Statin-Sensitive Akt1/Src/Caveolin-1 Signaling Enhances Oxidative Stress Resistance in Rhabdomyosarcoma
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bioinformatic Analysis
2.2. Reagents and Antibodies
2.3. Cell Cultures
2.4. ROS Measurement
2.5. IR Treatments
2.6. Immunoblotting Analysis
2.7. Clonogenic Assay
2.8. Immunofluorescence Analysis
2.9. PCR Analysis
2.10. Flow Cytometric Analysis
2.11. Neutral Red Assay
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
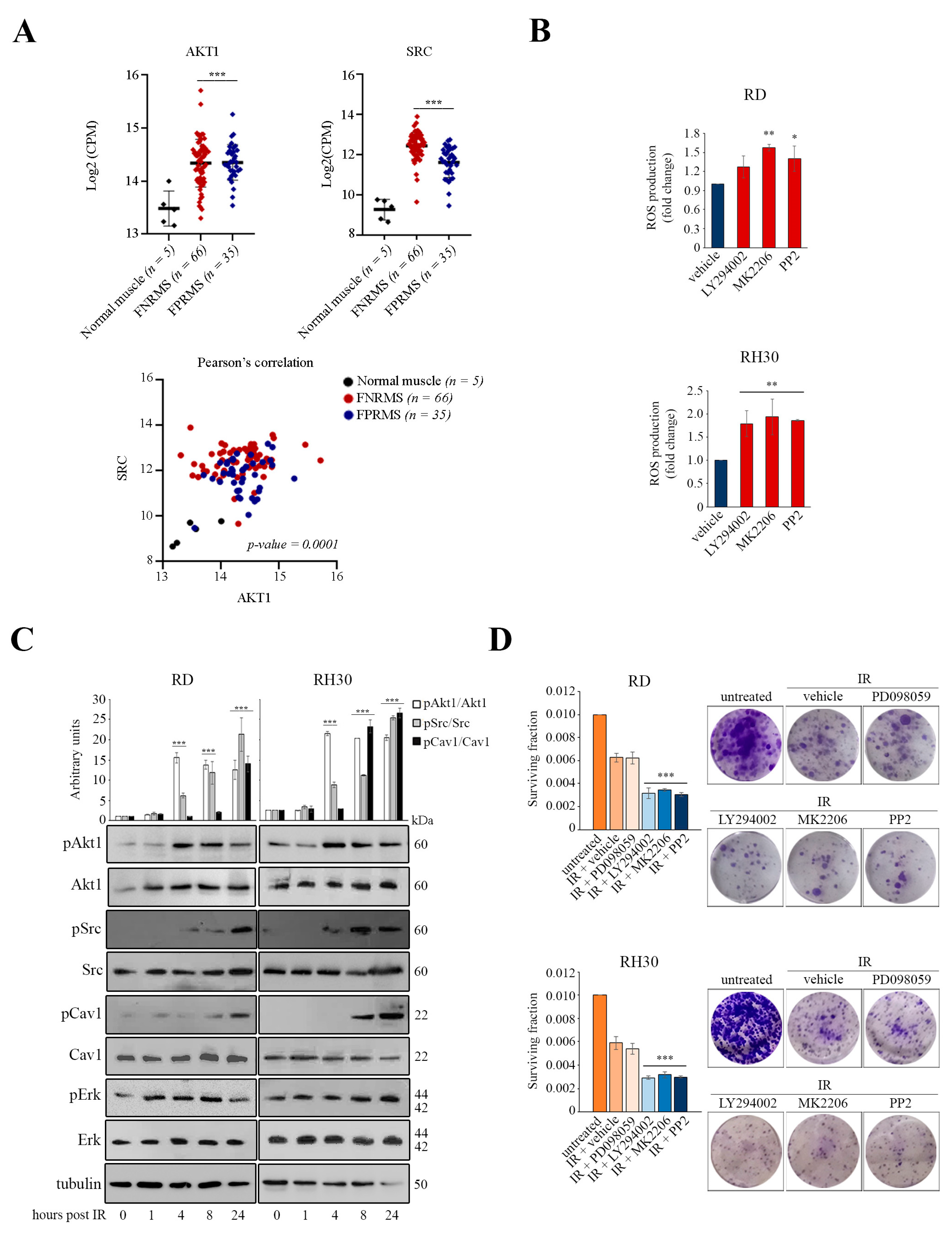
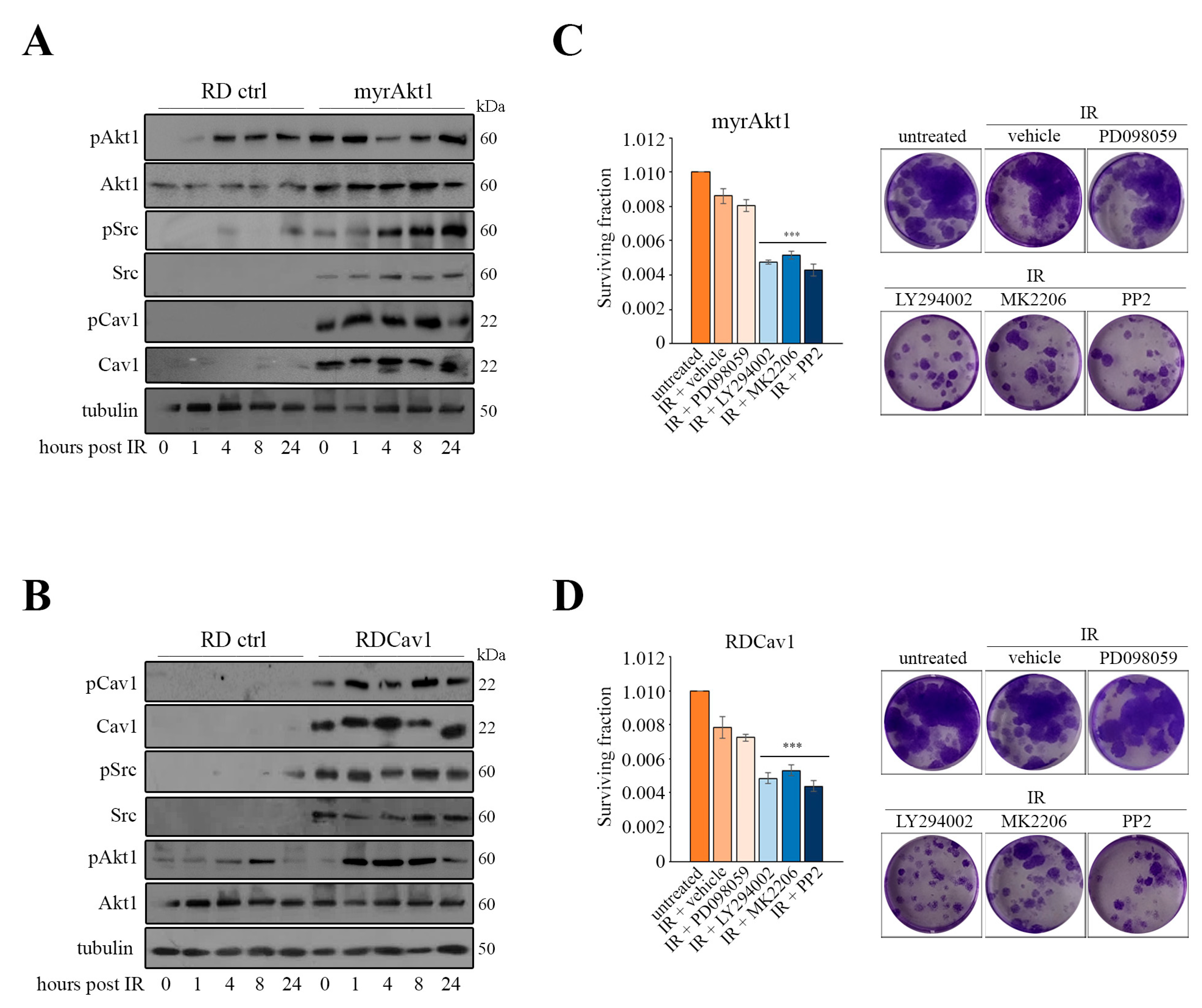
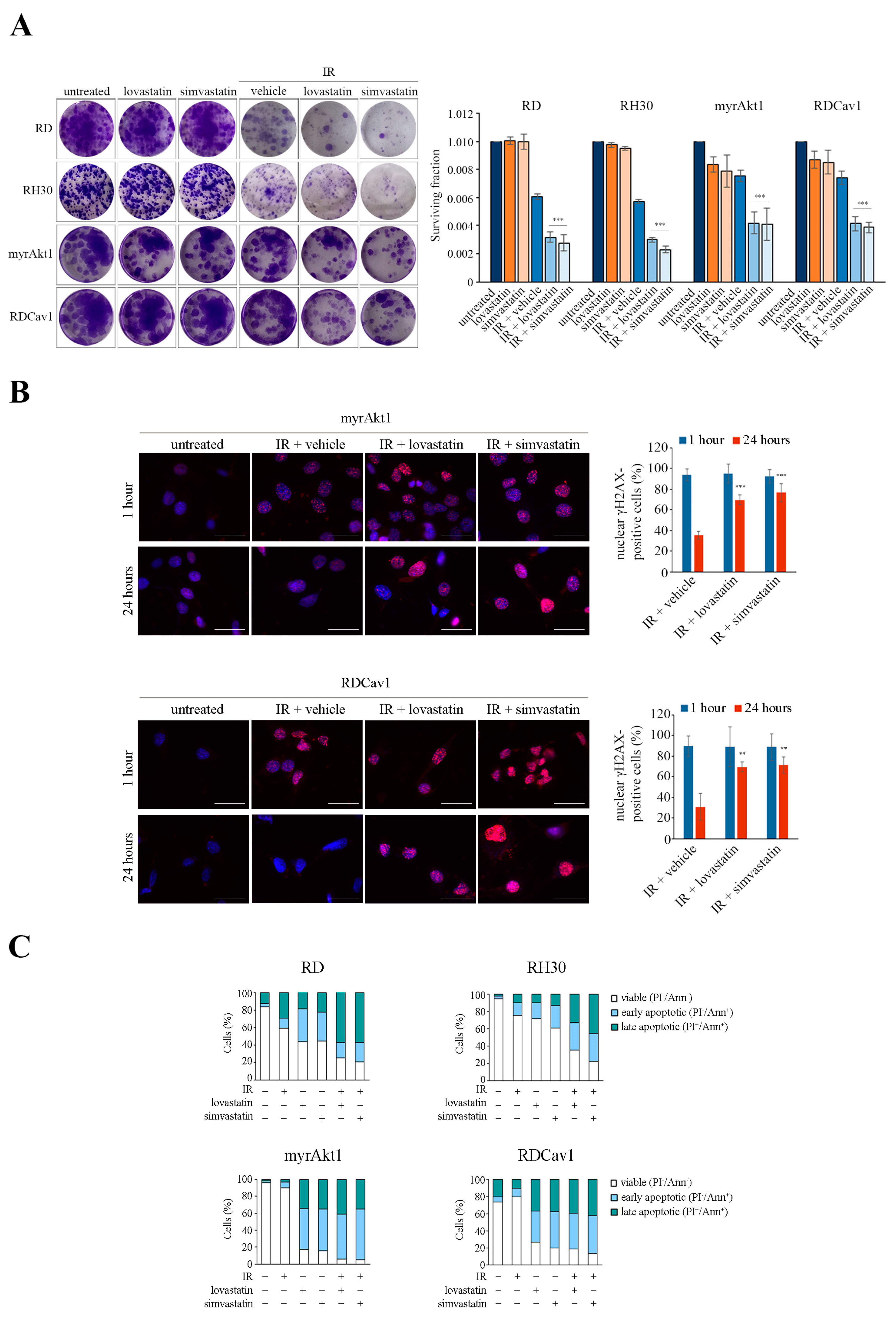
3.1. Activation of the Akt1/Src/Cav1 Axis Promotes Cell Survival in Post-Irradiated RD and RH30 Lines
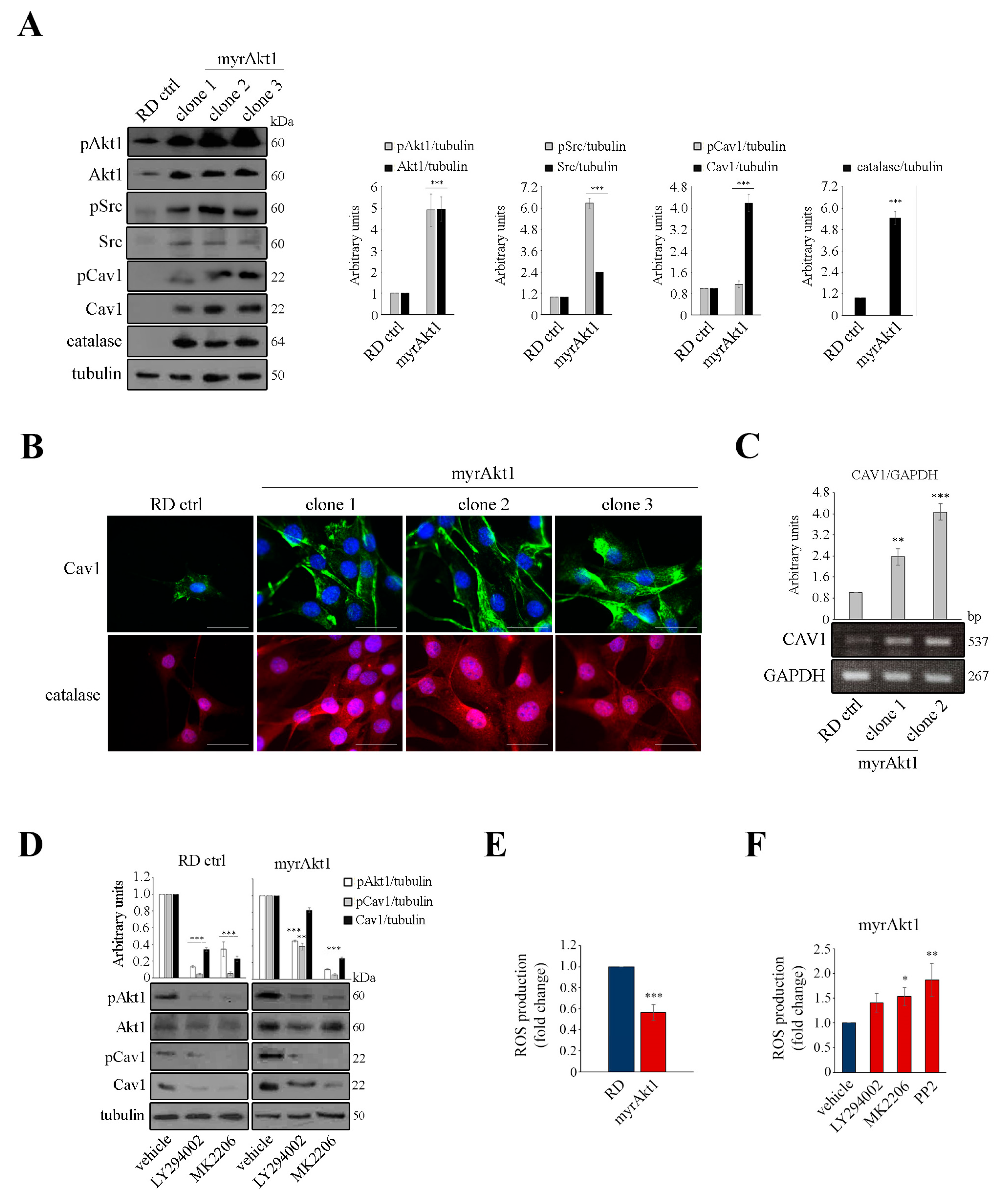
3.2. Akt1/Src/Cav1/Catalase Signaling Promotes Radioresistance by Buffering Oxidative Stress in RD Cells
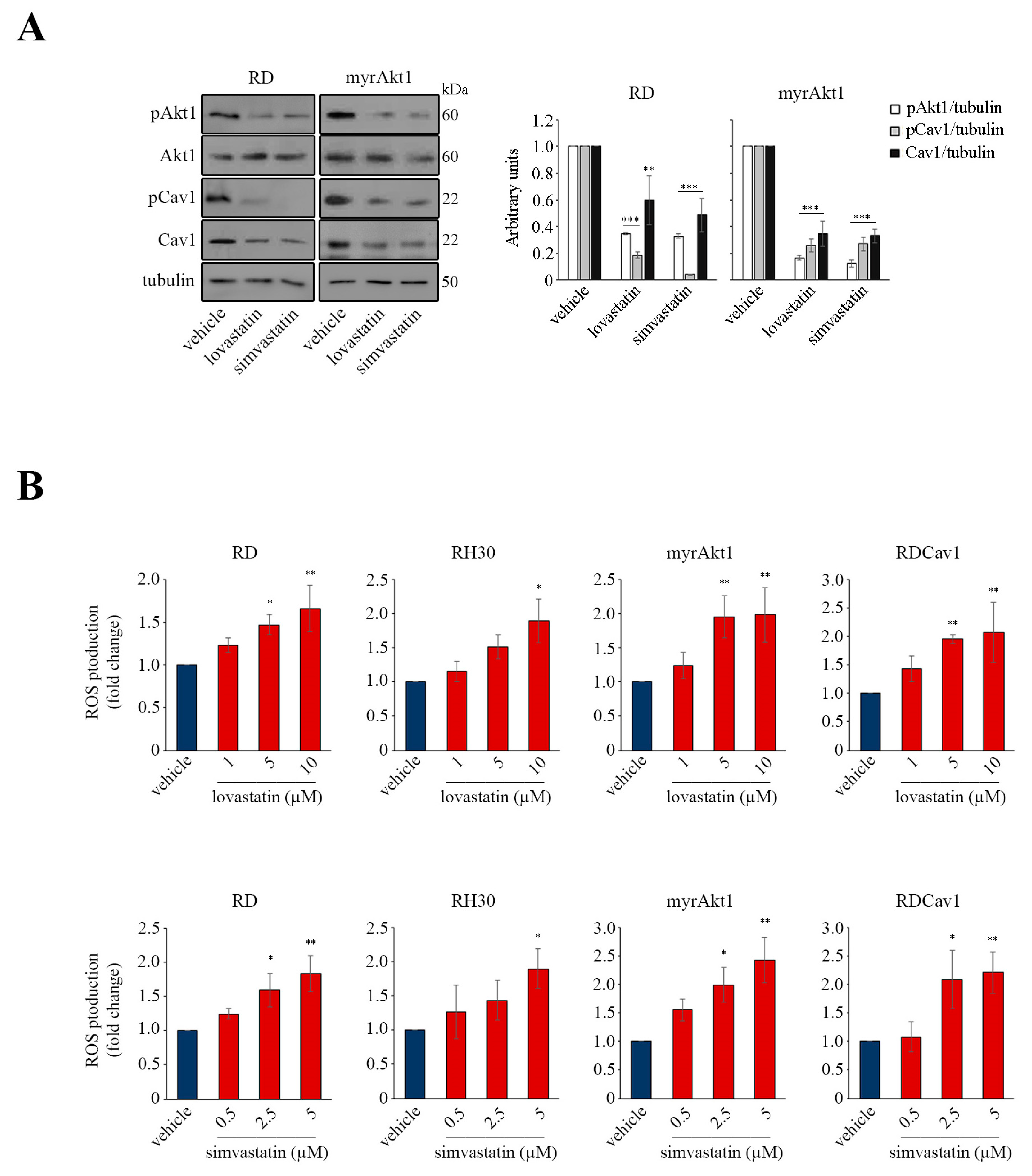
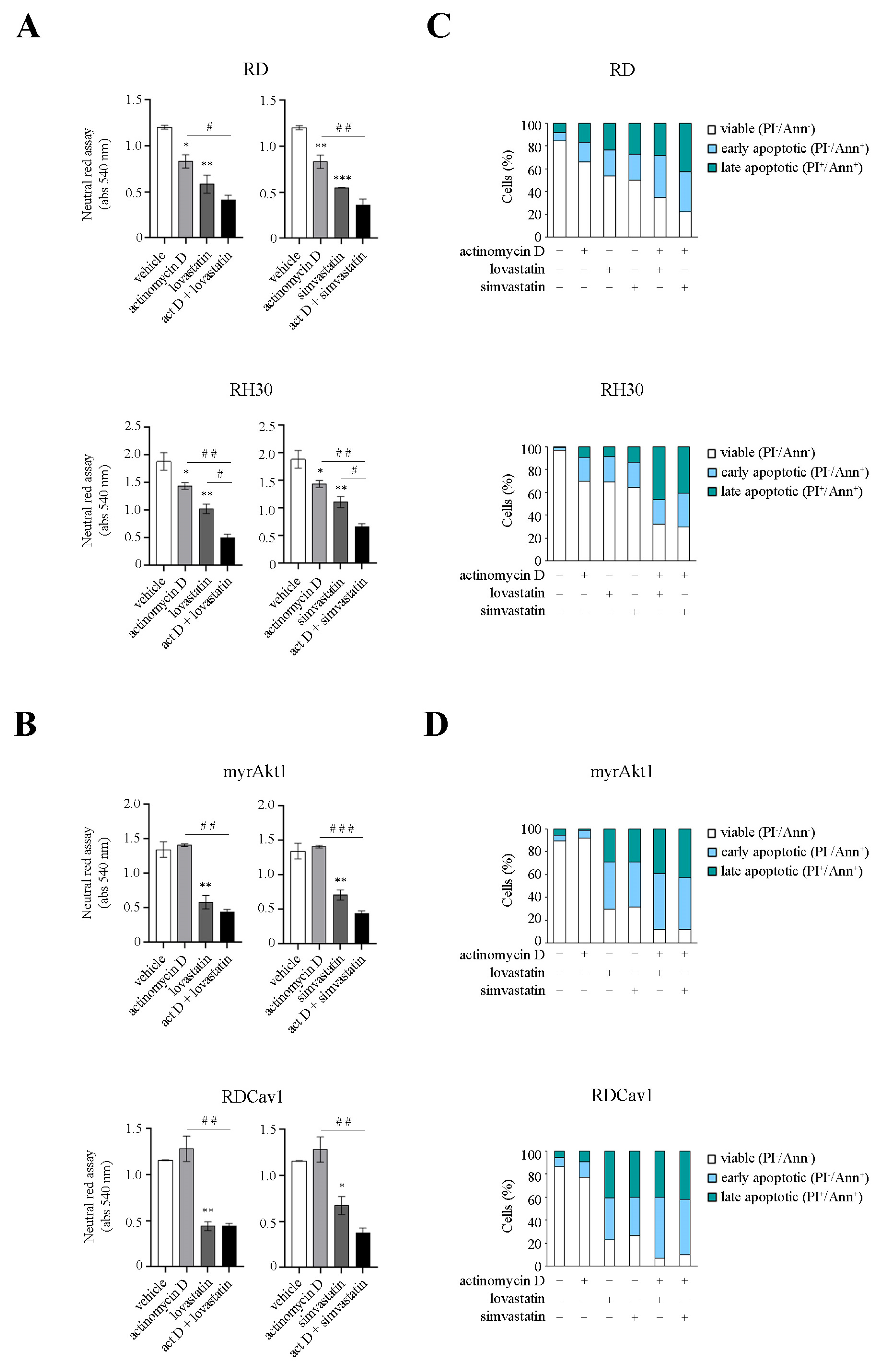
3.3. Statin Treatment Induces Radio- and Chemosensitization through Downregulation of Akt1/Cav1 Signaling and Increased Levels of Oxidative Stress
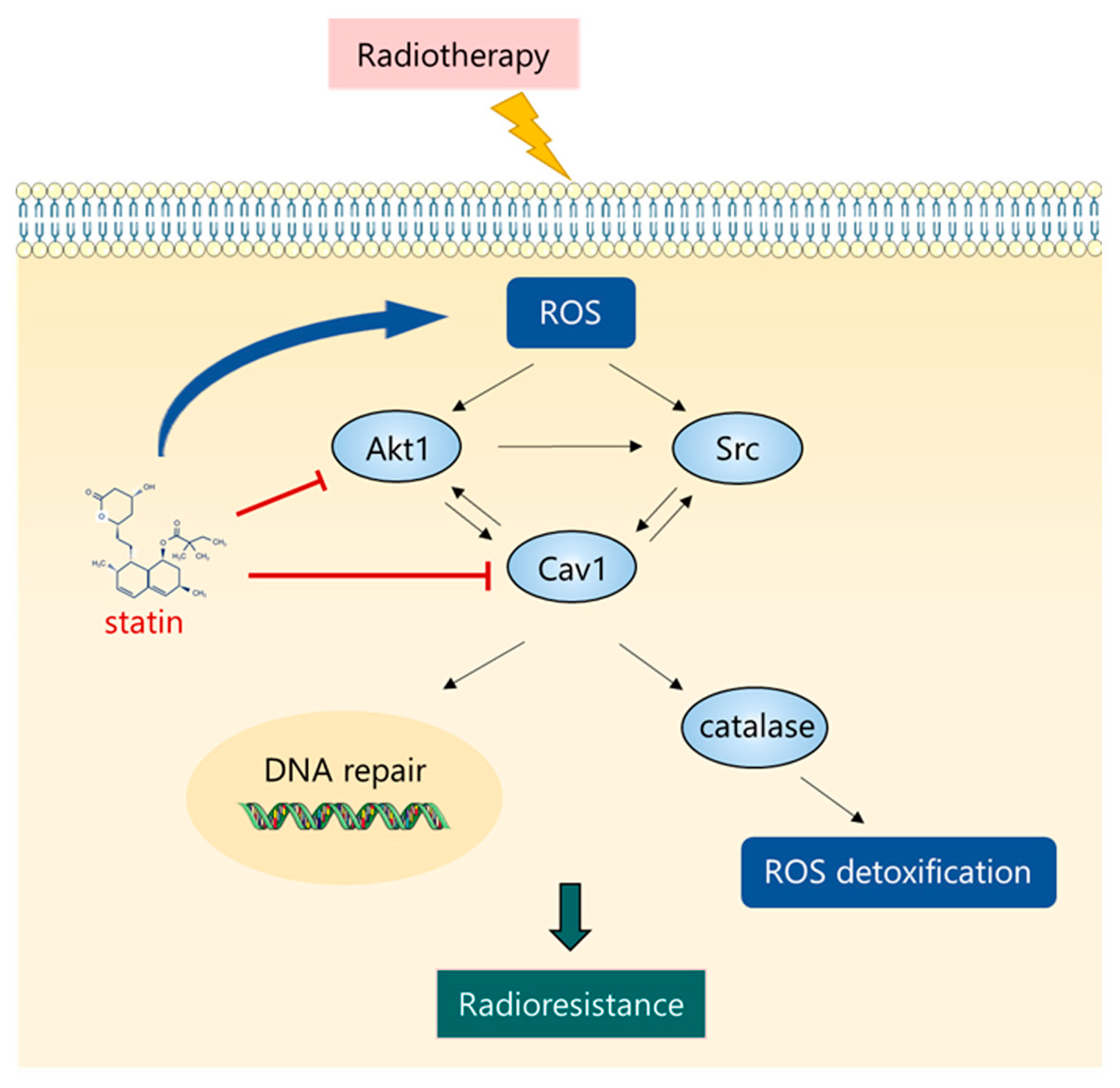
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Leiner, J.; Le Loarer, F. The current landscape of rhabdomyosarcomas: An update. Virchows. Arch. 2020, 476, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacenta, H.L.; Allen-Rhoades, W.; Langenau, D.; Houghton, P.J.; Keller, C.; Heske, C.M.; Deel, M.D.; Linardic, C.M.; Shern, J.F.; Stewart, E.; et al. Prioritization of Novel Agents for Patients with Rhabdomyosarcoma: A Report from the Children’s Oncology Group (COG) New Agents for Rhabdomyosarcoma Task Force. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camero, S.; Cassandri, M.; Pomella, S.; Milazzo, L.; Vulcano, F.; Porrazzo, A.; Barillari, G.; Marchese, C.; Codenotti, S.; Tomaciello, M.; et al. Radioresistance in rhabdomyosarcomas: Much more than a question of dose. