Perirenal Fat CT Radiomics-Based Survival Model for Upper Tract Urothelial Carcinoma: Integrating Texture Features with Clinical Predictors
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Patient Cohort
2.2. CT Imaging Protocol
2.3. Patient Follow-Up
2.4. Image Segmentation and Radiomics Feature Extraction
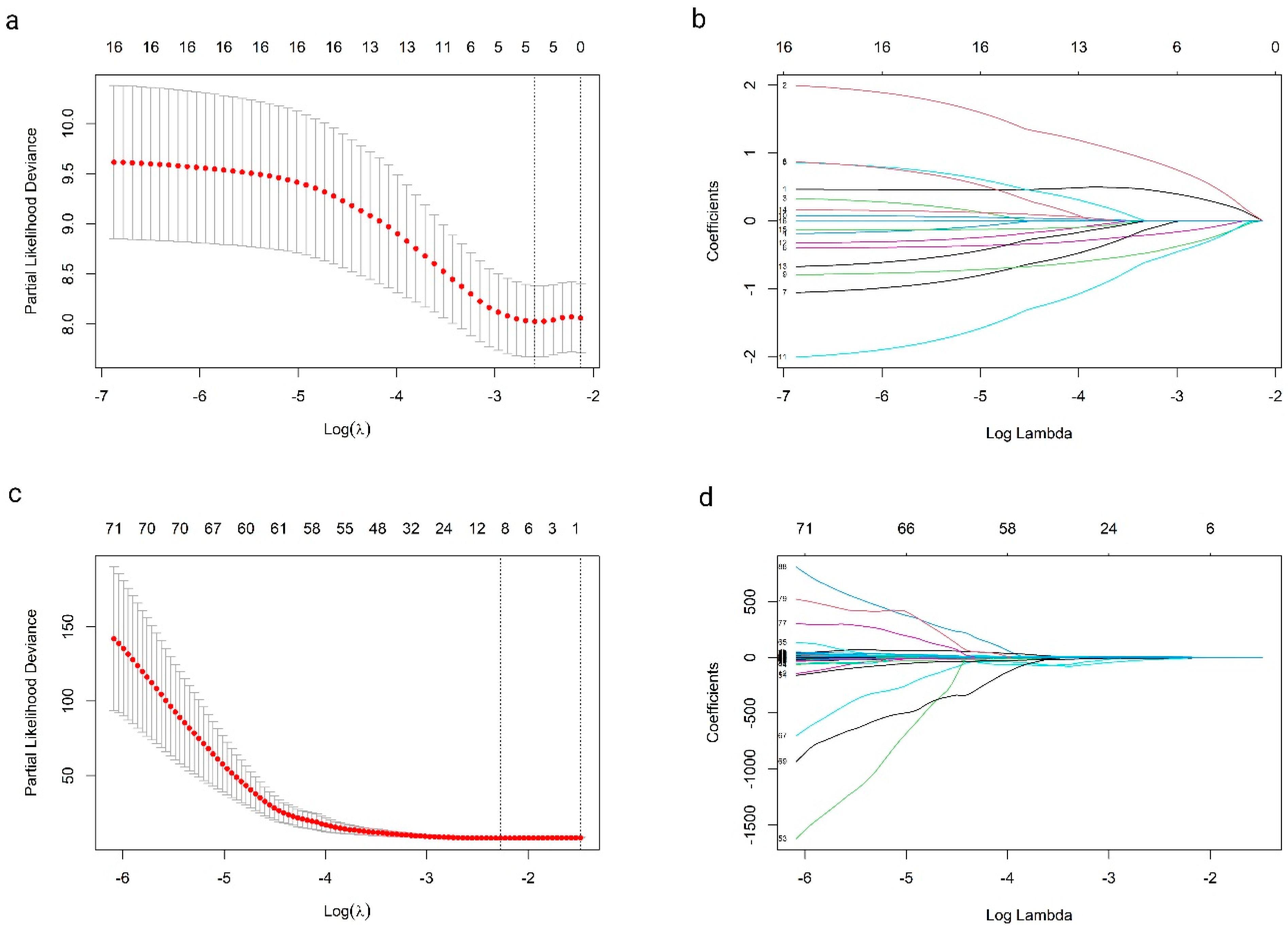
2.5. Feature Selection and Model Development
2.6. Statistical Analysis and Model Evaluation
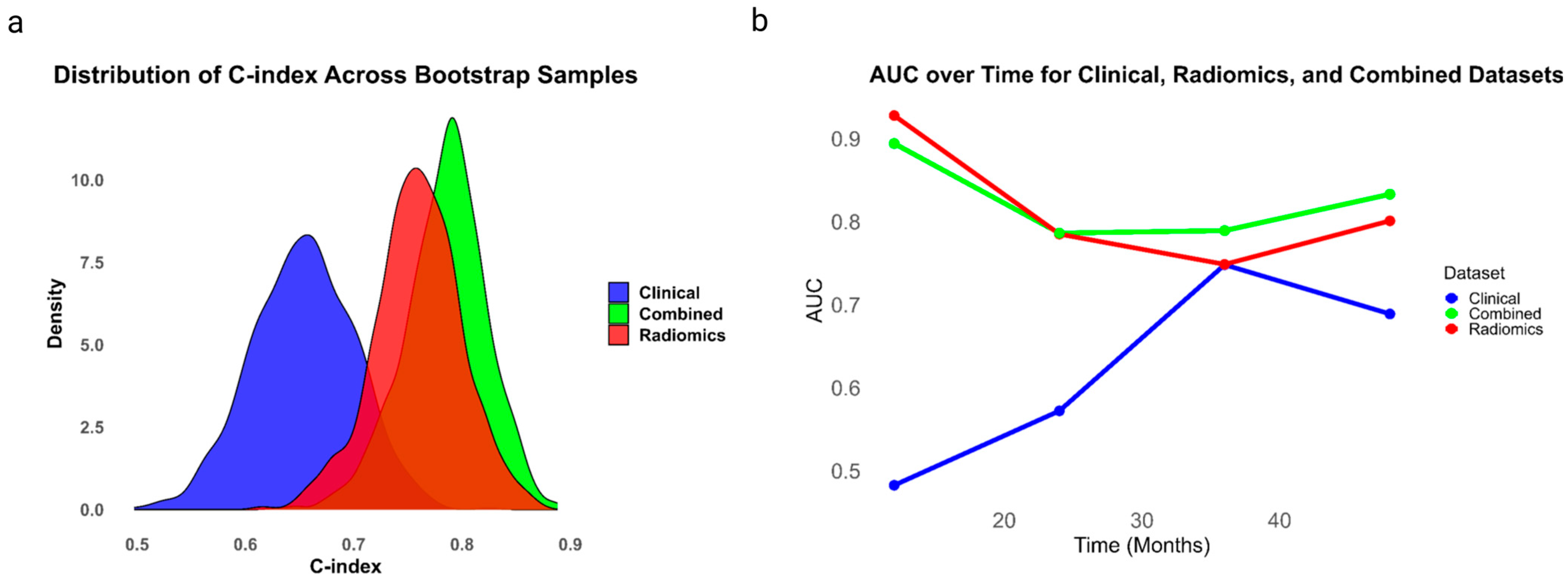
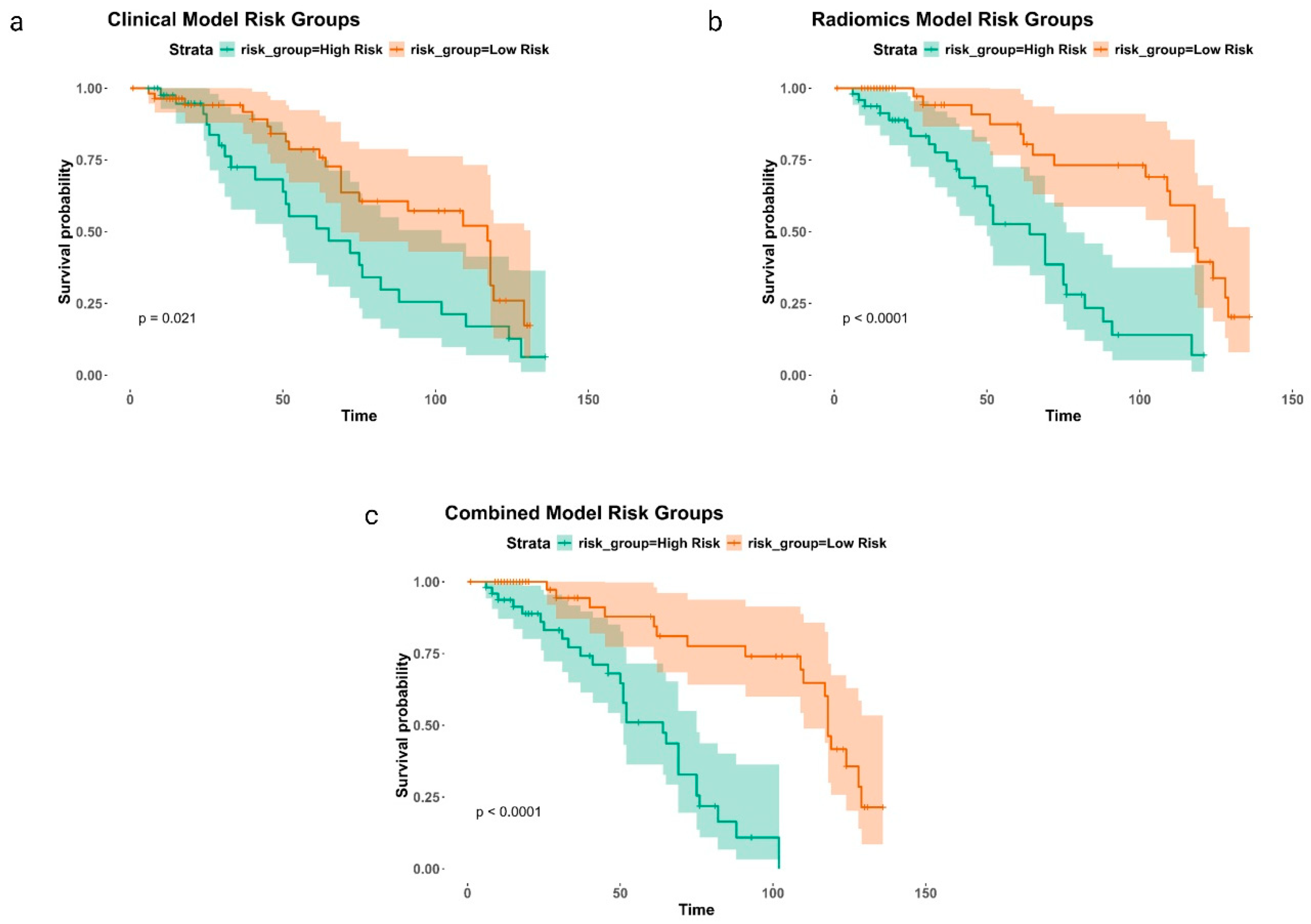
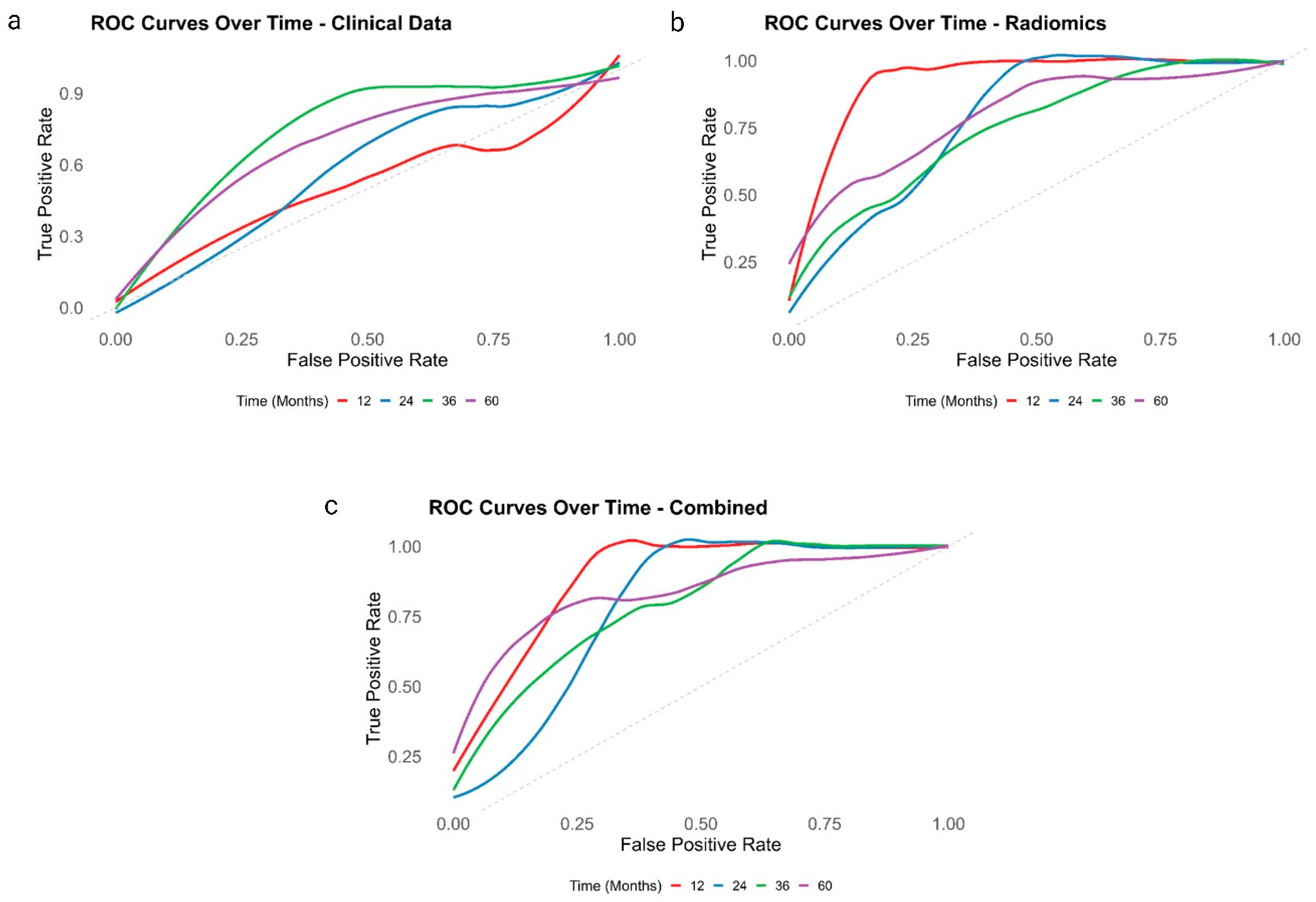
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rouprêt, M.; Seisen, T.; Birtle, A.J.; Capoun, O.; Compérat, E.M.; Dominguez-Escrig, J.L.; Andersson, I.G.; Liedberg, F.; Mariappan, P.; Mostafid, A.H.; et al. European Association of Urology Guidelines on Upper Urinary Tract Urothelial Carcinoma: 2023 Update. Eur. Urol. 2023, 84, 49–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colin, P.; Ouzzane, A.; Pignot, G.; Ravier, E.; Crouzet, S.; Ariane, M.M.; Audouin, M.; Neuzillet, Y.; Albouy, B.; Hurel, S.; et al. Comparison of oncological outcomes after segmental ureterectomy or radical nephroureterectomy in urothelial carcinomas of the upper urinary tract: Results from a large French multicentre study. BJU Int. 2012, 110, 1134–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lughezzani, G.; Jeldres, C.; Isbarn, H.; Sun, M.; Shariat, S.F.; Alasker, A.; Pharand, D.; Widmer, H.; Arjane, P.; Graefen, M.; et al. Nephroureterectomy and segmental ureterectomy in the treatment of invasive upper tract urothelial carcinoma: A population-based study of 2299 patients. Eur. J. Cancer 2009, 45, 