The Nitro Group Reshapes the Effects of Pyrido[3,4-g]quinazoline Derivatives on DYRK/CLK Activity and RNA Splicing in Glioblastoma Cells
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
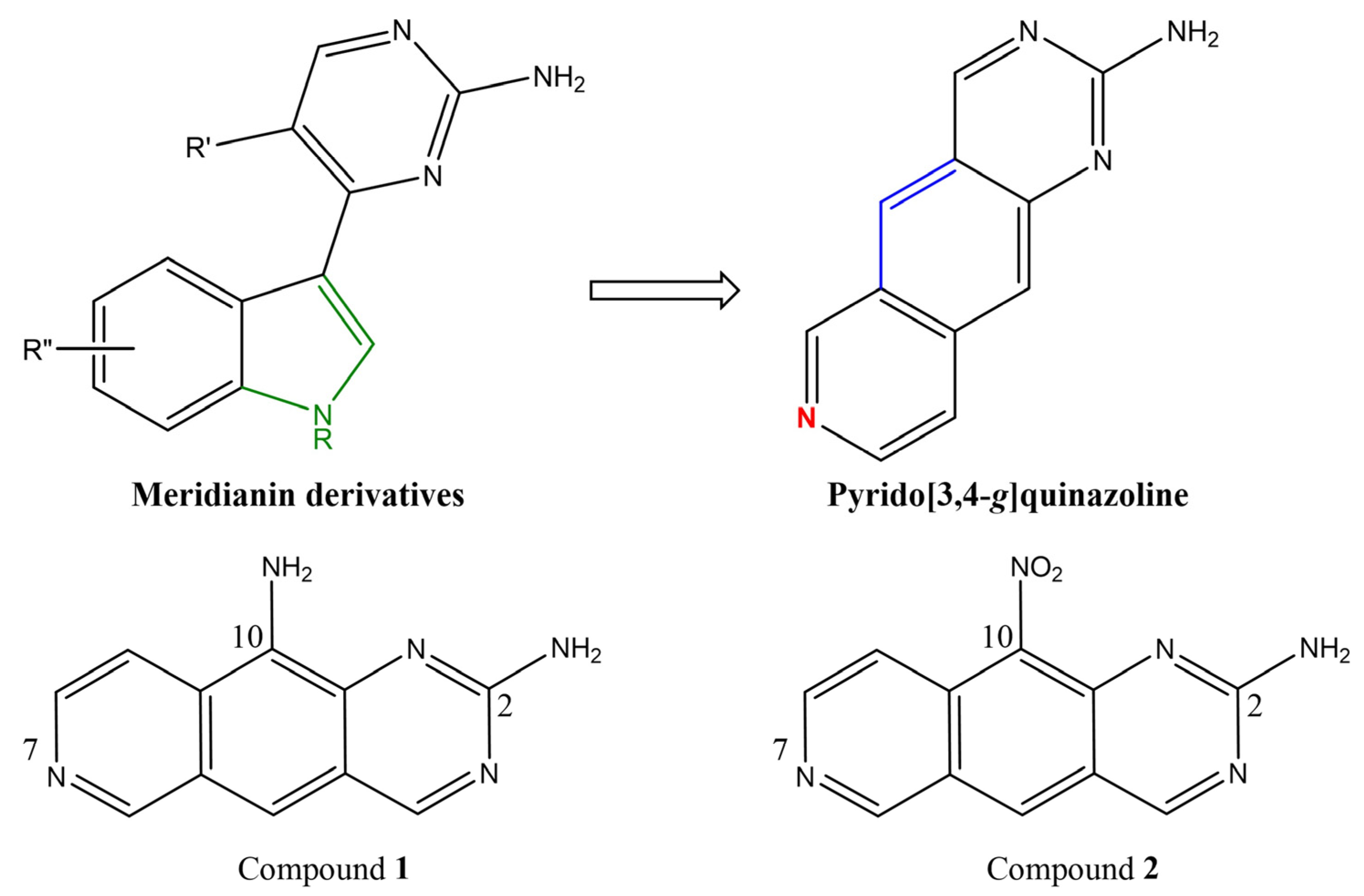
2.1. Pyrido[3,4-g]quinazoline Derivatives
2.2. In Vitro Kinase Assays
2.3. Quantum Chemical Calculations
2.4. Molecular Docking
2.5. MD Simulations
2.6. Analysis of MD Trajectories
2.7. Cell Culture and Viral Transduction
2.8. Cell Viability Assays
2.9. Precipitation of CLK4 Interacting Proteins
2.10. RNA Isolation and RT-PCR
2.11. Peptide Preparation for LC-MS/MS Analysis
2.12. LC-MS/MS Analysis
2.13. Protein Identification and Quantification
2.14. Plasmid Construction
2.15. RNA Sequencing
2.16. Analysis of Gene Expression and Alternative Splicing
2.17. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Differential Inhibition of DYRK/CLK Family Members by 1 and 2
3.2. Electron Parameters of Compounds 1 and 2
3.3. Molecular Docking of 1 and 2 into DYRK3 and CLK4 Models
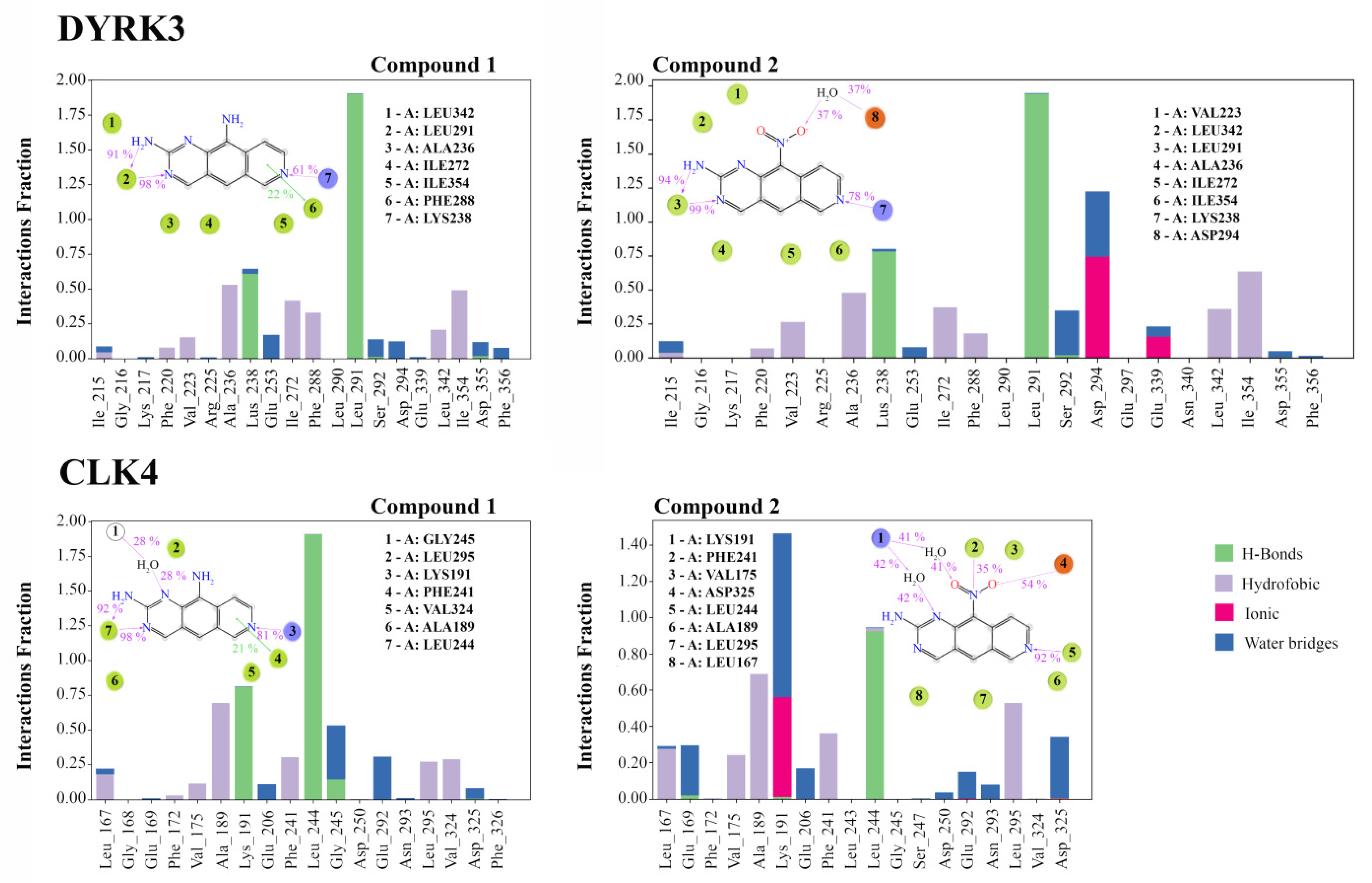
3.4. Analysis of Ligand–Target Interactions by MD
3.5. Differential Effect of Compounds 1 and 2 on RNA Splicing in GBM Neurospheres
3.6. Compound 2 Alters the Interactions of CLK4 with Its Substrates
3.7. Effect of Compound 2 on the Transcriptome of GBM Cells
4. Discussion
5. Study Limitations
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lindberg, M.F.; Meijer, L. Dual-specificity, tyrosine phosphorylation-regulated kinases (DYRKs) and cdc2-like kinases (CLKs) in human disease, an overview. