreatic Cancer Risk among Urban Chinese: Results from Two Prospective Cohort Studies. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2018, 27, 479–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, Y.H.; Lim, M.K.; Won, Y.J.; Park, S.M.; Chang, Y.J.; Oh, S.W.; Shin, S.A. Dietary preference, physical activity, and cancer risk in men: National health insurance corporation study. BMC Cancer 2008, 8, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.; Wu, Z.; Yang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, R. Association of genetic risk and lifestyle with pancreatic cancer and their age dependency: A large prospective cohort study in the UK Biobank. BMC Med. 2023, 21, 489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.Q.; Li, Q.J.; Hao, F.B.; Wu, Y.Q.; Liu, S.; Zhong, G.C. Adherence to the 2018 World Cancer Research Fund/American Institute for Cancer Research cancer prevention recommendations and pancreatic cancer incidence and mortality: A prospective cohort study. Cancer Med. 2020, 9, 6843–6853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenner, D.R.; Wozniak, M.B.; Feyt, C.; Holcatova, I.; Janout, V.; Foretova, L.; Fabianova, E.; Shonova, O.; Martinek, A.; Ryska, M.; et al. Physical activity and risk of pancreatic cancer in a central European multicenter case-control study. Cancer Causes Control 2014, 25, 669–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eberle, C.A.; Bracci, P.M.; Holly, E.A. Anthropometric factors and pancreatic cancer in a population-based case-control study in the San Francisco Bay area. Cancer Causes Control 2005, 16, 1235–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanley, A.J.; Johnson, K.C.; Villeneuve, P.J.; Mao, Y.; Canadian Cancer Registries Epidemiology Research, G. Physical activity, anthropometric factors and risk of pancreatic cancer: Results from the Canadian enhanced cancer surveillance system. Int. J. Cancer 2001, 94, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, M.; Tajima, K.; Takezaki, T.; Hamajima, N.; Hirose, K.; Ito, H.; Tominaga, S. Epidemiology of pancreatic cancer in Japan: A nested case-control study from the Hospital-based Epidemiologic Research Program at Aichi Cancer Center (HERPACC). Int. J. Epidemiol. 2003, 32, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parent, M.E.; Rousseau, M.C.; El-Zein, M.; Latreille, B.; Desy, M.; Siemiatycki, J. Occupational and recreational physical activity during adult life and the risk of cancer among men. Cancer Epidemiol. 2011, 35, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandhu, J.; De Rubeis, V.; Cotterchio, M.; Smith, B.T.; Griffith, L.E.; Brenner, D.R.; Borgida, A.; Gallinger, S.; Cleary, S.; Anderson, L.N. Trajectories of physical activity, from young adulthood to older adulthood, and pancreatic cancer risk; a population-based case-control study in Ontario, Canada. BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Dhakal, I.B.; Gross, M.D.; Lang, N.P.; Kadlubar, F.F.; Harnack, L.J.; Anderson, K.E. Physical activity, diet, and pancreatic cancer: A population-based, case-control study in Minnesota. Nutr. Cancer 2009, 61, 457–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batty, G.D.; Kivimaki, M.; Morrison, D.; Huxley, R.; Smith, G.D.; Clarke, R.; Marmot, M.G.; Shipley, M.J. Risk factors for pancreatic cancer mortality: Extended follow-up of the original Whitehall Study. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2009, 18, 673–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, I.M.; Sesso, H.D.; Oguma, Y.; Paffenbarger, R.S., Jr. Physical activity, body weight, and pancreatic cancer mortality. Br. J. Cancer 2003, 88, 679–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Kikuchi, S.; Tamakoshi, A.; Yagyu, K.; Obata, Y.; Inaba, Y.; Kurosawa, M.; Kawamura, T.; Motohashi, Y.; Ishibashi, T.; et al. Obesity, physical activity and the risk of pancreatic cancer in a large Japanese cohort. Int. J. Cancer 2007, 120, 2665–2671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, K.; Nagata, C.; Wada, K.; Tamai, Y.; Tsuji, M.; Takatsuka, N.; Shimizu, H. Cigarette smoking and other lifestyle factors in relation to the risk of pancreatic cancer death: A prospective cohort study in Japan. Jpn. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 41, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.M.Y.; Chu, K.H.; Daly, B.F.; Ruiter, T.; Dou, Y.; Yang, J.C.C.; de Winter, T.J.J.; Chhuor, J.; Wang, S.; Flibotte, S.; et al. Effects of hyperinsulinemia on pancreatic cancer development and the immune microenvironment revealed through single-cell transcriptomics. Cancer Metab. 