3291–3297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mbeutcha, A.; Rouprêt, M.; Kamat, A.M.; Karakiewicz, P.I.; Lawrentschuk, N.; Novara, G.; Raman, J.D.; Seitz, C.; Xylinas, E.; Shariat, S.F. Prognostic factors and predictive tools for upper tract urothelial carcinoma: A systematic review. World J. Urol. 2017, 35, 337–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seisen, T.; Peyronnet, B.; Dominguez-Escrig, J.L.; Bruins, H.M.; Yuan, C.Y.; Babjuk, M.; Boehle, A.; Burger, M.; Comperat, E.M.; Cowan, N.C.; et al. Oncologic Outcomes of Kidney-sparing Surgery Versus Radical Nephroureterectomy for Upper Tract Urothelial Carcinoma: A Systematic Review by the EAU Non-muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer Guidelines Panel. Eur. Urol. 2016, 70, 1052–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soria, F.; Shariat, S.F.; Lerner, S.P.; Fritsche, H.M.; Rink, M.; Kassouf, W.; Spiess, P.E.; Lotan, Y.; Ye, D.; Fernández, M.I.; et al. Epidemiology, diagnosis, preoperative evaluation and prognostic assessment of upper-tract urothelial carcinoma (UTUC). World J. Urol. 2017, 35, 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xylinas, E.; Kluth, L.; Passoni, N.; Trinh, Q.D.; Rieken, M.; Lee, R.K.; Fajkovic, H.; Novara, G.; Margulis, V.; Raman, J.D.; et al. Prediction of Intravesical Recurrence After Radical Nephroureterectomy: Development of a Clinical Decision-making Tool. Eur. Urol. 2014, 65, 650–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yafi, F.A.; Brimo, F.; Steinberg, J.; Aprikian, A.G.; Tanguay, S.; Kassouf, W. Prospective analysis of sensitivity and specificity of urinary cytology and other urinary biomarkers for bladder cancer. Urol. Oncol. Semin. Orig. Investig. 