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 1016894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shern, J.F.; Chen, L.; Chmielecki, J.; Wei, J.S.; Patidar, R.; Rosenberg, M.; Ambrogio, L.; Auclair, D.; Wang, J.; Song, Y.K.; et al. Comprehensive genomic analysis of rhabdomyosarcoma reveals a landscape of alterations affecting a common genetic axis in fusion-positive and fusion-negative tumors. Cancer Discov. 2014, 4, 216–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramadan, F.; Fahs, A.; Ghayad, S.E.; Saab, R. Signaling pathways in Rhabdomyosarcoma invasion and metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2020, 39, 287–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, N.; Lao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Gillespie, D.A. Akt: A double-edged sword in cell proliferation and genome stability. J. Oncol. 2012, 2012, 951724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manning, B.D.; Toker, A. AKT/PKB Signaling: Navigating the Network. Cell 2017, 169, 381–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petricoin, E.F.; Espina, V.; Araujo, R.P.; Midura, B.; Yeung, C.; Wan, X.; Eichler, G.S.; Johann, D.J.; Qualman, S.; Tsokos, M.; et al. Phosphoprotein pathway mapping: Akt/mammalian target of rapamycin activation is negatively associated with childhood rhabdomyosarcoma survival. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 3431–3440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Codenotti, S.; Zizioli, D.; Mignani, L.; Rezzola, S.; Tabellini, G.; Parolini, S.; Giacomini, A.; Asperti, M.; Poli, M.; Mandracchia, D.; et al. Hyperactive Akt1 Signaling Increases Tumor Progression and DNA Repair in Embryonal Rhabdomyosarcoma RD Line and Confers Susceptibility to Glycolysis and Mevalonate Pathway Inhibitors. Cells 2022, 11, 2859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shor, A.C.; Keschman, E.A.; Lee, F.Y.; Muro-Cacho, C.; Letson, G.D.; Trent, J.C.; Pledger, W.J.; Jove, R. Dasatinib inhibits migration and invasion in diverse human sarcoma cell lines and induces apoptosis in bone sarcoma cells dependent on SRC kinase for survival. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 2800–2808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Li, J.; Fang, B.; Edwards, A.; Zhang, G.; Bui, M.; Eschrich, S.; Altiok, S.; Koomen, J.; Haura, E.B. Phosphoproteomics identifies driver tyrosine kinases in sarcoma cell lines and tumors. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 2501–2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, J.; Chua, Y.X.; Glover, J.M.; Tyner, J.W.; Loriaux, M.M.; Kilcoyne, A.; Giles, F.J.; Nelon, L.D.; Carew, J.S.; Ouyang, Y.; et al. An adaptive Src-PDGFRA-Raf axis in rhabdomyosarcoma. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 426, 363–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, X.; Yeung, C.; Heske, C.; Mendoza, A.; Helman, L.J. IGF-1R Inhibition Activates a YES/SFK Bypass Resistance Pathway: Rational Basis for Co-Targeting IGF-1R and Yes/SFK Kinase in Rhabdomyosarcoma. Neoplasia 2015, 17, 358–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akshintala, S.; Sundby, R.T.; Bernstein, D.; Glod, J.W.; Kaplan, R.N.; Yohe, M.E.; Gross, A.M.; Derdak, J.; Lei, H.; Pan, A.; et al. Phase I trial of Ganitumab plus Dasatinib to Cotarget the Insulin-Like Growth Factor 1 Receptor and Src Family Kinase YES in Rhabdomyosarcoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2023, 29, 3329–3339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murata, M.; Peränen, J.; Schreiner, R.; Wieland, F.; Kurzchalia, T.V.; Simons, K. VIP21/caveolin is a cholesterol-binding protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 10339–10343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parton, R.G. Caveolae: Structure, Function, and Relationship to Disease. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2018, 34, 111–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faggi, F.; Mitola, S.; Sorci, G.; Riuzzi, F.; Donato, R.; Codenotti, S.; Poliani, P.L.; Cominelli, M.; Vescovi, R.; Rossi, S.; et al. Phosphocaveolin-1 enforces tumor growth and chemoresistance in rhabdomyosarcoma. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e84618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faggi, F.; Chiarelli, N.; Colombi, M.; Mitola, S.; Ronca, R.; Madaro, L.; Bouche, M.; Poliani, P.L.; Vezzoli, M.; Longhena, F.; et al. Cavin-1 and Caveolin-1 are both required to support cell proliferation, migration and anchorage-independent cell growth in rhabdomyosarcoma. Lab. Investig. 