The protein kinases are a large family of enzymes which catalyze protein phosphorylation at certain amino acids. There are two large subfamilies of protein kinases: the tyrosine kinases and the serine/threonine kinases. The human genome contains 518 protein kinases, 478 of which contain a typical protein kinase domain, while 40 contain atypical protein kinases [1]. Protein phosphorylation by kinases plays a significant role in the regulation of numerous cell processes, such as proliferation, cell growth, the cell cycle, cell differentiation, cell survival and apoptosis [2,3]. The aberrant regulation of kinases can lead to notable changes in these processes and can be central for various diseases, such as cancers, neurodegenerative diseases, inflammation, diabetes, kidney diseases and cardiovascular disorders [2,4]. Cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) are a subgroup of protein kinases which play a crucial role in the control of the cell cycle, proliferation, transcription and gene expression [5]. There are 21 genes that encode CDKs in the human genome, as well as 5 genes that encode similar protein kinases dubbed as CDK-like kinases (CDKLs) [6].
Small-molecule kinase inhibitors are gaining increasing importance in the field of drug research, development and use. There are many such inhibitors, some of which are more specific while some are less, and quite a few of them have already been approved for cancer therapy [7], or are at least in clinical studies of different phases [8,9,10]. CDK inhibitors are no exception, and there are many inhibitors used for research purposes and for therapeutic applications. Many CDK inhibitors have been enrolled in various phases of clinical trials both for cancers and other diseases [11,12,13]. This editorial will provide an overview of the inhibitors which are approved by U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of various diseases, as well as those which are granted the designation of orphan drugs.
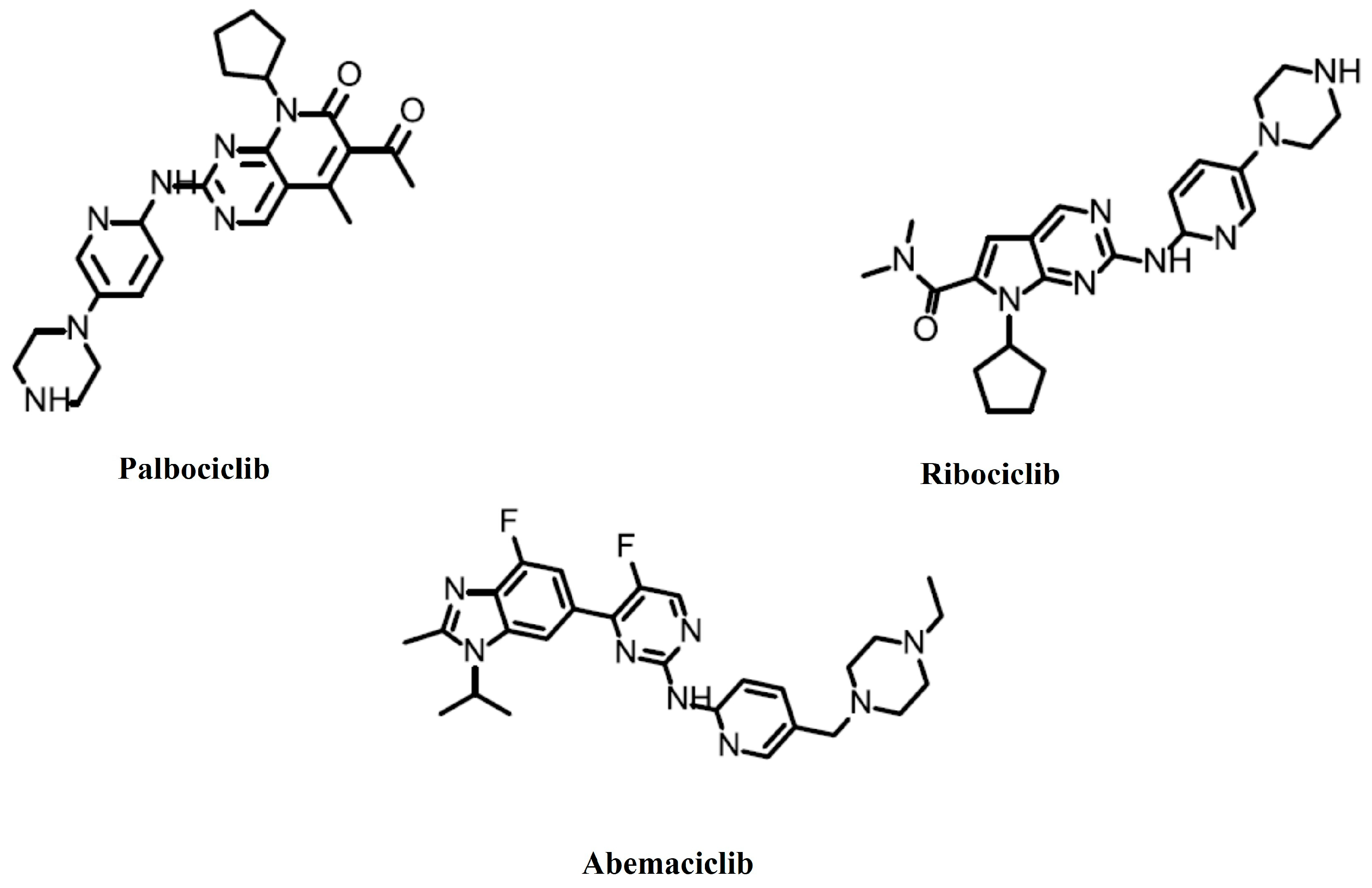