2015, 33, 66.e25–66.e31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanagi, M.; Terasaki, M.; Kiriyama, T.; Terasaki, Y.; Akatsuka, J.; Endo, Y.; Nishimura, T.; Shimizu, A.; Kondo, Y. Perirenal fat stranding as a predictor of disease progression after radical nephroureterectomy for renal pelvic urothelial carcinoma: A retrospective study. Discov. Oncol. 2023, 14, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, J.W.; Lee, J.N.; Park, K.M.; Byeon, K.H.; Cheon, H.; Ha, Y.S.; Choi, S.H.; Kim, B.S.; Kim, T.-H.; Yoo, E.S.; et al. Prognostic impact of perirenal fat stranding on oncologic outcomes in ureteral urothelial carcinoma. Investig. Clin. Urol. 2021, 62, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanagi, M.; Kiriyama, T.; Akatsuka, J.; Endo, Y.; Takeda, H.; Hamasaki, T.; Nishimura, T.; Kondo, Y. Preoperative analysis of factors associated with prolonged pneumoretroperitoneum time during retroperitoneal laparoscopic nephroureterectomy for upper tract urothelial carcinoma. BMC Urol. 2024, 24, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, A.D.; Krishna, S.; Schieda, N. Primary and secondary diseases of the perinephric space: An approach to imaging diagnosis with emphasis on MRI. Clin. Radiol. 2021, 76, 75.e13–75.e26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kallidonis, P.; Spinos, T.; Zondervan, P.; Nyirády, P.; Backhaus, M.R.; Micali, S.; Hruby, S.; Alvarez-Maestro, M.; Tatanis, V.; Liatsikos, E.; et al. Predictive Value of the Mayo Adhesive Probability (MAP) Score in Laparoscopic Partial Nephrectomies: A Systematic Review from the EAU Section of Uro-Technology (ESUT). Cancers 2024, 16, 1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambin, P.; Leijenaar, R.T.H.; Deist, T.M.; Peerlings, J.; De Jong, E.E.C.; Van Timmeren, J.; Sanduleanu, S.; Larue, R.T.H.M.; Even, A.J.G.; Jochems, A.; et al. Radiomics: The bridge between medical imaging and personalized medicine. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 14, 749–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parekh, V.; Jacobs, M.A. Radiomics: A new application from established techniques. Expert. Rev. Precis. Med. Drug Dev. 2016, 1, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillies, R.J.; Kinahan, P.E.; Hricak, H. Radiomics: Images are more than pictures, they are data. Radiology 2016, 278, 563–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kocak, B.; Baessler, B.; Bakas, S.; Cuocolo, R.; Fedorov, A.; Maier-Hein, L.; Mercaldo, N.; Müller, H.; Orlhac, F.; dos Santos, D.P.; et al. CheckList for EvaluAtion of Radiomics research (CLEAR): A step-by-step reporting guideline for authors reviewers endorsed by ESR and EuSoMII. Insights Imaging 2023, 14, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alqahtani, A.; Bhattacharjee, S.; Almopti, A.; Li, C.; Nabi, G. Radiomics-based machine learning approach for the prediction of grade and stage in upper urinary tract urothelial carcinoma: A step towards virtual biopsy. Int. J. Surg. 2024, 110, 3258–3268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Somiya, S.; Kobori, G.; Ito, K.; Nakagawa, H.; Takahashi, T.; Koterazawa, S.; Takaoka, N.; Haitani, T.; Nagahama, K.; Ito, M.; et al. Preoperative risk classification for intravesical recurrence after laparoscopic radical nephroureterectomy for upper tract urothelial carcinoma in a multi-institutional cohort. Int. J. Urol. 2023, 30, 853–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petros, F.G. Epidemiology, clinical presentation, and evaluation of upper-tract urothelial carcinoma. Transl. Androl. Urol. 2020, 9, 1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Characteristic | Value |