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Hady, A.K.; El-Gamil, D.S.; Abadi, A.H.; Abdel-Halim, M.; Engel, M. An overview of cdc2-like kinase 1 (Clk1) inhibitors and their therapeutic indications. Med. Res. Rev. 2023, 43, 343–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deboever, E.; Fistrovich, A.; Hulme, C.; Dunckley, T. The omnipresence of DYRK1A in human diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, L.; Terasaki, M.; Mattsson, C.L.; Teinturier, R.; Charbord, J.; Dirice, E.; Liu, K.-C.; Miskelly, M.G.; Zhou, Q.; Wierup, N.; et al. In vivo drug discovery for increasing incretin-expressing cells identifies DYRK inhibitors that reinforce the enteroendocrine system. Cell Chem. Biol. 2022, 29, 1368–1380.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, C.; Chen, C.; Qu, S.; Cao, N.; Luo, H.; Yu, C.; Wang, N.; Xue, Y.; Xia, X.; Fan, C.; et al. Inhibition of DYRK1A, via histone modification, promotes cardiomyocyte cell cycle activation and cardiac repair after myocardial infarction. eBioMedicine 2022, 82, 104139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wu, L.W.; Li, Z.D.; Zhang, M.M.; Wu, J.; Du, F.-H.; Zeng, L.-H.; Li, Y.-L. DYRK1A suppression attenuates HIF 1α accumulation and enhances the anti-liver cancer effects of regorafenib and sorafenib under hypoxic conditions. Int. J. Oncol. 2022, 60, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bullock, A.N.; Das, S.; Debreczeni, J.E.; Rellos, P.; Fedorov, O.; Niesen, F.H. Kinase domain insertions define distinct roles of CLK kinases in SR protein phosphorylation. Structure 2009, 17, 352–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aranda, S.; Laguna, A.; de