Palbociclib (PD0332991, Ibrance) (Figure 1) is a specific CDK4/6 inhibitor. It has a potency against cyclin D1/CDK4 (IC50 = 11 nM) and cyclin D1, 2, 3/CDK6 (IC50 = 16 nM), but almost none against other CDKs (IC50 > 10,000) [14]. In 2012, it was predicted that PD0332991 would be the first approved CDK inhibitor [15]. On 3 February 2015, the FDA granted accelerated approval to palbociclib for the treatment of postmenopausal patients with estrogen receptor-positive, HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer. It is to be used in combination with letrozole as an initial endocrine-based therapy for women with metastatic disease. Its approval was based on a randomized, multicenter, open-label phase I/II trial, PALOMA-1 [16], which was confirmed by PALOMA-2 [17] and PALOMA-4 [18] phase III trials. On 19 February 2016, the FDA approved palbociclib for use in combination with fulvestrant for the treatment of women with hormone receptor-positive, HER2-negative advanced or metastatic breast cancer with disease progression following endocrine therapy. This approval was based on a randomized, multicenter, open-label phase III trial, PALOMA-3 [19]. On 4 April 2019, the FDA approved a supplemental new drug application for palbociclib for male patients with hormone receptor-positive, HER2-negative advanced or metastatic breast cancer. This approval was primarily based on the results of the PALOMA-2 and PALOMA-3 trials and supported by data from two phase I studies with palbociclib in males [20].
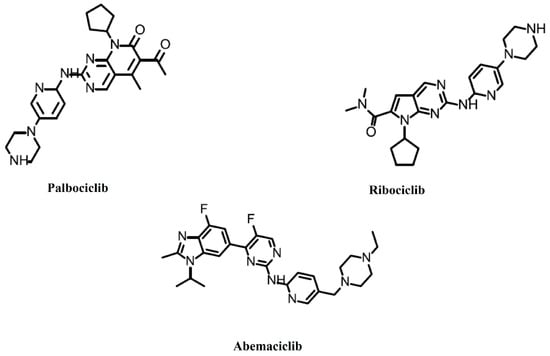
Figure 1.
Food and Drug Administration-approved CDK4/6 inhibitors.
Ribociclib (LEE011, KISQALI) (Figure 1) has slightly greater potency against cyclin D1/CDK4 (IC50 = 10 nM) than against cyclin D1, 2, 3/CDK6 (IC50 = 39 nM), but almost none against other CDKs (IC50 > 50,000) [21]. On 13 March 2017, the FDA approved ribociclib in combination with an aromatase inhibitor as an initial endocrine-based therapy for the treatment of postmenopausal women with hormone receptor-positive, HER2-negative advanced or metastatic breast cancer. This approval was based on a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, international clinical trial MONALEESA-2 [22], which was confirmed by MONALEESA-3 [23,24,25] and MONALEESA-7 [26,27] phase III trials. On 10 December 2021, the FDA approved ribociclib in combination with an aromatase inhibitor as an initial endocrine-based therapy in adult patients, or with fulvestrant as an initial endocrine-based therapy or following disease progression on endocrine therapy, in postmenopausal women and men. This approval was primarily based on the results of the MONALEESA-2 and MONALEESA-7 trials and supported by COMPLEEMENT-1 in males [28].