|---|---|
| Age, median (range) | 74 years (49–93) |
| Gender, n (%) | |
| Male | 61 (59%) |
| Female | 42 (41%) |
| Smoking Status, n (%) | |
| Current/Former | 80 (78%) |
| Never | 23 (22%) |
| BMI Category, n (%) | |
| Normal | 34 (33%) |
| Overweight | 35 (34%) |
| Obese | 34 (33%) |
| Tumor Location, n (%) | |
| Renal Pelvis | 49 (48%) |
| Ureter | 54 (52%) |
| Histological Grade, n (%) | |
| High grade | 73 (71%) |
| Low grade | 30 (29%) |
| T Stage, n (%) | |
| T1 | 58 (56%) |
| T2 | 18 (18%) |
| T3 or T4 | 27 (26%) |
| Carcinoma in situ, n (%) | 25 (23%) |
| Hydronephrosis, n (%) | 25 (23%) |
| Multifocal, n (%) | 38 (35%) |
| Tumor size, mean ± SD (cm) | 1.97 ± 0.83 |
| Deceased, n (%) | 58 (54%) |
| Recurrence, n (%) | 31 (29%) |
| Variable | Estimate | Std Error | Z Value | p Value | Exp (Coef) | 95% CI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tumor size | −0.41 | 0.25 | −1.69 | 0.091 | 0.66 | 1.50–2.91 |
| Size | 0.10 | 0.18 | 0.56 | 0.57 | 1.10 | 2.19–4.75 |
| Grade | 0.15 | 0.31 | 0.49 | 0.62 | 1.16 | 1.89–8.41 |
| Smoker | −0.25 | 0.18 | −1.42 | 0.16 | 0.78 | 1.73–3.01 |
| Cytology | −0.05 | 0.29 | −0.16 | 0.87 | 0.95 | 1.71–5.46 |
| Metastasis | 0.29 | 0.53 | 0.55 | 0.58 | 1.34 | 1.61–42.74 |
| Hydronephrosis | −0.53 | 0.36 | −1.46 | 0.14 | 0.59 | 1.34–3.31 |
| Body mass index | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.45 | 0.65 | 1.01 | 2.60–2.93 |
| Stage | −0.49 | 0.32 | −1.51 | 0.13 | 0.62 | 1.39–3.18 |