la Luna, S. DYRK family of protein kinases: Evolutionary relationships, biochemical properties, and functional roles. FASEB J. 2011, 25, 449–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moyano, P.M.; Němec, V.; Paruch, K. Cdc-like kinases (CLKs): Biology, chemical probes, and therapeutic potential. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esvan, Y.J.; Zeinyeh, W.; Boibessot, T.; Nauton, L.; Théry, V.; Knapp, S.; Chaikuad, A.; Loaëc, N.; Meijer, L.; Anizon, F.; et al. Discovery of pyrido[3,4-g]quinazoline derivatives as CMGC family protein kinase inhibitors: Design, synthesis, inhibitory potency and X-ray co-crystal structure. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 118, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tazarki, H.; Zeinyeh, W.; Esvan, Y.J.; Knapp, S.; Chatterjee, D.; Schröder, M.; Joerger, A.C.; Khiari, J.; Josselin, B.; Baratte, B.; et al. New pyrido[3,4-g]quinazoline derivatives as CLK1 and DYRK1A inhibitors: Synthesis, biological evaluation and binding mode analysis. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 166, 304–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusina, P.V.; Abdusheva, Y.R.; Gandalipov, E.R.; Panova, M.V.; Burdenkova, A.V.; Chalyi, V.; Brachs, M.; Stroganov, O.; Guzeeva, K.; Svitanko, I.; et al. Imidazole-4-N-acetamide derivatives as a novel scaffold for preferential targeting of cyclin dependent kinase 2. Cancers 2023, 15, 3766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Home-GraphPad. Available online: https://www.graphpad.com/ (accessed on 9 August 2023).