Abemaciclib (LY2835219, Verzenio) (Figure 1) has slightly greater potency against cyclin D1/CDK4 (IC50 = 2 nM) than against cyclin D1, 2, 3/CDK6 (IC50 = 10 nM), but significantly less against other CDKs (IC50 > 300) [29]. On 28 September 2017, the FDA approved abemaciclib in combination with fulvestrant for women with hormone receptor-positive, HER2-negative advanced or metastatic breast cancer with disease progression following endocrine therapy. This approval was based on MONARCH 2, a randomized, placebo-controlled, multicenter trial [30]. On 12 October 2021, the FDA approved abemaciclib with endocrine therapy (tamoxifen or an aromatase inhibitor) for the adjuvant treatment of adult patients with hormone receptor-positive, HER2-negative, node-positive early breast cancer at a high risk of recurrence. An additional requirement was having a Ki-67 score of greater than or equal to 20%. This approval was based on the monarchE trial [31,32]. On 3 March 2023, the FDA approved abemaciclib with endocrine therapy (tamoxifen or an aromatase inhibitor) for the adjuvant treatment of adult patients with hormone receptor-positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative, node-positive early breast cancer at a high risk of recurrence. This approval removed the Ki-67 testing requirement [33].
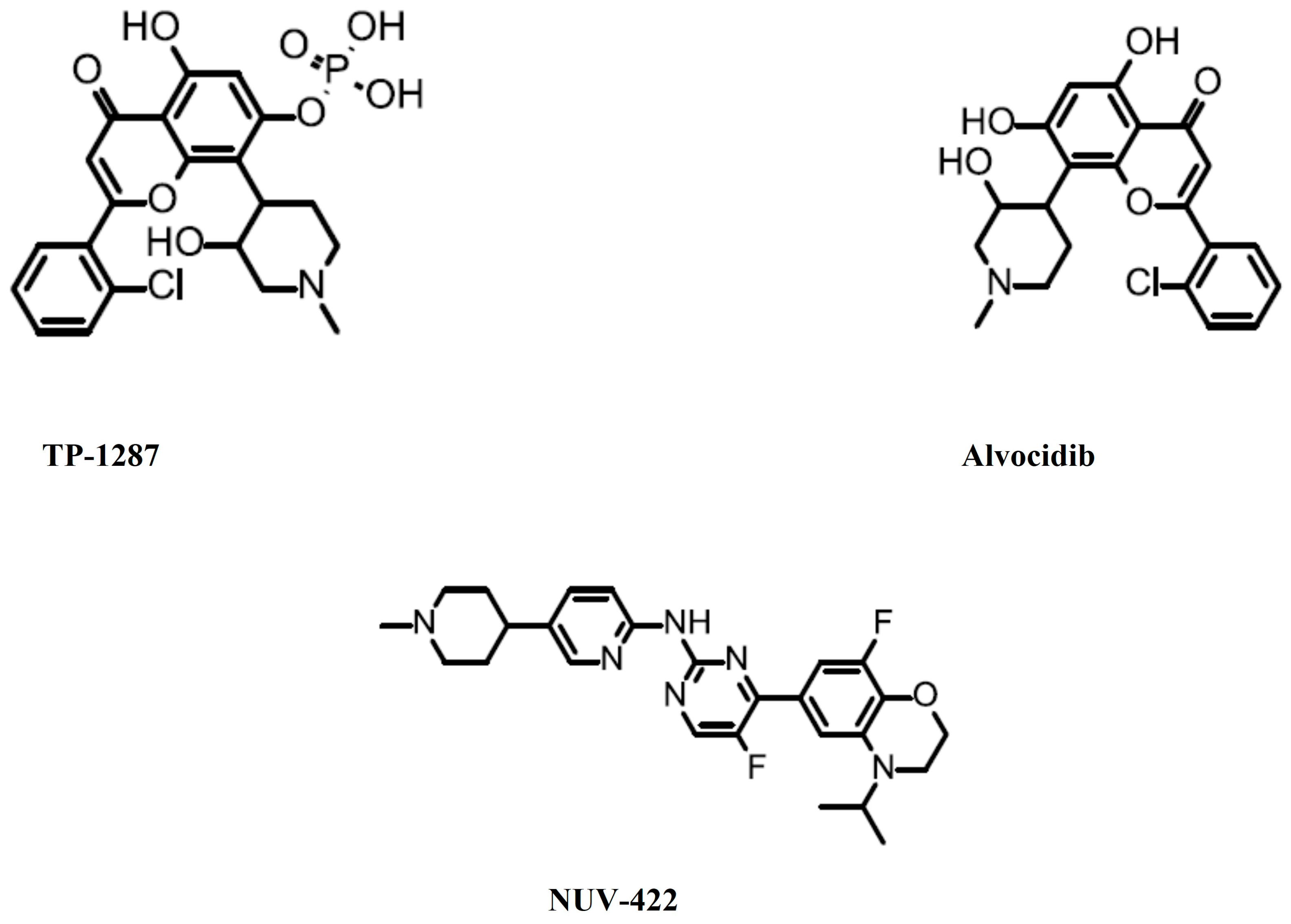
SLS009 (GFH009) (Figure 2) is a specific CDK9 inhibitor. It has a potency against cyclin T1/CDK9 (IC50 = 9 nM), but almost none against other CDKs (IC50 > 100 at least) [34]. On 11 October 2023, the FDA granted an orphan drug designation to SLS009 for the treatment