2015, 95, 585–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Codenotti, S.; Faggi, F.; Ronca, R.; Chiodelli, P.; Grillo, E.; Guescini, M.; Megiorni, F.; Marampon, F.; Fanzani, A. Caveolin-1 enhances metastasis formation in a human model of embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma through Erk signaling cooperation. Cancer Lett. 2019, 449, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glenney, J.R. Tyrosine phosphorylation of a 22-kDa protein is correlated with transformation by Rous sarcoma virus. J. Biol. Chem. 1989, 264, 20163–20166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, A.; Burgos-Ravanal, R.; González, M.F.; Huilcaman, R.; Lobos González, L.; Quest, A.F.G. Cell Intrinsic and Extrinsic Mechanisms of Caveolin-1-Enhanced Metastasis. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, T.H.; Dickson, F.H.; Timmins, L.R.; Nabi, I.R. Tyrosine phosphorylation of tumor cell caveolin-1: Impact on cancer progression. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2020, 39, 455–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Codenotti, S.; Marampon, F.; Triggiani, L.; Bonù, M.L.; Magrini, S.M.; Ceccaroli, P.; Guescini, M.; Gastaldello, S.; Tombolini, V.; Poliani, P.L.; et al. Caveolin-1 promotes radioresistance in rhabdomyosarcoma through increased oxidative stress protection and DNA repair. Cancer Lett. 2021, 505, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petragnano, F.; Pietrantoni, I.; Camero, S.; Codenotti, S.; Milazzo, L.; Vulcano, F.; Macioce, G.; Giordani, I.; Tini, P.; Cheleschi, S.; et al. Clinically relevant radioresistant rhabdomyosarcoma cell lines: Functional, molecular and immune-related characterization. J. Biomed. Sci. 2020, 27, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuzu, O.F.; Noory, M.A.; Robertson, G.P. The Role of Cholesterol in Cancer. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 2063–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, S.X.; Son, E.W.; Yao, R. iDEP: An integrated web application for differential expression and pathway analysis of RNA-Seq data. BMC Bioinform. 2018, 19, 534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galasso, M.; Gambino, S.; Romanelli, M.G.; Donadelli, M.; Scupoli, M.T. Browsing the oldest antioxidant enzyme: Catalase and its multiple regulation in cancer. Free Radic Biol. Med. 2021, 172, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, A.; Wu, Q.; Guo, J.; Ares, I.; Rodríguez, J.L.; Martínez-Larrañaga, M.R.; Yuan, Z.; Anadón, A.; Wang, X.; Martínez, M.A. Statins: Adverse reactions, oxidative stress and metabolic interactions. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 195, 54–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoyama, C.; Sueyoshi, Y.; Ema, M.; Mori, Y.; Takaishi, K.; Hisatomi, H. Induction of oxidative stress by anticancer drugs in the presence and absence of cells. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 14, 6066–6070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Erp, A.E.M.; Versleijen-Jonkers, Y.M.H.; van der Graaf, W.T.A.; Fleuren, E.D.G. Targeted Therapy-based Combination Treatment in Rhabdomyosarcoma. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2018, 17, 1365–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Stewart, E.; Shelat, A.A.; Qu, C.; Bahrami, A.; Hatley, M.; Wu, G.; Bradley, C.; McEvoy, J.; Pappo, A.; et al. Targeting oxidative stress in embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma. Cancer Cell 2013, 24, 710–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouellette, M.M.; Zhou, S.; Yan, Y. Cell Signaling Pathways That Promote Radioresistance of Cancer Cells. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alzahrani, A.S. PI3K/Akt/mTOR inhibitors in cancer: At the bench and bedside. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2019, 59, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Seitz, R.; Lisanti, M.P. Phosphorylation of caveolin by src tyrosine kinases. The alpha-isoform of caveolin is selectively phosphorylated by v-Src in vivo. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 3863–3868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, E.M.; Heidinger, J.M.; Levy, M.; Lisanti, M.P.; Ravid, T.; Goldkorn, T. Epidermal growth factor receptor exposed to oxidative stress undergoes Src- and caveolin-1-dependent perinuclear trafficking. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 14486–14493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Wang, N.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, F.; Wang, Z. Caveolin-1: An Oxidative Stress-Related Target for Cancer Prevention. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2017, 2017, 7454031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H.; Yue, J.; Pan, Z.; Wu, H.; Cheng, Y.; Lu, H.; Ren, X.; Yao, M.; Shen, Z.; Yang, J.M. Involvement of Caveolin-1 in repair of DNA damage through both homologous recombination and non-homologous end joining. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e12055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suchaoin, W.; Chanvorachote, P. Caveolin-1 attenuates hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative damage to lung carcinoma cells. Anticancer Res. 2012, 32, 483–490. [Google Scholar]
- Holmström, K.M.; Finkel, T. Cellular mechanisms and physiological consequences of redox-dependent signalling. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 15, 411–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, D.P.; Sies, H. The Redox Code. Antioxid Redox Signal 2015, 23, 734–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannoni, E.; Chiarugi, P. Redox circuitries driving Src regulation. Antioxid Redox Signal 2014, 20, 2011–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, T.C.; Fukada, T.; Tonks, N.K. Reversible oxidation and inactivation of protein tyrosine phosphatases in vivo. Mol. Cell 2002, 9, 387–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marone, R.; Cmiljanovic, V.; Giese, B.; Wymann, M.P. Targeting phosphoinositide 3-kinase: Moving towards therapy. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2008, 1784, 159–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viniegra, J.G.; Martínez, N.; Modirassari, P.; Hernández Losa, J.; Parada Cobo, C.; Sánchez-Arévalo Lobo, V.J.; Aceves Luquero, C.I.; Alvarez-Vallina, L.; Ramón y Cajal, S.; Rojas, J.M.; et al. Full activation of PKB/Akt in response to insulin or ionizing radiation is mediated through ATM. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 4029–4036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bozulic, L.; Surucu, B.; Hynx, D.; Hemmings, B.A. PKBalpha/Akt1 acts downstream of DNA-PK in the DNA double-strand break response and promotes survival. Mol. Cell 2008, 30, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Dai, X.; Yin, S.; Liu, P.; Hill, E.G.; Wei, W.; Gan, W. DNA-PK promotes activation of the survival kinase AKT in response to DNA damage through an mTORC2-ECT2 pathway. Sci. Signal 2022, 15, eabh2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werner, M.; Sacher, J.; Hohenegger, M. Mutual amplification of apoptosis by statin-induced mitochondrial stress and doxorubicin toxicity in human rhabdomyosarcoma cells. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2004, 143, 715–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araki, M.; Motojima, K. Hydrophobic statins induce autophagy in cultured human rhabdomyosarcoma cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 367, 462–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araki, M.; Maeda, M.; Motojima, K. Hydrophobic statins induce autophagy and cell death in human rhabdomyosarcoma cells by depleting geranylgeranyl diphosphate. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 674, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouitbir, J.; Charles, A.L.; Echaniz-Laguna, A.; Kindo, M.; Daussin, F.; Auwerx, J.; Piquard, F.; Geny, B.; Zoll, J. Opposite effects of statins on mitochondria of cardiac and skeletal muscles: A ’mitohormesis’ mechanism involving reactive oxygen species and PGC-1. Eur. Heart J. 2012, 33, 1397–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Mandal, C.C. Cholesterol-Lowering