| Multifocal | 0.11 | 0.31 | 0.37 | 0.71 | 1.12 | 1.85–7.67 |
| Location | −0.03 | 0.15 | −0.18 | 0.86 | 0.97 | 2.06–3.69 |
| Side | 0.04 | 0.15 | 0.26 | 0.79 | 1.04 | 2.17–4.03 |
| Gender | −0.12 | 0.15 | −0.77 | 0.44 | 0.89 | 1.94–3.31 |
| Age at operation | −0.04 | 0.17 | −0.23 | 0.82 | 0.96 | 1.98–3.87 |
| Variable | Estimate | Std Error | Z Value | p Value | Exp (Coef) | 95% CI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| original_glcm_InverseVariance | −0.74 | 0.17 | −4.35 | <0.001 | 0.48 | 1.40–1.94 |
| logarithm_firstorder_Entropy | −0.61 | 0.17 | −3.61 | <0.001 | 0.54 | 1.48–2.13 |
| original_glszm_LargeAreaEmphasis | 0.47 | 0.14 | 3.35 | <0.001 | 1.60 | 3.37–8.18 |
| exponential_glszm_GrayLevelNonUniformity | −0.69 | 0.20 | −3.35 | <0.001 | 0.50 | 0.34–0.75 |
| wavelet.HHL_gldm_LargeDependenceLowGrayLevelEmphasis | 0.65 | 0.20 | 3.21 | 0.0013 | 1.92 | 3.63–17.46 |
| wavelet.HHL_glszm_LargeAreaEmphasis | 0.59 | 0.19 | 3.15 | 0.0016 | 1.80 | 3.49–13.45 |
| wavelet.LHL_gldm_LargeDependenceLowGrayLevelEmphasis | 0.56 | 0.18 | 3.10 | 0.0019 | 1.75 | 3.41–11.98 |
| original_gldm_LargeDependenceLowGrayLevelEmphasis | 0.48 | 0.16 | 3.03 | 0.0024 | 1.61 | 3.27–8.94 |
| wavelet.HHL_firstorder_Maximum | −0.61 | 0.20 | −3.03 | 0.0025 | 0.54 | 1.44–2.24 |
| logarithm_glszm_GrayLevelNonUniformityNormalized | 0.45 | 0.15 | 2.97 | 0.0029 | 1.57 | 3.21–8.33 |
| wavelet.LHH_gldm_DependenceEntropy | −0.45 | 0.15 | −2.93 | 0.0034 | 0.64 | 1.61–2.37 |
| exponential_gldm_LargeDependenceHighGrayLevelEmphasis | 0.44 | 0.17 | 2.52 | 0.0118 | 1.55 | 3.01–8.77 |
| lbp.2D_firstorder_InterquartileRange | −0.37 | 0.15 | −2.49 | 0.0127 | 0.69 | 1.68–2.52 |
| wavelet.HHL_glszm_GrayLevelVariance | −0.49 | 0.20 | −2.49 | 0.0128 | 0.61 | 1.52–2.46 |