of patients with acute myeloid leukemia [35]. This was based on an open-label, single-arm, multicenter phase 1/2a trial (NCT04588922) in patients with relapsed/refractory AML and other hematologic malignancies [36]. On 30 October 2023, the FDA granted a fast-track designation for the treatment of relapsed or refractory peripheral T-cell lymphoma [37].
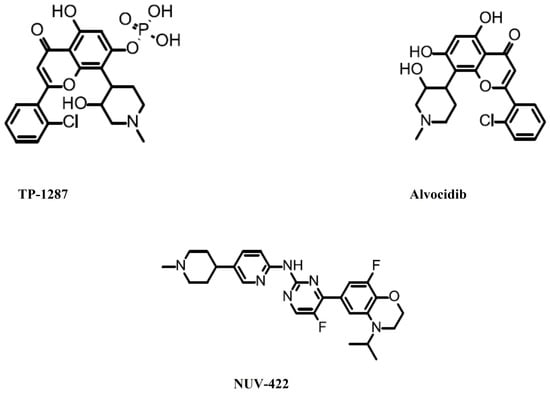
Figure 2.
Inhibitors granted an orphan drug designation by the Food and Drug Administration.
TP-1287 is a prodrug of alvocidib (Flavopiridol, L-868275, HMR-1275, NSC-649890) (Figure 2), which is a broad-range CDK inhibitor. It inhibits CDK1, CDK2, CDK9 (IC50 = 5–15 nM), CDK4, and CDK6 (IC50 = 40–300 nM) [13,38]. On 10 April 2023, the FDA granted an orphan drug designation to TP-1287 for the treatment of patients with Ewing sarcoma [39]. The FDA has also granted an orphan drug designation to alvocidib for the treatment of patients with acute myeloid leukemia [40].
NUV-422 (Figure 2) is an inhibitor of CDK2, CDK4 and CDK6. On 11 March 2021, the FDA granted an orphan drug designation to NUV-422 for the treatment of patients with malignant glioma [41]. This decision was based on a phase 1/2 study of NUV-422 (NCT04541225) in patients with high-grade gliomas [42]. However, this study was put on hold and later terminated due to the development of uveitis in patients [43]. The company eventually decided to discontinue the development of clinical development [44]. All of the inhibitor information mentioned in this editorial is summarized in Table 1.

Table 1.
Summary of all CDK inhibitors mentioned in this editorial.