Drugs on Akt Signaling for Prevention of Tumorigenesis. Front. Genet 2021, 12, 724149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mullen, P.J.; Yu, R.; Longo, J.; Archer, M.C.; Penn, L.Z. The interplay between cell signalling and the mevalonate pathway in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2016, 16, 718–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, A.; Jia, Z.; Qiao, C.; Wang, M.; Ding, X. Cholesterol metabolism in drug-resistant cancer (Review). Int. J. Oncol. 2020, 57, 1103–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Codenotti, S.; Sandrini, L.; Mandracchia, D.; Lorenzi, L.; Corsetti, G.; Poli, M.; Asperti, M.; Salvi, V.; Bosisio, D.; Monti, E.; et al. Statin-Sensitive Akt1/Src/Caveolin-1 Signaling Enhances Oxidative Stress Resistance in Rhabdomyosarcoma. Cancers 2024, 16, 853. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16050853
Codenotti S, Sandrini L, Mandracchia D, Lorenzi L, Corsetti G, Poli M, Asperti M, Salvi V, Bosisio D, Monti E, et al. Statin-Sensitive Akt1/Src/Caveolin-1 Signaling Enhances Oxidative Stress Resistance in Rhabdomyosarcoma. Cancers. 2024; 16(5):853. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16050853
Chicago/Turabian StyleCodenotti, Silvia, Leonardo Sandrini, Delia Mandracchia, Luisa Lorenzi, Giovanni Corsetti, Maura Poli, Michela Asperti, Valentina Salvi, Daniela Bosisio, Eugenio Monti, and et al. 2024. "Statin-Sensitive Akt1/Src/Caveolin-1 Signaling Enhances Oxidative Stress Resistance in Rhabdomyosarcoma" Cancers 16, no. 5: 853. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16050853
APA StyleCodenotti, S., Sandrini, L., Mandracchia, D., Lorenzi, L., Corsetti, G., Poli, M., Asperti, M., Salvi, V., Bosisio, D., Monti, E., Mitola, S., Triggiani, L., Guescini, M., Pozzo, E., Sampaolesi, M., Gastaldello, S., Cassandri, M., Marampon, F., & Fanzani, A. (2024). Statin-Sensitive Akt1/Src/Caveolin-1 Signaling Enhances Oxidative Stress Resistance in Rhabdomyosarcoma. Cancers, 16(5), 853. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16050853