| wavelet.HHL_gldm_DependenceNonUniformityNormalized | 0.40 | 0.17 | 2.41 | 0.0158 | 1.49 | 2.94–7.90 |
| Model | Feature | Coef | Std_Error | 95% CI | p_Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical | Size | 1.02 | 0.19 | 0.70–1.49 | 0.91 |
| Grade | 2.02 | 0.44 | 0.85–4.79 | 0.11 | |
| Smoker | 0.72 | 0.19 | 0.49–1.05 | 0.09 | |
| Cytology | 0.56 | 0.39 | 0.26–1.21 | 0.14 | |
| Stage | 0.38 | 0.43 | 0.16–0.88 | 0.02 | |
| Hydronephrosis | 0.45 | 0.40 | 0.20–0.98 | 0.04 | |
| PRF radiomics | wavelet.LHH_gldm_DependenceEntropy | 0.40 | 0.22 | 0.26–0.61 | <0.001 |
| exponential_glszm_GrayLevelNonUniformity | 0.49 | 0.19 | 0.33–0.71 | <0.001 | |
| exponential_gldm_LargeDependenceHighGrayLevelEmphasis | 1.57 | 0.18 | 1.12–2.22 | 0.01 | |
| Combined PRF radiomics + clinical | Stage | 0.46 | 0.35 | 0.23–0.92 | 0.03 |
| Hydronephrosis | 0.37 | 0.39 | 0.17–0.80 | 0.01 | |
| wavelet.LHH_gldm_DependenceEntropy | 0.38 | 0.22 | 0.24–0.58 | <0.001 | |
| exponential_glszm_GrayLevelNonUniformity | 0.37 | 0.21 | 0.25–0.57 | <0.001 | |
| exponential_gldm_LargeDependenceHighGrayLevelEmphasis | 1.64 | 0.19 | 1.14–2.38 | 0.01 | |
| Combined PRF + Tumor radiomics + clinical | Stage | 0.45 | 0.36 | 0.22–0.91 | 0.03 |
| Hydronephrosis | 0.47 | 0.43 | 0.20–1.11 | 0.08 | |
| wavelet.LHH_gldm_DependenceEntropy | 0.44 | 0.25 | 0.27–0.72 | <0.001 | |
| exponential_gldm_LargeDependenceHighGrayLevelEmphasis | 1.51 | 0.19 | 1.04–2.21 | 0.03 | |
| exponential_glszm_GrayLevelNonUniformity | 0.39 | 0.24 | 0.24–0.63 | <0.001 | |
| T.wavelet.LHL_glcm_Correlation | 1.24 | 0.20 | 0.84–1.84 | 0.28 | |
| T.wavelet.LLH_glcm_InverseVariance | 1.40 | 0.24 | 0.88–2.25 | 0.16 |