The successes and failures of CDK inhibitors show us that this chapter of targeted therapy is far from its conclusion. One way or another, we have 21 CDK genes in the human genome as well as 5 similar kinases, and a only couple of them have clinically approved inhibitors and/or are close to reaching this goal. Both broad-spectrum CDK inhibitors as well as very selective ones, or ones which are selective for a small group of CDKs, should still be considered. A lot of clinical and preclinical research has been performed on previously developed small-molecule inhibitors, as well as new approaches [45]. In addition, there is always a possibility to develop alternative modes of inhibition, such as peptides or aptamers.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.C. and J.S.; writing—original draft preparation, J.C.; writing—review and editing, J.S.; visualization, J.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Manning, G.; Whyte, D.B.; Martinez, R.; Hunter, T.; Sudarsanam, S. The protein kinase complement of the human genome. Science 2002, 298, 1912–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cicenas, J.; Zalyte, E.; Bairoch, A.; Gaudet, P. Kinases and Cancer. Cancers 2018, 10, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunter, T. Signaling--2000 and beyond. Cell 2000, 100, 113–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cicenas, J.; Kalyan, K.; Sorokinas, A.; Stankunas, E.; Levy, J.; Meskinyte, I.; Stankevicius, V.; Kaupinis, A.; Valius, M. Roscovitine in cancer and other diseases. Ann. Transl. Med. 2015, 3, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Tang, H.C.; Tsai, K.L. Unveiling the noncanonical activation mechanism of CDKs: Insights from recent structural studies. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2023, 10, 1290631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malumbres, M.; Harlow, E.; Hunt, T.; Hunter, T.; Lahti, J.M.; Manning, G.; Morgan, D.O.; Tsai, L.H.; Wolgemuth, D.J. Cyclin-dependent kinases: A family portrait. Nat. Cell Biol. 2009, 11, 1275–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cicenas, J.; Račienė, A. Anti-Cancer Drugs Targeting Protein Kinases Approved by FDA in 2020. Cancers 2021, 13, 947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicenas, J.; Zalyte, E.; Rimkus, A.; Dapkus, D.; Noreika, R.; Urbonavicius, S. JNK, p38, ERK, and SGK1 Inhibitors in Cancer. Cancers 2017, 10, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicenas, J. The Aurora kinase inhibitors in cancer research and therapy. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 142, 1995–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicenas, J.; Cicenas, E. Multi-kinase inhibitors, AURKs and cancer. Med. Oncol. 2016, 33, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicenas, J.; Meskinyte-Kausiliene, E.; Jukna, V.; Rimkus, A.; Simkus, J.; Soderholm, D. SGK1 in Cancer: Biomarker and Drug Target. Cancers 2022, 14, 2385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cicenas, J.; Kalyan, K.; Sorokinas, A.; Jatulyte, A.; Valiunas, D.; Kaupinis, A.; Valius, M. Highlights of the Latest Advances in Research on CDK Inhibitors. Cancers 2014, 6, 2224–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cicenas, J.; Valius, M. The CDK inhibitors in cancer research and therapy. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 137, 1409–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fry, D.W.; Harvey, P.J.; Keller, P.R.; Elliott, W.L.; Meade, M.; Trachet, E.; Albassam, M.; Zheng, X.; Leopold, W.R.; Pryer, N.K.; et al. Specific inhibition of cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 by PD 0332991 and associated antitumor activity in human tumor xenografts. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2004, 3, 1427–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennet, N. Oral CDK4/6 inhibitor in clinical trials. Lancet Oncol. 