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Mennucci, B.; Petersson, G.A.; et al. Gaussian 09; Gaussian, Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Truhlar, D.G. The M06 suite of density functionals for main group thermochemistry, thermochemical kinetics, noncovalent interactions, excited states, and transition elements: Two new functionals and systematic testing of four M06-class functionals and 12 other functionals. Theor. Chem. Acc. 2008, 120, 215–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaefer, A.; Horn, H.; Ahlrichs, R. Fully optimized contracted Gaussian-basis sets for atoms Li to Kr. J. Chem. Phys. 1992, 97, 2571–2577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaefer, A.; Huber, C.; Ahlrichs, R. Fully optimized contracted Gaussian-basis sets of triple zeta valence quality for atoms Li to Kr. J. Chem. Phys. 1994, 100, 5829–5835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cramer, C.J. Essentials of Computational Chemistry: Theories and Models, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: West Sussex, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Berman, H.M.; Westbrook, J.; Feng, Z.; Gilliland, G.; Bhat, T.N.; Weissig, H.; Shindyalov, I.N.; Bourne, P.E. The Protein Data Bank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallen, J.; Bergsdorf, C.; Arnaud, B.; Bernhard, M.; Brichet, M.; Cobos-Correa, A.; Elhajouji, A.; Freuler, F.; Galimberti, I.; Guibourdenche, C.; et al. X-ray structures and feasibility assessment of CLK2 inhibitors for Phelan-McDermid syndrome. ChemMedChem 2018, 13, 1997–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Cha, J.S.; Cho, Y.-S.; Kim, H.; Chang, N.; Kim, H.-J.; Cho, H.-S. Crystal structure of human dual-specificity tyrosine-regulated kinase 3 reveals new structural features and insights into its auto-phosphorylation. Mol. Biol. 2018, 430, 1521–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larionova, T.D.; Bastola, S.; Aksinina, T.E.; Anufrieva, K.S.; Wang, J.; Shender, V.O.; Andreev, D.E.; Kovalenko, T.F.; Arapidi, G.P.; Shnaider, P.V.; et al. Alternative RNA splicing modulates the composition of ribosomes and determines spatial phenotype of glioblastoma cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 2022, 24, 1541–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlyukov, M.S.; Antipova, N.V.; Balashova, M.V.; Vinogradova, T.V.; Kopantzev, E.P.; Shakhparonov, M.I. Survivin monomer plays an essential role in apoptosis regulation. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 23296–23307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://string-db.org (accessed on 1 December 2023).