| Model | C-Index (95% CI) | Integrated Brier Score | Optimism-Corrected C-Index | AUC at 12 Months | AUC at 36 Months | AUC at 60 Months |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical | 0.65 (0.55–0.76) | 0.19 | 0.63 | 0.53 | 0.75 | 0.69 |
| Radiomics | 0.76 (0.68–0.84) | 0.14 | 0.73 | 0.93 | 0.75 | 0.80 |
| Combined | 0.78 (0.71–0.86) | 0.13 | 0.75 | 0.89 | 0.79 | 0.84 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al Mopti, A.; Alqahtani, A.; Alshehri, A.H.D.; Li, C.; Nabi, G. Perirenal Fat CT Radiomics-Based Survival Model for Upper Tract Urothelial Carcinoma: Integrating Texture Features with Clinical Predictors. Cancers 2024, 16, 3772. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16223772
Al Mopti A, Alqahtani A, Alshehri AHD, Li C, Nabi G. Perirenal Fat CT Radiomics-Based Survival Model for Upper Tract Urothelial Carcinoma: Integrating Texture Features with Clinical Predictors. Cancers. 2024; 16(22):3772. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16223772
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl Mopti, Abdulrahman, Abdulsalam Alqahtani, Ali H. D. Alshehri, Chunhui Li, and Ghulam Nabi. 2024. "Perirenal Fat CT Radiomics-Based Survival Model for Upper Tract Urothelial Carcinoma: Integrating Texture Features with Clinical Predictors" Cancers 16, no. 22: 3772. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16223772
APA StyleAl Mopti, A., Alqahtani, A., Alshehri, A. H. D., Li, C., & Nabi, G. (2024). Perirenal Fat CT Radiomics-Based Survival Model for Upper Tract Urothelial Carcinoma: Integrating Texture Features with Clinical Predictors. Cancers, 16(22), 3772. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16223772