2012, 13, E91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaver, J.A.; Amiri-Kordestani, L.; Charlab, R.; Chen, W.; Palmby, T.; Tilley, A.; Zirkelbach, J.F.; Yu, J.; Liu, Q.; Zhao, L.; et al. FDA Approval: Palbociclib for the Treatment of Postmenopausal Patients with Estrogen Receptor-Positive, HER2-Negative Metastatic Breast Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 4760–4766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finn, R.S.; Martin, M.; Rugo, H.S.; Jones, S.; Im, S.A.; Gelmon, K.; Harbeck, N.; Lipatov, O.N.; Walshe, J.M.; Moulder, S.; et al. Palbociclib and Letrozole in Advanced Breast Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 1925–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, B.; Hu, X.; Li, W.; Sun, T.; Shen, K.; Wang, S.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Cui, S.; Tong, Z.; et al. Palbociclib plus letrozole versus placebo plus letrozole in Asian postmenopausal women with oestrogen receptor-positive/human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative advanced breast cancer: Primary results from PALOMA-4. Eur. J. Cancer 2022, 175, 236–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, N.C.; Slamon, D.J.; Ro, J.; Bondarenko, I.; Im, S.A.; Masuda, N.; Colleoni, M.; DeMichele, A.; Loi, S.; Verma, S.; et al. Overall Survival with Palbociclib and Fulvestrant in Advanced Breast Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 1926–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wedam, S.; Fashoyin-Aje, L.; Bloomquist, E.; Tang, S.; Sridhara, R.; Goldberg, K.B.; Theoret, M.R.; Amiri-Kordestani, L.; Pazdur, R.; Beaver, J.A. FDA Approval Summary: Palbociclib for Male Patients with Metastatic Breast Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 1208–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Loo, A.; Chopra, R. An orally bioavailable, selective small molecule inhibitor of CDK4/6—Reactivating Rb in cancer [abstract PR02: LEE011]. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2013, 12 (Suppl. S11). [Google Scholar]
- Shah, A.; Bloomquist, E.; Tang, S.; Fu, W.; Bi, Y.; Liu, Q.; Yu, J.; Zhao, P.; Palmby, T.R.; Goldberg, K.B.; et al. FDA Approval: Ribociclib for the Treatment of Postmenopausal Women with Hormone Receptor-Positive, HER2-Negative Advanced or Metastatic Breast Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 2999–3004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slamon, D.J.; Neven, P.; Chia, S.; Fasching, P.A.; De Laurentiis, M.; Im, S.A.; Petrakova, K.; Bianchi, G.V.; Esteva, F.J.; Martín, M.; et al. Overall Survival with Ribociclib plus Fulvestrant in Advanced Breast Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 514–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerusalem, G.; Delea, T.E.; Martin, M.; De Laurentiis, M.; Nusch, A.; Beck, J.T.; Chan, A.; Im, S.A.; Neven, P.; Lonshteyn, A.; et al. Quality-Adjusted Survival with Ribociclib Plus Fulvestrant Versus Placebo Plus Fulvestrant in Postmenopausal Women with HR±HER2- Advanced Breast Cancer in the MONALEESA-3 Trial. Clin. Breast Cancer 2022, 22, 326–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neven, P.; Fasching, P.A.; Chia, S.; Jerusalem, G.; De Laurentiis, M.; Im, S.A.; Petrakova, K.; Bianchi, G.V.; Martín, M.; Nusch, A.; et al. Updated overall survival from the MONALEESA-3 trial in postmenopausal women with HR+/HER2− advanced breast cancer receiving first-line ribociclib plus fulvestrant. Breast Cancer Res. 2023, 25, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Im, S.A.; Lu, Y.S.; Bardia, A.; Harbeck, N.; Colleoni, M.; Franke, F.; Chow, L.; Sohn, J.; Lee, K.S.; Campos-Gomez, S.; et al. Overall Survival with Ribociclib plus Endocrine Therapy in Breast Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.S.; Im, S.A.; Colleoni, M.; Franke, F.; Bardia, A.; Cardoso, F.; Harbeck, N.; Hurvitz, S.; Chow, L.; Sohn, J.; et al. Updated Overall Survival of Ribociclib plus Endocrine Therapy versus Endocrine Therapy Alone in Pre- and Perimenopausal Patients with HR+/HER2- Advanced Breast Cancer in MONALEESA-7: A Phase III Randomized Clinical Trial. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 28, 851–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.J.; Osgood, C.L.; Feng, Z.; Bloomquist, E.W.; Tang, S.; Chang, C.J.G.; Ricks, T.K.; Hou, S.C.; Pierce, W.F.; Rivera, D.R.; et al. FDA Approval Summary: Ribociclib Indicated for Male Patients with Hormone Receptor-Positive, HER2-Negative Advanced or Metastatic Breast Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2023, 29, 5008–5011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gelbert, L.M.; Cai, S.; Lin, X.; Sanchez-Martinez, C.; Del Prado, M.; Lallena, M.J.; Torres, R.; Ajamie, R.T.; Wishart, G.N.; Flack, R.S.; et al. Preclinical characterization of the CDK4/6 inhibitor LY2835219: In-vivo cell cycle-dependent/independent anti-tumor activities alone/in combination with gemcitabine. Investig. New Drugs 2014, 32, 825–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FDA OKs Abemaciclib for ER+, HER2- Breast Cancer. Cancer Discov. 