- Kashyap, M.K.; Kumar, D.; Villa, R.; La Clair, J.J.; Benner, C.; Sasik, R.; Jones, H.; Ghia, E.M.; Rassenti, L.Z.; Kipps, T.J.; et al. Targeting the spliceosome in chronic lymphocytic leukemia with the macrolides FD-895 and pladienolide-B. Haematologica 2015, 100, 945–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawellek, A.; McElroy, S.; Samatov, T.; Mitchell, L.; Woodland, A.; Ryder, U.; Gray, D.; Lührmann, R.; Lamond, A.I. Identification of small molecule inhibitors of pre-mRNA splicing. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 34683–34698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czabotar, P.E.; Garcia-Saez, A.J. Mechanisms of BCL-2 family proteins in mitochondrial apoptosis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2023, 24, 732–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Fan, L.; Edmonson, M.N.; Shaw, T.; Boggs, K.; Easton, J.; Rusch, M.C.; Webb, T.R.; Zhang, J.; Potter, P.M. Inhibition of SF3B1 by molecules targeting the spliceosome results in massive aberrant exon skipping. RNA 2018, 24, 1056–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Wan, X.; Huang, T.; Zeng, C.; Sastry, N.; Wu, B.; James, C.D.; Horbinski, C.; Nakano, I.; Zhang, W.; et al. SRSF3-regulated RNA alternative splicing promotes glioblastoma tumorigenicity by affecting multiple cellular processes. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 5288–5301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Xie, Y.; Huang, J.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, W.; Li, Z.; Bian, J. A critical update on the strategies towards small molecule inhibitors targeting Serine/arginine-rich (SR) proteins and Serine/arginine-rich proteins related kinases in alternative splicing. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2022, 70, 116921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, B.Y.; Chiu, K.; Chung, H.; Bossard, C.; Nguyen, J.D.; Creger, E.; Eastman, B.W.; Mak, C.C.; Ibanez, M.; Ghias, A.; et al. The CLK inhibitor SM08502 induces anti-tumor activity and reduces Wnt pathway gene expression in gastrointestinal cancer models. Cancer Lett. 2020, 473, 186–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoda, A.; Morishita, D.; Ochi, Y.; Mizutani, A.; Takeda, J.; Tozaki, H.; Satoh, Y.; Nannya, Y.; Makishima, H.; Miyake, H.; et al. CTX-712, a novel Clk inhibitor targeting myeloid neoplasms with SRSF2 mutation. Blood 2021, 138 (Suppl. S1), 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brahmaiah, D.; Bhavani, A.K.D.; Aparna, P.; Kumar, N.S.; Solhi, H.; Le Guevel, R.; Baratte, B.; Ruchaud, S.; Bach, S.; Singh Jadav, S.; et al. Discovery of DB18, a potent inhibitor of CLK kinases with a high selectivity against DYRK1A kinase. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2021, 31, 115962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee Walmsley, D.; Murray, J.B.; Dokurno, P.; Massey, A.J.; Benwell, K.; Fiumana, A.; Foloppe, N.; Ray, S.; Smith, J.; Surgenor, A.E.; et al. Fragment-derived selective inhibitors of dual-specificity kinases DYRK1A and DYRK1B. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 8971–8991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindberg, M.F.; Deau, E.; Arfwedson, J.; George, G.; George, P.; Alfonso, P.; Corrionero, A.; Meijer, L. Comparative efficacy and selectivity of pharmacological inhibitors of DYRK and CLK protein kinases. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 66, 4106–4130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolcher, A.; Babiker, H.M.; Chung, V.; Kim, E.; Moser, J.; Karim, R.; Vandross, A.; Sommerhalder, D.; Scott, A.J.; Fakih, M. Initial results from a Phase 1 trial of a first-in-class pan-CDC-like kinase inhibitor (SM08502) with proof of mechanism in subjects with advanced solid tumors. Cancer Res. 2021, 81 (Suppl. S13), CT112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, T.; Yonemori, K.; Koyama, T.; Katsuya, Y.; Sato, J.; Fukuhara, N.; Miyake, H.; Tanoue, Y.; Tozaki, H.; Mizutani, A.; et al. A first-in-human phase I study of CTX-712 in patients with advanced, relapsed or refractory malignant tumors. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 3080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoyama, H.; Ando, K.; Fukuhara, N.; Iida, H.; Fukuhara, S.; Miyake, H.; Tanoue, Y.; Yamamoto, M.; Tozaki, H.; Mizutani, A. A first-in-human Phase I study of CTX-712 in patients with advanced, relapsed or refractory malignant tumors-hematologic malignancies dose escalation cohort. Blood 2022, 140, 6211–6212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, D.S.; Kurzrock, R.; Naing, A.; Wheler, J.; Falchook, G.; Schiffman, J.; Faulkner, N.; Pilat, M.J.; O’Brien, J.; LoRusso, P. A phase I, open-label, single-arm, dose-escalation study of E7107, a precursor messenger ribonucleic acid (pre-mRNA) spliceosome inhibitor administered intravenously on days 1 and 8 every 21 days to patients with solid tumors. Investig. New Drugs 2013, 32, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, E.; Pineda, J.; Kim, W.; Chen, S.; Bourcier, J.; Stahl, M.; Hogg, S.; Bewersdorf, J.P.; Han, C.; Singer, M.E.; et al. Modulation of RNA splicing enhances response to BCL2 inhibition in leukemia. Cancer Cell 2022, 41, 164–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Protein Kinase | Compound 1 | Compound 2 |
|---|---|---|
| DYRK1A | 28 ± 6 | 159 ± 18 |
| DYRK1B | 22 ± 5 | 63 ± 14 |
| DYRK2 | 31 ± 6 | 80 ± 16 |
| DYRK3 | 154 ± 18 | 16 ± 5 |
| DYRK4 | 1220 ± 192 | 9420 ± 221 |
| CLK1 | 41 ± 8 | 87 ± 12 |
| CLK2 | 350 ± 28 | 391 ± 40 |
| CLK3 | 4630 ± 150 | 4660 ± 122 |
| CLK4 | 58,700 ± 1266 | 81 ± 10 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Borisevich, S.S.; Aksinina, T.E.; Ilyina, M.G.; Shender, V.O.; Anufrieva, K.S.; Arapidi, G.P.; Antipova, N.V.; Anizon, F.; Esvan, Y.J.; Giraud, F.; et al. The Nitro Group Reshapes the Effects of Pyrido[3,4-g]quinazoline Derivatives on DYRK/CLK Activity and RNA Splicing in Glioblastoma Cells. Cancers 2024, 16, 834. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16040834
Borisevich SS, Aksinina TE, Ilyina MG, Shender VO, Anufrieva KS, Arapidi GP, Antipova NV, Anizon F, Esvan YJ, Giraud F, et al. The Nitro Group Reshapes the Effects of Pyrido[3,4-g]quinazoline Derivatives on DYRK/CLK Activity and RNA Splicing in Glioblastoma Cells. Cancers. 2024; 16(4):834. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16040834
Chicago/Turabian StyleBorisevich, Sophia S., Tatiana E. Aksinina, Margarita G. Ilyina, Victoria O. Shender, Ksenia S. Anufrieva, Georgij P. Arapidi, Nadezhda V. Antipova, Fabrice Anizon, Yannick J. Esvan, Francis Giraud, and et al. 2024. "The Nitro Group Reshapes the Effects of Pyrido[3,4-g]quinazoline Derivatives on DYRK/CLK Activity and RNA Splicing in Glioblastoma Cells" Cancers 16, no. 4: 834. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16040834
APA StyleBorisevich, S. S., Aksinina, T. E., Ilyina, M. G., Shender, V. O., Anufrieva, K. S., Arapidi, G. P., Antipova, N. V., Anizon, F., Esvan, Y. J., Giraud, F., Tatarskiy, V. V., Moreau, P., Shakhparonov, M. I., Pavlyukov, M. S., & Shtil, A. A. (2024). The Nitro Group Reshapes the Effects of Pyrido[3,4-g]quinazoline Derivatives on DYRK/CLK Activity and RNA Splicing in Glioblastoma Cells. Cancers, 16(4), 834. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16040834