2022, 10, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieman, D.C.; Wentz, L.M. The compelling link between physical activity and the body’s defense system. J. Sport Health Sci. 2019, 8, 201–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Sousa, C.V.; Sales, M.M.; Rosa, T.S.; Lewis, J.E.; de Andrade, R.V.; Simoes, H.G. The Antioxidant Effect of Exercise: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Sports Med. 2017, 47, 277–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hojman, P.; Gehl, J.; Christensen, J.F.; Pedersen, B.K. Molecular Mechanisms Linking Exercise to Cancer Prevention and Treatment. Cell Metab. 2018, 27, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, N.; Zhou, Y.; Dong, X.; Ding, M. The antitumor mechanisms of aerobic exercise: A review of recent preclinical studies. Cancer Med. 2021, 10, 6365–6373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esteves, M.; Monteiro, M.P.; Duarte, J.A. Role of Regular Physical Exercise in Tumor Vasculature: Favorable Modulator of Tumor Milieu. Int. J. Sports Med. 2021, 42, 389–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosebrock, K.; Sinn, M.; Uzunoglu, F.G.; Bokemeyer, C.; Jensen, W.; Salchow, J. Effects of Exercise Training on Patient-Specific Outcomes in Pancreatic Cancer Patients: A Scoping Review. Cancers 2023, 15, 5899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neuzillet, C.; Bouche, O.; Tournigand, C.; Chibaudel, B.; Bauguion, L.; Bengrine-Lefevre, L.; Lopez-Trabada Ataz, D.; Mabro, M.; Metges, J.P.; Pere-Verge, D.; et al. Effect of Adapted Physical Activity in Patients with Advanced Pancreatic Cancer: The APACaP GERCOR Randomized Trial. J. Natl. Compr. Canc. Netw. 2023, 21, 1234–1242.e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikkelsen, M.K.; Lund, C.M.; Vinther, A.; Tolver, A.; Johansen, J.S.; Chen, I.; Ragle, A.M.; Zerahn, B.; Engell-Noerregaard, L.; Larsen, F.O.; et al. Effects of a 12-Week Multimodal Exercise Intervention Among Older Patients with Advanced Cancer: Results from a Randomized Controlled Trial. Oncologist 2022, 27, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulia, K.A.; Sarantis, P.; Antoniadou, D.; Koustas, E.; Papadimitropoulou, A.; Papavassiliou, A.G.; Karamouzis, M.V. Pancreatic Cancer and Cachexia-Metabolic Mechanisms and Novel Insights. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamel, F.H.; Basha, M.A.; Alsharidah, A.S.; Salama, A.B. Resistance Training Impact on Mobility, Muscle Strength and Lean Mass in Pancreatic Cancer Cachexia: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Clin. Rehabil. 2020, 34, 1391–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mylius, C.F.; Mooiweer, Y.; Krijnen, W.P.; Takken, T.; van Munster, B.C.; van der Schans, C.P.; Klaase, J.M. Changes in Self-Reported and Device-Measured Physical Activity Before Abdominal Resection Surgery: A Meta-Analysis. Clin. Rehabil. 2024, 38, 216–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bos, M.D.; Oor, J.E.; Goense, L.; Meyer, N.H.; Bockhorn, M.; Hoogwater, F.J.H.; Klaase, J.M.; Nijkamp, M.W. Association Between Physical Activity and Pancreatic Cancer Risk and Mortality: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cancers 2024, 16, 3594. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16213594
Bos MD, Oor JE, Goense L, Meyer NH, Bockhorn M, Hoogwater FJH, Klaase JM, Nijkamp MW. Association Between Physical Activity and Pancreatic Cancer Risk and Mortality: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cancers. 2024; 16(21):3594. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16213594
Chicago/Turabian StyleBos, Mylena D., Jelmer E. Oor, Lucas Goense, N. Helge Meyer, Maximilian Bockhorn, Frederik J. H. Hoogwater, Joost M. Klaase, and Maarten W. Nijkamp. 2024. "Association Between Physical Activity and Pancreatic Cancer Risk and Mortality: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Cancers 16, no. 21: 3594. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16213594
APA StyleBos, M. D., Oor, J. E., Goense, L., Meyer, N. H., Bockhorn, M., Hoogwater, F. J. H., Klaase, J. M., & Nijkamp, M. W. (2024). Association Between Physical Activity and Pancreatic Cancer Risk and Mortality: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cancers, 16(21), 3594. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16213594