2017, 7, OF1. [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Royce, M.; Osgood, C.; Mulkey, F.; Bloomquistm, E.; Pierce, W.F.; Roy, A.; Kalavar, S.; Ghosh, S.; Philip, R.; Rizvi, F.; et al. FDA Approval Summary: Abemaciclib with Endocrine Therapy for High-Risk Early Breast Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 1155–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raheem, F.; Ofori, H.; Simpson, L.; Shah, V. Abemaciclib: The First FDA-Approved CDK4/6 Inhibitor for the Adjuvant Treatment of HR+ HER2- Early Breast Cancer. Ann. Pharmacother. 2022, 56, 10600280211073322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FDA D.I.S.C.O. Burst Edition: FDA Approval of Verzenio (Abemaciclib) with Endocrine Therapy for Patients with HR-Positive, HER2-Negative, Node-Positive, Early Breast Cancer. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/drugs/resources-information-approved-drugs/fda-disco-burst-edition-fda-approval-verzenio-abemaciclib-endocrine-therapy-patients-hr-positive (accessed on 24 March 2023).
- Zhou, F.; Tang, L.; Le, S.; Ge, M.; Cicic, D.; Xie, F.; Ren, J.; Lan, J.; Lu, Q. The pharmacodynamic and mechanistic foundation for the antineoplastic effects of GFH009, a potent and highly selective CDK9 inhibitor for the treatment of hematologic malignancies. Oncotarget 2023, 14, 997–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FDA Awards Orphan Drug Designation to SLS009 in AML. Available online: https://www.onclive.com/view/fda-awards-orphan-drug-designation-to-sls009-in-aml (accessed on 11 October 2023).
- A Study of GFH009 in Patients with Hematologic Malignancies. Available online: https://classic.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04588922 (accessed on 1 September 2023).
- SLS009 Earns FDA Fast Track Designation for R/R PTCL. Available online: https://www.targetedonc.com/view/sls009-earns-fda-fast-track-designation-for-r-r-ptcl (accessed on 30 October 2023).
- Albert, T.K.; Rigault, C.; Eickhoff, J.; Baumgart, K.; Antrecht, C.; Klebl, B.; Mittler, G.; Meisterernst, M. Characterization of molecular and cellular functions of the cyclin-dependent kinase CDK9 using a novel specific inhibitor. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 171, 55–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FDA Grants Orphan Drug Status to TP-1287 for Ewing Sarcoma. Available online: https://www.targetedonc.com/view/fda-grants-orphan-drug-status-to-tp-1287-for-ewing-sarcoma (accessed on 11 April 2023).
- Orphan Drug Status for Alvocidib. Available online: https://journals.lww.com/oncology-times/fulltext/2014/05250/orphan_drug_status_for_alvocidib.39.aspx (accessed on 25 May 2014).
- FDA Grants Orphan Drug Designation to Novel CDK2/4/6 Inhibitor in Malignant Gliomas. Available online: https://www.targetedonc.com/view/fda-grants-orphan-drug-designation-to-novel-cdk2-4-6-inhibitor-in-malignant-gliomas (accessed on 11 March 2021).
- Study of NUV-422 in Adults with Recurrent or Refractory High-grade Gliomas and Solid Tumors. Available online: https://classic.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04541225 (accessed on 14 July 2023).
- FDA Halts Phase 1/2 Trial Evaluating NUV-422 in Solid Tumors. Available online: https://www.targetedonc.com/view/fda-halts-phase-1-2-trial-evaluating-nuv-422-in-solid-tumors (accessed on 28 June 2022).
- Nuvation Bio Announces Discontinuation of NUV-422 Clinical Development Program. Available online: https://investors.nuvationbio.com/news/news-details/2022/Nuvation-Bio-Announces-Discontinuation-of-NUV-422-Clinical-Development-Program/default.aspx (accessed on 1 August 2022).
- Mughal, M.J.; Bhadresha, K.; Kwok, H.F. CDK inhibitors from past to present: A new wave of cancer therapy. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2023, 88, 106–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).